parasitology- Nematodes (unit 15+16)
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
round
nematodes are commonly called _____worms
Adenophorea (aphasmidea)
Secementea (phasmidea)
what are the 2 main nematode subclasses?
yes
do nematodes have a complete digestive tract?
dioecious
(and have sexual dimorphism)
are nematodes hermaphrodites or dioecious?
yes
(sexual dimorphism)
can you tell female and male nematodes apart?
covers external surface, including mouth, anus, vagina, and excretory pore; has papillae and alae
describe the cuticle of a nematode
contractile myofibrils
what type of musculature do nematodes have?
they have 1 dorsal and 2 lateral lips,
Ancylostomids have ventral lips that are modified into teeth/plates
describe the lips of a nematode
chitinous organs of male nematodes, inserted into female genital opening
what are spicules?
small, chitinous structure of male nematodes, acting as a guide for the spicules
what is gubernaculum?
structures of male nematodes used to embrace and hold the female during copulation
what is the copulatory bursa and bursal rays?
alae
what are these 2 structures called?

inflations of the cuticle around the mouth and near the esophagus
what are cervical/cephalic papillae?
leaf crown
what is the name for the rows of papillae surrounding the rim of the buccal capsule?
a buccal capsule
at the mouth of some nematodes
what is this?
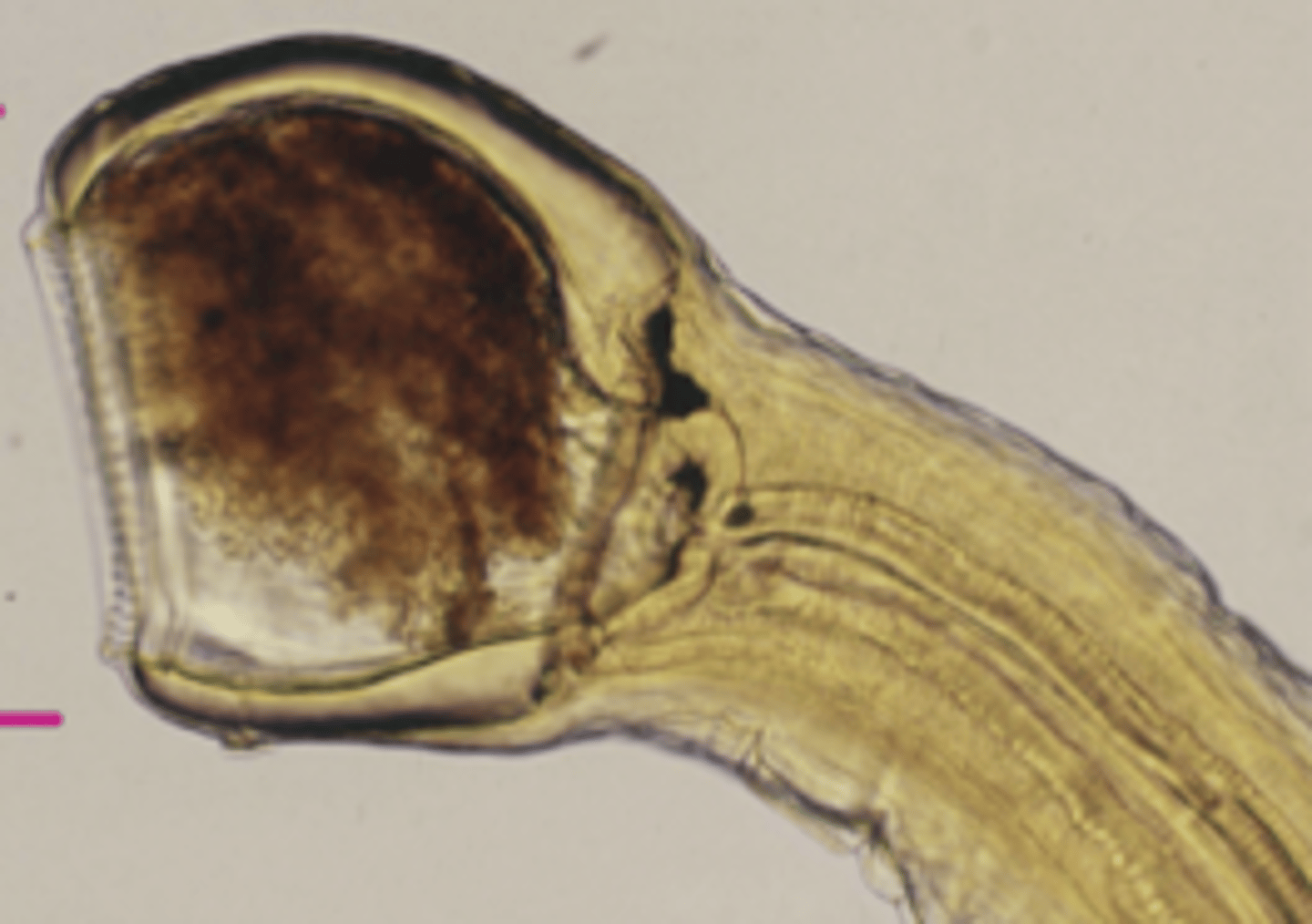
rhabditiform
what type of esophagus is this?
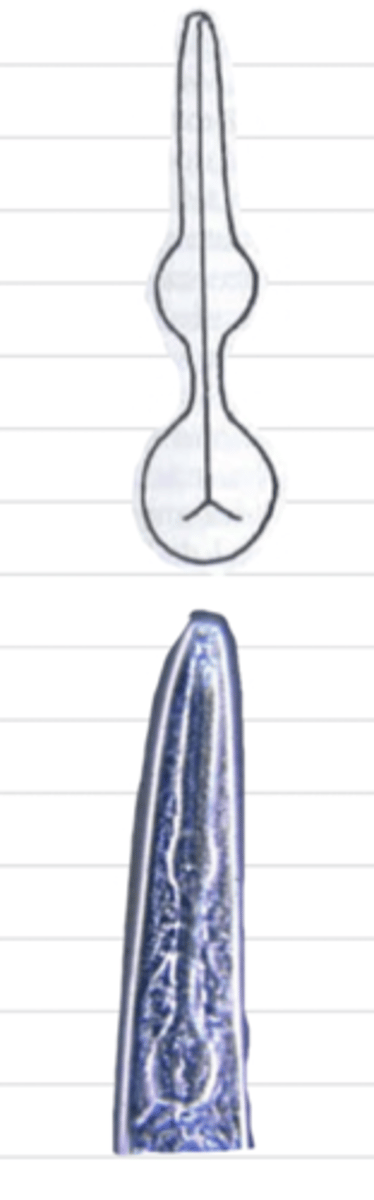
strongyliform
what type of esophagus is this?
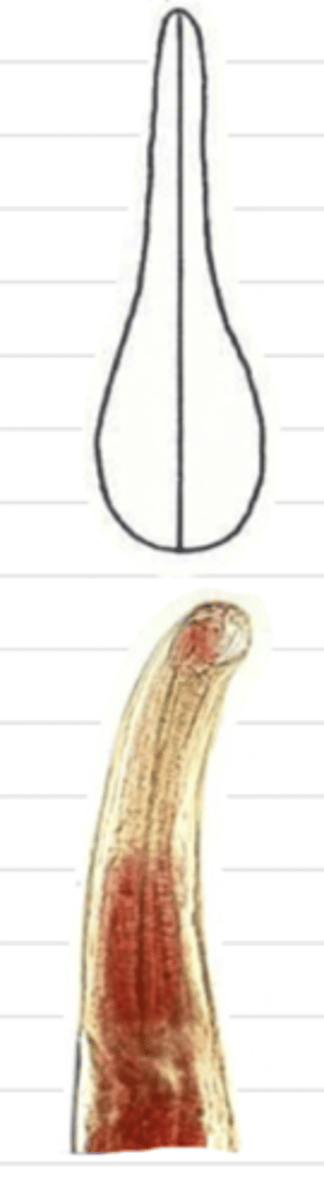
filariform
what type of esophagus is this?
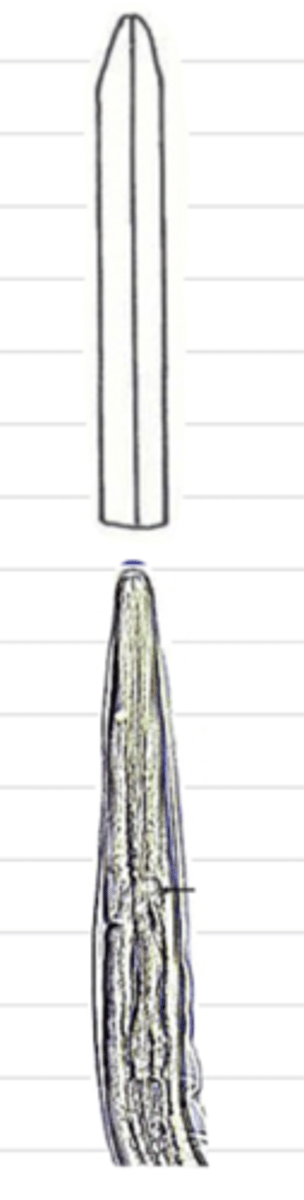
oxyuriform
what type of esophagus is this?
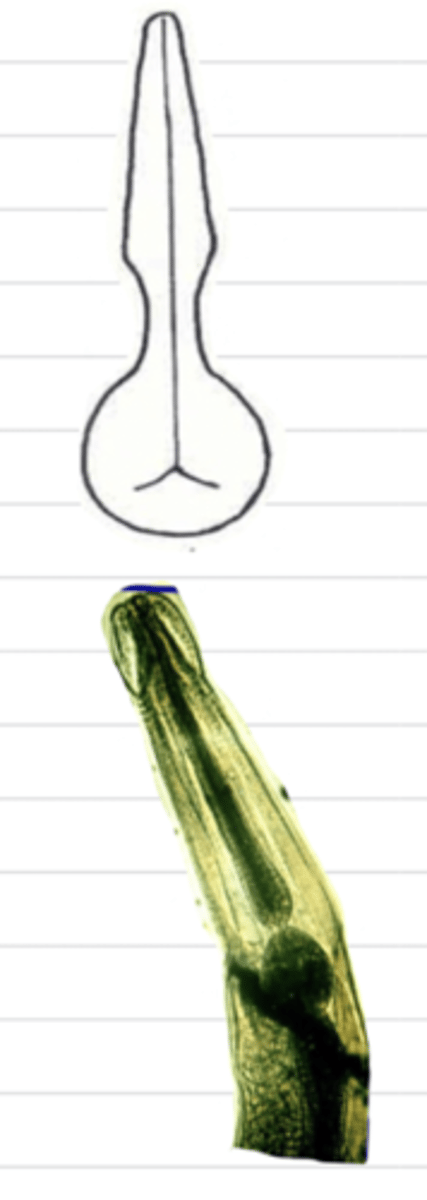

stichosome/moniliform
what type of esophagus is this?

cloaca
in males, the genital tract opens up into a _____
primitive, with canals ("lateral cords"), and an excretory pore, located ventrally, near the esophagus
describe the excretory system of nematodes
2 ganglions, connected by fibers in the esophageal ring, giving rise to 6 nervous cords
describe the nervous system of nematodes
phasmids
amphyds
cervical+caudal papillae
genital papillae
what sensitive organs do nematodes have?
sensory organs for chemorrepulsion, located caudally next to the anus
what are phasmids?
amphyds
what sensory organs are next to the mouth and are for chemoreception?
tacticle sensory organs
what is the purpose of cervical and caudal papillae?
tactile and chemorreceptor organs
nect to the cloaca
what are genital papillae?
1 testes
vas deferens
terminal vesicle
muscular ejaculatory duct
cloaca
1-2 spicules
gubernaculum
copulatory bursa
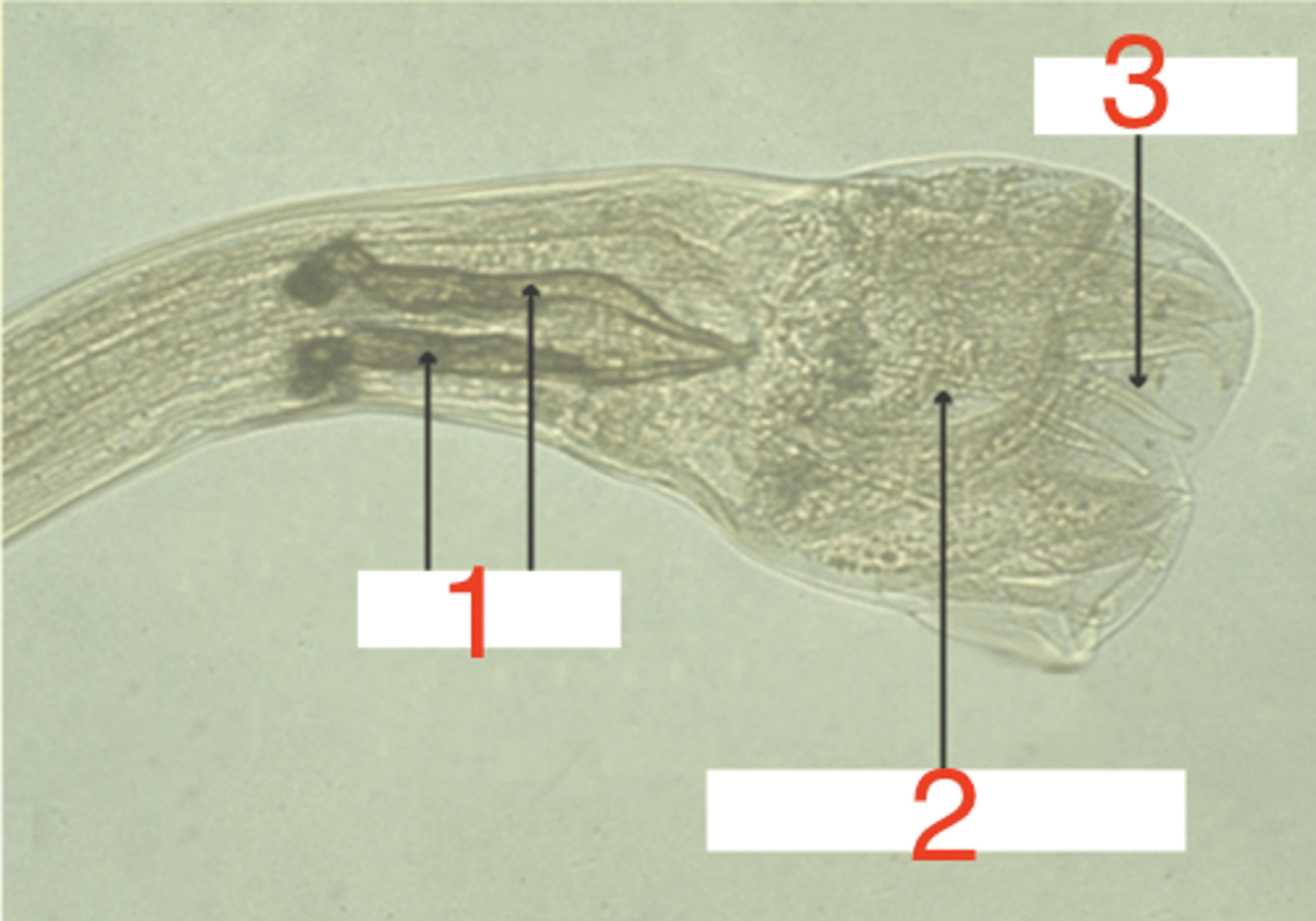
what structures are included in the reproductive system of a male nematode?
male- it has spicules, a copulatory bursa, and bursal rays
is this a male or female nematode? why?
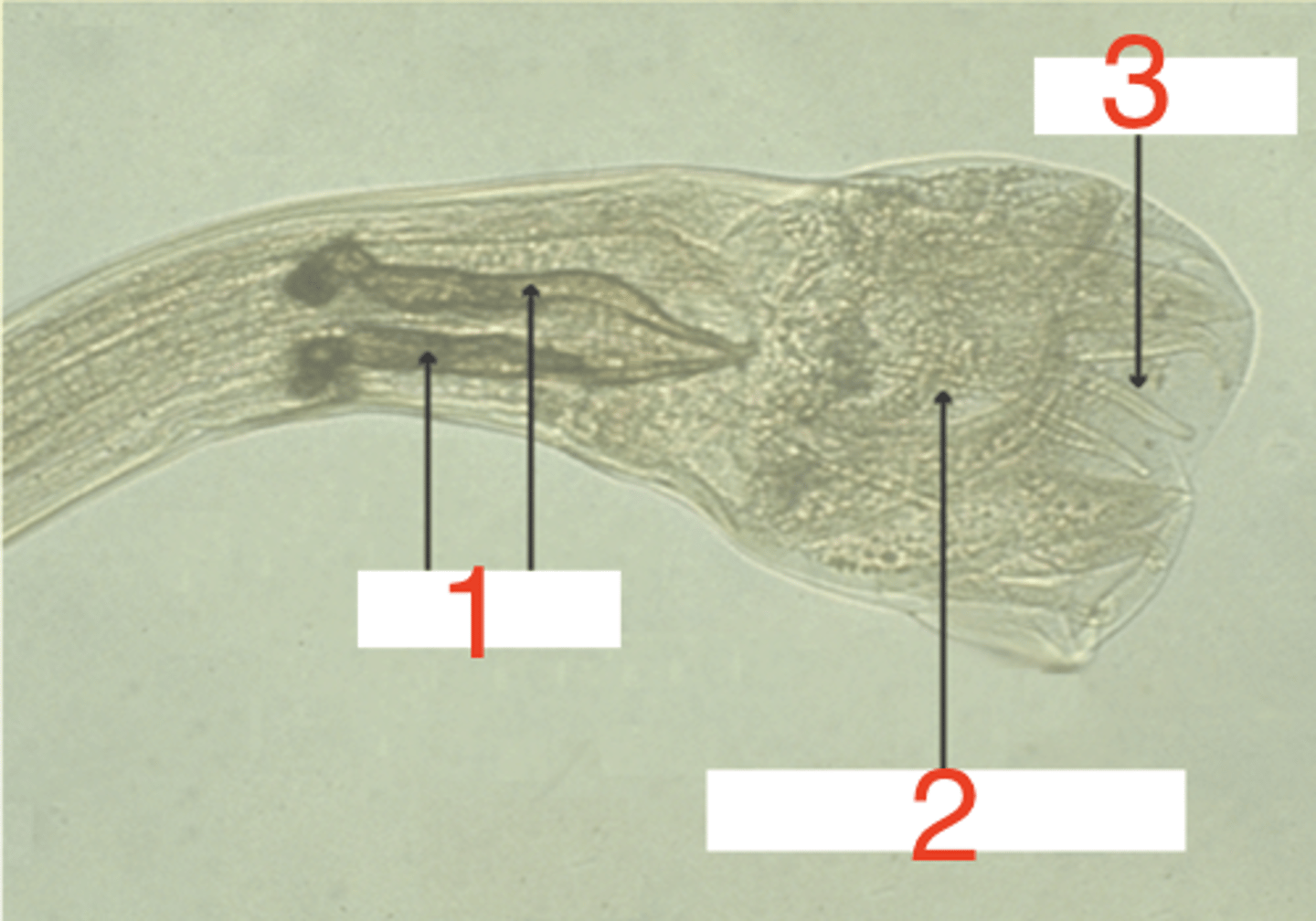
spicules
what is 1?

copulatory bursa
what is 2?
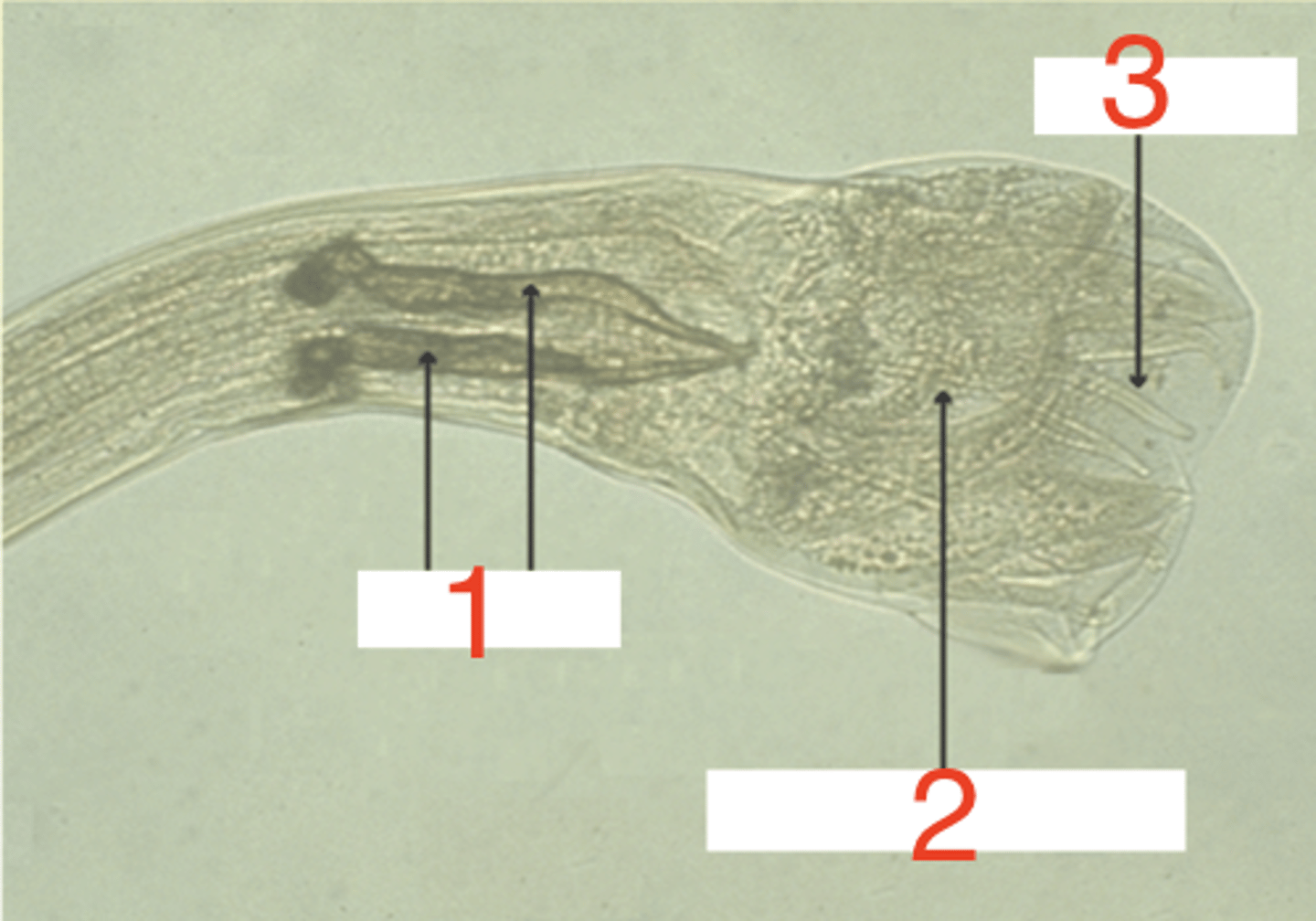
bursal ray
what is 3?
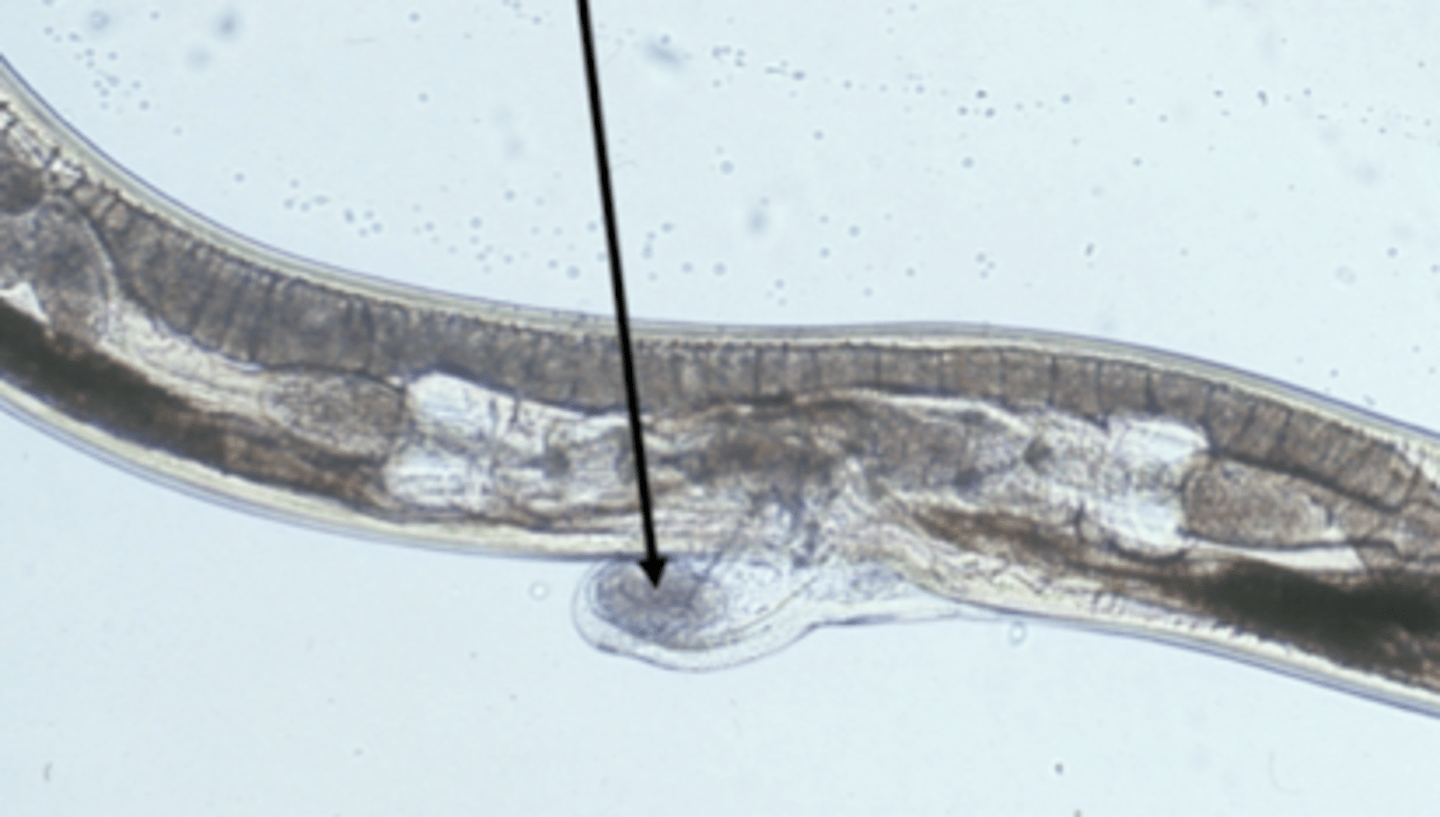
the vulvar flap
what is the arrow pointing to?
2 ovaries (except Aphasmidea)
oviduct
uterus (1 or 2)
ventral and medial genital pore
vulvar flap
seminal receptacle
describe the reproductive tract of a female nematode
reproductive organ of female nematodes, it is a uterine expansion where fertilization occurs
what is a seminal receptacle?
DH
nematodes always mate in the _____
both
do nematode eggs hatch in the host or the environment?
they can lay:
unembryonated eggs (oviparous)
embryonated eggs (ovoviviparous)
live larva (viviparous)
do nematodes lay embryonated or unembryonated eggs?
larval development involves 4 moults/ecdysis
what is Maupa's theory?
1. free L3 ingested by DH
2. free L3 crosses through DH's skin
3. Ingestion of eggs with L2/L3
4. Ingestion of IH with L3 inside
5. Ingestion of paratenic host with L3 inside
6. Active inoculation of L3 by vectors
what are the different options for L3 to infect a host?
Enoplida
Dioctophymatida
what 2 orders are included in subclass Adenophorea?
stichosome
what type of esophagus does order Enoplida have?
L1
what stage of order Enoplida is infective?
NO
does order Enoplida have phasmids?
Trichinellidae, Trichuridae, Capillarridae
which is the main families belonging to Enoplida?
small
male has 2 claspers at the end
viviparous
L1 has a stylet to penetrate blood vessels
describe the morphology of nematodes belonging to the family Trichinellidae
penetration of blood vessels
L1 of family Trichinellidae has a stylet- what is this for?
direct
autoheteroxenous- same host as IH and DH
L1 is ingested, then it penetrates enterocytes, where it goes through 4 moults and becomes adult. Then, they copulate, the male dies, and the female lays L1 (viviparous), which travels via lymph and blood vessels to striated muscle, where it creates cysts, encapsulated by a thick collagen capsule. The muscular fibers that the L1 is encysted in become "nurse cells" (big nucleus, more mitochondria and ER, no myofilaments, anaerobic metabolism).
what type of life cycle does family Trichinellidae have?
host cells that support and nourish the larva phase of the nematode. it has a large nucleus, many mitochondria and ER, no myofilaments, and does anaerobic metabolism.
what is a nurse cell?
no, they are bad hosts and the nematode's cycle cannot continue inside of them
are humans good hosts for the family Trichinellidae?
they get clinical signs in 1-2 days after infection, including a cutaneous rush during the migration of the nematode and periocular edema. nurse cells are formed in 2-8 weeks
what happens to humans if they are infected by a nematode of family Trichinellidae?
family Trichinellidae (Trichinella)
this describes the life cycle of which nematodes?
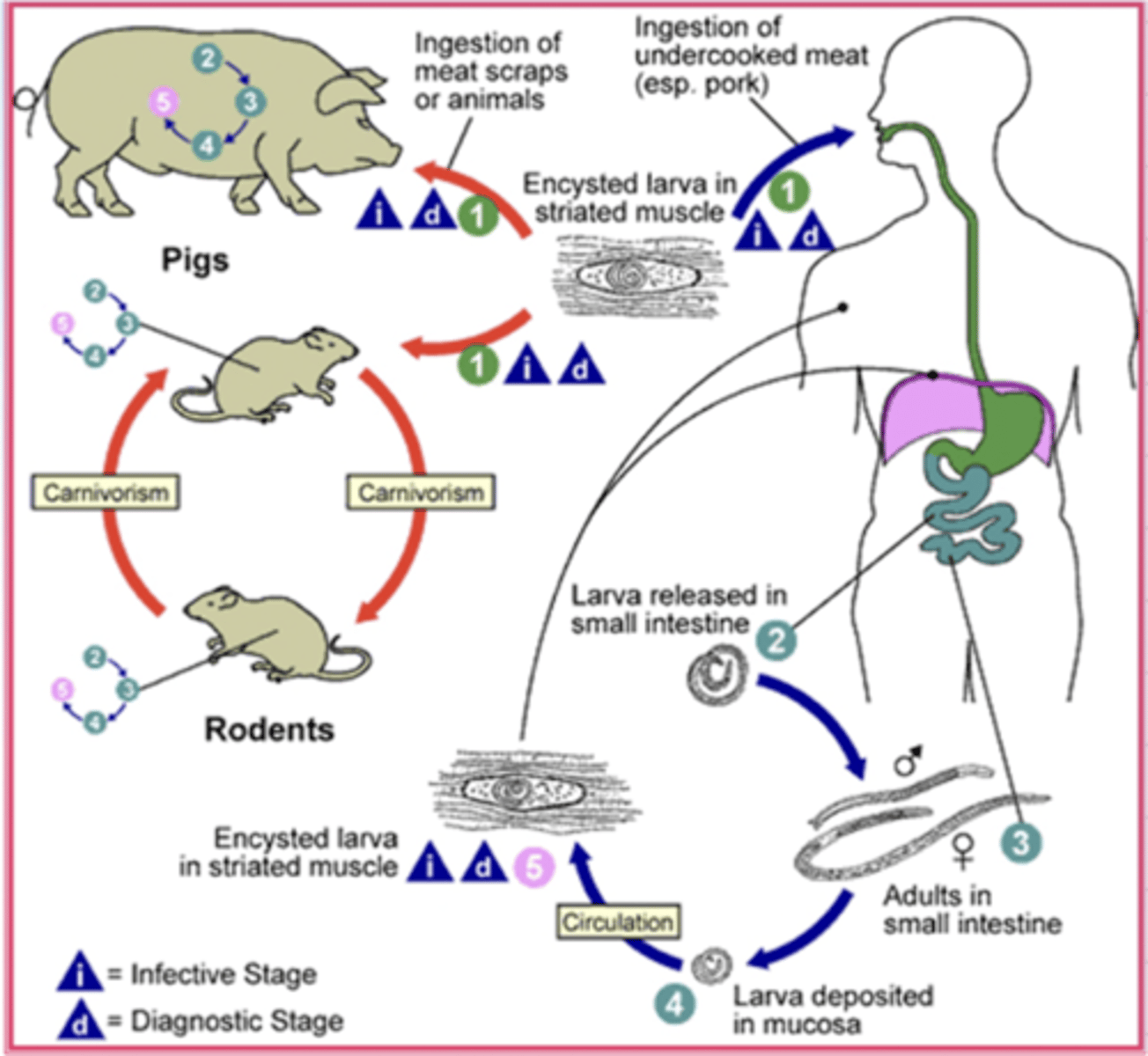
ingestion of parasitized animals
herbivores are sometimes infected if larva is eliminated in feces or if carcasses with the parasite contaminate the environment. this is rare
how do animals/humans get infected by family Trichinellidae?
feeding animals with swine remains from the slaughterhouse or hunting
the main source of infection by family Trichinellidae is....
whip worms
genus Trichuris are commonly known as...
Trichinella
what important genus included in family Trichinellidae?
family Trichuridae
genus Trichuris
what genus and family?

long and narrow anterior end, short and thick posterior end
males with a curled tail, 1 spicule, and a spicular sheath
females with a straight posterior end
describe the morphology of genus Trichuris. how can we differentiate between males and females?
lemon shaped
brown/yellow
2 polar plugs
resistant to environmental conditions
unembryonated
describe Trichuris eggs
Trichuris
this egg belongs to the genus _____
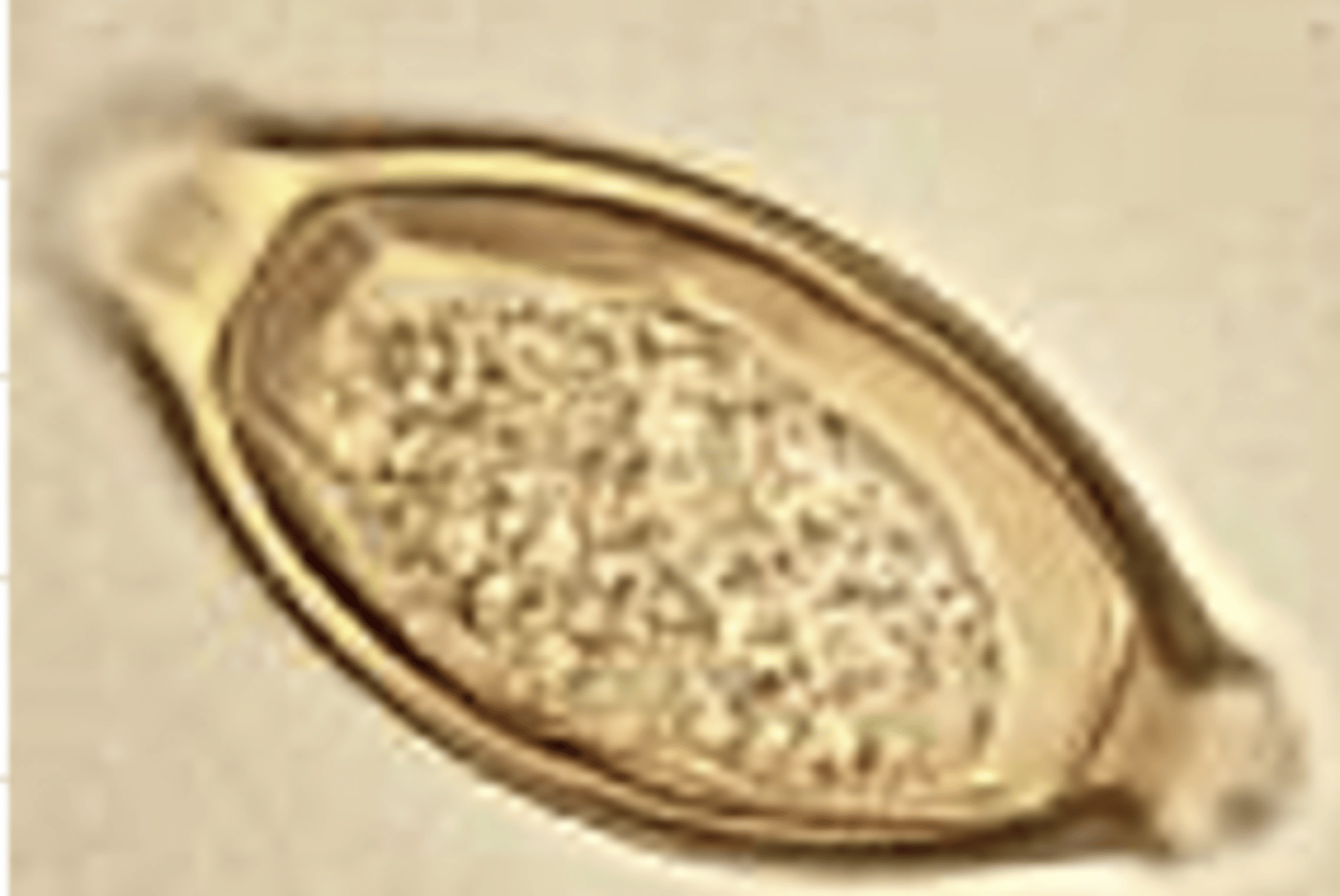
unembryonated
does genus Trichuris lay embryonated or unembryonated eggs?
T. ovis
T. skrjabini
which species in genus Trichuris affects the caecum of cattle, sheep, and goats?
caecum and colon of swine
what animal and organ does Trichuris suis infect?
T. vulpis
which species in genus Trichuris infects the caecum of dogs, wolves, and foxes?
T. trichiura
which species of genus Trichuris infects humans?
T. spiralis
T. britovi
T. pseudospiralis
all have adults that infect the small intestine of mammals (ex- humans, swine, horses, rats) and in all, the L1 is in the striated muscle. BUT, T. spiralis and T. britovi form intramuscular collagen cysts and T. pseudospiralis does not
what are the 3 important Trichinella species, and what is the difference between them?
direct
is the life cycle of Trichuris direct or indirect?
eggs are shed with feces, then L1 develops, and then the animal ingests L1
how are animals infected by Trichuris?
Trichinella
which Enoplida genus has L1 that develops in striated muscle of the host?
Trichinella
which genus is this?

direct
host ingests L1 that has been shed out as eggs in feces. it penetrates intestines and goes through 4 moults and then emerges as adults in the large intestine.
describe the life cycle of genus Trichuris
Capillaria
which genus?
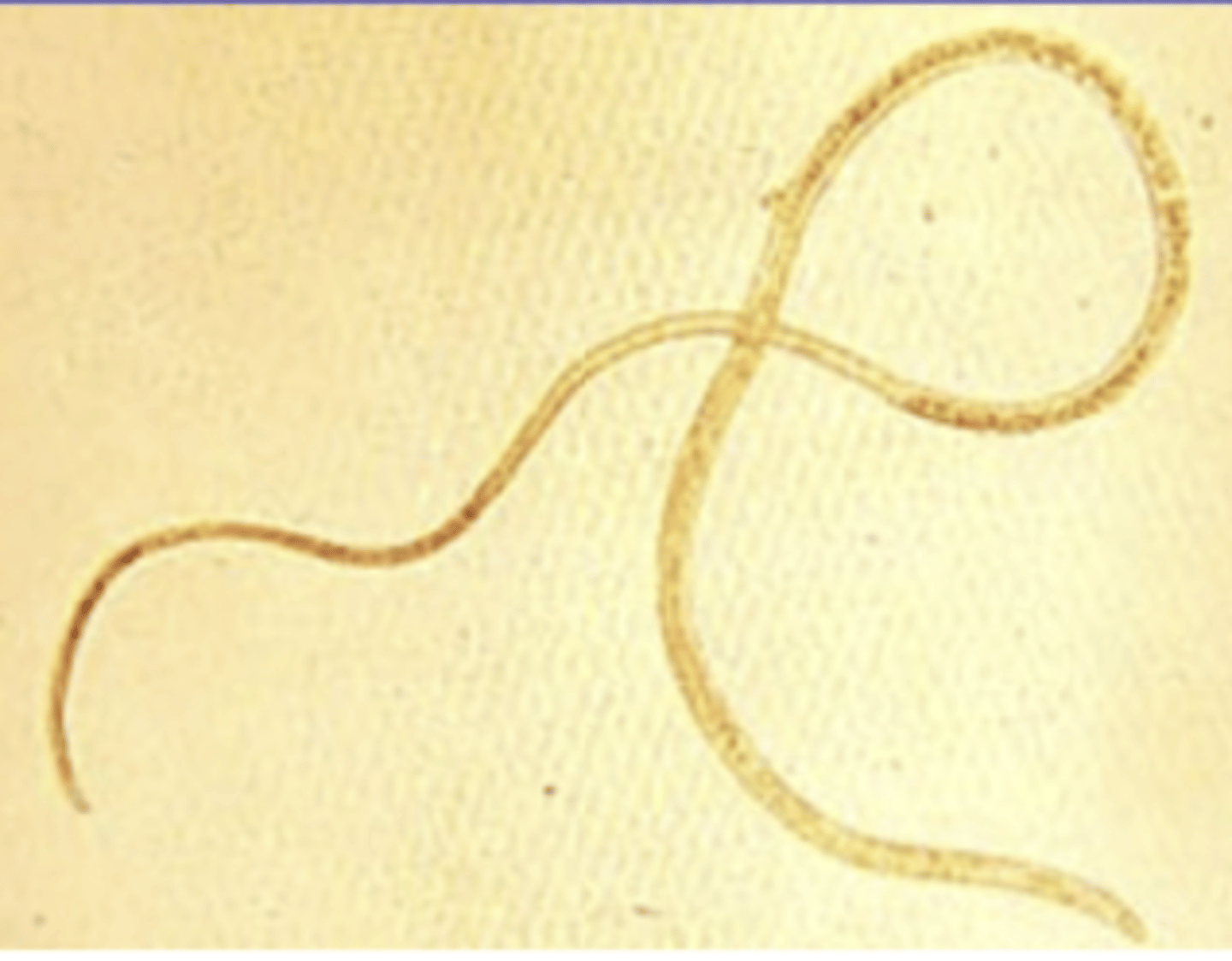
Capillaria
this egg belongs to what genus?
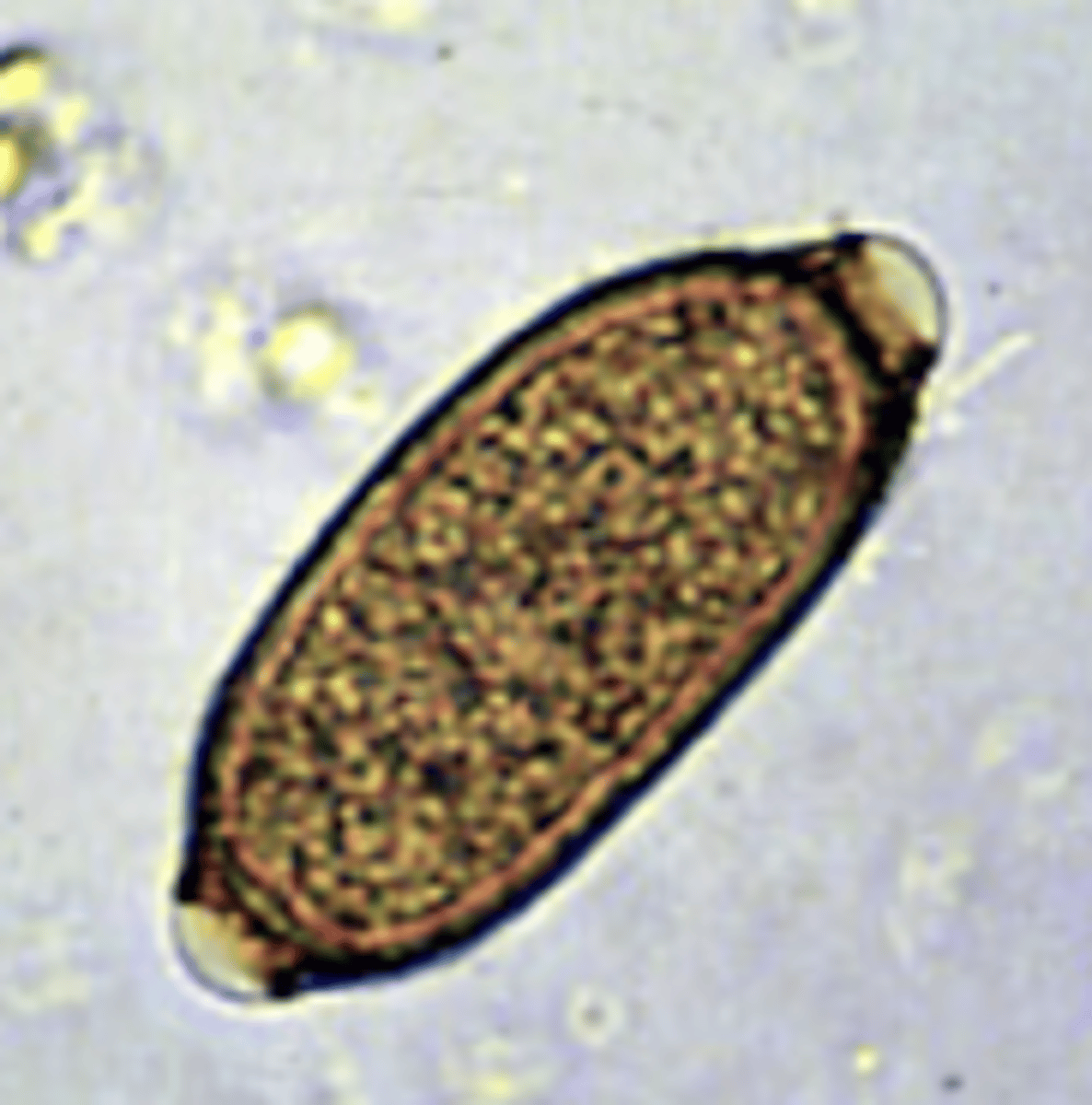
C. caudinflata- duodenum and ileum of poultry, pigeons, wild birds
C. contorta- crop, esophagus, oropharyngeal cavity of ducks and turkeys
what species of genus Capillaria infects birds?
Capillaria caudinflata
which nematode infects the duodenum and ileum of poultry, pigeons, and wild birds?
crop, esophagus, oropharyngeal cavity of turkeys and ducks
what species and organ does Capillaria contorta infect?
C. feliscati
C. hepatica
C. aerophila
which Capillaria species infect mammals?
bladder of cats
what species and organ does Capillaria feliscati infect?
Capillaria feliscati
which species infects the bladder of cats?
liver of rodents, rabbits, dogs, and humans
what species and organ does Capillaria hepatica infect?
Capillaria hepatica
what species of nematode infects the liver of rodents, rabbits, dogs, and humans?
trachea and bronchi of carnivores
what species and organ does Capillaria aerophila infect?
Capillaria aerophila
which nematode infects the trachea and bronchi of carnivores?
unembryonated eggs eliminated in feces
mammal-infecting Capillarias have a direct life cycle, with earthworms as their paratenic host
bird-infecting Capillarias have an indirect or direct life cycle, with earthworms as their IH (if indirect)
describe the life cycle of genus Capillaria
earthworms
Capillaria uses _____ as their paratenic host
Trichinellidae
Capillarridae
Trichuridae
what families are included in order Enoplida?
Dioctophyma renale
what one species do we study in order Dioctophymatida?
kidneys (parenchyma and renal pelvis) of ichthyophagus carnivores
what species and organ does Dioctophyma renale infect?
yes, although their main host is ichthyophagus carnivores, Dioctophyma renale can also infect horses, swine, cattle, and humans
can Dioctophyma renale infect humans?
Dioctophyma renale
which is the longest nematode?
Dioctophyma renale
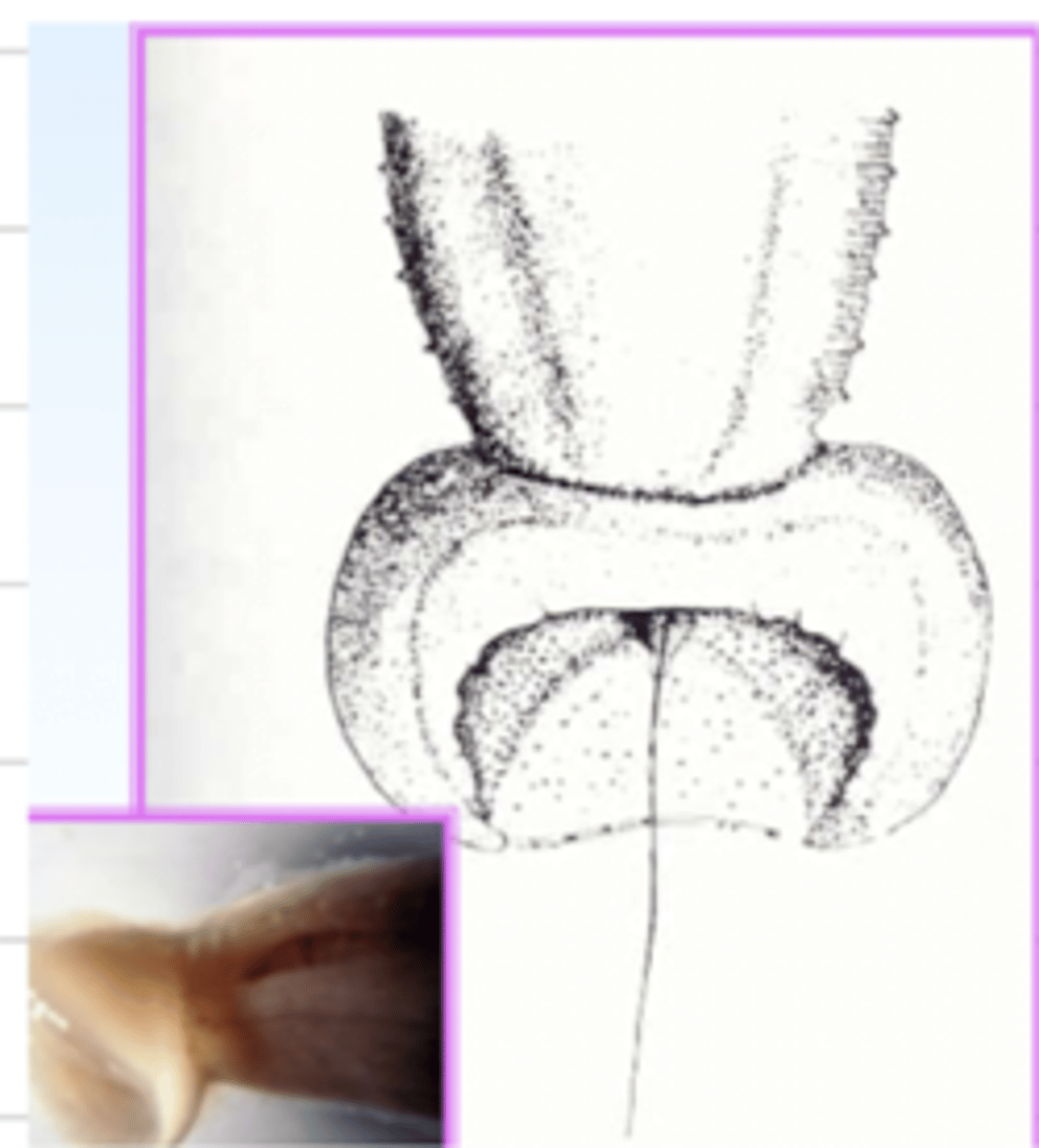
this bell-shaped bursa and 1 spicule belongs to what species?
Dioctophyma renale
this is the egg of what nematode?

barrel shape
yellow/brown
unembryonated
thick-pitted shell
describe the eggs of Dioctophyma renale
Trichinella- it is viviparous
which Enoplida nematode does not lay eggs?
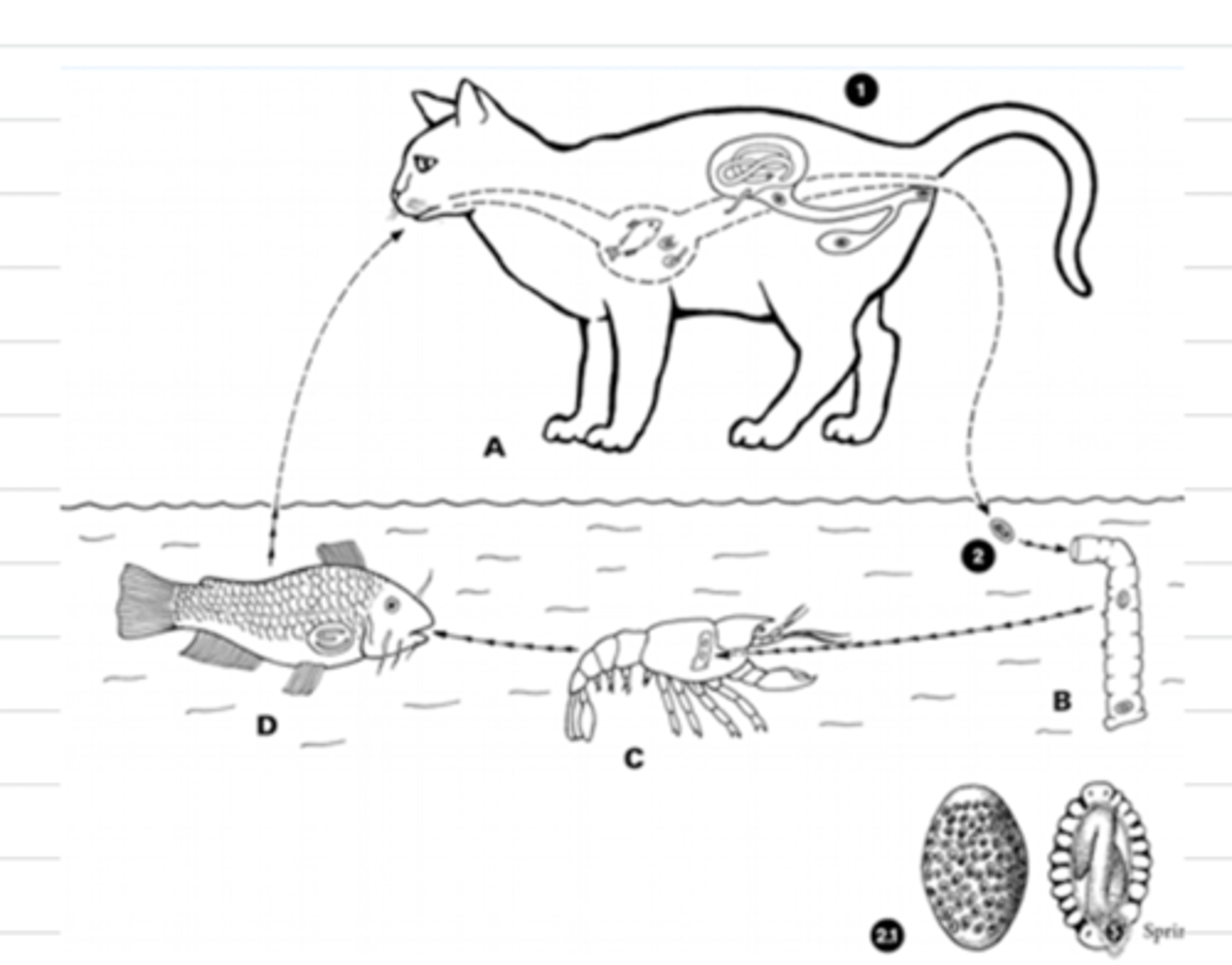
1. eggs eliminated with urine and develop in water
2. eaten by IH (parasitic annelids of crayfish) and hatch and develop until L4 is formed
3. DH eats annelid or parasitized crayfish
4. L4 penetrates the intestinal wall and reaches the kidney
- can use fish/frogs as a paratenic host
describe the life cycle of Dioctophyma renale
frogs and fish
what can act as a paratenic host for Dioctophyma renale?
parasitic annelids of crayfish
what is the IH of Dioctophyma renale?
Dioctophyma renale
which species performs hyperparasitism (infects a parasite)?
Dioctophyma renale
this is the life cycle of what nematode?