G) gas exchange, H) plant transport
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Process requires the uptake of oxygen and release of carbon dioxide
The oxygen diffuses down the concentration gradient from a high concentration (outside the leaf) to a low concentration (inside the leaf) the cells use oxygen in respiration so the concentration is always low inside respiring cells.
The carbon dioxide diffuses down the concentration gradient from a high concentration (inside the leaf) to a low concentration (outside the leaf)
gas exchange during photosynthesis
requires uptake of carbon dioxide and release of oxygen
carbon dioxide diffuses down the concentration gradient from a region of high concentration (outside the leaf) to a region of low concentration (inside the leaf)
Oxygen diffuses down the concentration gradient from an area of high concentration (inside the leaf) to a low concentration (outside the leaf)
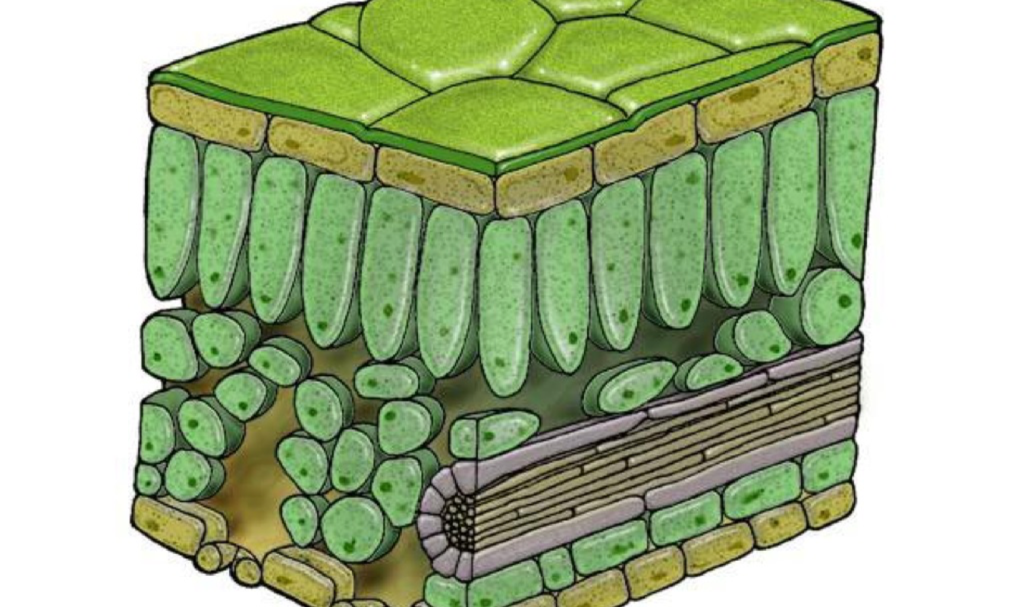
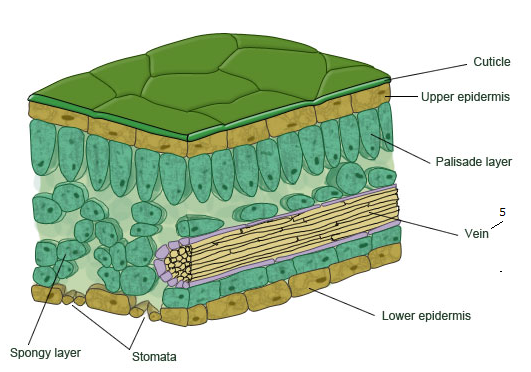
how is the structure of leaf adapted for gas exchange
The leaf has thin walls which gives a short diffusion distance
They are flat providing a large surface area to volume ratio
They have many stomata which allows movement of gases in and out of the air spaces inside the leaf to maintain a steep concentration gradient
Air spaces allow gas movement around the mesophyll cells
Many stomata in lower epidermis open in sunlight to allow gas movement in and out of the leaf
Close contact between the cells and air spaces allows efficent gas exchange for photosynthesis and respiration.
Thick, waxy cuticle to reduce water loss and reflect heat
Large, fleshy stems to store water
Spines instead of leaves to reduce water loss and protect themselves from grazing animals
Shallow, widespread roots to catch as much rainfall as possible when it comes
Some cacti species have very deep roots to find water underground
stomata role in gas exchange
spaces found between two guard cells
found in the lower epidermis of the leaf
The guard cells = responsible for the opening and closing of the stomatal pore which controls gas exchange and water loss
Stomas open when water moves (by osmosis) into the guard cells and causes them to become turgid
this allows gases to diffuse in and out the leaf and the stomata tend to be open when there's plenty of water and sunlight
Stomatas close when guard cells lose water (by osmosis) so they become flaccid
this then prevents any diffusion in and out of the leaf and the stomata close due to low water or low sunlight
method for investigate the effect of light on net gas exchange from a leaf, using hydrogen-carbonate indicator
Measure out 20cm3 of hydrogen carbonate indicator into 4 boiling tubes
Put some cotton wool into each boiling tube Label the boiling tubes A, B, C, D
Tube A - put in no leaf (it's a control tube)
Tube B - place a leaf in tube and leave in light
Tube C - place a leaf in tube and wrap in aluminium foil so to block out light
Tube D - place a leaf in tube and wrap in a gauze to allow partial light.
Put a bung on all 4 tubes Leave in light for some time
the tube was placed in light with a leaf which is photosynthesizing and respiring
because the plant would be photosynthesizing more than respiring the hydrogen carbonate indicator will turn purple as there is less carbon dioxide than atmospheric levels
the leaf was wrapped with aluminium foil so could not have access to sunlight
no light means that the leaf could not photosynthesizing but only respiring meaning carbon dioxide would be being produces
The indicator will turn yellow as the carbon dioxide levels have gone beyond normal atmospheric levels.
this leaf only had partial light so the rate of photosynthesis and respiration were equal meaning there was no net change in carbon dioxide levels so indicator will remain orange/red
the intercostal muscles contracts and move the ribs upwards and outwards
this increases the volume of the lungs which reduces the pressure inside the lungs
so, the air moves in to equalise it
the intercostal muscles relax and move downwards and inwards which reduces the volume of the lungs and forces air outward
The ribs move down and inwards
bronchi role
distribute the air throughout the lungs
they carry the air to and from the lungs
Bronchioles role
found at the end of the bronchi
they carry air to the alveoli
Alveoli role
tiny air sacks where gas exchange occurs
they are at the end of the bronchioles
This Is where oxygen moves into the blood and carbon dioxide moves out
A huge combined surface area
Moist, thin walls to maximise diffusion
Millions of capilaries behind the walls
destroy the cilia which carries away the dust and microbes trapped in mucus
therefore causes a buildup of mucus which can cause bronchitis
this also causes a smoker's cough to try remove mucus
destroy alveoli walls and causes them to merge which decreases the surface to volume ratio for gas exchange
This causes insufficent gas exchange and will increase the risk of Emphysema - shortness of breath
causes blood vessels to narrow, placing a strain on circulatory system and resulting in the increase in blood pressure
The narrowing of blood vessels can cause the increasing risk of coronary heart disease as there is a buildup fat globules.
Exercise causes the frequency of breathing to increase in order to provide more oxygen for respiration and to pay off any oxygen debt.
After exercise breathing rate continuous to be the same increased rate as more oxygen is needed to break down the lactic acid produces.
They have a larger surface area in relation to their volume, hence having a large surface area to volume ratio
With this large surface area to volume ratio, they have an efficient rate of diffusion which allows them to solely rely on diffusion.
they have a small surface area in relation to their volume, and hence have a small surface area to volume ratio
With a small surface area to volume ratio, Multicellular organisms therefore have inefficient rate of diffusion, preventing cell to rely on diffusion to transport necessary substances in and out of the cell
phloem role
The phloem moves food substances that the plant has produced by photosynthesis to where they are needed for processes
Transport in the phloem is both up and down the stem the phloem is made up of cells called sieve tubes and companion cells
Specialized for transport and has no nuclei
Each sieve tube has a perforated end so its cytoplasm connects one cell to the next
Transport of substances requires energy
One or more companion cells attached to each sieve tubes provides the energy
A sieve tube would be completely dependent on its companion cell
xylem transports water and minerals from the roots up the plant stem and into the leaves
Most of the cells making up the xylem are specialised cells called vessels
A root hair cell is a specialized root cell of a plant that absorb water and mineral ions from the soil for plant growth
The water moves into the root hair cell by osmosis as there is a strong concentration of water in the soil and a low concentration of water inside the root hair cell
Root hair cell adaptations
large surface area to volume ratio which increases the rate of water absorption
as light intensity increases the rate of transpiration increases
this is because it stimulates more stoma to open