Bio 2 Exam 1
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
phylogeny
the evolutionary history and relationship of an organism or group of organisms
phylogenetic tree
is a diagram used to reflect evolutionary relationships among organisms or groups of organisms (they are hypothesis because we will fully know their extent)
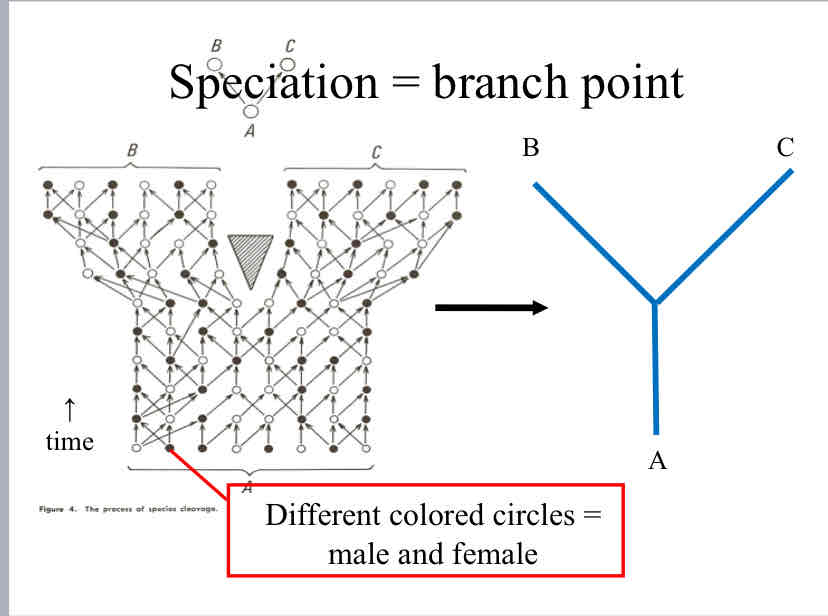
branch point
the point where a split occurs, and represents where a single lineage evolved into a distinct new one due to the environment.
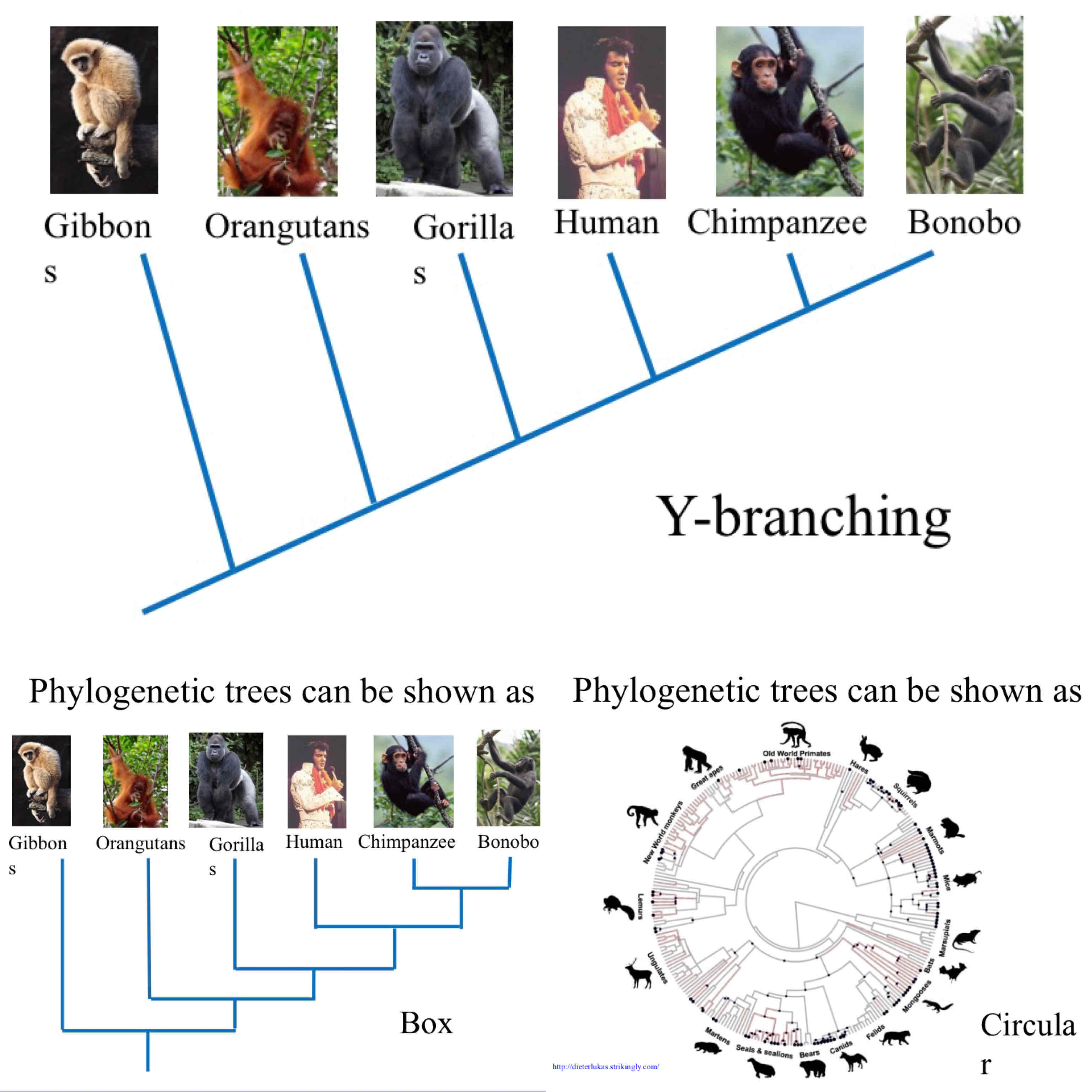
The 3 types of phylogenetic trees
Y- Branching, Box, and Circular
Parsimony
means that events occurred in the simplest, most obvious way (with the fewest changes)
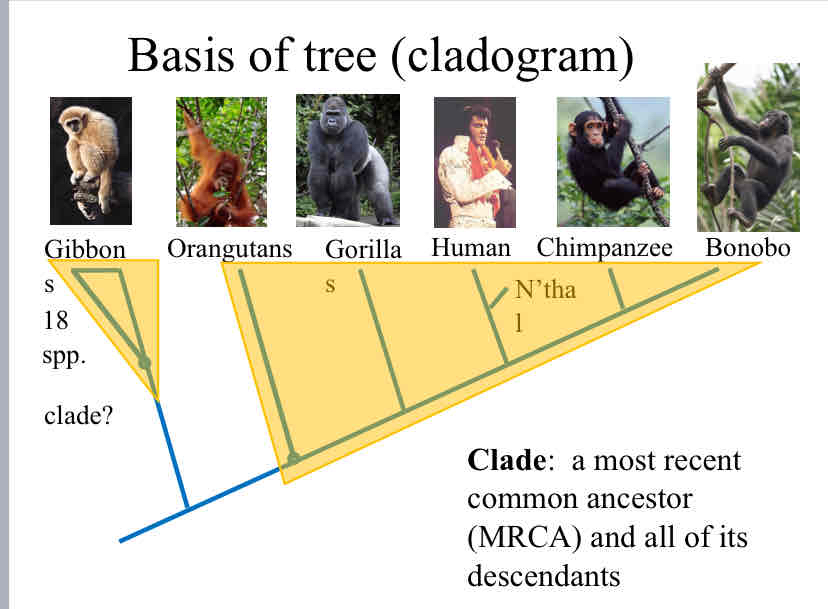
Clade
a most recent common ancestor (MRCA) and all of its descendants
MRCA
Most Recent Common Ancestor
Sister Taxa
two species or clades that are each other’s closest relatives on a given tree
Homology
shared traits that came from a common ancestor due to the similarities
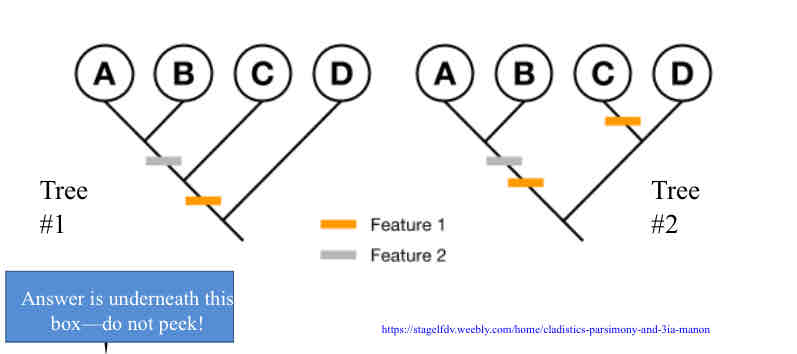
Practice Question (Parismony) - Which tree below is most parsimonious (has the maximum parsimony)?
Tree #1
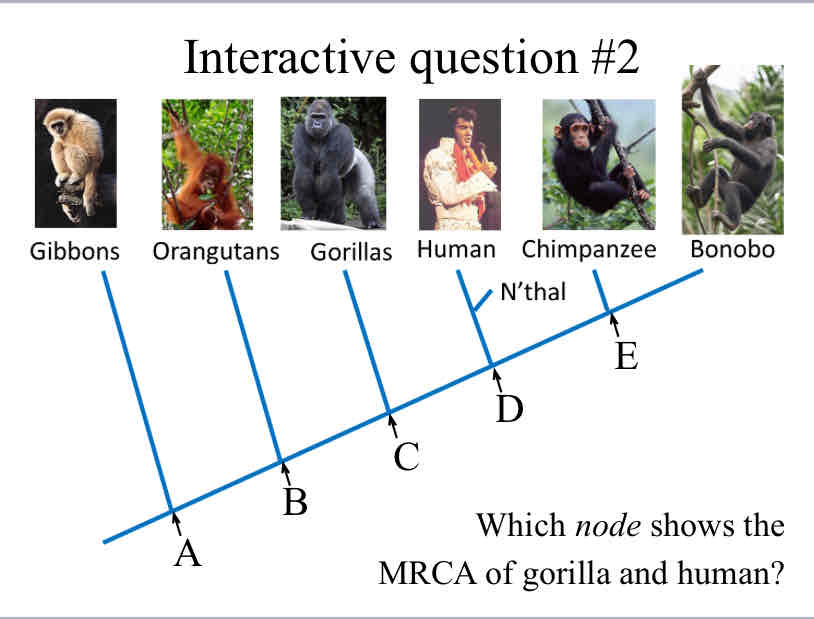
Practice Question (MRCA) - Which node shows the MRCA of gorilla and human?
C
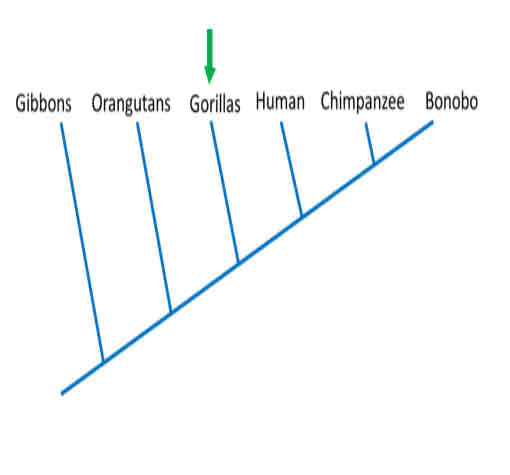
According to this tree, the closest relatives (sister taxa) of gorillas are
Humans + chimpanzees + bonobos
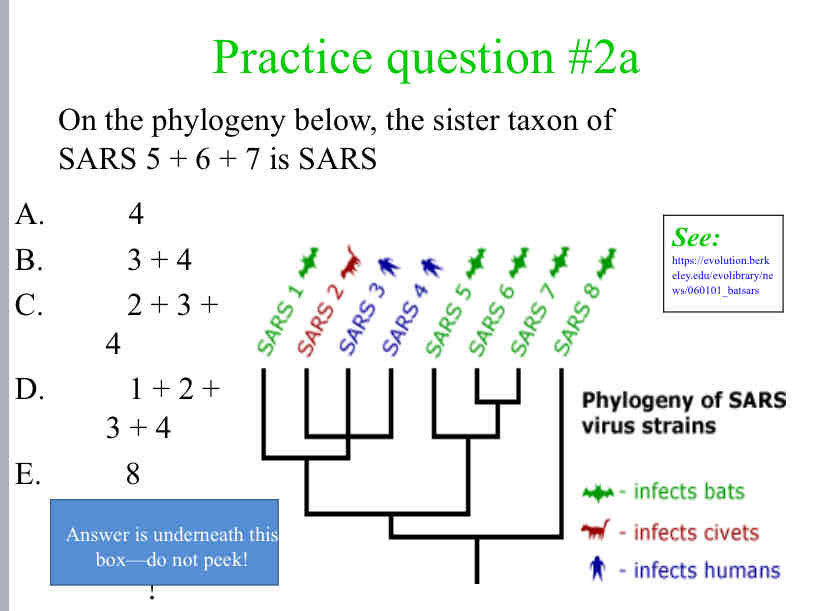
Practice Question (Sister Taxa) - On the phylogeny below, the sister taxon of SARS 5 + 6 + 7 is SARS
8
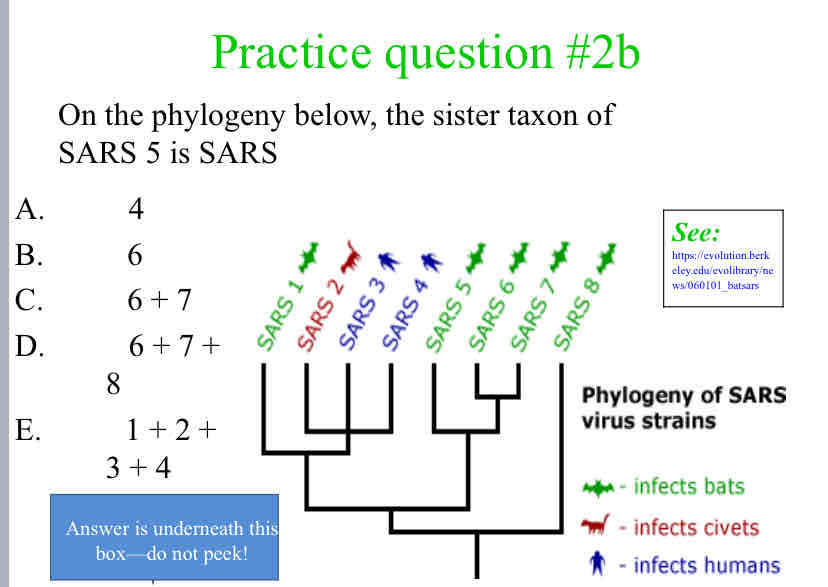
Practice Question (Sister Taxon) - On the phylogeny below, the sister taxon of SARS 5 is SARS
6 + 7 + 8
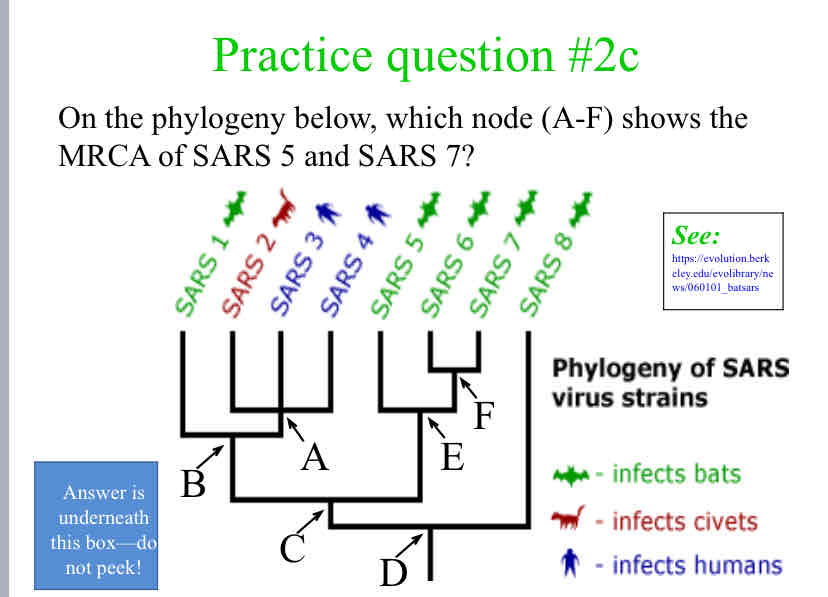
Practice Question (MRCA) - On the phylogeny below, which node (A-F) shows the MRCA of SARS 5 and SARS 7?
E
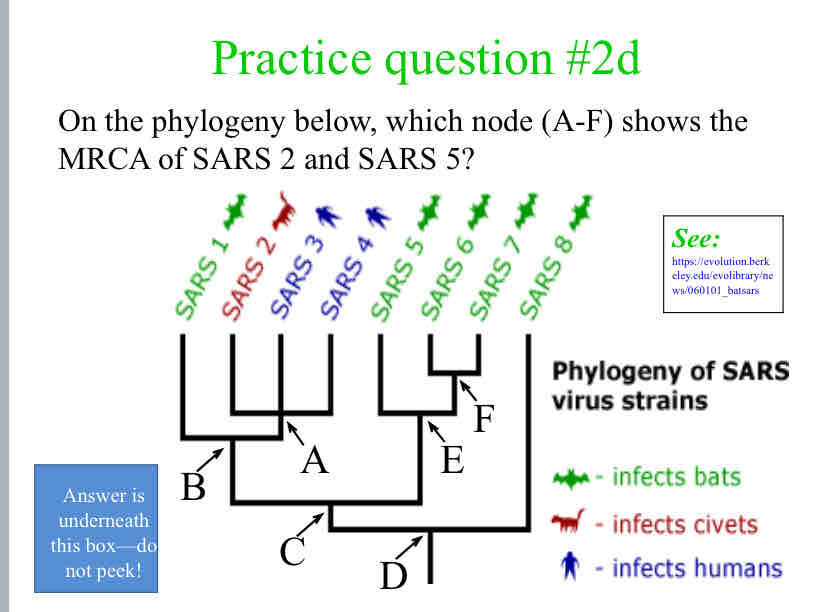
Practice Question (MRCA) - On the phylogeny below, which node (A-F) shows the MRCA of SARS 2 and SARS 5?
C

Practice Question (MRCA) - Which letter (A-E) shows the MRCA of platypus and elephant?
D
Ancestral Trait
old trait that came before
Derived Trait
new trait that came after
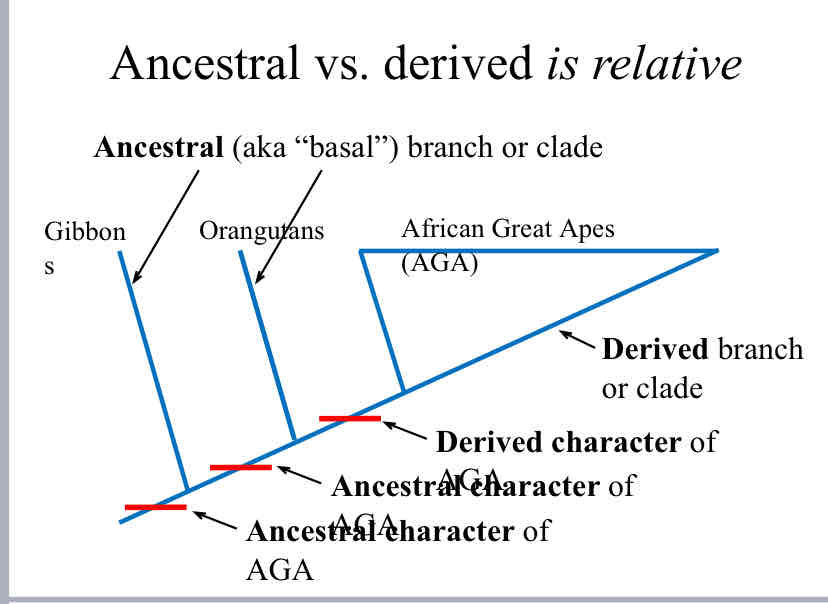
Ancestral vs. Derived traits are
relative
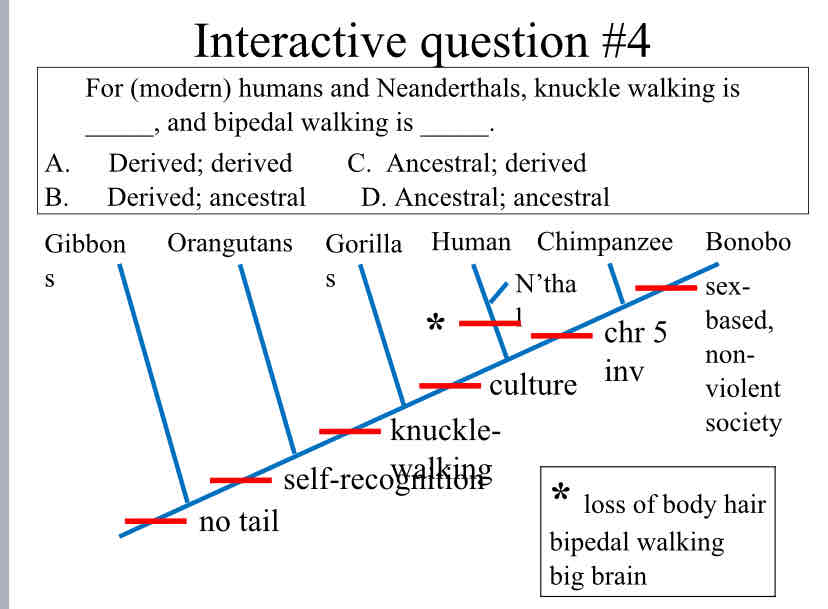
Practice Question (Traits) - For (modern) humans and Neanderthals, knuckle walking is _____, and bipedal walking is ____.
Ancestral ; Derived
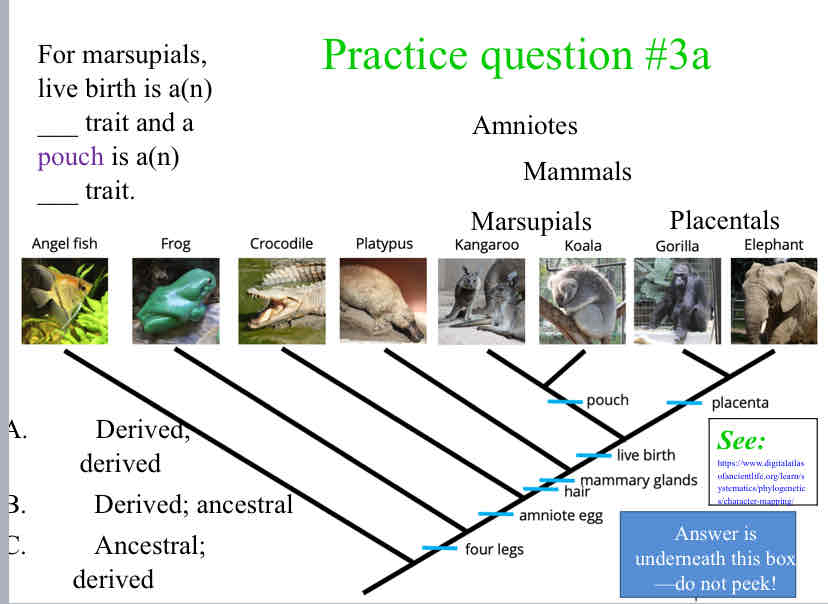
Practice Question (Traits) - For marsupials, live birth is a(n) ___ trait and a pouch is a(n) ___ trait.
Ancestral ; Derived
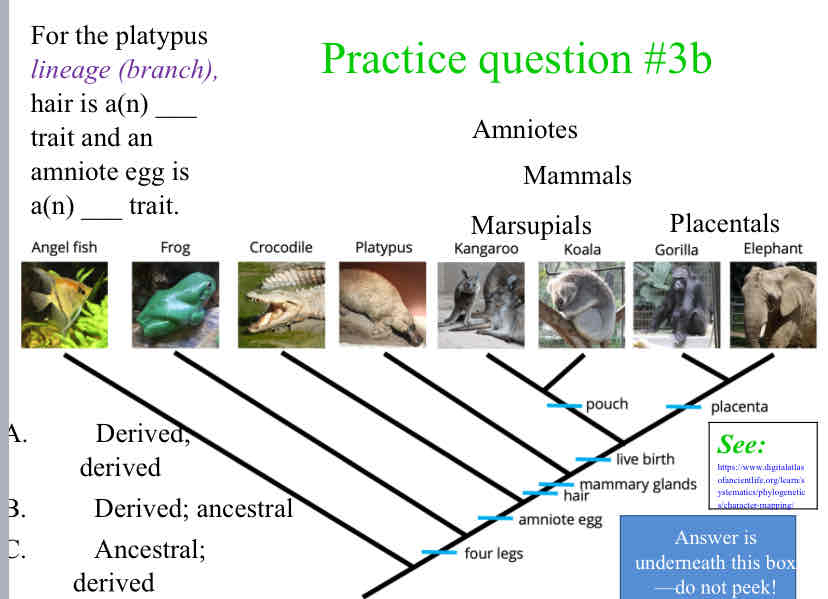
Practice Question (Traits) - For the platypus lineage (branch), hair is a(n) ___ trait and an amniote egg is a(n) ___ trait.
Derived ; Ancestral
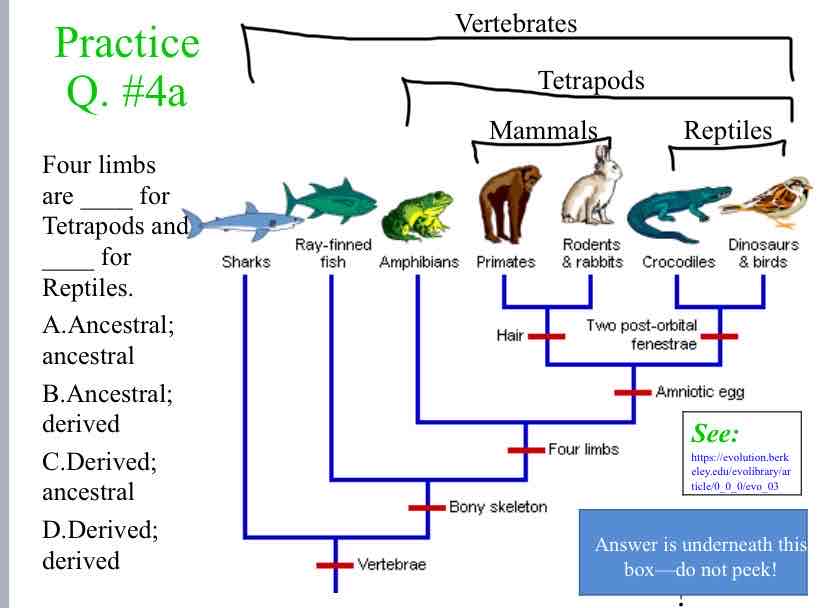
Practice Question (Traits) - Four limbs are ____ for Tetrapods and ____ for Reptiles.
Derived ; Ancestral
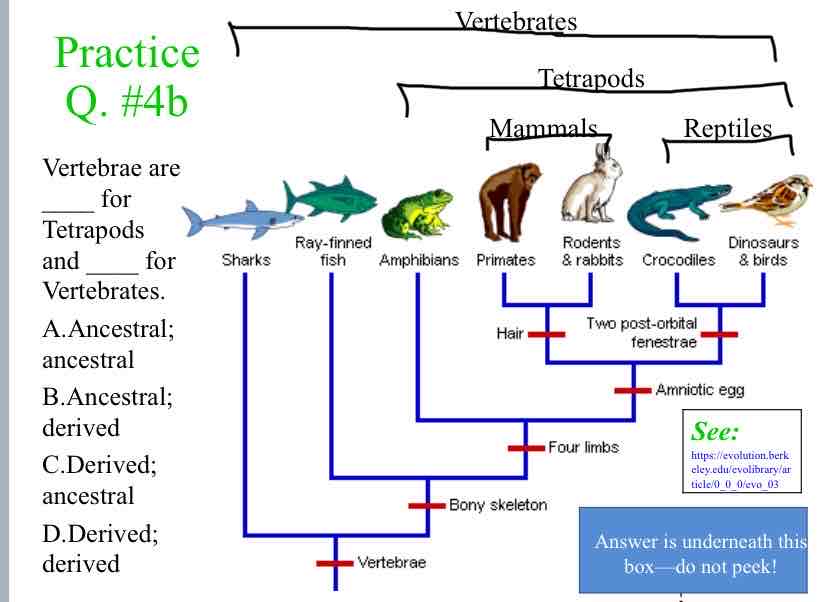
Practice Question (Traits) - Vertebrae are ____ for Tetrapods and _____ for Vertebrates.
Ancestral ; Derived
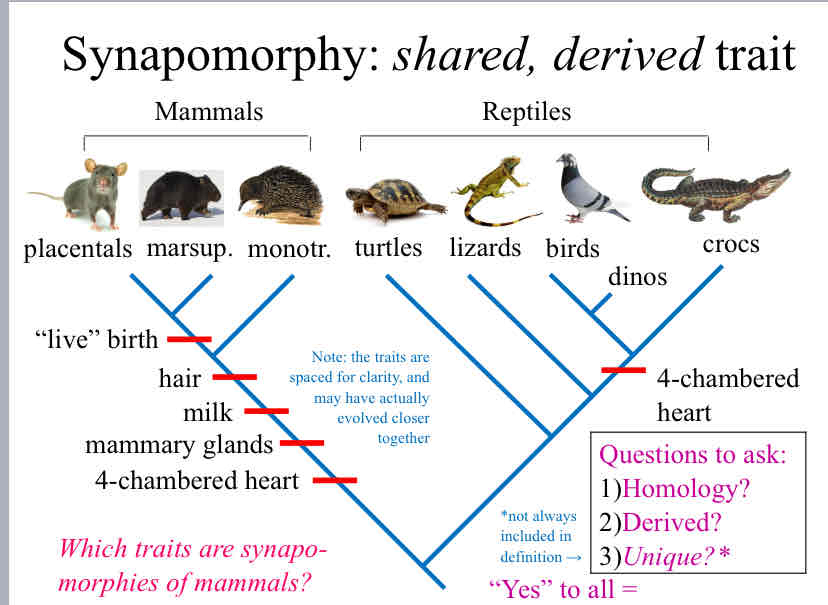
Synapomorphy
a shared, derived trait
3 questions to determine them
1) Homology? are they shared
2) Derived ? is it a new trait
3) Unique ? are the traits unique to the organism or group
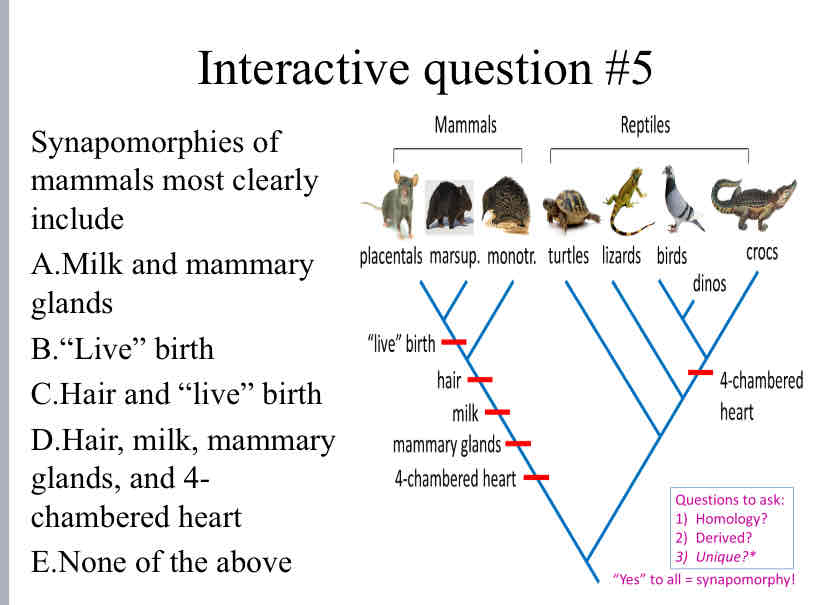
Practice Question (Synapomorphies) - Synapomorphies of mammals most clearly include
Milk and mammary glands
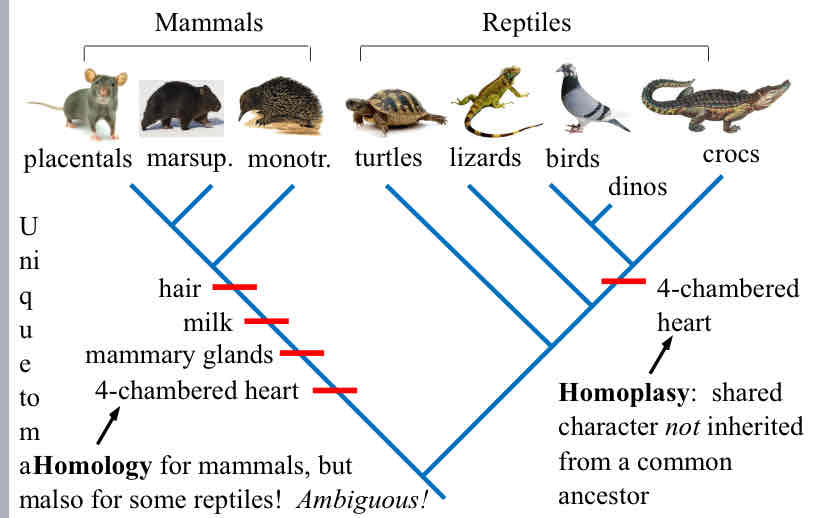
Homoplasy
shared character not inherited from a common ancestor
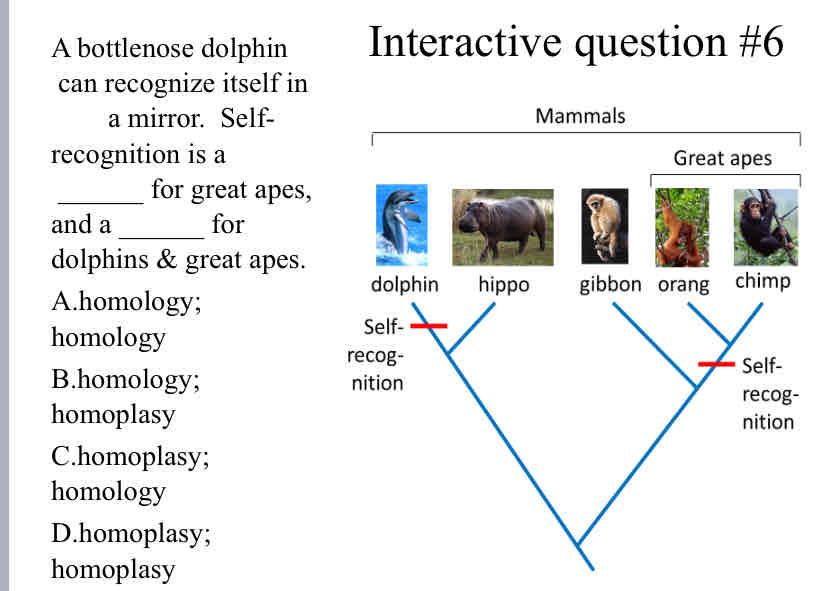
Practice Question (Shared Traits) - A bottlenose dolphin can recognize itself in a mirror. Self-recognition is a ______ for great apes, and a ______ for dolphins & great apes.
Homology ; Homoplasy
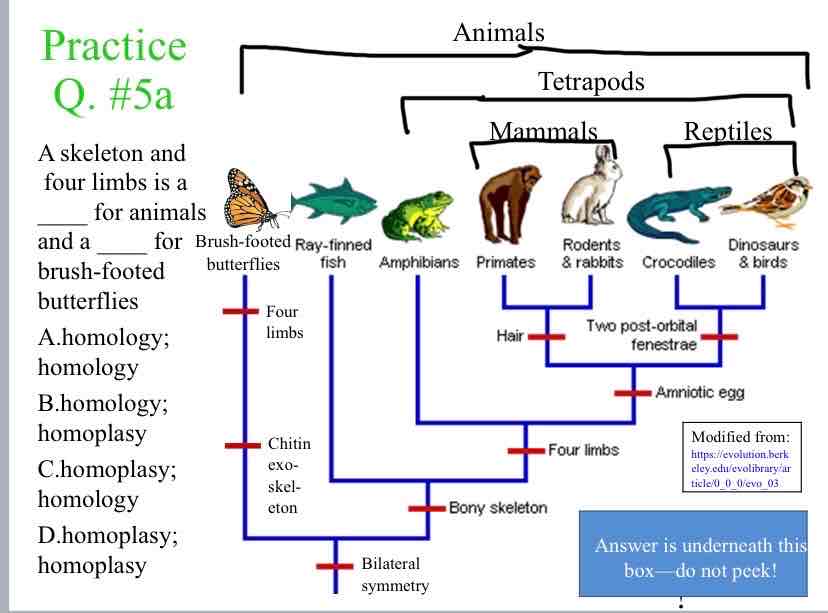
Practice Question (shared traits) - A skeleton and four limbs is a ____ for animals and a ____ for brush-footed
Homoplasy ; Homology
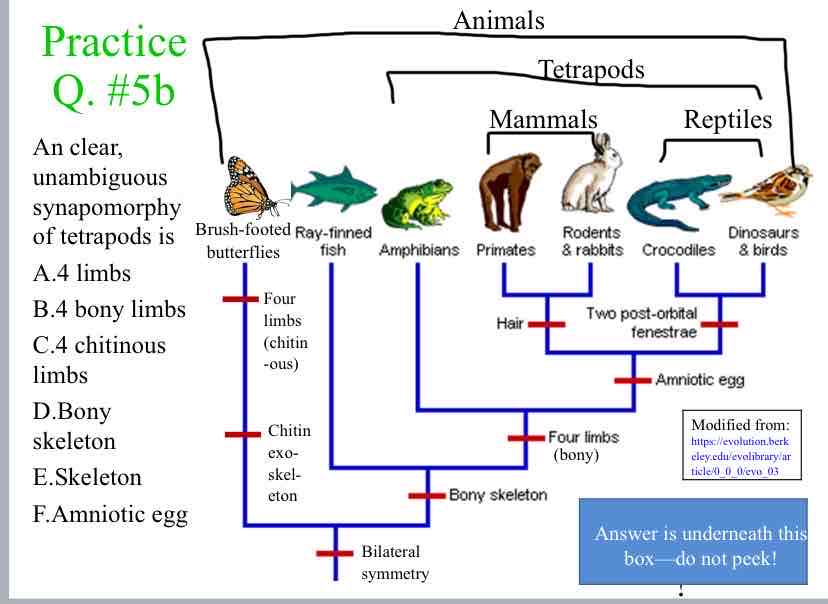
Practice Question (Shared Traits) - An clear, unambiguous synapomorphy of tetrapods is
4 bony limbs
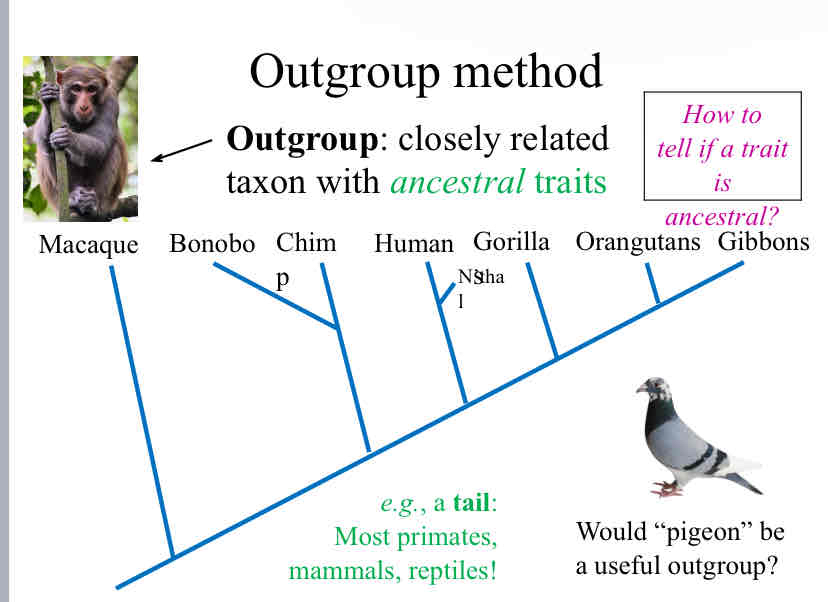
Outgroup
closely related taxon with ancestral traits
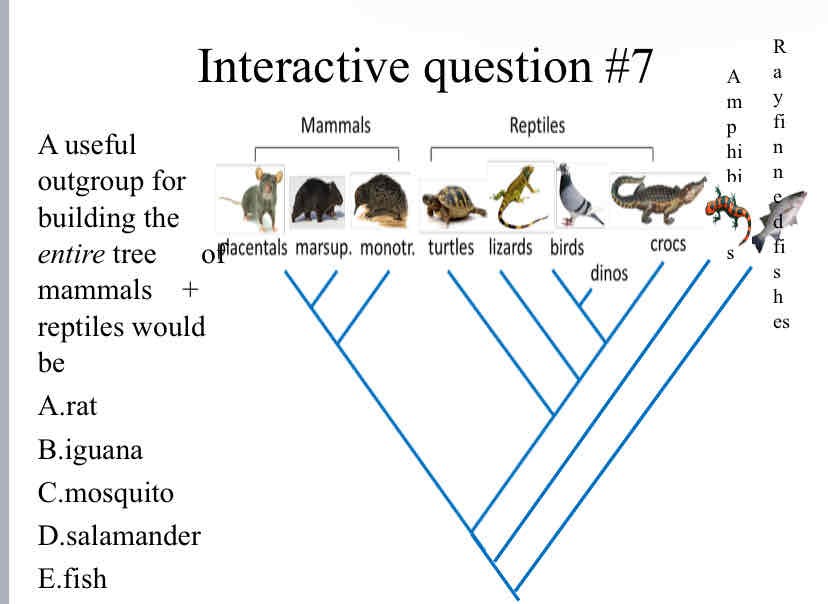
A useful outgroup for building the entire tree of mammals + reptiles would be
Salamander
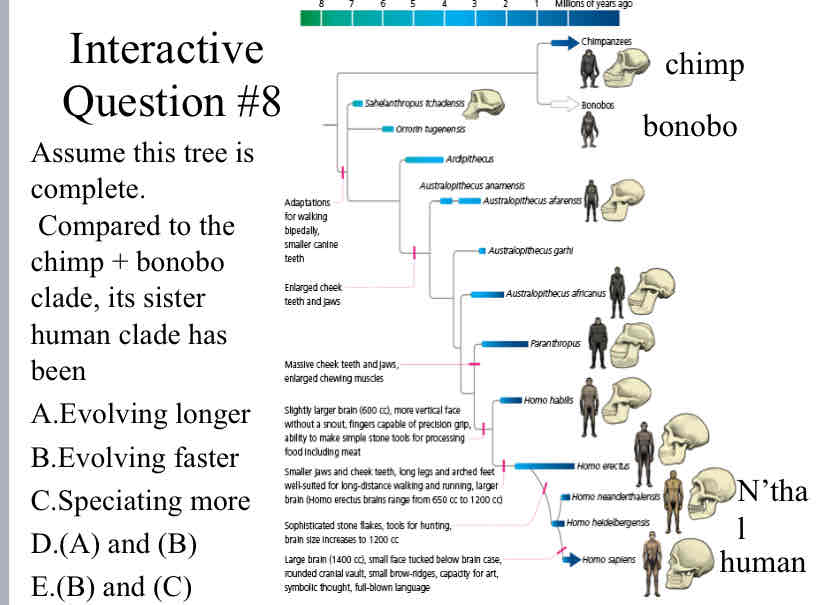
Assume this tree is complete. Compared to the chimp + bonobo clade, its sister human clade has been
(B) and (C)
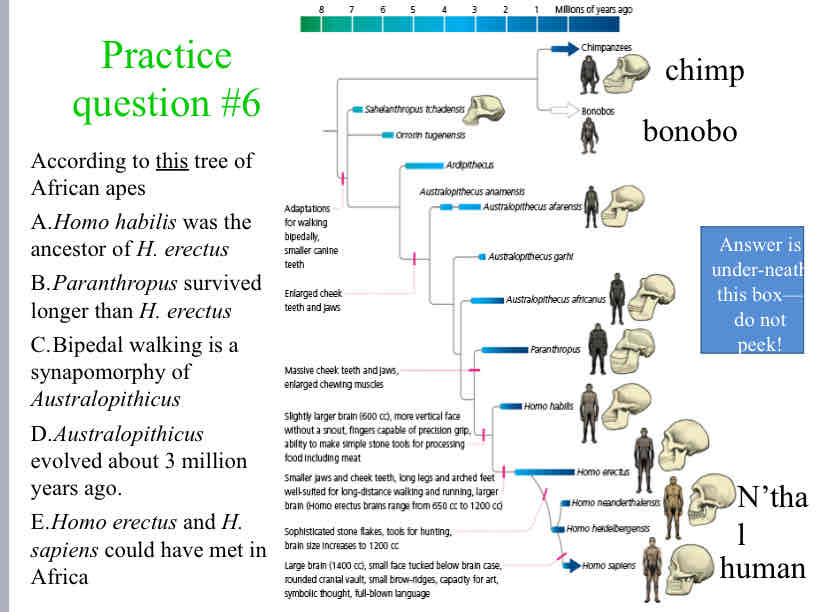
According to this tree of African apes
Homo erectus and H. sapiens could have met in Africa
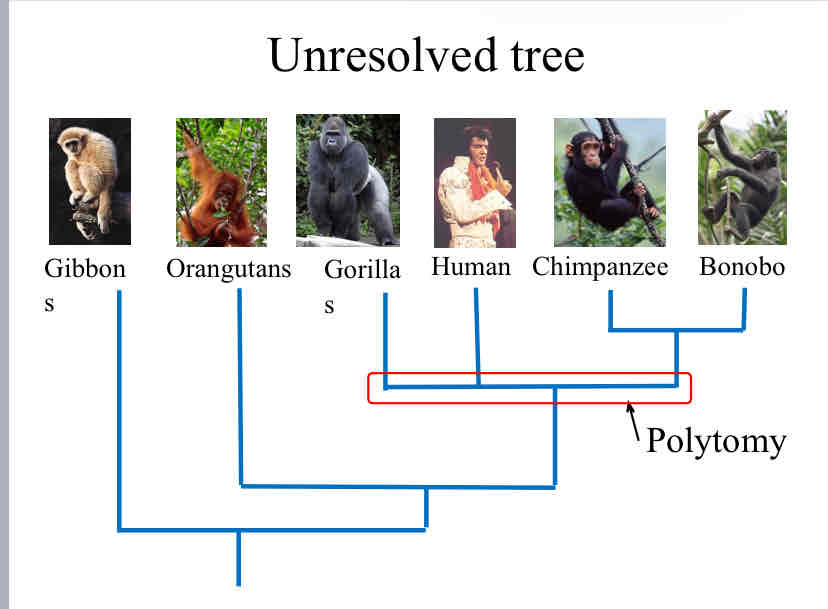
Polytomy
A node on a phylogeny where more than two lineages descend from a single ancestor
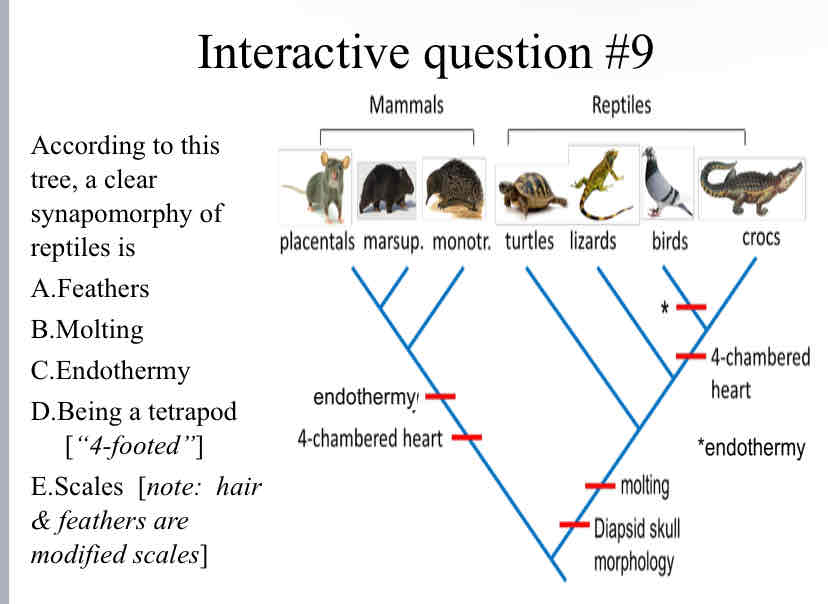
According to this tree, a clear synapomorphy of reptiles is
Molting
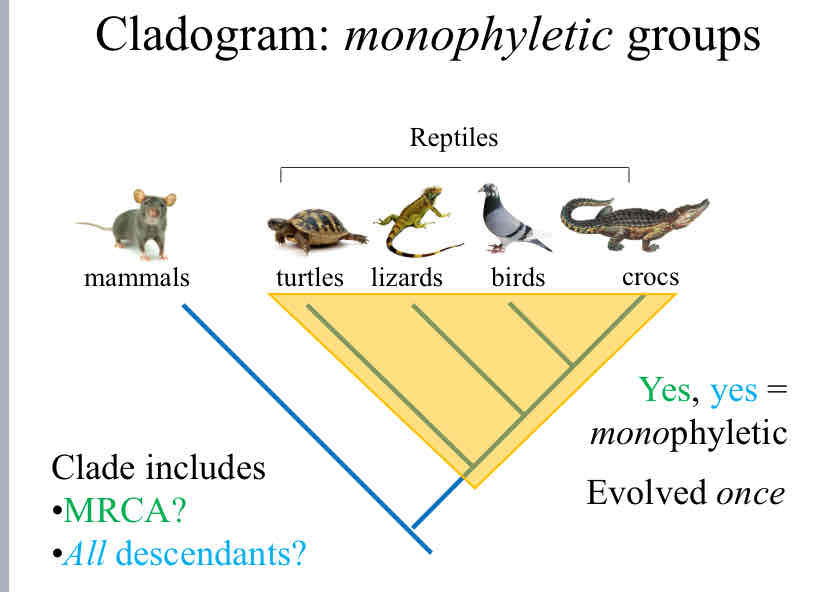
Monophyletic
when a group includes a most recent common ancestor and ALL of it’s descendants
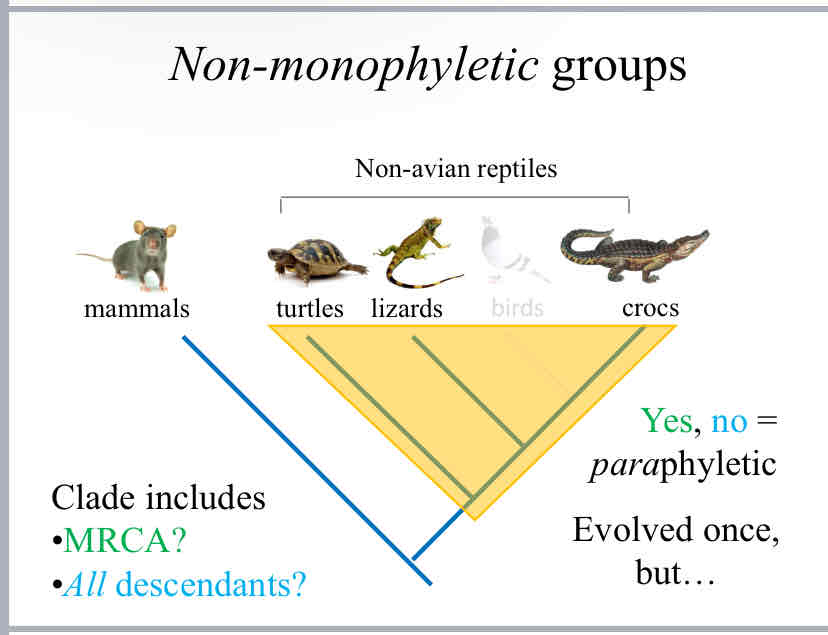
Paraphyletic
when a group includes a most recent common ancestor and some of its descendants
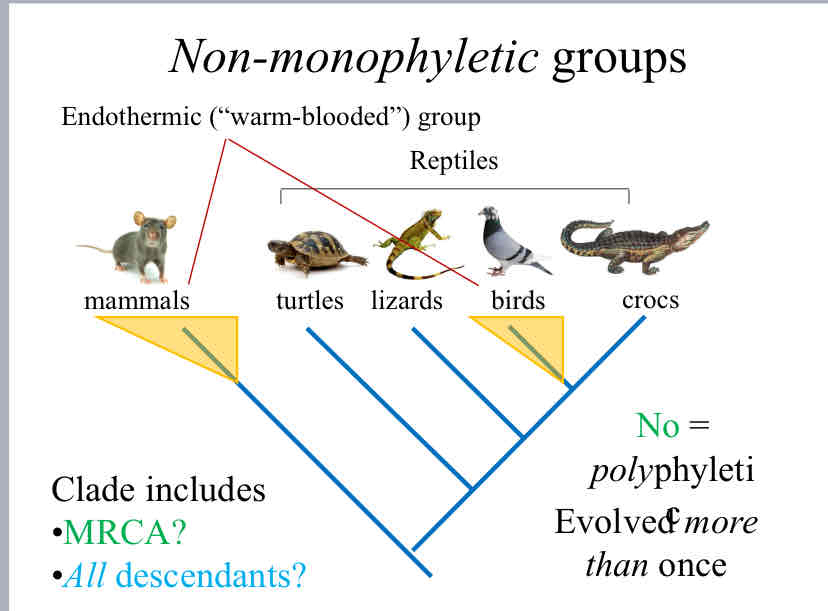
Polyphyletic
groups that share traits however they have a different most recent common ancestor
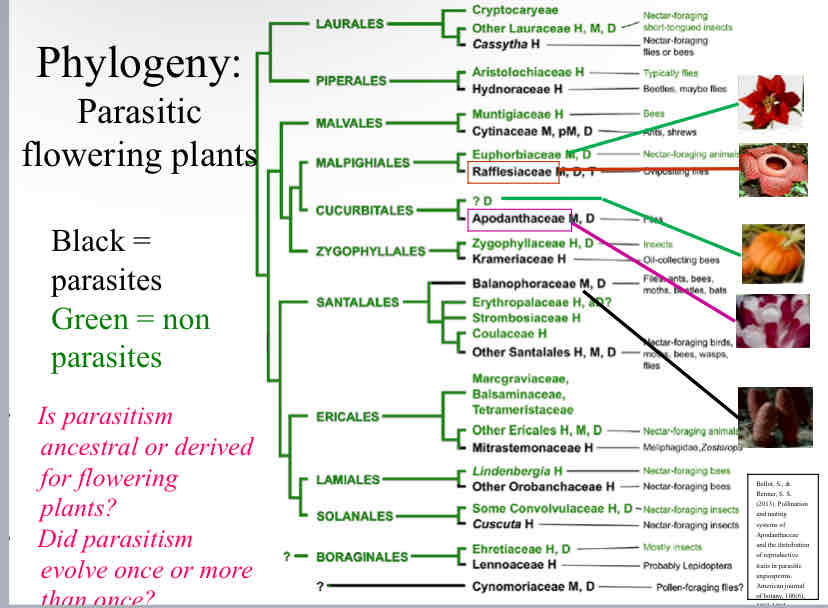
Parasitic Plants (those in blackshow) are show to be what type of group ?
Polyphyletic
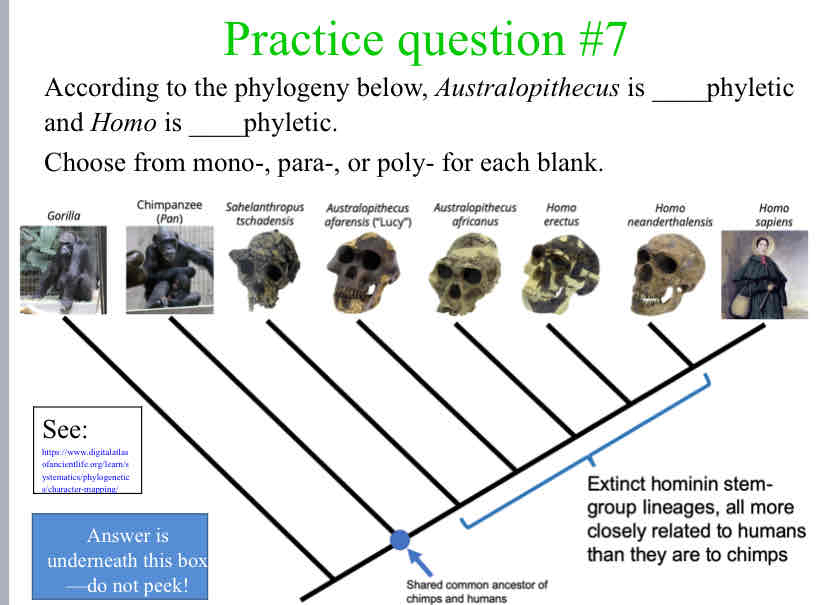
According to the phylogeny below, Australopithecus is ____phyletic and Homo is ____phyletic.
Para ; Mono
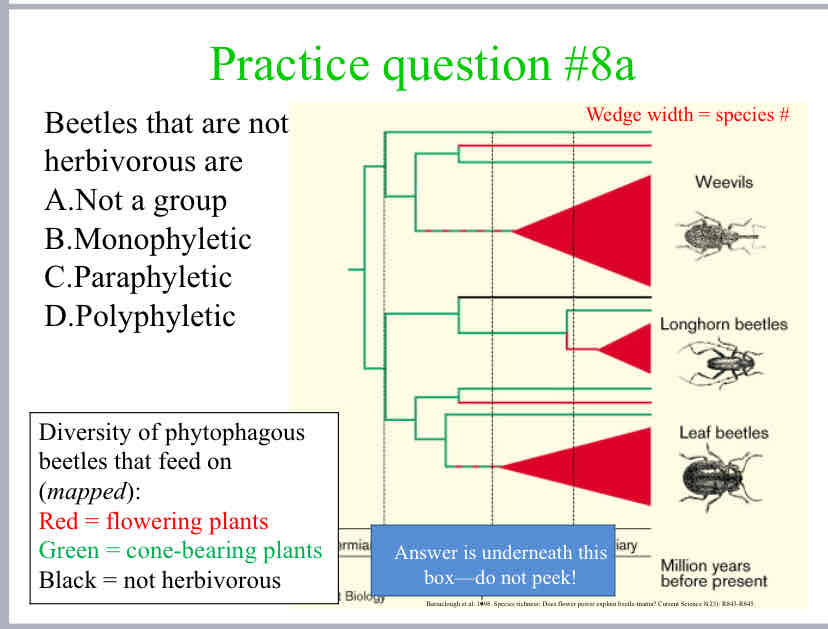
Beetles that are not herbivorous are
Monophyletic
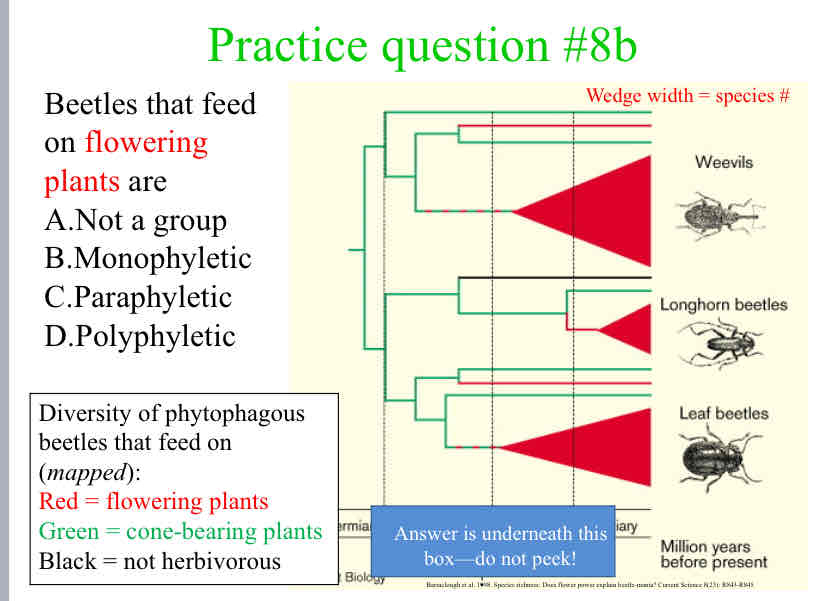
Beetles that feed on flowering plants are
Polyphyletic
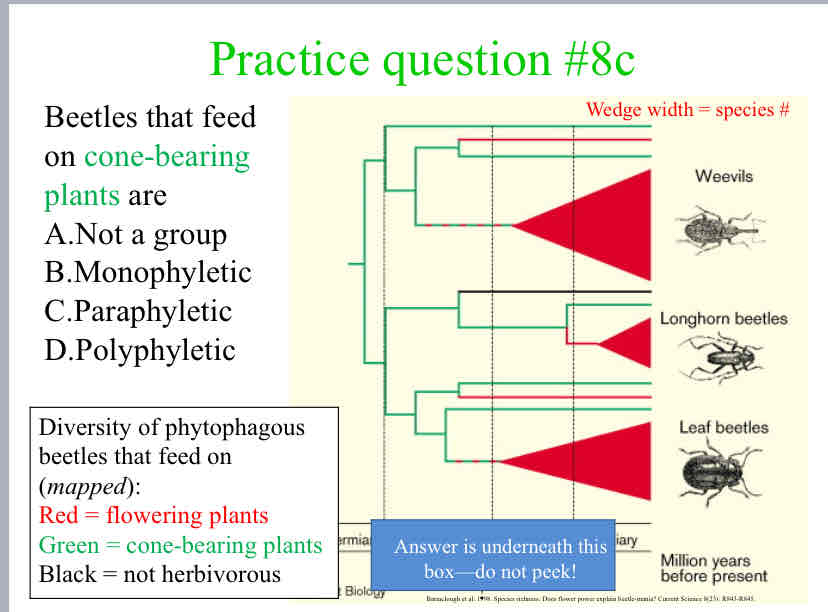
Beetles that feed on cone-bearing plants are
Paraphyletic
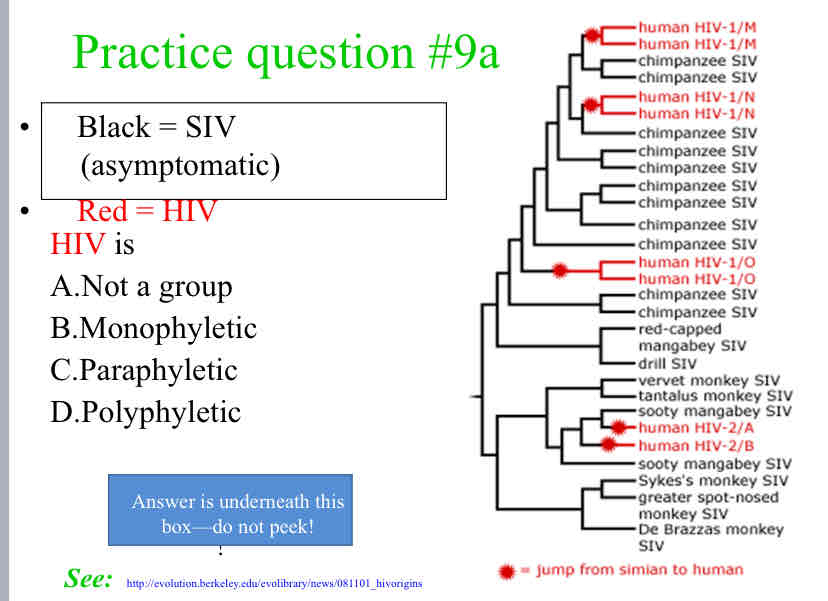
HIV is
Polyphyletic
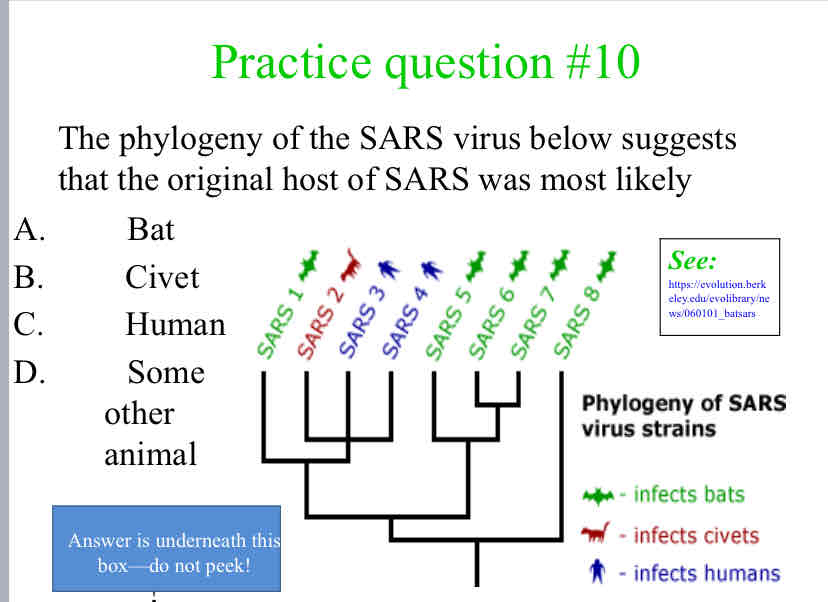
The phylogeny of the SARS virus below suggests that the original host of SARS was most likely
Bat
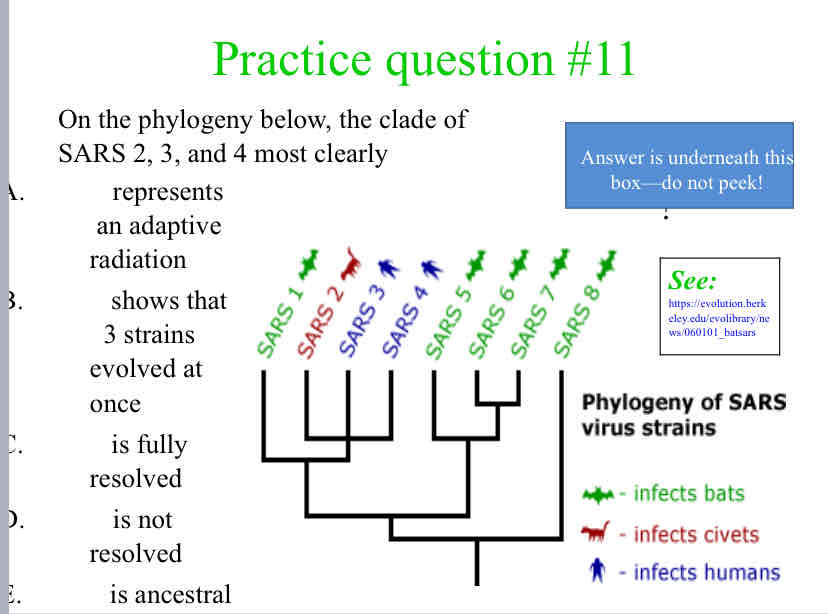
On the phylogeny below, the clade of SARS 2, 3, and 4 most clearly
is not resolved
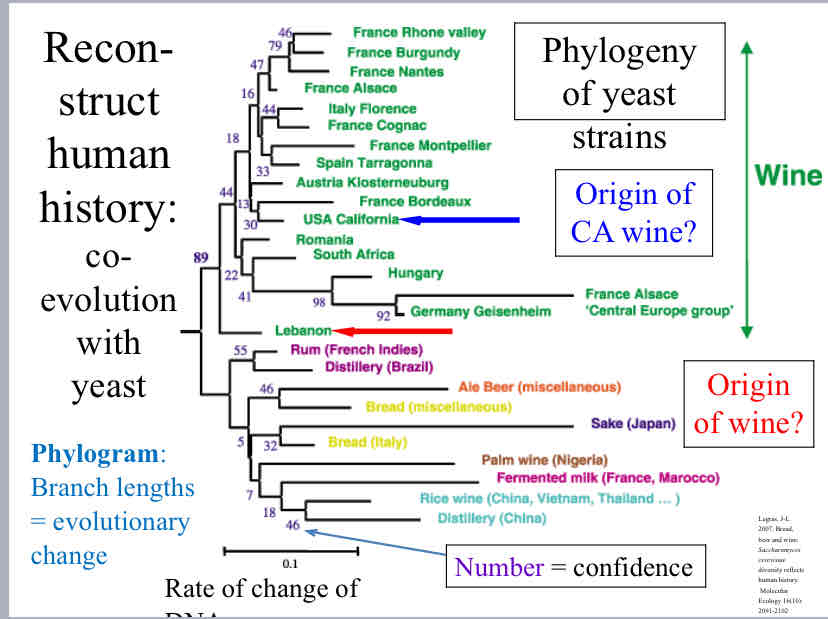
Phylogram
a type of phylogenetic tree where the branch lengths signify evolutionary change

Big Bang
theory on how the universe expanded from a single point of high density and temperature
Supernovas
they are early stars made from dust and gas
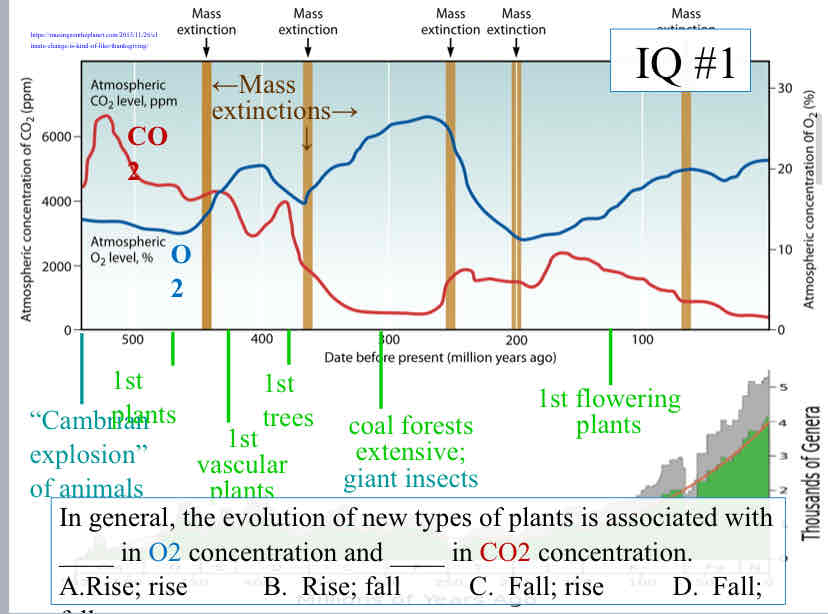
Practice Question (Life’s Origins) - In general, the evolution of new types of plants is associated with ____ in O2 concentration and ____ in CO2 concentration
Rise ; Fall
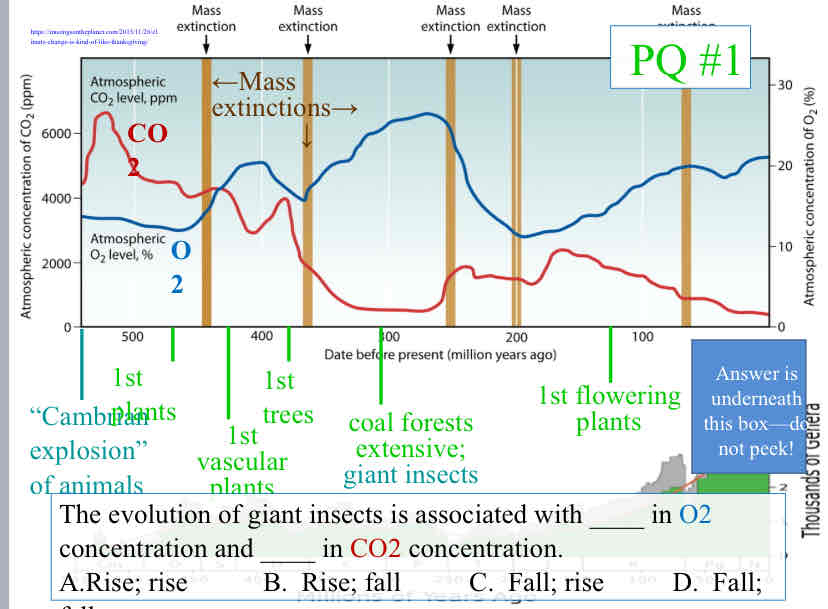
Practice Question (Life’s Origins) - The evolution of giant insects is associated with ____ in O2 concentration and ____ in CO2 concentration
Rise ; Fall
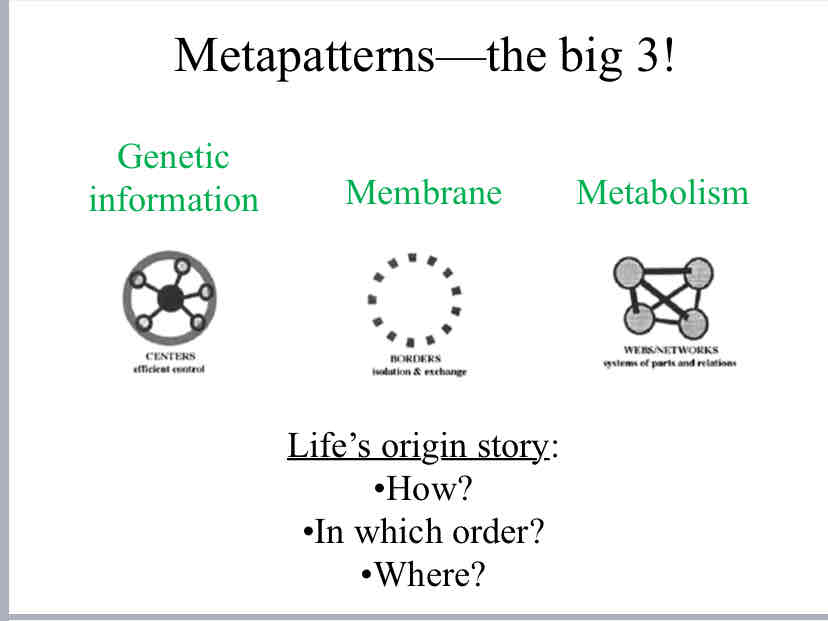
Big 3 Metapatterns
Genetic Information
Membrane
Metabolism (Chemical Reaction)
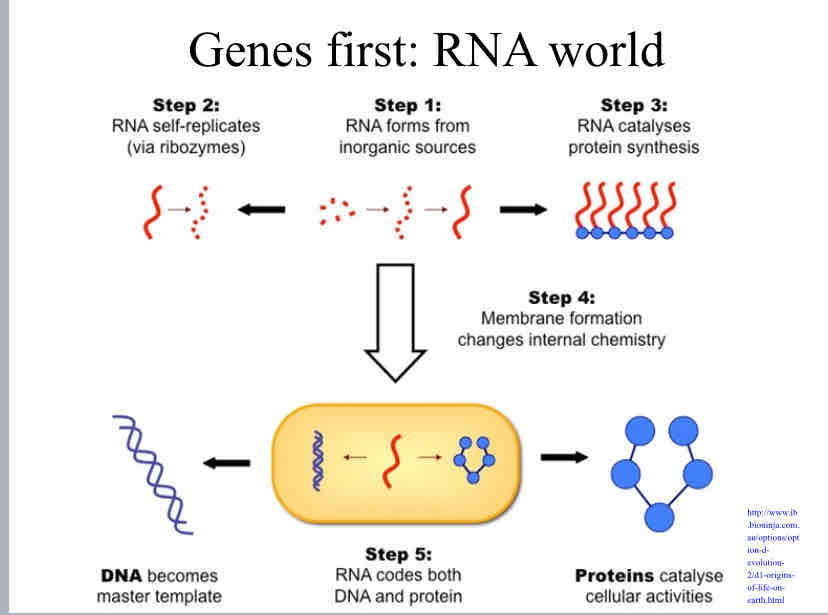
Genes First Hypothesis
States that life began from self replicating RNA.
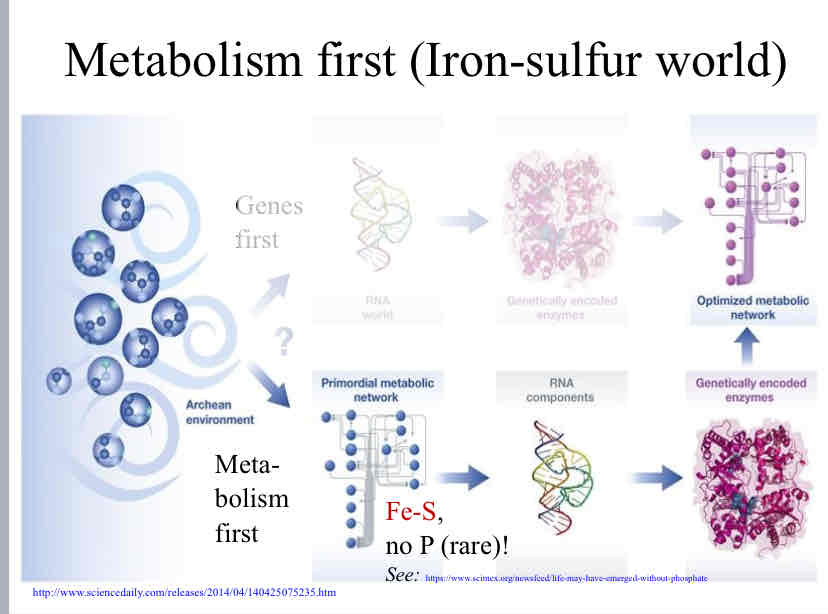
Metabolism First Hypothesis
States that life began from chemical reactions placing them before genetic material
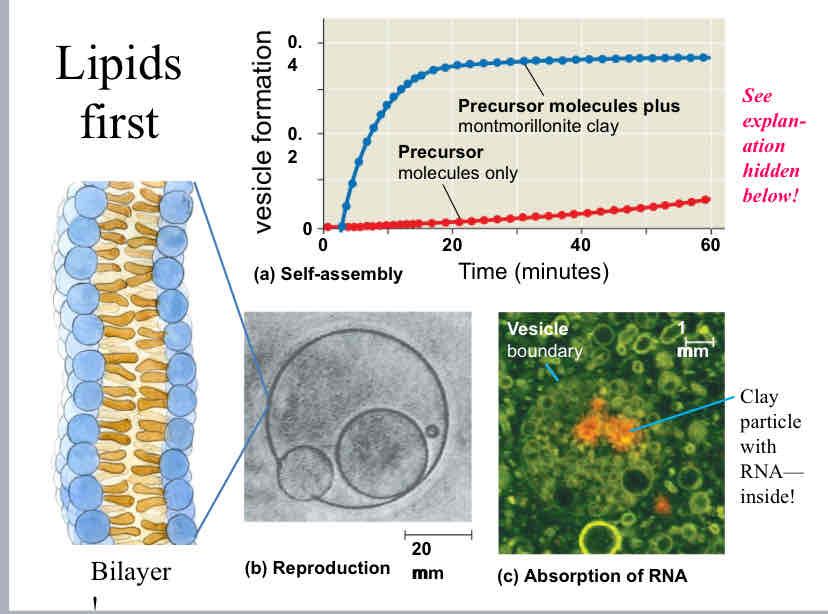
Lipids first hypothesis
States life began from self-assembling structures.

Practice Question (Early Earth) - Compared to volcanic vents, snowball Earth would have _____ energy available for chemical synthesis, and organic molecules that formed would be ____ stable.
Less; More

Practice Question (Origins of Life) - "Intelligent design" (creationism) is not a scientific hypothesis because it is not
Testable
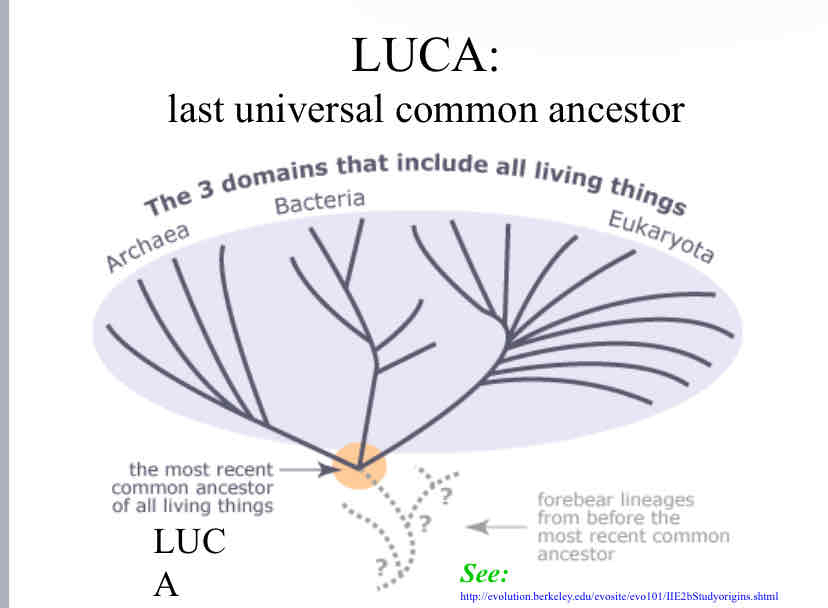
LUCA
Last Universal Common Ancestor
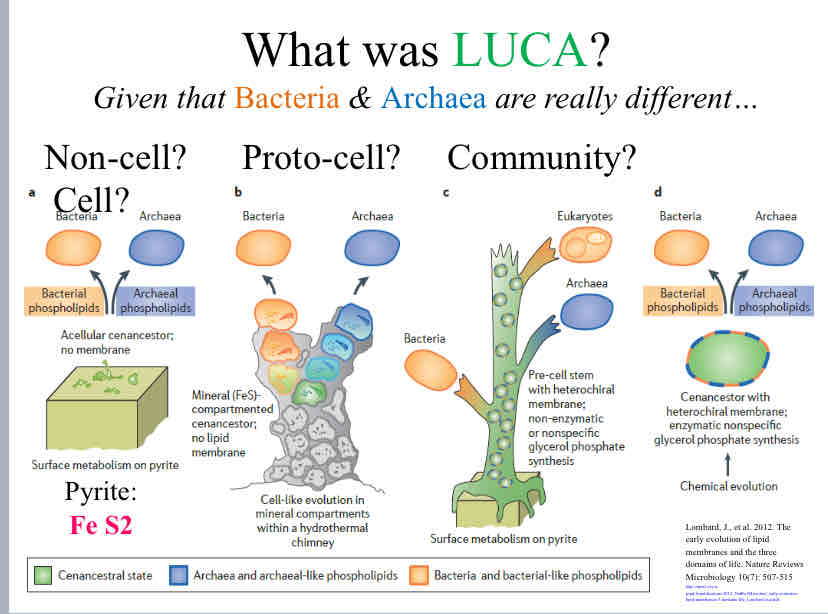
Luca Hypothesis
Non Cell
Proto - Cell
Community
Cell
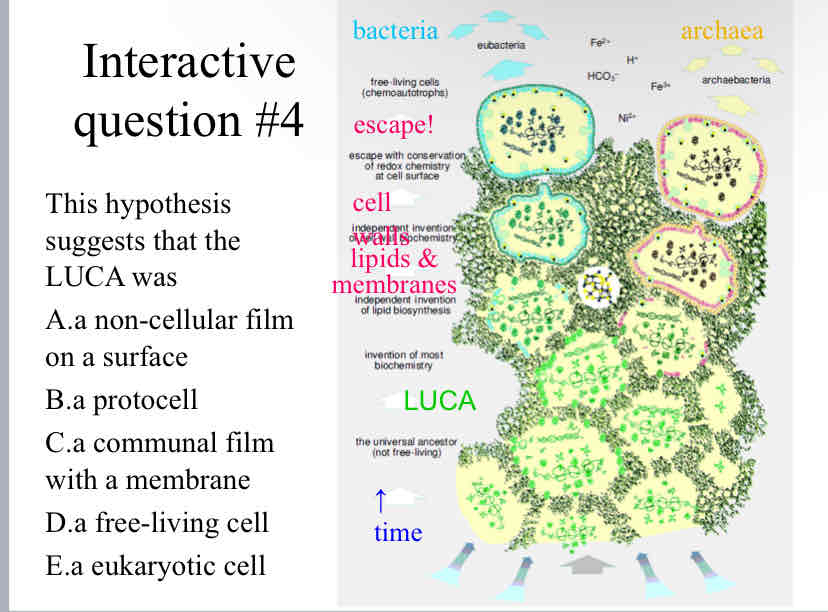
Practice Question (Origins of Life) - This hypothesis suggests that the LUCA was
a protocell
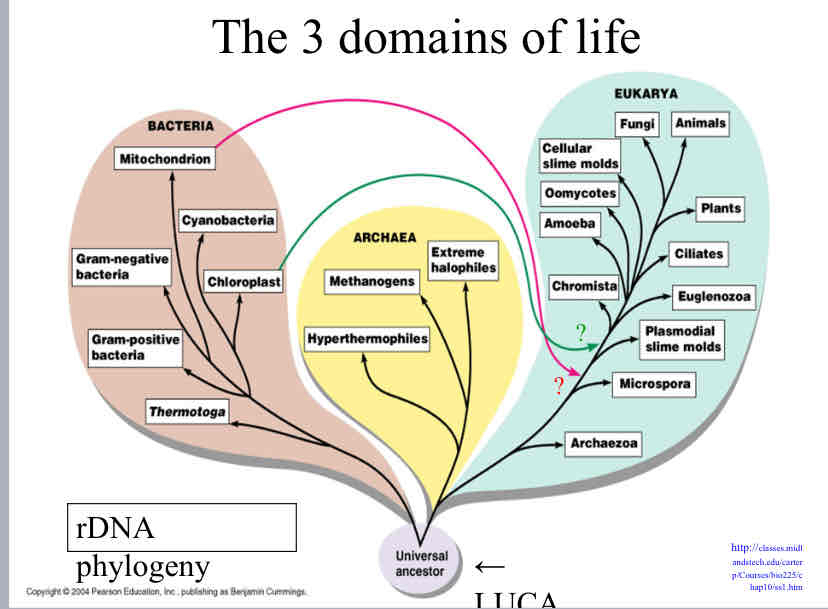
3 domains of life
Bacteria
Archaea
Eukarya
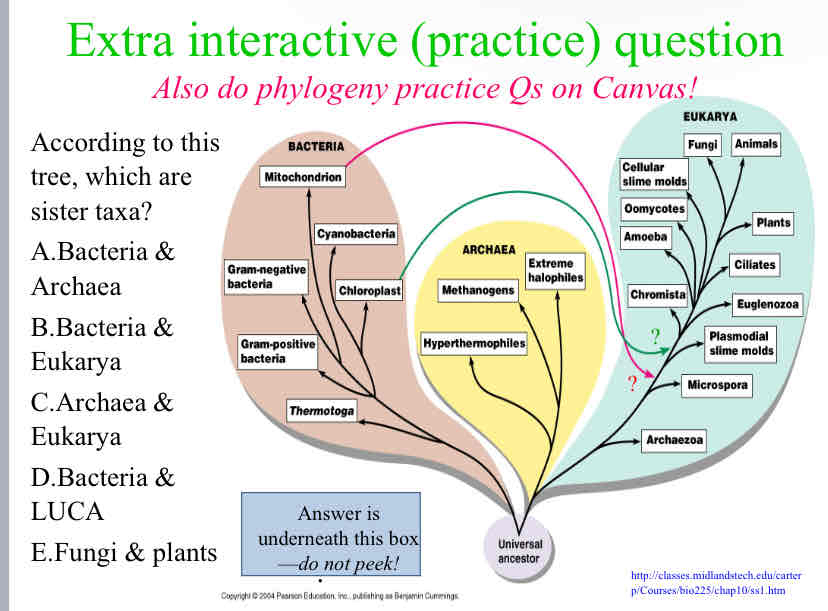
According to this tree, which are sister taxa?
Archaea and Eukarya

Practice Question (Bio Classification) - What Plant is this ?
D
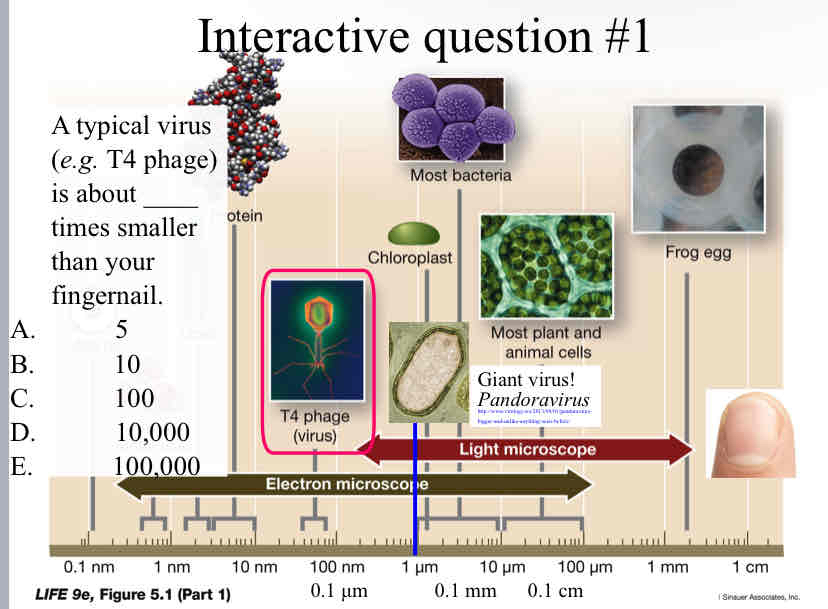
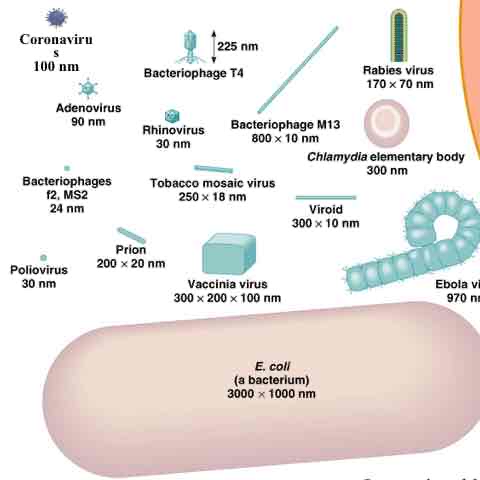
Practice Question ( Virus Size) - A typical virus (e.g. T4 phage) is about ____ times smaller than your fingernail.
100,000
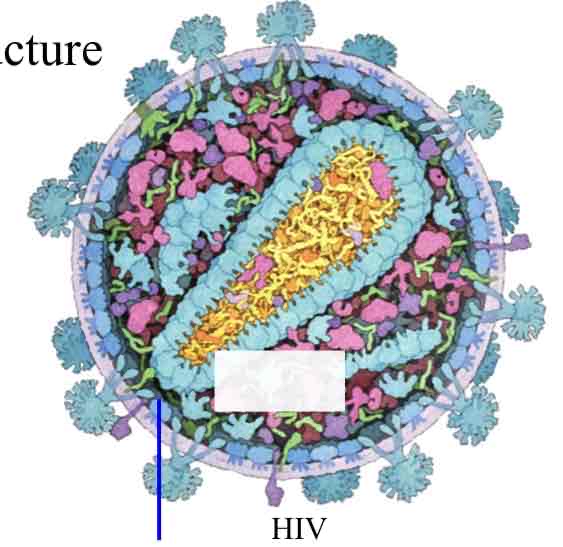
HIV Virus
All Have :
Genome (RNA or DNA)
Capsid (protein)
Some Have :
Envelope (membrane)
Envelope Proteins

Coronavirus
All Have :
Capsid (protein)
Some Have :
Envelope (membrane)
Envelope Proteins
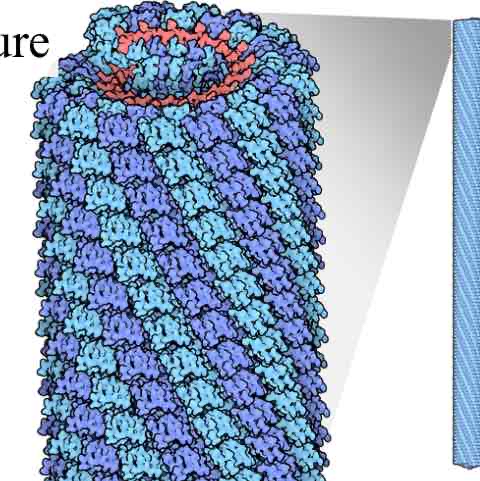
Tobacco mosaic virus
All Have :
Genome (RNA or DNA)
Capsid (Protein)
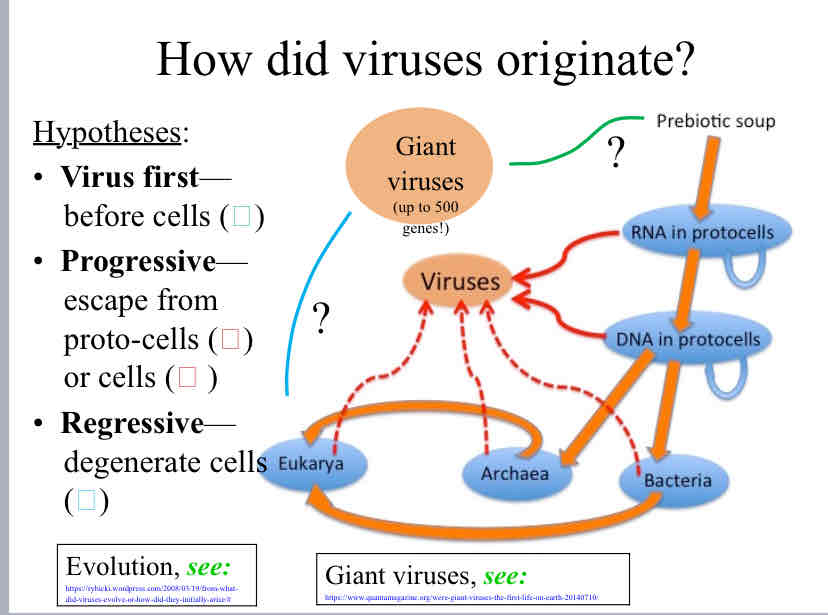
How did viruses originate
3 possible theories
Virus first - came before cells
Progressive - escape from proto-cells
Regressive - degenerate cells
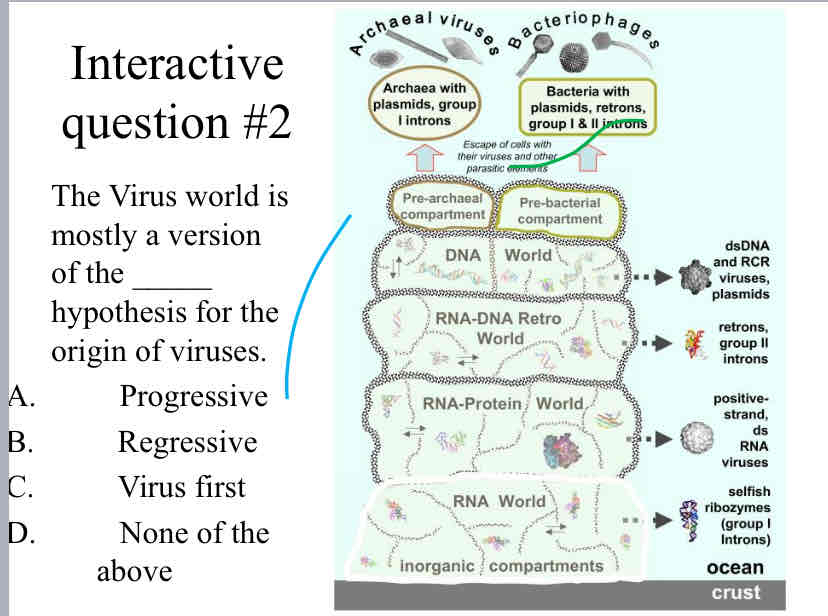
The Virus world is mostly a version of the _____ hypothesis for the origin of viruses
Progressive
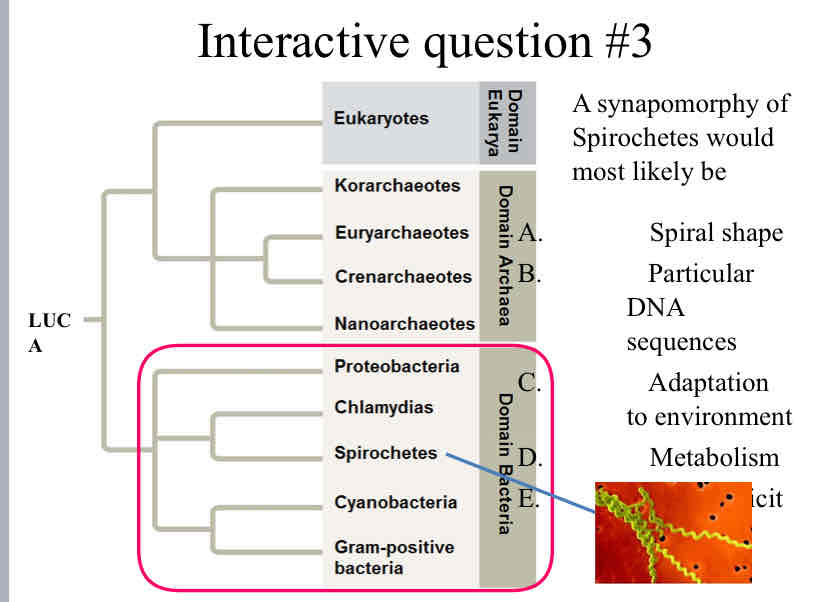
Practice Question (Bacteria) - A synapomorphy of Spirochetes would most likely be
B. Particular DNA Sequences
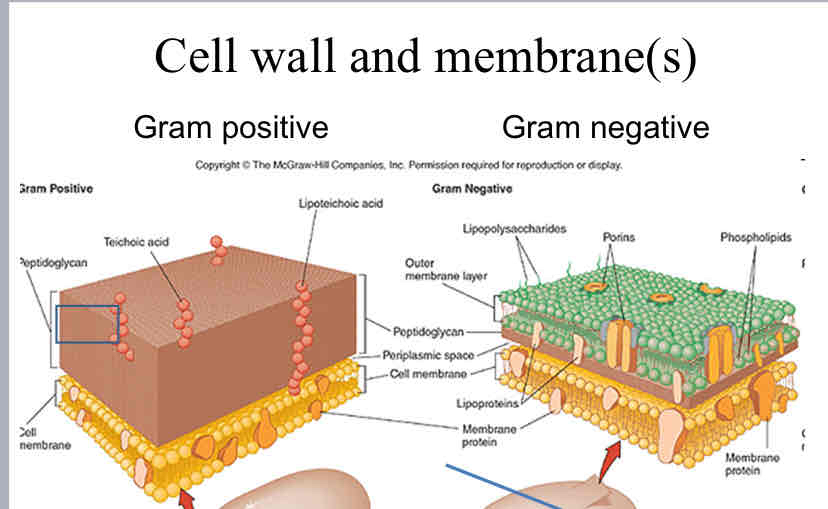
Gram Positive vs. Gram Negative Bacteria
Gram Positive
Thick Wall
1 membrane
Gram Negative
Thin wall
2 membranes : outer and inner
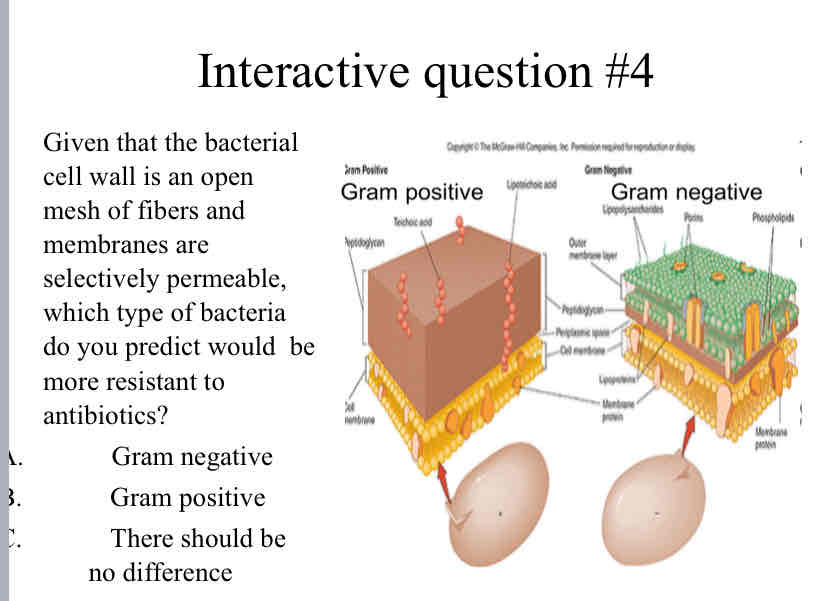
Practice Question (Bacteria) - Given that the bacterial cell wall is an open mesh of fibers and membranes are selectively permeable, which type of bacteria do you predict would be more resistant to antibiotics?
Gram Negative
Are viruses alive
evidence that they aren’t :
they are non cellular
they have no metabolism
many crystalline outside of host
evidence that they are :
they have DNA or RNA
they can replicate , mutate , and evolve
Prokaryotes Internal Membranes
Increases surface area for metabolism
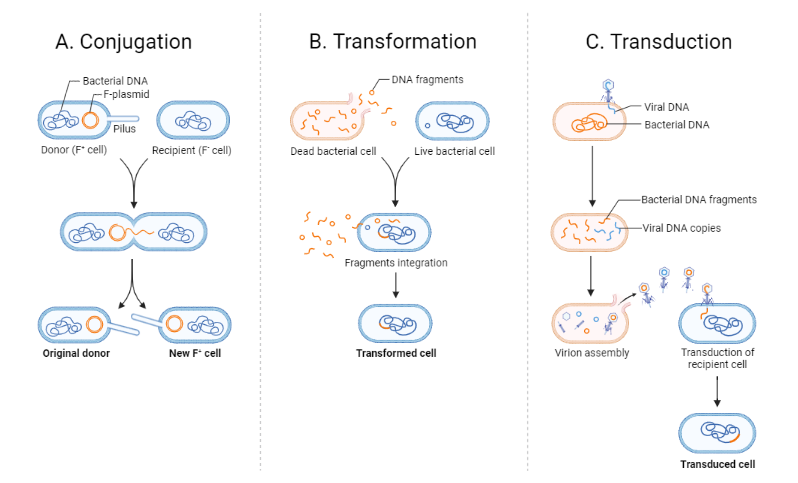
The 3 methods of genetic recombination by horizontal gene transfer, in bacteria
Transformation
Conjugation
Transduction

Bacterial Diversity : Shape
Bacteria can come in different forms such as :
Spheres (coccus)
Rods (bacillus)
or Corkscrew (spirillum)
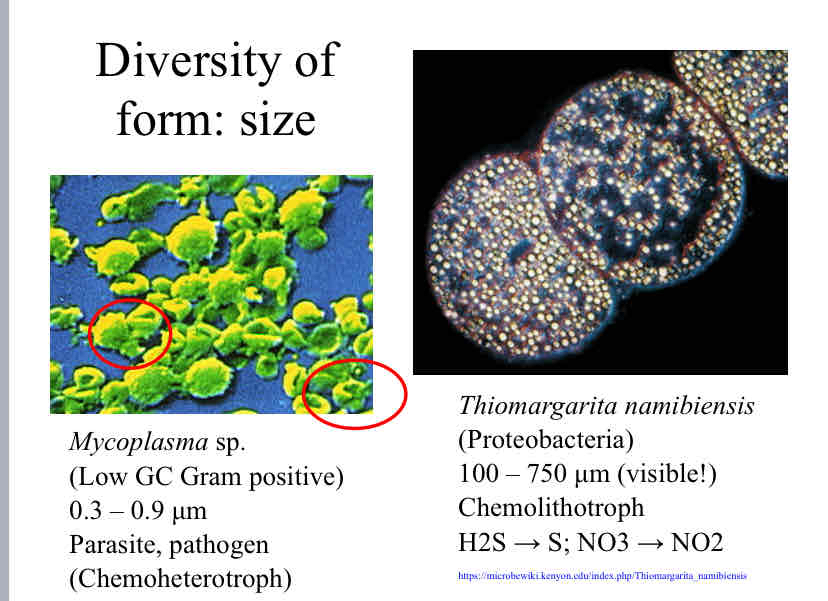
Bacterial Diversity : Size
Bacteria can also come in different sizes : either microscopic , or big enough that they are visible to the naked human eye.
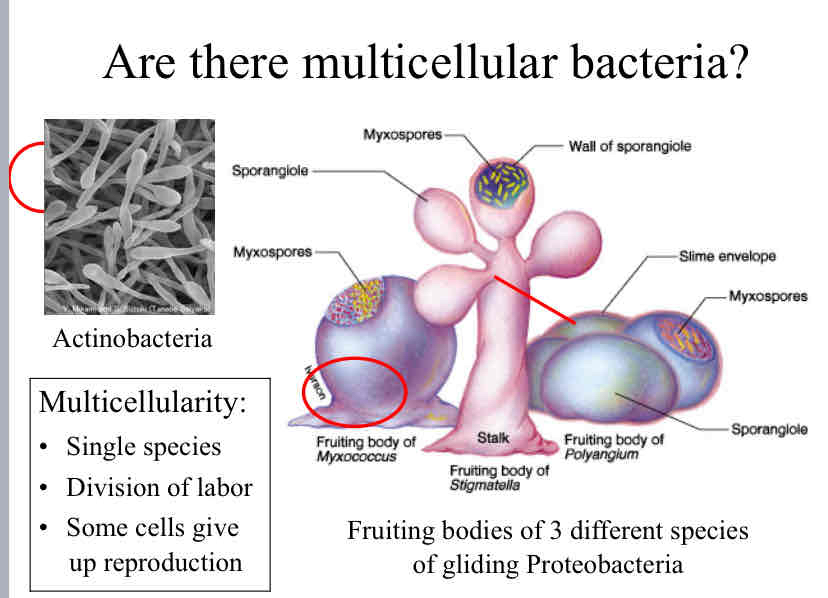
Multicellular Bacteria
is a single species
division of labor
some cells give up reproduction
examples include Actinobacteria and fruiting bodies of proteobacteria
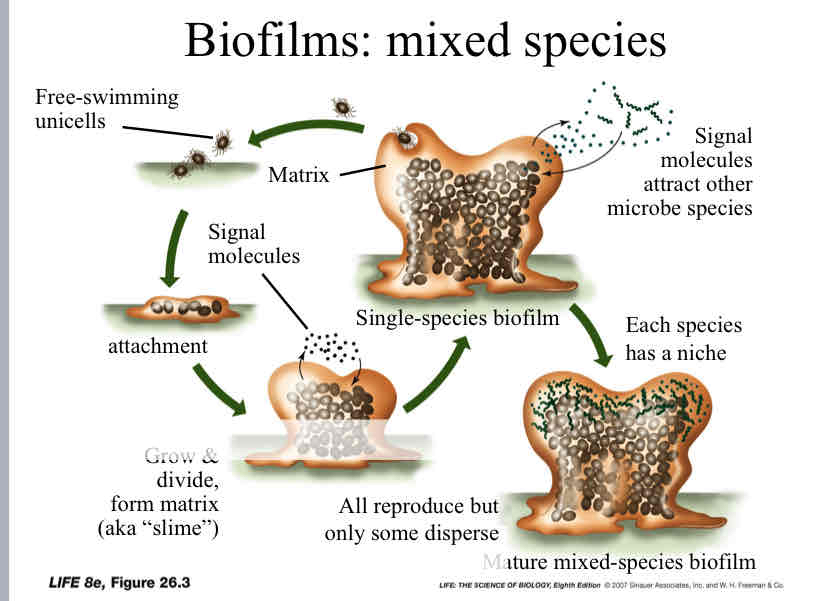
Biofilms
a type of bacteria that is of mixed species and can be found in many places such as :
soil & desert crusts
ocean, shores, streams
tree trunks and branches
water pipes
on and in other organism
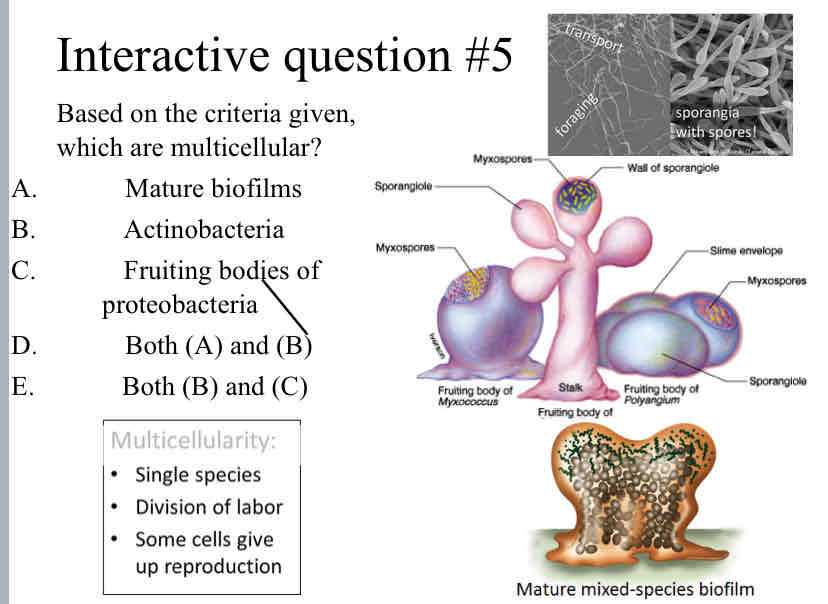
Practice Question (Bacteria) - Based on the criteria given, which are multicellular?
Both (B) and (C)
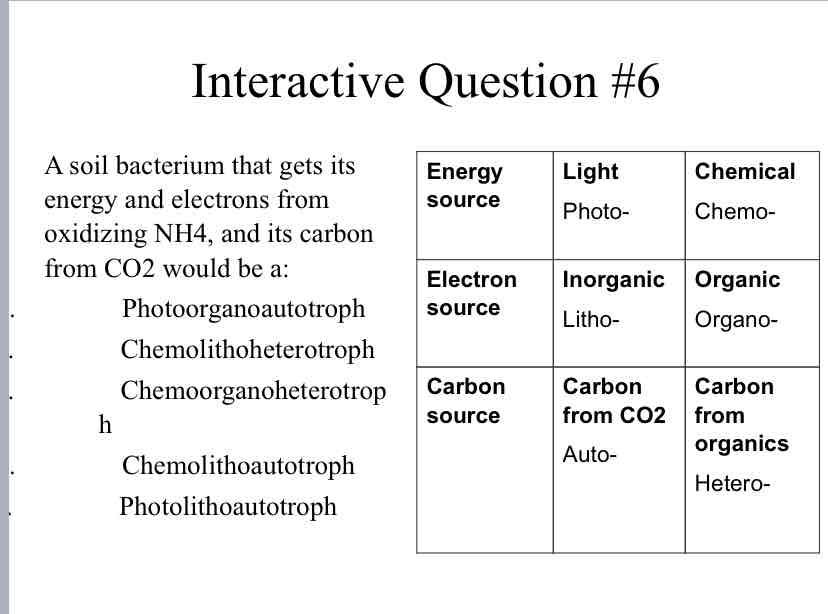
Practice Question (Metabolism) - A soil bacterium that gets its energy and electrons from oxidizing NH4, and its carbon from CO2 would be a:
Chemolithoautotroph
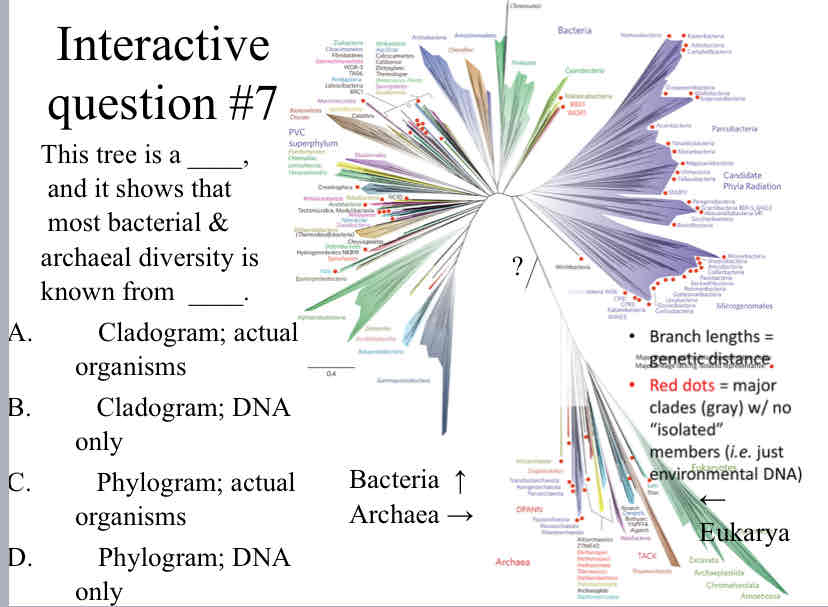
Practice Question (Phylogenetic Trees) - This tree is a ____, and it shows that most bacterial & archaeal diversity is known from
Phylogram ; DNA only
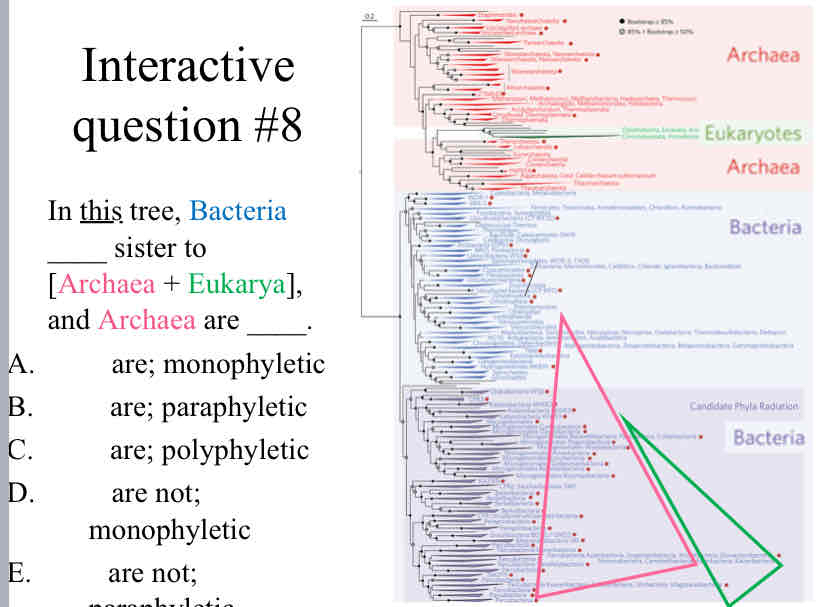
Practice Question (Phylogenetic Trees) - In this tree, Bacteria ____ sister to Archaea + Eukarya , and Archaea are ____.
are ; paraphyletic
Archaea
similar morphology to bacteria , however differ in
• gene expression
• cell structure
unique membrane phospholipids
unique crystal protein wall
unique flagella
Some archaea are thermophiles, a type of extremophile.
meaning they grow best and thrive in very high temperatures , but can in general be found anywhere such as oceans, soil, animal guts and even our skin.

Why are plants and other organisms green ?
They have pigments and when the light hits them , what is reflected back is the color we see (green leaves as an example). All other colors are absorbed.
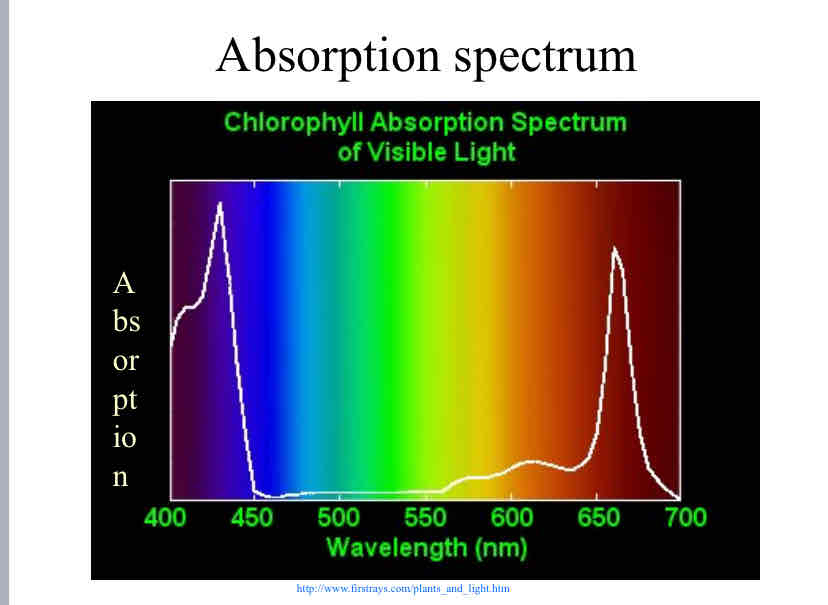
Absorbtion Spectrum
shows which colors absorb more than others , a low absorption level signifies a higher reflection and therefore a color we can see.
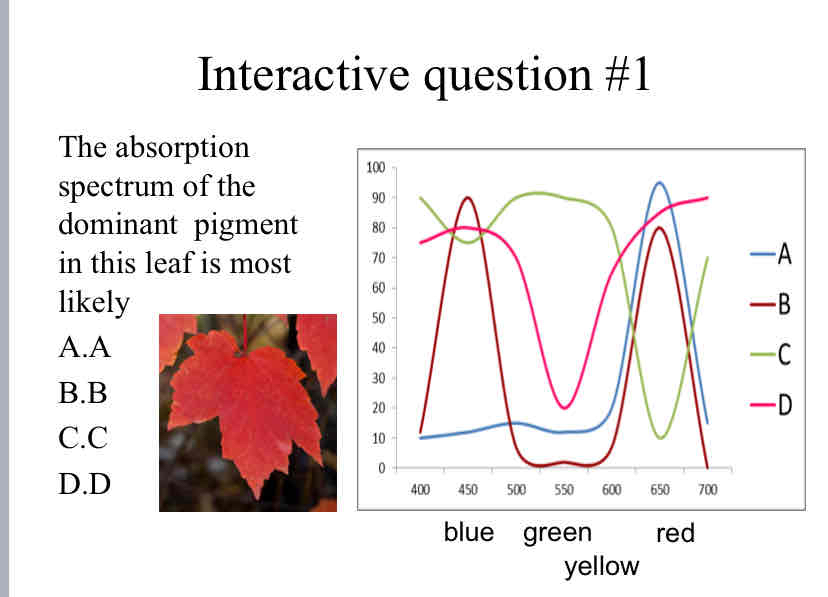
Practice Question (Color Absorption) - The absorption spectrum of the dominant pigment in this leaf is most likely ?
C
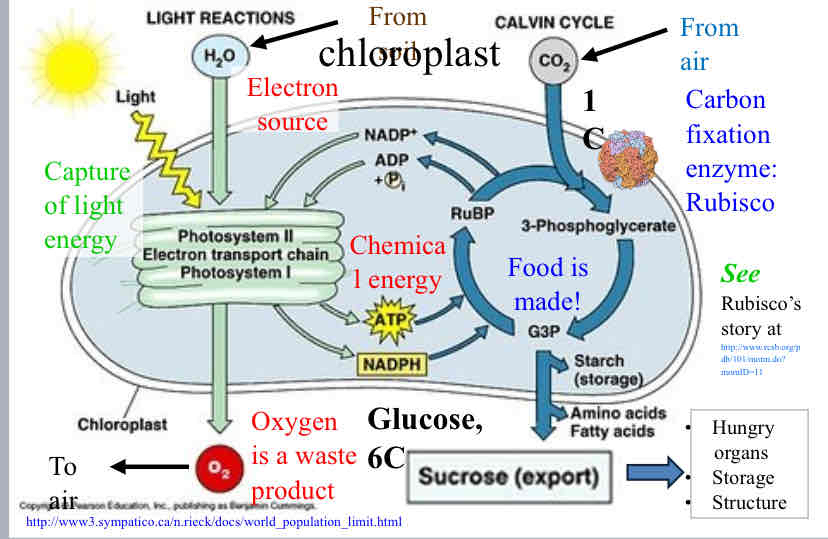
What is the name of this process ?
Photosynthesis
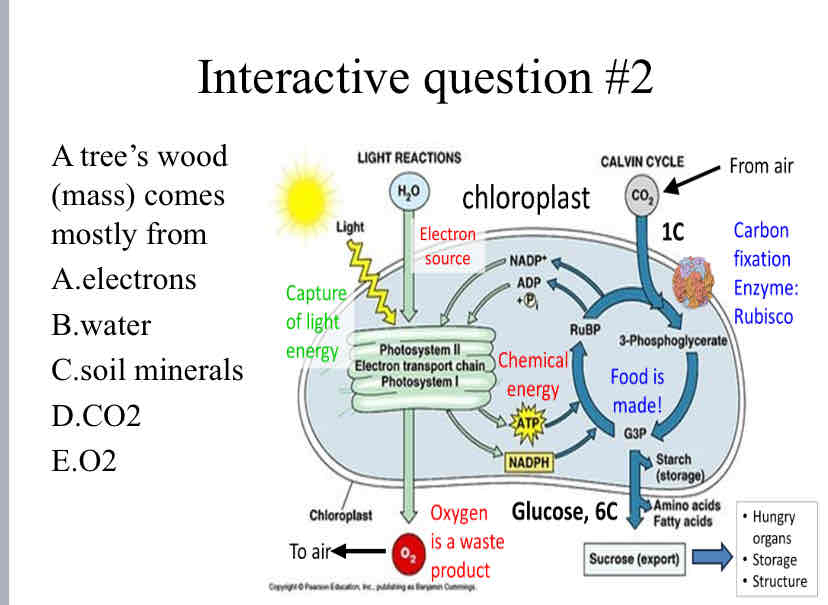
Practice Question (Photosynthesis) - A tree’s wood (mass) comes mostly from
D. CO2
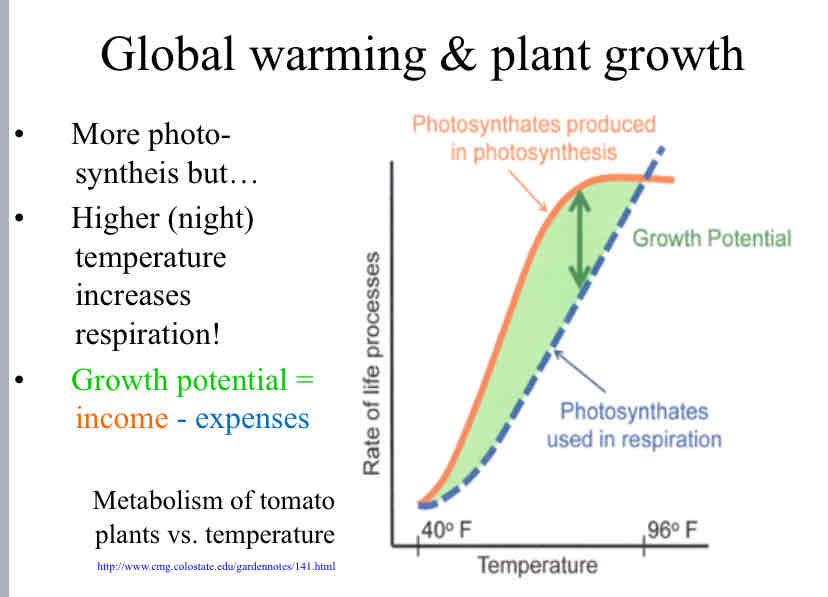
Global Warming & Plan Growth
Global Warming increases photosynthesis but also increases respiration thereby decreasing the growth potential of plants
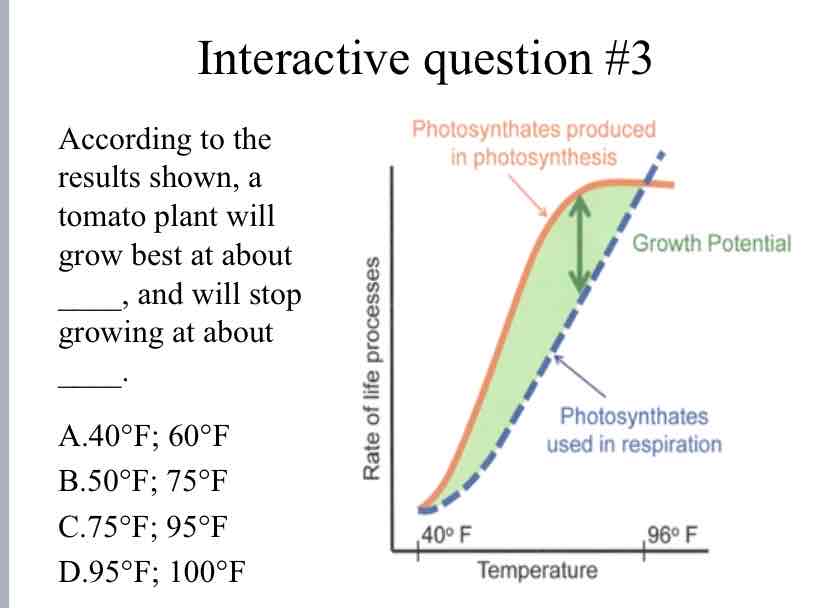
Practice Question (Plant Growth) - According to the results shown, a tomato plant will grow best at about ____, and will stop growing at about ____.
75°F ; 95° F
Global Warming & Food Security
CO2 enrichment, but there is a nutrient limitation on photosynthesis
Plants grow more, but incorporate less nutrients
Insects grow faster, and are hungrier , eating more plants than usual
Less nutritious food & more crop losses
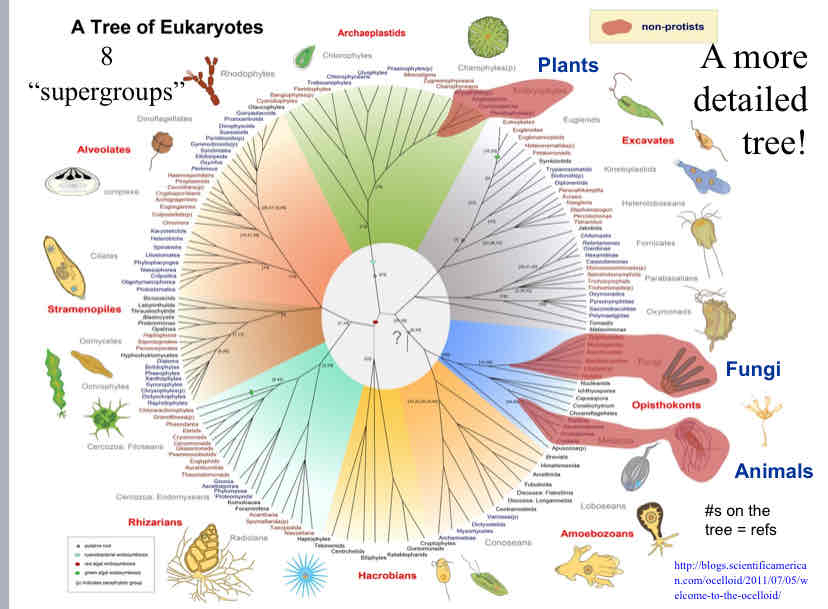
Protists
(mostly) microbial eukaryotes
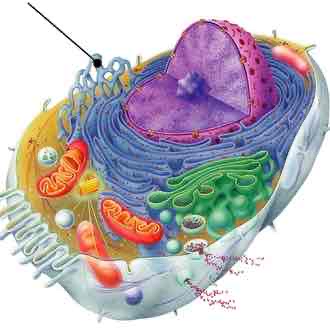
Eukaryotic Cell
main difference between prokaryotes is they have organelles surrounded by membrane
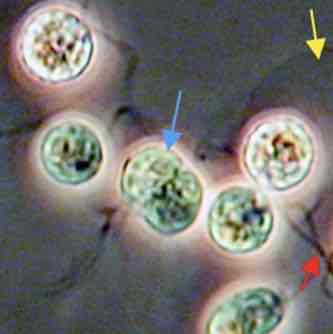
Sex in unicellular eukaryotes
involves
1) mating of + and - genes
2) fertilization
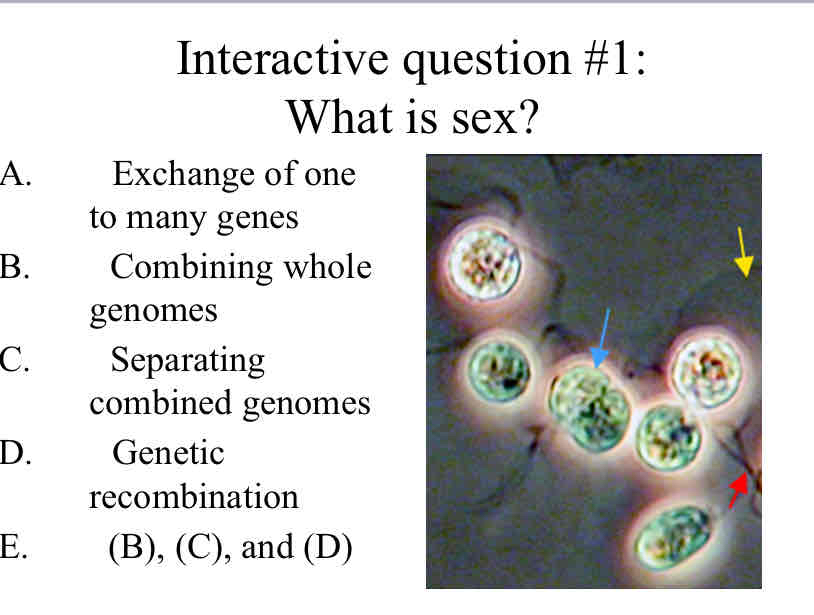
Practice Question (Unicellular Eukaryotes) - What is sex ?
(B) Combining whole genomes
(C) Separating combined genomes
(D) Genetic recombination
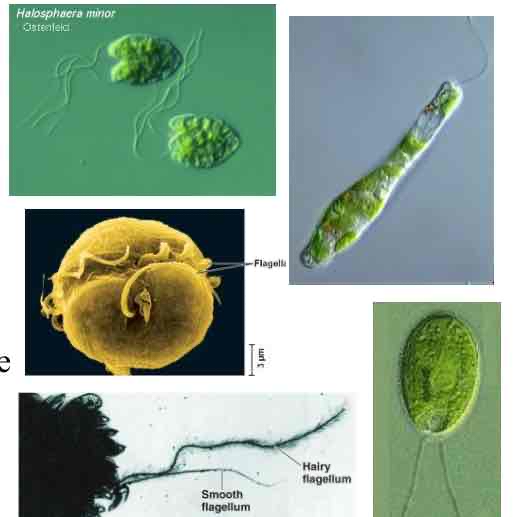
Eukaryotic Flagella
presence is not informative, homoplasious for phylogeny
morphology can be homologous