Biochemistry I Module of the MCAT Self Prep eCourse: Lesson 1: Amino Acids and Proteins (Pro)
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
Lesson 1: Amino Acids and Proteins
Lesson 1: Amino Acids and Proteins
NOTE: Quizlet cards marked with CRB indicates that these flashcards cover the content found in the Content Review Books. Cards not marked with CRB cover the video playlist content. Enjoy! :)
NOTE: Quizlet cards marked with CRB indicates that these flashcards cover the content found in the Content Review Books. Cards not marked with CRB cover the video playlist content. Enjoy! :)
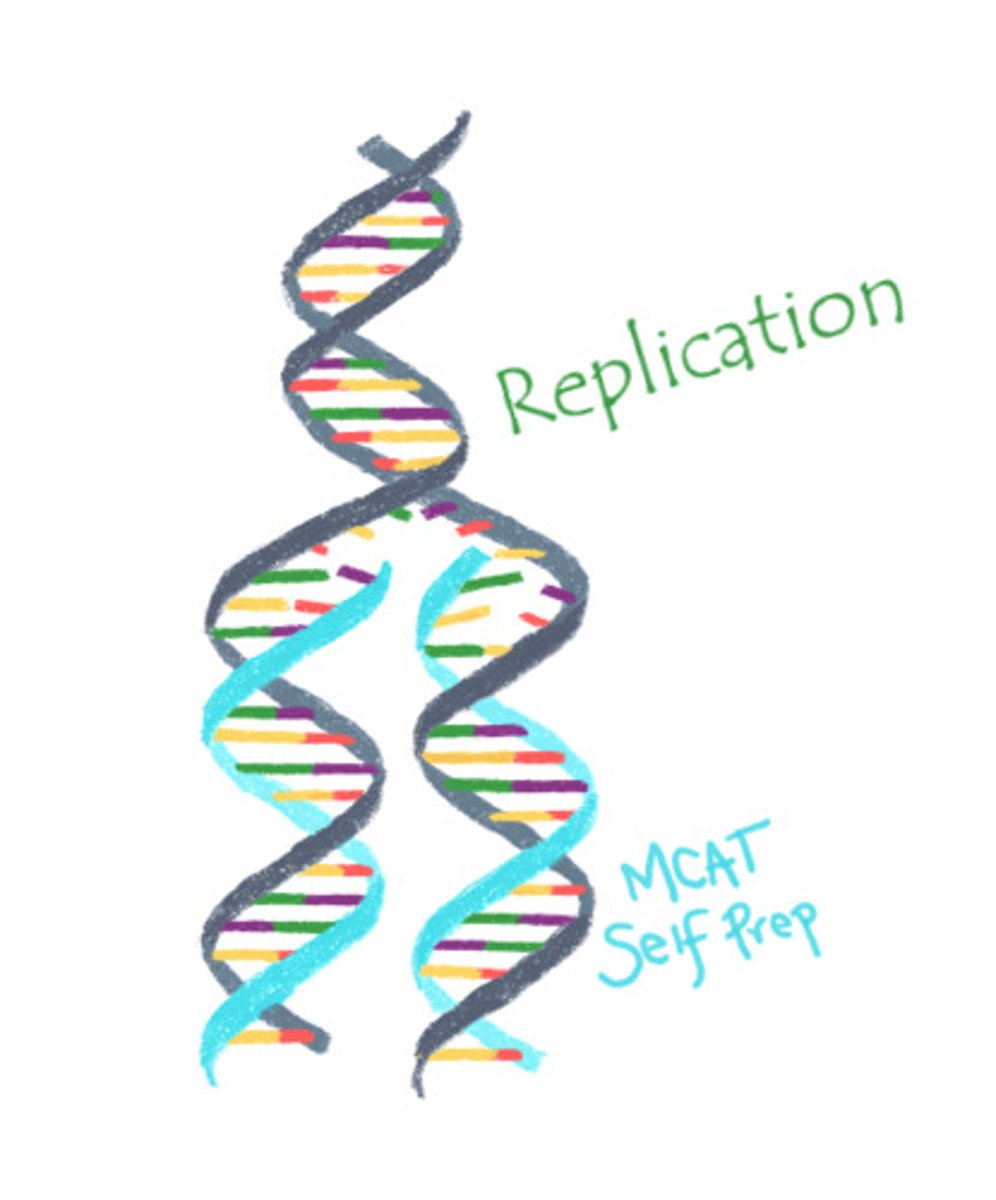
DNA copies itself through a process known as:
(A) Replication
(B) Translation
(C) Transcription
(D) Integration
(A) Replication
DNA copies itself through a process known as replication.
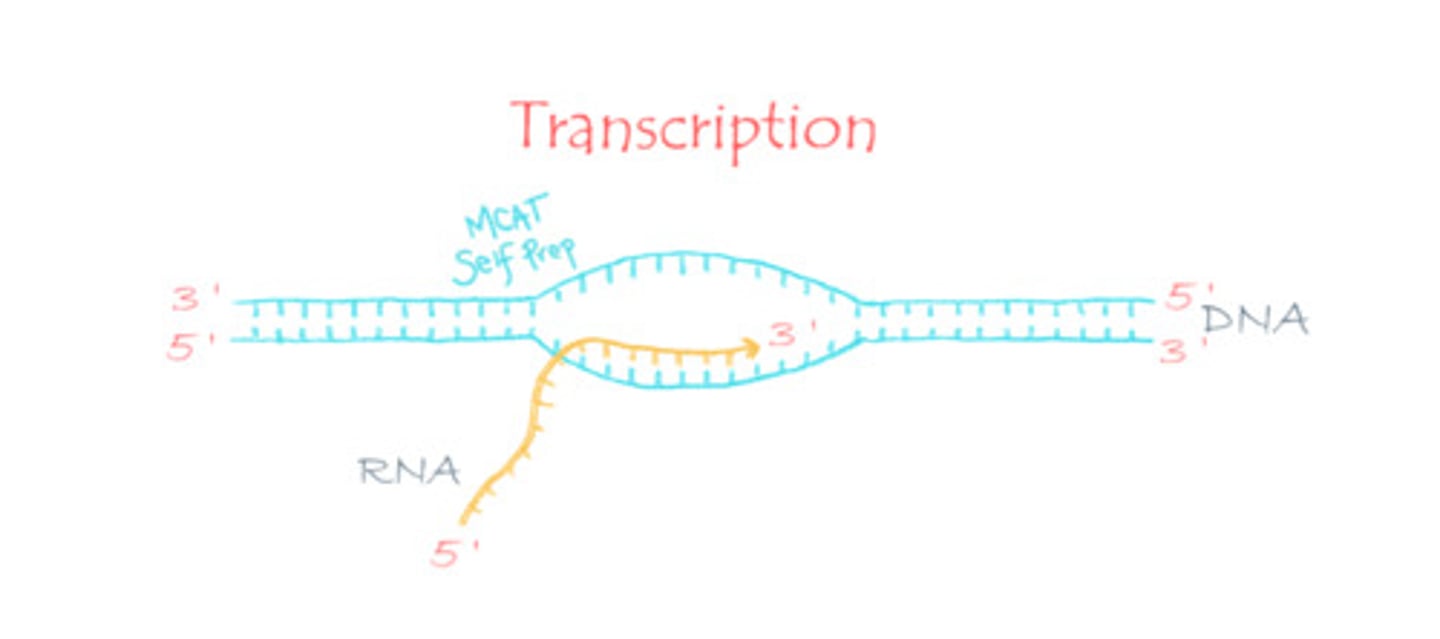
DNA is used as a template to generate RNA in a process known as:
(A) Replication
(B) Translation
(C) Transcription
(D) Integration
(C) Transcription
DNA is used as a template to generate RNA in a process known as transcription.
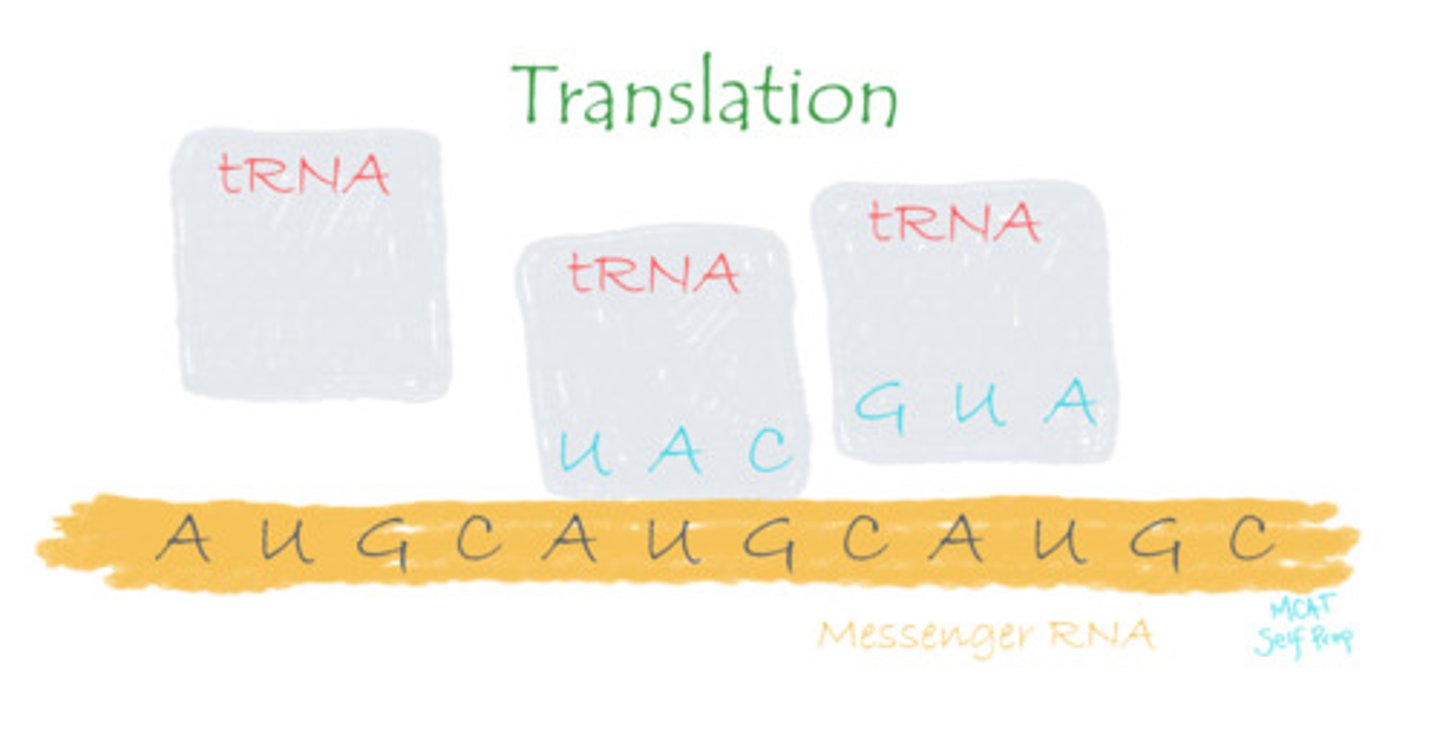
Protein is generated using RNA as instructions in a process known as:
(A) Replication
(B) Translation
(C) Transcription
(D) Integration
(B) Translation
Protein is generated using RNA as instructions in a process known as translation.
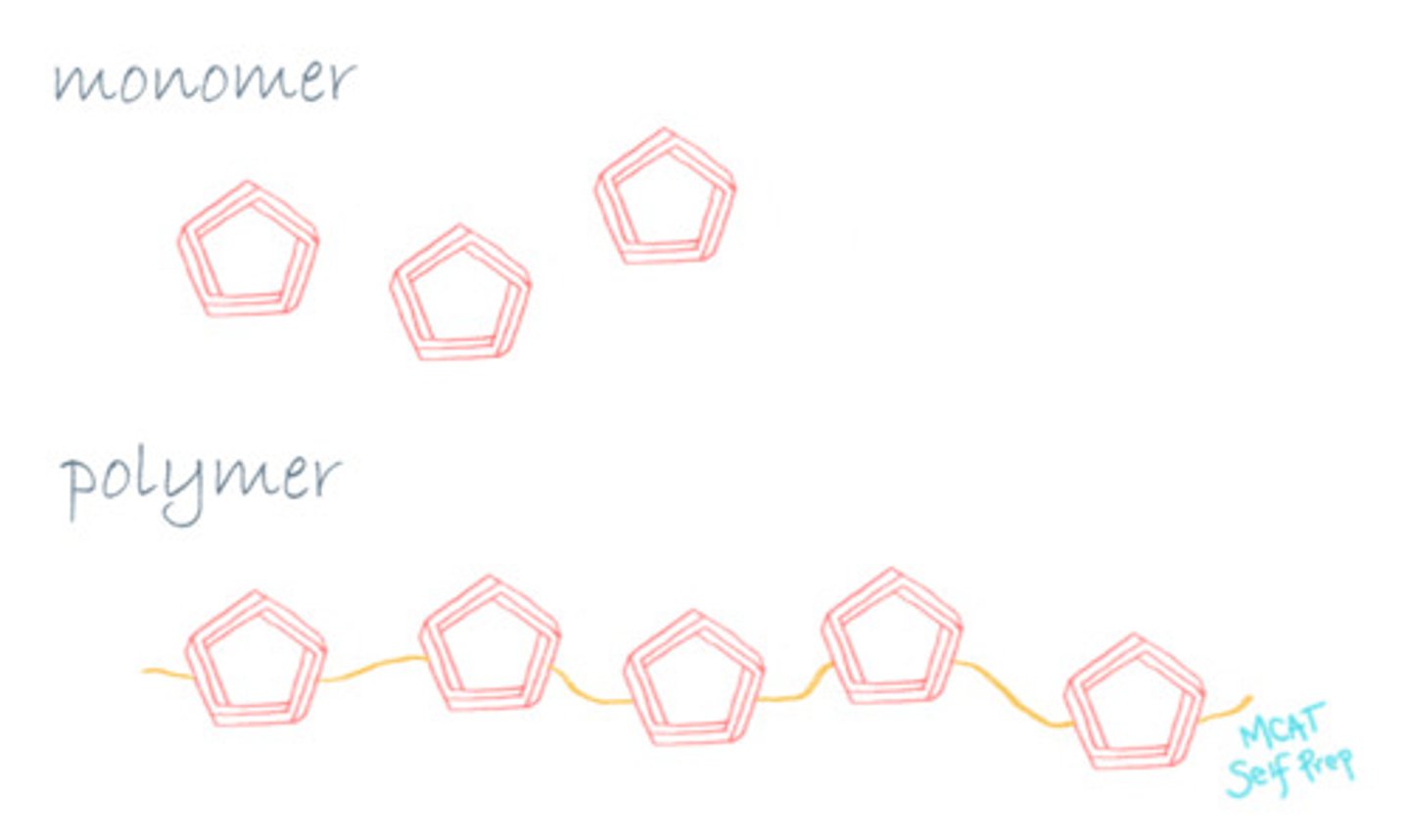
Compare Polymers and Monomers.
Polymers are made up of individual sub-units called monomers.
True or False? DNA, RNA, and protein are all linear polymers.
True. The structure of DNA, RNA, and protein is similar in that they are all linear polymers because each individual unit (or monomer) is attached to only one or two other units, resulting in a long chain.
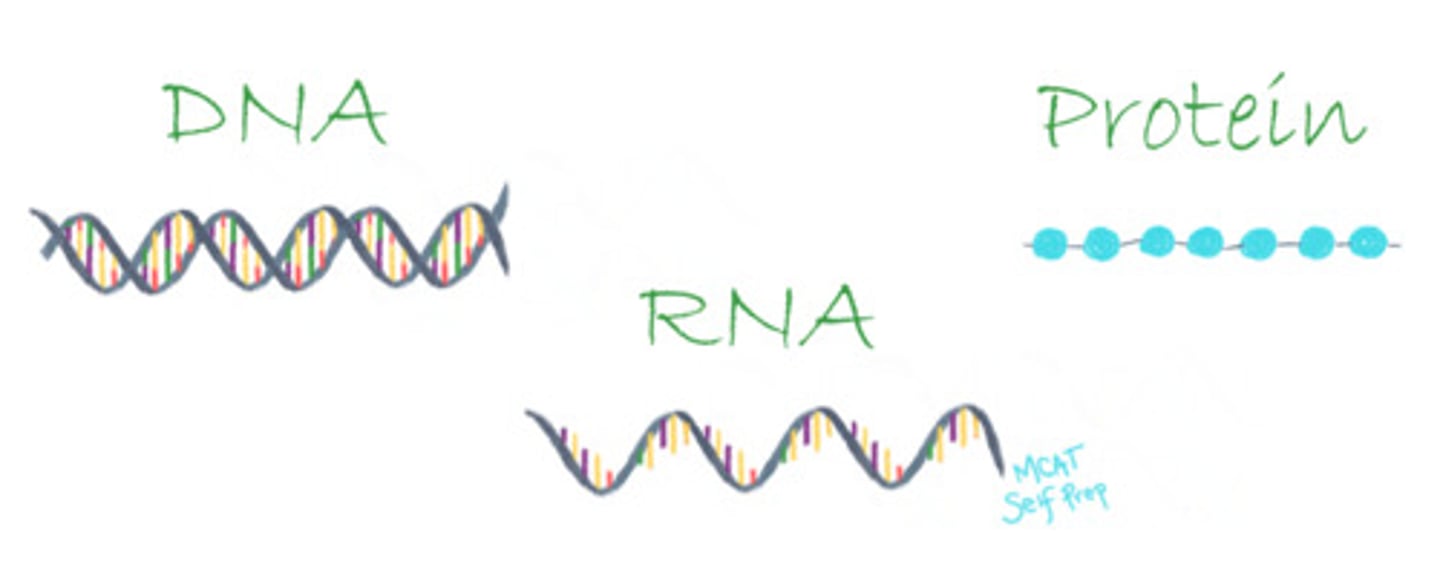
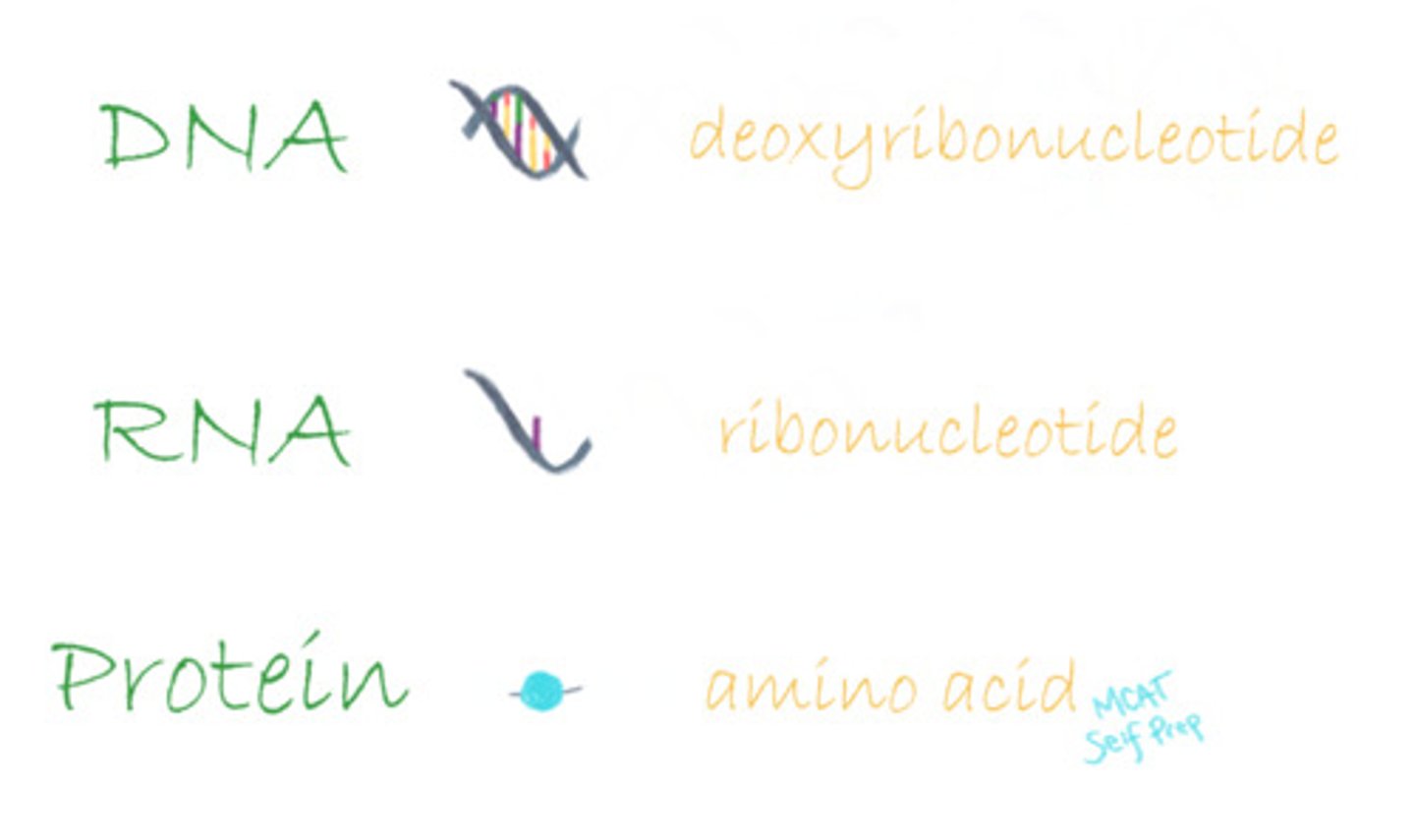
What monomers make up DNA? RNA? Protein?
The monomers that make up DNA are known as deoxyribonucleotides.
The monomers that make up RNA are known as ribonucleotides.
The monomers that make up protein are known as amino acids.
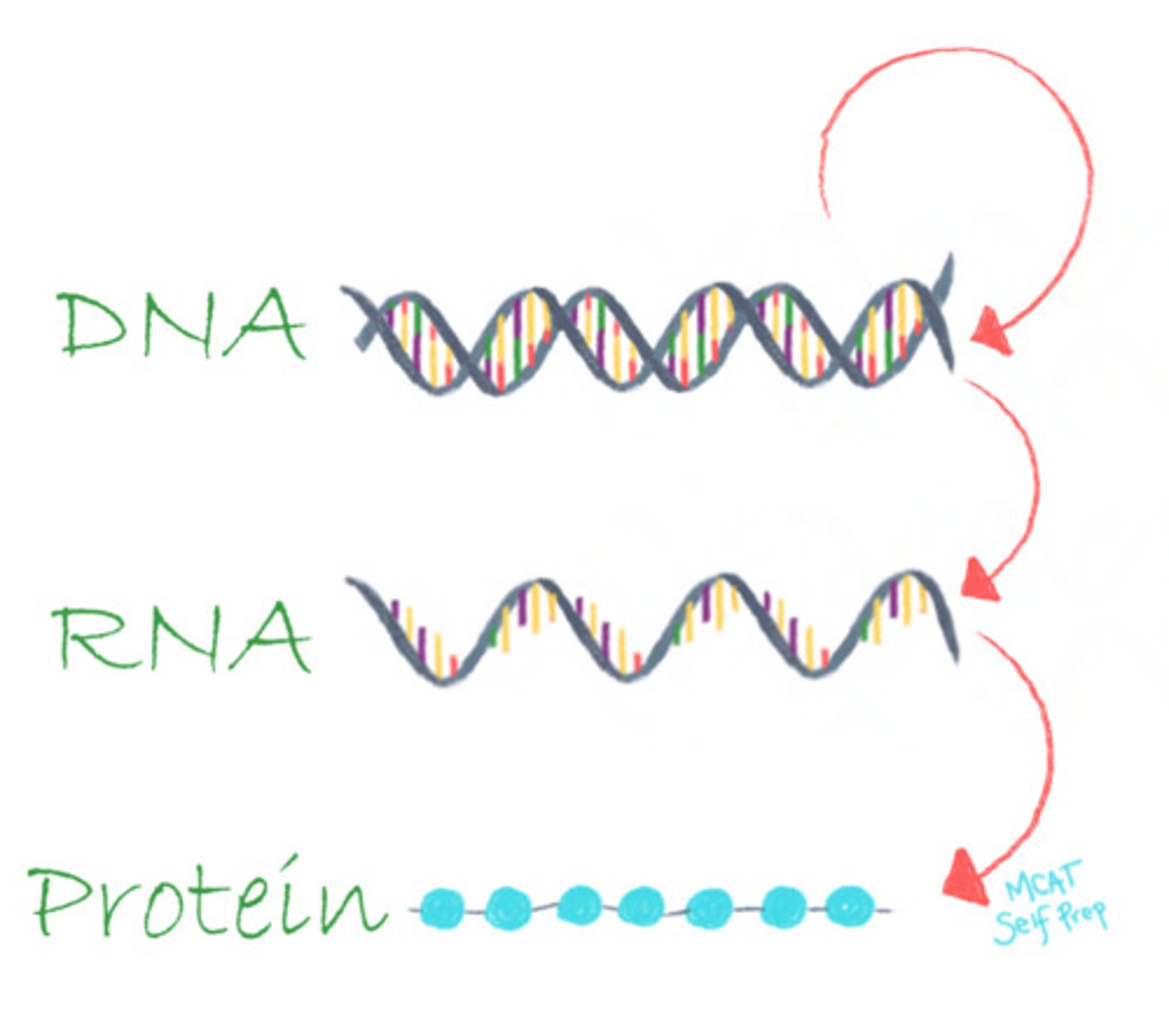
What benefits does the linear polymer structure of DNA, RNA, and protein provide during transcription and translation?
The linear polymer structure of DNA, RNA, and protein helps to transfer and preserve the encoding of information during transcription and translation.
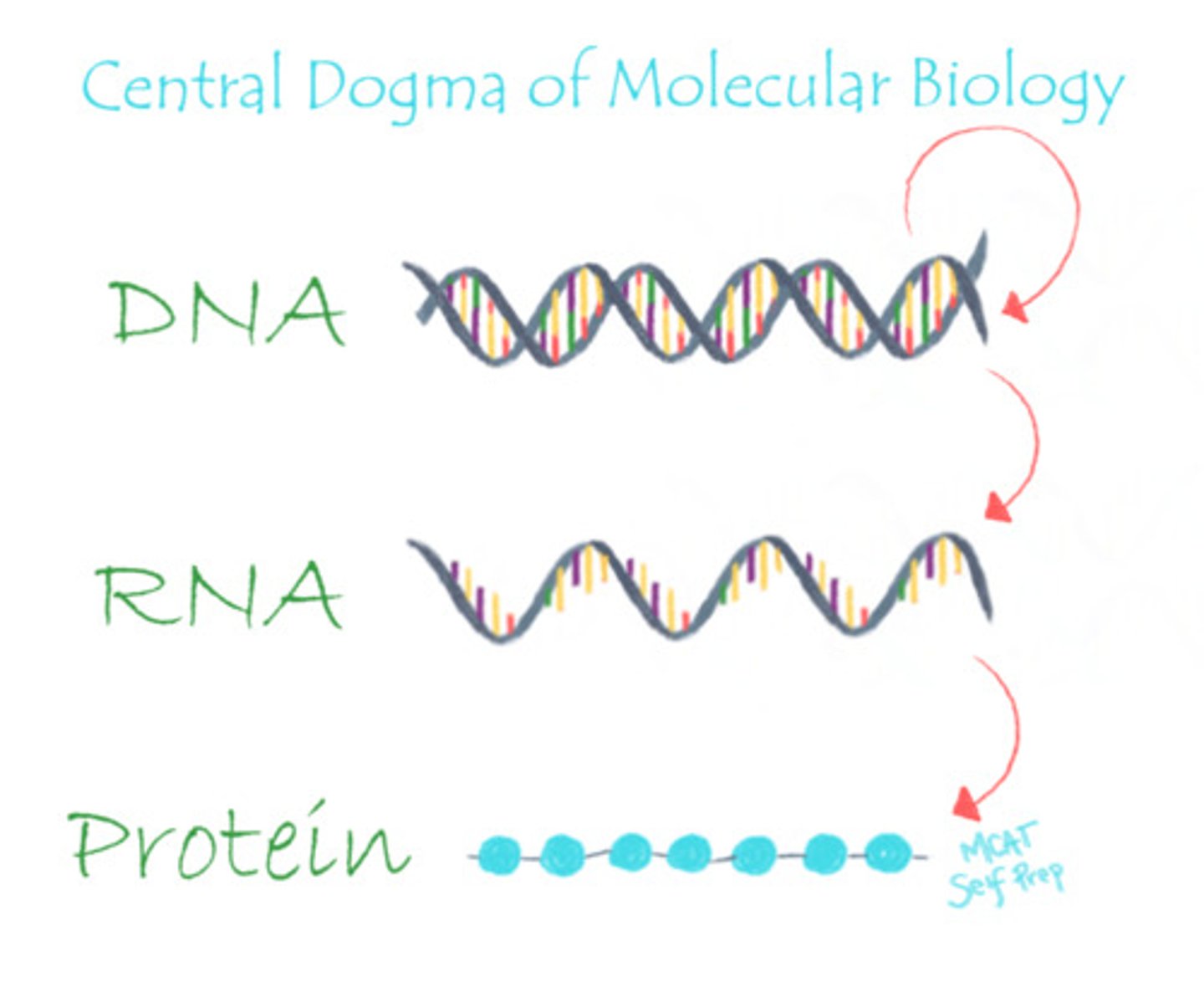
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
DNA makes RNA, which makes protein.
How can one easily differentiate transcription and translation using base words "script" and "translate"?
The word "script" refers to written forms. Transcription goes from one written form (DNA) to another (RNA) using a common "alphabet" (aka nucleic acids).
Translation refers to the need to "translate" from one language to another. Here, nucleic acids from one language (RNA) are translated into amino acids of another language (protein).
RNA is used as a template in the formation of cDNA through the process of:
(A) Reverse Replication
(B) Reverse Translation
(C) Reverse Transcription
(D) Reverse Integration
(C) Reverse Transcription
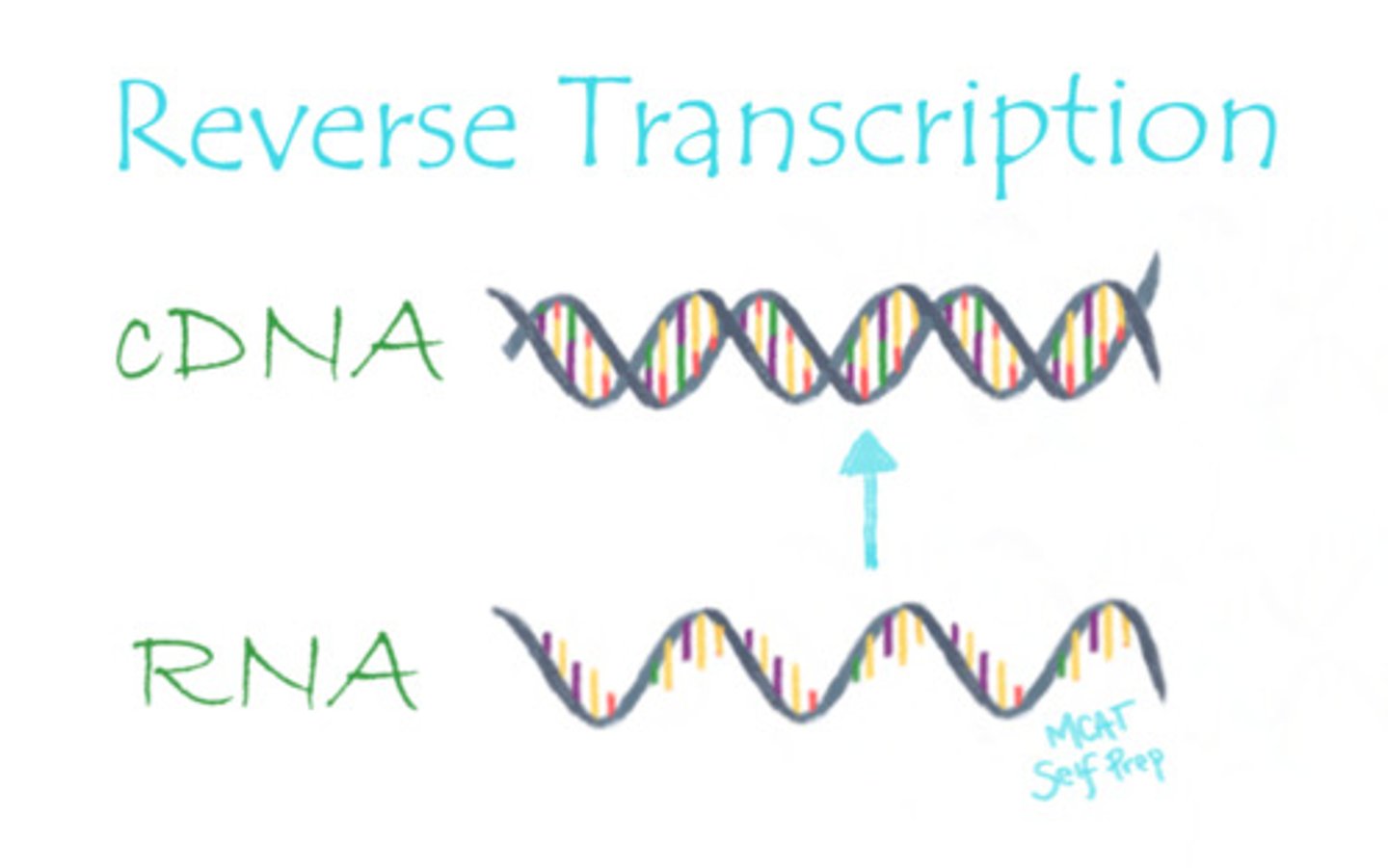
What is the function of reverse transcriptase?
Reverse transcriptase is the enzyme that carries out reverse transcription, in which complementary DNA (cDNA) is generated from an RNA template.
What is most likely to occur if a patient with HIV is administered a medicinal drug that deactivates the enzyme reverse transcriptase?
(A) The patient will die.
(B) The patient's chances at survival will increase.
(C) The patient's chances at survival will decrease, but they will not die.
(D) The patient may go into a coma.
(B) The patient's chances at survival will increase.
Reverse transcriptase is used by HIV to reverse transcribe the retrovirus's RNA into DNA, which can then be integrated into the host's DNA. Deactivating reverse transcriptase will halt this process, which is essential for propagating HIV's lifecycle. This is an effective treatment against HIV!
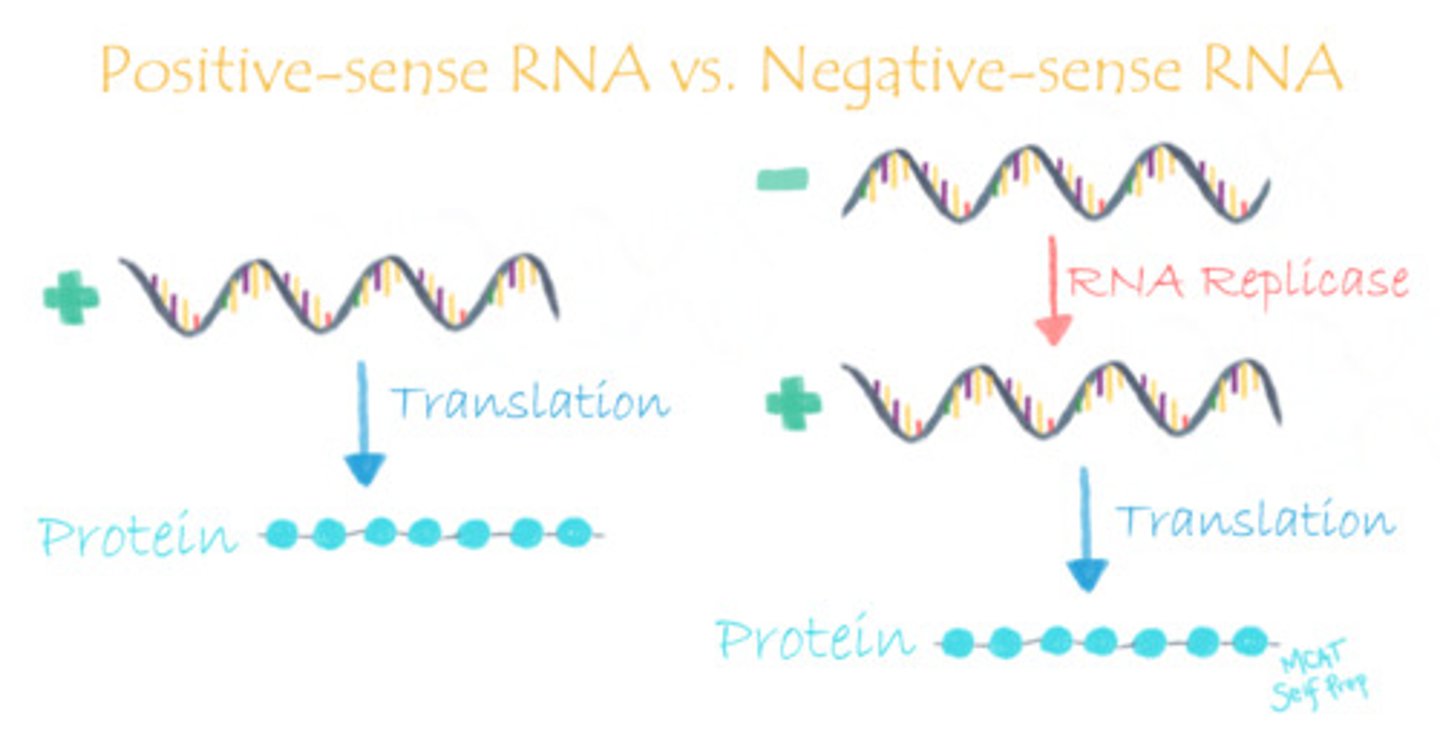
True or False? The genetic material of (+)ssRNA viruses (such as coronavirus) is translated immediately by host cell machinery as compared with DNA viruses and retroviruses.
True. The genetic material of (+)ssRNA viruses (such as coronavirus) is translated immediately by host cell machinery as compared with DNA viruses and retroviruses.
CRB Describe the differences in translation between (+)ssRNA viruses (like the Coronavirus) and (-)ssRNA viruses (like the influenza virus).
(+)ssRNA viruses have their genome stored as RNA that can readily be translated to form the proteins that they need.
(-)ssRNA Viruses, however, need to transcribe the (+) version of the RNA so it can be readily translated by the host cell's machinery. These viruses need an extra step of processing!
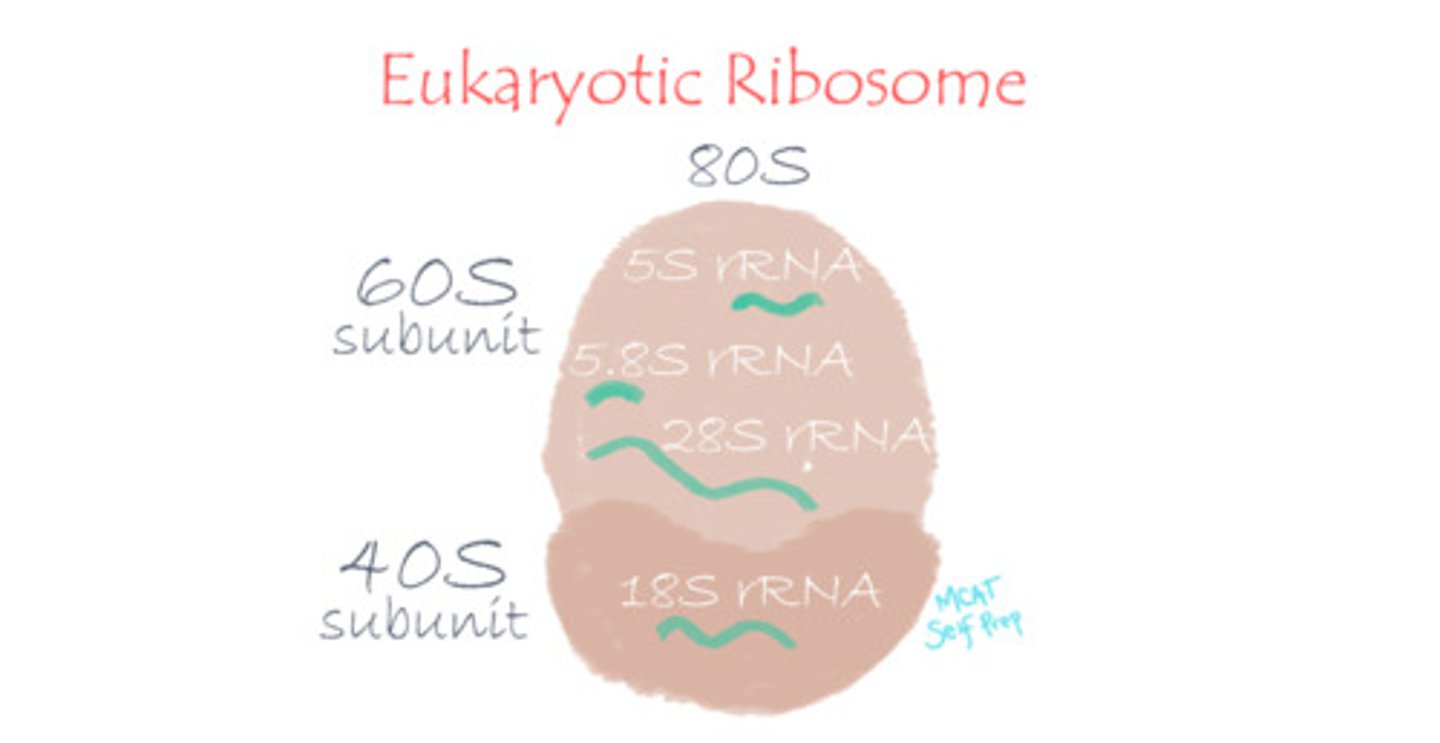
Which of the following are examples of non-coding RNA (ncRNA)? Why are they called that?
I. tRNA
II. mRNA
III. rRNA
(A) I Only
(B) II Only
(C) I and II Only
(D) I and III Only
(D) I and III Only
Transfer RNA (tRNA) and Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) are both examples of non-coding RNA (ncRNA) because they are not translated into a protein themselves. Instead, these biomolecules assist in the process of translation by helping messenger RNA (mRNA) create proteins.
What is the primary function of transfer RNA (tRNA) vs. ribosomal RNA (rRNA)?
Transfer RNA (tRNA) carries amino acids to the ribosome and acts as a "bridge" by matching a codon in mRNA with its corresponding amino acid.
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is responsible for the structure and function of the ribosome.
Do the discoveries of reverse transcription, RNA viruses and noncoding RNA support or violate the central dogma?
These discoveries violate the central dogma. These are processes that use mechanisms that run counter to the central dogma.
Compare Epigenetics with typical genetics. Give an example of each.
Epigenetics is the study of heritable changes in gene activity not caused by changes in DNA sequence. Examples of Epigenetics include DNA methylation and histone acetylation. Both cause heritable changes in DNA expression without changing DNA sequences.
Typical genetics is the study of heritable changes in gene activity caused by changes in DNA sequence. For instance, your DNA is very similar in sequence to that of your mom and dad and the sequences of this DNA are what result in having similar physical characteristics to your parents.
How is it that a muscle cell and a skin cell have the same DNA when they are completely different from one another in terms of cell function?
Epigenetic mechanisms allow the transcription of only certain genes within the genome. The DNA is the same, but the modifications of the DNA are different, leading to different gene expression. Thus, the DNA of a muscle and skin cell may be the same, but the protein in each cell is completely different.
Peptide bonds are a special kind of link between:
(A) Monosaccharides
(B) Amino Acids
(C) Nucleic Acids
(D) Monopeptides
(B) Amino Acids
Amino acids are linked together through bonds known as peptide bonds.
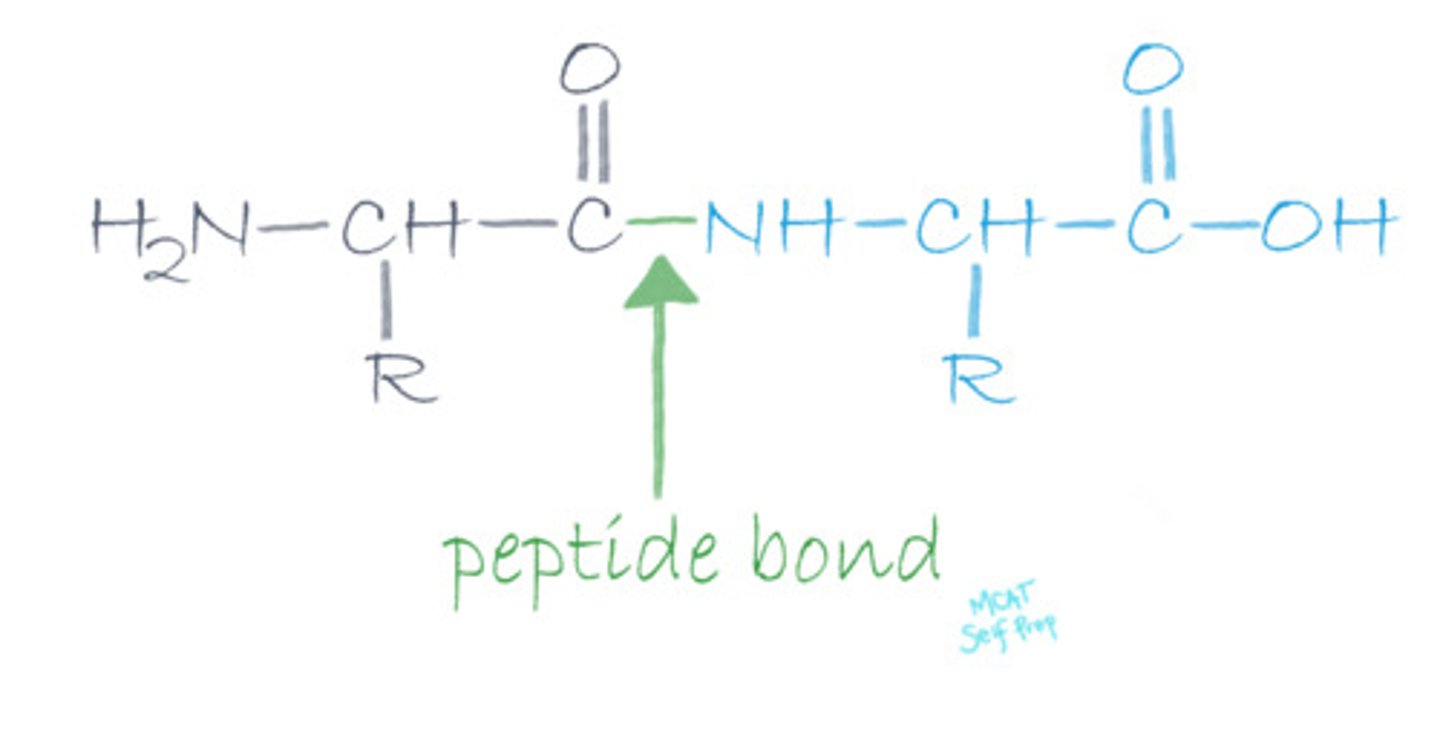
CRB If there are only enough peptide bonds in a molecule so that you could count them all on your fingers and toes, then what type of peptide would this be?
(A) Peptides
(B) Oligopeptides
(C) Proteins
(D) Polypeptides
(B) Oligopeptides
Oligopeptides have up to 20 amino acids in them.
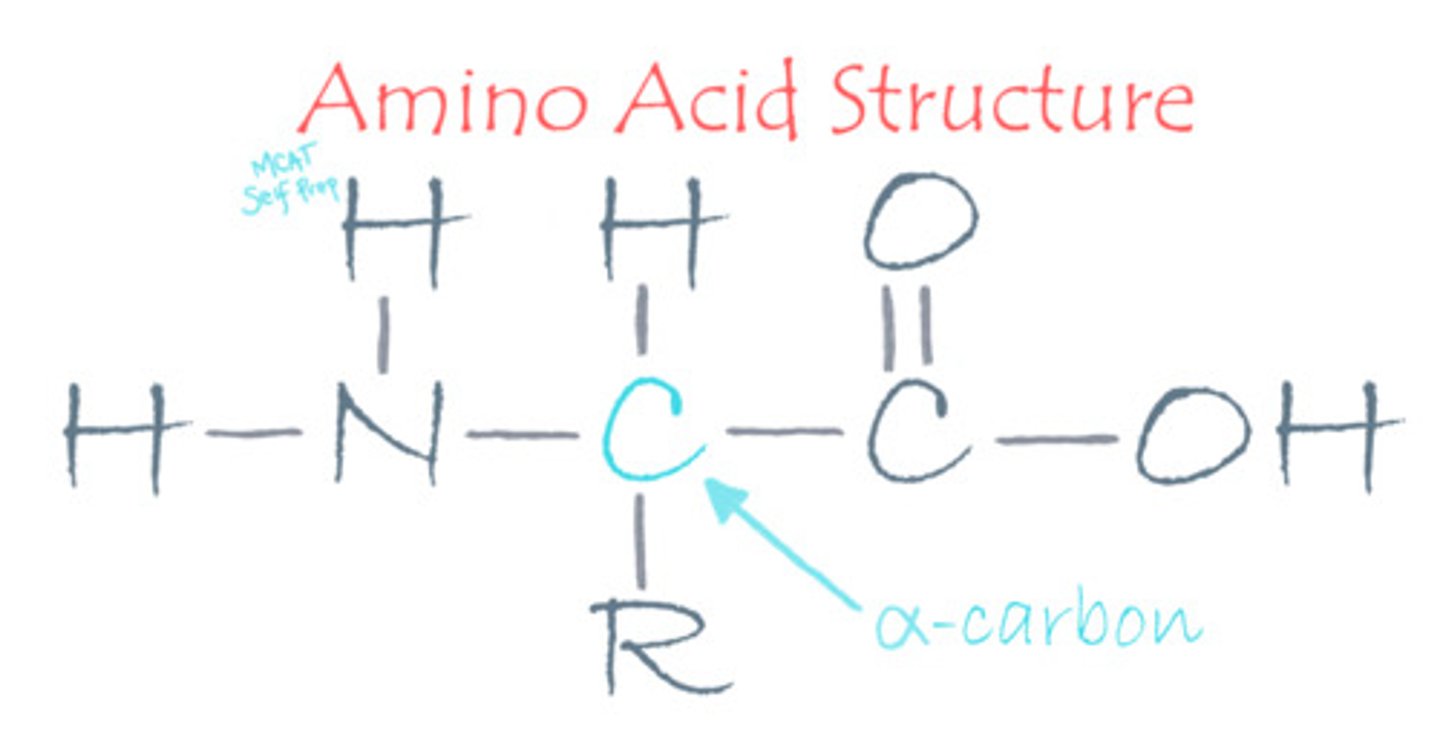
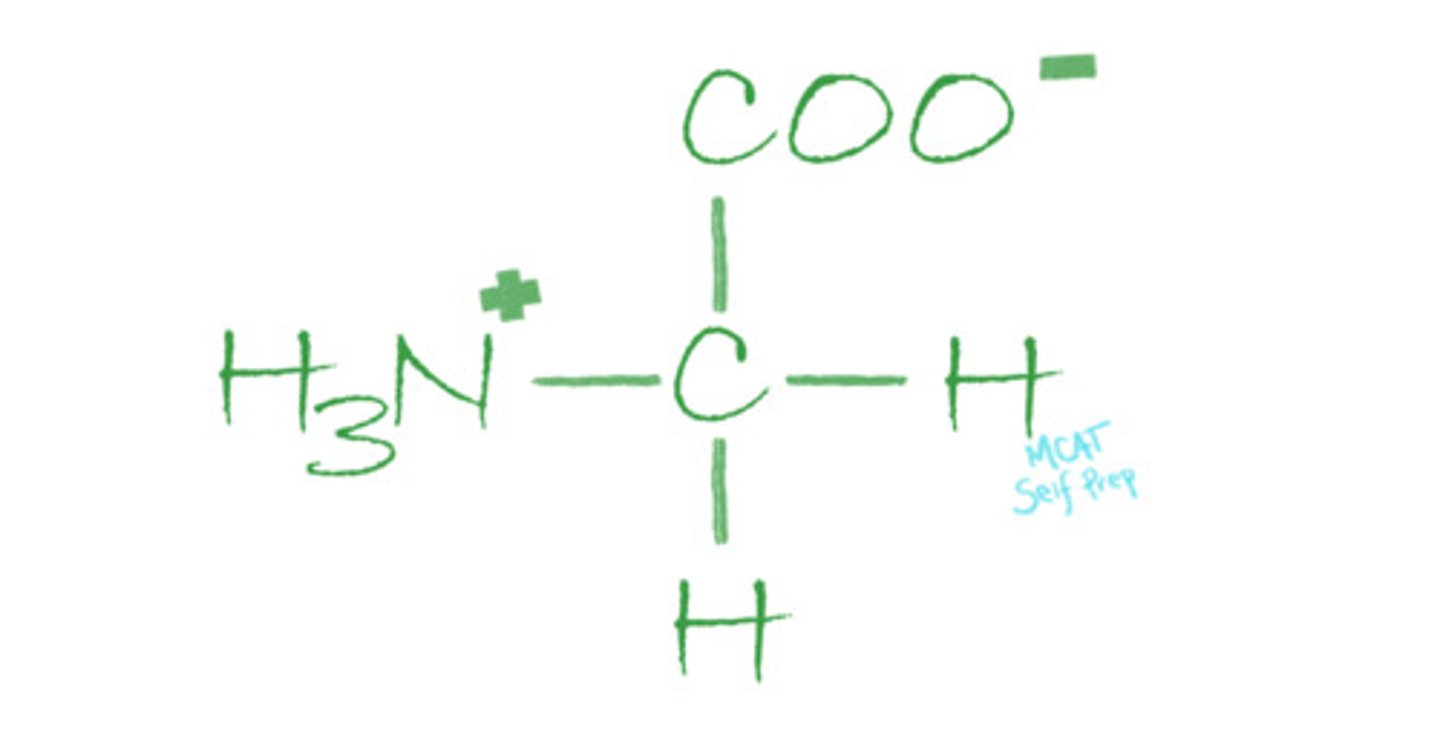
Draw an amino acid with its four substituents. Circle the alpha carbon.
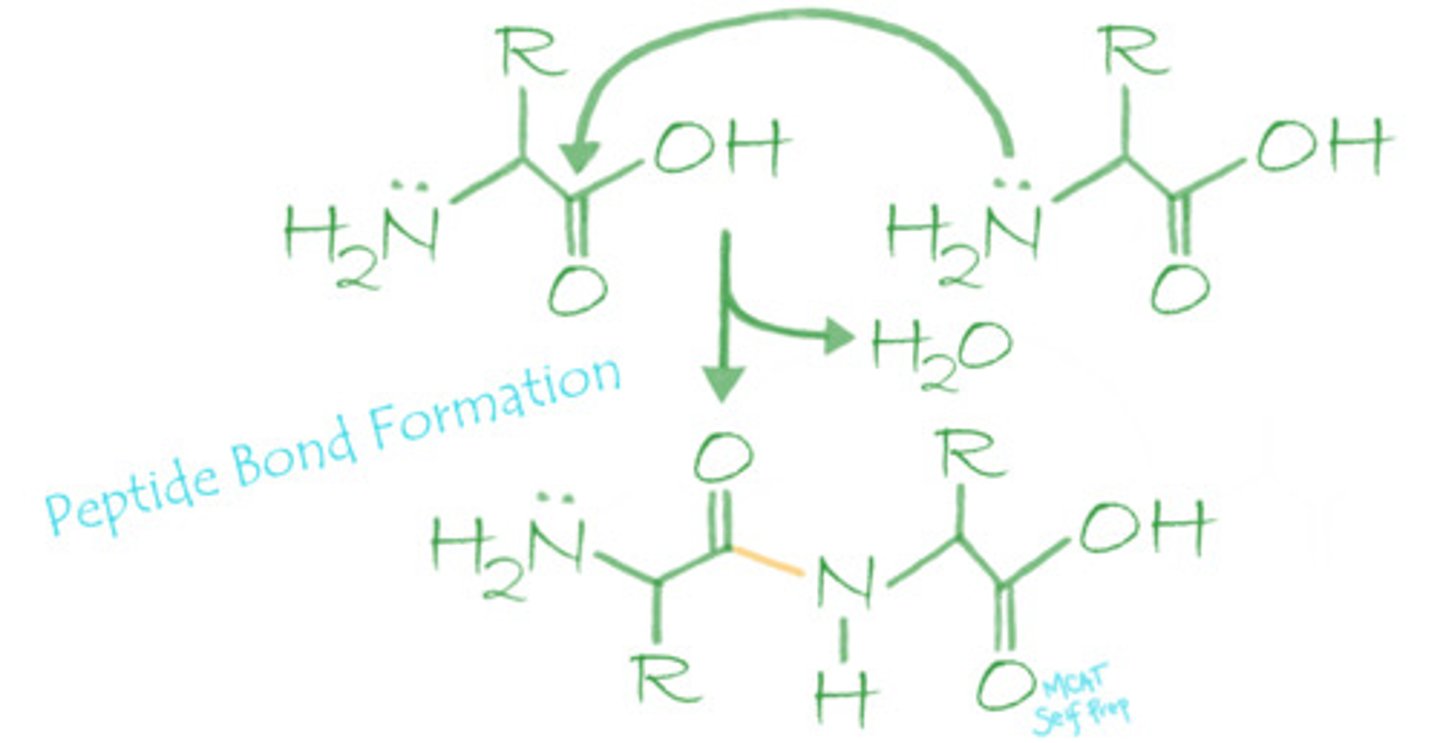
Peptide bonds are formed via what mechanism? Explain or draw out this mechanism.
(A) Hydration
(B) Hydrolysis
(C) Condensation
(D) Oxidation-reduction
(C) Condensation
Peptide bonds are formed by the nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction, which is a type of condensation reaction. The electron pair on the amino group of one amino acid will nucleophilically attack the carbonyl carbon of the carboxyl group of another amino acid, releasing a water molecule and forming a peptide bond.
A peptide bond is an example of a(n):
(A) Amide group
(B) Amino group
(C) Carboxylic acid group
(D) Hydroxy group
(A) Amide group
A peptide bond is an example of an amide group.
Draw out the resonance structures that make up a peptide bond.
The peptide bond resonance structures share electrons between the oxygen and nitrogen atoms.
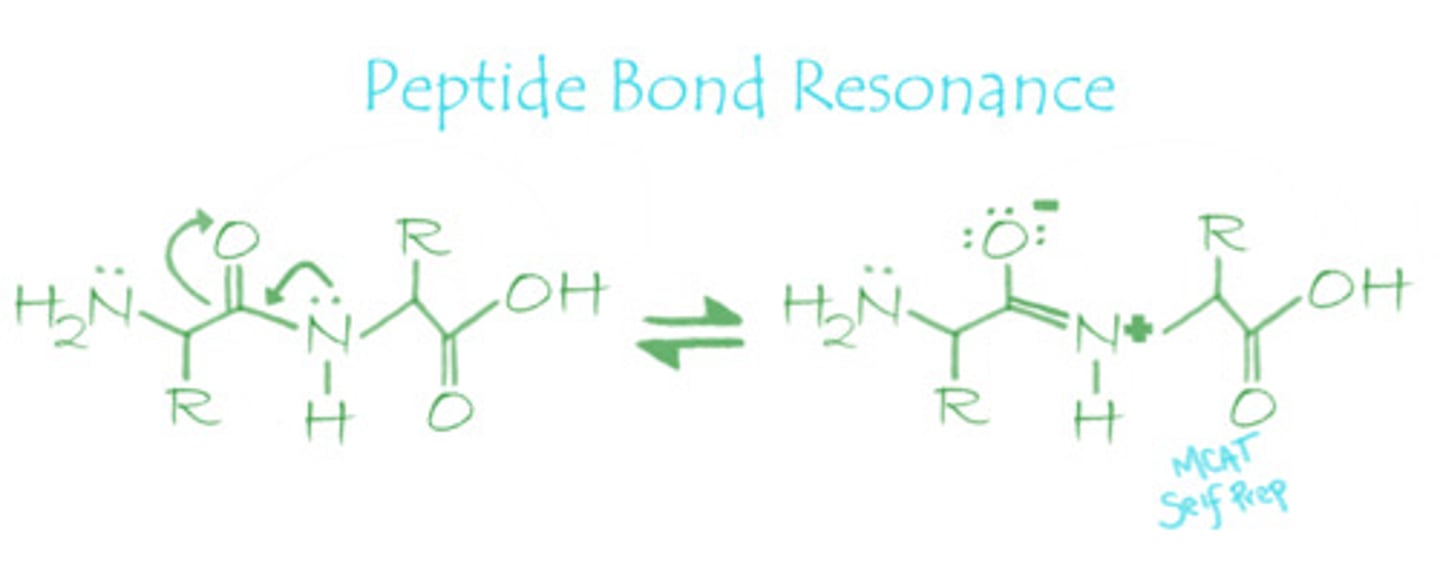
The resonance structure of the peptide bond has a double bond character. Which of the following correctly describe the peptide bond?
I. Rigid
II. Planar
III. Does not rotate
(A) I Only
(B) I and II Only
(C) II and III Only
(D) I, II, and III
(D) I, II, and III
Since there is double bond character in a peptide bond, the peptide bond is very rigid, planar, and does not rotate.
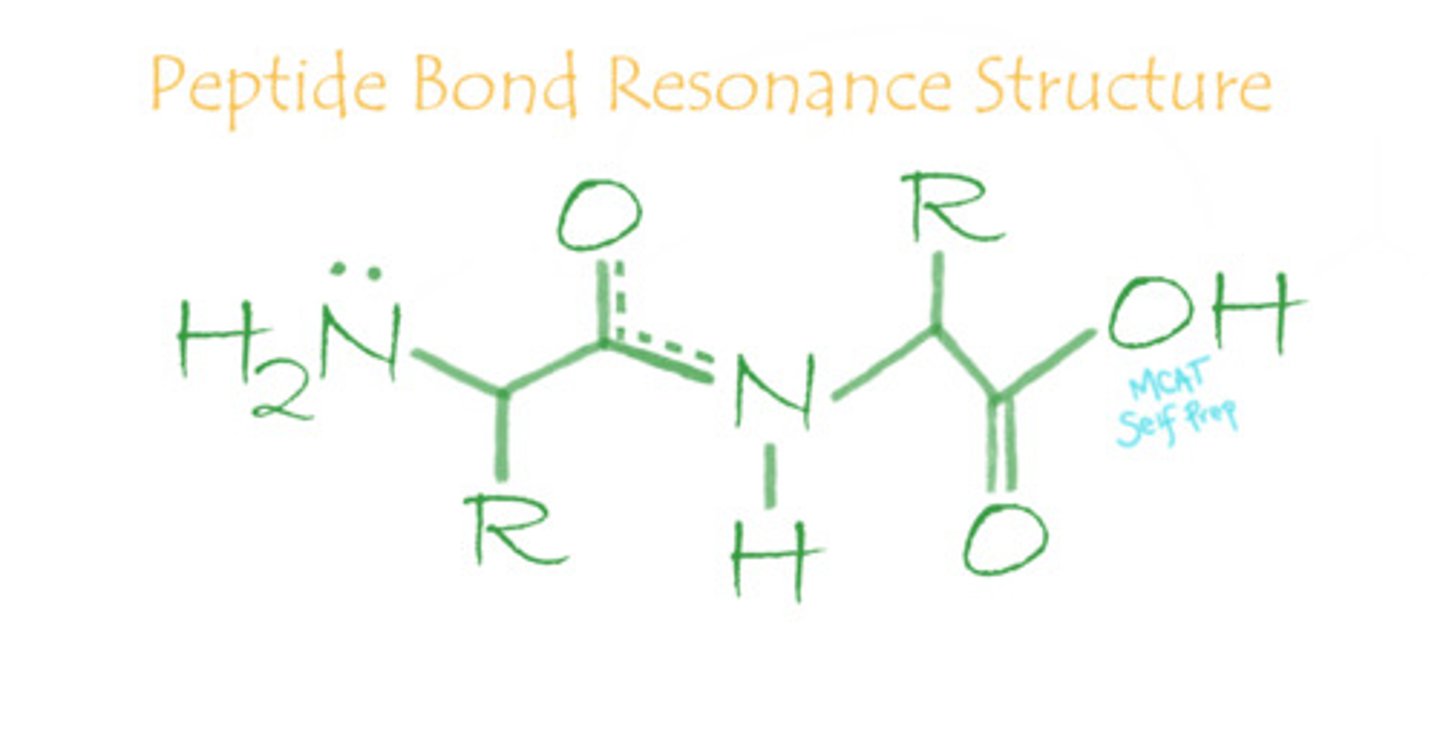
True or False. Due to the rigidity of the peptide bond, proteins cannot fold.
False. Do not confuse the rigidity of the peptide bond with the entire polypeptide structure. Remember that alpha carbon atoms can still freely rotate.
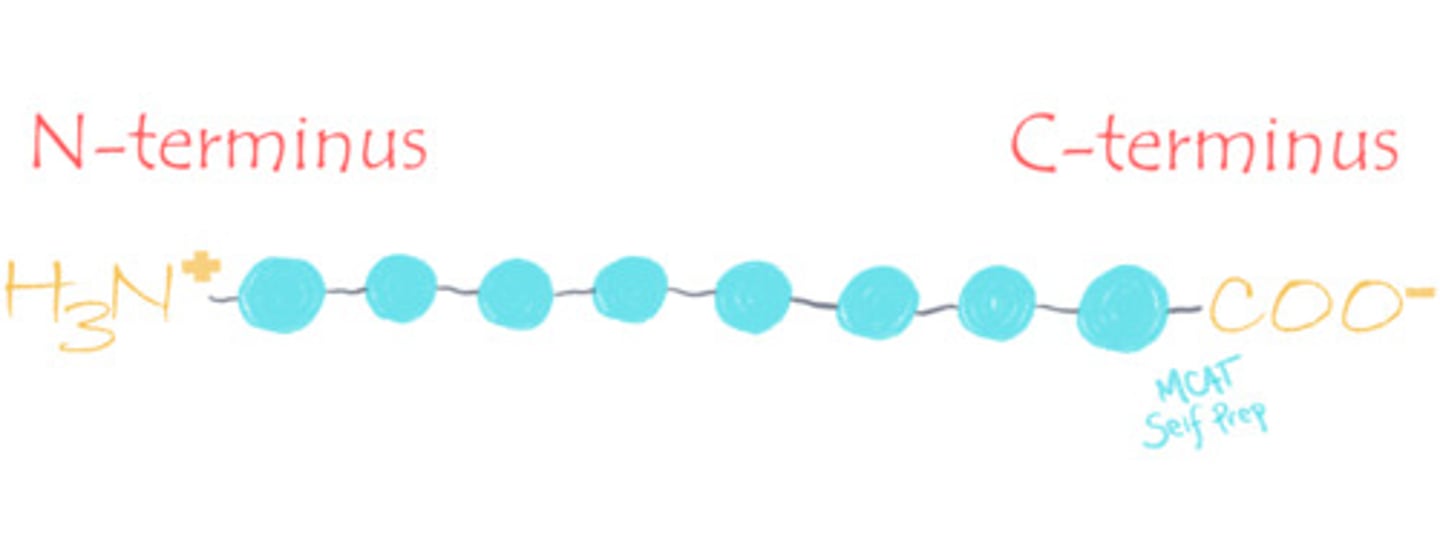
In an amino acid, what does the N-terminus refer to compared the C-terminus? Which terminus is made first during translation?
The N-terminus includes the first amino acid of a protein, which has a free amino group at this end of the polypeptide chain. This is made first.
The C-terminus includes the final amino acid of a protein, and is therefore where synthesis of a polypeptide ends. There is a free carboxyl group at this end of the polypeptide chain.
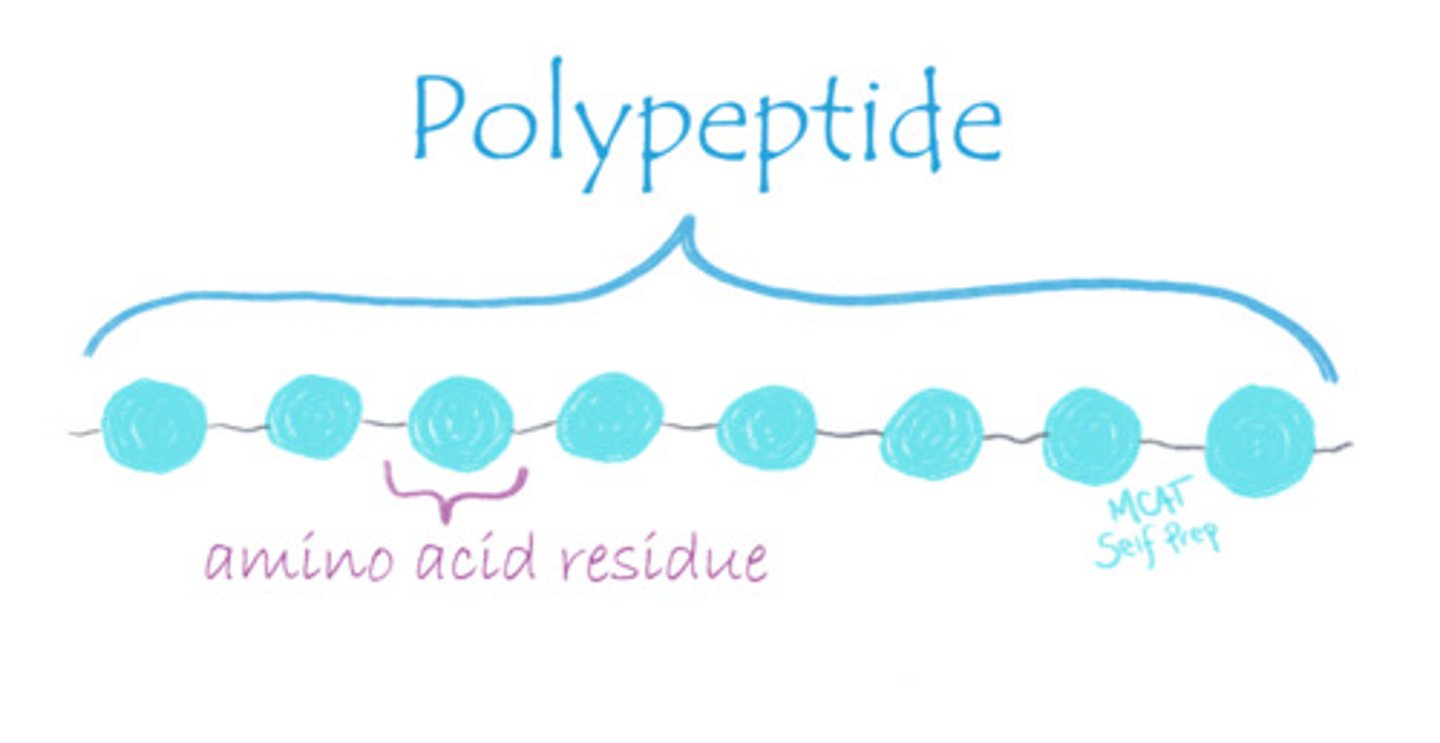
What does the term "residue" refer to?
(A) A single atom within a molecule
(B) A single amino acid within a polypeptide chain
(C) A single polypeptide within a protein
(D) A single protein within a cell
(B) A single amino acid within a polypeptide chain
The term "residue" refers to a single amino acid within a polypeptide chain because some of the molecules of the amino acid are lost in the condensation reaction to form peptide bonds, leaving a "residue" behind.
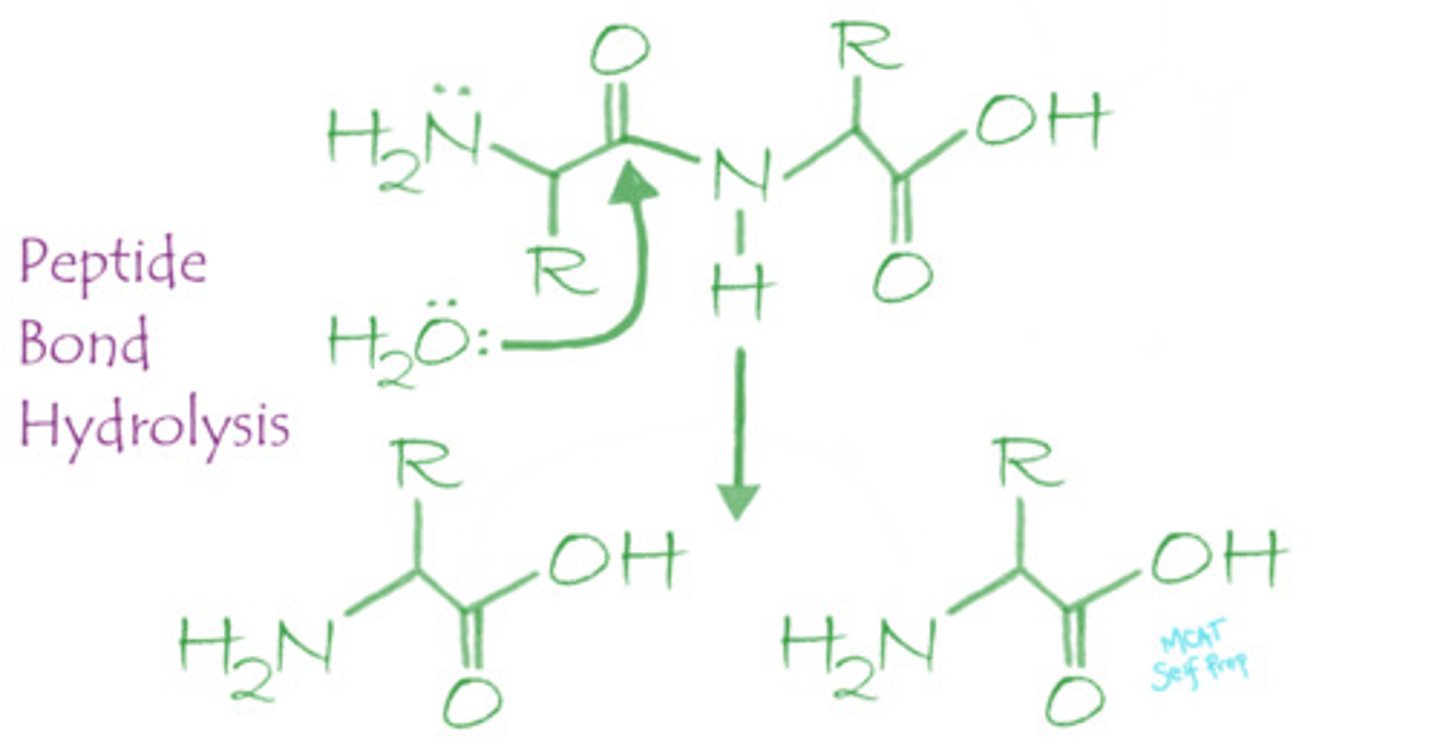
Peptide bonds are broken via what mechanism? Explain or draw out this mechanism.
(A) Hydration
(B) Hydrolysis
(C) Condensation
(D) Oxidation-reduction
Peptide bonds are broken down via a hydrolysis reaction. Hydrolysis uses water as a reactant to break peptide bonds with the help of either strong acids or proteolytic enzymes (proteases).
CRB So, because Hydrolysis will break down peptide bonds, does that mean that all proteins should be hydrophobic?
No, proteins have many polar groups, and some can be quite soluble (like albumin). Hydrolysis typically also requires that strong acid or proteolytic enzymes be present to drive the reaction forward.
What is the difference between acid hydrolysis and proteolysis when breaking a peptide bond?
Acid Hydrolysis: Breaks/cleaves a peptide bond in a non-specific way and requires acid and heat.
Proteolysis: Breaks/cleaves specific peptide bonds within the polypeptide chain using a protease enzyme.
An enzyme called Trypsin produced in the pancreas cleaves the carboxyl end of either arginine or lysine. Would this be considered acid hydrolysis or proteolysis? Why?
Proteolytic cleavage (proteolysis) because Trypsin (a protease) cleaves at a specific location (C terminus end of Arg and Lys).
Proline has a unique amino group. In what way is it unique?
Proline's amino group is a secondary instead of primary amino group. The R group of Proline is bound to the amino group, forming a ring.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
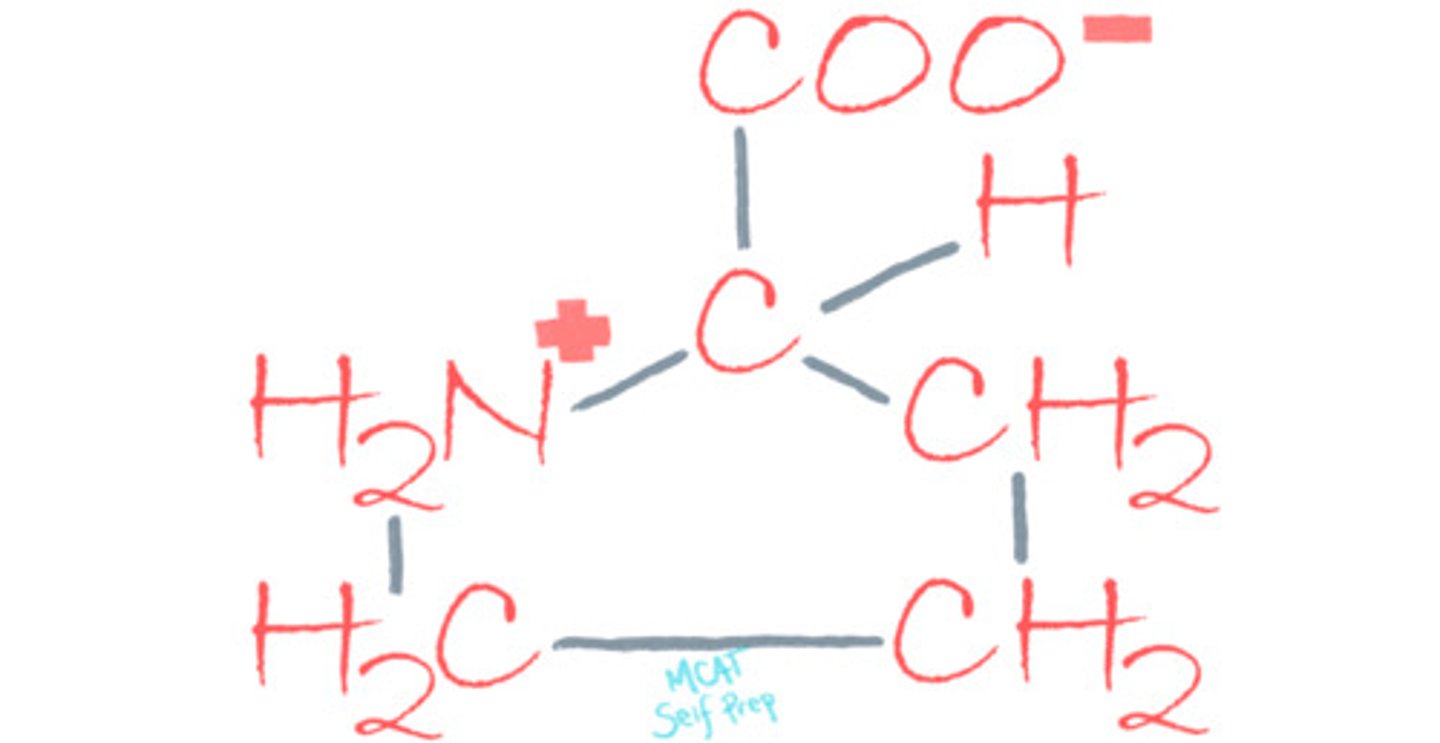
Which amino acid is most likely to be found at the active site of an enzyme? Why?
(A) His
(B) Pro
(C) Gly
(D) Cys
(A) His
Histidine, because its side chain has a pKa (6.5) roughly equal to physiological pH (7.4) thus allowing histidine to exist in both its protonated and deprotonated form. This way, His can both stabilize or destabilize a substrate during catalysis.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
Would Histidine's R Group be protonated or deprotonated at a pH of 4.0?
Protonated because the pH (4.0) < pKa (6.5)
When pH < pKa, then the amino acid will be in its protonated form.
When pH > pKa, then the amino acid will be in its deprotonated form.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
CRB If the pH were equal to the pKa of an amino acid's R-group, what percentage of the amino acids' R-groups would be deprotonated?
(A) 16%
(B) 33%
(C) 50%
(D) 75%
(C) 50%
When the pH is equal to the pKa of any functional group, then half of that functional group will be deprotonated.
Looking under a microscope, you see that there is a disruption in the pattern of a protein's secondary structure. Which amino acid(s) is/are likely responsible for this pattern of disruption?
I. R
II. G
III. P
(A) I Only
(B) II and III Only
(C) I and III Only
(D) I, II, and III
(B) II and III Only
Proline and glycine are likely to cause a disruption in an alpha helix protein structure because proline has an inflexible secondary alpha amino group tied up with its side chain. This inflexible ring ends up adding a kink to the alpha helix.
Glycine has a hydrogen atom as its side chain, making it very small and flexible.
Remember this: glycine & proline = "alpha helix breakers."
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
A scientist shines plane polarized light through various amino acids. Which amino acid will not show optical activity?
(A) Thr
(B) Arg
(C) Gly
(D) Glu
(C) Gly
Glycine is the only amino acid that does not rotate the plane of plane-polarized light because glycine is an achiral compound, making it optically inactive.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
Which amino acid is able to form disulfide bridges within a polypeptide chain or between two different polypeptide chains?
(A) Phe
(B) Cys
(C) Gln
(D) Met
(B) Cys
Cysteine is able to form disulfide bridges within a polypeptide chain or between two different polypeptide chains.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
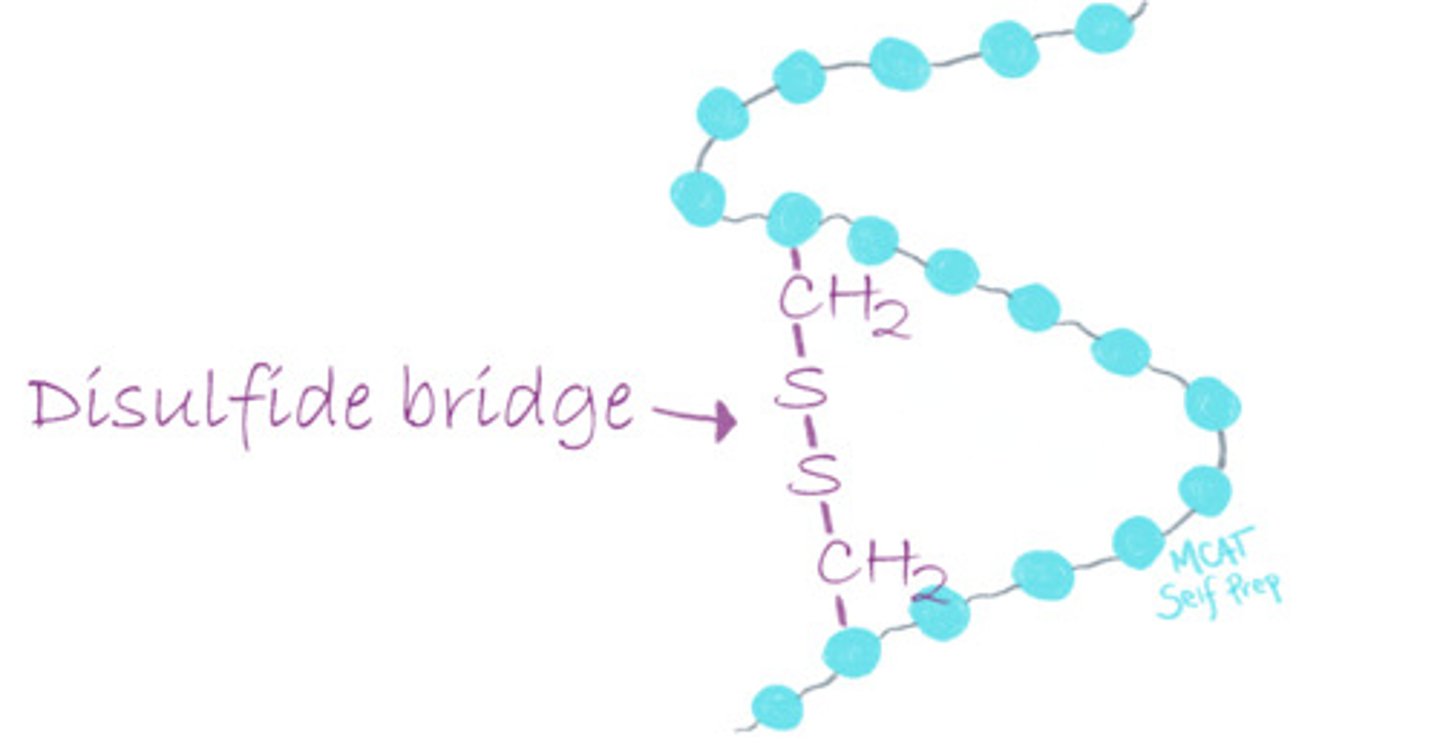
What happens to the structure of cysteine when it goes from the intracellular to the extracellular space?
Cysteine changes from its reduced form (-SH) in the intracellular environment to its oxidized form (disulfide bond) in the extracellular space.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
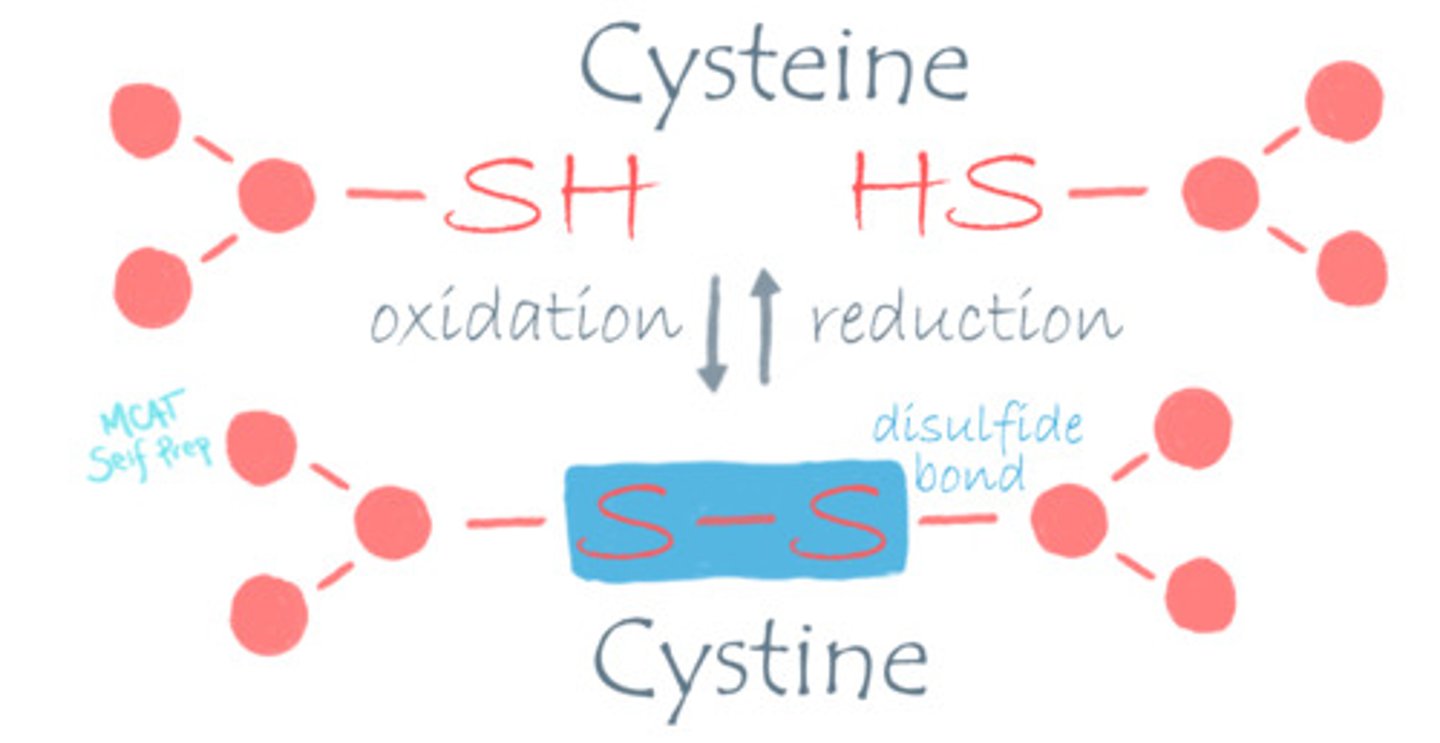
An unknown, rare disease causes a breakdown of polypeptide chains by disrupting its tertiary and quarternary structure. Which amino acid is likely involved? Why?
(A) His
(B) Pro
(C) Gly
(D) Cys
(D) Cys
Disulfide bridges contribute to the tertiary and quarternary structure of a protein; thus, the pathology of the disease is most likely affecting the amino acid cysteine's ability to form disulfide bridges in an oxidized environment (which typically favors the formation of disulfide bridges).
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
What is the difference between Cysteine and Cystine?
Cysteine refers to the reduced form.
Cystine refers to the oxidized form.
Think about the e being electrons, which are found in the reduced form (OIL RIG).
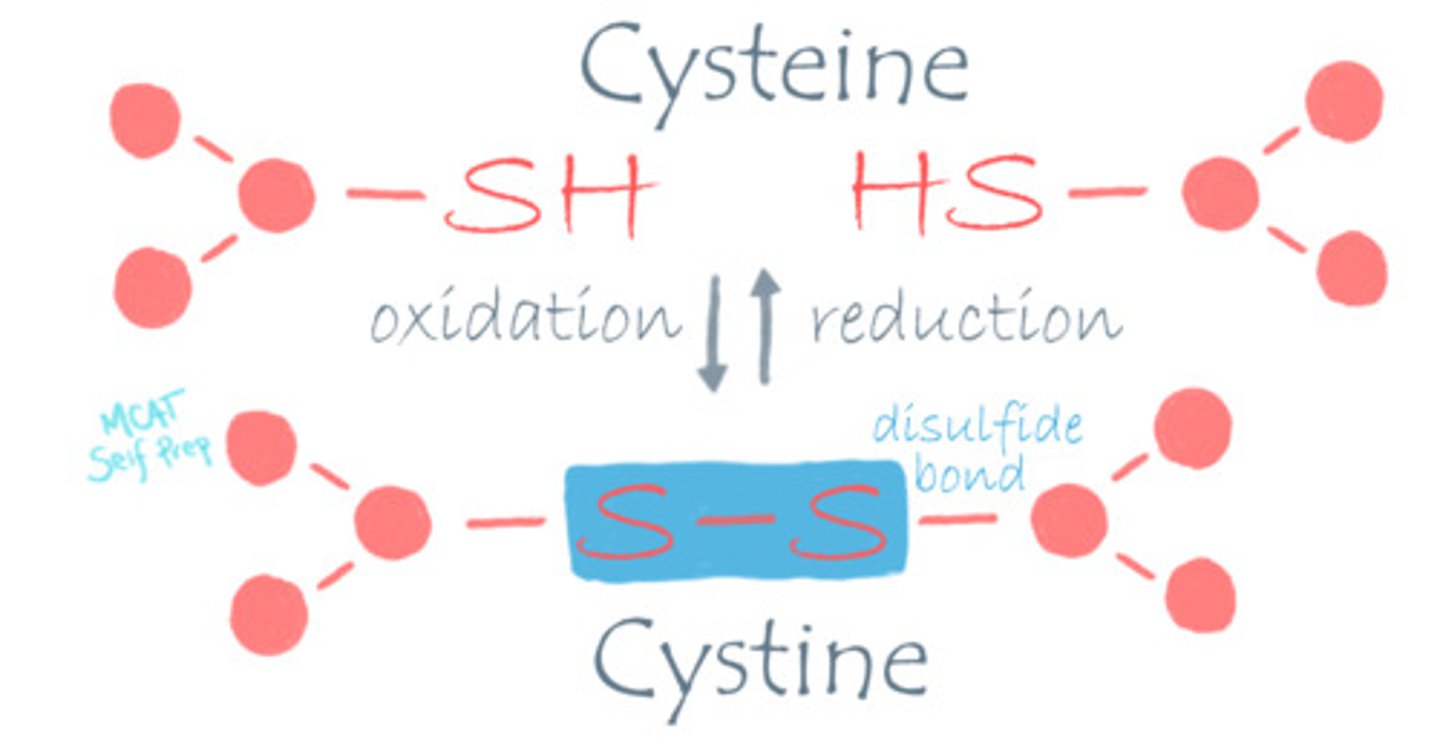
Which amino acid does not have a chiral alpha carbon?
(A) His
(B) Pro
(C) Gly
(D) Cys
(C) Gly
Glycine is the only amino acid that does not have a chiral alpha carbon.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
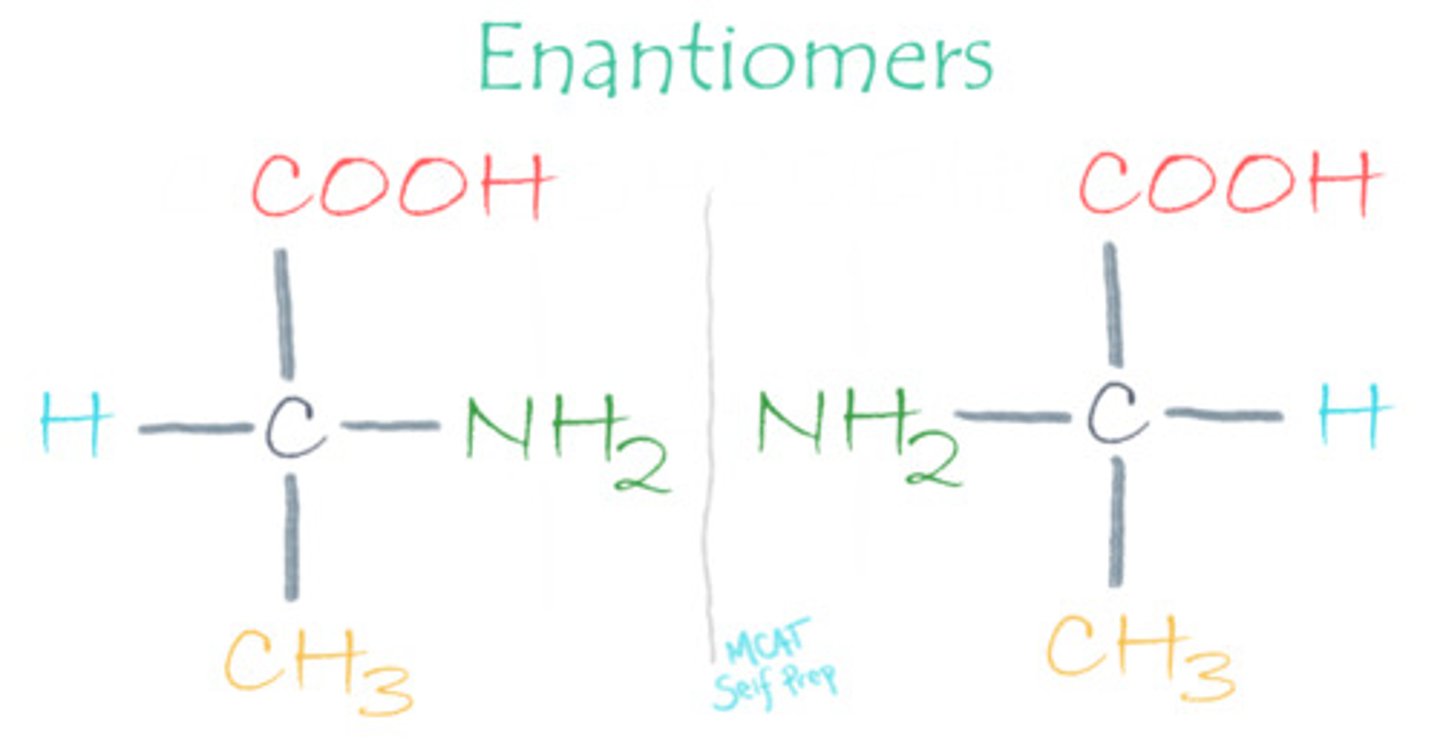
Draw the fischer projection of both an L- and D-amino acid. Which bonds are pointing towards you? Which bonds are pointing away from you?
L-amino acid has an amino group shown on the Left side in a Fischer projection while the D-amino acid has an amino group shown on the right side of a Fischer projection.
Horizontal bonds are pointing towards you and vertical bonds are pointing away from you.

What makes a molecule considered an enantiomer?
Enantiomers are mirror-image molecules that are not superimposable.
Which form of amino acids, L- or D-amino acids, is found in the human body?
L-amino acids are the only form that will be found in the human body.
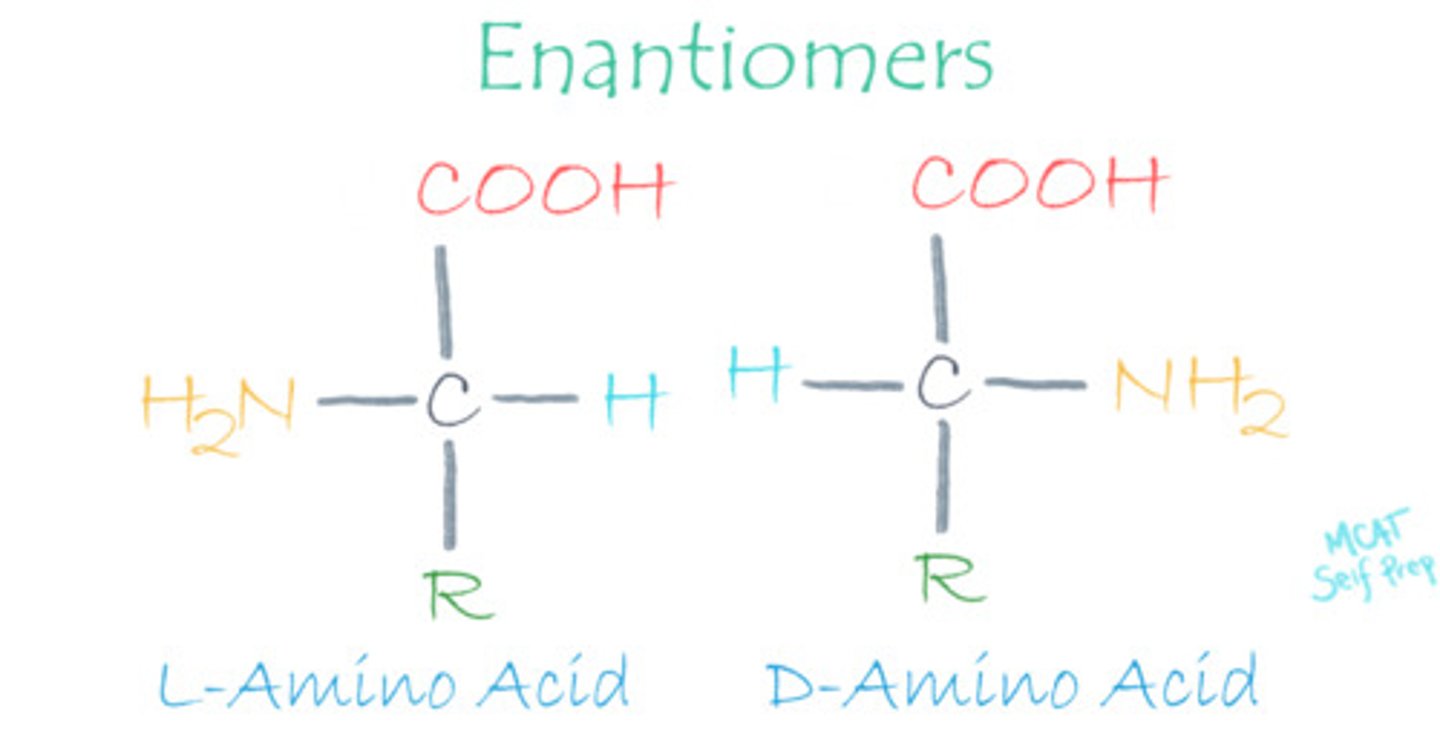
CRB All but one of the chiral amino acids have an absolute configuration of S. Which chiral amino acid does not?
(A) Gly
(B) Cys
(C) Thr
(D) Pro
(B) Cys
Cysteine has a R-absolute configuration, not S.
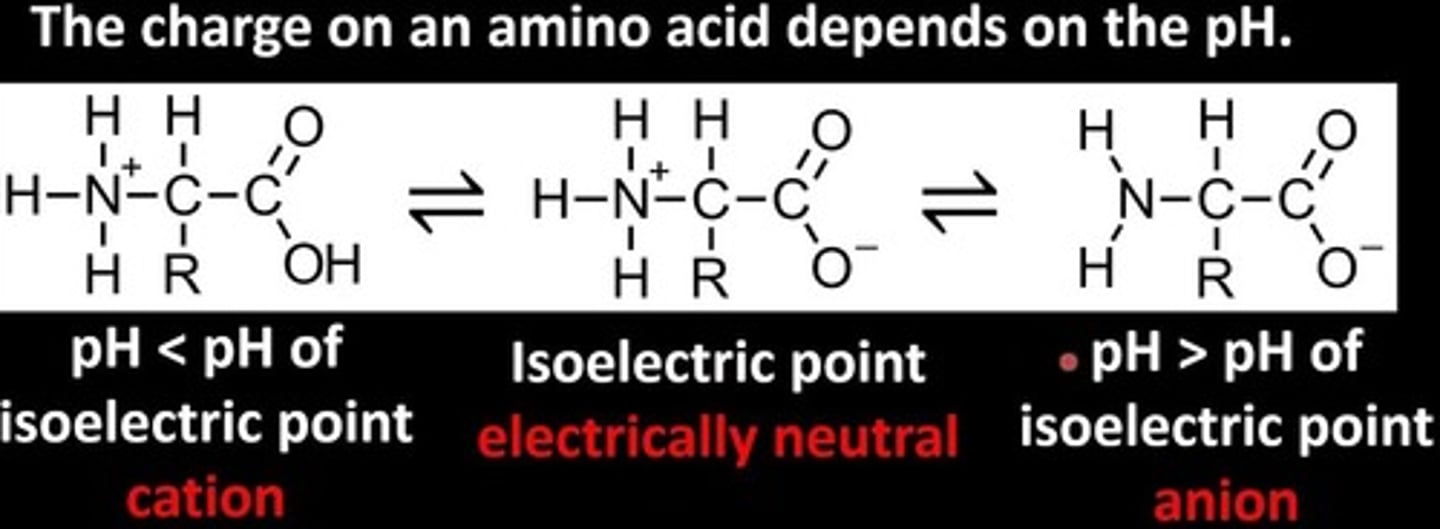
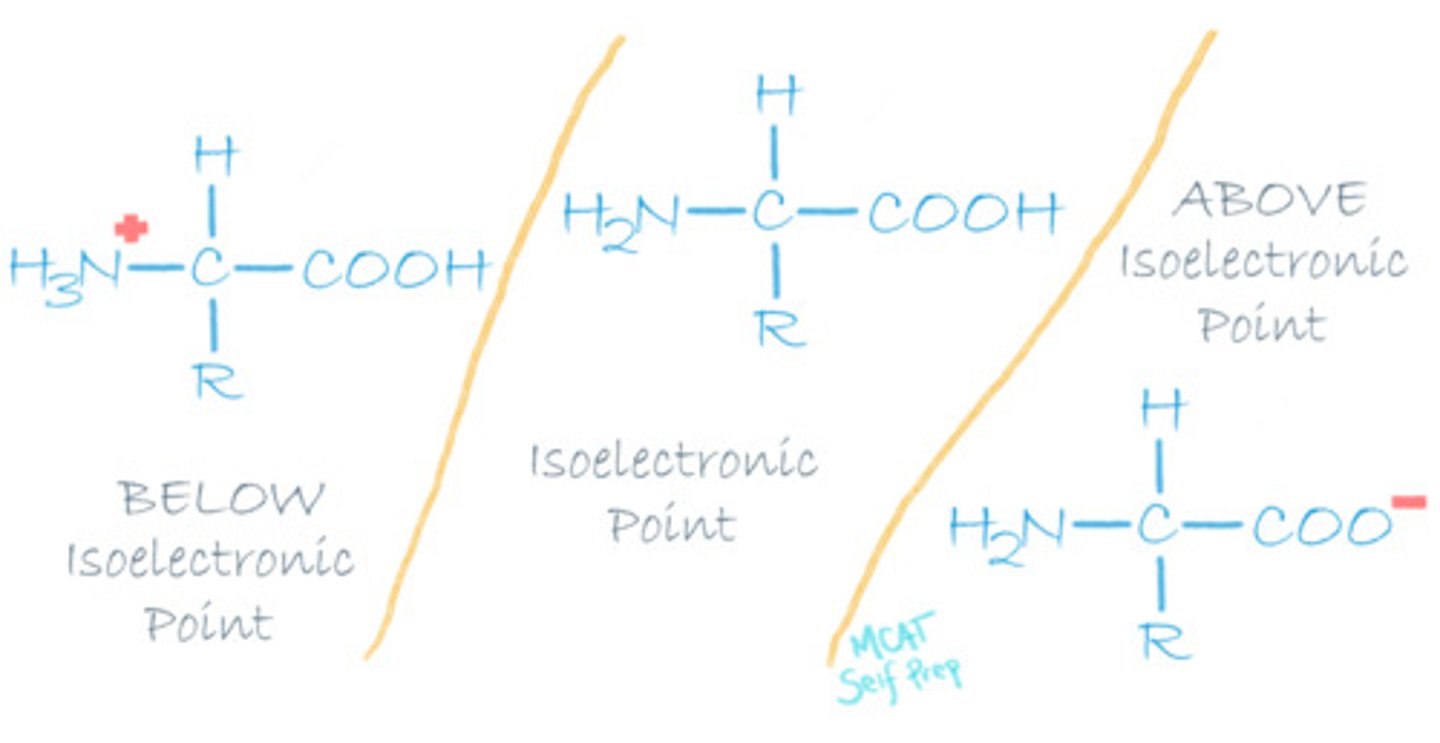
What is the isoelectric point of an amino acid?
The Isoelectric Point is the pH at which an amino acid exists in a neutral form with zero charge.
Note that this picture is for amino acids with uncharged R groups. The charge on the R group is considered when finding the isoelectric points of amino acids!
What is the approximate pKa of the amino group of an Amino Acid?
(A) 2
(B) 6
(C) 9
(D) 12
(C) 9
The amino group on the amino acid is a proton acceptor, making it basic with a pKa around 9.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
What is the approximate pKa of the carboxylic acid group of an Amino Acid?
(A) 2
(B) 6
(C) 9
(D) 12
(A) 2
The carboxylic acid group of the amino acid is a proton donor, making it acidic with a pKa around 2.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
What is the difference between the zwitterionic and non-zwitterionic form of an amino acid?
An amino acid with both a negative charge and a positive charge present on the carboxylic acid group and amino group, respectively, is called a zwitterion.
Its non-zwitterionic form entails both groups having no charge.
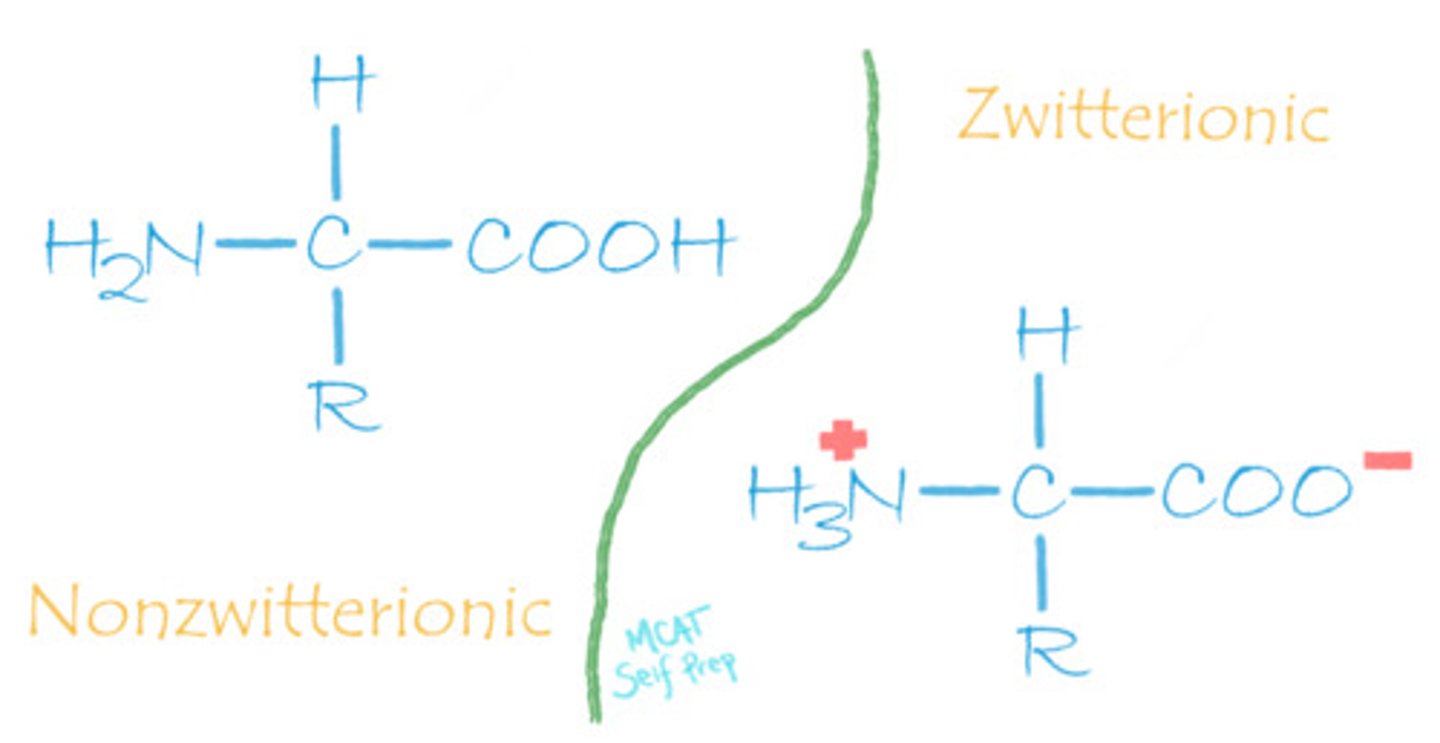
CRB Which of the following best describes the fact that amino acids can both accept and donate a proton, based on having both acidic and basic functional groups?
(A) Aliphatic
(B) Amphoteric
(C) Aromatic
(D) Zwitterionic
(B) Amphoteric
When will an amino acid be fully protonated vs. fully deprotonated?
At a low pH, the amino acid will be fully protonated with a positive net charge.
At a high pH, the amino acid will be fully deprotonated with a negative net charge.
What is the pKa of the R group for Asp? Glu? His? Cys? Tyr? Lys? Arg?
Aspartate - 3.9
Glutamate - 4.1
Histidine - 6.0
Cysteine - 8.4
Tyrosine - 10.5
Lysine - 10.5
Arginine - 12.5
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
How do you calculate the isoelectric point of an amino acid?
The pI for a simple compound can be calculated by averaging
the 2 pKa's that are relevant to the concentration of the
molecule in its neutral charge state.
Neutral R group: the pI is the average of the carboxylic acid group and amino group pKa values.
Acidic R group: the pI is the average of the carboxylic acid group and side chain pKa values.
Basic R group: the pI is the average of the amino group and side chain pKa values.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
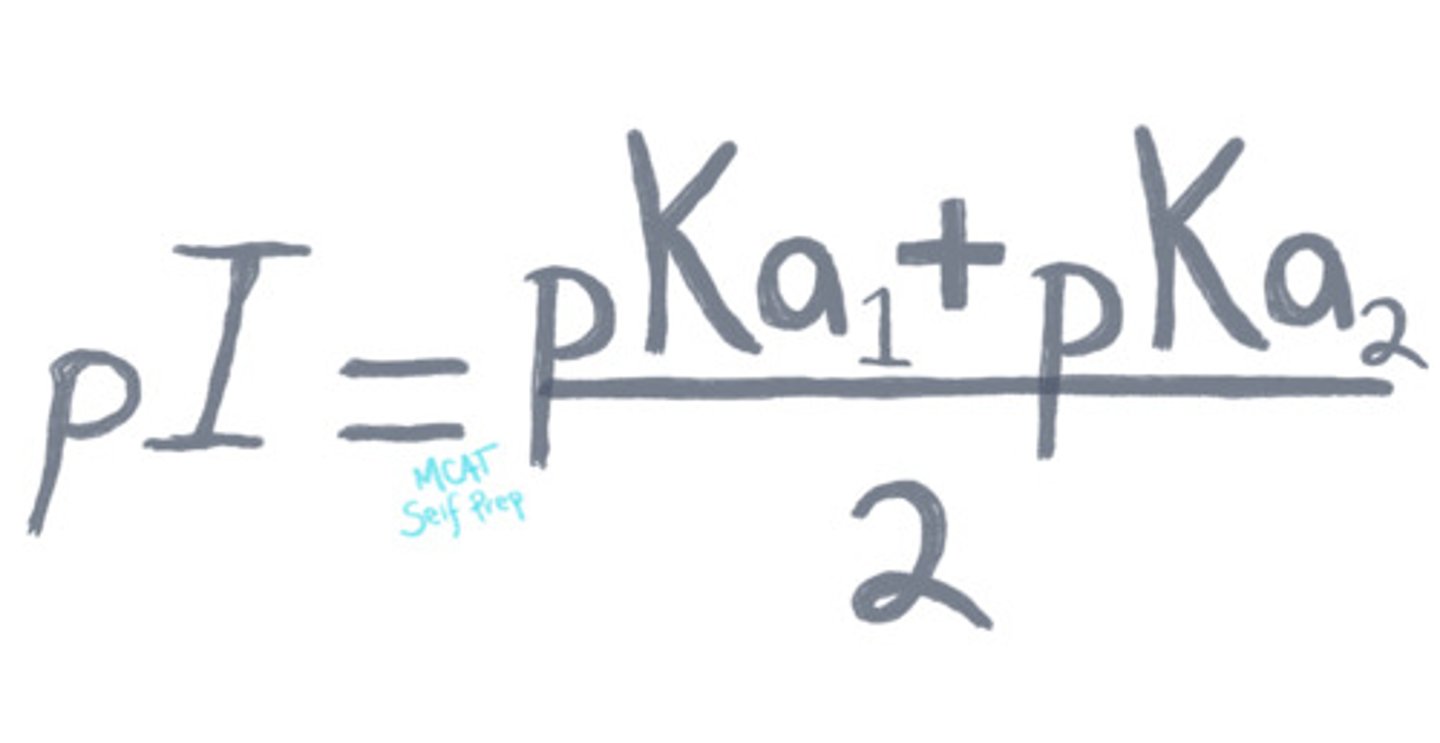
CRB Which of the following is NOT one of the nonpolar amino acids?
(A) Glycine
(B) Proline
(C) Threonine
(D) Valine
(C) Threonine
Threonine has a hydroxyl group in its R-group, making it a polar amino acid.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
What is the isoelectronic point for glutamic acid with α-carboxyl (α-COOH, pK1 = 2.19), α-amino (α-NH3+, pK2 = 9.67), and R-group carboxyl (R-COOH, pKR = 4.25)?
(A) 2.19
(B) 3.22
(C) 6.02
(D) 7.45
(B) 3.22
Because glutamic acid has an acidic R-group, the pI can be calculated by averaging of the carboxylic acid group and R-group side chain. Thus, (( α-COOH, pK1 = 2.19)+(R-COOH, pKR = 4.25))/2= 3.22.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
Amino acids with an alkyl R-group are:
(A) Hydrophillic
(B) Hydrophobic
(C) Aromatic
(D) Acidic
(B) Hydrophobic
Amino acids with an alkyl R-group are hydrophobic.
Which amino acid would you expect to find facing the inside of the lipid bilayer in an integral membrane protein?
(A) D
(B) Y
(C) R
(D) L
(D) L (Leucine)
You would expect to find hydrophobic (nonpolar) amino acids, such as amino acids with alkyl groups and aromatic rings as their side chains facing the lipid bilayer.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
Which of the Aromatic Amino Acids is most polar, and least likely to be seen facing the lipid bilayer?
(A) S
(B) W
(C) F
(D) Y
(D) Y
Tyrosine (Y) and S (Serine) each have a hydroxy (-OH) group in its R group. The oxygen atom has two lone pairs of electrons, which are free to hydrogen bond and contribute to the polarity of the molecule.
However, Serine is not aromatic, whereas Tyrosine is. This make Tyrosine the best answer.
Which amino acid would you expect to find on the surface of a soluble protein?
(A) E
(B) I
(C) P
(D) F
(A) E (Glutamate)
You would expect to find polar, hydrophilic amino acids with side chains containing O, S or N atoms.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
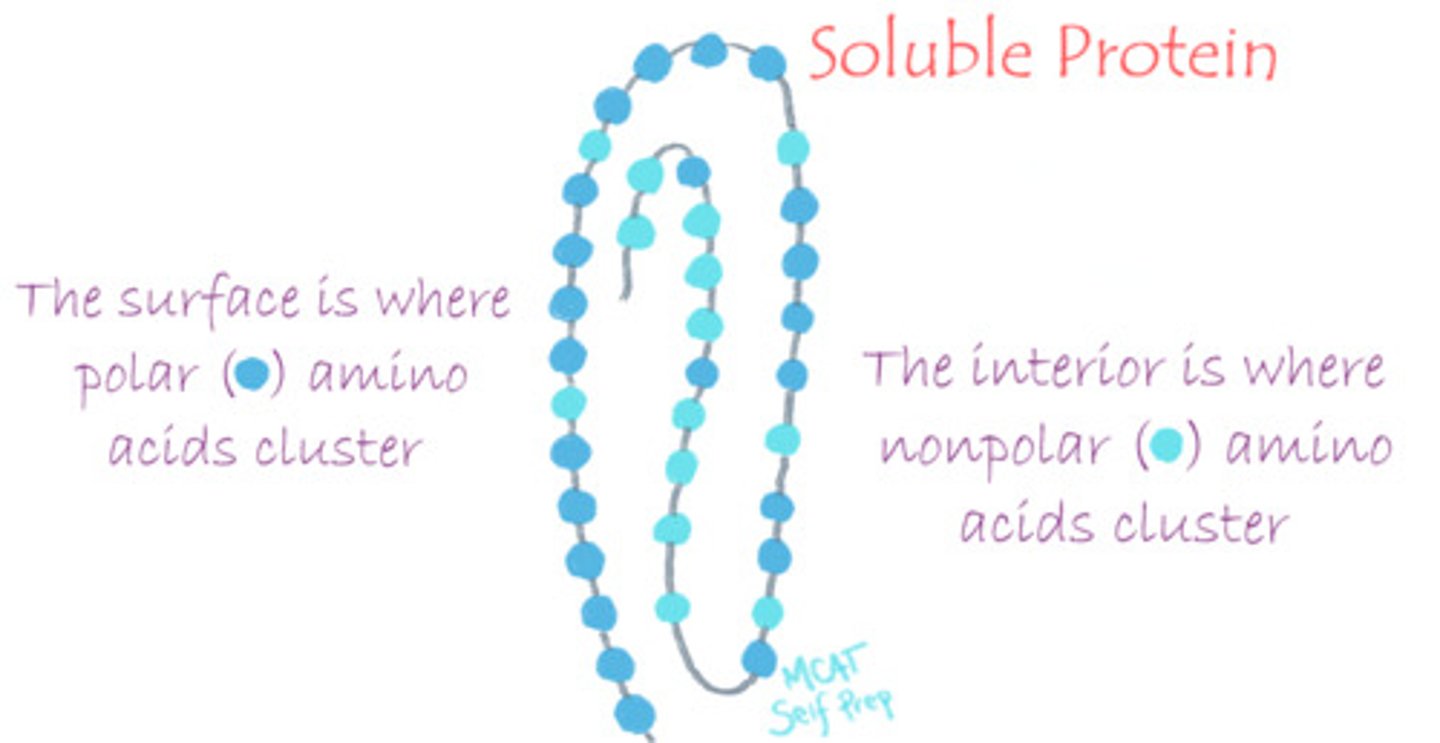
CRB True or false? Because D and E are typically deprotonated at physiological pH, you should expect to see them named as zwitterions.
False. The R groups of D and E are typically deprotonated at physiological pH, but they also contain the ionizable carboxyl (deprotonated at physiological pH) and amino (protonated at physiological pH) groups. Adding up the charges of these three groups, you should expect to see D and E named as anions.
Acidic, polar amino acids have R groups containing which functional group?
(A) Hydroxyl
(B) Carboxyl
(C) Amino
(D) Thiol
(B) Carboxyl
Acidic amino acid R-groups contain carboxylic acids as seen in Aspartic and Glutamic acid.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
What functional groups do the R-groups of neutral, polar amino acids have that the R-groups of neutral, non-polar amino acids do not?
I. Thiol
II. Hydroxy
III. Amide
(A) I Only
(B) III Only
(C) I and II Only
(D) I, II, and III
(D) I, II, and III
Neutral polar amino acids often contain OH (Hydroxy Groups), S atoms (Thiol Groups), or Amide groups (Carboxylic Acid derivative with an Amino group). Neutral, non polar amino acids contain uncharged, alkyl or aromatic side chains.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
CRB Which of the following amino acids' R groups could NOT be Phosphorylated by a Kinase?
(A) S
(B) T
(C) W
(D) Y
(C) W
W (Tryptophan) is the only one of the choices that does not include a hydroxy (-OH) group. A kinase adds on a phosphate group to a molecule by removing a hydrogen and creating a bond between the oxygen of the hydroxy group and the phosphate of the phosphate group (O-P).
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
Which bond stabilizes the primary structure of a protein?
(A) Hydrogen Bonds
(B) Covalent Bonds
(C) Van Der Waals Forces
(D) Dipole-dipole Interactions
(B) Covalent Bonds
The primary structure describes the linear sequence of amino acids stabilized by peptide bonds.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
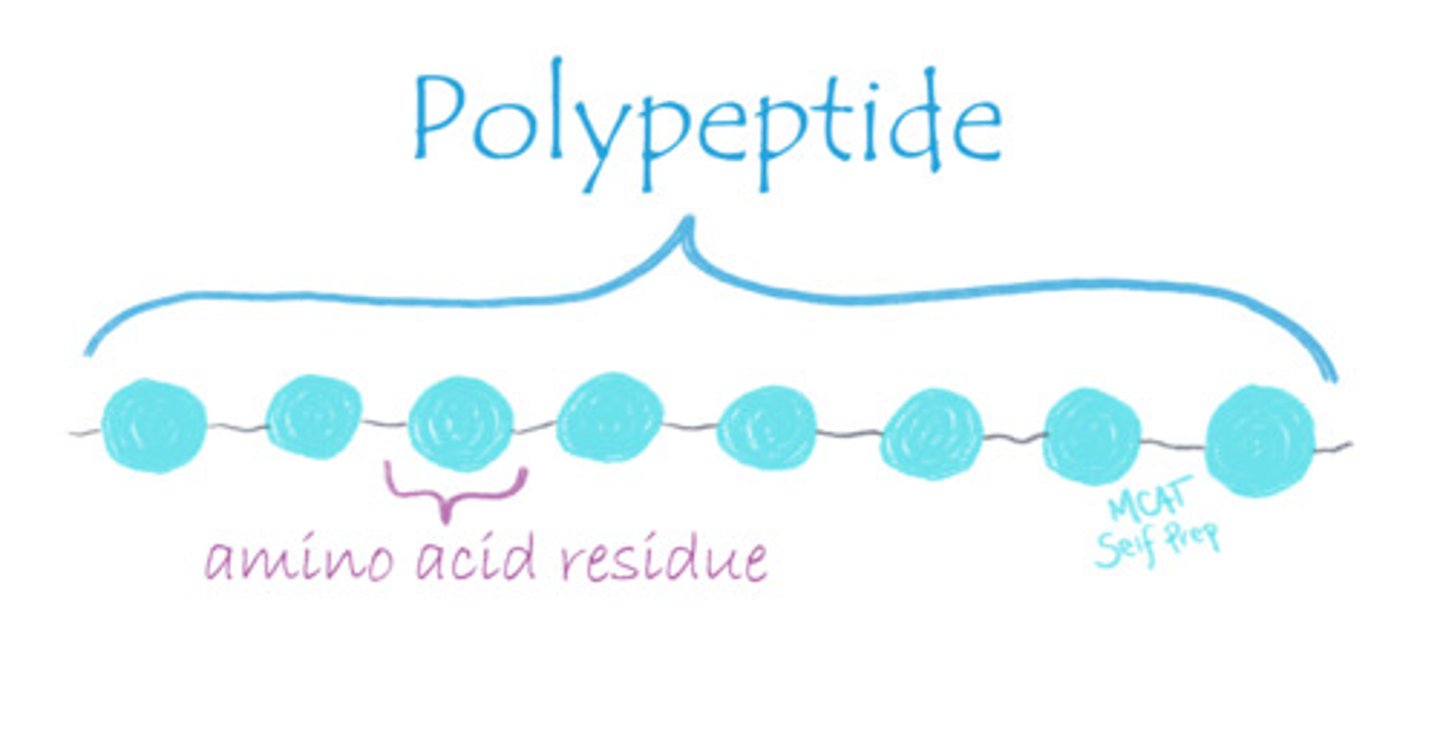
CRB Which of the four levels of structure of proteins could be determined in a lab by sequencing?
(A) Primary
(B) Secondary
(C) Tertiary
(D) Quaternary
(A) Primary
The Primary Structure of peptides could be determined in a lab by sequencing.
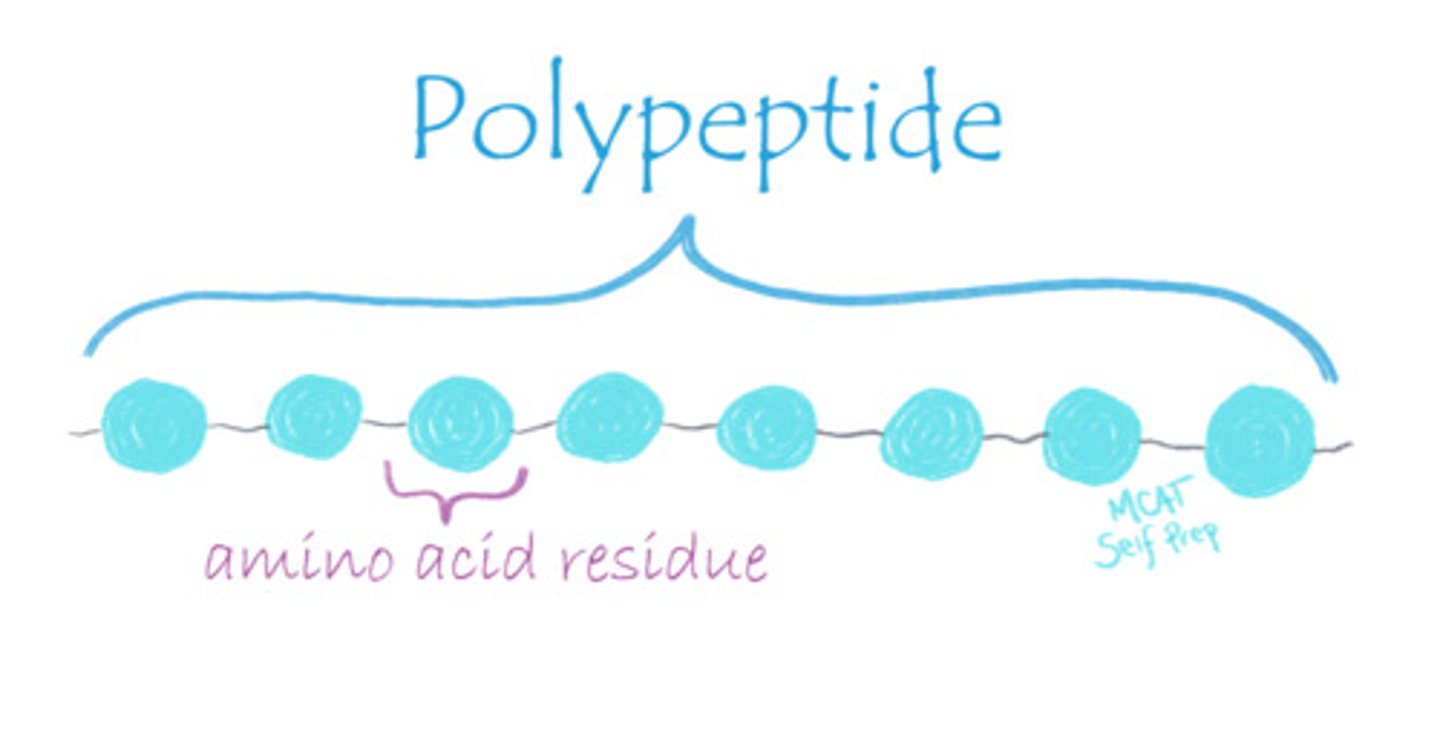
Which bond stabilizes the secondary structure of a protein?
(A) Hydrogen Bonds
(B) Covalent Bonds
(C) Van Der Waals Forces
(D) Dipole-dipole Interactions
(A) Hydrogen Bonds
The secondary structure of a protein is referred to as the way that a linear sequence of amino acids folds upon itself, such as an alpha helix or beta sheet. Secondary structure is stabilized by hydrogen bonds.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
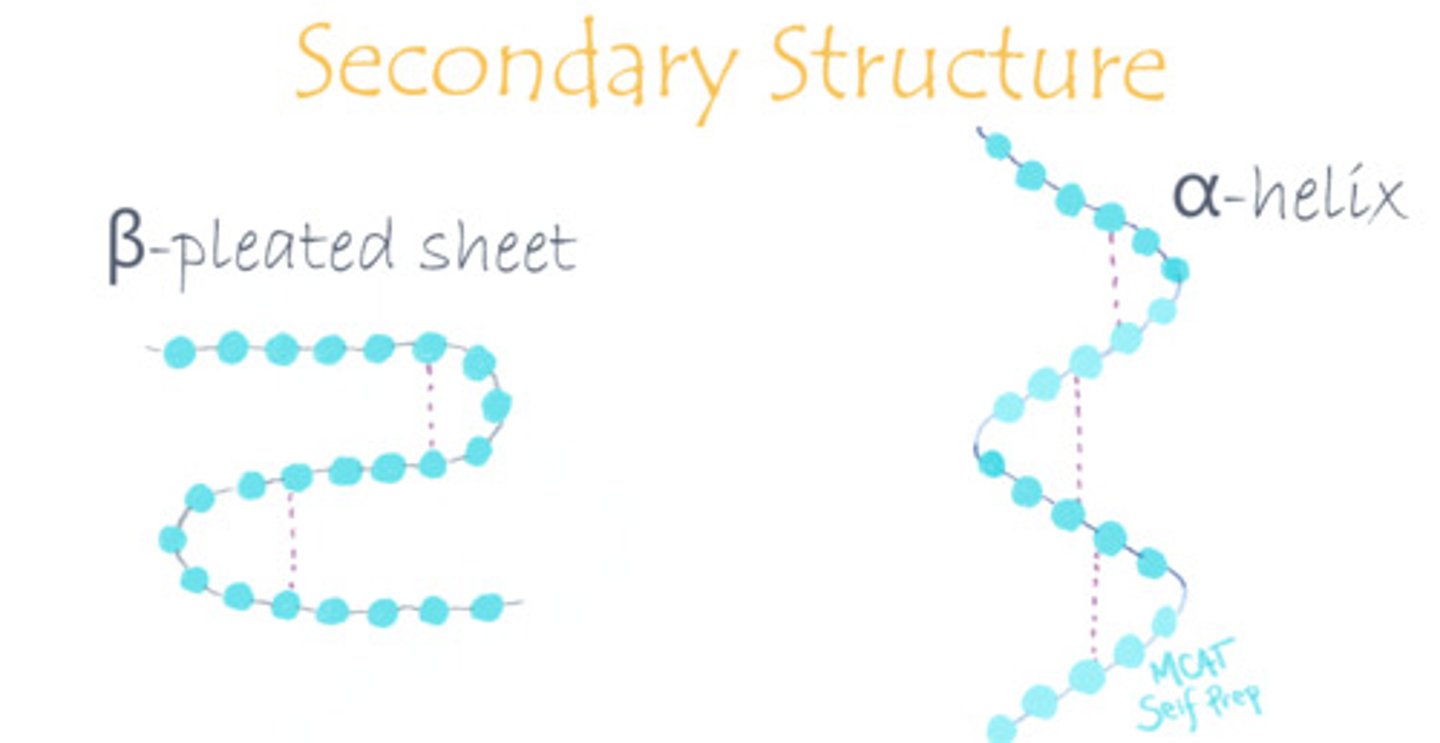
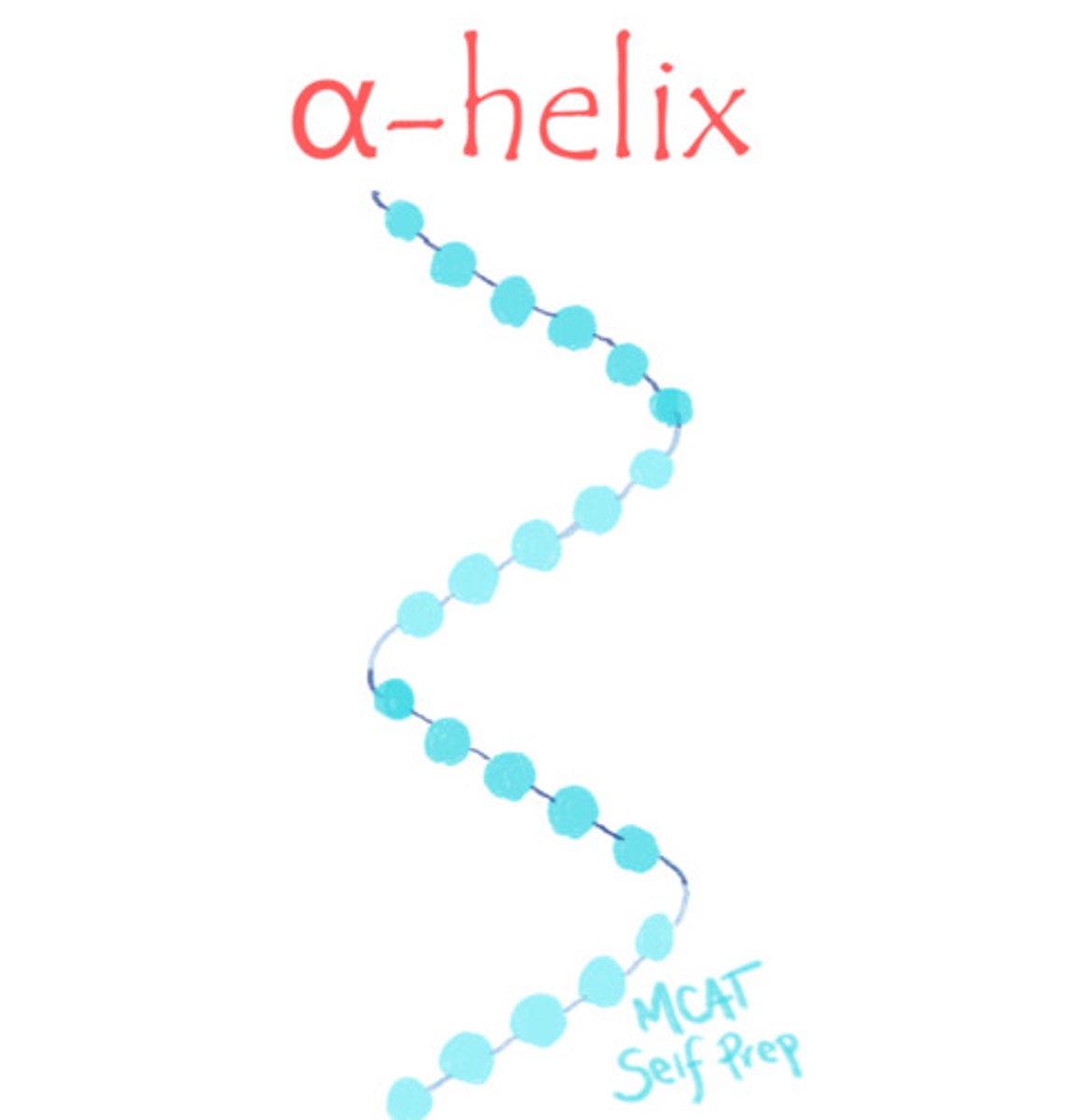
Draw out an alpha-helix and a beta-pleated sheet, focusing on their differences.
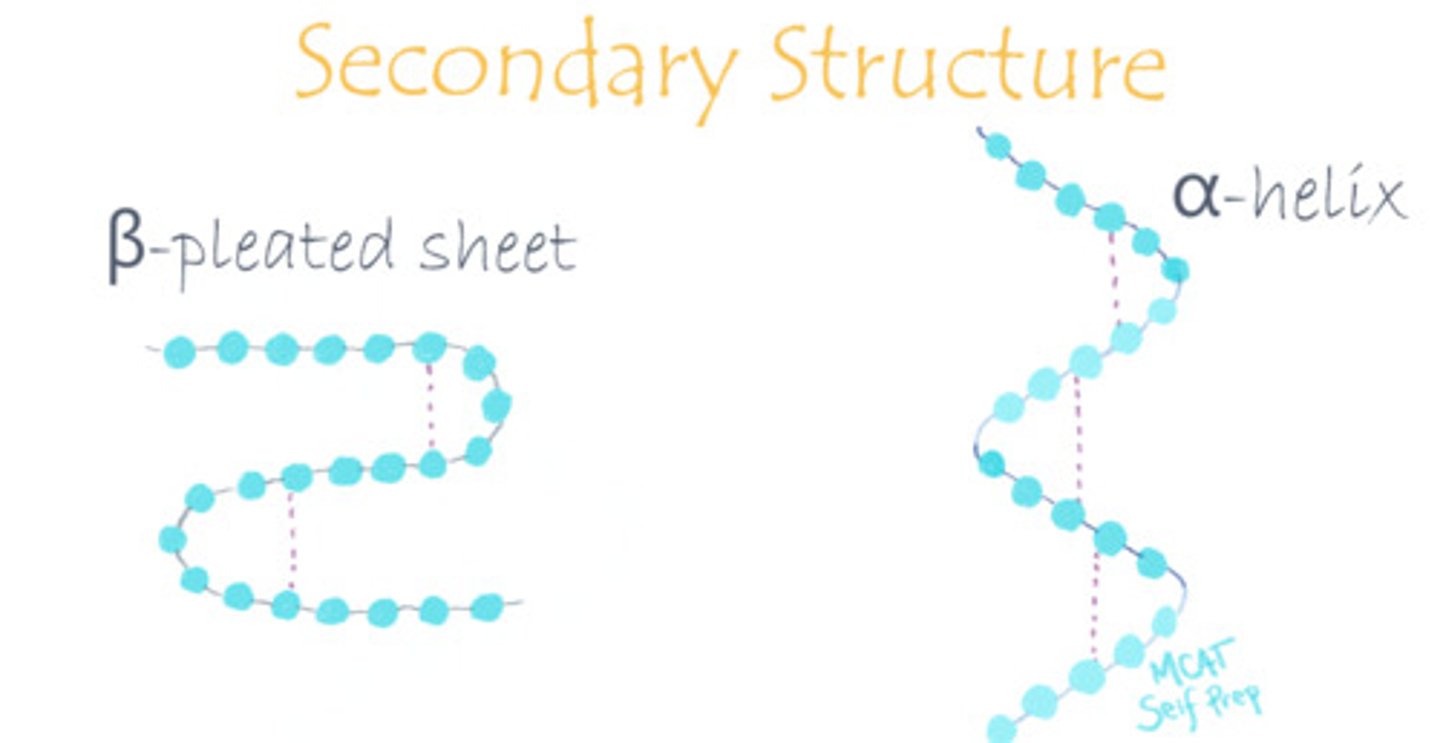
Draw out parallel and antiparallel beta-pleated sheets, focusing on their differences.
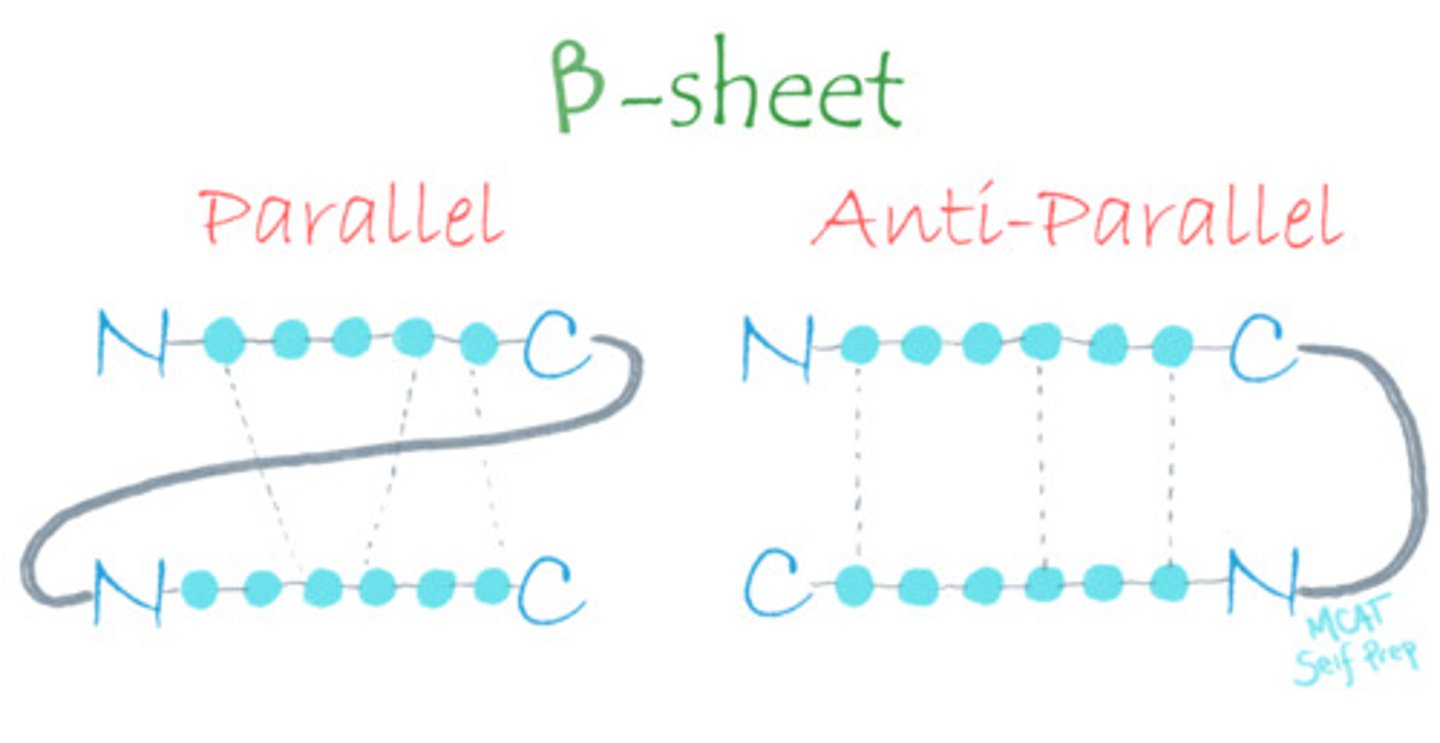
CRB True or false? Keratin is known for being a fibrous protein in human hair, skin and nails, and has lots of beta-pleated sheets.
False. Keratin is known for being a fibrous protein in human hair, skin and nails, and has lots of alpha-helices.
The human and mammalian version of keratin uses alpha-helices, whereas reptiles and birds use a beta-keratin with beta-pleated sheets.
CRB Compare Fibrous and Globular Proteins.
Fibrous proteins resemble long sheets and strands, whereas Globular proteins are more rounded.
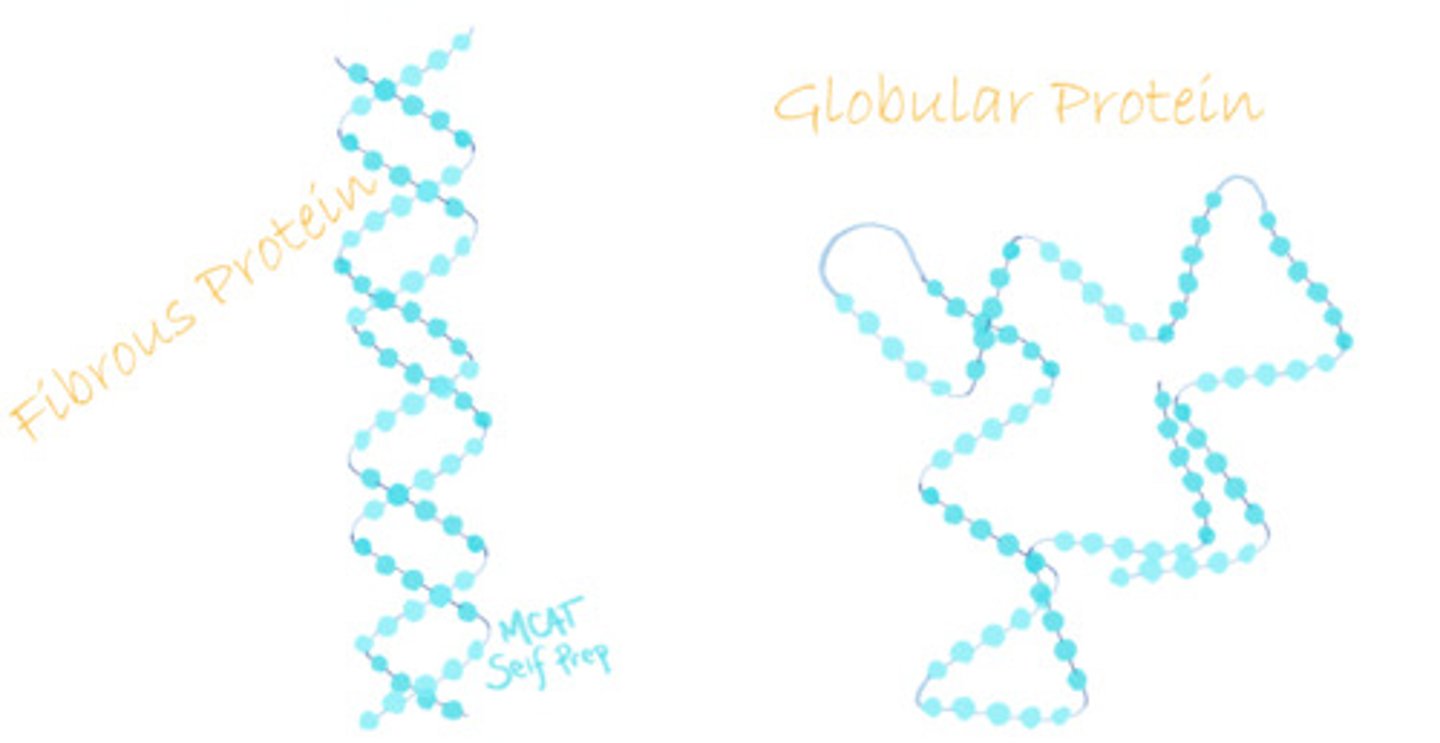
CRB Which of the following best describes the solubility of Fibrous and Globular Proteins in polar solvents (i.e. water)?
(A) Neither Fibrous nor Globular proteins are soluble.
(B) Fibrous proteins are not soluble, but Globular proteins will dissolve.
(C) Fibrous proteins are not soluble, but Globular Proteins are somewhat soluble and will form colloids.
(D) Fibrous proteins are somewhat soluble and may form colloids, and Globular protiens will dissolve.
(C) Fibrous proteins are not soluble, but Globular Proteins are somewhat soluble and will form colloids.
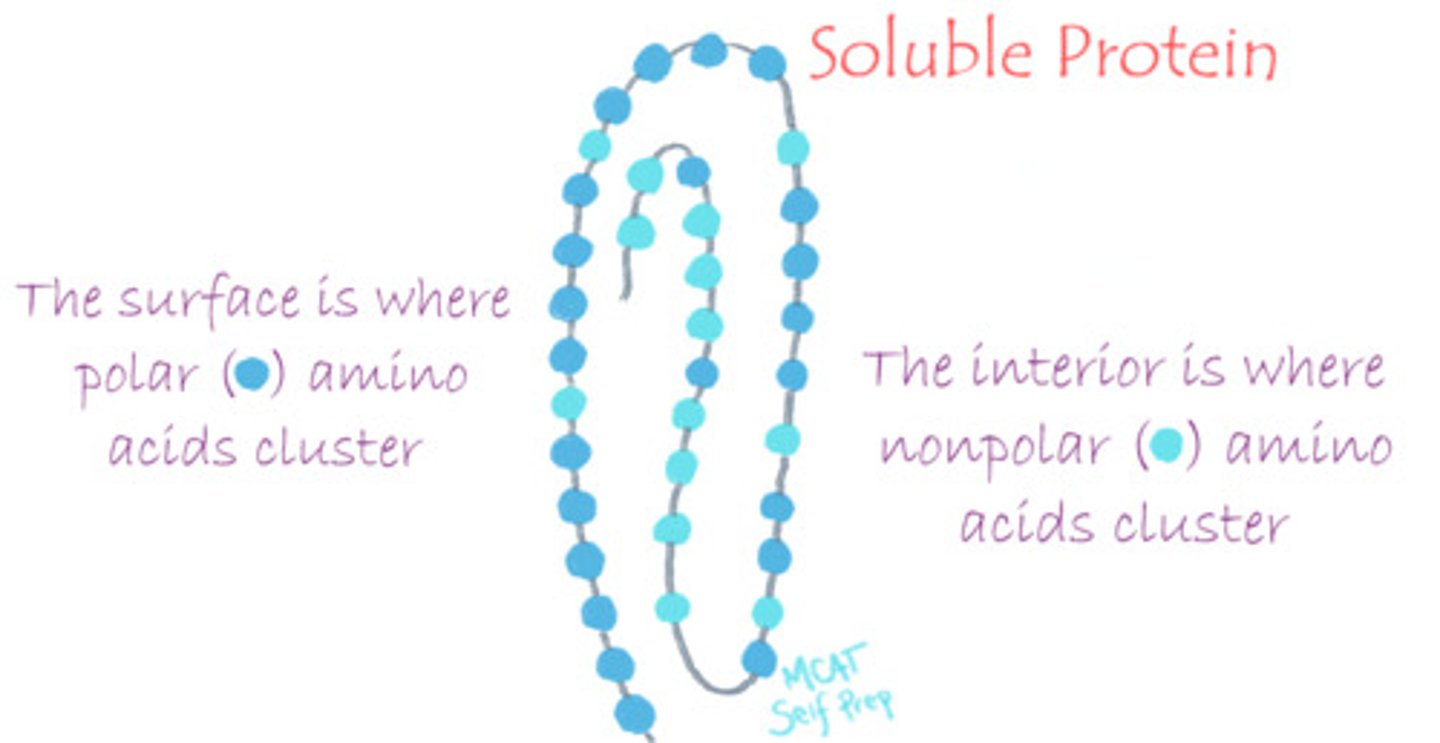
What is the tertiary structure of a protein?
Tertiary structure refers to a higher order of folding within a polypeptide chain or the many different folds within a polypeptide. It depends on distant group interactions.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
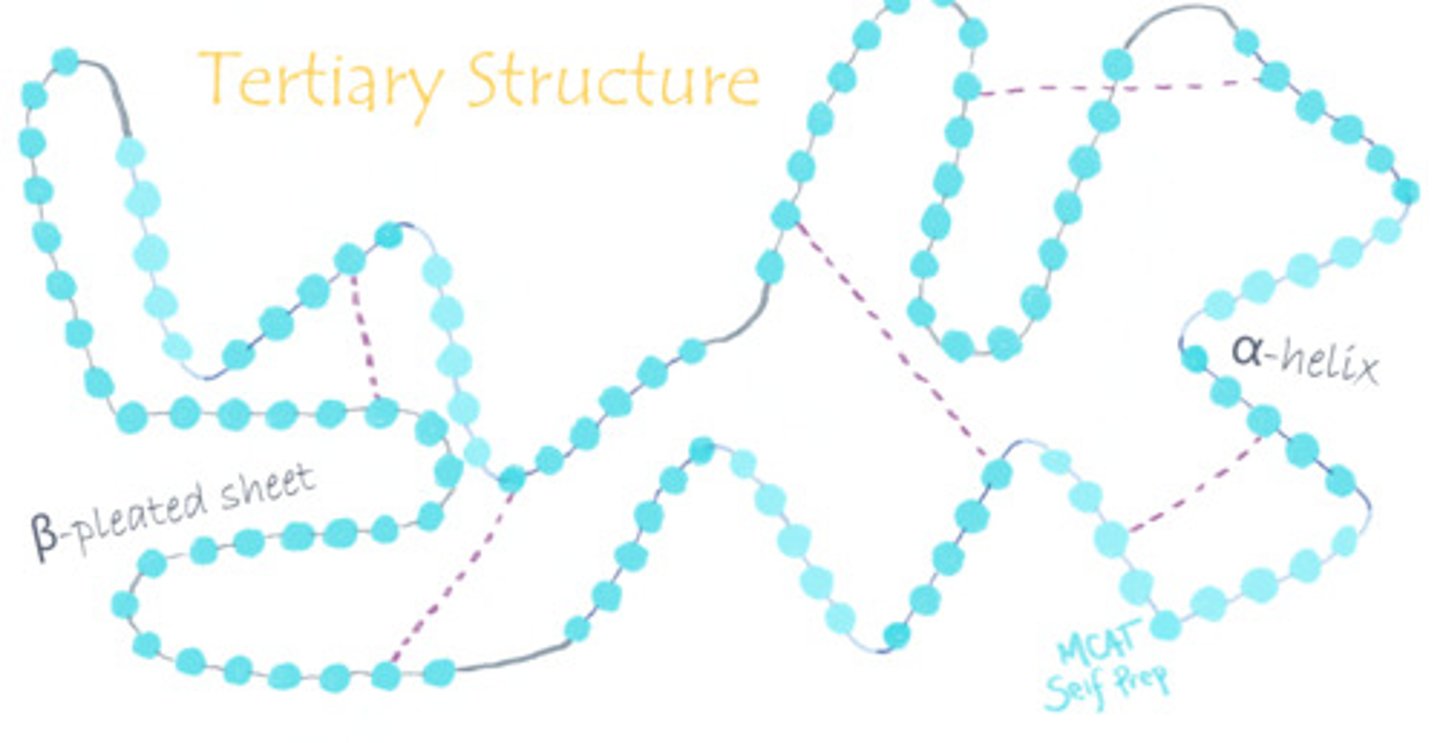
Envision a polypeptide. What part of the polypeptide is considered the backbone?
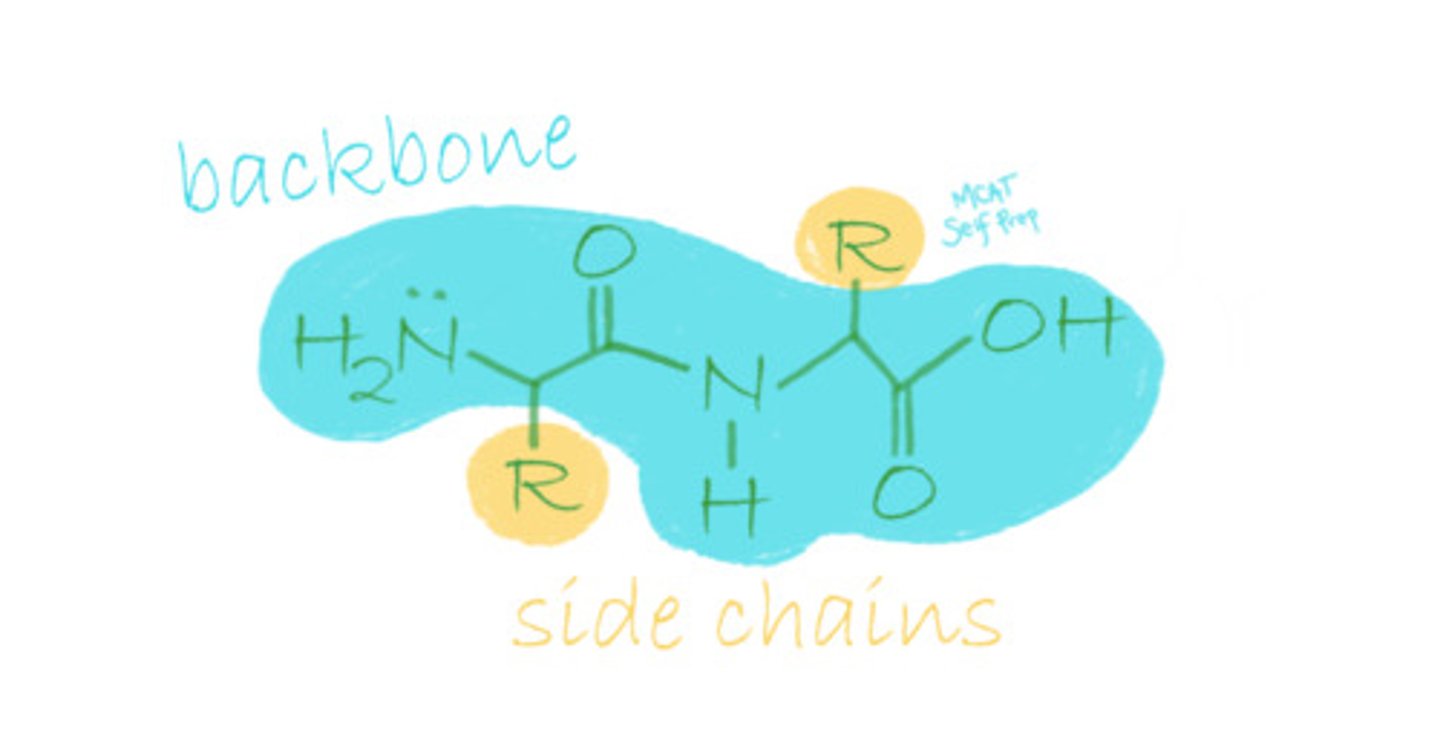
True or False? Secondary structure is determined by interactions between the polypeptide's backbone, while tertiary structure is determined by interactions between polypeptide R-groups.
True. Secondary structure is determined by interactions between the polypeptide's backbone, while tertiary structure is determined by interactions between polypeptide R-groups.
Which side of a cell membrane would one find disulfide bonds?
(A) Extracellular
(B) Intracellular
(C) Within the cell membrane
(D) In the nucleus
(A) Extracellular
Disulfide bonds are found in the extracellular space which is an oxidative environment.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
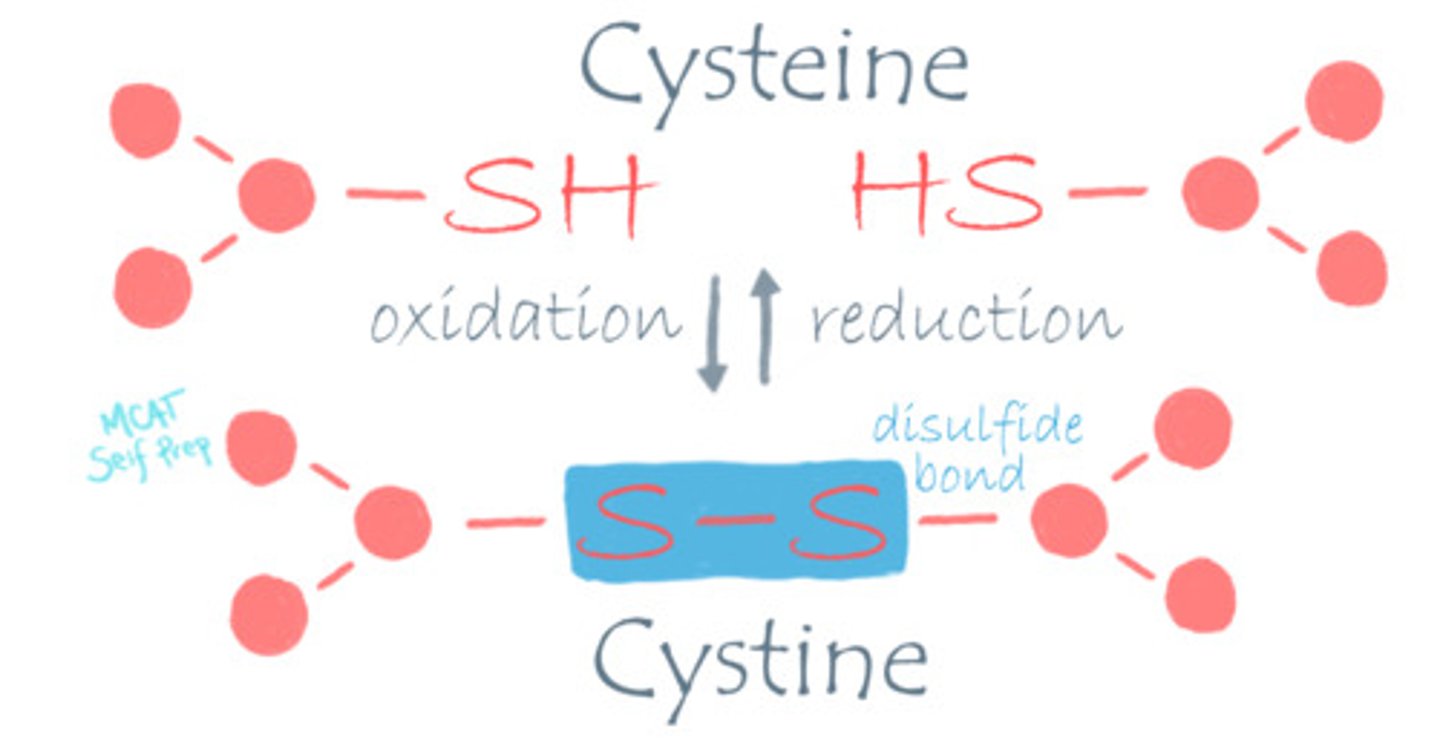
What makes the intracellular space a reducing environment?
Cells contain many antioxidants to protect from oxidative damage to important structures, creating a reducing environment inside the cell. The extracellular space does not have these same antioxidants.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
The tertiary structure of a protein and quaternary structure of a protein are similar in that they are stabilized by the same interactions, which include which of the following?
I. Hydrogen Bonding
II. Disulfide Bonds
III. Peptide Bonds
(A) I Only
(B) III Only
(C) I and II Only
(D) I, II, and III
(C) I and II Only
The tertiary and quaternary structure of a protein are both stabilized by the same type of interactions, which are:
- Hydrogen bonding
- Van der Waals forces
- Disulfide bonding
- Hydrophobic interactions
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
What is the quaternary structure of a protein?
The quaternary structure of the protein refers to the bonding/interaction of multiple polypeptides. Each polypeptide is called a subunit. For instance, 2 subunits = dimer, 3 subunits = trimer, 4 subunits = tetramer, >4 subunits = multimer.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
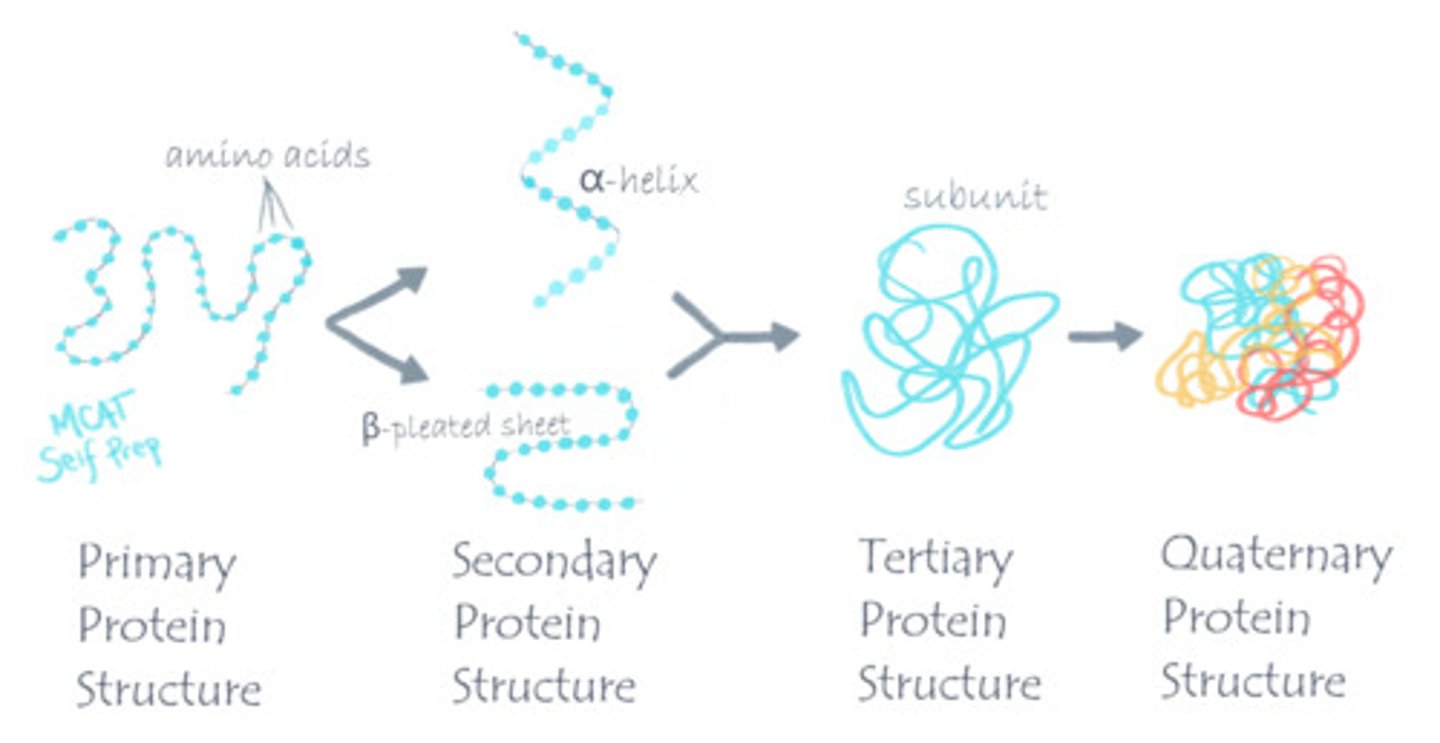
Summarize the difference between primary, secondary, tertiary, and quarternary structure.
Primary structure is the sequence of amino acids.
Secondary structure is the folding of a polypeptide into alpha helices and beta-pleated sheets due to backbone interactions.
Tertiary Structure is the further folding of a polypeptide due to R-group interactions.
Quarternary Structure consists of the interactions between multiple polypeptides.
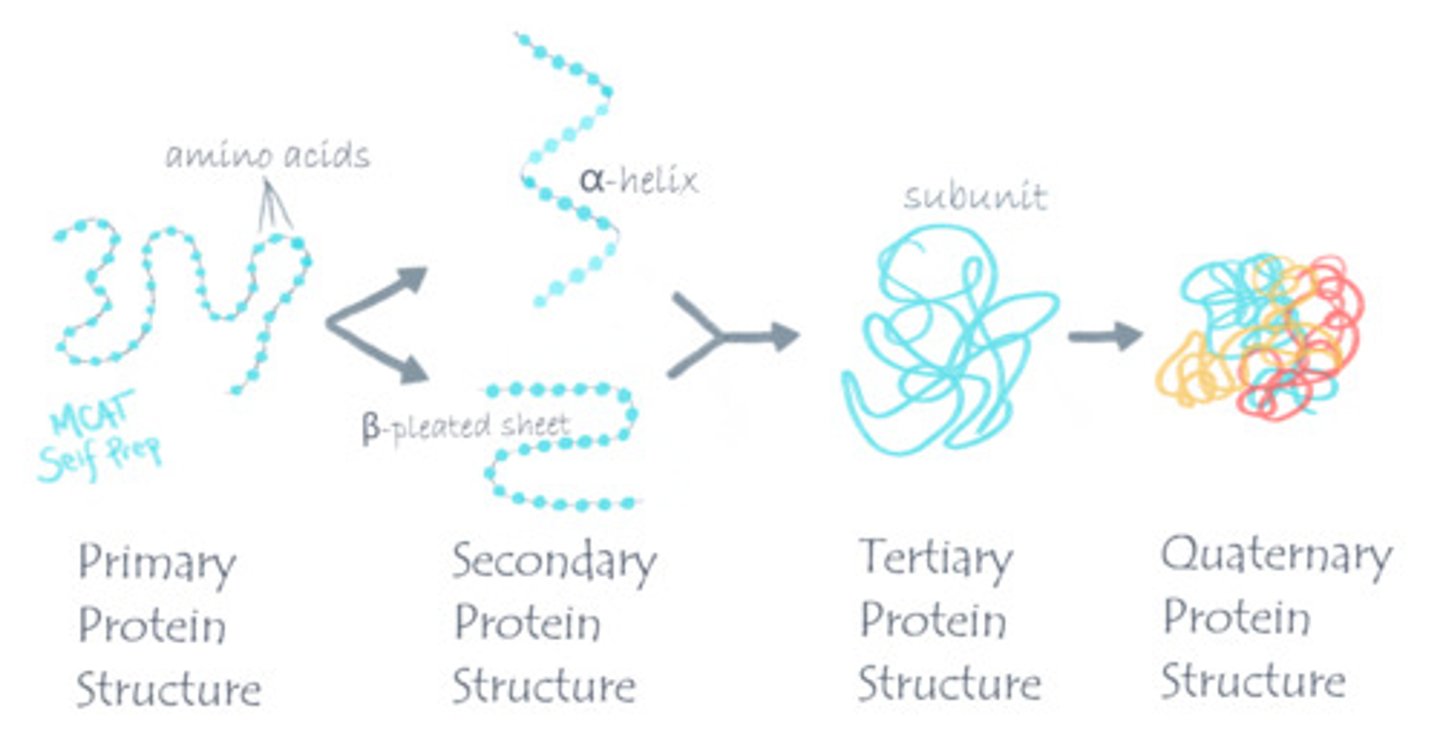
What is the difference between a conformational protein vs. a denatured protein?
A conformational protein is properly folded and active.
A denatured protein means the protein is an unfolded and inactive protein.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
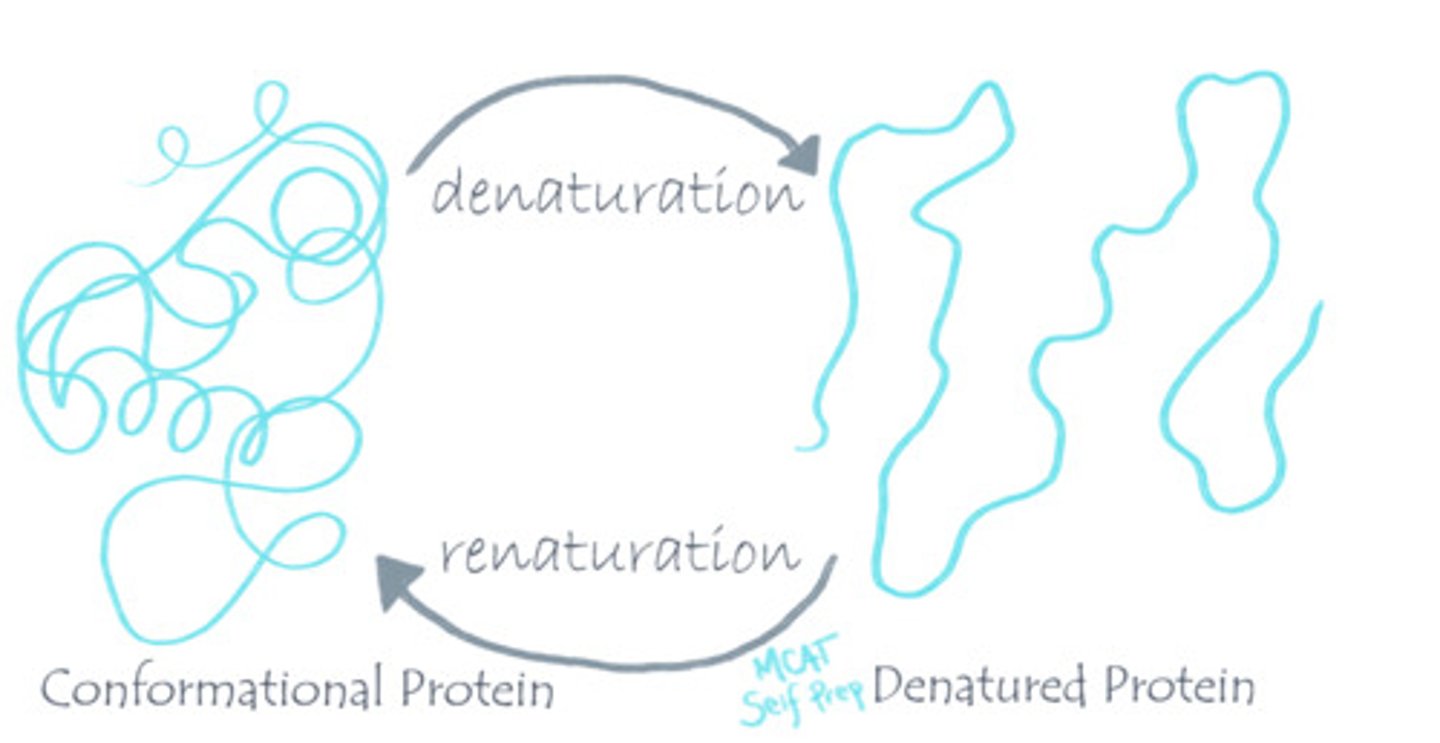
CRB Which of the following levels of protein structure must be disrupted during Denaturation?
(A) Primary
(B) Secondary
(C) Tertiary
(D) Quaternary
(C) Tertiary
The Tertiary Structure of proteins must be disrupted in Denaturation.
Secondary or Quaternary Structure may be disrupted as well.
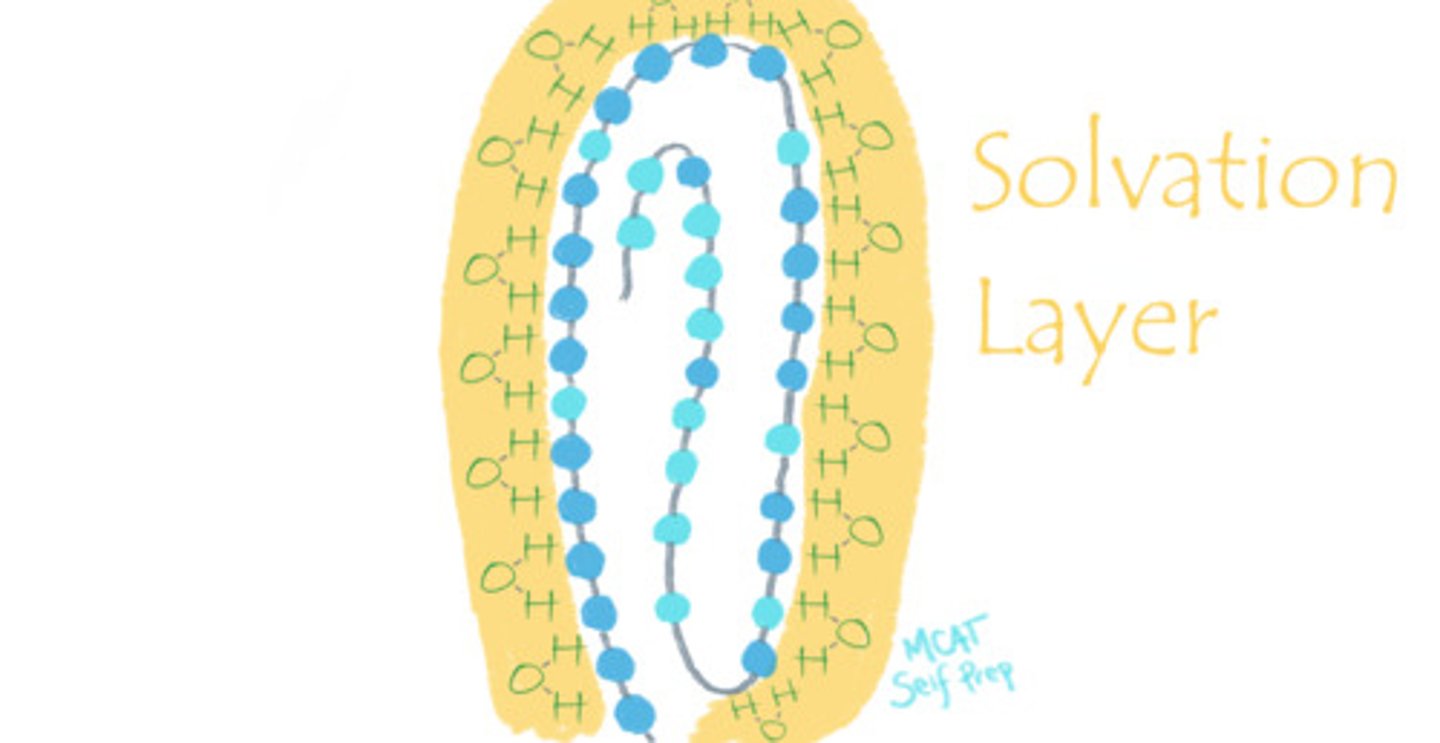
What is the "solvation shell"? What is its role?
The solvation shell is the layer of solvent that surrounds a protein. An example of a solvation shell is when the partially-negative oxygen atoms of water molecules surround the positively charged amino acid residues on the exterior surface of a protein, thus stabilizing the conformation of this protein.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
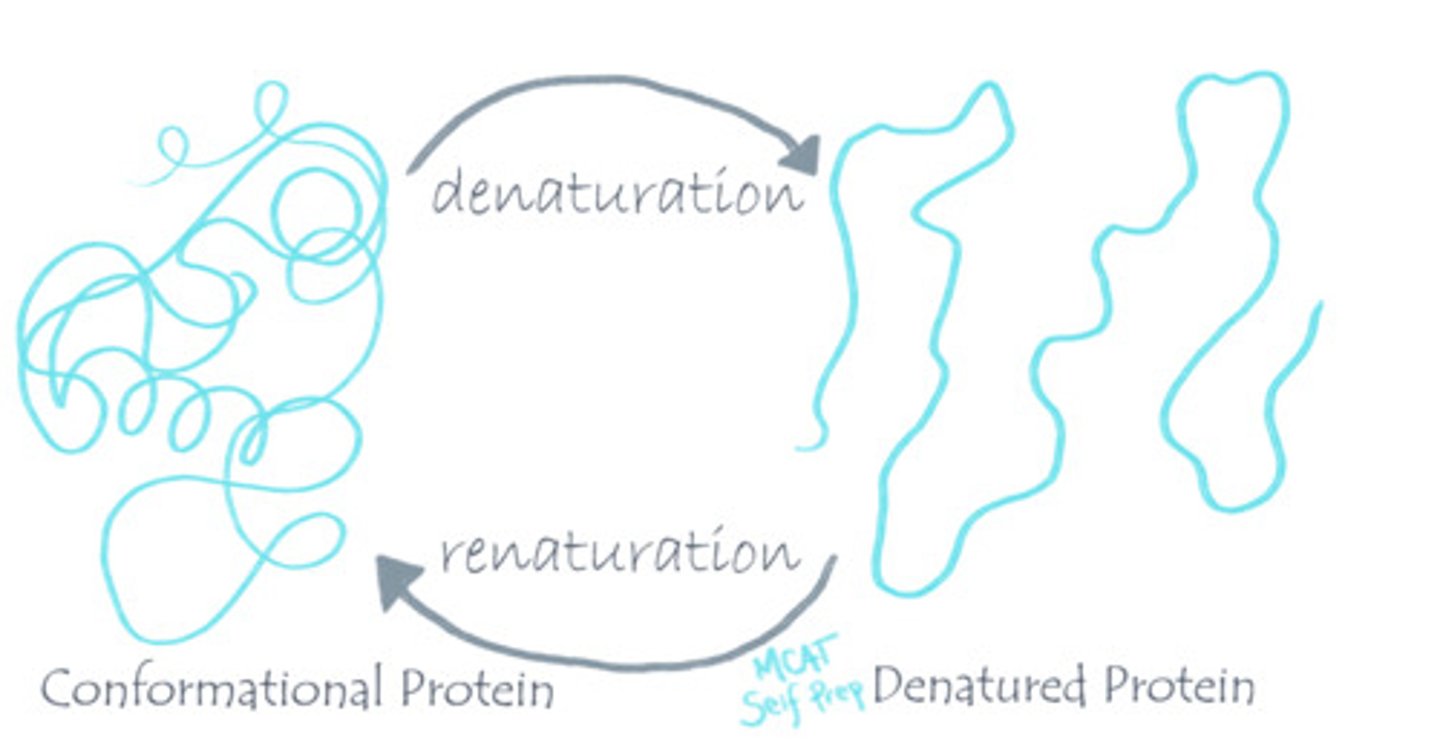
If you denature a protein by adding heat, all different levels of protein structure will be disrupted except for which level? Why?
(A) Primary Structure
(B) Secondary Structure
(C) Tertiary Structure
(D) Quarternary Structure
(A) Primary Structure
Primary structure because peptide bonds are not broken simply due to the addition of heat.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
What method is best if you want to break only the ionic bonds in protein? Which level(s) of protein structure will be affected?
I. Secondary Structure
II. Tertiary Structure
III. Quarternary Structure
(A) I Only
(B) III Only
(C) II and III Only
(D) I, II, and III
(C) II and III Only
Changing the pH surrounding the protein will disrupt all ionic bonds in a protein, which mainly denature tertiary and quaternary structures of a protein.
Keep in mind that the Hydrogen Bonds are formed between the Carboxy Group and the Amino Group, forming the secondary structure of a polypeptide. When these are part of a peptide chain, it would take a very large change in pH to deprotonate or protonate them.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
How would a chemical denaturant affect proteins? Which levels of protein structure would be affected?
I. Secondary Structure
II. Tertiary Structure
III. Quarternary Structure
(A) I Only
(B) III Only
(C) II and III Only
(D) I, II, and III
(D) I, II, and III
Chemical denaturants often disrupt the hydrogen bonding within a protein, thus affecting all levels of protein structure except for the primary structure.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
What is typically thought of as the only method to denature the primary structure of a protein?
Using an enzyme is primarily thought of as the method to denature the primary structure of a protein and release individual amino acids.
You could also do this with EXTREME heat and pH.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
What happens to the conformational stability of an egg as it is being digested in your stomach?
The conformational stability of the proteins in the egg decreases. Your digestive enzymes break peptide bonds in order to absorb amino acids into blood stream. We then can use the individual amino acids for protein synthesis.
Struggling with the one-letter abbreviations, three-letter abbreviations, structures, and the essential properties of Amino Acids? Learn how to conquer any Amino Acid MCAT question using Andrew's Amino Acid Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-amino-acid-mastery-course/
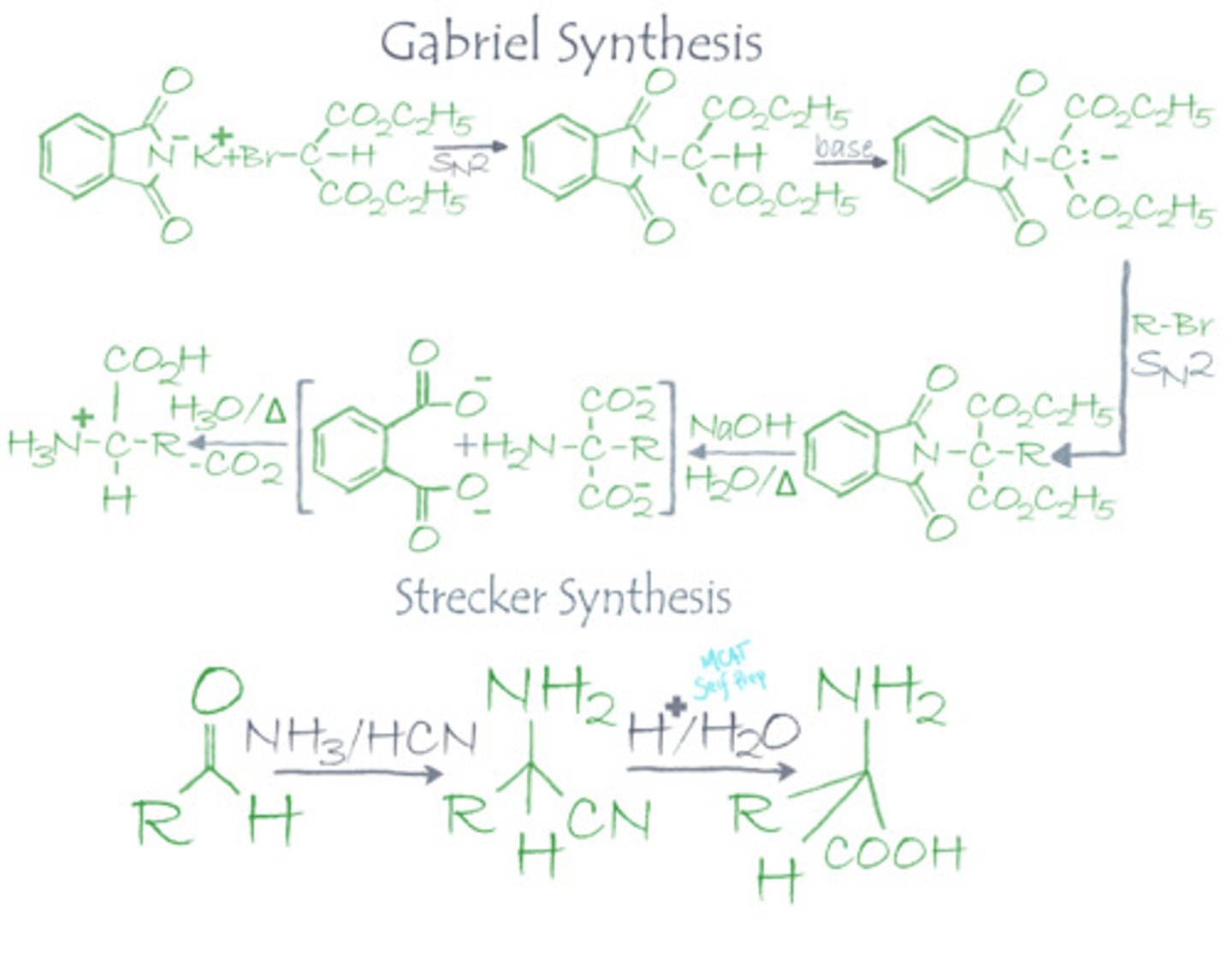
Compare and contrast the two following alpha amino acid synthesis reactions: Gabriel Synthesis and Strecker Synthesis
Draw out these procedures for extra credit.
The gabriel synthesis starts with N-pthalamidomalonic ester "Thad", which protects both the amine group and carboxylic acid. The alpha-carbon will be alkylated, hydrolyzed, and then heated for a decarboxylation.
The strecker synthesis is much more simple and efficient. It starts with ammonia, KCN, and an aldehyde/ketone. The aldehyde/ketone and ammonia will react to form an imine, which in acid with KCN will form a nitrile, and hydrolysis in acid will yield the alpha-amino-acid.
CRB Which of the following general statements about Amino Acids are true?
I. Bacteria can use D-amino acids in proteins, but humans typically do not.
II. Not all amino acids in the human body are in the genetic code and/or are incorporated into proteins.
III. All of the amino acids that are in the genetic code have their carboxyl and amine groups bound to the same carbon.
(A) III only
(B) I and II only
(C) I and III only
(D) I, II and III
(D) I, II and III
Each of the following statements are true:
I. Bacteria can use D-amino acids in proteins, but humans typically do not.
II. Not all amino acids in the human body are in the genetic code and/or are incorporated into proteins.
III. All of the amino acids that are in the genetic code have their carboxyl and amine groups bound to the same carbon (the alpha carbon).
CRB Which of the following terms best describes the amino acids that are coded for in the human genetic code?
(A) Coded Amino Acids
(B) Natural Amino Acids
(C) Proteinogenic Amino Acids
(D) Nucleogenic Amino Acids
(C) Proteinogenic Amino Acids
Proteinogenic Amino Acids are the ones coded for in the human genetic code, and are incorporated into proteins.
CRB True or false? Conjugated Proteins have Prosthetic Groups, which can vary from organic molecules to metals, covalently attached to them.
True. Conjugated Proteins have Prosthetic Groups, which can vary from organic molecules to metals, covalently attached to them.