bio lecture c9
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Diarthrosis (synovial)
joint in which two bones are separated by a joint cavity, Most are freely mobile
Most structurally complex type of joint
Most likely to develop painful dysfunction
articular cartilage
layer of hyaline cartilage that covers the facing surfaces of two bones
Usually 2 or 3 mm thick
joint (articular) cavity
separates articular surfaces
synovial fluid
slippery lubricant in joint cavity
Rich in albumin and hyaluronic acid
Gives it a viscous, slippery texture like raw egg whites
Nourishes articular cartilage and removes waste
Makes movement of synovial joints almost friction free
joint (articular) capsule
connective tissue that encloses the cavity and retains the fluid
Outer fibrous capsule: continuous with periosteum of adjoining bones
Inner, cellular, synovial membrane: composed mainly of fibroblast-like cells that secrete synovial fluid and macrophages that remove debris from the joint cavity
shock absorber
function: In a few synovial joints, fibrocartilage grows inward from the joint capsule
Articular disc forms a pad between articulating bones that crosses the entire joint capsule
Bursa
fibrous sac filled with synovial fluid, located between muscles, where tendons pass over bone, or between bone and skin
Cushions muscles, helps tendons slide more easily over joints, modifies direction of tendon pull
tendon sheath
elongated cylindrical bursa wrapped around a tendon
In hand and foot
tendon
strip of collagenous tissue attaching muscle to bone
ligament
strip of collagenous tissue attaching one bone to another
warms
Exercise __________ synovial fluid
Becomes less viscous, more easily absorbed by cartilage
cushion, warm up period
Cartilage then swells and provides a more effective ________
_________ before vigorous exercise helps protect cartilage from undue wear and tear
more rapidly
Without exercise, cartilage deteriorates _______ from inadequate nutrition and waste removal
lever
any elongated, rigid object that rotates around a fixed point called a fulcrum, bones
rotation
occurs when an effort applied overcomes resistance (load) at some other point
Structure of the articular surfaces
Strength and tautness of ligaments and joint capsules
Action of the muscles and tendons
ROM determined by
1.__________
2.__________
3.___________
Elbow—olecranon of ulna fits into olecranon fossa of humerus
Stretching of ligaments increases range of motion
Double-jointed people have long or slack ligaments
Nervous system monitors joint position and muscle tone
Muscle tone—state of tension maintained in resting muscles
stationary axis
A moving bone has a relatively ____________ of rotation that passes through the bone in a direction perpendicular to the plane of movement
Multiaxial joint
3 planes of movement,
shoulder joint has ___three__ degrees of freedom or axes of rotation
Other joints are monoaxial or biaxial
1
how many degrees of freedom does the elbow have
ball and socket joint
Smooth, hemispherical head fits within cup-like socket
Only multiaxial joints in body
Examples: shoulder, hip
3 planes of movement=more unstable
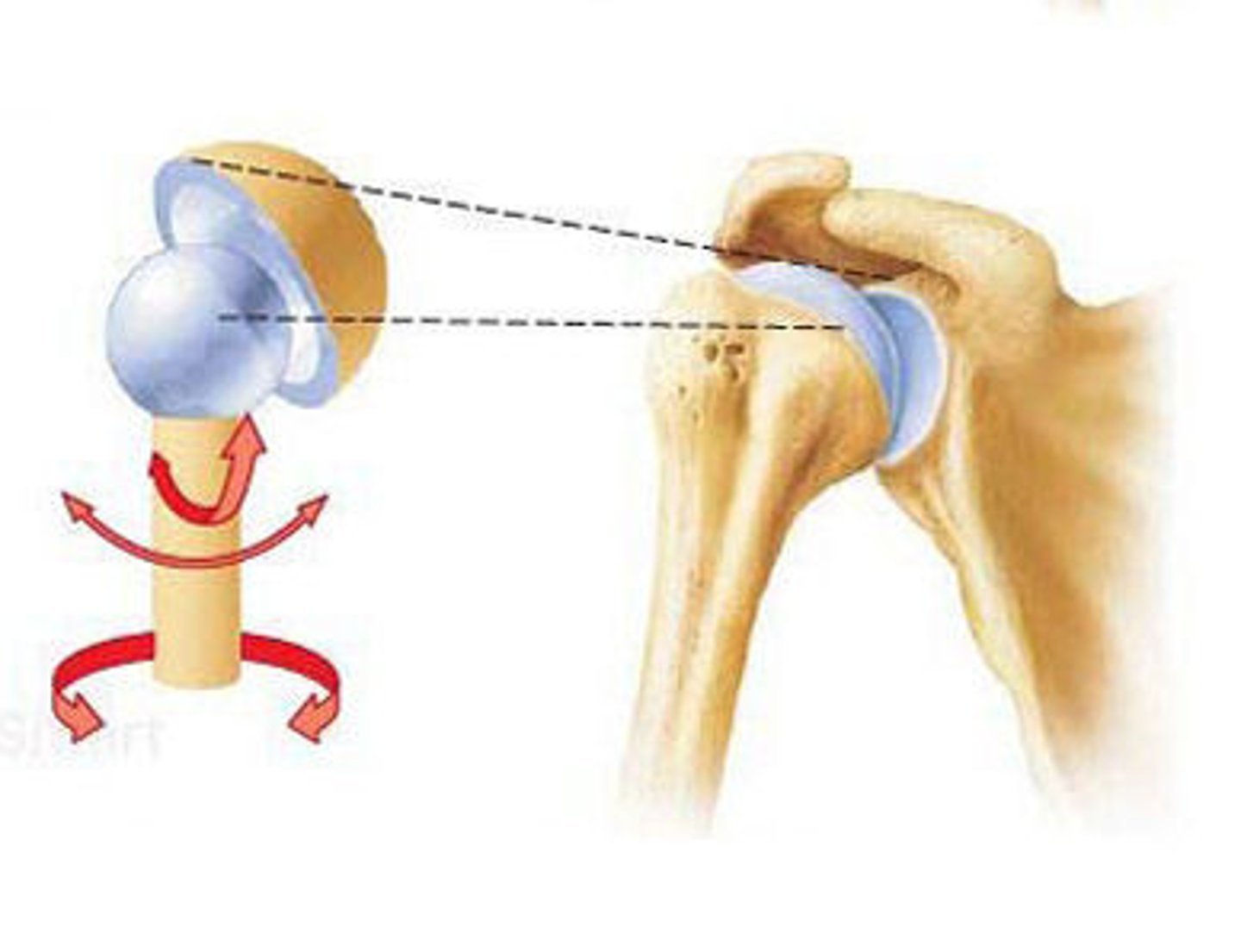
Condylar (ellipsoid) joints
Oval convex surface of one bone fits into a complementary-shaped depression on the other
Biaxial joints—movement in two planes
Examples: radiocarpal joint, metacarpophalangeal joints
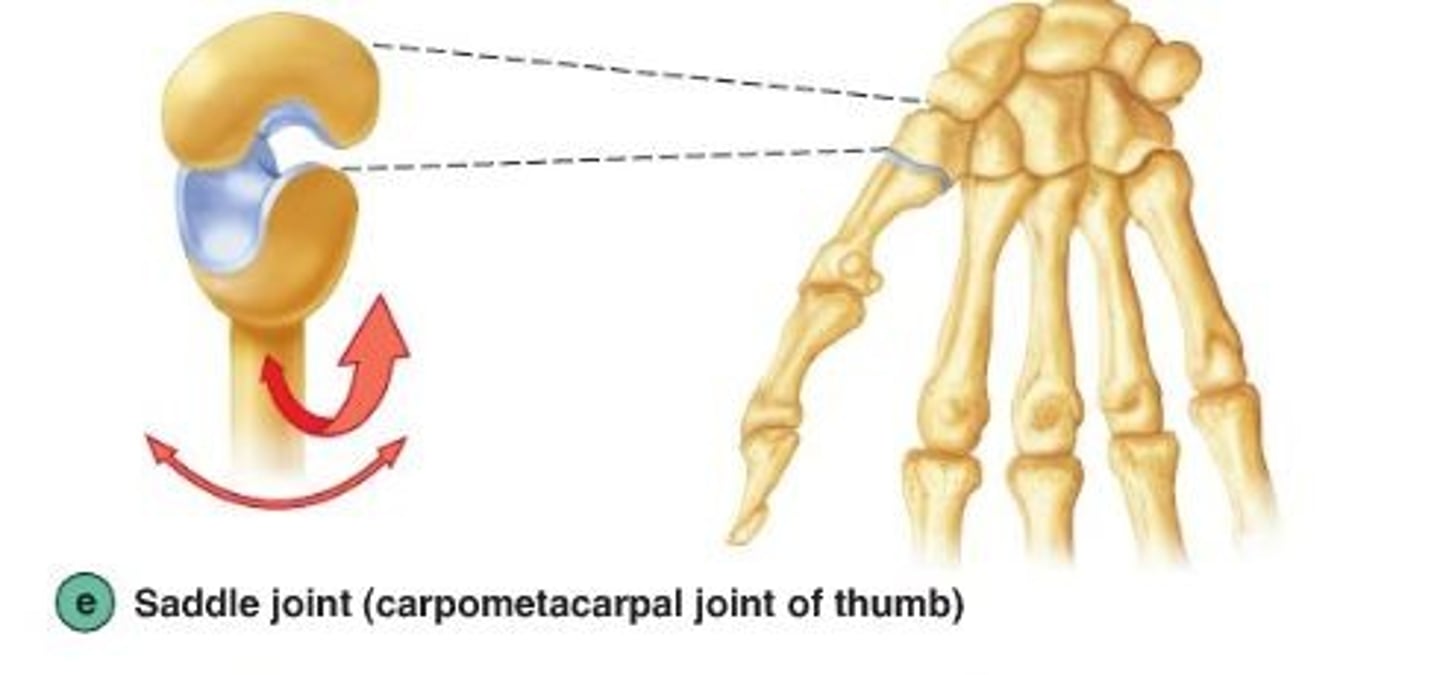
saddle joint
Both bones have an articular surface that is shaped like a saddle, one concave, the other convex
Biaxial joints
Examples: trapeziometacarpal (opposable thumb), sternoclavicular joint
more stable than ball and socket and condylar
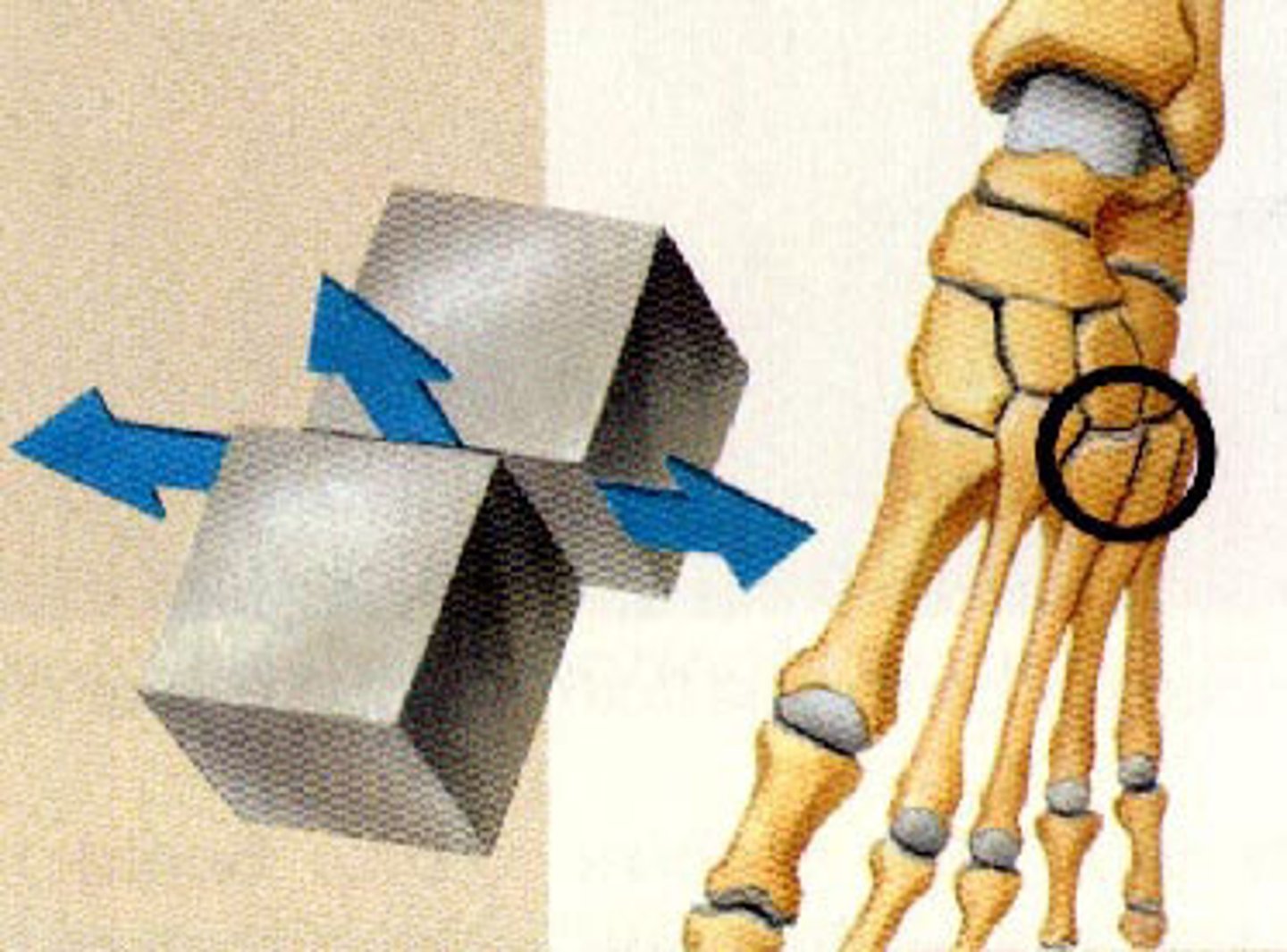
plane (gliding) joint
Flat articular surfaces, bones slide over each other
Usually biaxial joints
Examples: between carpal bones of wrist; between tarsal bones of ankle; also between articular processes of vertebrae
occasionally monoaxial
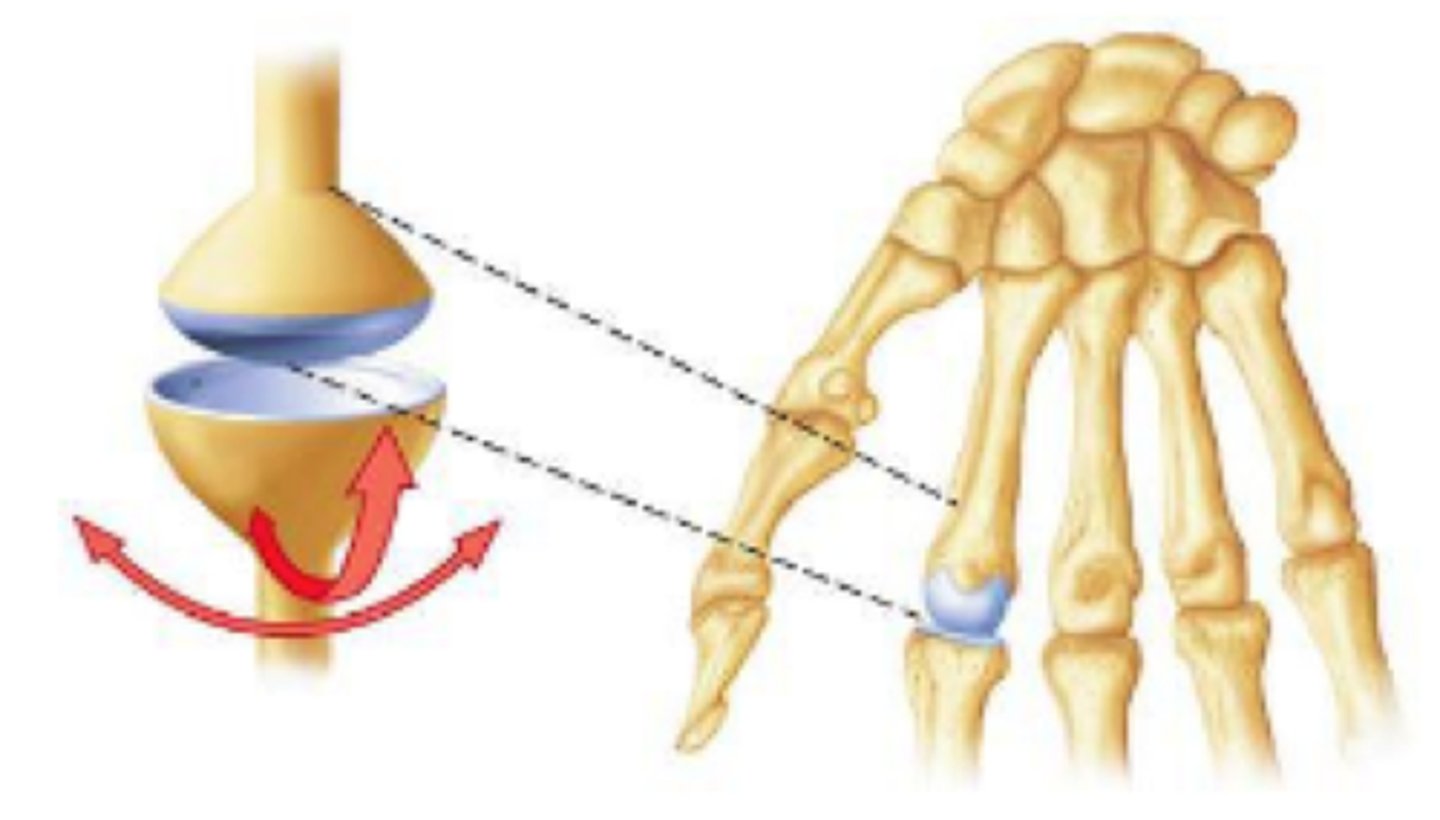
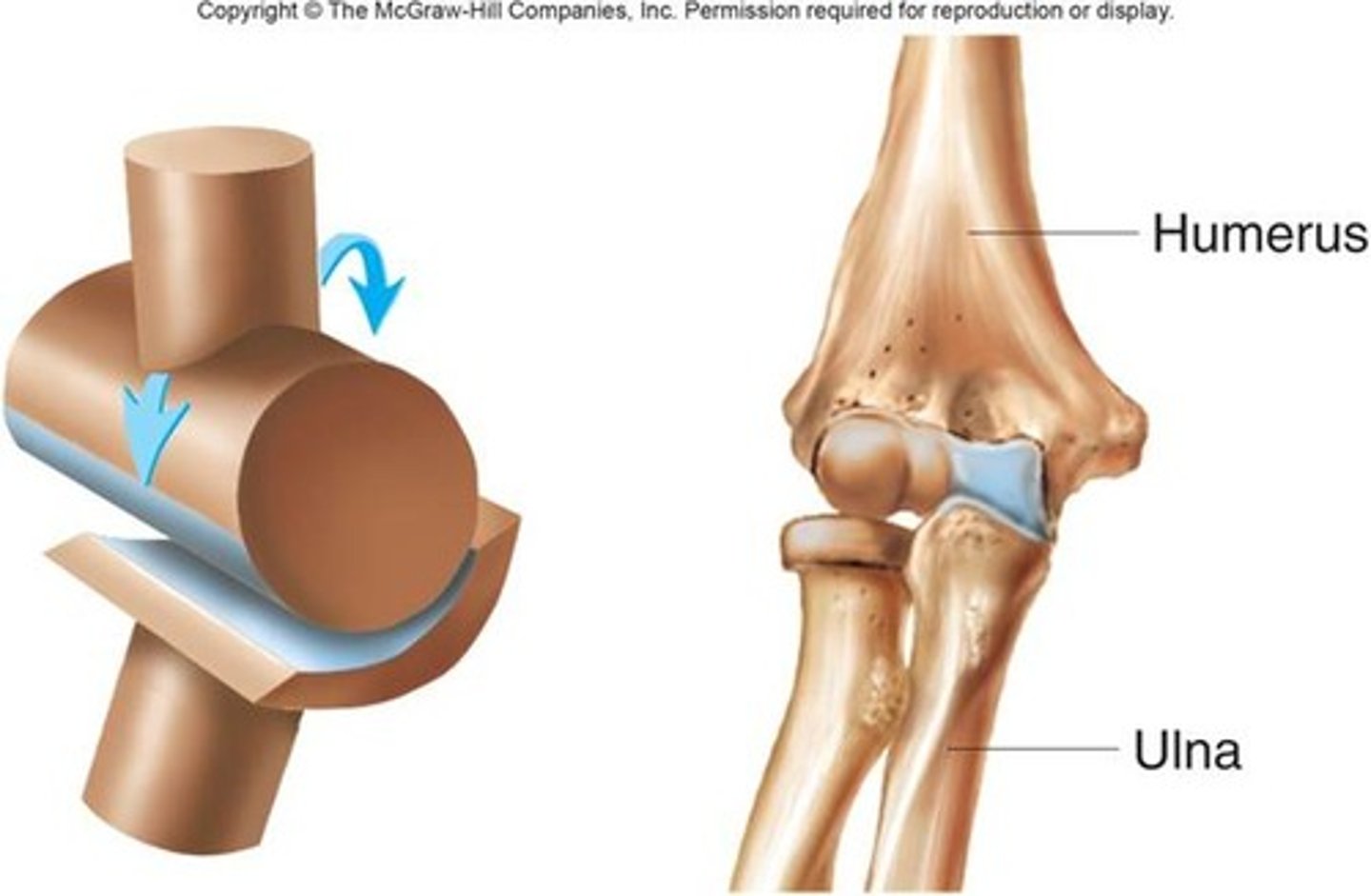
hinge joint
One bone with convex surface fits into a concave depression of another bone
Monoaxial joints—move freely in one plane
Examples: elbow, knee, joints within fingers, toes
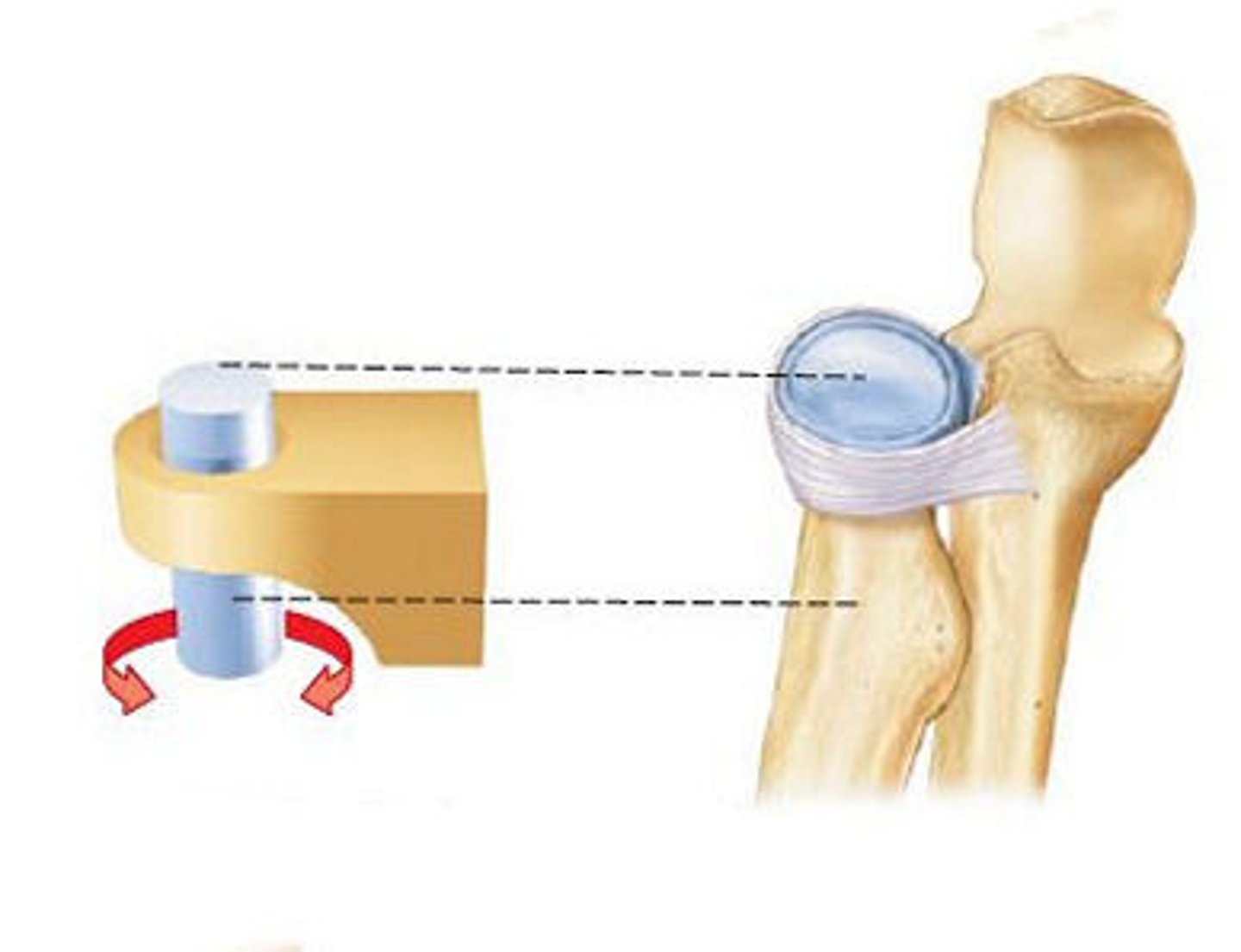
pivot joints
A bone spins on its longitudinal axis
Monoaxial joints
Examples: atlantoaxial joint (C1 and C2), radioulnar joint at the elbow
monoaxial
What kind of joint is the most stable?
zero position
the position of a joint when a person is in the standard anatomical position
Joint movements described as deviating from the zero position or returning to it
pair opposites together
palms anterior in anatomical pos
flexion
movement that decreases joint angle
Common in hinge joints
extension
movement that straightens a joint and returns a body part to the zero position
Hyperextension
extension of a joint beyond the zero position
Flexion and extension occur at nearly all diarthroses, hyperextension is limited to a few
abduction
movement of a body part in the frontal plane away from the midline of the body
Hyperabduction: raise arm over back or front of head
adduction
movement in the frontal plane back toward the midline
Hyperadduction: crossing fingers, crossing ankles
elevation
movement that raises a body part vertically in the frontal plane
depression
movement that lowers a body part in the same plane
protraction
the anterior movement of a body part in the transverse (horizontal) plane
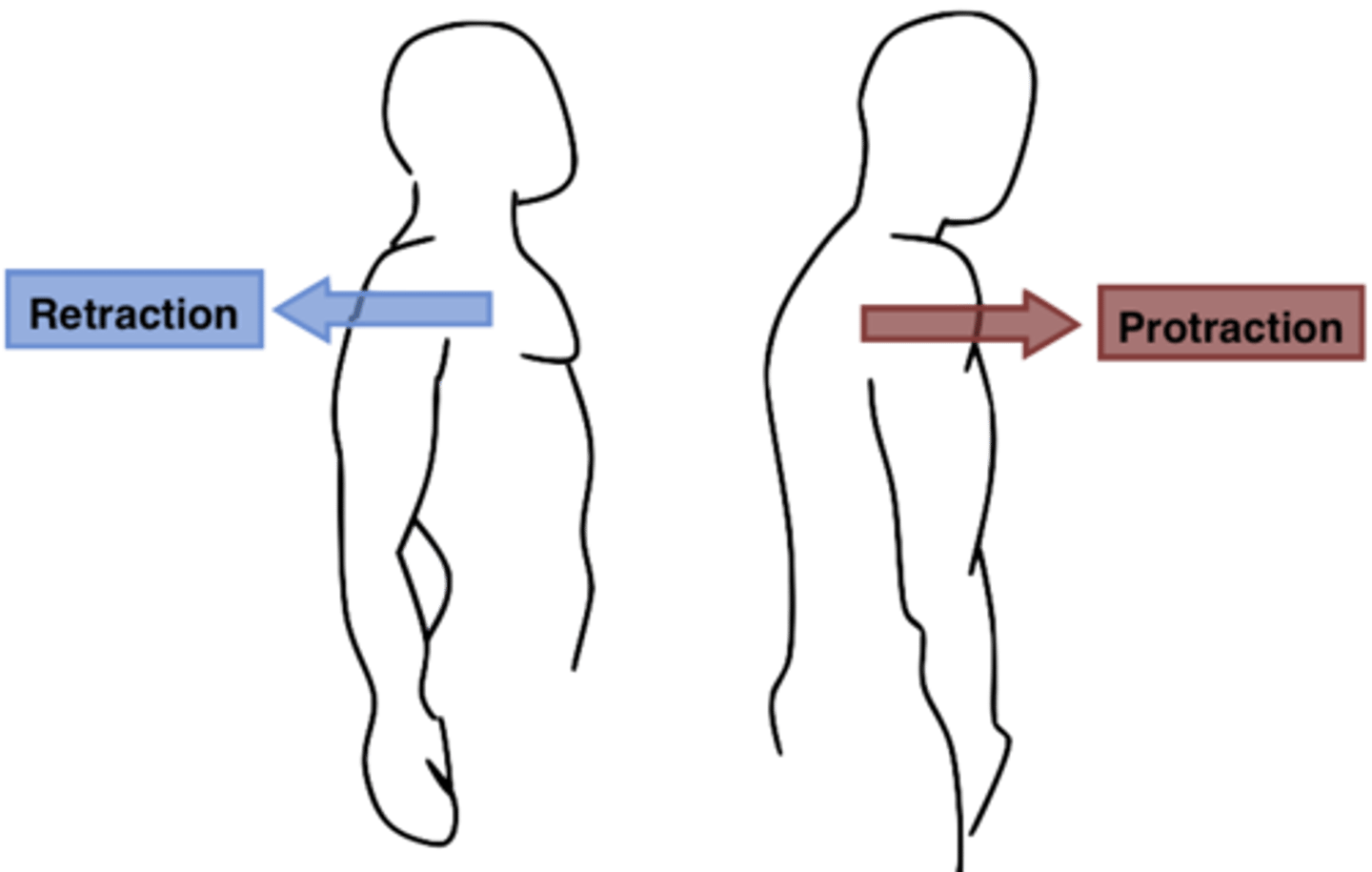
retraction
posterior movement
roatation
movement in which a bone spins on its longitudinal axis
Rotation of trunk, thigh, head, or arm
Medial (internal) rotation turns the bone inward
Lateral (external) rotation turns the bone outward
pronation
forearm movement that turns palm to face either posteriorly or downward
Head of radius spins
Radius crosses stationary ulna like an X
supination
forearm movement that turns palm to face anteriorly or upward
Forearm supinated in anatomical position
Radius is ____paralell___ to the ulna
lateral flexion
tilting the head or trunk to the right or left at the midline
lateral excursion
right or left movement from the zero position of mandible
flexion, extension
______ vs. _____ of fingers —curling vs. straightening them
radial abduction
moving thumb away from index finger (90°)
medial excursion
movement back to the median, zero position
___side to side______ grinding during chewing
synovial fluid
_____________ less abundant and articular cartilage thinner or absent producing friction that causes pain
Osteoarthritis is common cause of physical disability