Chem 1LC Final Prep: Essential Safety Terms & Errors
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
What are the appropriate actions to take in the event of a spill?
1. contaminated clothing must be.....
2. use a spill pillow to...
3. if splashed with large quantity of a chemical...
4. if solid is spilled....
5. eyewashes should be use for at least 15 minutes
-contaminated clothing must be removed and treated as hazardous waste
-use a spill pillow to absorb liquids with nontoxic vapors
-if splashed with large quantity of a chemical, use shower immediately
-if solid is spilled wash and scrape off, then wash with water
-eyewashes should be use for at least 15 minutes
What are the four key steps for responding to a spill? (ECIM)
Evacuate- large spills/hazardous
Communicate: notify an instructor or stock staff of location and contents
Isolate: contain spill with pillows
Mitigate: Clean up spill, instructor decides if you can clean it up
What are the two steps when you are on fire?
stop, drop and roll; wrap the person in a fire blanket
How do you use a fire extinguisher? (PASS)
PASS
Pull: the safety pin
Aim: base of the fire
Squeeze: handle to begin discharge
Sweep: discharge back and fourth
Match the part of the fire tetrahedron with the way to remove it:
heat, oxygen, chemical chain reaction, fuel
heat: pour water
oxygen: carbon dioxide fire extinguisher blanket
chemical chain reaction: halon fire extinguisher
fuel: minimize flammable solvents
Match fire class with their fuelfor the fire:
(A, B, C, D)
A. Paper, clothing, plastics
B. Oil, organic solvents, gasoline
C. Hot plates, computers
D. Reactive metals (ie: sodium or litium)
Facts about fire
-Water cannot be used to extinguish a class ___ fire
-Removing heat keeps the ___ from vaporizing
-The fuel must be _____ to burn
-Water cannot be used to extinguish a class D fire
-Removing heat keeps the fuel from vaporizing
-The fuel must be vaporized to burn
Which of the following are true about bleach?
-Nitrile gloves have a ___ min breakthrough time for bleach
-Bleach is a weak reducing agent
-Bleach can causes severe ___ burns and ____ damage
-If a significant amount of ____ is spilled on you, get into the _____ immediately
-Bleach forms poisonous chlorine and chloramine gas when combined with ____
-Nitrile gloves have a 480 min breakthrough time for bleach
-Bleach can causes severe skin burns and eye damage
-If a significant amount of bleach is spilled on you, get into the shower immediately
-Bleach forms poisonous chlorine and chloramine gas when combined with ammonia
What percentage of known chemicals have safety data sheets?
0.1%
Who creates SDS?
chemical suppliers
What GHS components are incorporated in SDS?
pictograms
signal words
hazard ratings
hazard statements
precautionary statments
SDS is written for a (professional or industrial) setting, because of this, chemical hazards and personal protective equipment requirements may be (under or overstated).
SDS is written for an indurstial setting, because of this, chemical hazards and personal protective equipment requirements may be overstated.
Rearrange these steps for using SDS:
-Look at the procedures for safe handling
-compare label info to ensure you have right SDS
-determine hazard class
1. compare label info to ensure you have right SDS
2. determine hazard class
3. Look at the procedures for safe handling
What should be done while handling a corrrosive?
-if exposed...
-discard _____ after contamination of taking off
-wear _____, _____, and _______
-carry bottles in _______ _______
-use in the fume hood if the ______ is a _______ hazard
-long or short clothing? ____-shedding closed toed shoes
-know the location of the ____ stations
-if exposed wash off skin immediately
-discard gloves after contamination of taking off
-wear gloves, goggles, and lab coat
-carry bottles in secondary containers
-use in the fume hood if the _corrosive is a inhalant hazard
-long clothing water-shedding closed toed shoes
-know the location of the eyewash stations
random error (pick two)
-reduced by using a best fit line
-failure to read the last sig figs
-inaccurate calibration of pH probe
-result of equipment failure
-consistently reading buret volume by looking up at liquid level
-light source on spectrometer dims over time
-causes outlier than can be determined by "Q-test"
-measured by calculating standard deviation
-eliminated by good experimental methods, more than 1 calibration step
-using graduated cylinder instead of volumetric flask to make standard deviations
random error:
-measured by calculating standard deviation
-reduced by using a best fit line,
instrumental error (pick two)
-reduced by using a best fit line
-failure to read the last sig figs
-inaccurate calibration of pH probe
-result of equipment failure
-consistently reading buret volume by looking up at liquid level
-light source on spectrometer dims over time
-causes outlier than can be determined by "Q-test"
-measured by calculating standard deviation
-eliminated by good experimental methods, more than 1 calibration step
-using graduated cylinder instead of volumetric flask to make standard deviations
instrumental error:
-inaccurate calibration of pH probe
-light source on spectrometer dims over time
methodological error (pick two)
-reduced by using a best fit line
-failure to read the last sig figs
-inaccurate calibration of pH probe
-result of equipment failure
-consistently reading buret volume by looking up at liquid level
-light source on spectrometer dims over time
-causes outlier than can be determined by "Q-test"
-measured by calculating standard deviation
-eliminated by good experimental methods, more than 1 calibration step
-using graduated cylinder instead of volumetric flask to make standard deviations
methodological error:
-consistently reading buret volume by looking up at liquid level
-using graduated cylinder instead of volumetric flask to make standard deviations
systematic error (pick one)
-reduced by using a best fit line
-failure to read the last sig figs
-inaccurate calibration of pH probe
-result of equipment failure
-consistently reading buret volume by looking up at liquid level
-light source on spectrometer dims over time
-causes outlier than can be determined by "Q-test"
-measured by calculating standard deviation
-eliminated by good experimental methods, more than 1 calibration step
-using graduated cylinder instead of volumetric flask to make standard deviations
systematic error:
-eliminated by good experimental methods, more than 1 calibration step
gross error (pick two)
-reduced by using a best fit line
-failure to read the last sig figs
-inaccurate calibration of pH probe
-result of equipment failure
-consistently reading buret volume by looking up at liquid level
-light source on spectrometer dims over time
-causes outlier than can be determined by "Q-test"
-measured by calculating standard deviation
-eliminated by good experimental methods, more than 1 calibration step
-using graduated cylinder instead of volumetric flask to make standard deviations
gross error:
-causes outlier than can be determined by "Q-test"
-result of equipment failure
personal error (pick one)
-reduced by using a best fit line
-failure to read the last sig figs from a buret
-inaccurate calibration of pH probe
-result of equipment failure
-consistently reading buret volume by looking up at liquid level
-light source on spectrometer dims over time
-causes outlier than can be determined by "Q-test"
-measured by calculating standard deviation
-eliminated by good experimental methods, more than 1 calibration step
-using graduated cylinder instead of volumetric flask to make standard deviations
-failure to read the last sig figs from a buret
Which of the following play significant roles in the extent of injury or harm when exposed to a hazardous chemical?
-atmospheric pressure
-relative humidity-availability of safety equipment
-the amount of chemical one is exposed to
-the amount of time one is exposed to the chemical
-how the chemical entered the body
-the amount of chemical one is exposed to
-the amount of time one is exposed to the chemical
-how the chemical entered the body
match to minimize exposure:
ingestion, eye exposure, inhalation, skin exposure, injection:
-cap flasks containing volatile liquids
-clean surfaces, wear gloves and lab coat
-do not put anything in your mouth thats been in the lab
-always wear goggles
-use dustpan and broom to clean up broken glass
ingestion: do not put anything in your mouth thats been in the lab
eye exposure: always wear goggles
inhalation: cap flasks containing volatile liquids
skin exposure: clean surfaces, wear gloves and lab coat
injection: use dustpan and broom to clean up broken glass
match the airborne particle with its description
mists, fumes, dusts, smoke, nanoparticles
-tiny liquid droplets
-solid particles suspended in the air
-colloidal suspension of liquid particles in the air
-ultra fine homogenous partiles
-mixture of dry particles and drops of liquid
mists-tiny liquid droplets
dusts-solid particles susended in the air
fumes-colloidal suspension of liquid particles in the air
nanoparticles-ultra fine homogenous partiles
smoke-mixture of dry particles and drops of liquid
What are parts of the design of laboratory ventilation? (ie: fume hoods and hallways)
-lab air leaves through the fume hoods
-air enters the labs through heating/cooling ducks and hallway air
-hallway air flows into the lab
1. Wear safety [1], not safety glasses, and lab aprons at all times.
Wear prescription eye glasses underneath goggles.
2. Wear clothing providing [2] protection. Shorts, Capri pants, sandals, slip on shoes, minis, and bare stomach, shoulders, or backs are not allowed in the labs.
1. Goggles
2. Maximum
3. Conduct myself in a mature fashion. Excessive noise or [3] behaviors are NOT permitted.
4. Note the exact location of all [4] and learn its proper use.
3. disruptive
4. safety eqipment
5. Perform reactions using (or evolving) noxious or highly combustible chemicals in a [5].
6. Report and [6] all spills immediately.
5. fume hood
6. clean up
[7] from eating, drinking, smoking, or chewing gum in lab.
[8] of any cracked or broken glassware.
7. refrain
8. dispose
9. Extinguish all flames or ignition sources when using [9] and/or volatile chemicals.
10. Place all left‑over chemicals in the appropriate collection bottles in the hood. Do NOT dump chemicals into the [10].
9. flammable
10. sink or trash
11. Perform only supervised and authorized experiments in lab. An [11] must be present at all times and all procedures must be followed.
12. Use tongs or protective gloves to handle [12] objects.
11. instructor
12. hot
13. Add concentrated [13] slowly to water while stirring when diluting - NEVER the reverse!
14. Use [14] procedures and precautions when inserting glass tubing into a rubber stopper.
13. acid
14. correct
15. Properly label all chemical containers and [15] labels before using chemicals.
14. Store all book bags, purses, coats, etc., in [16] areas to avoid clutter
15. read
16. designated
17. I will [17] my workspace and wash hands frequently during lab and thoroughly before leaving lab.
18. Think before acting and use [18] judgement and care in the lab.
19. [19] report all injuries to the instructor no matter how small the injury appears.
17. Clean
18. good
19. immediatly
What is the most appropriate action if a chemical has just splashed on a person's face in lab?
wash ____ (with or without) removing goggles
wash face without reomving goggles
If large portions of a person's body are exposed to harmful chemicals, what should be done?
use safety shower
What is the minimum amount of time an area of a person's body that has been exposed to harmful chemicals should be washed? (in minutes)
15 minutes
What should be done...
1. ...in case of a fire? (ENM)
2. ...if the fire alarm sounds? (SUE)
3. ...if an accident occurs? (NADS)
What should be done...
1. ...in case of a fire? (ENM)
-Evaluate the situation
-Notify the lab instructor
-Move away from the fire.
2. ...if the fire alarm sounds? (SUE)
-Stop chemical reactions and lower hood sashes
-Unplug electrical equipment
-Evacuate the building by taking the stairs.
3. ...if an accident occurs? (NADS)
-Notify the lab instructor.
-Act quickly.
-Do not panic.
-Seek medical attention
When should gloves be worn?
Group of answer choices
-working on computers
-outside of lab
-handling toxic or corrosive chemicals
-upon first entering the lab
handling toxic or corrosive chemicals
1. What should you do when working with a heat source?
-Always assume that glassware and metal objects are hot
-Utilize a fume hood
-do nothing
-all of these
2. What should you do when working with a volatile chemical?
-work near a heat source
-mix it with oxidizing agents
-work in the fume hood
-all of these
3. What should you do when working with a bottle containing a chemical?
-Never assume that the cap is tightened.
-All of these
-Hold the bottle with the label in the palm of your hand.
-Grasp the bottle firmly
1. all of these
2. work in the fume hood (mixing volatile chemicals with oxidizing agents is highly hazardous lol)
3. all of these
Before coming to lab, which ones should you do?
-eat food
-read and understand experimental procedures and safety precautions
-dress properly.
-eat food
-read and understand experimental procedures and safety precautions
-dress properly.
Which of the following is NOT allowed in lab?
-food
-drink
-eye glasses
-mixing chemicals without specific instruction from the lab instructor
-cell phones
-students who are not enrolled in the lab section
-open flame
-backpacks
-Drinking water (or anything else)
-food
-drink
-students who are not enrolled in the lab section
-mixing chemicals without specific instruction from the lab instructor
-open flame
What should be worn in the laboratory?
-yoga pants
-long pants
-closed toe water shedding shoes
-tank top shirt
-goggles
-bare back dress
-capri pants
-sandals
-lab coat
-long pants
-closed toed water shedding shoes
-goggles
-lab coat
What should a student locate when entering lab?
-fire extinguisher
-safety shower
-Stairwells
-eye wash stations
-fire extinguisher
-safety shower
-Stairwells
-eye wash stations
a ________ error is created by using the wrong indicator for an acid-base titration
-what category of error is this in?
a methodological error is created by using the wrong indicator for an acid-base titration
-systematic
a ______ error occurs when an experimenter records only even numbers for the last digit of buret volumes.
-what category of error is this in?
a personal error occurs when an experimenter records only even numbers for the last digit of buret volumes.
-systematic
the three types of systematic errors are ______ , ______ and ______
methodological, personal, instrumental
A _____ error is caused by an experimenter's carelessness or equipment failure.
gross error is caused by an experimenter's carelessness or equipment failure.
a ______ (or indeterminate) error is caused by uncontrollable fluctuations in variables that affect experimental results.
a random (or indeterminate) error is caused by uncontrollable fluctuations in variables that affect experimental results.
a ______ error results when a spectrometer drifts away from calibrated settings;
-what category of error is this in?
an instrumental error results when a spectrometer drifts away from calibrated settings;
Fire extinguishers are located by...
Fire extinguishers are located by each door of the lab.
Sodium bicarbonate and Solusorb
-what is it inside of?
-location?
-use of these chemicals?
Sodium bicarbonate and Solusorbs:
-inside of: buckets
-located: in the front of the lab
-neutralize/absorb chemical spills on the floor or lab tables
where are first-aid kits located?
in the stock room
Whats is the function of each of the following items inside of the spill kit?
-absorbent barrier
-flattened absorbent barriers
-splash goggles
-sodium bicarbonate
-absorbent barrier to collect strong liquids and acids
-flattened absorbent barriers: to clean he rest of the spill
-splash goggles: for more coverage
-sodium bicarbonate: its basic so it can neutralize acids
Water is used by firefighters to control heat inside of a burning building. As the water turns to steam, it absorbs heat from the fire. What is the term for the energy required to turn water to steam?
-liquid to gas
-evaporation
Fill in the blank for each fire extinguishing method:
-Put a beaker over the candle to remove all _____
-Blow the flame out to disrupt the_____ ______ reaction by disrupting the ____ to _____ ratio
-Light a match and place it in the crucible. The back (lit or unlit) end of the match should rest on the top edge of the crucible.
-Squirt the flame out with a small squeeze bottle of _____.
-Put a beaker over the candle to remove all oxygen
-Blow the flame out to disrupt the chemical chain reaction by disrupting the fuel to oxygen ratio
-Light a match and place it in the crucible. The back unlit end of the match should rest on the top edge of the crucible.
-Squirt the flame out with a small squeeze bottle of water
whats a corrosive do?
How was the sponge able to be corroded by the strong acid?
-How does this relate to your skin's composition and corrosive safety?
-destroying other substances as they cause a chemical reaction.
-sponges are carbon based compounds
-Human skin is made of cells in which the membranes are composed of carbohydrates, which makes us carbon-based (organic) compounds
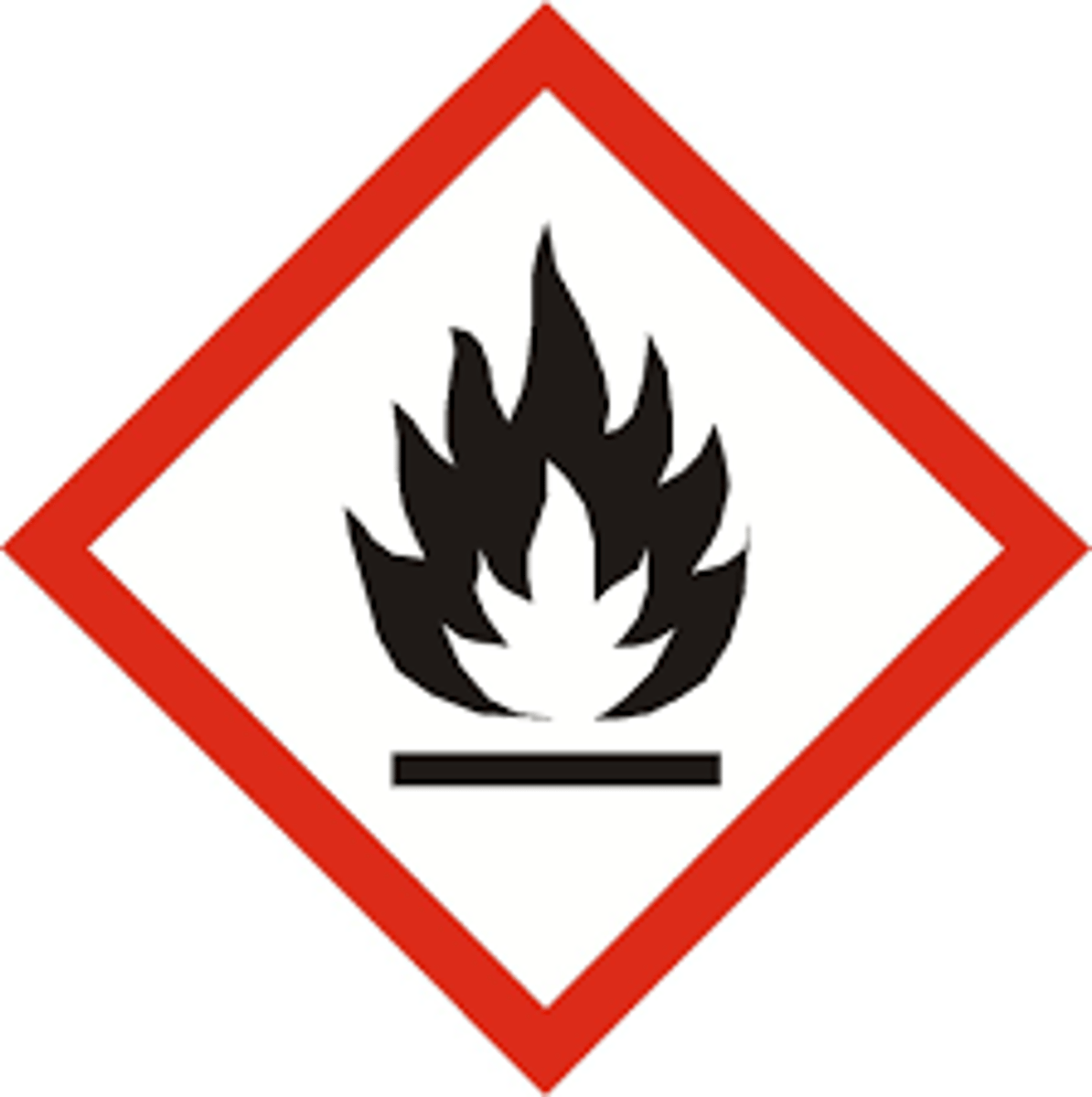
What does the
"fire" GHS symbol mean?
flammable (ignites and burns)

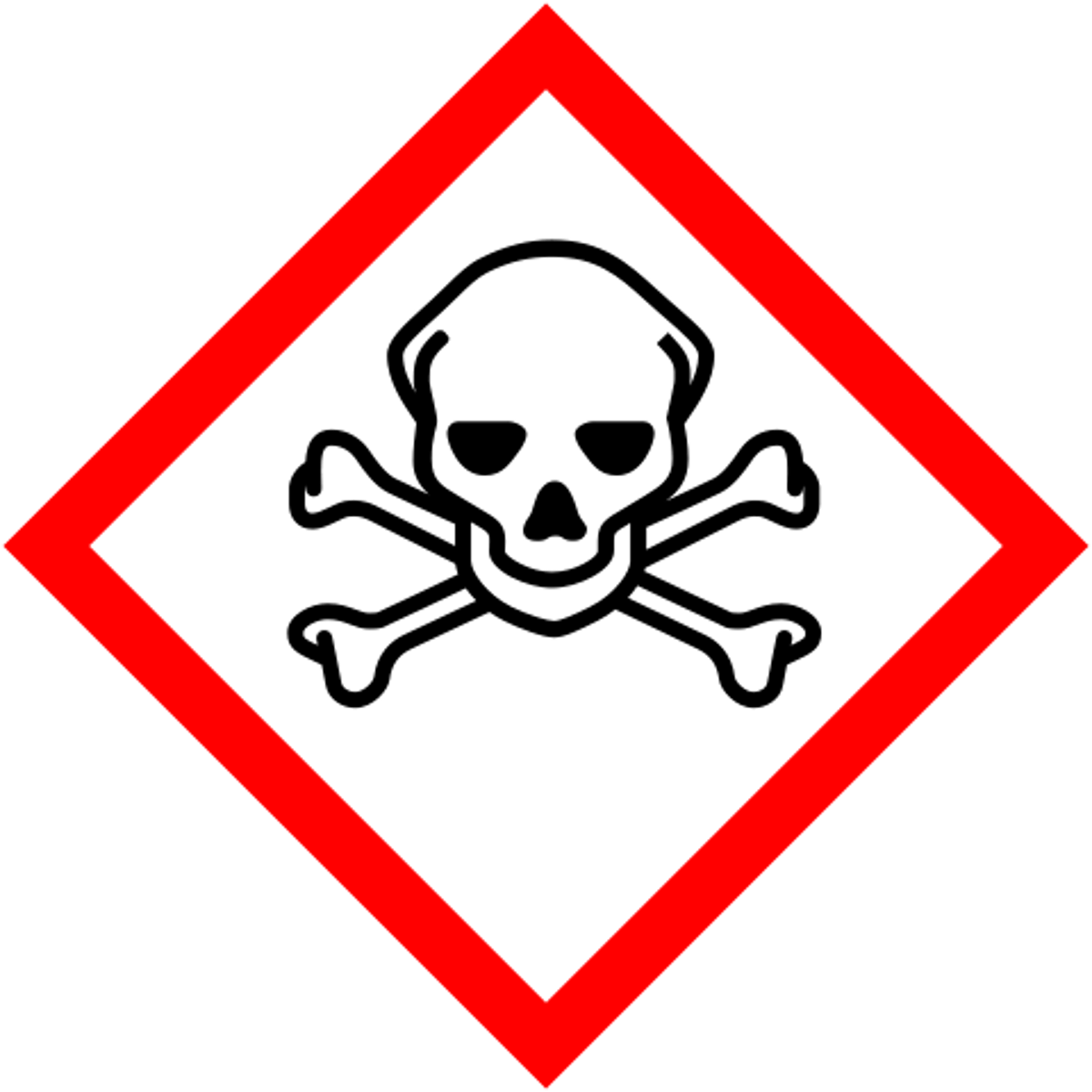
what does the "skull and cross bones" GHS symbol stand for?
toxic (death via short exposure or small amounts)

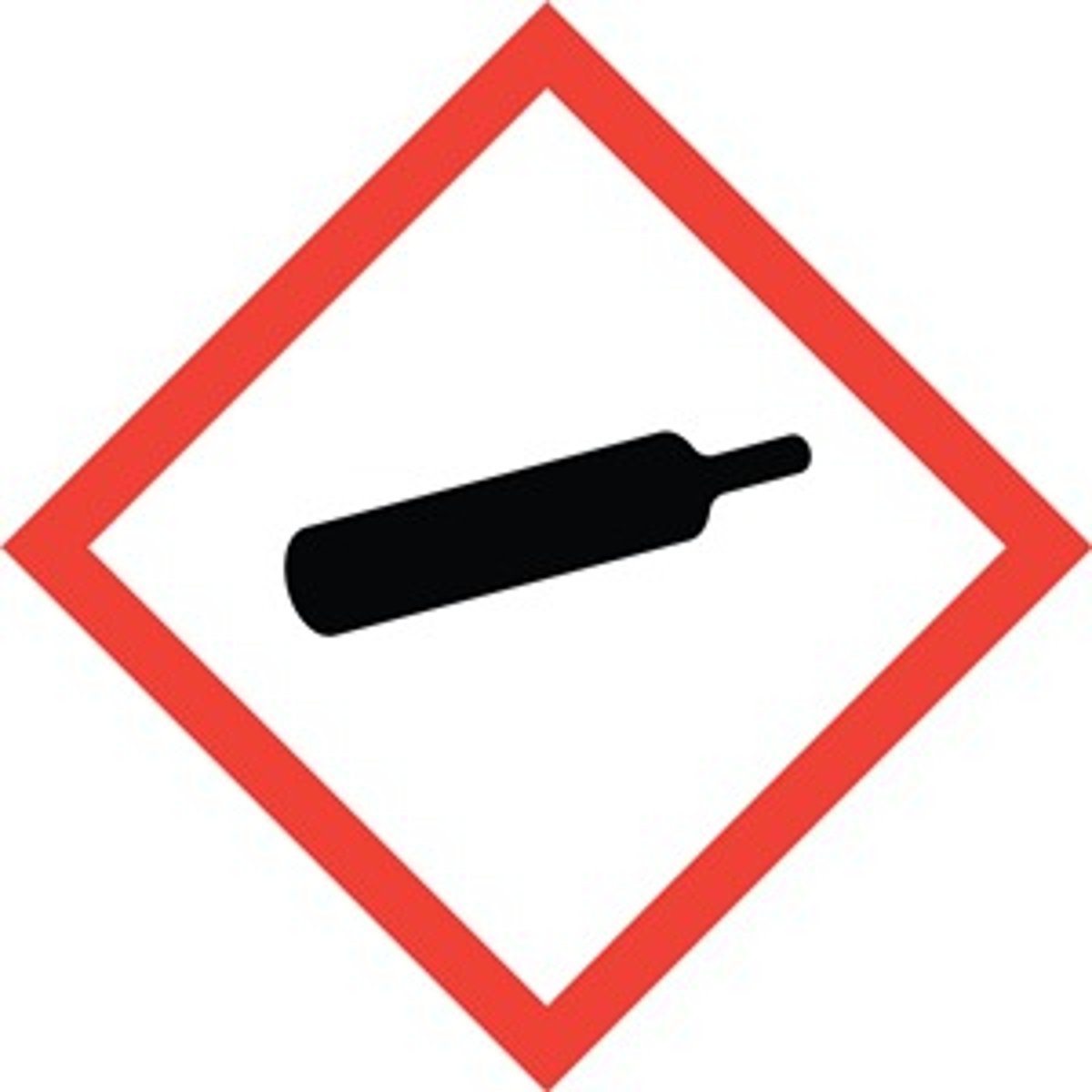
what does the "gas tank" GHS symbol stand for?
compressed gas

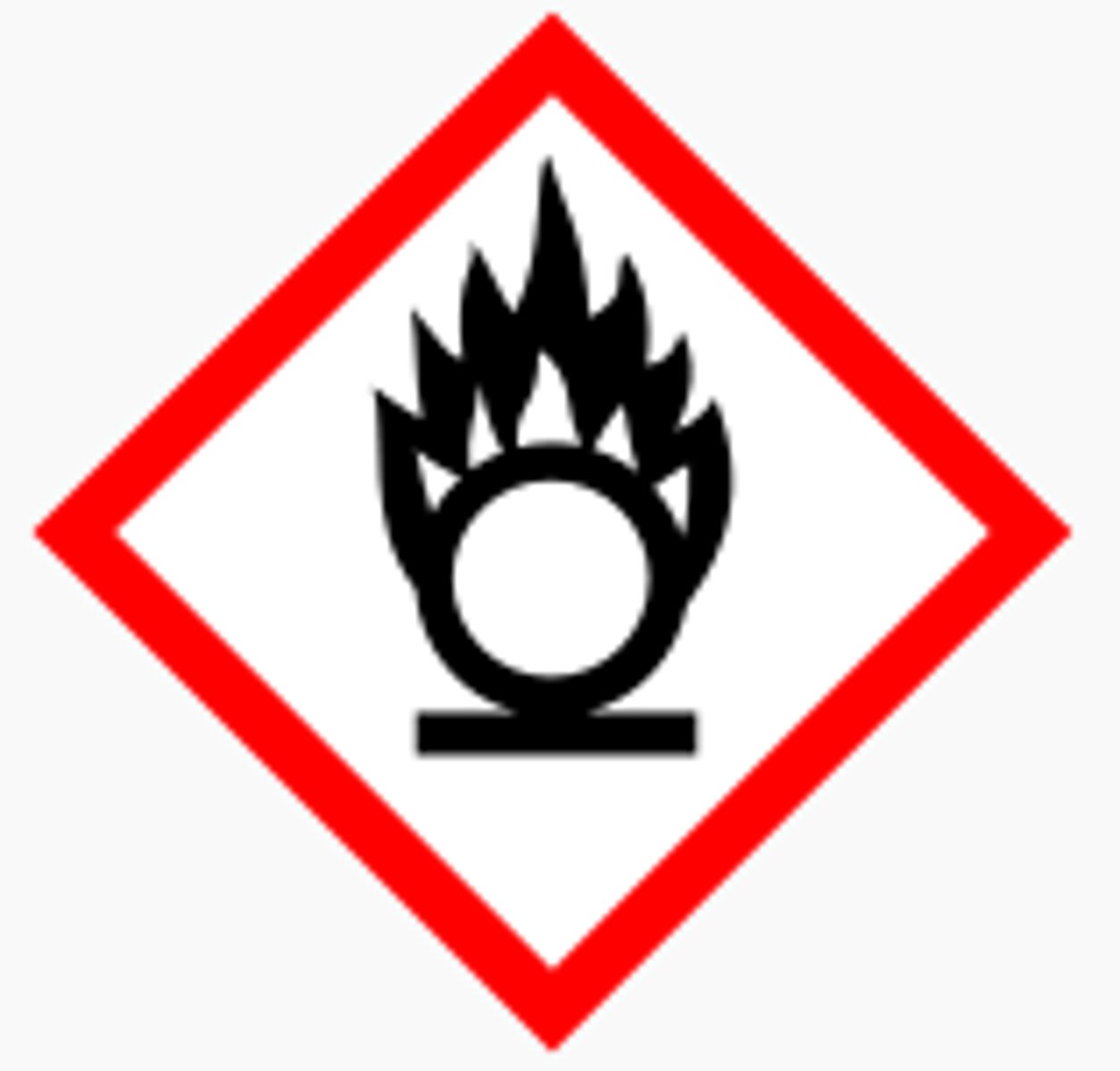
What does the "O with fire" GHS symbol stand for?
oxidizing (fire caused by increasing concentration of oxygen in the air)

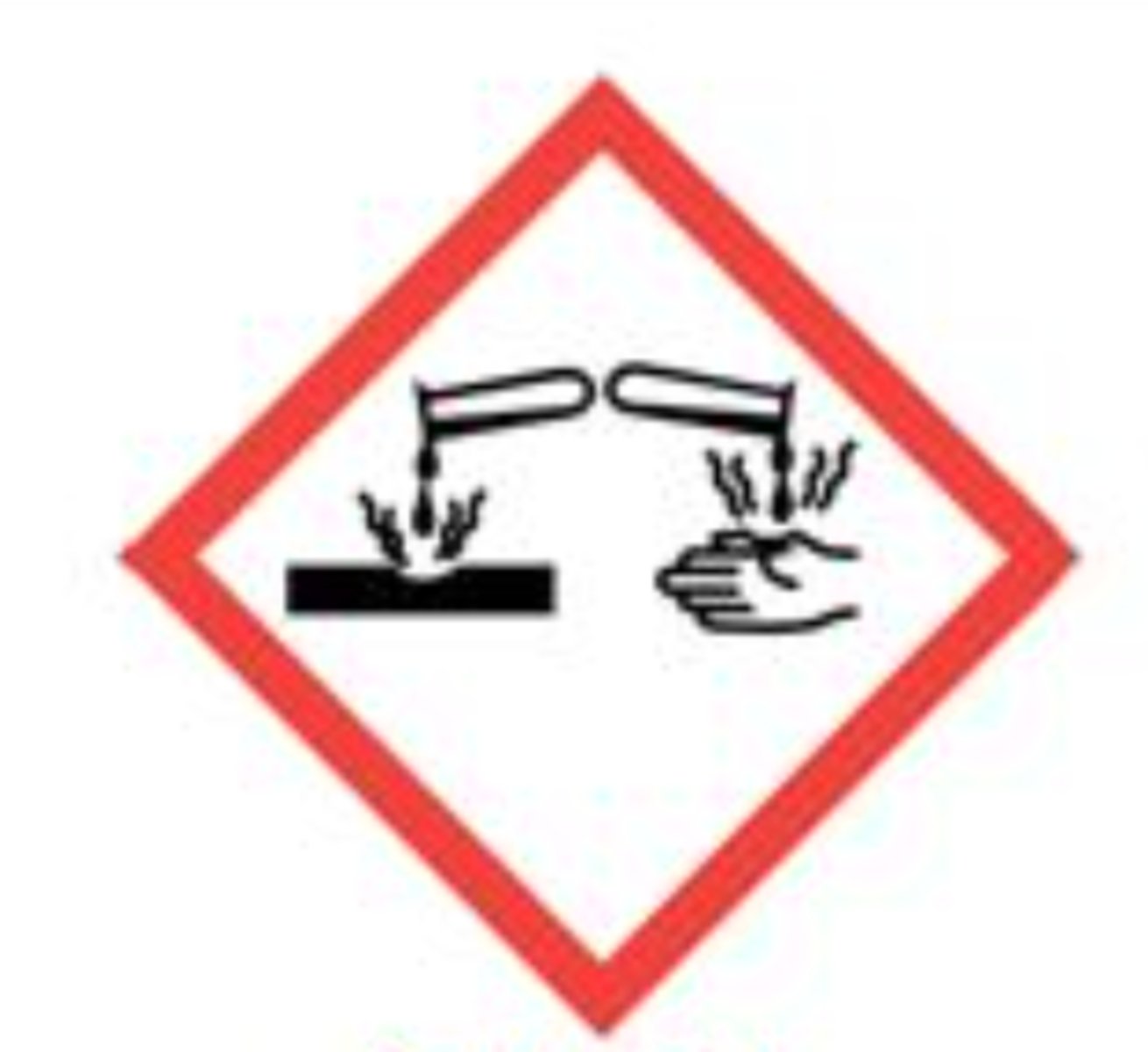
What does the "two flasks pouring on a hand and a table" GHS stand for?
corrosive (destroys living tissue on skin)

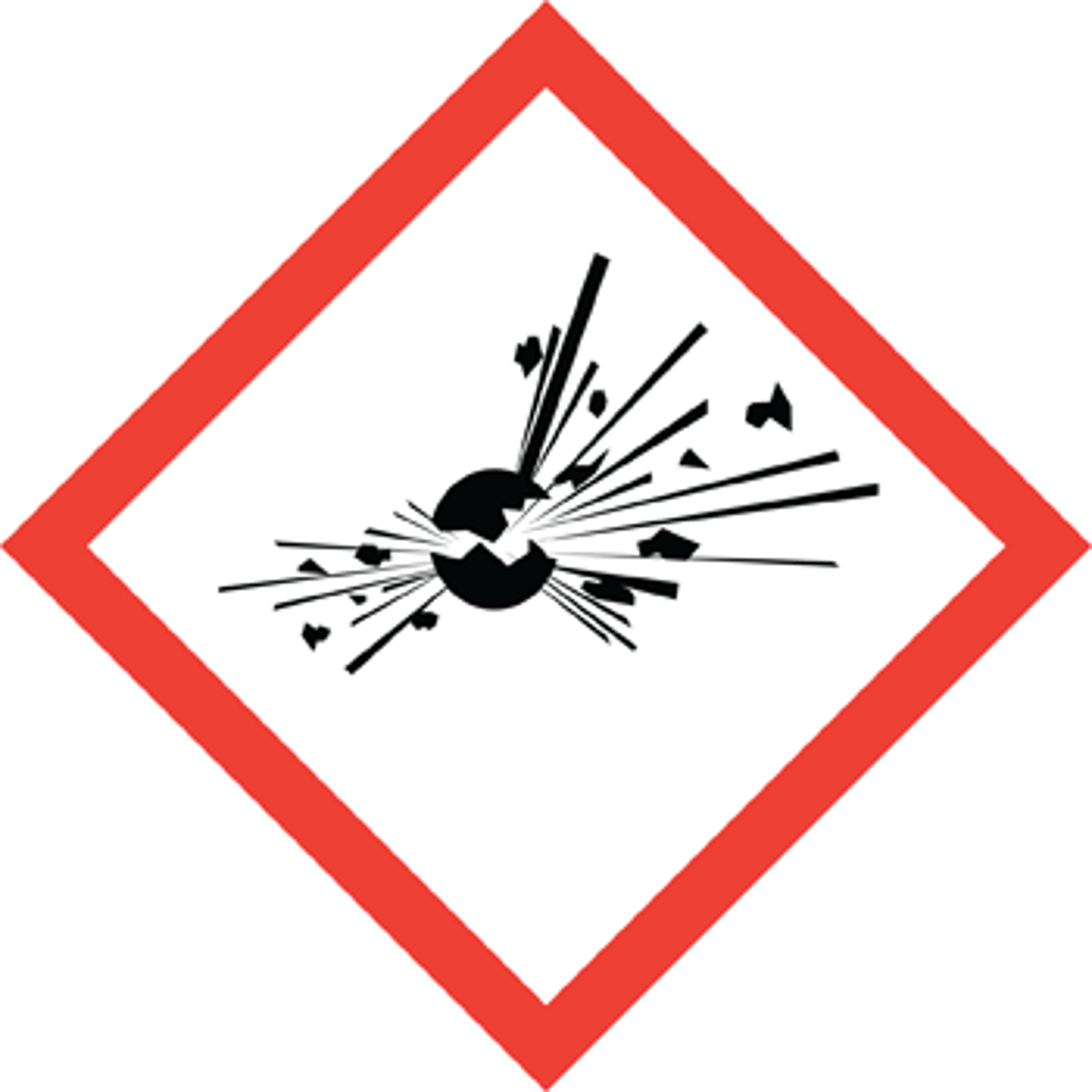
what does the "explosion"GHS symbol stand stand for?
explosive

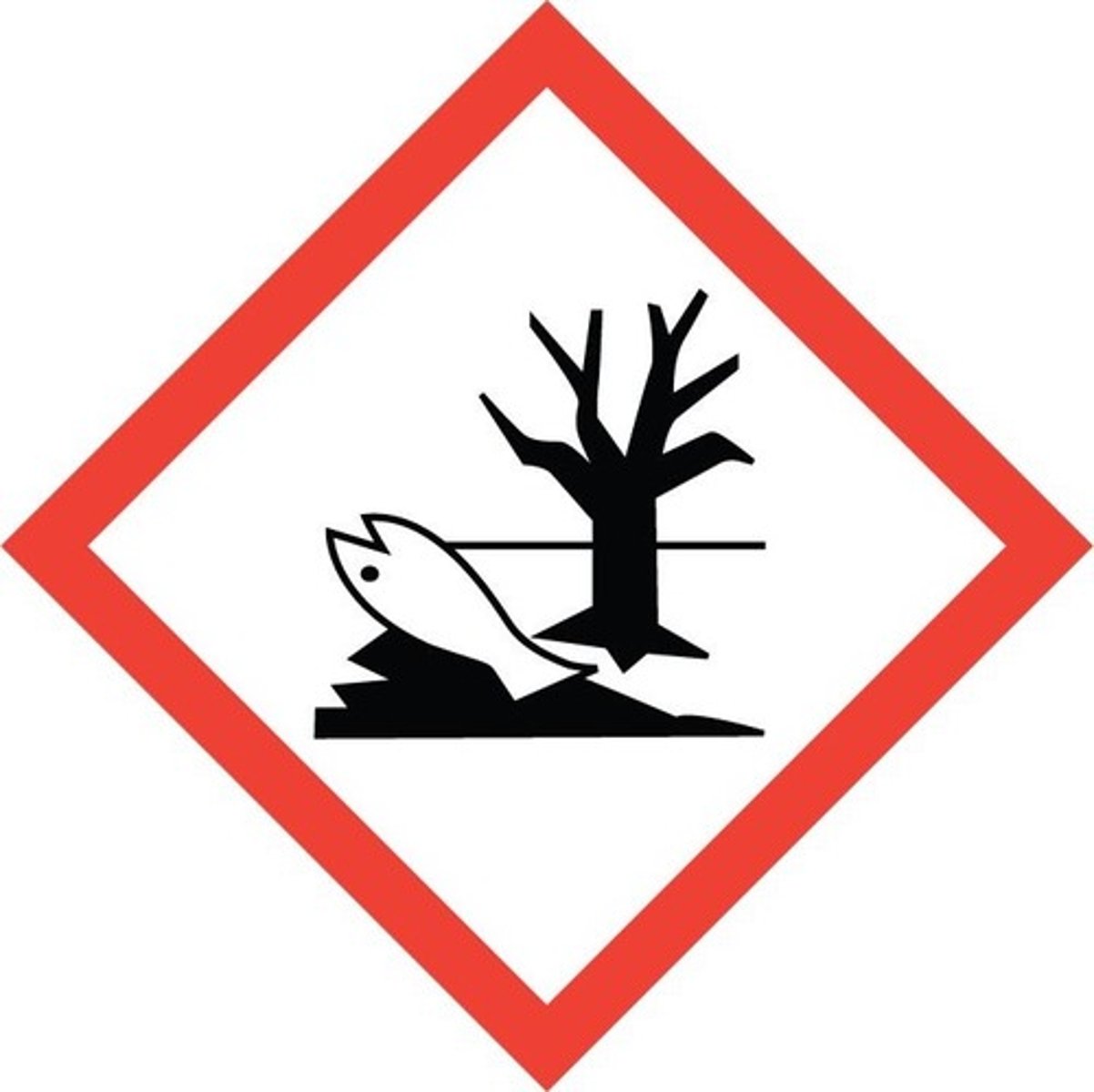
what does the "dead fish in the lake"GHS symbol stand for?
environment (damage to the aquatic environment)

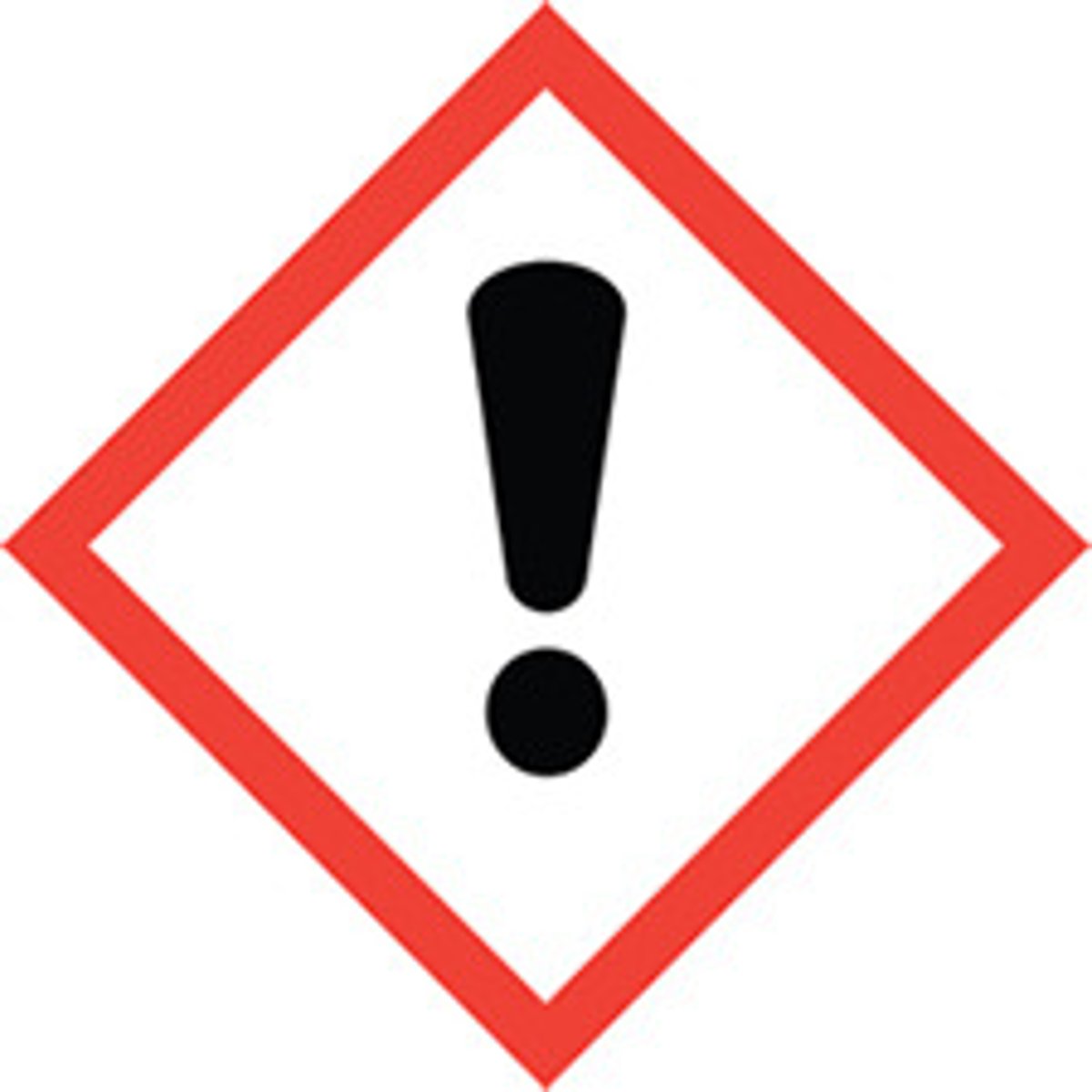
What does the "exclamation mark" GHS symbol stand for?
irritant; skin sensitizer(less serious health effects)

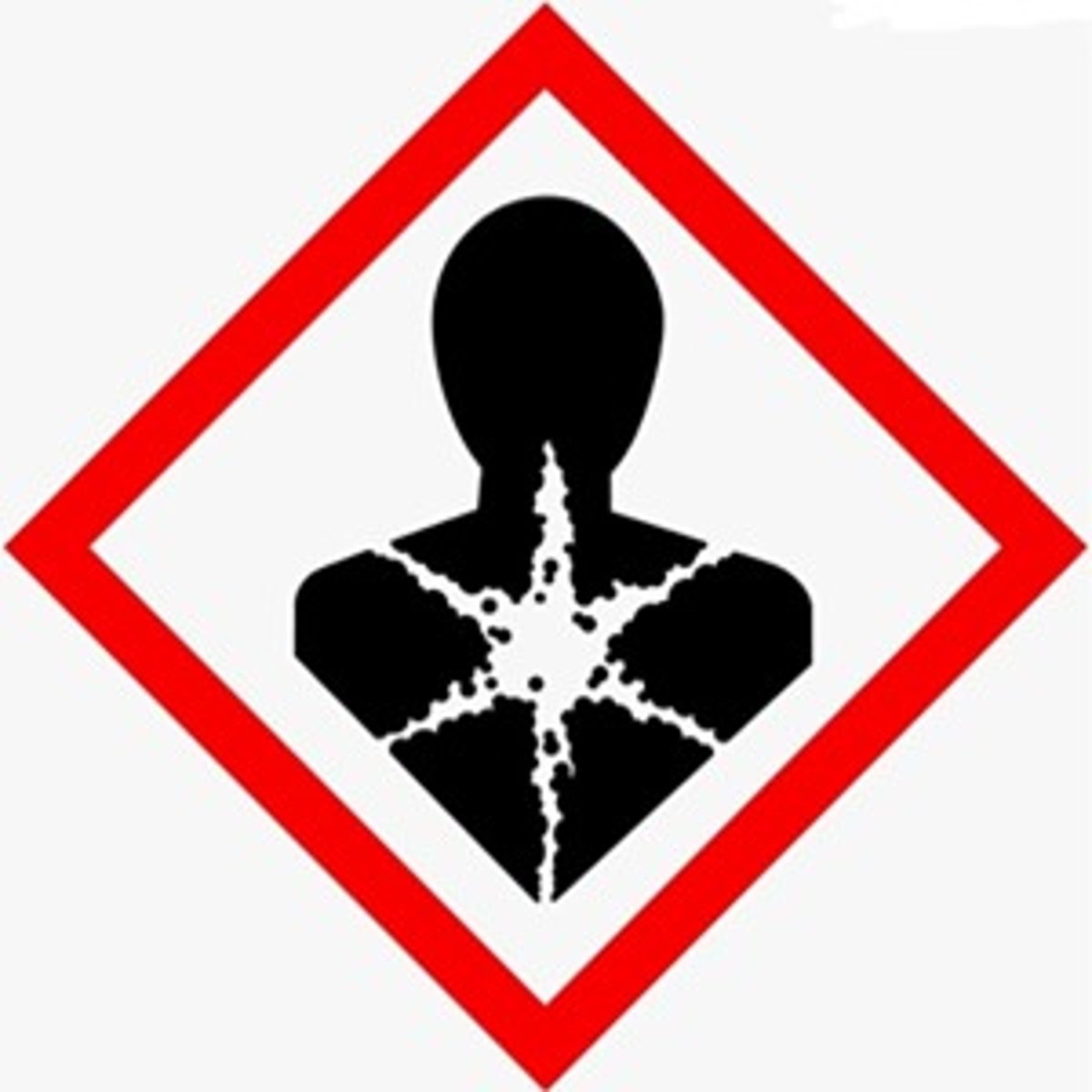
what does the "man with a star on his chest" GHS symbol stand for?
Health Hazard (serious health effects)

Exposure routes: You are done pumping gas and pulling the nozzle out of the car's tank but the gas continues to flow spraying you in the face. Your eyes start to burn and you have to remove your contacts.
is this an instance of:
inhalation, skin or eye absorption, ingestion, or injection?
skin or eye absoprtion
Exposure routes: You choose a beaker without realizing it has a small star crack in the bottom. The beaker is filled halfway with methanol and placed on the hotplate which is turned on to heat the solution. The beaker shatters as you pick it up, cutting your hand.
-is this an instance of:
inhalation, skin or eye absorption, ingestion, or injection?
injection
Exposure routes: You are distracted when you enter the lab and forget to cover your laptop keyboard with plastic wrap. Later that day you are at the library studying and you realize a solid is on your trackpad. You lick your finger to wet the trackpad in an attempt to remove the solid. It doesn't come off the first time, so you lick the finger again. Your mouth becomes numb.
-is this an instance of:
inhalation, skin or eye absorption, ingestion, or injection?
ingestion
It's your turn to clean the bathroom at the apartment. You start out using ammonia, but the smell is terrible, so you switch to bleach without washing away all the ammonia. Pretty soon you eyes are watering and you are coughing badly.
-is this an instance of:
inhalation, skin or eye absorption, ingestion, or injection?
inhalation

What type if eye protection provides the best protection against a chemical splash?
chemical splash goggles
How do you quickly assess your planned procedure? (RAMP)
-Recognize the hazard of acid to the eyes
-Assess procedure, their knowledge and exposure proability
-Minimize risk of exposure by wearing goggles
-Prepare for emergencies by location eyewash station
Which is the more hazardous? Warning or Danger?
Danger
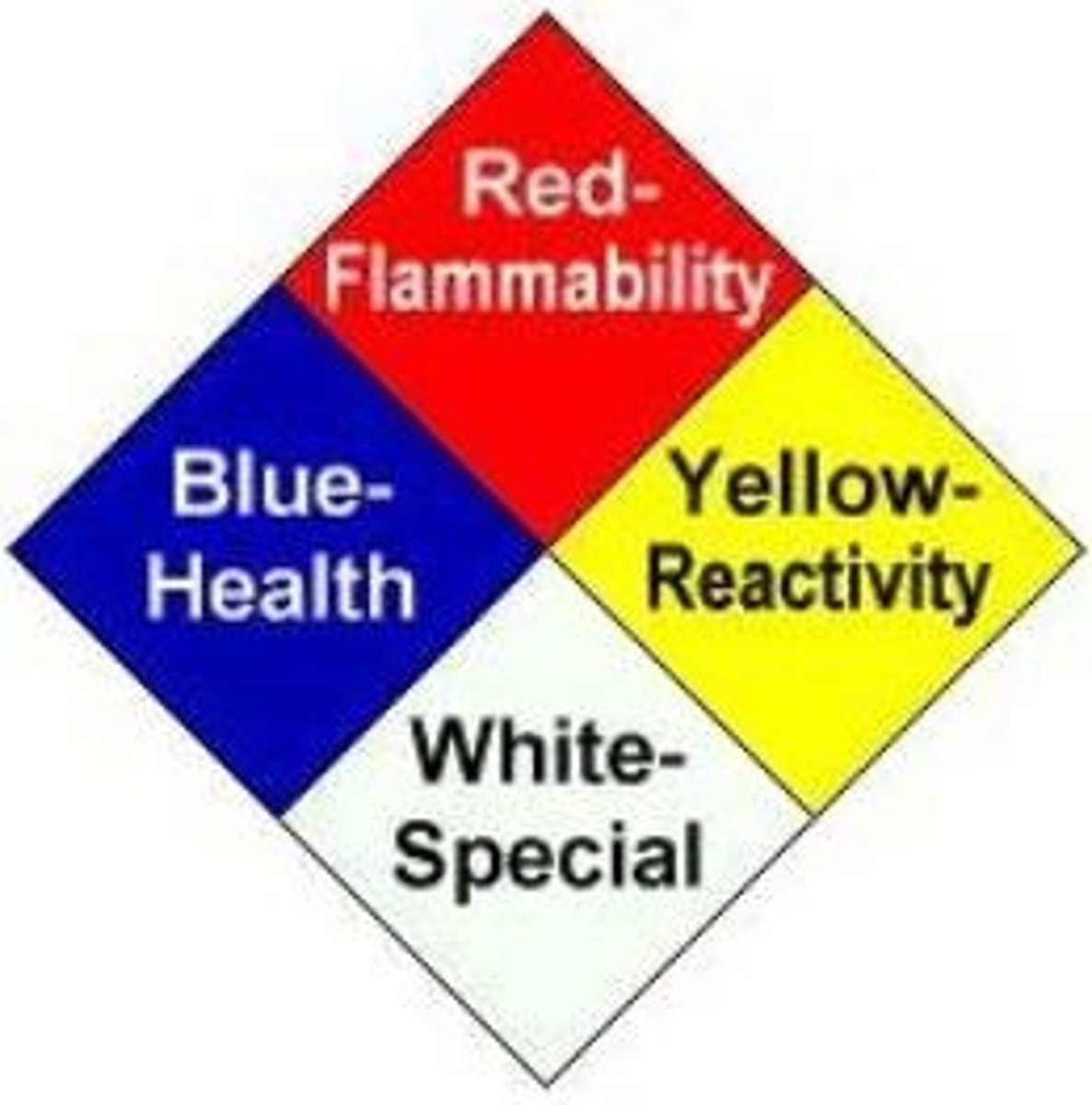
what would each of the following GHS symbol names fit into the NFPA Diamond (blue= health; red= flamability; yellow= instability; white= special; or none)?
-Toxicity
-Environment
-Oxidizer
-Health Hazard
-Flammable
-Corrosive
-irritant
-compressed gas
-explosive
1. Health: Toxicity, Health Hazard, Corrosive, explosive
2. Flammability: flammable
3. Instability: Irritant
4. Special Hazards: Oxidizer
0. None: Environmental, compressed gas
Who's gonna Ace this practical?
YOU! (-Yash)