3.11 Small mammal dental disease
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Rabbit right maxillary dentition
101-102 (incisors)
(no canines)
106-108 (premolars)
109-111 (molars)
Rabbit left mandibular dentition
301 (incisor)
(no canines)
307-308 (premolars)
309-311 (molars)
Rabbit total teeth
28
Rabbit causes of dental disease (3)
Dietary - inadequate dental wear
MBD (nutritional 2ndary hyperthyroidism)
Genetic predisposition (eg netherland dwarf small faces - less space)
Where do spurs/outgrowths form on upper and lower cheek teeth of rabbits?
Upper - buccal aspect (lateral)
Lower - lingual aspect (medial)
Signs of rabbit dental disease (5)
Reduced appetite or selective eating (hay consumption reduced)
Drooling
Weight loss
Reduced grooming and perineal caecotroph accumulation
Pressure on tooth roots → abscessation
ocular discharge (if maxillary)
facial swellings
Myomorph dental formula
1/1 incisors
(0 canines)
(0 premolars)
3/3 molars
Hystricomorph dental formula
1/1 incisors
(0 canines)
1/1 premolars
3/3 molars
Why does guinea pig mandibular teeth overgrowth present more frequently with tongue trapping VS rabbits?
Rabbits have more upright mandibular teeth
Why are chinchillas particularly prone to soft tissue damage in the mouth?
Teeth close to tongue and cheek
4 views minimum for small mammal dental X rays
Lateral
2x lateral oblique
Dorsoventral
(rostrocaudal)
2 types of malocclusion in rabbits
Wave mouth and step mouth
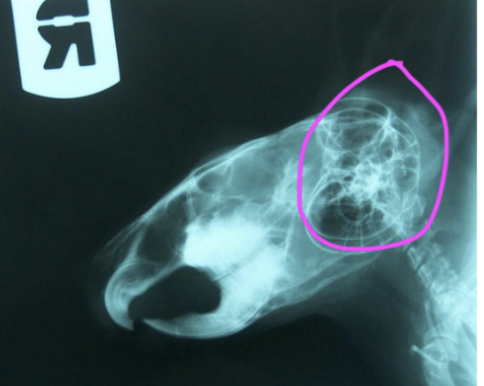
Species
Chinchilla - large tympanic bulla
Why should cheek teeth never be clipped in small mammals?
Splintering → trauma and pulp exposure
Why is rasping bad in small animals?
Iatrogenic trauma → can slip and hit veins in back of mouth, or move the teeth
2 types of mouth gag in small mammal dentistry
Tabletop gag (± light)
Fewer assistants required, but less flexible and difficult to close quickly
Traditional mouth gag
Extra people often needed for holding, but more flexible and easy to close
3 ways to manage ongoing dental disease
High fiber diet with hay → abrasion
If already severe root disease - painful to chew
Avoid museli mixes → selective feeding
Regular dental checks with treatment
generally aim for every 3-6 months for healthy animals
Severe → ongoing analgesia due to pain
Why should imaging always be done before incisor removal?
Ensure tooth roots aren’t so diseased the skull will basically fall apart right after extraction
Why should incisor sockets always be flushed?
Tooth roots are deep - infections can easily seed
List 4 topical treatment options for rabbit dental disease.
Manuka honey
high osmolarity, low pH
Topical antibiotics (eg eyedrops)
F10 ointment
Lots of flushing - physical movement gets infection out
Name 3 teeth retrobulbar abscesses are frequently associated with.
More caudal cheek teeth:
Premolar 3
Molars 1 or 2