Campbell Biology Chapter 8,9,&10
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/104
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
1
New cards
Metabolism
The totality (all) of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism; Manages the material and energy resources of the cell.
2
New cards
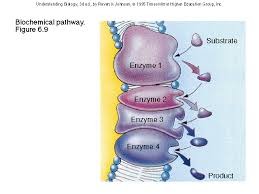
Metabolic Pathway
Begins with a specific molecule(s), which is then altered in a series of defined steps, resulting in a certain product(s). Each step in the pathway is catalyzed by a specific enzyme.
3
New cards
Catabolic Pathways
Breaks down complex molecules to simpler compounds; Releases energy. (i.e. cellular respiration)
4
New cards
Anabolic Pathways
Consumes energy to build complicated molecules from simpler ones. (also called biosynthetic pathways) (i.e. synthesizing proteins from amino acids)
5
New cards
Bioenergetics
The study of how energy flows through living organisms; how an organism manages their energy.
6
New cards
Energy
The ability to cause change. Some forms of energy can be used to do work (move matter against opposing forces).
7
New cards
Kinetic Energy
The energy an object has due to its motion.
8
New cards
Heat (Thermal Energy)
Kinetic energy associated with the random movement of atoms or molecules.
9
New cards
Potential Energy
The energy stored by matter as a result of its location or spatial arrangement.
10
New cards
Chemical Energy
Potential energy available for release in a chemical reaction.
11
New cards
Thermodynamics
The study of energy transformations that occur in a collection of matter. Closed systems and Open systems (organisms are Open systems)
12
New cards
First Law of Thermodynamics
The principle of conservation of energy: Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
13
New cards
Entropy
A quantitative measure of disorder or randomness, symbolized by S.
14
New cards
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy of the universe.
15
New cards
Spontaneous Process
A process that can occur without an input of energy. (For a process to occur without an input of energy it must increase the entropy of the universe.)
16
New cards
Free Energy
The portion of a system's energy that can perform work when temperature and pressure are uniform throughout the system.
17
New cards
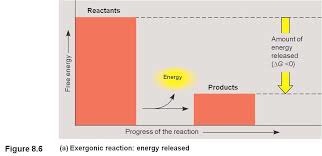
Exergonic Reaction
A spontaneous chemical reaction in which there is a net release of free energy.
18
New cards
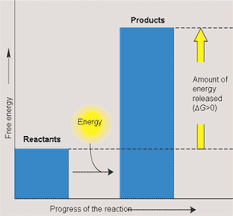
Endergonic Reaction
A non-spontaneous chemical reaction in which free energy is absorbed from the surroundings.
19
New cards
A cell's 3 main kinds of work
Chemical, transport, and mechanical.
20
New cards
Energy Coupling
In cellular metabolism, the use of energy released from an exergonic reaction to drive an endergonic reaction.
21
New cards
ATP is composed of
Ribose, Adenine (nitrogenous base), and 3 phosphate groups.
22
New cards
Activation Energy
The energy needed to start a chemical reaction.
23
New cards
Enzyme's Substrate
The reactant that an enzyme acts on.
24
New cards
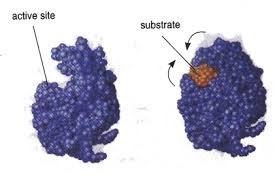
Enzyme-Substrate Complex
A temporary complex formed when an enzyme binds to its substrate molecule(s).
25
New cards
Active Site
The specific portion of an enzyme that attaches to the substrate by means of weak chemical bonds.
26
New cards
Induced Fit
the change in shape of the active site of an enzyme so that it binds more snugly to the substrate, induced by entry of the substrate.
27
New cards
An enzyme's activity can be affected by
Temperature, pH, and chemicals that influence the enzyme.
28
New cards
Cofactors
Non-protein molecule or ion that is required for the proper functioning of an enzyme, can be permanently bound to the active site or may bind loosely and reversibly along the substrate during catalysis
29
New cards
Coenzyme
An organic molecule serving as a cofactor. Most vitamins function in important metabolic reactions.
30
New cards
Competitive Inhibitors
A substance that reduces the activity of an enzyme by entering the active site in place of the substrate whose structure it mimics.
31
New cards
Noncompetitive Inhibitors
A substance that reduces the activity of an enzyme by binding to a location remote from the active site, changing its shape so that it no longer binds to the substrate.
32
New cards
Allosteric regulation
the binding of a regulatory molecule to a protein at one site that affects the function of the protein at a different site.
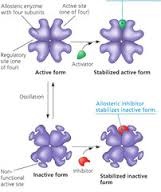
33
New cards
Cooperativity
A kind of allosteric regulation whereby a shape change in one subunit of a protein caused by substrate binding is transmitted to all the others, facilitating binding of subsequent substrate molecules.
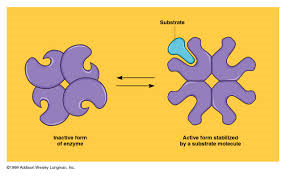
34
New cards
Feedback Inhibition
A method of metabolic control in which the end product of a metabolic pathway acts as an inhibitor of an enzyme within that pathway.
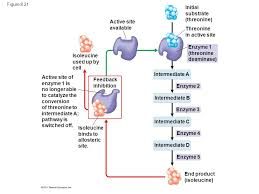
35
New cards
Fermentation
A partial degradation of sugars, or other organic fuel that occurs without the use of oxygen.
36
New cards
Energy Flow and Chemical Recycling in Ecosystem
Energy flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and ultimately leaves as heat, while the chemical elements essential to life are recycled.
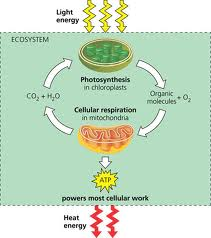
37
New cards
Food provides food for cellular respiration exhausting carbon dioxide and water
Organic + Oxygen ---> Carbon + Water + Energy
Compounds Dioxide
Compounds Dioxide
38
New cards
Aerobic Respiration
Oxygen is consumed as a reactant along with the organic fuel.
39
New cards
Cellular Respiration
The metabolic processes whereby certain organisms obtain energy from organic molecules; aerobic and anaerobic.
40
New cards
Cellular Respiration Diagram
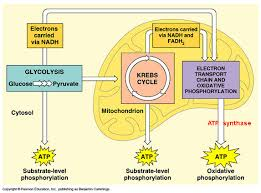
41
New cards
Summary Equation (Cellular Respiration)
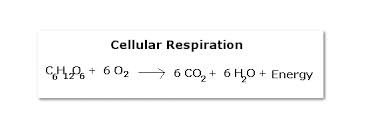
42
New cards
Redox Reactions
A chemical reaction involving the transfer of one or more electrons from one reactant to another; also called oxidation-reduction reaction.
43
New cards
Oxidation
The loss of electrons from a substance involved in a redox reaction.
44
New cards
Reduction
The addition of electrons to a substance involved in a redox reaction.
45
New cards
Oxidizing Agent
The electron acceptor in a redox reaction.
46
New cards
Reducing Agent
The electron donor in a redox reaction.
47
New cards
NAD+
An organic molecule that serves as an electron carrier by being oxidized to NAD+ and reduced to NADH.
48
New cards
NADH
the reduced form of NAD+; an electron-carrying molecule that functions in cellular respiration.
49
New cards
Electron Transport Chain
A sequence of electron carrier molecules (membrane proteins) that shuttle electrons during the redox reactions that release energy used to make ATP. (O2 pulls electrons down the chain)
50
New cards
Glycolysis
a metabolic process that breaks down carbohydrates and sugars through a series of reactions to either pyruvic acid or lactic acid and release energy for the body in the form of ATP; first step in cellular respiration.
51
New cards
Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs cycle)
In cellular respiration, series of chemical reactions that break down glucose and produce ATP; energizes electron carriers that pass the energized electrons on to the electron transport chain; second step in cellular respiration.
52
New cards
Oxidative Phosphorylation
The production of ATP using energy derived from the redox reactions of an electron transport chain; generates almost 90% of the ATP; the third major stage of cellular respiration.
53
New cards
Oxidative Phosphorylation
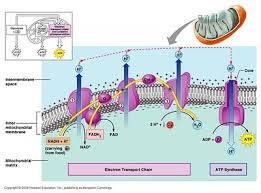
54
New cards
Substrate-level Phosphorylation
The formation of ATP by an enzyme directly transferring a phosphate group to ADP from an intermediate substrate in catabolism; occurs during glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
55
New cards
Cytochromes
An iron-containing protein that is a component of electron transport chains in the mitochondria and chloroplasts of eukaryotic cells and the plasma membranes of prokaryotic cells.
56
New cards
Acetyl CoA
The entry compound for the citric acid cycle in cellular respiration formed from two-carbon fragment of pyruvate attached to a coenzyme
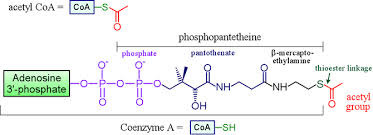
57
New cards
ATP Synthase
Large protein that uses energy from H+ ions to bind ADP and a phosphate group together to produce ATP.
58
New cards
Chemiosmosis
An energy-coupling mechanism that uses energy stored in the form of a H+ gradient across a membrane to drive cellular work, such as the synthesis of ATP. Most ATP synthesis in cells occurs by chemiosmosis.
59
New cards
Proton-motive Force
The potential energy stored in the form of an electrochemical gradient, generated by the pumping of hydrogen ions across biological membranes during chemiosmosis.
60
New cards
Alcohol Fermentation
Anaerobic ATP-forming pathway. Pyruvate from glycolysis is degraded to acetaldehyde, which accepts electrons from NADH to form ethanol; NAD+ needed for the reactions is regenerated. Net yield: 2 ATP.
61
New cards
Lactic Acid Fermentation
series of anaerobic chemical reactions in which pyruvic acid uses NADH to form lactic acid and NAD+, which is then used in glycolysis; supplies energy when oxygen for aerobic respiration is scarce; releases no CO2.
62
New cards
Obligate Anaerobes
an organism that only carries out fermentation or anaerobic respiration. Cannot survive in the presence of O2.
63
New cards
Facultative Anaerobes
An organism that makes ATP by aerobic respiration if oxygen is present but that switches to fermentation under anaerobic conditions.
64
New cards
Beta Oxidation
A metabolic sequence that breaks fatty acids down to two-carbon fragments which enter the Krebs cycle as acetyl CoA.
65
New cards
Photosynthesis
The process that converts solar energy into chemical energy.
66
New cards
Autotrophs
Organisms that are able to make their own food
67
New cards
Heterotrophs
organisms that depend on other organisms for their food
68
New cards
Chlorophyll
green pigment in plants that absorbs light energy used to carry out photosynthesis
69
New cards
Stomata
Pore-like openings in leaves that allow gases (CO2 enters and O2 exits) and water to diffuse in and out of the leaves.
70
New cards
Mesophyll
the tissue in the interior of the leaf
(30-40 chloroplasts)
(30-40 chloroplasts)
71
New cards
Thylakoids
saclike photosynthetic membrane found in chloroplasts. when stacked they are called grana
72
New cards
Stroma
the dense colorless fluid in the chloroplast.
73
New cards
Oxidized in photosynthesis
H2O
74
New cards
Reduced in photosynthesis
CO2
75
New cards
Light reactions
In thylakoids H2o is split, releases O2, reduces NADP+ to NADPH, makes ATP from ADP by photophosphorylation .
76
New cards
Calvin cycle
In stroma forms sugar from CO2 using ATP and NADPH; Begins with carbon fixation.
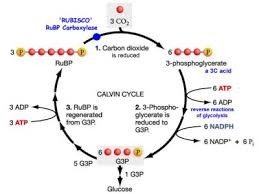
77
New cards
Carbon fixation
The incorporation of CO2 into organic compounds
78
New cards
Wavelength
The distance between crests of waves, such as those of the electromagnetic spectrum.
79
New cards
Electromagnetic spectrum
the entire frequency range of electromagnetic waves
80
New cards
Photons
particles of light.
81
New cards
Spectrophotometer
Measures the ability of a pigment to absorb various wavelengths of light
82
New cards
Absorption spectrum
a graph plotting a pigment's light absorption versus wavelength
83
New cards
Chlorophyll a
A type of blue-green photosynthetic pigment that participates directly in the light reactions.
84
New cards
Action spectrum
A graph that profiles the relative effectiveness of different wavelengths of radiation in driving a particular process
85
New cards
Chlorophyll b
A type of yellow-green accessory photosynthetic pigment that transfers energy to chlorophyll a.
86
New cards
Carotenoids
accessory pigment; absorb excessive light that would damage chlorophyll
87
New cards
Photosystem
in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, a cluster of chlorophyll and other pigment molecules that harvest light energy for the light reactions of photosynthesis
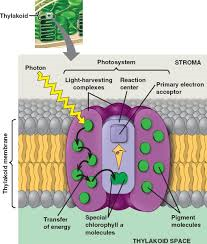
88
New cards
Reaction-center complex
A complex of proteins associated with a special pair of chlorophyll, a molecule, and a primary electron acceptor. Located centrally in a photosystem, this complex triggers the light reactions of photosynthesis. Excited by light energy, the pair of chlorophylls donates an electron to the primary electron acceptor, which passes an electron to an electron transport chain.
89
New cards
light-harvesting complexes
(pigment molecules bound to proteins) funnel the energy of photons to the reaction center
90
New cards
Primary electron acceptor
A specialized molecule sharing the reaction center with the chlorophyll a molecule; it accepts an electron from the chlorophyll a molecule.
91
New cards
Photosystem ll
functions first and is the best at absorbing a wavelength of 680 nm (P680)
92
New cards
Photosystem l
(P700) occurs 2nd
93
New cards
Linear electron flow
Primary Pathway: involves both photosystems and produces ATP and NADPH using light energy
94
New cards
Cyclic electron flow
uses only photosystem I and produces ATP, but not NADPH
95
New cards
Chemiosmosis
A process for synthesizing ATP using the energy of an electrochemical gradient and the ATP synthase enzyme.
96
New cards
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P)
A three-carbon carbohydrate that is the direct product of the Calvin cycle; it is also an intermediate in glycolysis.
97
New cards
3 Phases of the Calvin Cycle
Carbon fixation, Reduction, Regeneration of the CO2 acceptor (RuBP)
98
New cards
Rubisco
Ribulose carboxylase, the enzyme that catalyzes the first step of the Calvin cycle (the addition of CO2 to RuBP, or ribulose bisphosphate).
99
New cards
Photorespiration
a metabolic pathway in plants that consumes oxygen, produces carbon dioxide, generates no ATP, and reduces photosynthesis
100
New cards
Mesophyll cells
more loosely arranged cells between the bundle sheath and leaf surface cells (C4)