Intro to Behavioral Endocrinology
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
behavioral endocrinology
study of interactions between hormones and behavavior
hormones
- long lasting chemical messengers released from endocrine glands throughout the body
- act on targets throughout development and across the lifespan
endocrine system glands
- secrete chemicals into the bloodstream in chemical form
- produce long-lasting responses over time
- influence metabolism and development
nervous system cells
- travel to target tissues via electrical current
- produce fast responses
- influence acute changes in body systems
hormone chemicals
- travel via the blood stream to targets
- affect other cells already present in the body and brain
- effects can be fast (adrenaline) or slow (steroids)
5 systems of endocrine communication
intracrine, autocrine, paracrine, endocrine, ectocrine
intracrine
within the cell
autocrine
with its own cell surface
paracrine
between cells
endocrine
with distance target cells
ectocrine
between animals,
ex. phermones
hormones and behavior?
hormones do NOT produce behavior directly but alter the probability and expression of behaviors in response to specific stimuli
- hormones can only influence things to be better or worse but not directly effect them
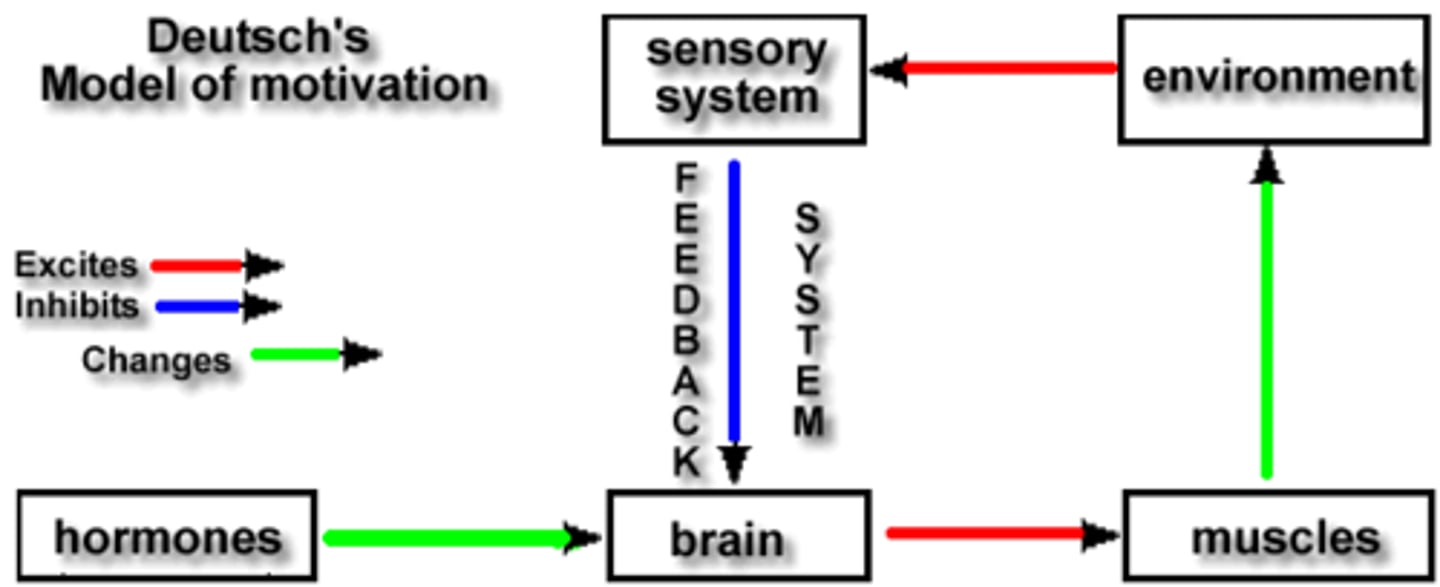
Deutsch's Model of Motivation,
how do hormones affect behavior?
an animal's motivation is regulated by a feedback loop from the environment, allowing it to monitor and adjust its behavior based on whether it has reached its goal
the animal's sensory system inputs signals to the brain when a goal is achieved, which then inhibits the motivational drive, and stopping the behavior