Transition metals L2
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
two coordinate
complexes involve a central metal atom bonded to two ligands, forming linear structure
three coordinate
quadrupole complexes involve a central metal atom bonded to three ligands, typically trigonal planar
four coordinate
complexes involve a central metal atom bonded to four ligands, typically forming a tetrahedral (common first row) or square planar geometry. (90 bond angles common 2nd 3rd row TMs w/ d8 config)
five coordinate
complexes involve a central metal atom bonded to five ligands, often forming a trigonal bipyramidal or square pyramidal geometry.
six coordinate
complexes involve a central metal atom bonded to six ligands, typically forming an octahedral geometry.
ionisation isomers (type of structural)
Same empirical formula but different inner sphere / outer sphere combinations
hydration isomers
Same empirical formula but different inner sphere / outer sphere combinations
involving water exchange
linkage isomer
Same empirical formula but different ways of bonding a ligand to the metal, often involving different donor atoms.
coordination isomers
the anion and cation complexes of a coordination
compound exchange one or more ligands
geometric isomer
the anion and cation complexes of a coordination
compound exchange one or more ligands (cis and transplatin, mer and fac)
tetrahedral complex with chiral centers have enantiomers as non-superimposable
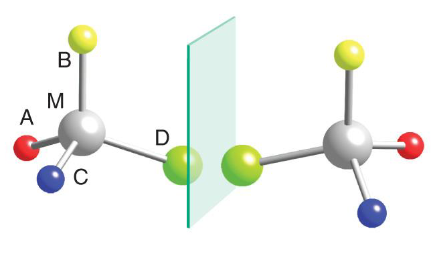
Octahedral bis- and tris-chelate complexes