Physiology Lecture 27 - Immune Organs
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
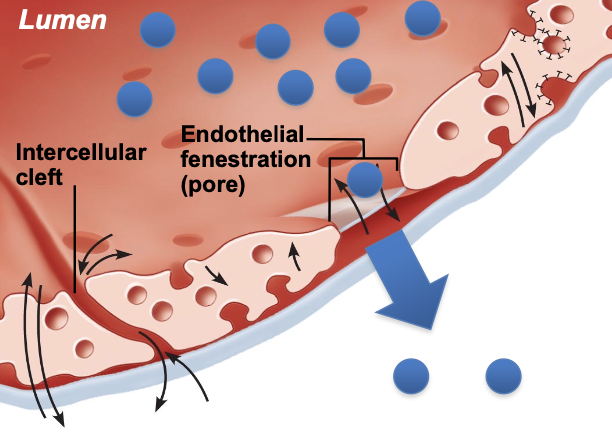
what pushes fluid out?
capillary hydrostatic pressure
what is hydrostatic pressure?
force exerted by fluid against a wall
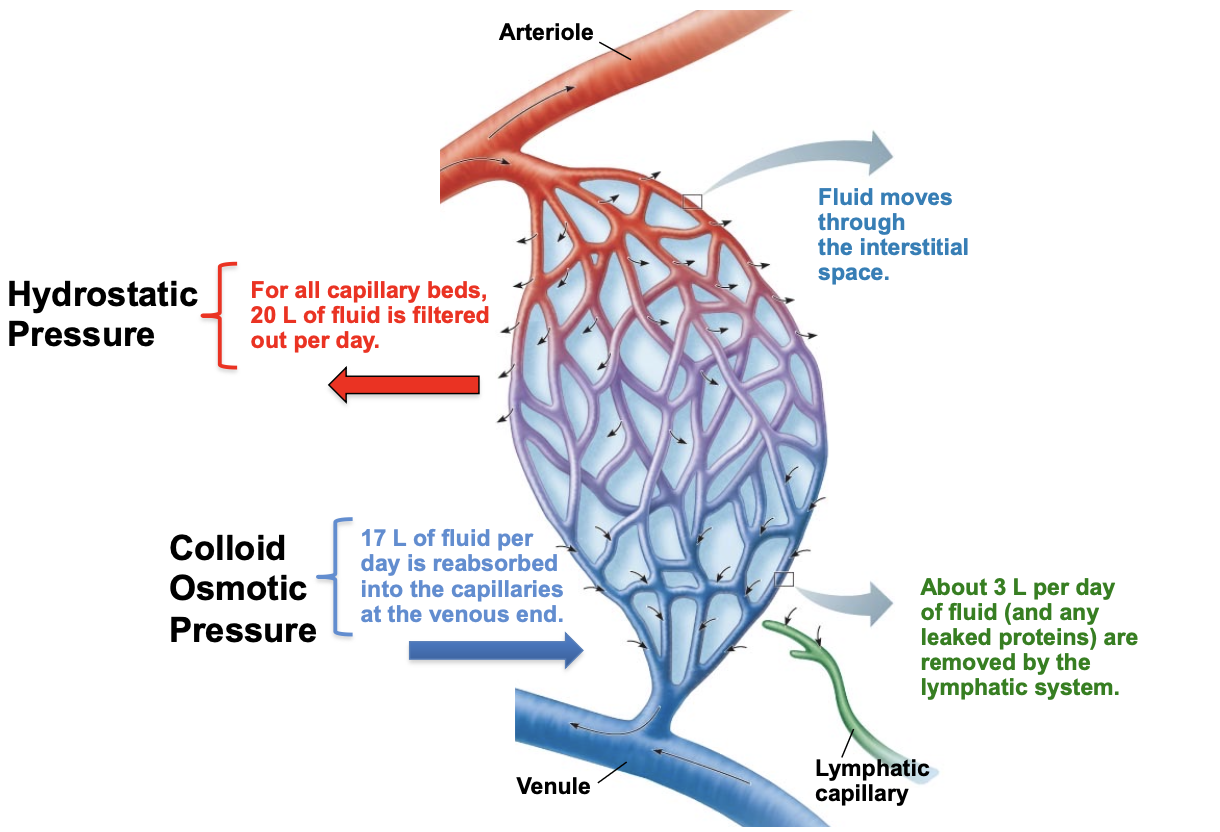
how much fluid is pushed out each day?
20L
how do you retain fluid in blood?
colloid osmotic pressure
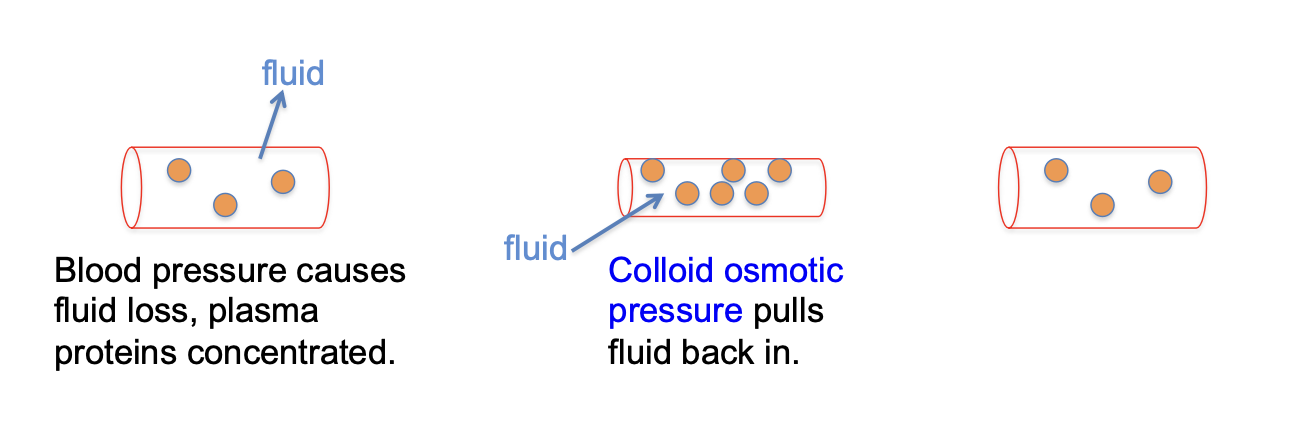
what is colloid osmotic pressure created by?
non-diffusible molecules that draw some fluid back
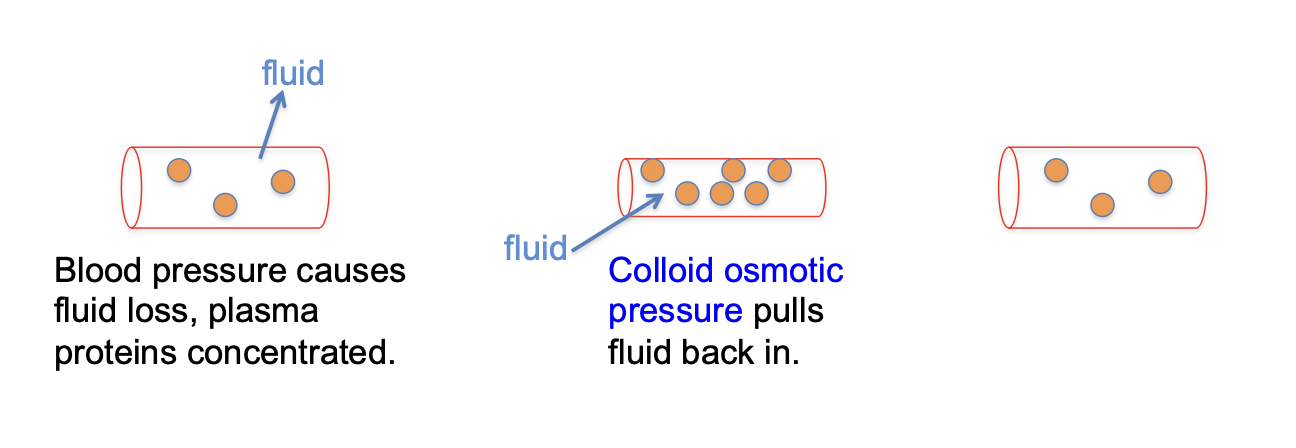
besides colloid osmotic pressure, what else returns fluid to blood?
lymphatic system
via colloid osmotic pressure how much fluid per day is reabsorbed into the capillaries at the venous end?
17L
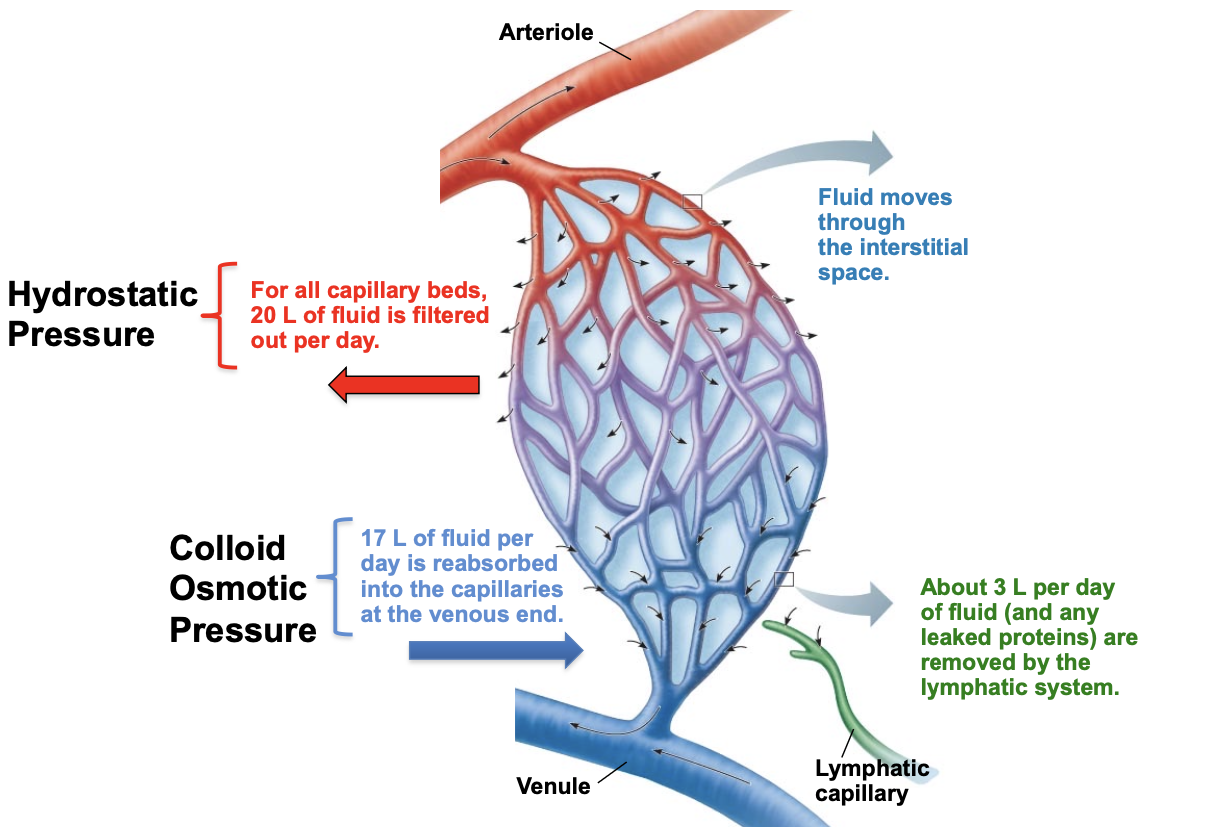
for all capillary beds, how much fluid is filtered out per day via hydrostatic pressure?
20L
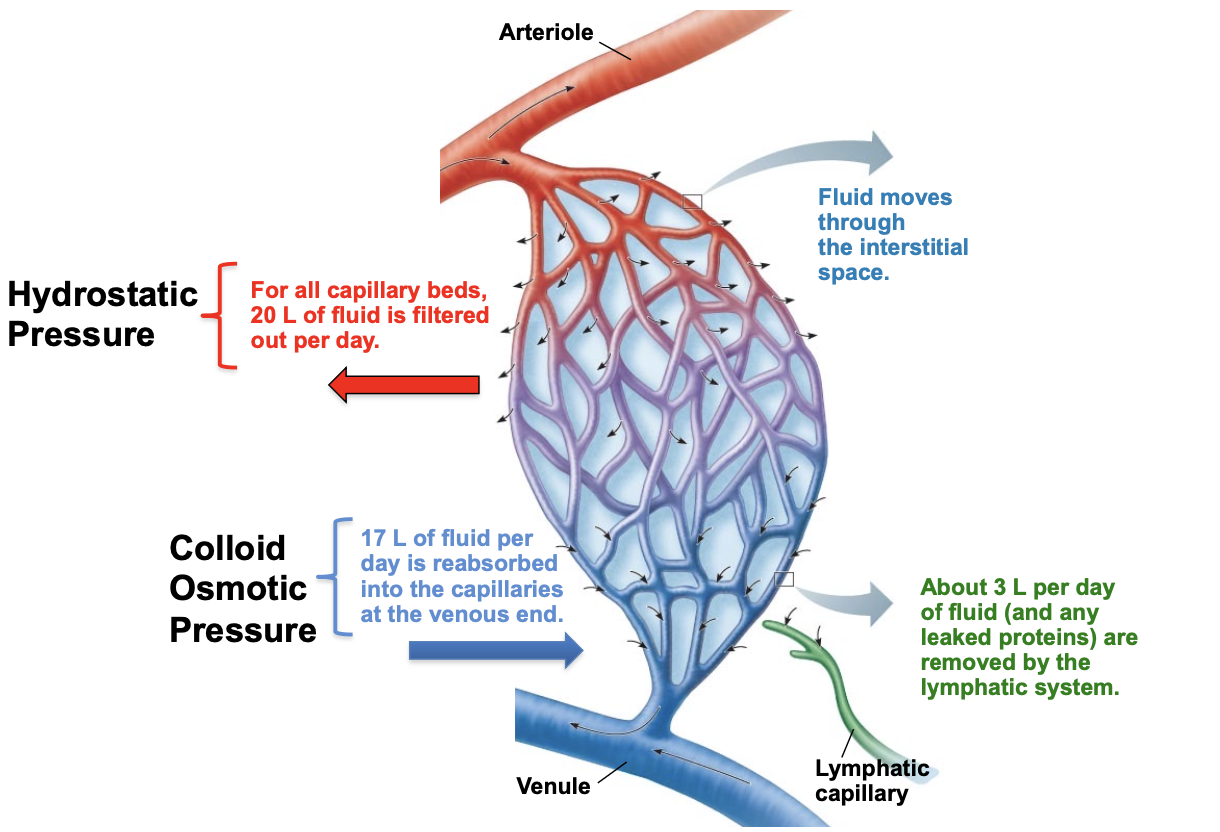
fluid moves through the _______ ________
interstitial space
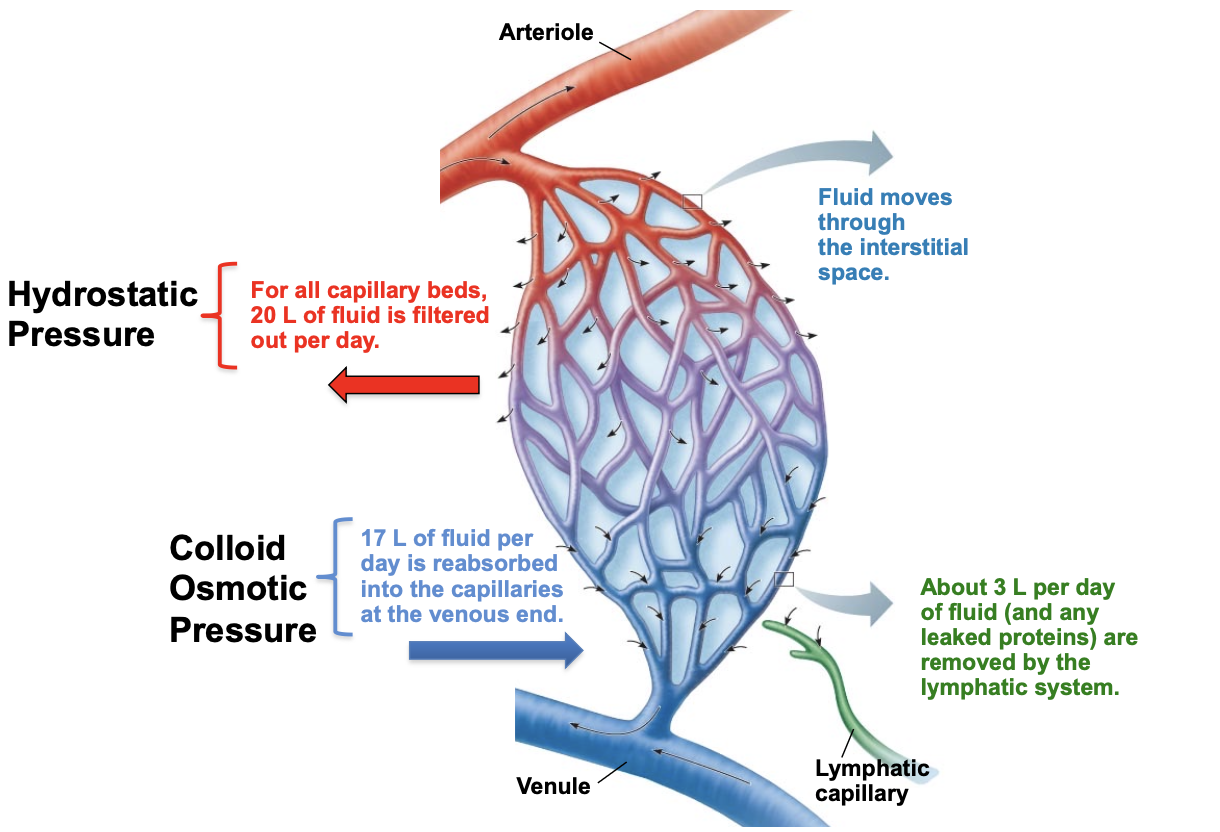
about how many liters of fluid per day are removed by the lymphatic system?
3L
what is the lymphatic system?
network of vessels that take up fluid from the interstitial space and return it to the blood
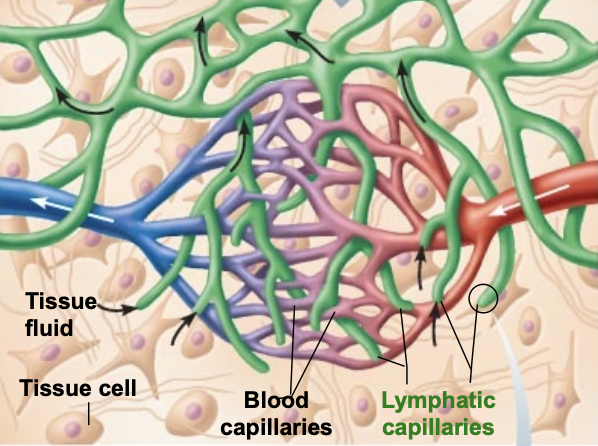
lymphatic capillary ends have ______ anchored to ______ ______
minivalves anchored to connective tissue
_______ fluid levels pull minivalves apart
increased fluid levels
once fluid enters lymphatic capillaries, it is called ______
lymph
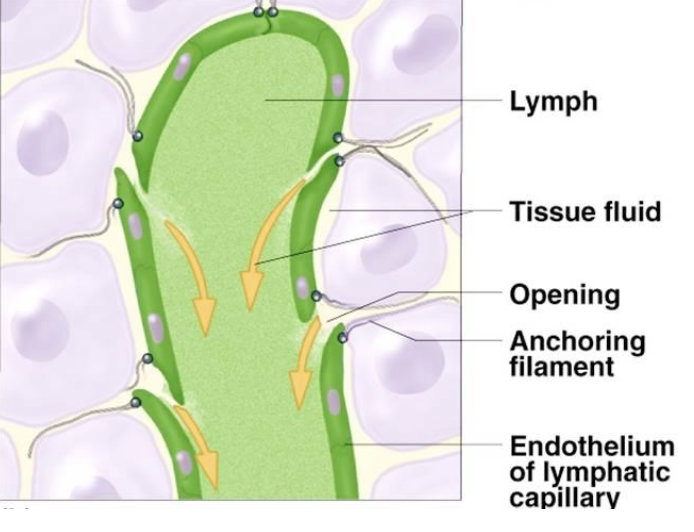
lymphatic vessels are all over the body except ______ and ______
bone, teeth
where does lymph go?
all roads lead to the heart
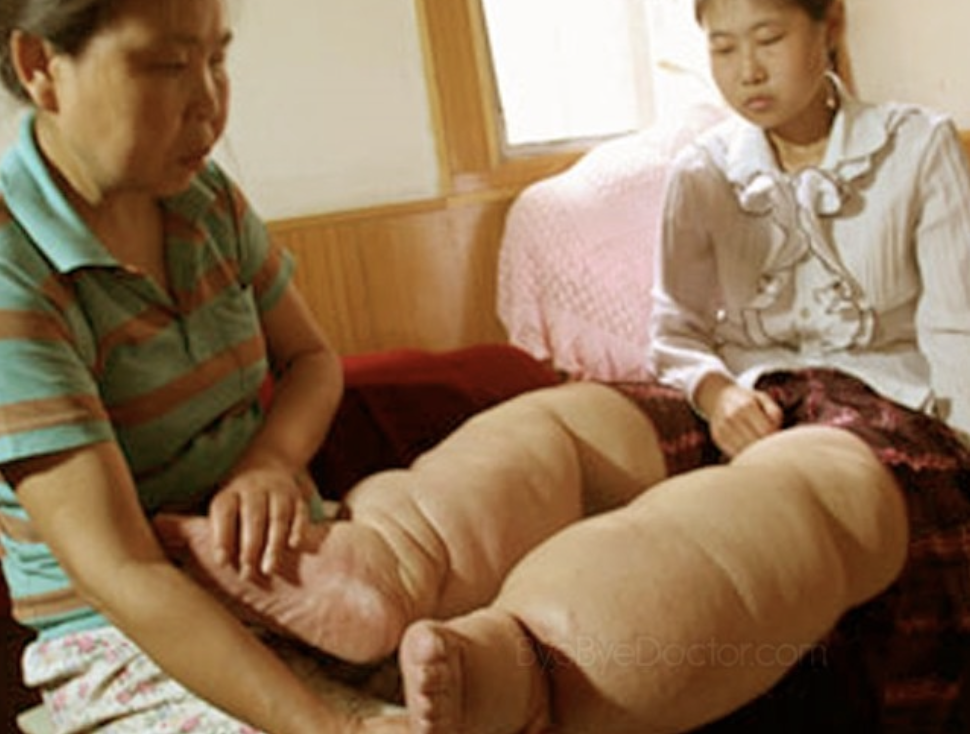
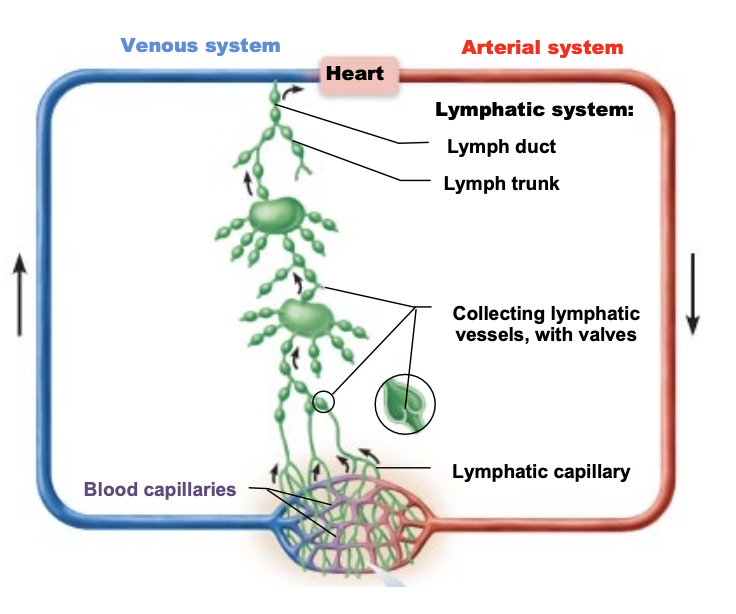

what is going on here?
extreme lymphatic disruptions
_______ is cleansed of debris and surveyed for pathogens
lymph
lymph travels through ______ _____
lymph nodes
what do immune cells do to pathogens?
detect and eliminate pathogens
what are lymph nodes?
solid spherical bodies that cluster along lymphatic vessels
what do lymph nodes provide for immune cells?
a meeting, surveillance, proliferation site for immune cells
what are the two cells of lymphoid organs?
lymphocytes and antigen presenting cells
what are lymphocytes?
the soldiers, T cells, B cells
what are T cells?
T lymphocytes, manage response, attack infected cells
what are B cells?
B lymphocytes, produce antibodies
what are macrophages?
antigen presenting cells, phagocytose foreign substances and present antigens
what are dendritic cells?
antigen presenting cells, capture antigens in tissues and bring them back to the lymph node
what bring in lymph to the lymph nodes?
afferents bring in lymph
what returns lymph to the body from the lymph nodes?
efferents return lymph
what is the cortex in lymph nodes?
dividing B cells (germinal centers), T cells in transit
what is the medulla in lymph nodes?
drains sinuses that allow lymph efflux
other lymphoid organs protect the body, but ONLY _____ ____ filter lymph
lymph nodes
what are some other lymphoid organs besides the lymph nodes?
tonsils, thymus, spleen, peyer’s patches, appendix
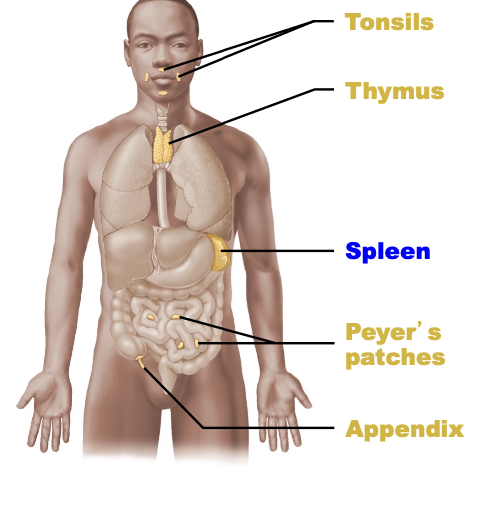
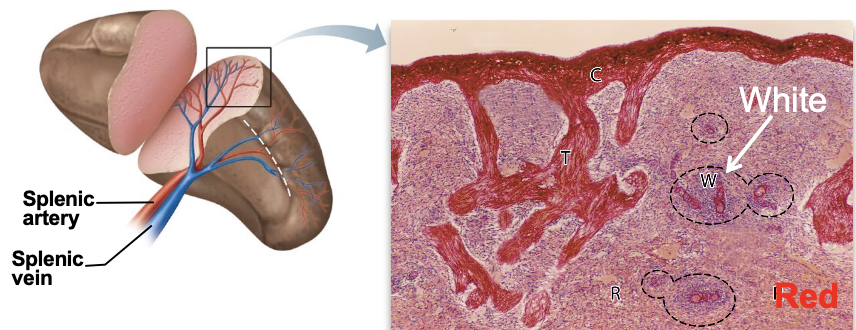
what does the spleen do?
immune surveillance of blood (white pulp), removal of old RBCs (red pulp)