Plant Cell Structure and Membrane Dynamics: Key Concepts for Biology
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Plant Cell Types
Different categories of cells in plants, each with specific functions.
Cell Wall
A box-like structure surrounding plant cells, providing support and protection.
Protoplasm
The living content of a cell, including the cytoplasm and organelles.
Organelles
Specialized structures within a cell that perform distinct functions.
Epidermis
The outer layer of cells in plants that serves as a barrier against water loss and pathogens.
Epidermal Gland Cells
Cells that produce substances to protect plants from herbivores.
Green Leaf Cells
Cells that perform photosynthesis by converting sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into carbohydrates.
Vascular Cells
Cells responsible for the transport of water, minerals, and organic molecules throughout the plant.
Petal Cells
Cells that contain pigments to attract pollinators.
Scent Cells
Cells that produce fragrances to attract pollinators.
Dividing Cell Dimensions
A cube-shaped cell measuring 12µm x 12µm x 12µm.
Epidermal Cell of Lily
Flat, paving stone-shaped cells measuring 45µm x 143µm x 15µm.
Photosynthetic Cell in Leaf of Pear
Short cylinder-shaped cell measuring 7.4µm x 55µm.
Weater-conducting Vessel Cell in Oak
Long cylinder-shaped cell measuring 20µm x 60,000µm.
Fiber Cell in Hemp
Cells that provide structural support and strength to the plant.
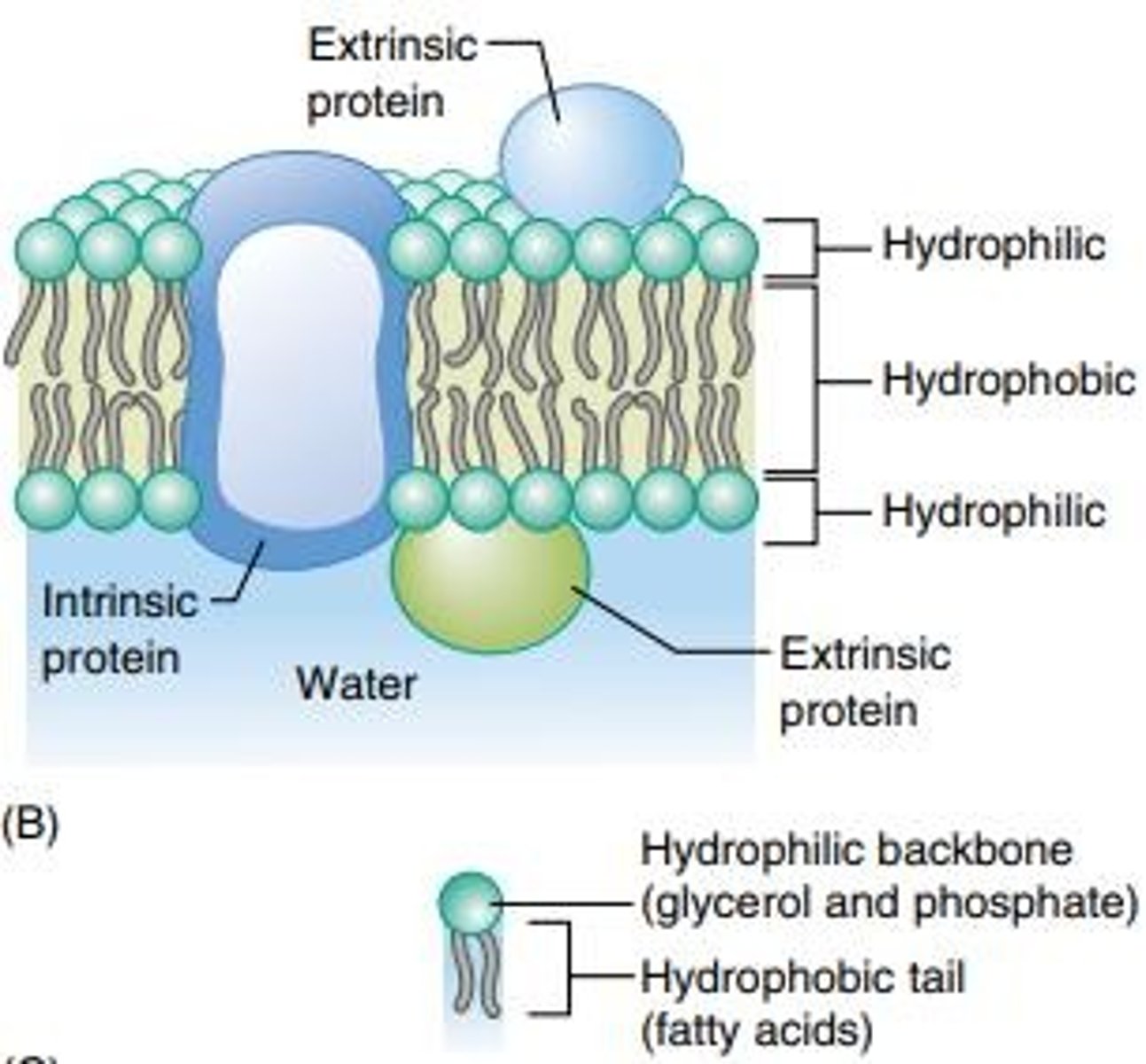
Intrinsic Proteins
Proteins that are partially immersed in the lipid bilayer of membranes.
Extrinsic Proteins
Proteins located outside the membrane that interact with the lipid bilayer.
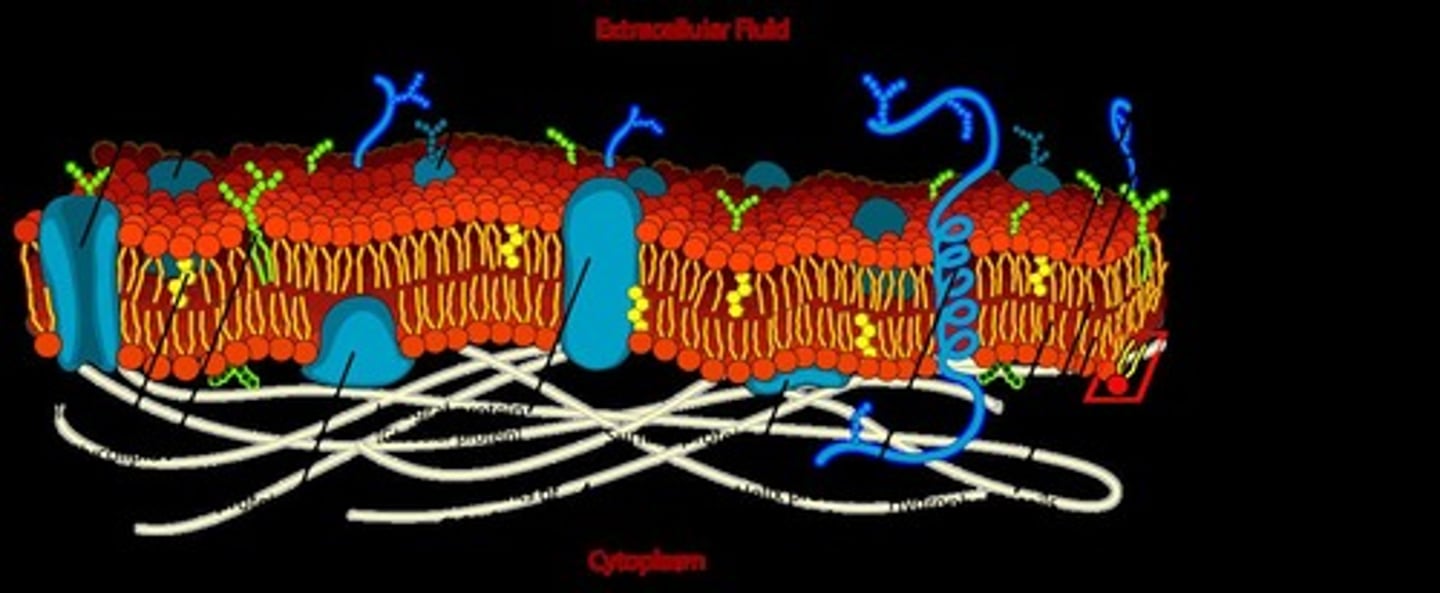
Fluid Mosaic Model
A model describing the structure of cell membranes as a dynamic, fluid-like arrangement of phospholipids and proteins.
Monolayer
A single layer of phospholipids formed when poured onto calm water.
Bilayer
A double layer of phospholipids formed when the lipid layer is agitated.
Domains
Small discrete regions formed by proteins interacting with adjacent proteins in membranes.
Membrane Composition
Biological membranes are composed of proteins and two layers of phospholipid molecules, typically in a ratio of 60% proteins and 40% lipids.
Cell Membrane Function
Regulates the passage of molecules into and out of cells and organelles.
Exocytosis
Vesicles release contents outside the cell, used for removing wastes, debris, proteins, polysaccharides, and mucilage.
Endocytosis
Outer membrane invaginates, then pinches off to form a vesicle, capturing extracellular material, common for algae and microscopic organisms for food uptake.
Selective Permeability
Allows certain substances to pass more easily than others; hydrophobic substances pass through more readily than charged ones.
Facilitated Diffusion
Uses large intrinsic proteins that form hydrophilic channels, helping charged substances cross the membrane without energy.
Active Transport
Involves molecular pumps that bind and transport substances using energy (ATP), allowing cells to accumulate substances against a concentration gradient.
Compartmentalization
Essential for organizing different cellular processes; each membrane-enclosed compartment can specialize in specific functions.
Membrane Fusion
Allows transport of materials within the cell; vesicles fuse with target membranes, contributing to membrane growth.
Plasma Membrane
Outermost boundary of protoplast, selectively permeable, controlling what enters and exits.
Impermeable Membrane
Nothing passes through; no biological membrane is impermeable to everything.
Freely Permeable Membrane
Virtually anything can pass through.
Selectively Permeable Membrane
Certain substances pass through rapidly, others pass through slowly.
Facilitated Diffusion (Definition)
The presence of large intrinsic membrane proteins allows hydrophilic, charged molecules to diffuse through the membrane.
Active Transport (Definition)
Large intrinsic membrane proteins bind a molecule and force it through the membrane, consuming energy in the process.
Glycoproteins
Proteins that have one or more oligosaccharide chains (glycans) covalently attached to them.
Glycolipids
Lipids with a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule attached.
Oligosaccharides
Short-chain sugars, each with about 4-15 sugar residues.
Hydrophobic Substances
Substances that pass through the membrane more readily than charged ones.
Charged Substances
Require assistance to cross the membrane.
Vesicle Lumen
Can carry substances to be processed at the destination.
Giant Cells
Plant cells tend to be larger than animal cells but both types are usually microscopic.
Unusual Cells
Many plant cells die as a necessary part of their development.
Flagella
Sperm cells of plants such as mosses, ferns, and some seed plants that swim.
Nucleolus
Site of ribosome assembly.
Central Vacuole
Stores water, ions, pigments, waste; regulates cell expansion via turgor pressure; has a digestive role breaking down aging organelles.
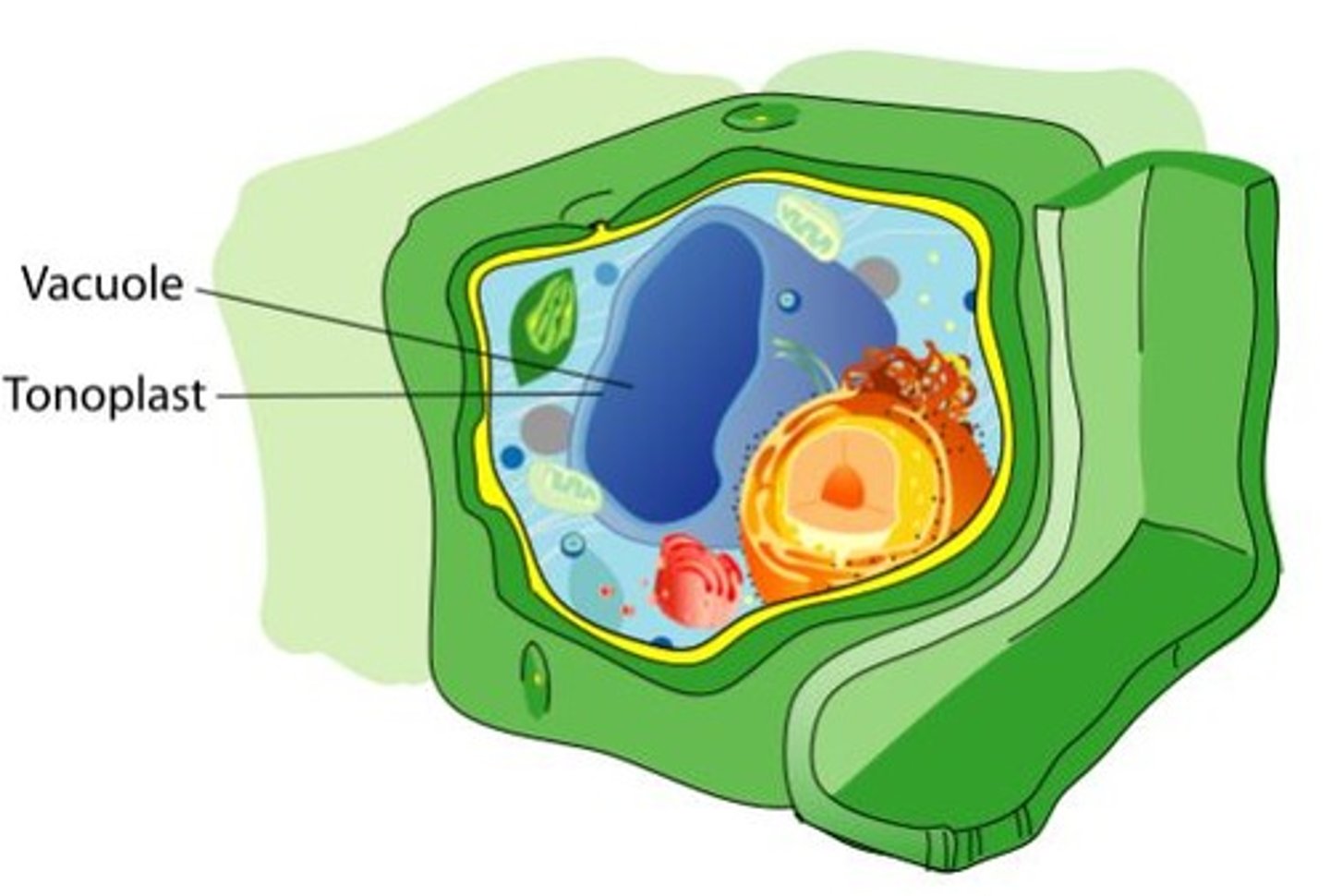
Tonoplast
The membrane surrounding the central vacuole, impermeable to stored waste.
Eukaryotic Cells
Cells that have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists.
Prokaryotic Cells
Simpler cells that do not have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles, found in Domain Bacteria and Domain Archaea.
Cytoplasm
Everything in protoplasm except the nucleus and vacuole, includes cytosol and all other organelles.
Mitochondria
Site of cellular respiration, converts sugars to ATP, has its own DNA and ribosomes.
Ribosomes
Site of protein synthesis, can be free in cytosol or bound to the endoplasmic reticulum.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Double-membrane organelles involved in membrane production and the synthesis of proteins (Rough ER) and lipids (Smooth ER).
Plastids
Double-membrane organelles that contain circular DNA and are primarily responsible for photosynthesis.
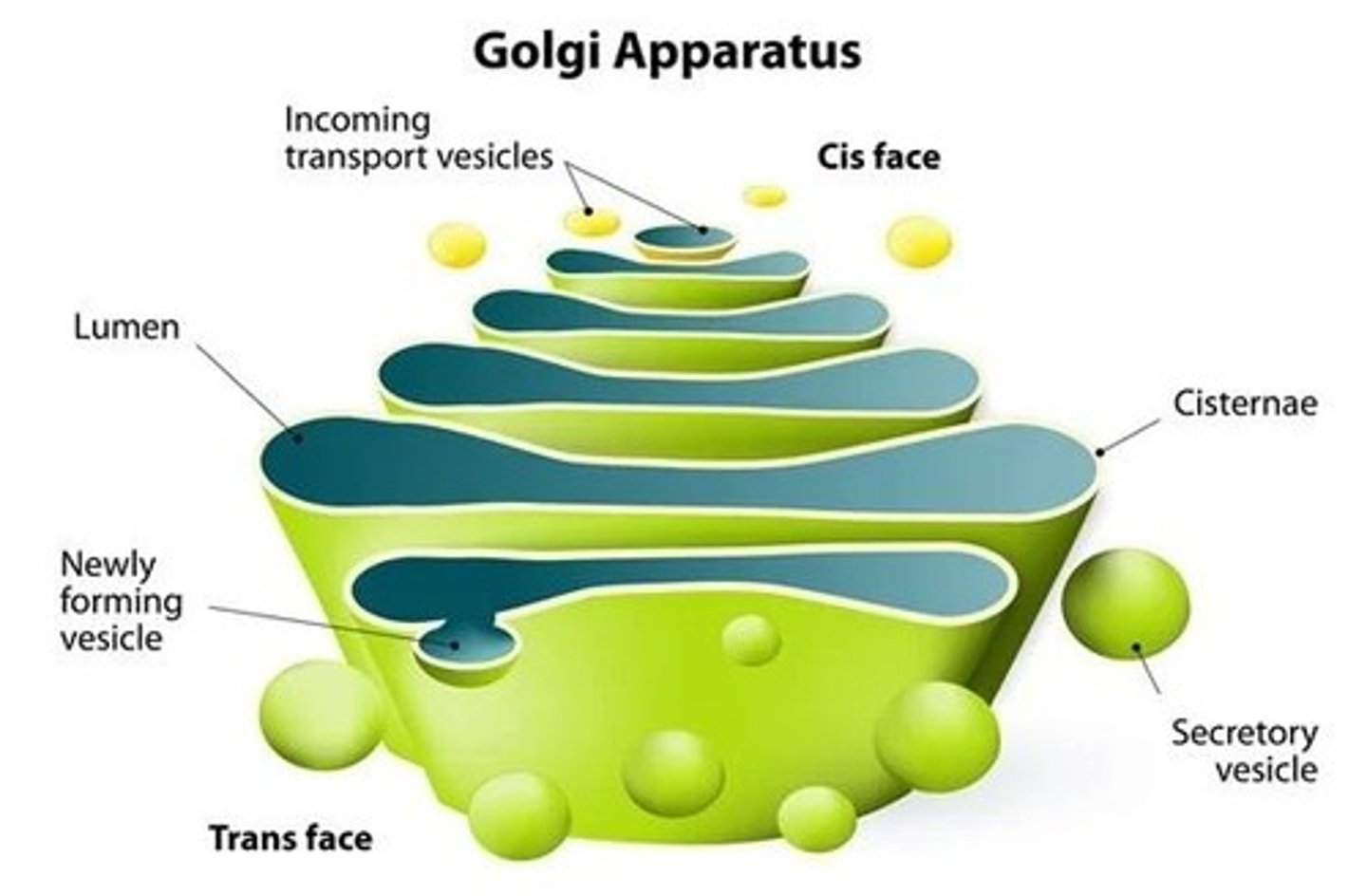
Dictyosomes (Golgi Bodies)
'Factories' of plant cells that modify and package vesicle contents and secrete via exocytosis.
Microbodies
Small, single-membrane organelles present in almost all plant cells, including peroxisomes and glyoxysomes.
Cytosol (Hyaloplasm)
Gel-like matrix with water, enzymes, and molecules, containing free ribosomes, microtubules, and microfilaments.
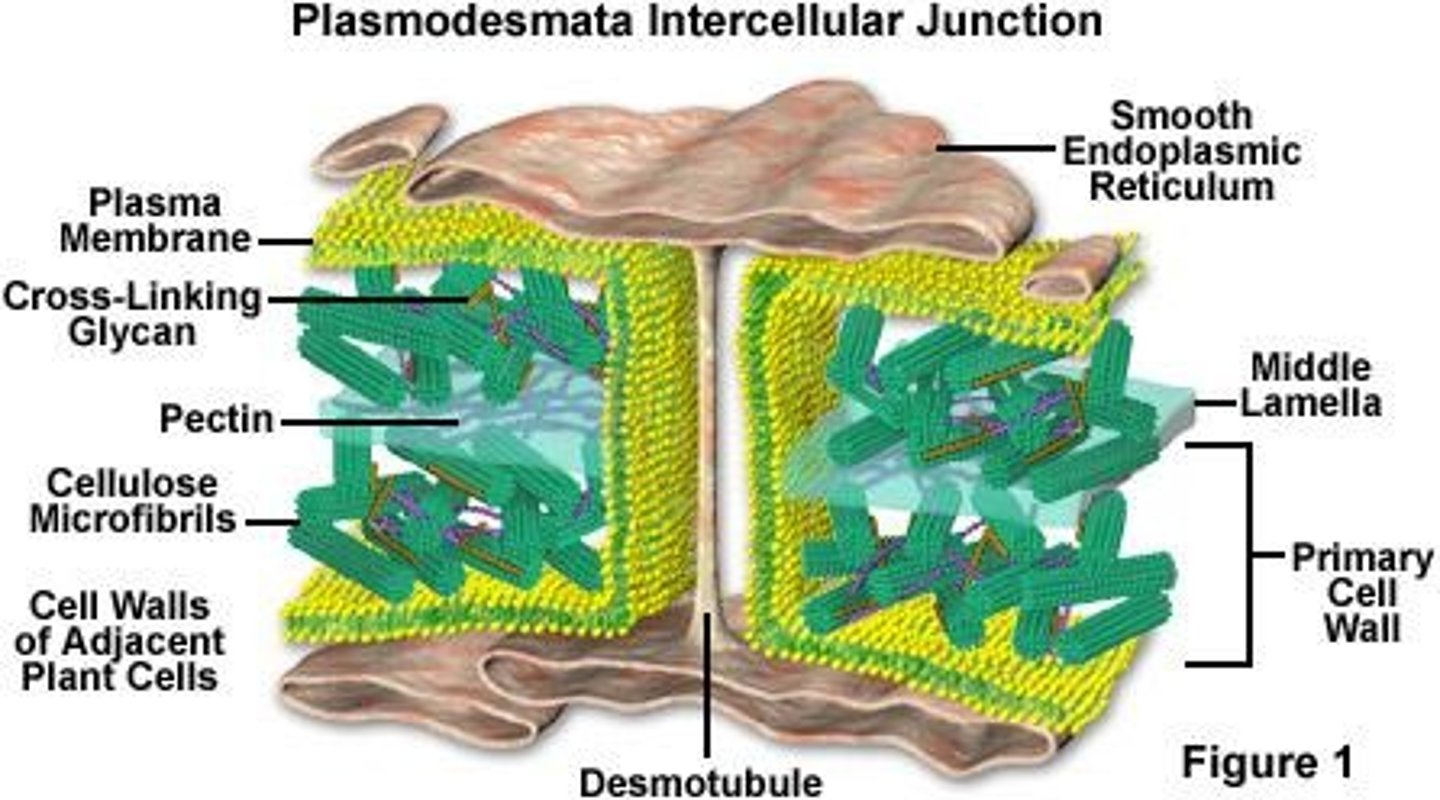
Plasmodesmata
Channels between plant cells that allow cytoplasmic and membrane continuity and enable intercellular communication.
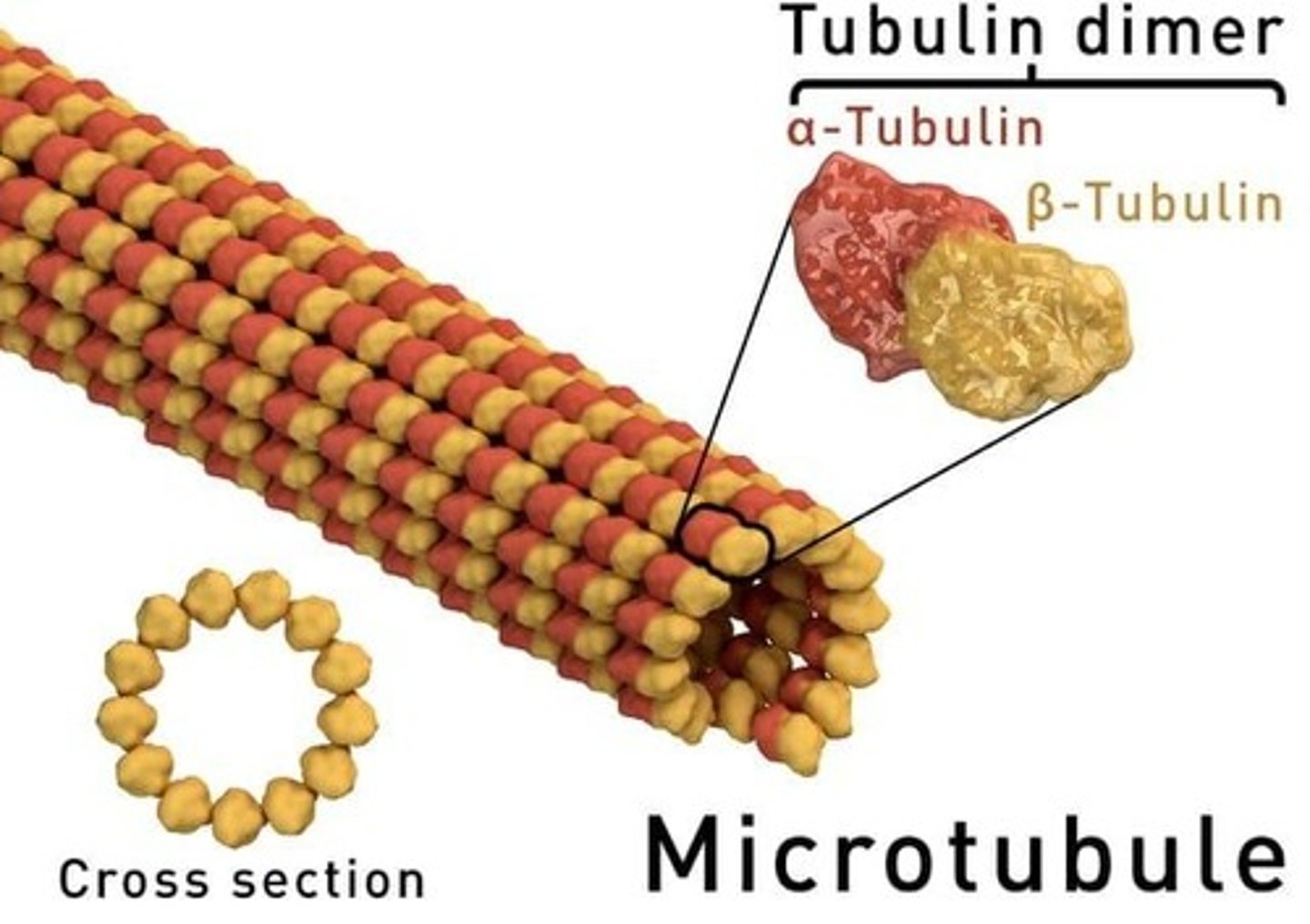
Microtubules
Tubes made of tubulin dimers that form the cytoskeleton, direct organelle movement, and are involved in cell division.
Microfilaments
Made of actin, thinner than microtubules, involved in movement and shape changes.
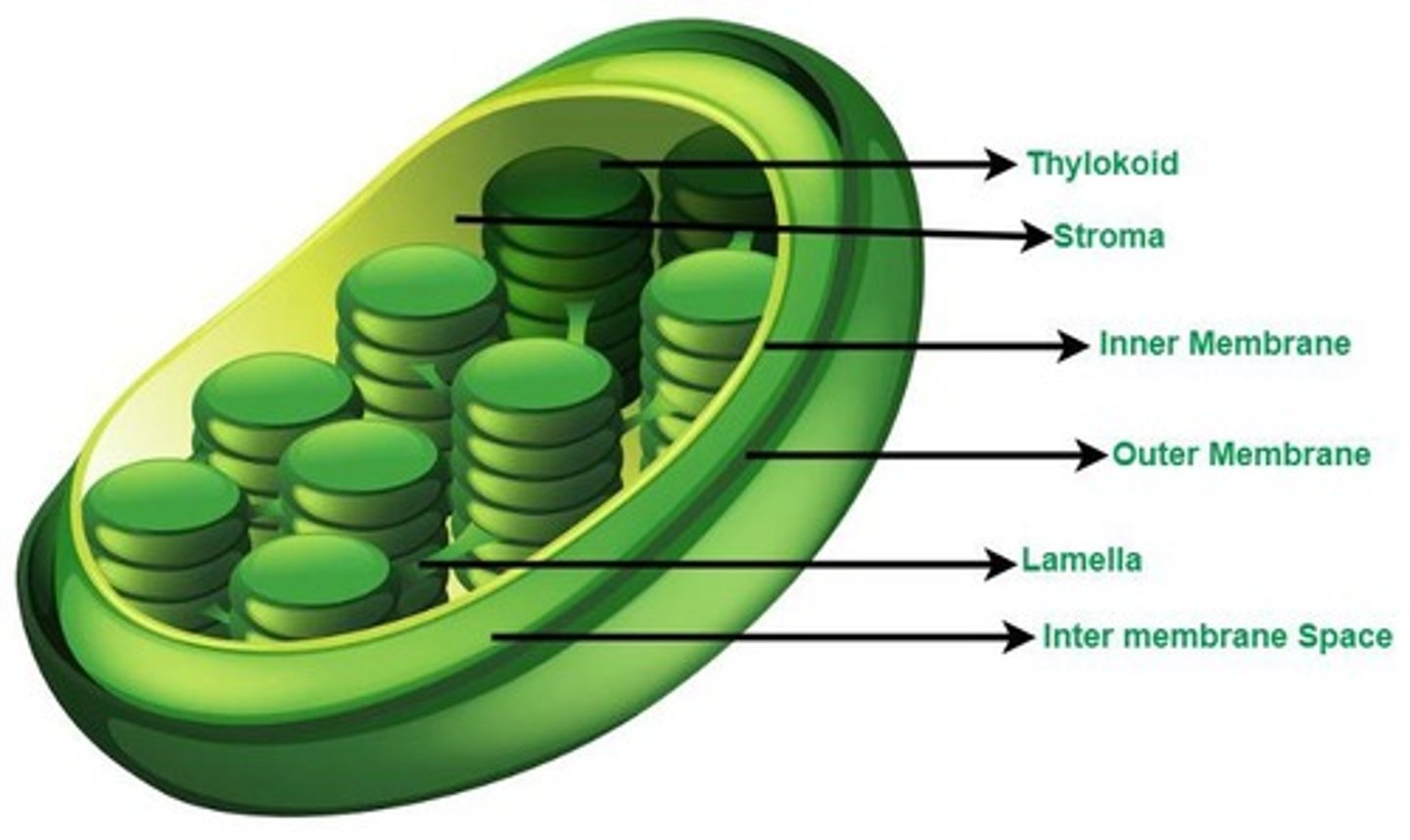
Chloroplasts
Plastids responsible for photosynthesis, containing grana (stacks of thylakoids).
Amyloplasts
Plastids that store starch.
Chromoplasts
Plastids that contain colored lipids.
Leucoplasts
Colorless plastids involved in lipid synthesis.
Etioplasts
Intermediate form of plastids before chloroplasts in dark-grown tissue.
Proplastids
Plastids of young, rapidly dividing cells.