IMC Unit 2: Accounting
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
What are the objectives of accounts
SUMMARISE RESULTS of transactions to help management run
company
REPORT to interested parties THE STATE OF AFFAIRS of the
company
What do large companies have to provide annually
Income statement
Balance sheet
Director’s report
Auditor’s report
Cash flow statement
Statement of changes in equity
What must Listed Companies also provide
Half-yearly INTERIM reports
What are Small an Medium-Sized companies exempted from
Delivering full annual financial statements to the Registrar of Companies
File abbreviated financial statements
What is a Small company
Turnover < £6.5mn
Balance Sheet < £3.26mn
Avg No. Employees < 50
What is a Medium-Sized company
Turnover < £25.9mn
Balance Sheet < £12.9mn
Avg No. Employees < 250
What are the different ways a company can be formed
Public
Private
What are the UK accounting standards
Financial Reporting Standards (FRSs), issued by the Financial
Reporting Council (FRC)
What are the International accounting standards
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRSs), issued by the
International Accounting Standards Board (IASB)
When are UK accounts prepared under IFRS?
Applies to CONSOLIDATED accounts of LISTED companies
What companies use UK generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP)
Companies not using IFRS
These companies comply with UK standards issued by the FRC
What makes up UK GAAP
FRS 102
Reporting Requirements of the Companies Act 2006
What is FRS 102
Took effect for accounting periods ending on or after 1st January
2015
SINGLE STANDARD covering the various different items
previously covered under separate standards
What is the Role of the Auditor
To report to shareholders on whether the accounts
• Have been properly prepared; and
• Give a ‘true and fair view
What are the different types of audit report
Unqualified (‘clean’/’clear’)
Qualified
What are the difference between Qualified and Unqualified audit reports
Unqualified
The auditor is happy with the financial statements.
Qualified
The auditor found some issues, but they’re not serious enough to invalidate the whole report.
What are the different categories of assets
Non-Current assets
Current assets
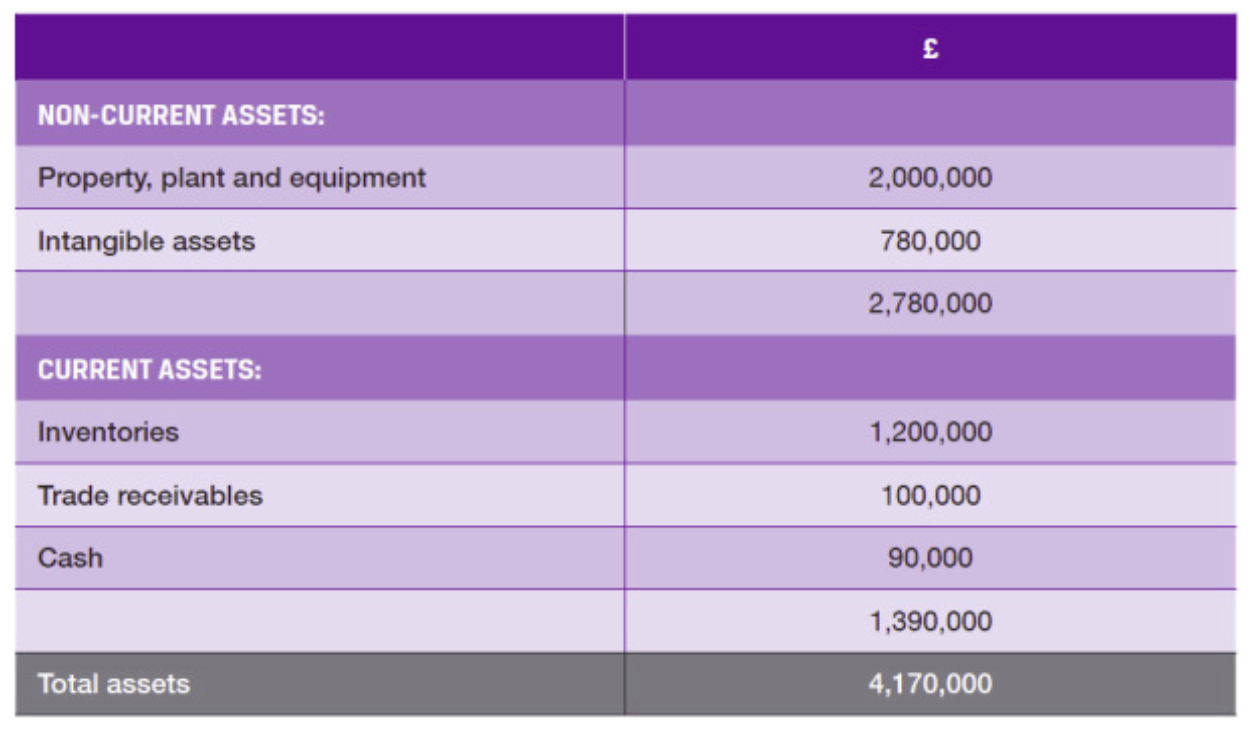
What are Non-Current assets
Assets a company expects to use, sell, or convert into cash within one year
How are Non-Current assets carried in the balance sheet
at COST (or VALUATION), less ACCUMULATED
DEPRECIATION
What are Current assets
Assets that a company plans to keep for more than one year and uses to run the business over time.
What are some examples of current assets
Inventories
Receivables
Cash
What categories of inventories
Raw materials
Work in progress
Finished goods
How are current assets treated in accounting
Value at the LOWER of COST and NET REALISABLE VALUE
What is Net Realisable Value
The estimated selling price minus costs to complete and sell.
What are the 3 possible cost flow assumptions in accounting for current assets
First in first out (FIFO)
Last in first out (LIFO)
Weighted average
What does FIFO assume
Oldest items are sold first.
Ending inventory reflects newer, higher value items
What does LIFO assume
Newest items are sold first.
Ending inventory reflects older, lower value items.
What does Weighted Average assume
Averages the cost of all inventory items.
How do prices affect the cost flow assumptions
Method | Impact on Profit |
|---|---|
FIFO | Higher profit |
LIFO | Lower profit |
Weighted Avg. | Moderate profit |
How can Cash expenditure be recorded
Capital expenditure (‘capitalised’)
Revenue expenditure (‘expensed’)
What is Capital Expenditure
Creates or improves an asset
What is Revenue Expenditure
Reduces Profit
What are Intangible assets
Non-Physical assets like goodwill, development expenditure, patents, trademarks and copyrights
What is Goodwill
An intangible asset that shows up when one company buys another for more than the value of its net assets.
When does Goodwill arise
On the purchase of a company
= Purchase Consideration - Net Assets Acquired
What is the formula for Goodwill
Goodwill = Purchase Consideration - Net Assets Acquired
How is Goodwill accounted for (IAS 36)
Capitalise in the balance sheet
Only amortise if can’t be maintained indefinitely
Annual impairment reviews (if not amortised
What are the different methods of Depreciation
Straight line Method
Reducing Balance Method
What is the formula for annual depreciation under the straight line method

A machine has a cost of £20,000, a useful life of four years and an expected scrap value of £2,000.
What is the carrying value of the machine in the balance sheet at the end of year 3 using straight line depreciation?
Annual Depreciation = (20000-2000)/4
= 4500
Depeciation at end of year 3 = 4500×3 = 13500
Carrying value at t=3 =20000-13500
=6500
What is the formula for annual depreciation under the reducing balance method
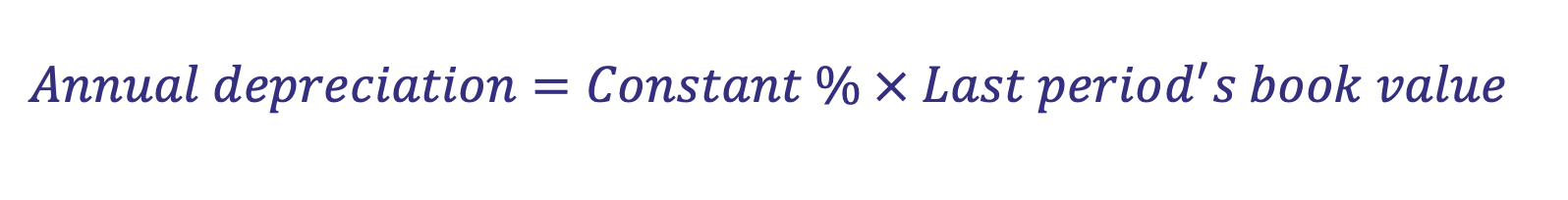
A machine has a cost of £20,000 and a useful life of four years.
What is the carrying value of the machine in the balance sheet at the end of year 2 using 25% reducing balance depreciation?
20000 × 0.75² = 11250
What need tobe disclosed on the sale of assets
Gain or Loss on disposal
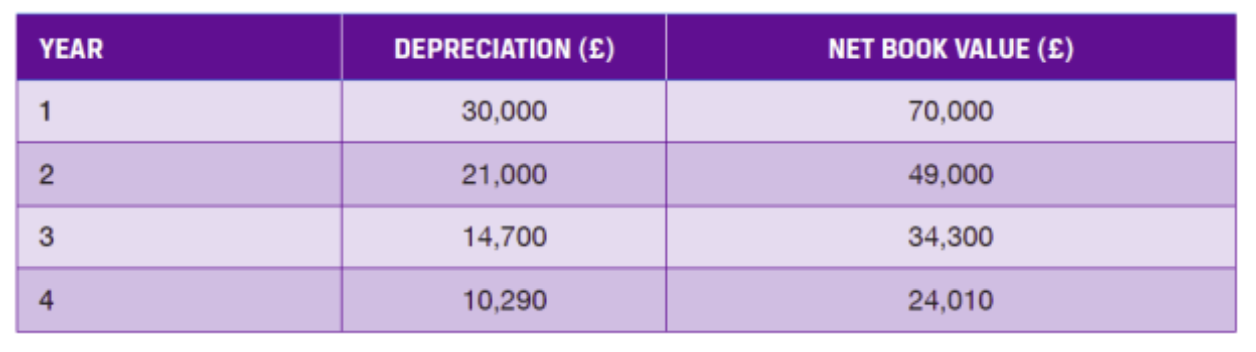
A machine has a cost of £100,000 and a useful life of eight years.
Depreciation is charged at 30% reducing balance. What will the gain
or loss on disposal be if the machine is sold for £30,000 at the end of year 4?
Value at T=4 = £100,000 × 0.74 = £24010
Gain on disposal = £30,000 - £24,010 = £5,990
What are the different categories of liabilites
Non-Current Liabilities
Current Liabilities
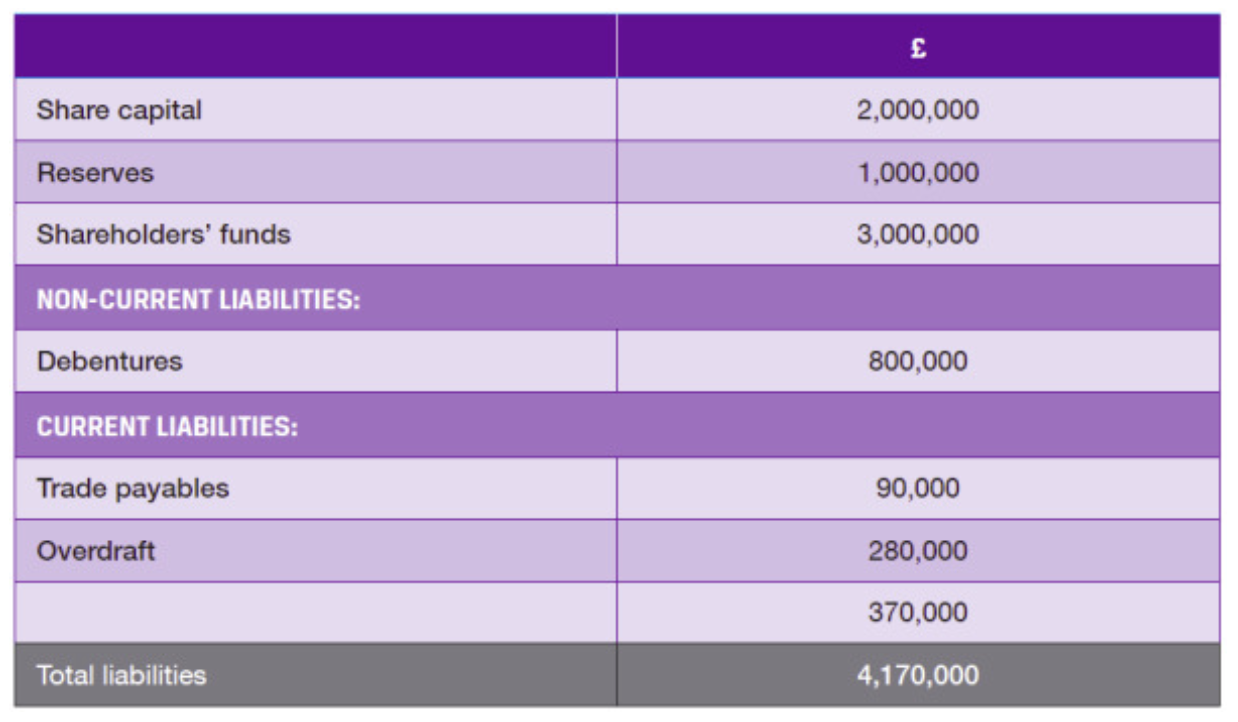
What is Share Capital
The NOMINAL VALUE of issued share
What are Reserves
Parts of shareholders’ equity that arise from profits, revaluations, or premiums. They’re not part of the nominal share capital
What is Share Premium
The amount by which shares have been issued in excess of nominal
value
What are the uses of share premium
Funding’ scrip issues
Writing off start up cost
What are Scrip Issues
Issuing bonus shares to existing shareholders.
What does writing off start-up costs mean
Covering expenses related to issuing shares
What is Revaluation Reserve
Cumulative surplus on the revaluation of assets
Arises when assets (like property) are revalued upwards.
What is Profit and Loss Reserve
This is where retained earnings go
DISTRIBUTABLE profit
What are Non-Current Liabilities
Additional sources of capital over and above shareholders’ funds
Financial obligations that a company must settle after more than one year.
What are some examples of Non-Current Liabilities
Debentures (secured debt capital)
Unsecured debt capital
Loans from financial institutions
What is the advantage of Non-Current assets over equity
Interest is tax-deductible: It’s paid from pre-tax profits, reducing taxable income.
What are the risks Non-Current assets over equity
Interest and capital have to be repaid when du
What are Current Liabilities
Financial obligations—debts or payments that must be settled within one year
What are Contingent Liabilities
POTENTIAL liabilities that did not exist at the balance sheet date
What are some examples of Contingent Liabilites
Potential liabilities from court action
Good sold under warranty/guarantee
How are Contingent Liabilities treated in accounting (IAS 37)
Not sufficiently predictable to warrant a provision, so DISCLOSE
EXISTENCE in the note to accounts
When do accounting issues for pensions arise
DEFINED BENEFIT pension scheme
How are Pension Costs treated in accounting (IAS 19)
Cost of employee benefits should be recognised in the period in
which they are EARNED (not paid)
How should Pension surplus or deficit should be recognised in the balance sheet
Fair Value of Plan Assets - Fair Value of Defined Benefit Obligation
What are Post-Balance Sheet Events
Events occurring between the balance sheet date and the date the
accounts are approved
What is an Adjusting Event (Post-Balance Sheet Events (IAS 10))
Subsequent evidence of a condition THAT EXISTED at the balance
sheet date, e.g. obsolete stock
ADJUST accounts
What is an Non-Adjusting Event (Post-Balance Sheet Events (IAS 10))
Event occurring AFTER the balance sheet date (but before the
accounts are approved), e.g. major acquisition/disposal
DISCLOSE in accounts
What are the objectives of accounting treatment for Financial Instruments (IFRS 9 (instruments), IAS 32 (presentation) & IFRS 7 (disclosures))
Clarify the classification of liabilities vs. equity
Prescribe strict conditions for the offset of assets and liabilities
Require disclosure about financial instruments
What is Equity
No contractual obligation to pay cash or another financial asset.
How is financial liability different from equity
There is a contractual obligation to deliver cash or another asset.
How is the decision made on whether something is a liability or an equity
Based on the substance of the contract, not just its legal label
E.g. a preference share with a mandatory redemption and fixed
rate dividend will be recognised as a LIABILITY
How do hedges have to be disclosed
Fair value hedges
Cash flow hedges
Are disclosed separately
How are financial assets categorised for disclosed
• Held for trading through the profit and loss account
• Held to maturity investments: quoted long-term debt investments
• Loans and receivables: unquoted financial assets
• Available-for-sale financial assets: financial assets not included
above
Which financial asset categories are held at fair value in the balance sheet
Held for trading through the profit and loss account
Available-for-sale financial assets: financial assets not included
above
How are financial liabilities categorised for disclosed
Fair value through profit and loss: trading liabilities
Measured at amortised cost: default category for liabilities
Which financial liabilities categories are held at fair value in the balance sheet
Fair value through profit and loss: trading liabilities
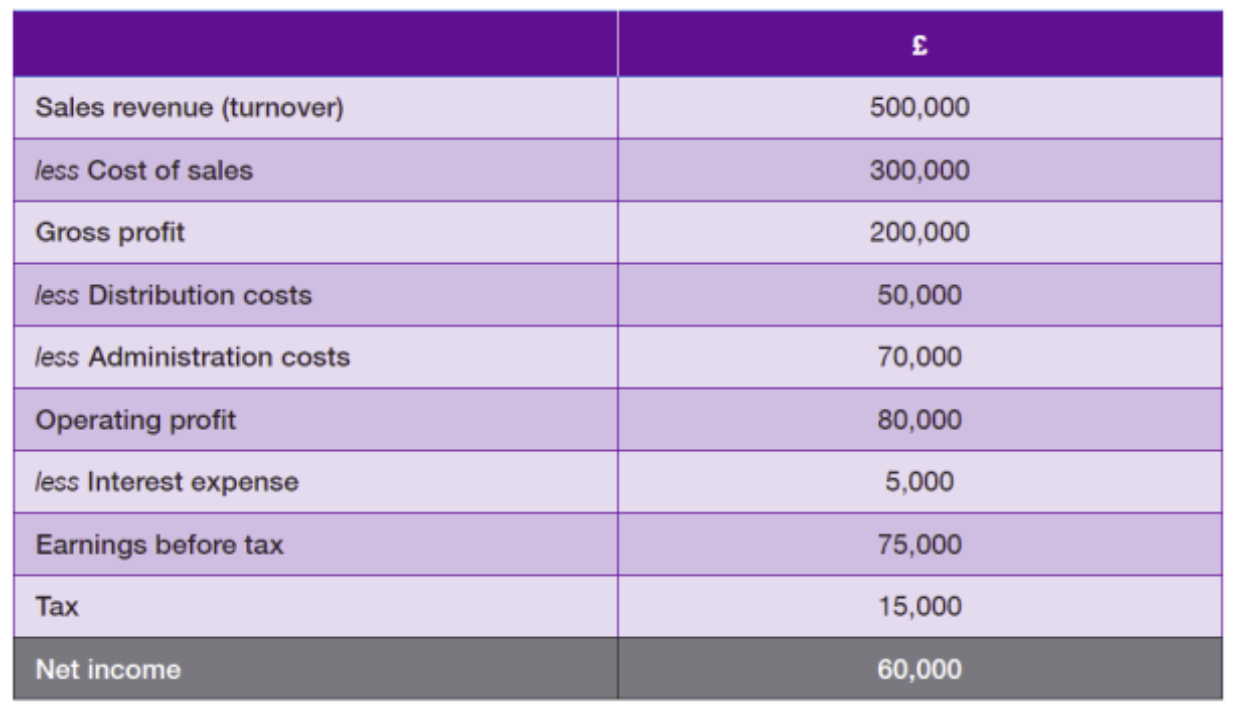
How is the income statement formatted
What is involved in the statement of changes in Equity
Changes to:
• Share capital
• Share premium
• Revaluation reserve
• Profit and loss reserve (including dividend distributions
How are cash flows classified in the cash flow statement
Operating activities
Investing activities
Financing activities
Example of net cash flow from operating activities
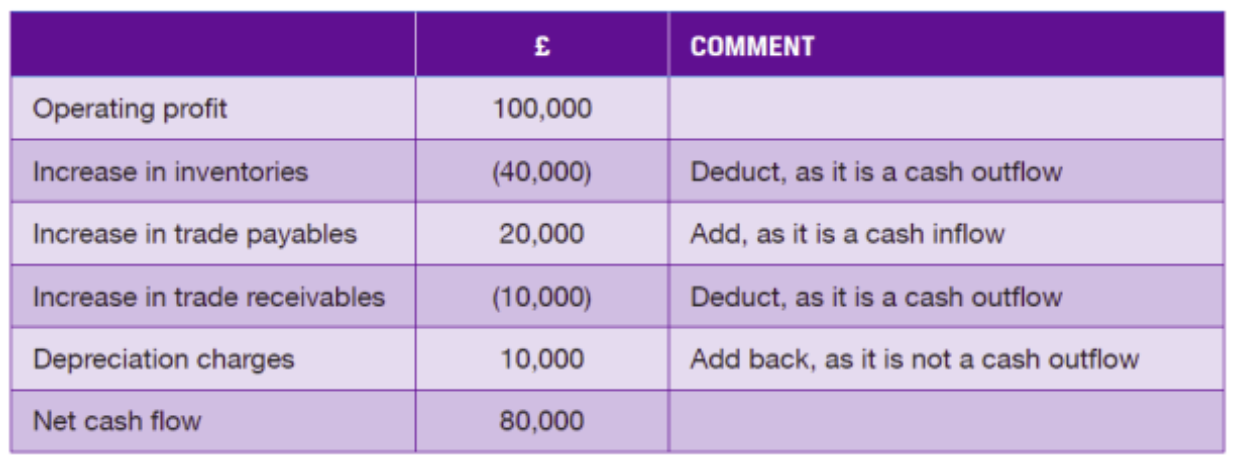
A company has an operating loss of £6m in the income statement for the period. During the period depreciation was £6m, work-in-progress decreased by £2m and both accounts receivable and accounts payable increased by £1m each.
What is net cash flow from operating activities for the period?
Operating loss: –£6m
Add back depreciation: +£6m
Work-in-progress decrease: +£2m
Receivables increase: –£1m
Payables increase: +£1m
--------------------------------------------------
Net cash flow: +£2m
What is a Parent company/holding company (IAS 27)
Holds the majority of the voting rights (greater than 50%) in
another company (a ‘subsidiary’); and/or
Exercises dominant influence

What is the formula for Return on capital employed (ROCE)

What is the formula for Return on equity (ROE)

What is operational gearing
The sensitivity of operating profit to changes in sales revenue
What are the two potential formulas for operational gearing

Example of operational gearing
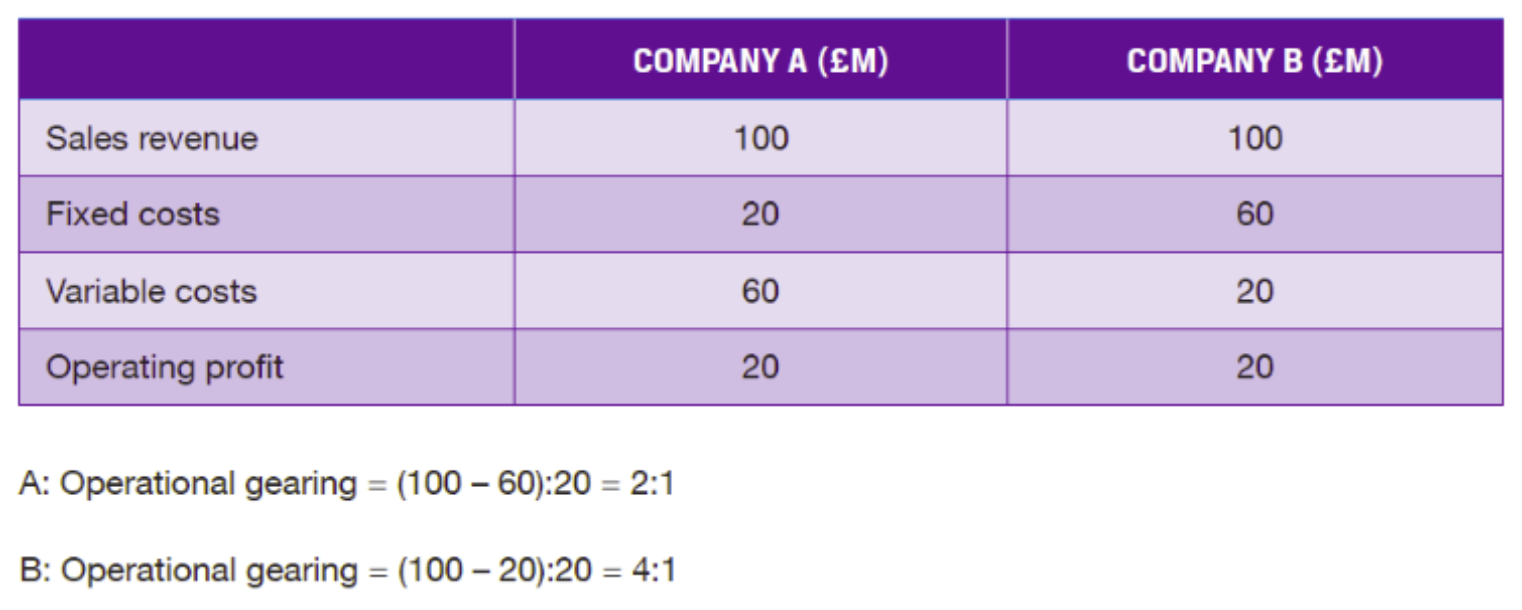
What is the impact on operating profit of a 10% increase in revenue for Company A and Company B?
Company A Operating Profit: 24
Company B Operating Profit: 28
The company with higher operational gearing, Company B’s operational profit increased by more
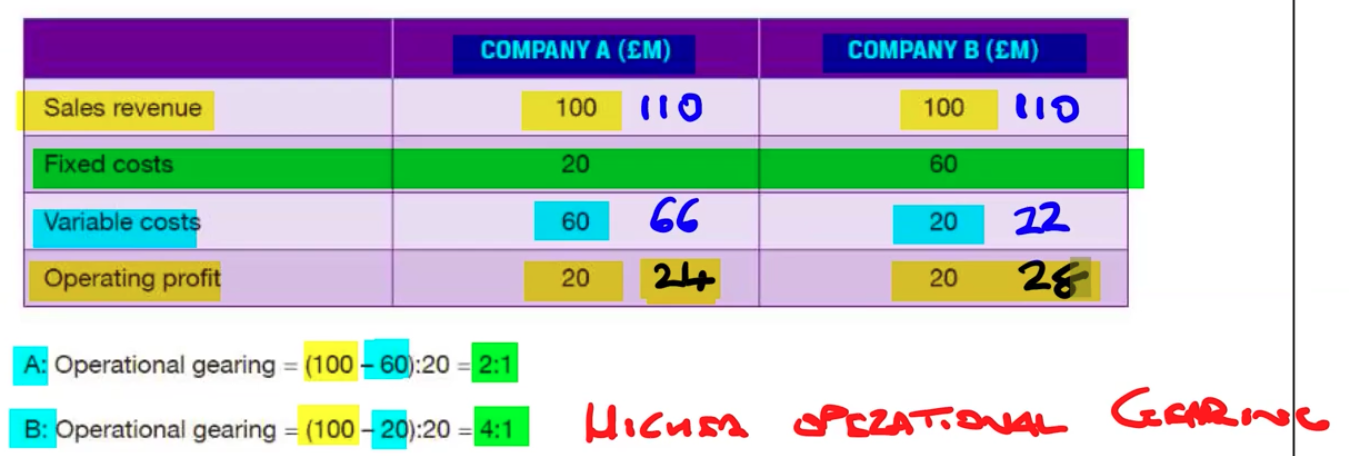
If revenues are increasing do you want a company with higher or lower operational gearing
If markets and revenue are rising, generally you want a company with higher operational gearing.
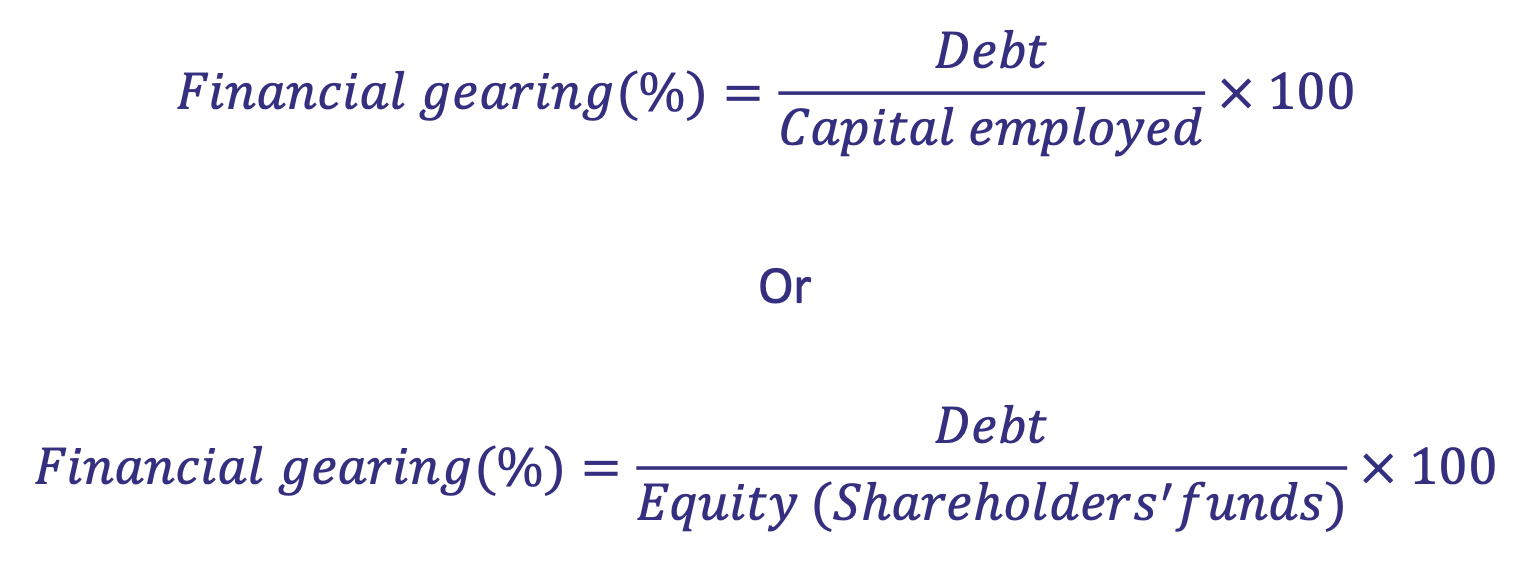
What are the two potential formulas for financial gearing
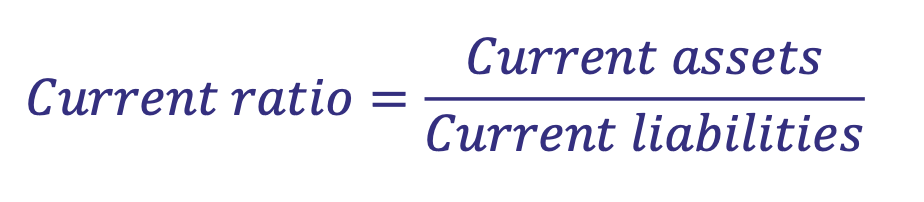
What is the formula for Current Ratio
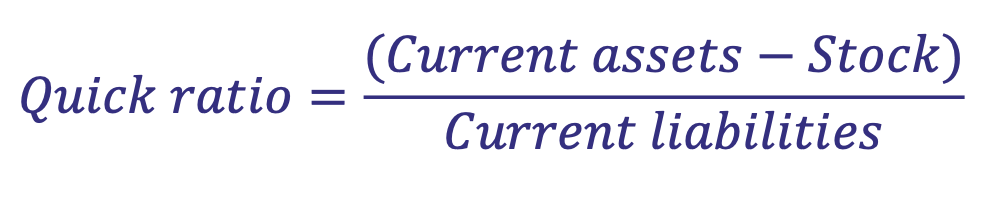
What is the formula for Quick Ratio