Lesson 3: Elasticity of Demand
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
3 ways to increase profits of a business
Selling more units
cut your costs
Raise price (not necessarily)
Why raising prices wont necessarily increase profits of business
The Law of Demand tells us that increased price causes a decrease in quantity demanded but it doesn’t tell us by how much (where the concept of elasticity comes in)
Elasticity
A measurement of how responsive one variable is to a change in another variable. It can be used with all sorts of variables
How does elasticity relate to increasing profits of a business
We look at the price elasticity of demand (how sensitive the quantity of a good that people demand is to a change in price of that good) when trying to increase profits
Price elasticity of demand (demand elasticity)
A measure of how much the quantity demanded changes when the price changes
Simple Price Elasticity of Demand Formula

Demand Elasticity Continuum
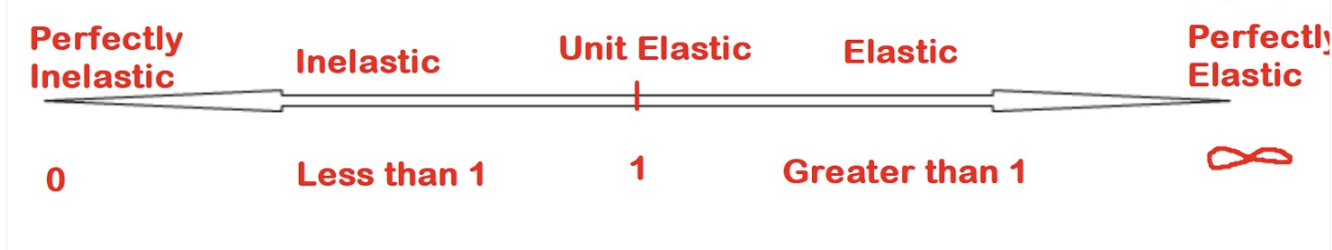
Perfectly inelastic demand
change in price results in NO change in quantity demanded of a product
elasticity coefficient=0
Inelastic Demand
when the % change in quantity demanded is less than the % change in price
Elasticity coefficient < 1
Unit Elastic Demand
when the % change in quantity demanded is equal to the % change in price
Elasticity coefficient = 1
Elastic Demand
when the % change in quantity demanded is more than the % change in price
Elasticity coefficient >1
Perfectly Elastic Demand
buyers will only buy at one price → small change in price → infinite change in quantity demanded
Elasticity Coefficient approaches infinity
Demand is inelastic when..
a given change in price causes a relatively smaller change in quantity demanded
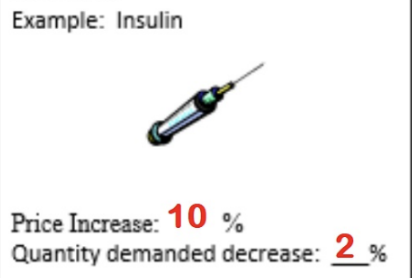
Demand is unit elastic when..
a given change in price causes a proportional change in quantity demanded

Demand is elastic when..
a given change in price causes a relatively larger change in the quantity demanded

Problem of the simple Demand elasticity formula
The senstivity of the change in quantity shouldn’t depend on whether the price goes up or down
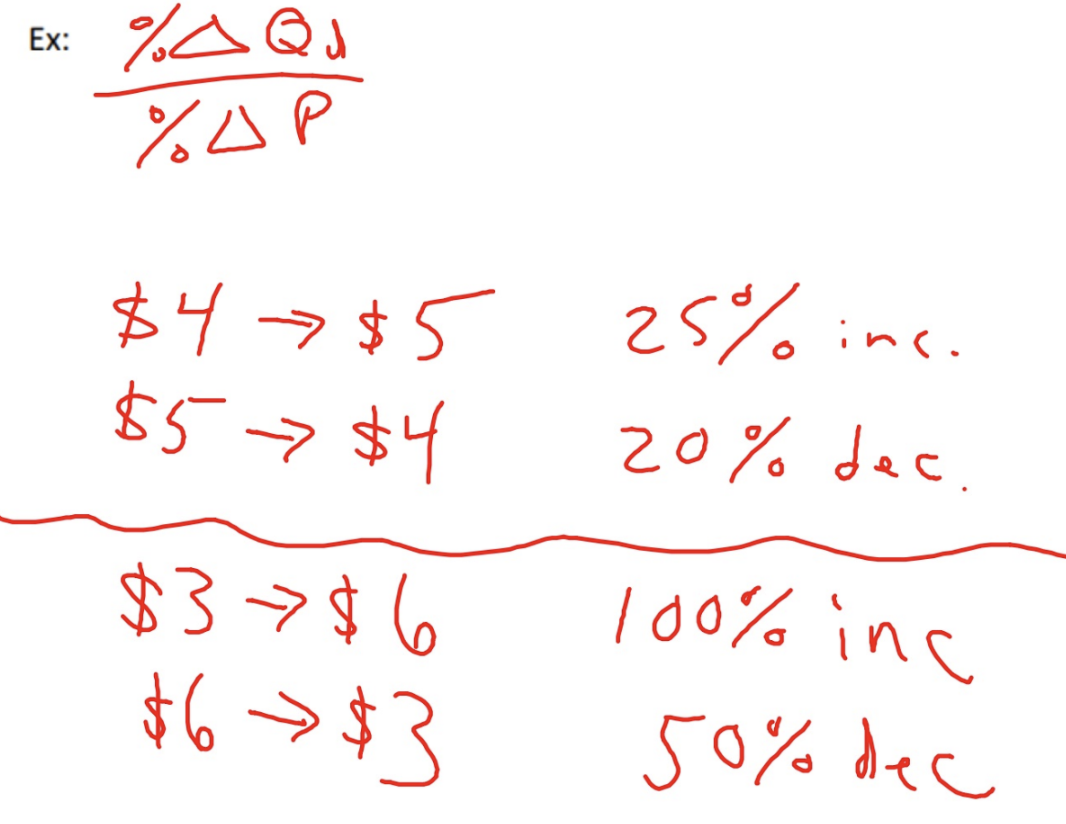
Midpoint Formula (Arc Method)
Calculates price elasticity across a price quantity range to overcome the problem of selecting the reference points for price and quantity. In this formula, the average of the 2 quantities and the average of the 2 prices are used as reference points. USE THE ABSOLUTE VALUE
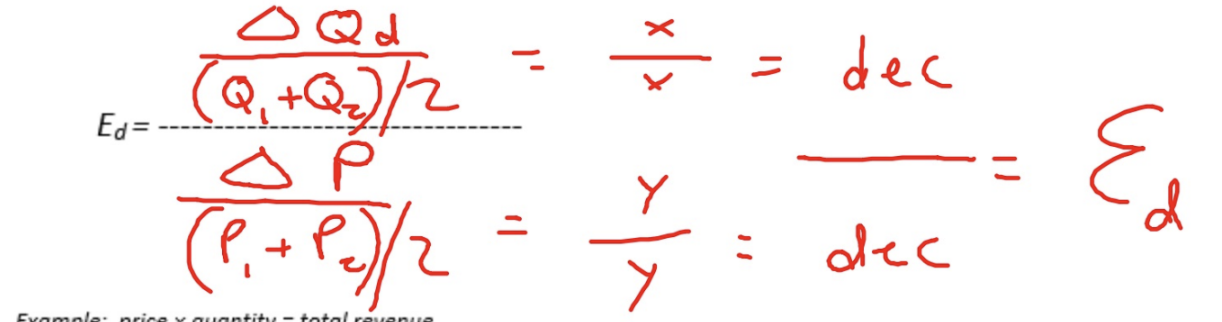
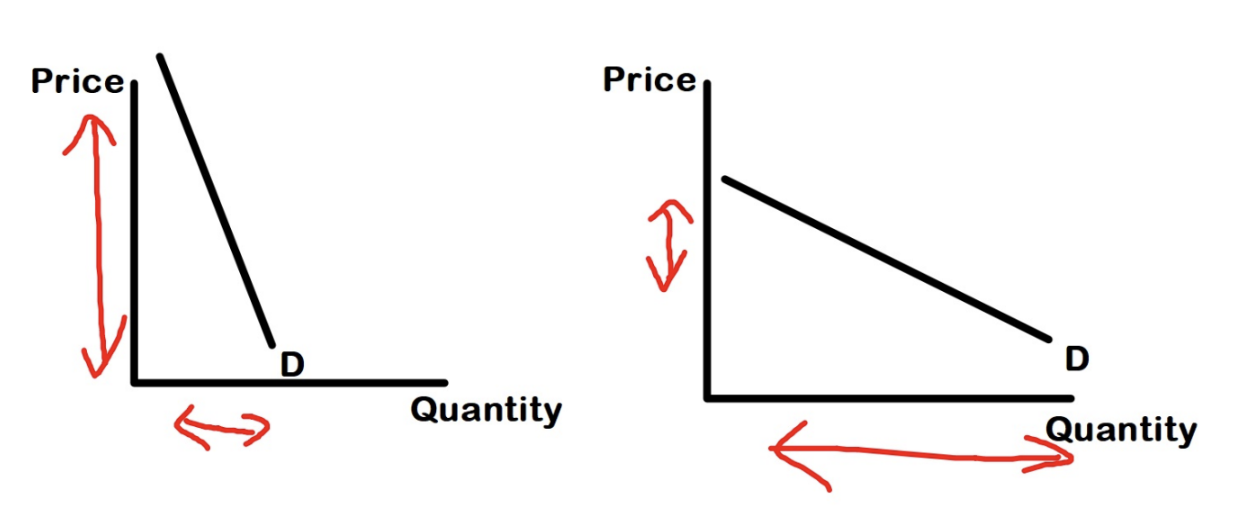
Slope of Demand Curve and Elasticity
If we generalize: steeper slopes show inelastic demand while flatter slopes show elastic demand
Slope of Demand Curve…
DOES NOT MEASURE ELASTICITY (elastic at higher prices, changes in sensitivity to how much money lost differs from $1 to $100)
4 Determinants of Demand Elasticity (LIST)
Luxuries vs Necessities
Proportion of one’s Income used
Number of Substitutes
Time frame available to adjust the price change
Luxuries vs Necessities
Necessities tend to have inelastic demand whereas luxuries tend to have more elastic demand (ex. Diapers are a necessity for anyone with a baby and going out to dinner is NOT)
Is the good habit-forming?
Consumers become less sensitive to the price of the good if they buy something out of habit (it has become the default choice) (ex. Going to a pizza place everyday even when they raise their prices)
Addictive products
Tend to be more severe in their behavior results → these will be very inelastic
Proportion of One’s Income used
products that take up a high percentage of one’s income will have a more elastic demand
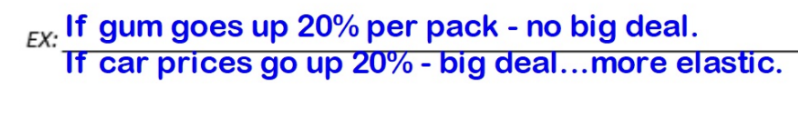
Number of Substitutes
The more close substitutes there are in the market, the more elastic is demand because consumers find it easy to switch

Breadth of the definition of the product
If the good is broadly defined (i.e., the demand for autos in general), demand is often inelastic, as opposed to a good that’s more narrowly defined (i.e., the demand for Honda Civic). Then the demand tends to be more elastic
Time frame to adjust to the price change
Demand is more price elastic the longer that consumers have to respond to a price change. They have more time to search for cheaper substitutes and switch their spending

Off-peak vs peak demand
Demand is more price inelastic at peak times and more elastic at off-peak times

Total Revenue Formula
Price x Quantity = Total Revenue
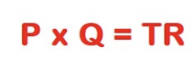
Total Revenue (TR) changes when..
Price changes
The total revenue test shows when demand is..
inelastic, unit elastic, and inelastic
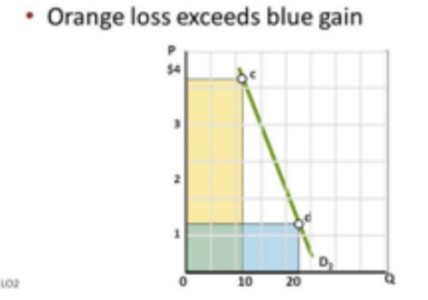
The price effect dominates with..
Lower price and inelastic demand
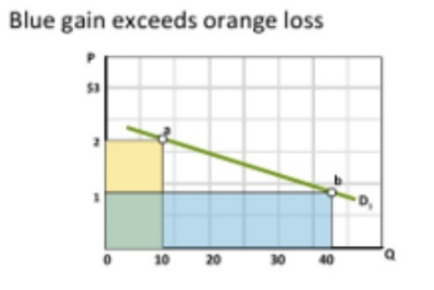
The quantity effect dominates with..
Lower price and elastic demand
Increase in price for Inelastic demand
Increase in total revenue for Inelastic Demand
Decrease in Price for Inelastic Demand
Decrease in Total Revenue for Inelastic Demand
Increase/Decrease in Price of Unit Elastic Demand
No change in Total Revenue
Increase in Price of Elastic Demand
Decrease in Total Revenue of Elastic Demand
Decrease in Price of Elastic Demand
Increase in Total Revenue of Elastic Demand