6.2 The Blood System
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Aorta
the main artery of circulatory system that carries blood from the left side of the heart to the arteries of all limbs and organs except the lungs.
Arteriole
a small terminal branch of an artery that connects with a capillary.
Artery
a vessel that carries blood away from the heart to organs through the body.
Atrium (plural atria)
a chamber that receives blood returning to the heart.
Blood pressure
the hydrostatic force that blood exerts against the wall of a blood vessel.
Capillary
a microscopic blood vessel that penetrates the tissues and consists of a single layer of endothelial cells to allow exchange with interstitial fluid.
Cardiac output
the volume of blood pumped per minute by the left ventricle of the heart.
Diastolic pressure
the minimum blood pressure during relaxation of heart muscles.
Elastic fibres
a thick, yellow connective-tissue fibre composed principally of elastin and characterized by giving great elasticity to tissues in the body.
Epinephrine
a hormone produced as a response to stress, also called adrenaline.
Medulla
the lowest part of the brain that controls autonomic and homeostatic functions.
Myogenic contraction
a contraction of the heart without external stimulation from a nerve.
Pacemaker
a specialized region of the right atrium that sets the rate of heart contraction, also called the sinoatrial (SA) node.
Pulmonary circulation
the separated circulatory system that links the lungs and heart in humans.
Pulse
the force of blood leaving the heart in one heartbeat; it is felt where arteries pass near the skin.
Systemic circulation
the separated circulatory system that links the heart to the rest of the body.
Systolic pressure
the maximum blood pressure caused by heart muscles contracting and pumping blood.
Valve
a membranous structure in a hollow organ or passage that folds or closes to prevent the return flow of the body fluid passing through it.
Vasoconstriction
when the circular muscles in the artery wall contract, narrowing the lumen.
Vasodilation
when the circular muscles relax, increasing the lumen size and hence blood flow to downstream tissues.
Vein
a vessel that returns blood to the heart.
Ventricles
the chambers on the left and right side of the heart that receive blood from the atria and contract to force it into the aorta and pulmonary artery respectively.
4 main components of blood
Plasma
Red blood cells (erythrocytes)
White blood cells (leukocytes)
Platelets (thrombocytes)
Things that are transported by the blood plasma
Nutrients, Antibodies, Carbon dioxide, Hormones, Oxygen, Urea, Heat

William Harvey’s findings on the circulation of blood
William Harvey disproved the prior theories of Galen by suggesting that:
The major blood vessels (arteries & veins) are part of a single connected blood network. Blood flow is unidirectional (due to valves) & continuously flows (it is not consumed by the body). The heart is a central pump (blood carried from the heart by arteries & to the heart by veins)
Pulmonary circulation
Deoxygenated blood returns from the body (via vena cava) to the RIGHT side of the heart. It is pumped (by right atrium/ right ventricle) to the lungs via the pulmonary artery
Systemic circulation
Oxygenated blood returns from the lungs (via pulmoary vein) to the LEFT side of the heart. It is pumped (by left atrium/ left ventricle) to the body via the aorta
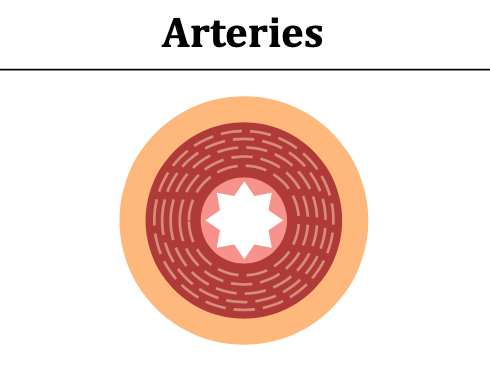
ARTERIES info
Structure: thick walls & narrow lumens (because they transport blood at high pressure)
Blood Speed: Fast
Blood Pressure: High (80-120 mmHg)
Size if Lumen: Narrow
Valves: NO
Wall Composition: Thick wall with large amounts of muscle & elastic fibres
Function: carry blood FROM heart (ADIEU)
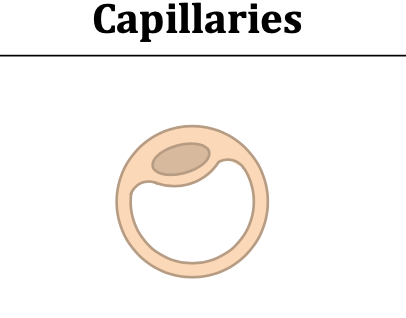
CAPILLARIES Info
Structure: have walls that are single cell thick (because they exchange materials between blood & tissue)
Blood Speed: slow
Blood Pressure: Low (around 20 mmHg)
Size if Lumen: extremely narrow
Valves: NO
Wall Composition: Extremely thin wall composed of single layer epithelium
Function: Gas/ material exchange
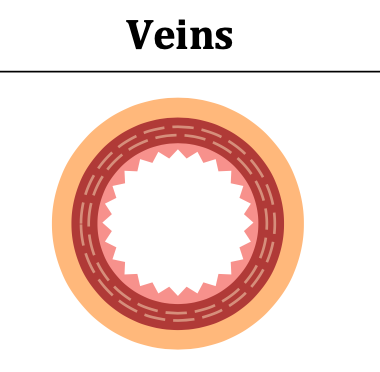
VEINS info
Structure: thin walls with wide lumens & valves (because they transport blood at low pressure; have valves to prevent backflow)
Blood Speed: slow
Blood Pressure: Low (around 15 mmHg)
Size if Lumen: wide
Valves: YES
Wall Composition: thin wall with small amounts of muscle & elastic fibres
Function: carry blood TO heart (viva amor)
role of valves in the circulation of blood
Valves in veins & the heart ensure that the circulation of blood is UNIDIRECTIONAL by preventing BACKFLOW. Heart valves include AV valves (tricuspid & bicuspid) & semilunar valves (pulmonary & aortic valves)
Which blood vessel supply the heart with oxygen & nutrients?
Coronary arteries
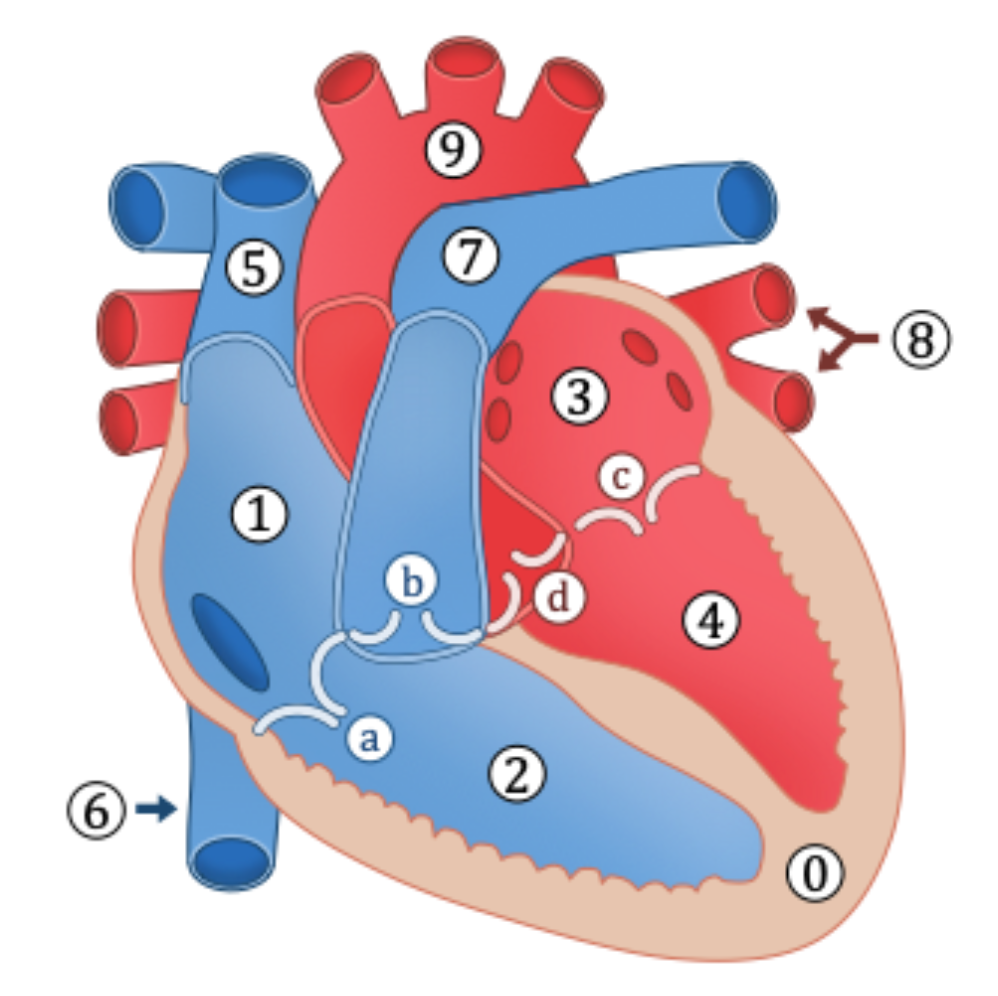
structure of heart
Myocardium (thicker on the left side of heart)
Right Atrium
Right Ventricle
Left Atrium
Left Ventricle
Superior vena cava
Inferior vena cava
Pulmonary artery
Pulmonary vein
Aorta
a. Tricuspid valve (AV valve)
b. Pulmonary valve (semilunar valve)
c. Bicuspid valve (AV valve)
d. Aortic valve (semilunar valve)
Electrical events that trigger the contraction of heart muscle fibres
The heart beat is myogenic - meaning cardiac contraction is initiated by the heart. Electrical signals are intitiated by the sinoatrial (SA) node (the pacemaker).
It stimulates the atria to contract & also relays signals to an atrioventricular node. The atrioventricular node sends signals via the Bundle of His to Purkinje fibres. These fibres innevrate the ventricles & cause them to contract
Role of the medulla & epinephrine (adrenaline) in regulating heart rate
The SA node (pacemaker) maintains the hearts normal sinus rhythm (60-100 bpm). The pacemaker may be resulated by the medulla (brainstream), with sympatheic nerves increasing heart rate by releasing noradrenaline & parasympathetic nerves decreasing the heart rate by releasing acetylcholine. Heart rate may also be increased by the release of epinephrine (aka adrenaline) into the bloodstream)
Systole vs diastole
Systole describes the period of heart contraction, whereas
Diastole describes the period of heart relaxation
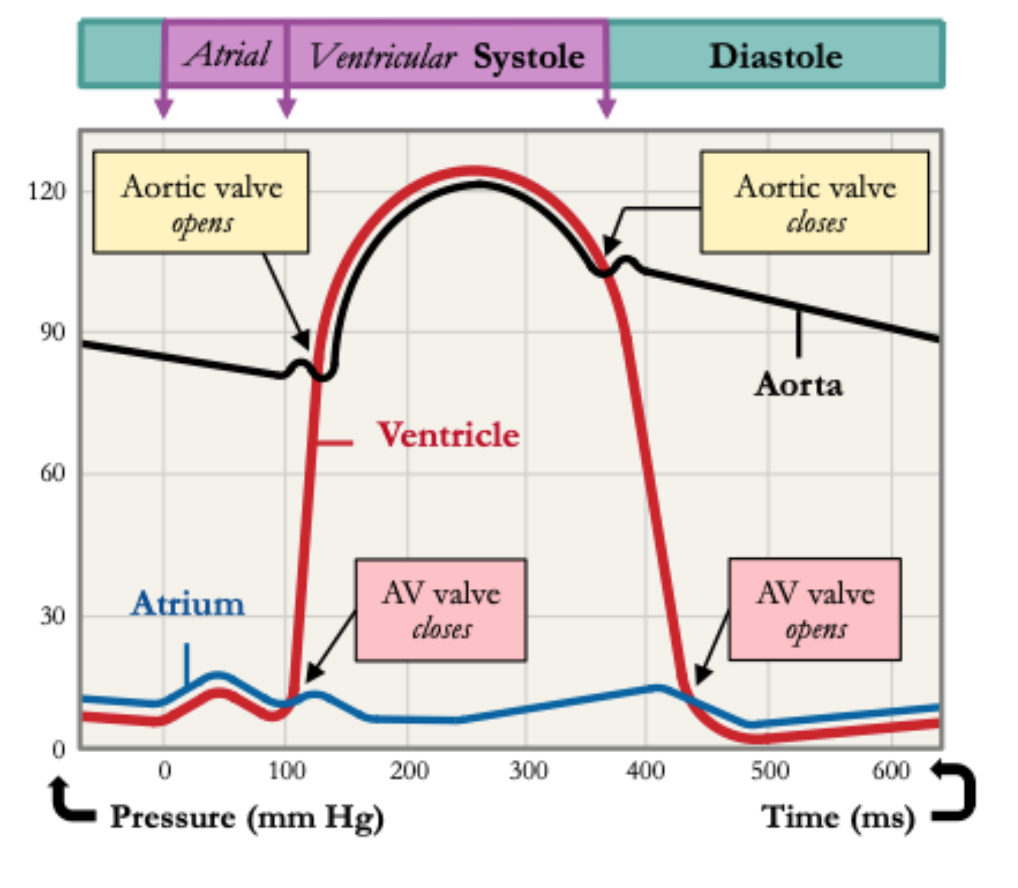
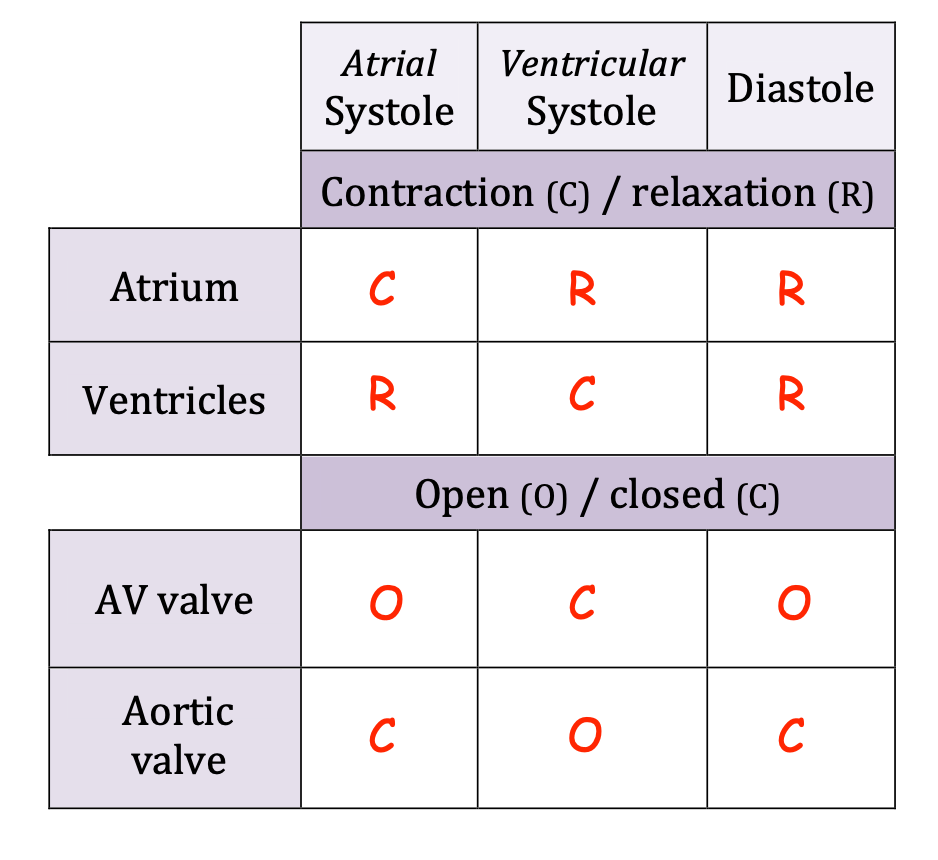
Pressure changes in the heart during the CARDIAC CYCLE
Blood returning to the heart will flow into the atria & ventricles as the pressure in them is lower. As ventricles fill, atria contract (atrial systole), increasing pressure in atria & forcing blood into the ventricles. As ventricles contract, ventricular pressure exceeds atrial pressure & AV valves close to prevent back flow. When ventricular pressure exceeds pressure in aorta, the aortic valve opens to release blood into the aorta. As blood exits the ventricle, ventricular pressure falls below aortic pressure, so the aortic valve closes. When ventricular pressure drops below atrial pressure, the AV valve opens & cycle begins again.
Causes & consequences of occlusions to the coronary arteries
Causes:
Atherosclerosis can be caused by age, hypertension, obesity, diseases (eg. diabetes), smoking, genetics, diet (high levels of trans fat) & lack of exercise
Consequences:
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) occurs when coronary arteries become narrower. Coronary arteries oxygenate heart tissue so their occlusion results in myocardial infarctions (heart attacks)