Conventional Tomography
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is conventional tomography?
A radiographic technique that is designed to bring into focus only that anatomy lying in a plane of interest while blurring structures on either side of the plane
What is the tomographic principal?
The x-ray tube and image receptor move in opposite directions around a stationary fulcrum (pivot point) during the exposure
An object placed in the fulcrum will appear ______, while objects outside the focal plane will appear ________
Sharp, blurred
The greater the distance from the fulcrum, the _____ the blurring
Greater
What is blur?
Loss of nearly all recorded detail of objects outside the focal plane
The tomographic amplitude (TA) is the ___________ the tube travels (always equal to or greater than the exposure amplitude)
Total distance
The exposure amplitude (EA) is the distance the tube travels during?
The exposure
Fulcrum
Pivot point around which the tube and IR move
Focal plane (or object plane)
Area within the image that is in focus and shows satisfactory detail
What is the Grossman Principal?
The fulcrum is fixed and the patient (table height) is moved up and down to change the focal (section) level
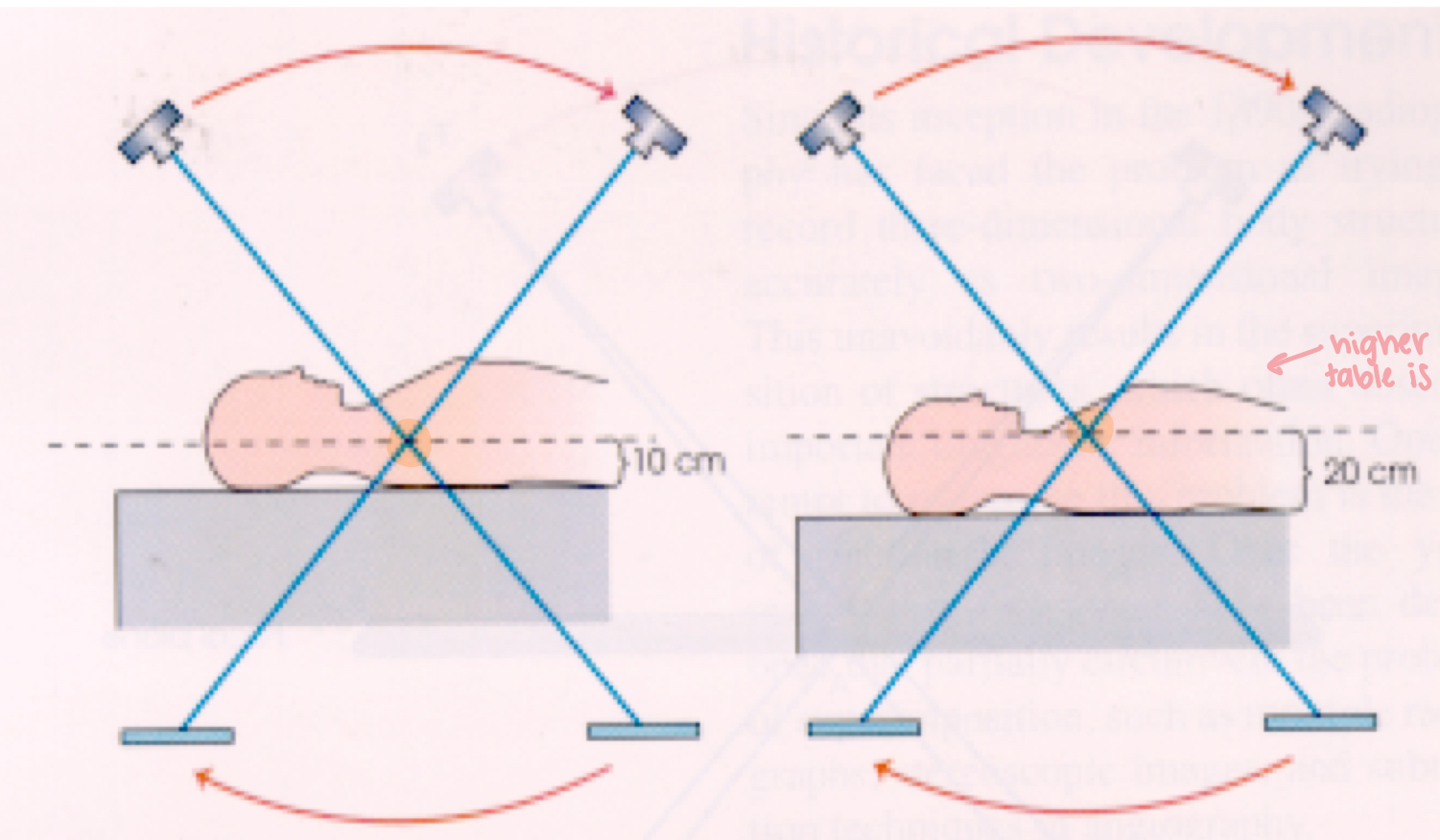
What is this image demonstrating?
Grossman principal
What is the Planigraphic principal?
The fulcrum is adjustable while the patient remains stationary (most common)
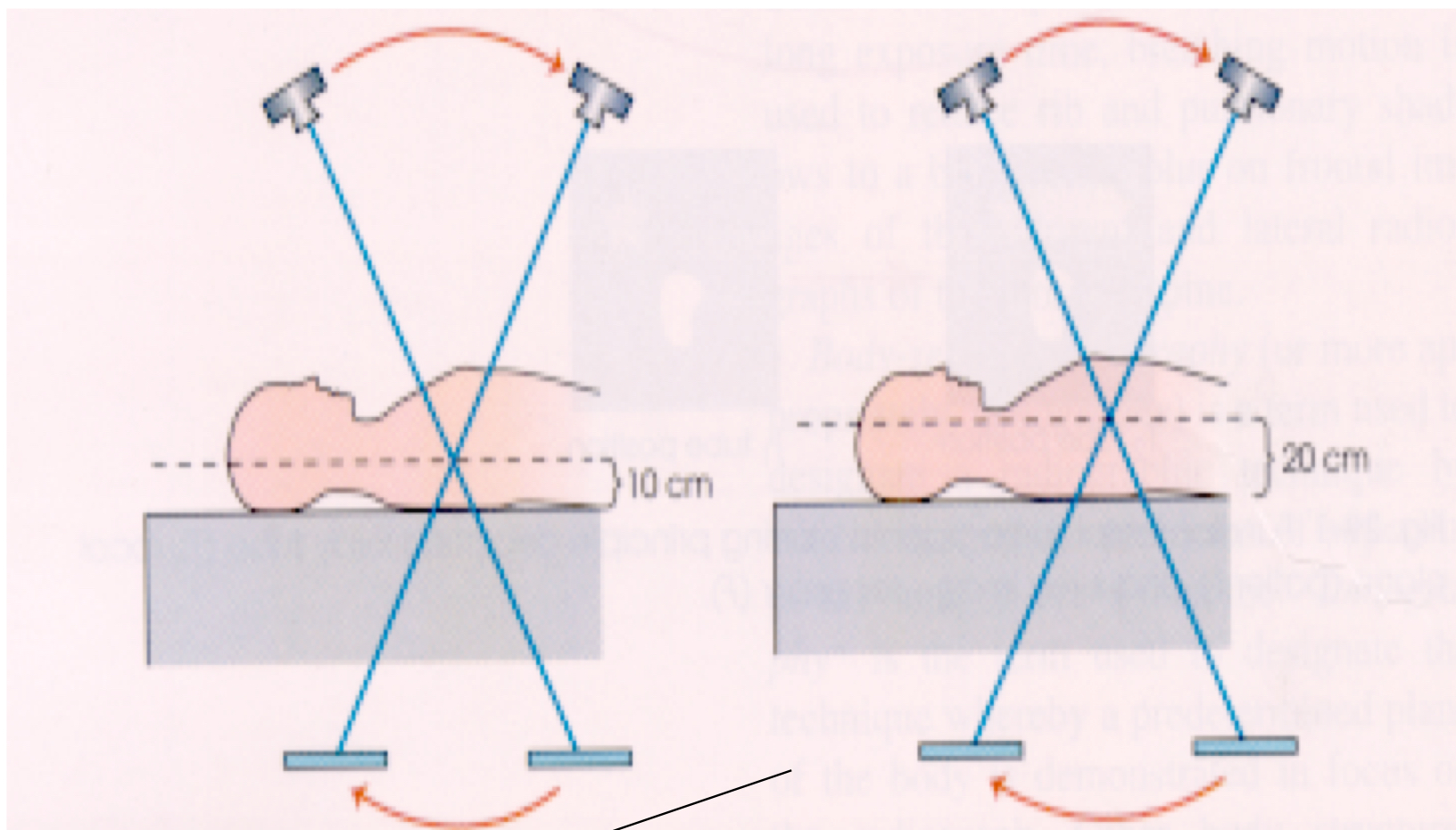
What is this image demonstrating?
Section (slice) thickness
depth of the focal plane (area within focus)
controlled by the exposure angle/amplitude
The exposure angle is ______ proportional to the section thickness
Inversely
The ______ the angle (the more the tube in moving), the thinner the slice
Greater
What is the exposure angle for regular x-ray?
0
Section interval
the distance between the fulcrum levels of successive slices
should not exceed the section thickness
What is the tomographic tube movement usually?
Linear or complex (pluri-directional)
Linear tube movement
the simplest motion
tube travels in a straight line
the SID and OID change during tube travel
used for and IVU
The tube motion should be _________ to the long axis of the object
Perpendicular
The total tomographic arc is limited to ____ degrees
48
What are the complex tube movements?
curvilinear (maintains SID and OID)
circular
elliptical
figure eight
trispiral
hypocycloidal
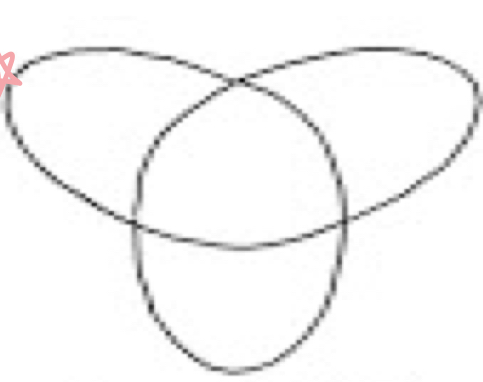
What tube movement is this?
Hypocycloidal
Tri-spiral and hypocycloidal movements give the ________ tomographic amplitudes and the ________ cut
Maximum, thinnest
What are try-spiral and hypocycloidal movements used for?
Carpal bones and the auditory ossicles
Complex motions often require ____ to _____ second exposures
3-6
What does a long exposure time mean for your mA?
Small mA
Zonography
specialized tomographic procedure
usually 1-5 degree angles are used
large slice thickness
used to located a lesion when the exact location is unknown (ex: lung lesion)
Panoramic tomography
slit scan radiography of the curved surfaces
used for the mandible, teeth, facial bones, etc
both the tube and the film rotate past the slit during the exposure
What line has to be parallel to the floor for panoramic tomography
IOML
Where does the fulcrum go for panoramic tomography?
Middle of head