CHEM FINAL
1/162
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
163 Terms
What are mixtures?
Physical combination of 2 or more substances in variable amounts
What are Molecules?
2 or more atoms chemically bonded together
What are atoms?
The smallest unit of an element that retains the characteristics of that element
What are allotropes?
2 or more forms of the same element that differs in their chemical structure and therefore there properties.
Allotrope exaples?
O: Oxygen atom
O2: Oxygen molecule
O3: Ozone
How are mixtures seperated?
By physical means
How are compounds seperated?
Chemical methods
How is the periodic table arranged?
The periodic table is arranged through Columns/groups and Rows/periods.
Which elements have similar chemical properties
Coulmns/Groups
Diatomic element
Atoms are the same
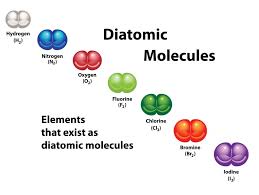
Compound
If atoms are different
Metals
Solid; Good conductors of heat and electricity
Non-Metals
Can be in any state; Poor conductors of heat and electricity
Metalloids
Between Metals and Nonmetals; Semiconductors
What is a graphite Allotrope
Carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal structure
Dimond Allotrope
Carbon atoms covalently bonded to each other in a lattice structure
Carbon nanotubes
Arranged in a tube structure
Air is a _____ mixture of gases
Homogenous
Heterogeneous
is a type of mixture in which the composition is not uniform throughout. The different components of the mixture remain separate and can often be seen or easily distinguished
Heterogeneous examples
Sand, Water, Salad
What is a homogeneous mixture?
Mixtures with a uniform composition throughout. The individual components are evenly distributed and not distinguishable.
Homogenous examples
Saltwater, air, vinegar
What is the EPA?
develops and enforces regulations as well as offer financial assistance, research, environmental education and publish their findings to the public.
What is the AQI Index
AQI maps show criteria air pollutants, O3 and PM
What is a secondary pollutant?
A secondary pollutant is not directly emitted, it forms when other primary pollutants react in the atmosphere.
What is the difference between complete and incomplete combustion?
if there is not enough oxygen present it is an incomplete combustion. Complete combustion is a chemical reaction in which a hydrocarbon reacts with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide
What are the properties of Radon
Radon is a gas that is colorless, orderless and tasteless
What is the matter that has definete shape and size
solids
What changes volume when they are poured?
liquids
An elements atomic number is always a
Integer
In the periodic table groups of elements are arranged
Vertically
The atomic number of an atom is the number of _____ in the atoms nucleus
Protons
which gas remains in the same amount in inhaled and exhaled air?
Argon
What does a catalytic converter do?
Convert nitrogen oxides into nitrogen gas and oxygen gas
Which elements would you expect to have similar chemical properties in the periodic table?
The elements that exist in the same groups
The amount of particular has is higher in the exhaled air compared to its inhaled air which gas is it?
Carbon Dioxide
How are primary pollutants different from secondary?
Primary pollutants are emitted directly from the source, whereas secondary pollutants
are formed when other primary pollutants react in the atmosphere
Many policies, organizations, agencies, and systems have been developed to help and
monitor air quality in the United States. Among these legislations, which one talks about
establishing air quality standards?
Clean air act
Frequency
Number of wave cycles
Wavelength
Distance Wave travels in one cycle
Amplitude
Height of Crest
What are elements
They are the basic building blocks of all matter and are composed of only one type of atom.
How do we classify matter?
Based on the physical and chemical properties
What is the composition of air?
78% Nitrogen; 21% Oxygen; 1% other
What is Nonrenewable energy?
Energy that cannot be replenished on a human timescale
What is renewable energy?
Energy that can be naturally replenished within a short period of time
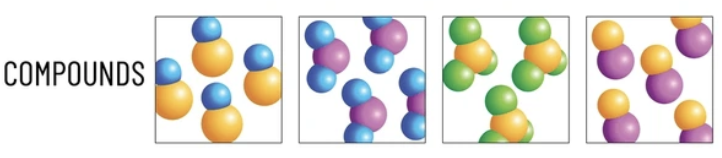
What are compounds
substances formed when two or more elements chemically combine in fixed proportions.
What is Green Chemistry?
It seeks to minimize the environmental and health impacts of chemical production
Light consists of what?
Electromagnetic waves
Photons
light particles that contain energy
Wave particle duality
Light can behave like a wave and a particle
Absorption
Energy is added to and electron as it jumps from a lower energy level to a higher one
Emmission
Energy released when an election falls from a higher energy level to a lower one
IR rays
Make molecules move, rotate, vibrate
UV rays
Have enough energy to break bonds
Montreal protocol
Treaty for phasing out the productions of CFCs
UV light has____ than the visible light
Higher
Does the chapman cycle keep the concentration of O2 and O3 constant in the atmosphere
Yes
What light has the longest wave
Radio wave
What type of photon will have the highest energy
X-ray photon
Is the ozone in the troposphere (bad, criteria air pollutant) chemically different from the ozone in the stratosphere (good, protective layer)
No
What were the goals of the Montreal protocol
Reduce and eliminate the use of CFCs
Reduce ozone in the stratosphere
What are the electrons in the outermost energy levels called?
Valence electrons
Ionic binding
Losing/gaining electrons
Covalent bonding
Sharing electrons
Chemical bond
When electrons are transferred or shared
Covalent compound
Electrons are shared between atoms
Ionic compounds
Electrons are transferred from one atom to another
Isotopic mass
Mass of a specific isotope of the element
Average atomic mass
Weighted average mass of all naturally occurring isotopes of an element
Cations
positive and formed by loss of electrons
Anions
Negative and formed by gain of electrons
Global Warming Potential (GWP)
a measure of how much heat a gas traps in the atmosphere up to a specific time horizon, relative to carbon dioxide.
The greenhouse effect refers to the process by which
atmospheric gases trap and return infrared radiation radiated by Earth
Much methane from anaerobic decomposition is trapped under permafrost. What will happen as the global temperatures rise?
Methane levels in the atmosphere will increase.
Which explanation accounts for the fact that, on average, cloudy nights are warmer than clear nights?
Clouds are composed of water vapor and H2O is a strong greenhouse gas.
If the greenhouse effect traps about 80% of the IR radiation, how much does the enhanced greenhouse effect trap?
More than 80%
A common analogy used to talk about the greenhouse effect is that it is like putting a blanket on when you’re cold - it holds the radiated heat near your body.
How would you explain the enhanced greenhouse effect using the same analogy?
putting on more blankets
Which statement correctly describes the relationship between O2/O3 molecules and frequency of light?
Higher frequency light is required to break O2 molecules apart because the bond is stronger.
What international agreement attempted to reduce greenhouse gas emissions?
Kyoto Protocol
Ocean acidification can significantly affect marine life. Which statement about ocean acidification is TRUE?
When CO2 dissolves in ocean waters, it forms carbonic acid that will lower the pH of the water.
The frequency of light is
directly proportional to its energy.
Ozone in our atmosphere is important because it
absorbs some UV radiation.
Which international treaty was designed to protect the ozone layer by phasing out the production
of numerous substances responsible for ozone depletion
Montreal Protocol
What effect does chlorine radicals have on the ozone layer?
Chlorine radicals decrease the concentration of ozone in the stratosphere
Which UV radiation of the UV radiation spectrum has the highest energy
UV-C
Which of the following is not a greenhouse gas?
nitrogen
Ocean acidification can significantly affect marine life. Which statement about ocean acidification
is TRUE?
When CO2 dissolves in ocean waters, it forms carbonic acid that will lower the pH of the
water
What was the IPCC's recommendation about the rise in global temperature?
To limit our rise in average global temperature to ~1.5°C.
Which of the following will contain the most heat?
A bucket filled with water at 0 c
An exothermic reaction
gives out energy to the environment.
Burning a piece of wood is an exothermic process. Which of the following events doesn’t take place in this exothermic process?
Heat is absorbed
It requires absorption of 334 Joules of energy to melt one gram of ice. What type of process is this?
Endothermic
Our modern power plants operate through a series of events. Which of the following events doesn’t happen in the modern power plant?
Light energy of the sun is converted into kinetic energy.
Why don't modern fossil fuel power plants operate at 100% efficiency?
It is impossible to operate at 100% efficiency as unorganized energy is transformed to organized energy.
intermolecular forces
bonds holding molecules together in solid/liquid
phase) are broken in vaporization
Biodiesel
fuel is made from natural, renewable sources
Bioethanol
is renewable, but more expensive than gasoline.
Geothermal
heat from the core of the Earth