Heart, Lungs, and Peripheral Vessels
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Respiratory Assessment Subjective Data
Cough, shortness of breath, chest pains, history of infections, smoking history, and environmental exposure (work environment, harsh chemicals, smoke, etc)
Inspection of Respiratory System
Shape and configuration, patient's facial expression, LOC, Skin color/condition, and quality of respirations (effort, symmetry, accessory muscle usage.)
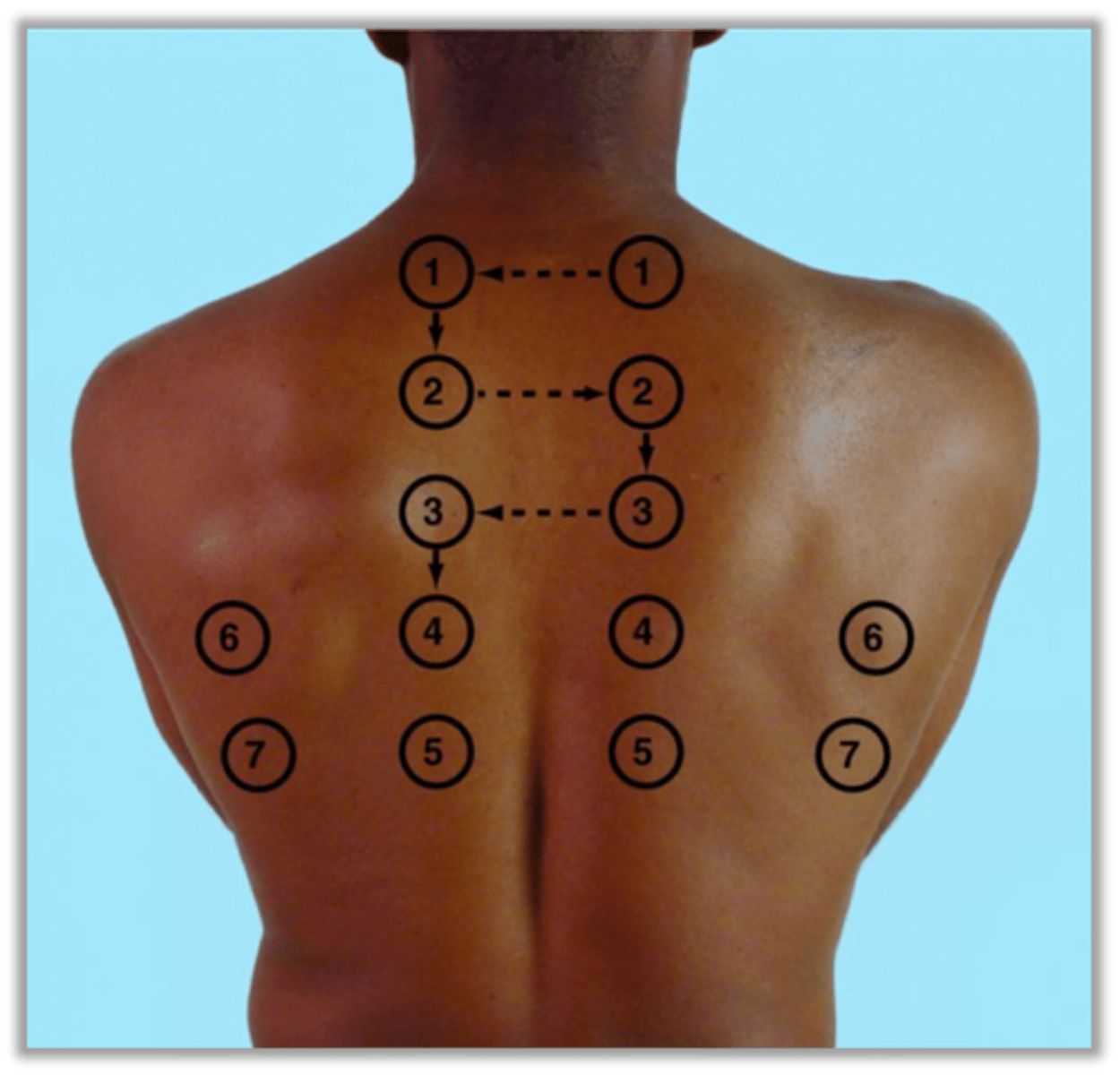
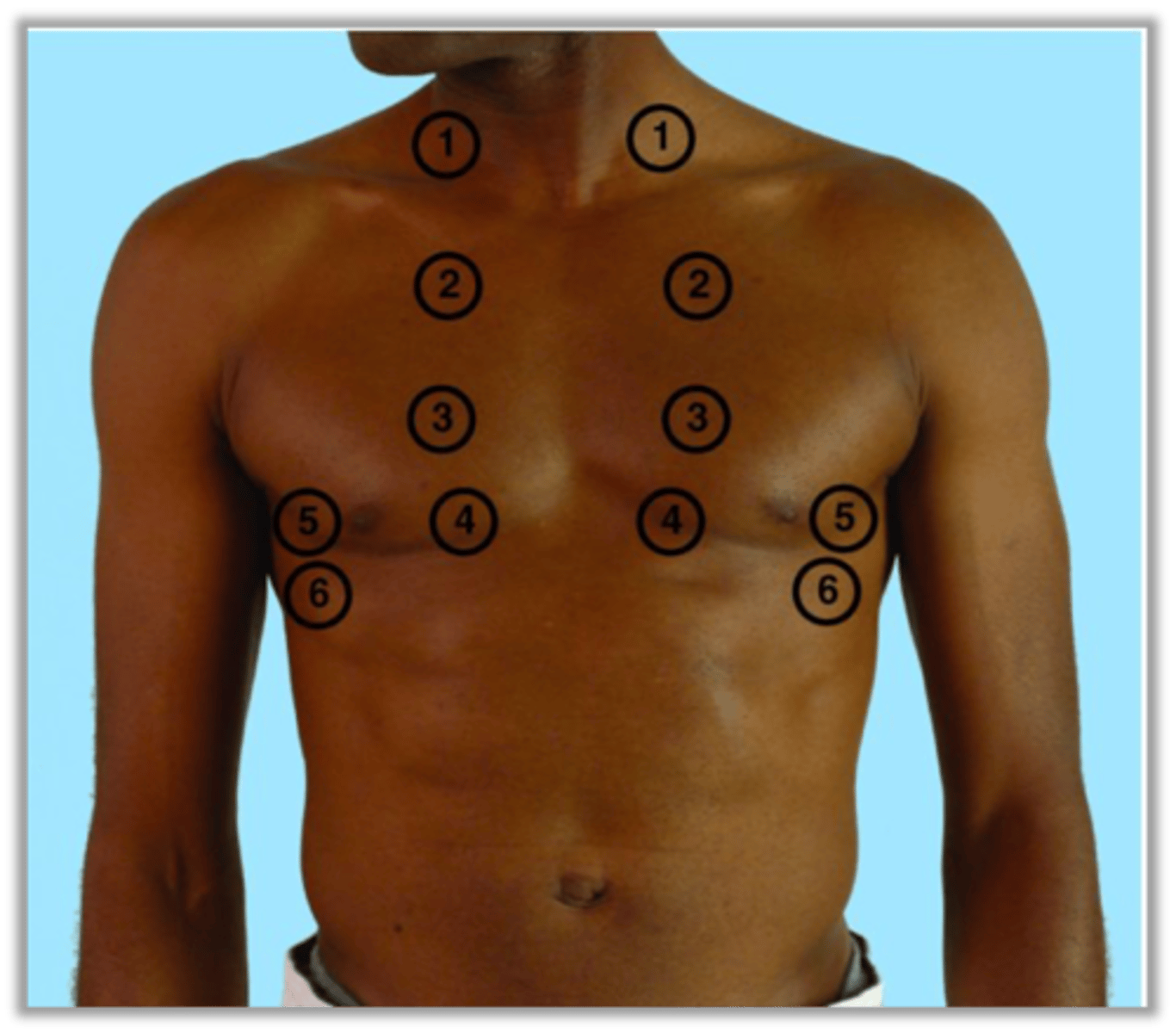
Auscultation of Respiratory System
Evaluate Bilaterally as well as anterior and posterior sides
One full breath at each location, deciphering if normal or abnormal sounds (adventitious sounds)
When assessing a person with breast tissue that may interfere with ausculation, displace breast tissue as necessary
Adventitious Sounds
Any abnormal respiratory sounds. Crackles (rales), Wheezing, or Rhonci
Auscultatory Areas Respiratory System (Posterior)
Auscultatory Areas Respiratory System (Anterior)
Pulmonary Function Measurement
Incentive Spirometer (Inhalation Exercise)
Pulse Oximeter (Hemoglobin Saturation)
6-Minute Walk Test (6MWT)
Cardiac Blood Flow
1. superior and inferior caval veins
2. rt atrium
3. tricuspid valve
4. rt ventricle
5. pulmonic valve
6. pulmonary artery
7. lungs
8. pulmonary veins
9. lt atrium
10. mitral valve
11. lt ventricle
12. aortic valve
13. aorta
14. body
Cardiac Conduction
SA node: "pacemaker" intrinsic rate of 60-100 bpm
AV node: 40-60 bpm
Purkinje Fibers: 20-40 bpm
Rhythmicity
Regular generation of an action potential by the heart's conduction system
Automaticity
The ability of the heart to generate and conduct electrical impulses on its own.
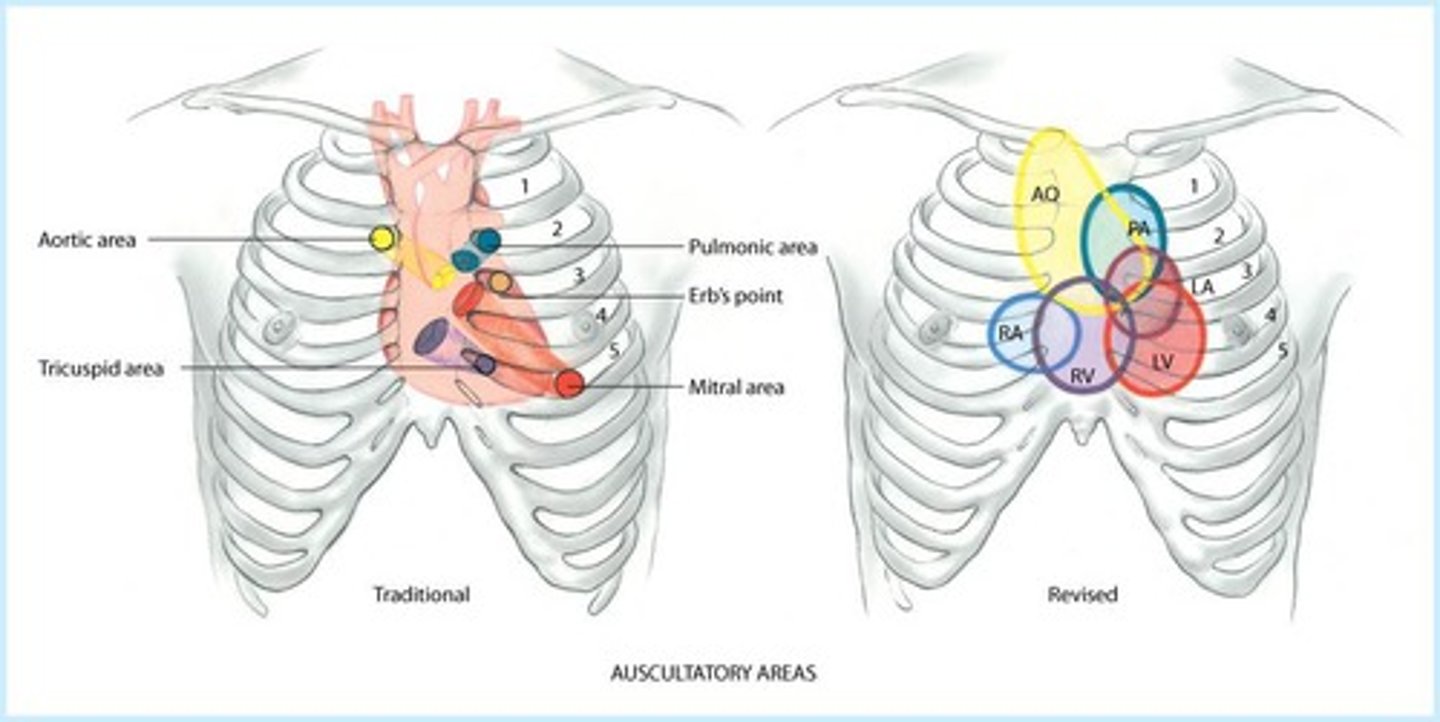
Auscultatory Areas
APE To Man: Aortic, Pulmonic, Erb's point, Tricuspid, Mitral
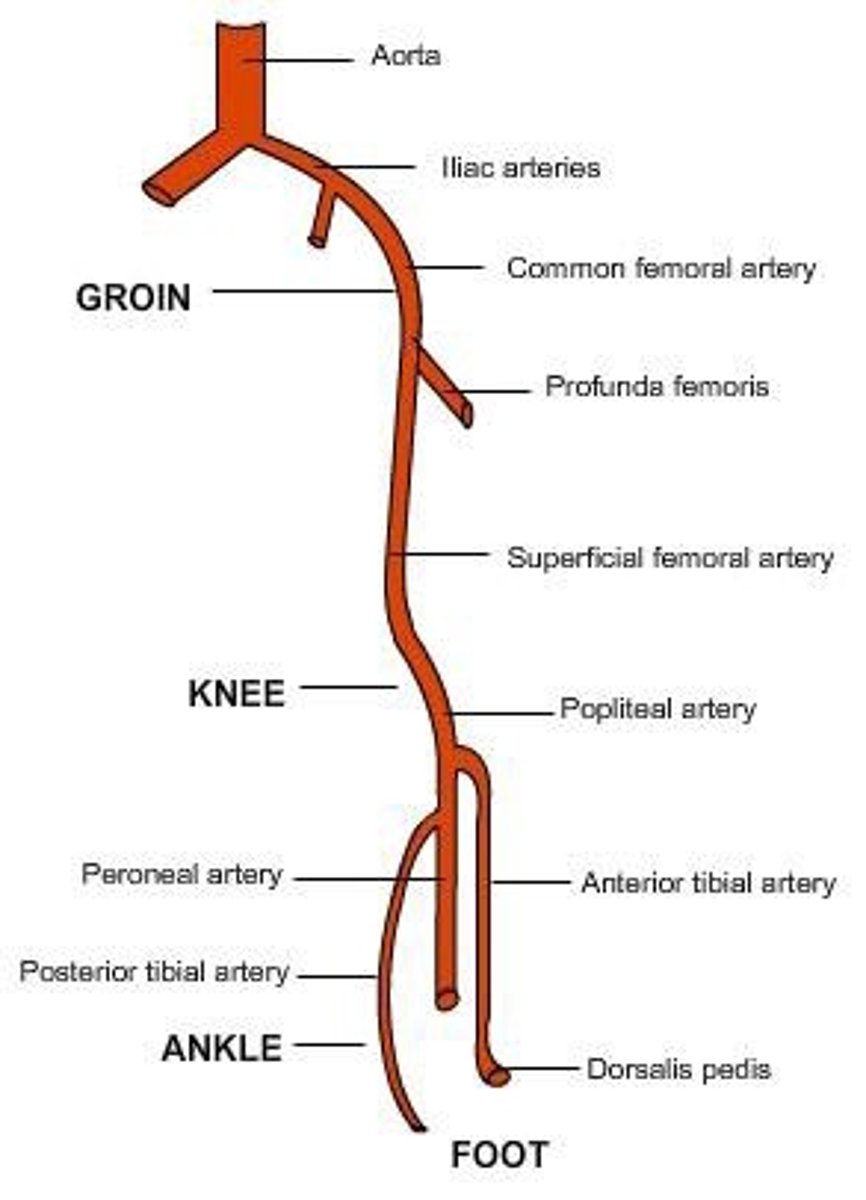
Lower Extremity Arteries
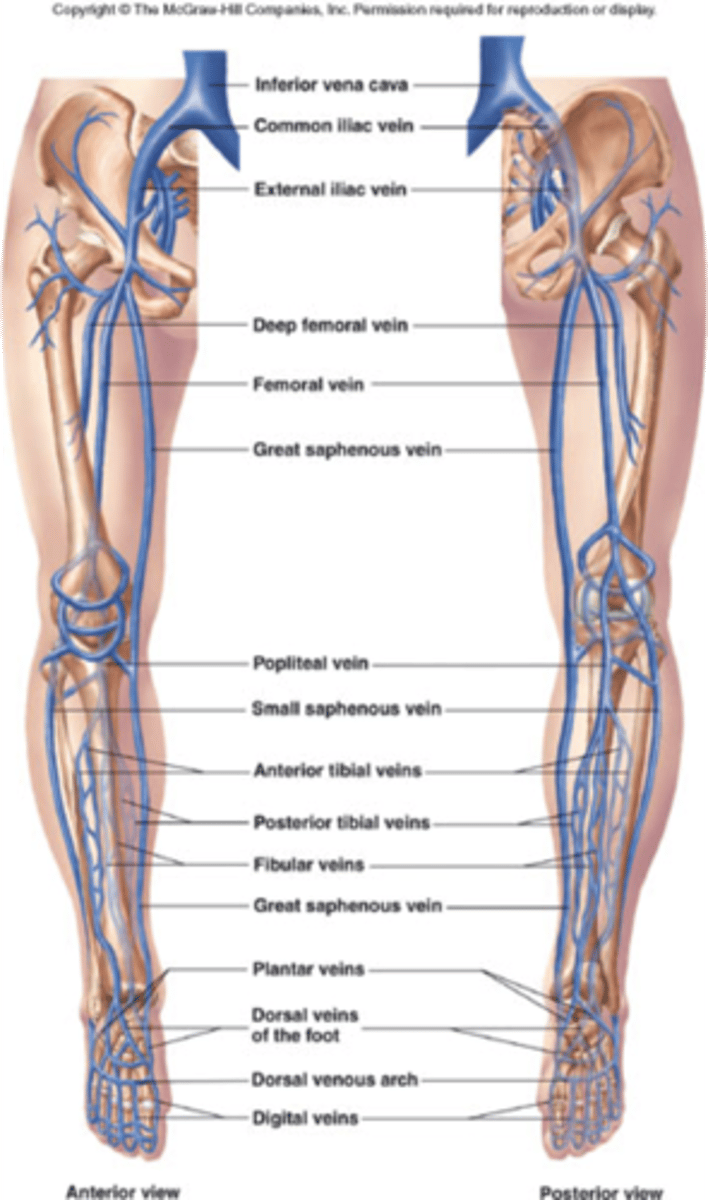
Lower Extremity Veins
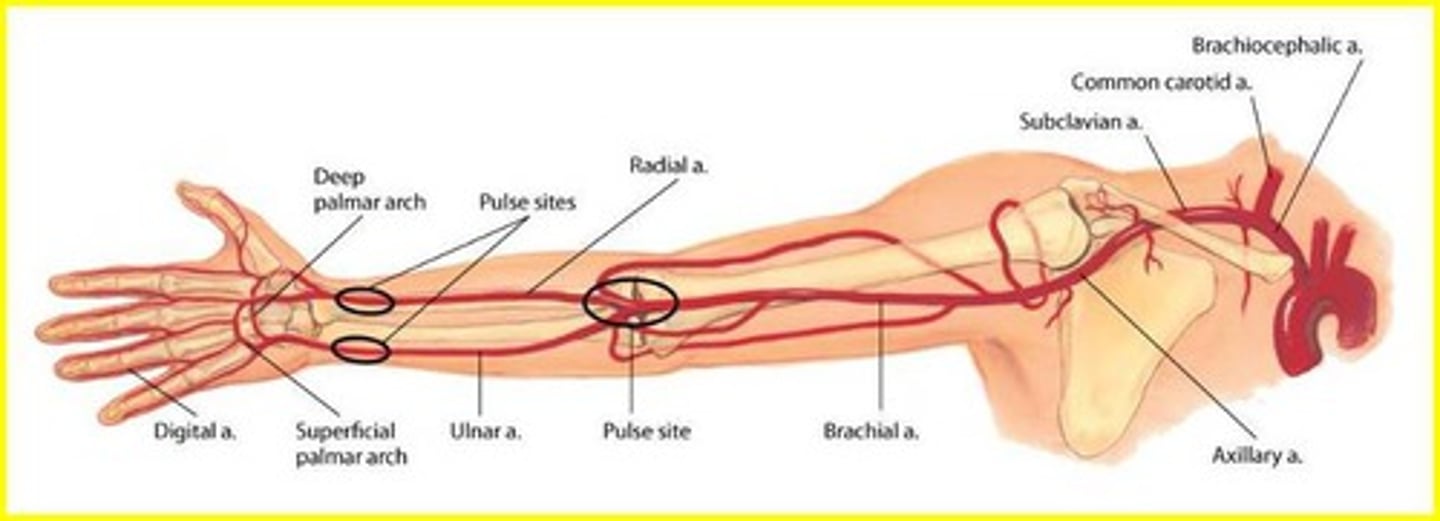
Arteries in the Arm
Peripheral Vasculature: Arteries
- Delivers oxygen + nutrients
- High-pressure
- Accessible to Examination: Temporal, Carotid, Brachial, Radial, Femoral, Popliteal, Dorsalis Pedis, Posterior Tibial
Peripheral Vasculature: Veins
- More veins than arteries
- Goes back to the heart by returning mostly deoxygenated blood and its waste products
- Low Pressure System
Inspection and Palpation of Peripheral Vasculature: Upper Extremities
- Lift the person's hands in your hands, inspect color, temperature, texture, and turgor
- Note the presence of lesions, edema, orc lubbing
- Check capillary refill
- Radial and brachial pulse (grade-amplitude)
Inspection and Palpation of Peripheral Vasculature: Lower Extremities
- Uncover Legs; DO NOT uncover genitalia
- Assess for Edema
- Skin
- PT and DP Pulses (Can use doppler)
- Monofilament Test
Edema
Abnormal accumulation of fluid in interstitial spaces of tissues.
Pneumothorax
Air in the pleural cavity caused by a puncture of the lung or chest wall