Ento: Insect Morphology (ch2)
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
“ad”
suffix meaning toward
proximal
nearer to the center
distal
farther(distant from) the center
What is the purpose of Antenna
Sensory appendage, detecting information
What are the types of Antennae
Filiform, Setaceous, Plumose, Moniliform, Serrate, Pectinate, Aristate, Geniculate(elbowed), Stylate, Capitate, Clavate, Lamellate
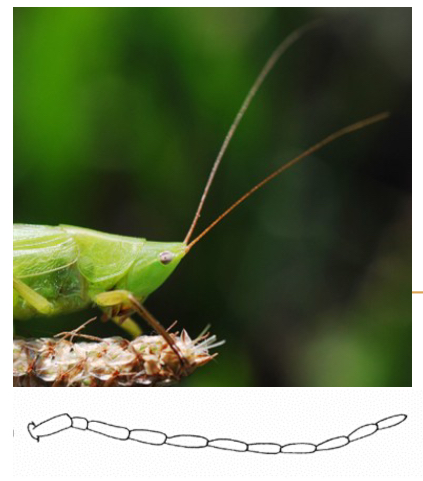
Filiform Antennae
Slender, thread like antennae used for detecting stimuli
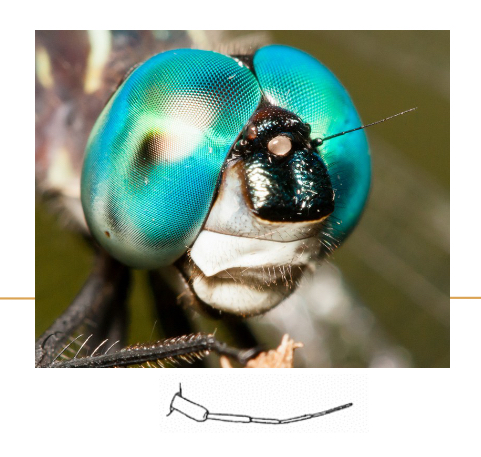

Setaceous Antennae
named after the Latin term “seta” meaning bristle used to detect stimuli such as odors, air currents, and movement
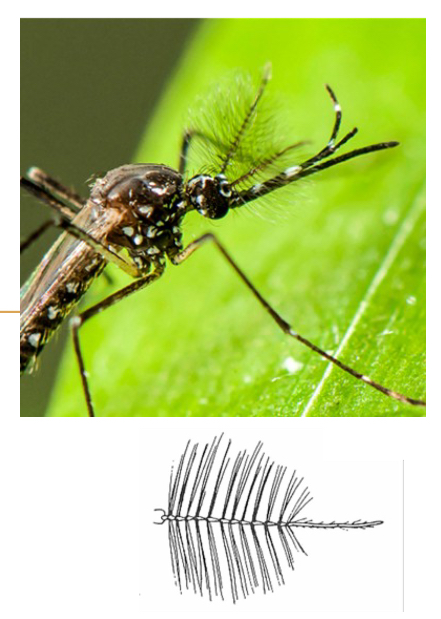

Plumose Antennae
Feathery/branched structure used for detecting airborne chemicals

Moniliform Antennae
resembles a string of beads, primarily used for detecting odors and tastes
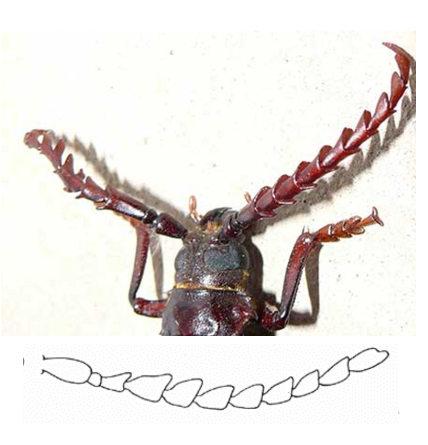

Serrate Antennae
Saw-like appearance, primarily used for enhanced sensory perception and tactile sensation
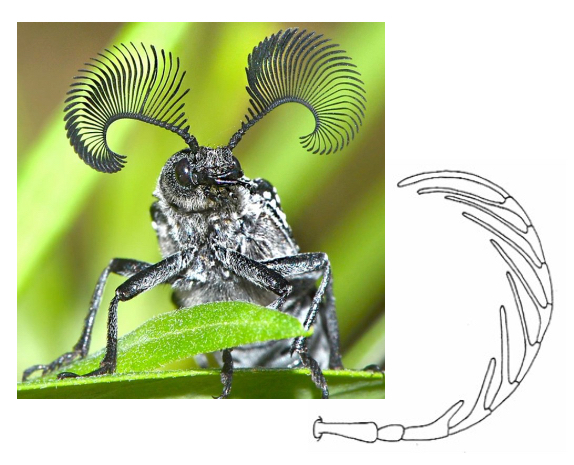

Pectinate Antennae
Comb-like with numerous branches to increase surface area, used to detect airborne chemicals and pheromones from potential mates
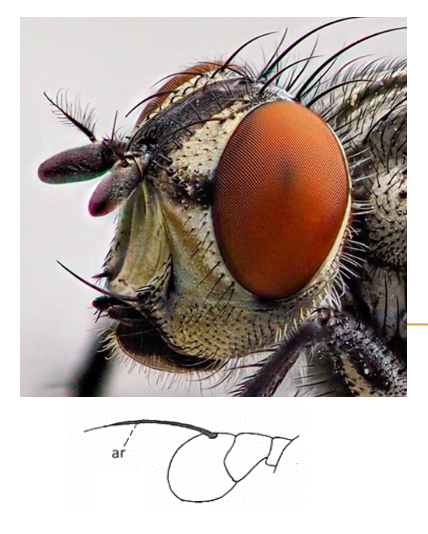

Aristate Antennae
Bristle-like structure, used for detecting vibrations and air movements
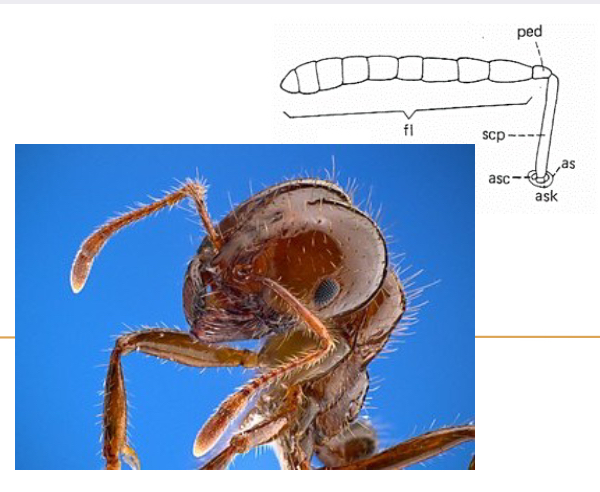
Geniculate Antennae
Characterized by its elbow like bend, primarily functioning as a sensory organ to find food, communicate and navigate

Stylate Antennae
Sensory appendage with bristle like structure at tip, used for detecting stimuli like chemical signals, humidity, and air movement
What does the prefix “gnatho” mean
Jaw
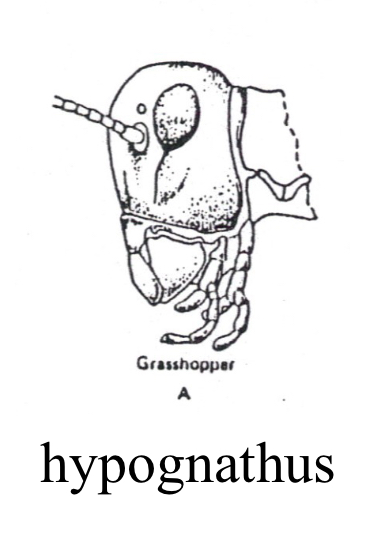
Hypognathous
mouth parts are directed downwards, used to feed on surfaces below insect
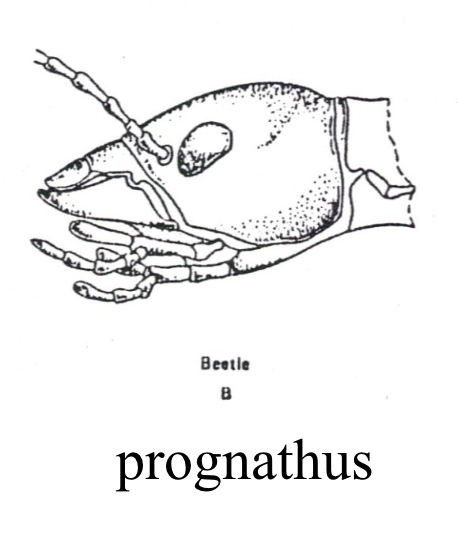
Prognathous
mouthparts are directed forward for predation and burrowing
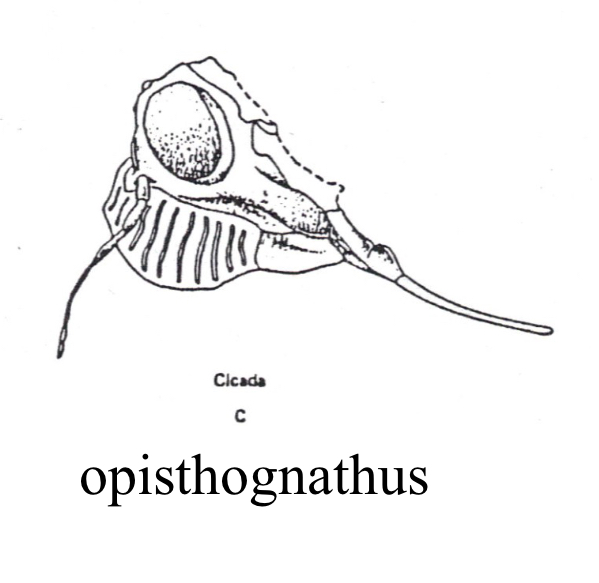
Opisthognathous
mouthparts directed back and downward, used for feeding of liquids and soft foods
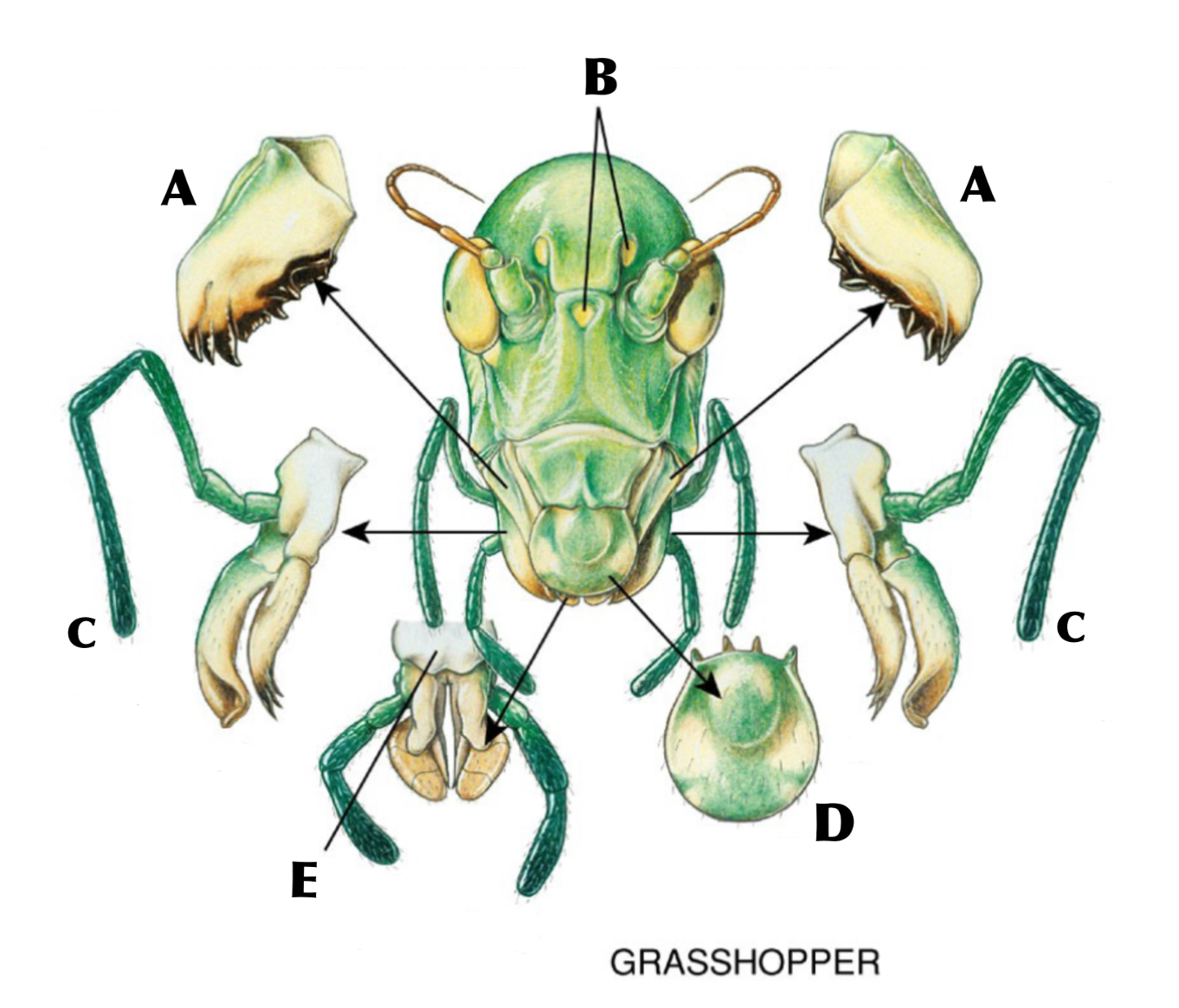
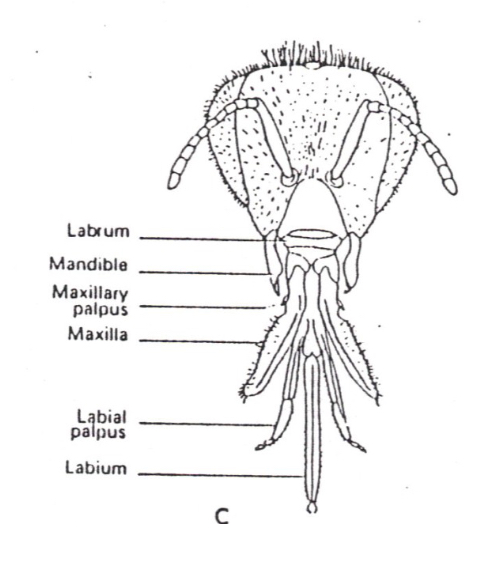
What is A
Mandibles
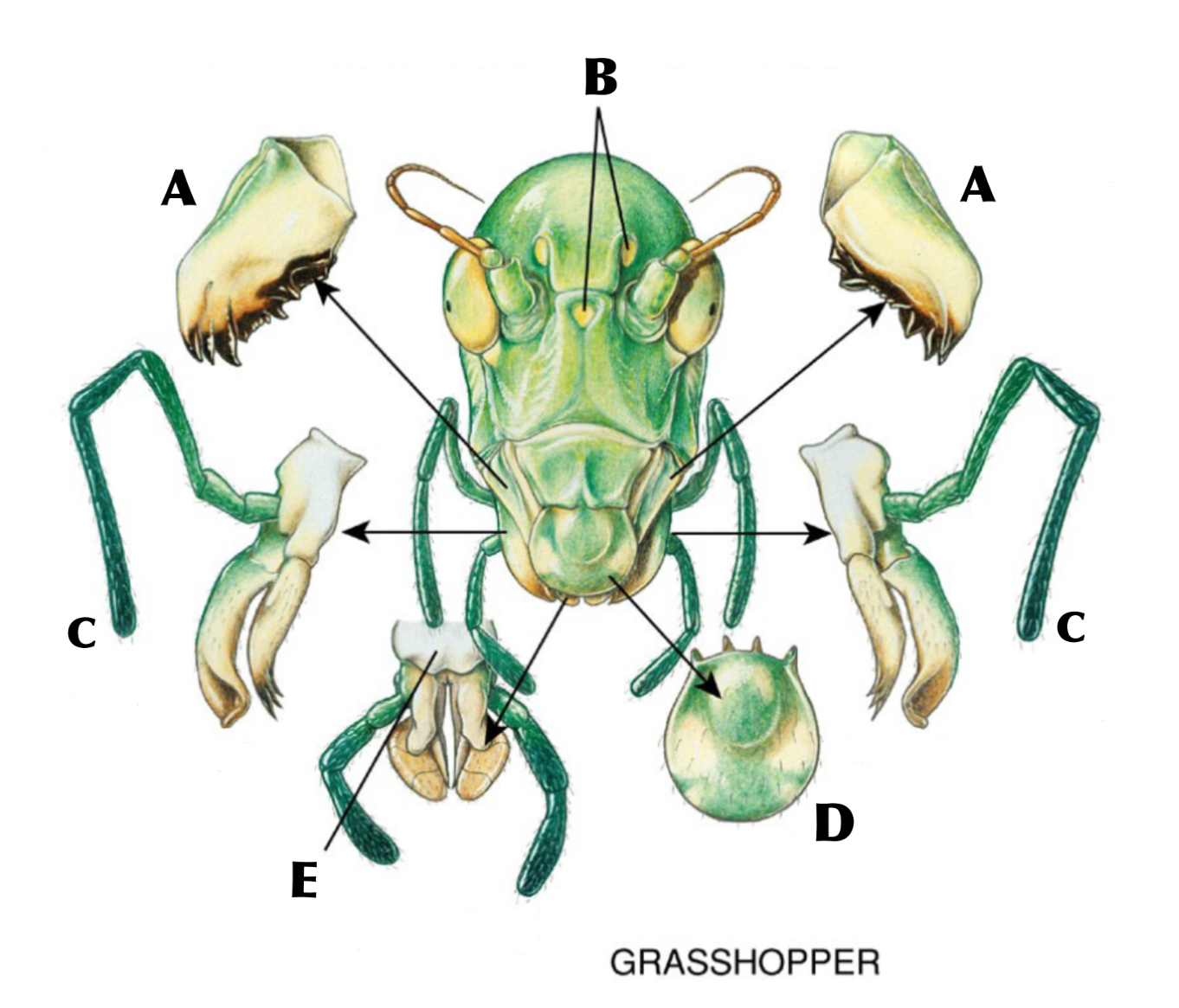
What is B
Ocelli
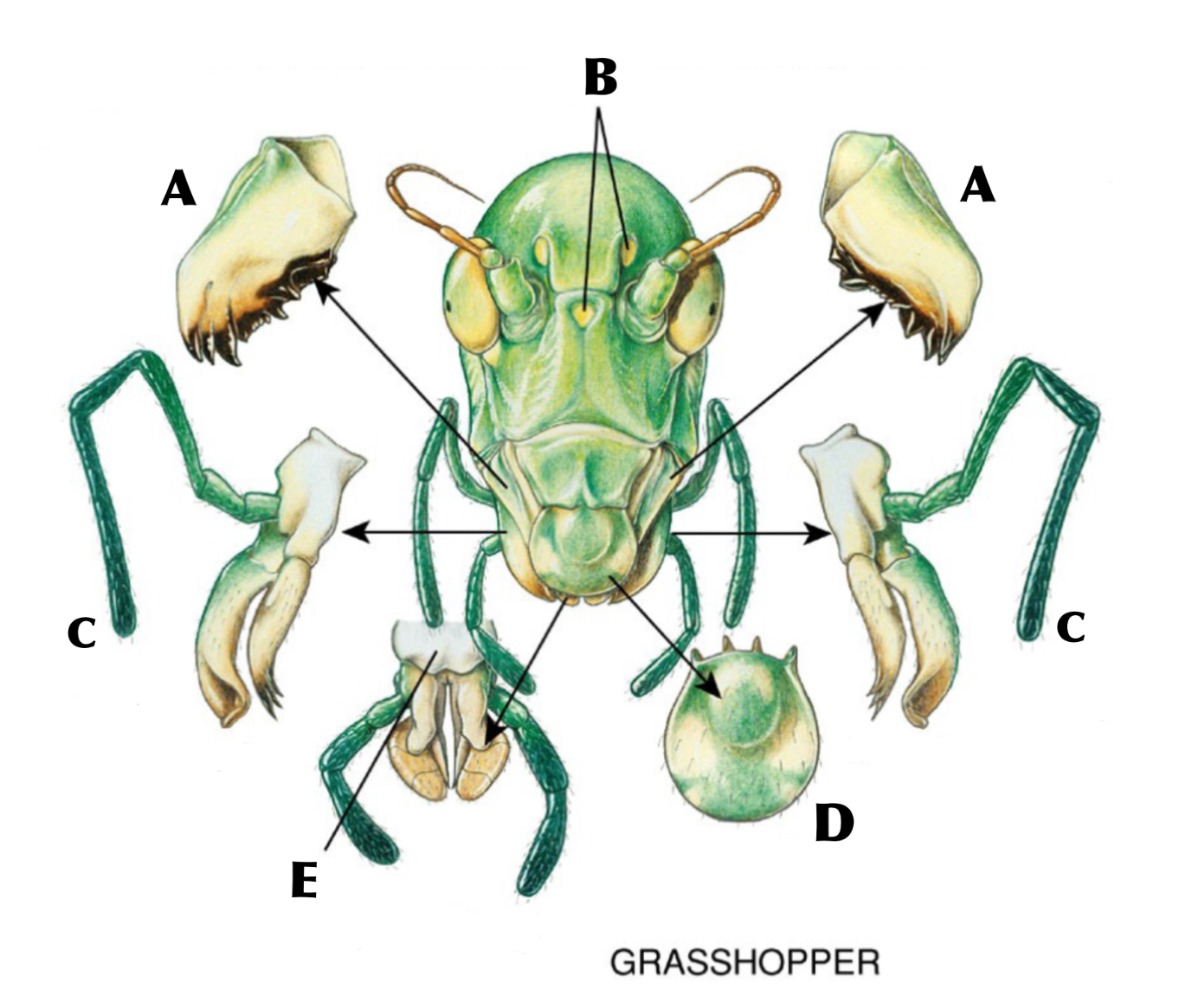
What is C
Maxilla with maxillary palp
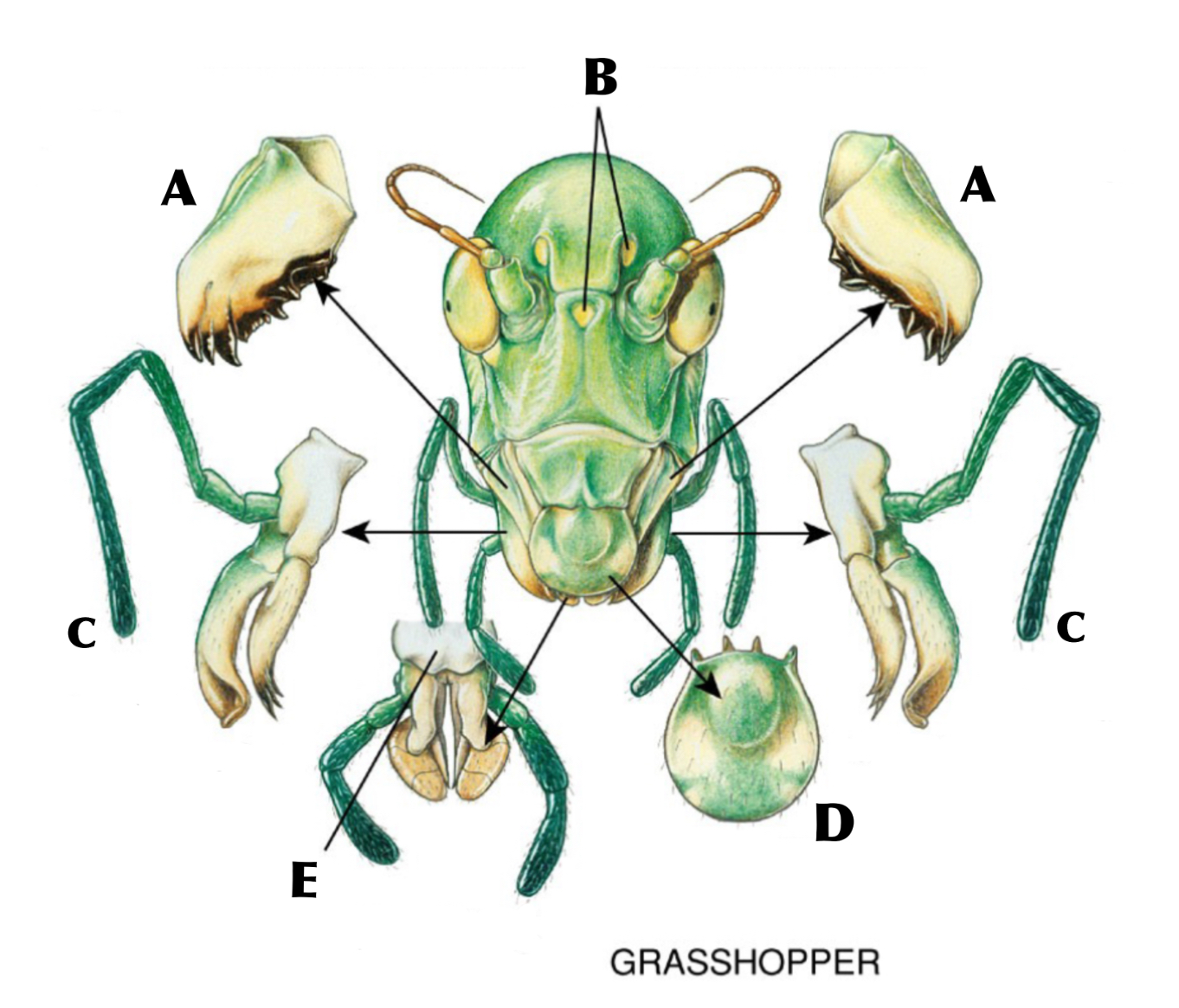
What is D
Labrum
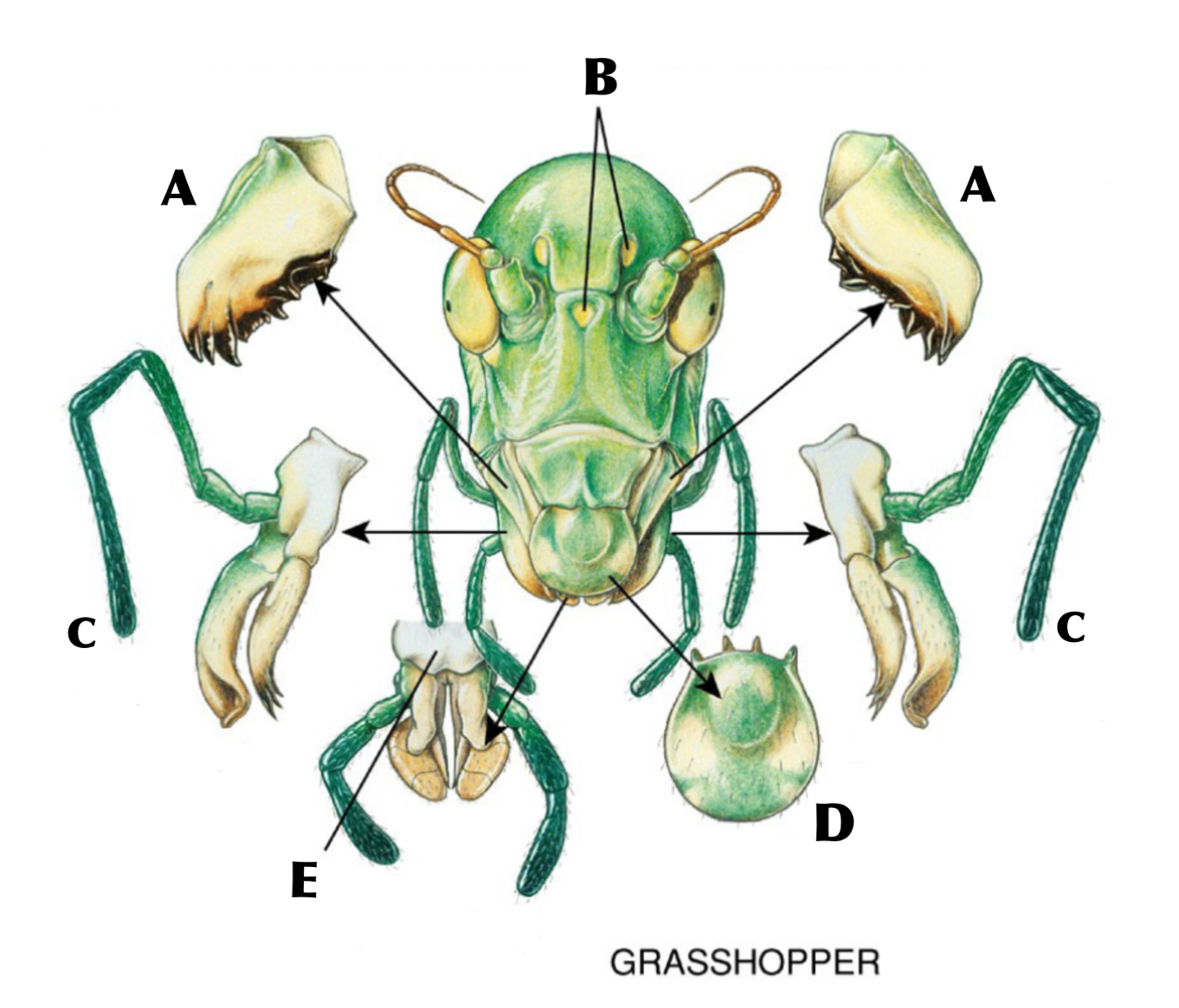
What is E
Labium with labial palps
Palpate
examine by touch
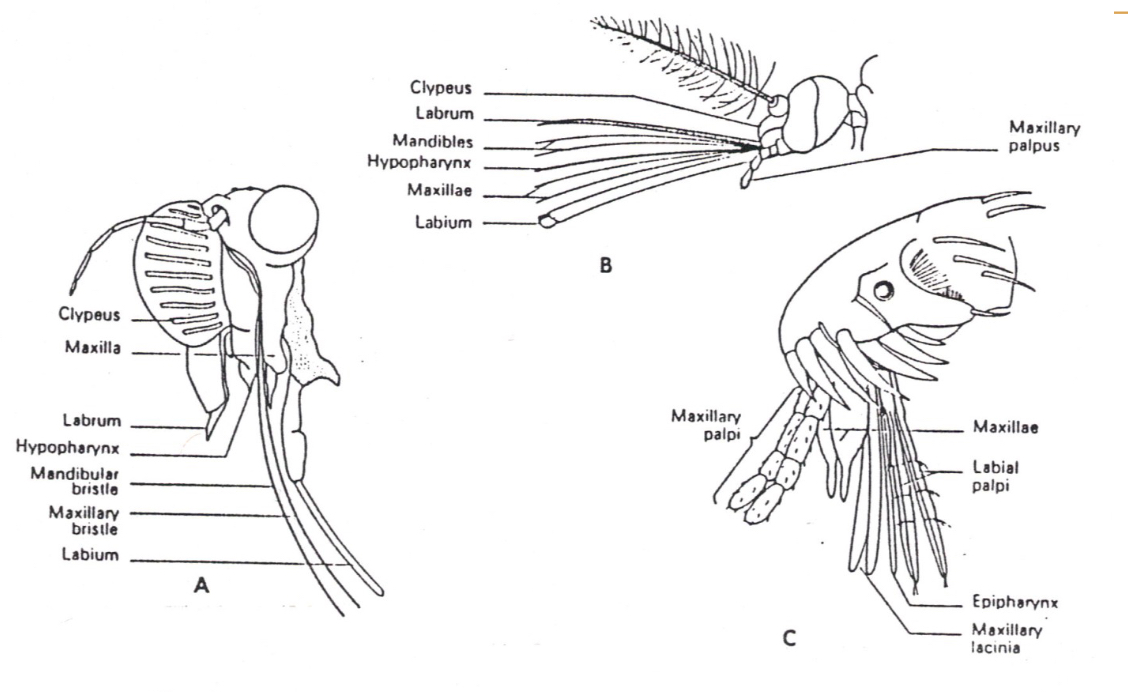
Piercing-sucking mouth parts
specialized structures adapted for feeding on liquids, primarily by penetrating tissues and extracting fluids, found in insects like mosquitoes, aphids, and true bugs, consist of slender, needle-like stylets enclosed within a sheath or proboscis
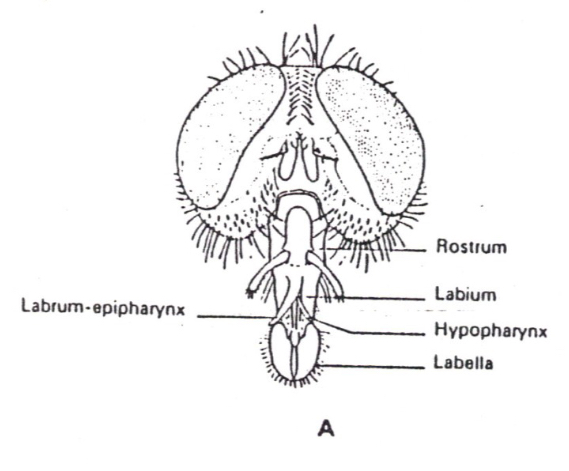
Sponging Mouth parts
specialized for feeding on liquids; the labium is modified into a sponge-like structure called the labellum, which is used to soak up liquids, this structure contains pseudotrachea, which are minute food channels that help draw liquid food into the insect's digestive system
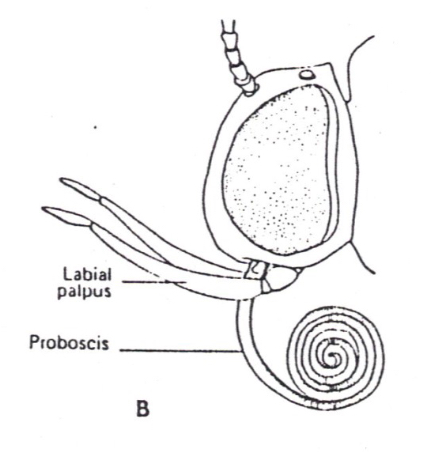
siphoning mouthparts
adapted for feeding on liquids, particularly nectar, characterized by a long, tube-like structure called a proboscis, which functions like a straw to suck up fluids
Chewing-lapping mouthparts
combine chewing and lapping mechanisms, allowing them to consume both solid and liquid food
What are the different kings of sucking mouthparts found in insects
Piercing-sucking, Sponging, Siphoning, Chewing-Lapping
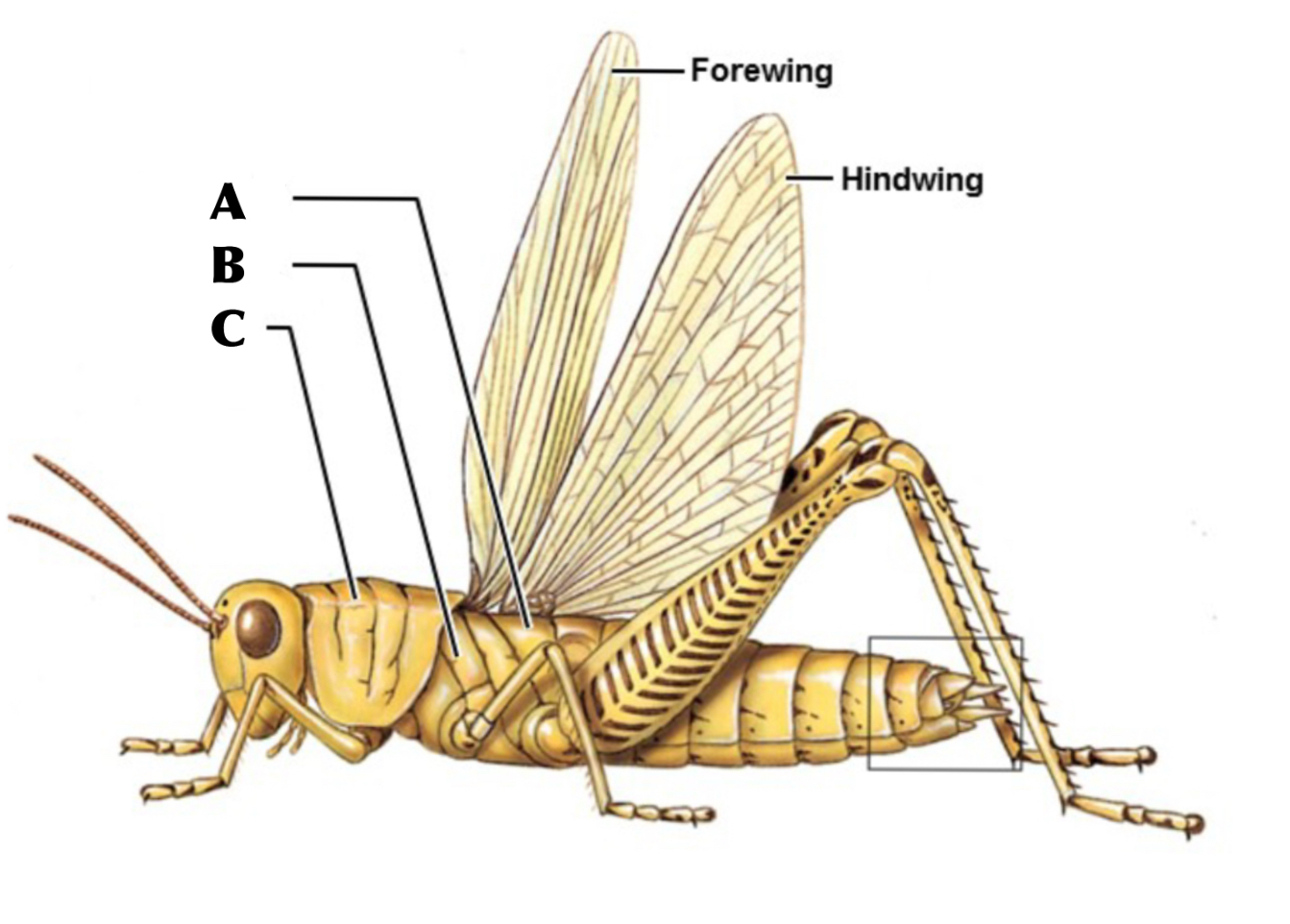
What is A
metathorax
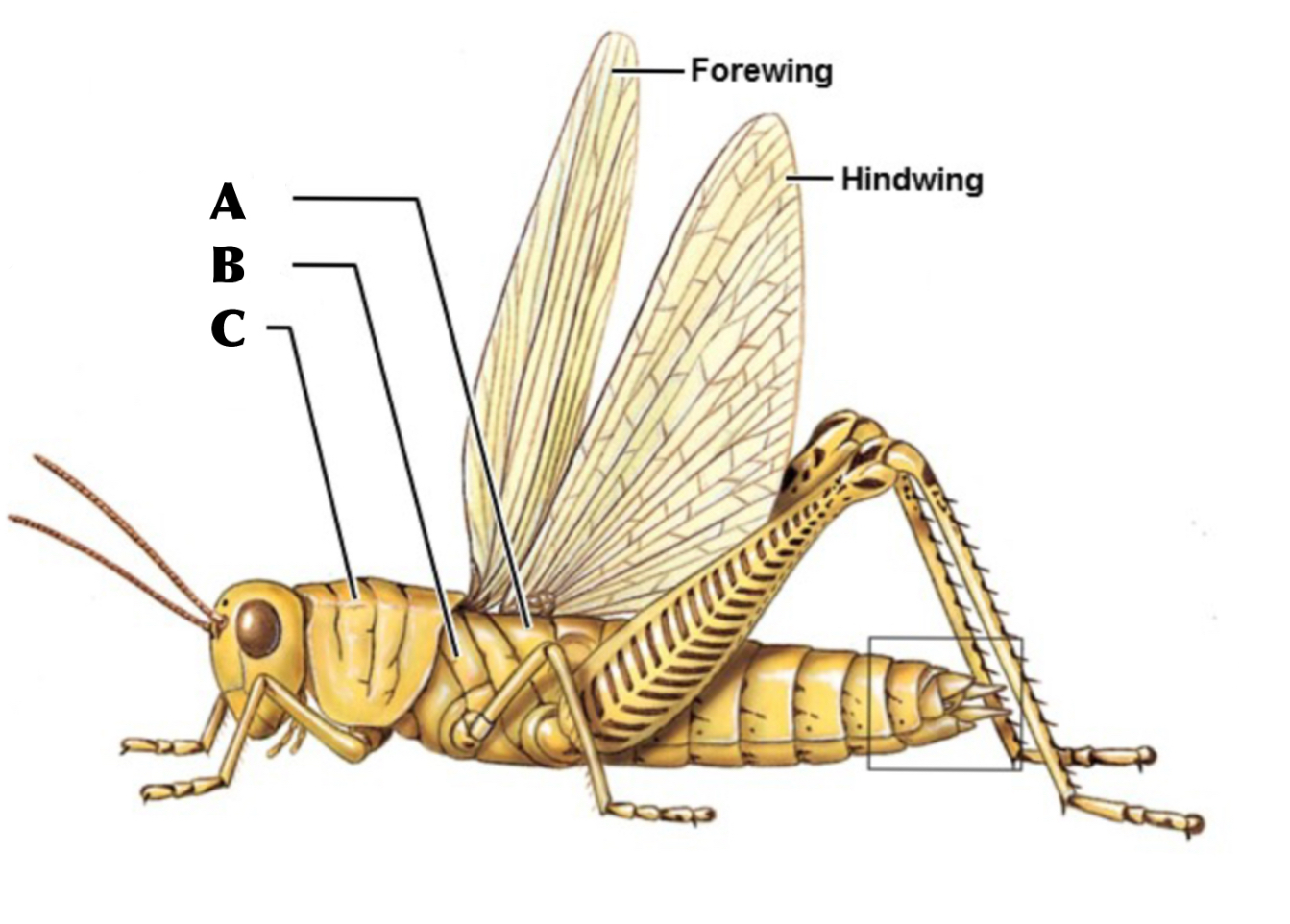
What is B
Mesothorax
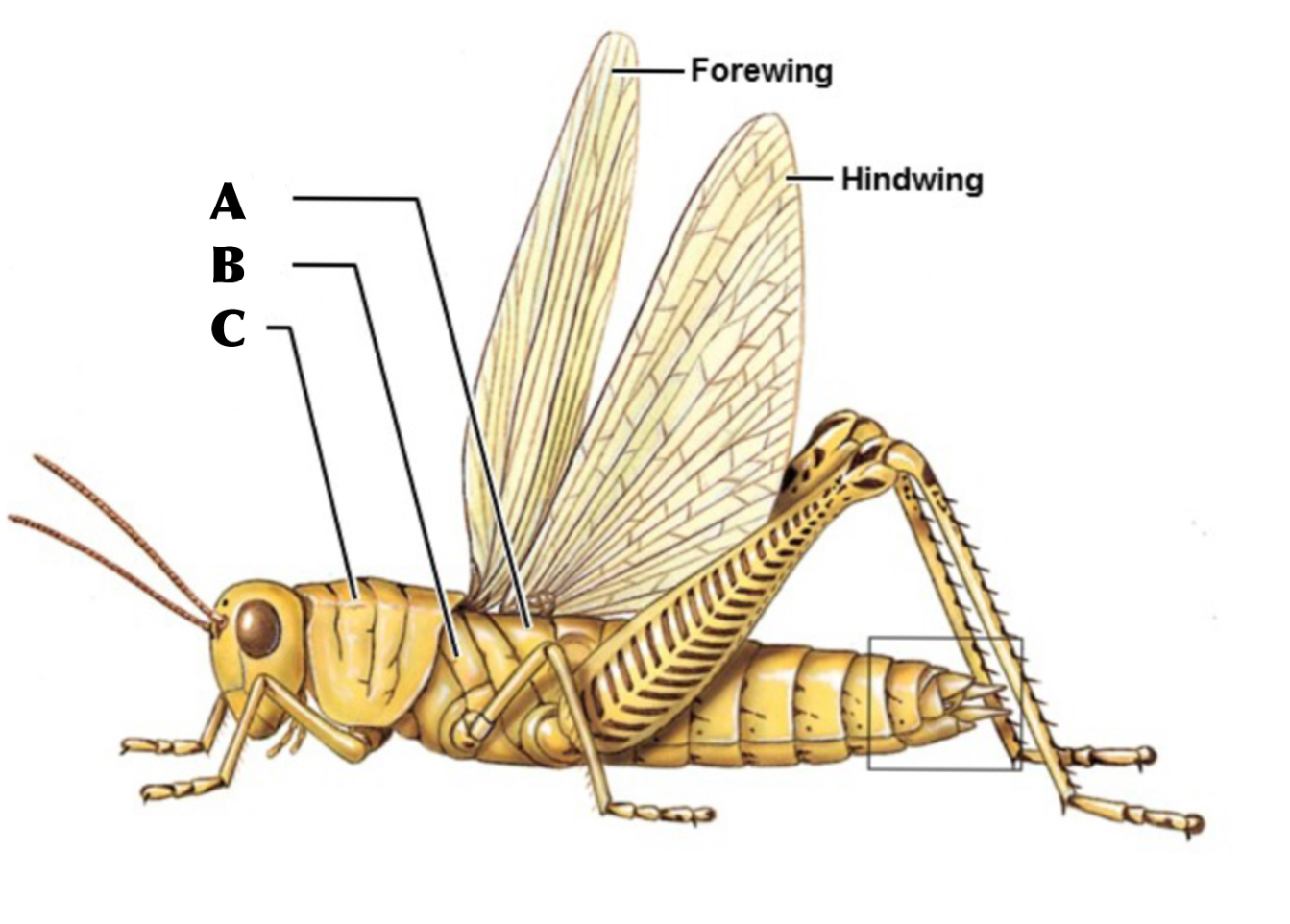
What is C
Prothorax
What are the sections of the thorax from anterior to posterior
Prothorax, Mesothorax, Metathorax
What does the suffix “-mere”
part or segment
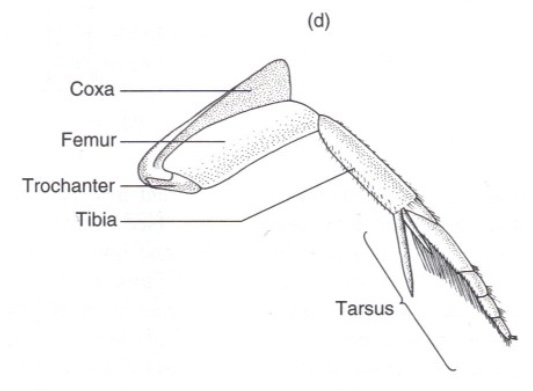
Pretarsus
The distal segment of the leg in many insects, often including a pair of claws
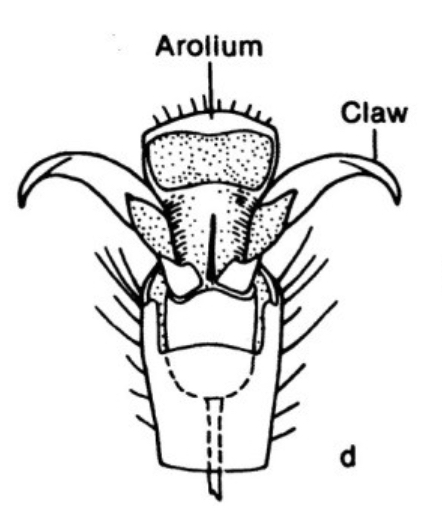
Arolium
cushion-like adhesive pads found on the ends of tarsus on legs in insects like flies and bees
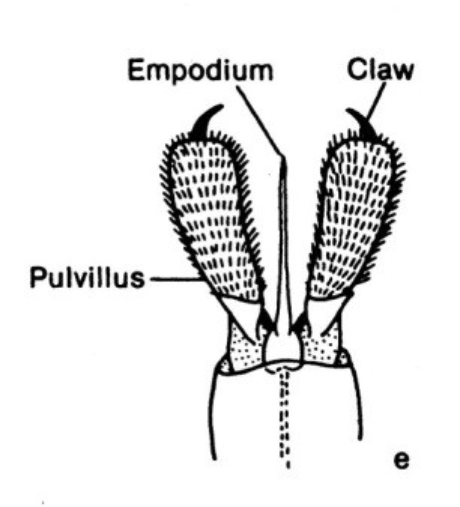
Pulvillus
cushion-like adhesive pad found on the feet between the claws, on either side of the arolium of many insects —(add photo)
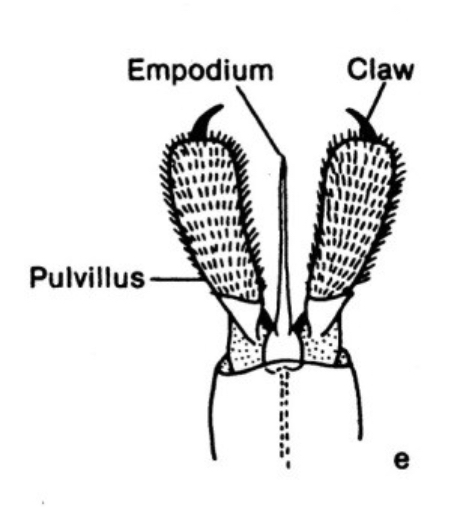
Empodium
a small, often bristle-like, structure found between the claws on an insect's tarsus —(add photo)
What are the different types of legs found in Insects
Fossorial, Cursorial, Saltatorial, Raptorial, Natatorial
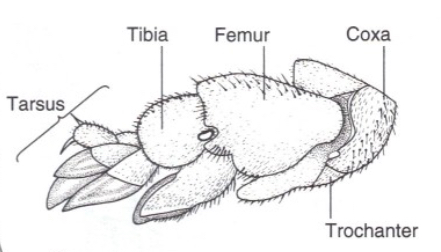
What are Fossorial type legs used for?
digging and burrowing
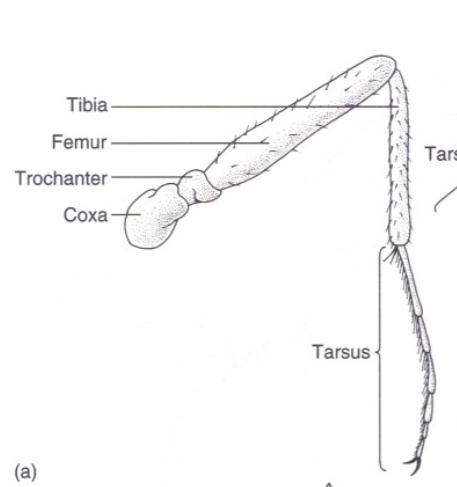
What are Cursorial type legs used for?
Running, locomotion
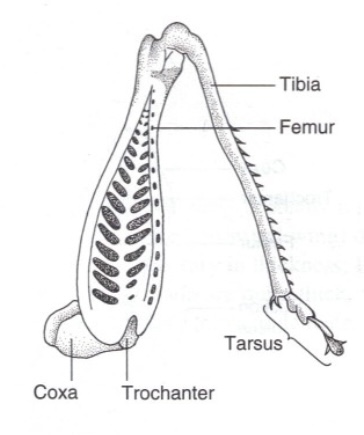
What are Saltatorial type legs used for?
Jumping
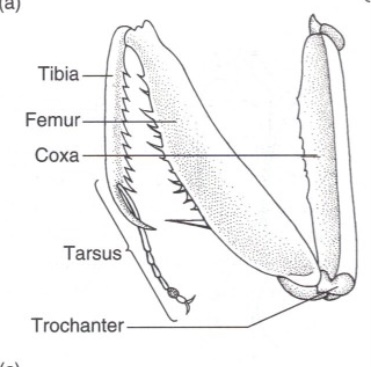
What are Raptorial type legs used for?
Capturing and holding prey
What are Natatorial type legs used for?
Swimming
What are the types of wings?
Membranous, Tegmina, Elytra, Hemelytra
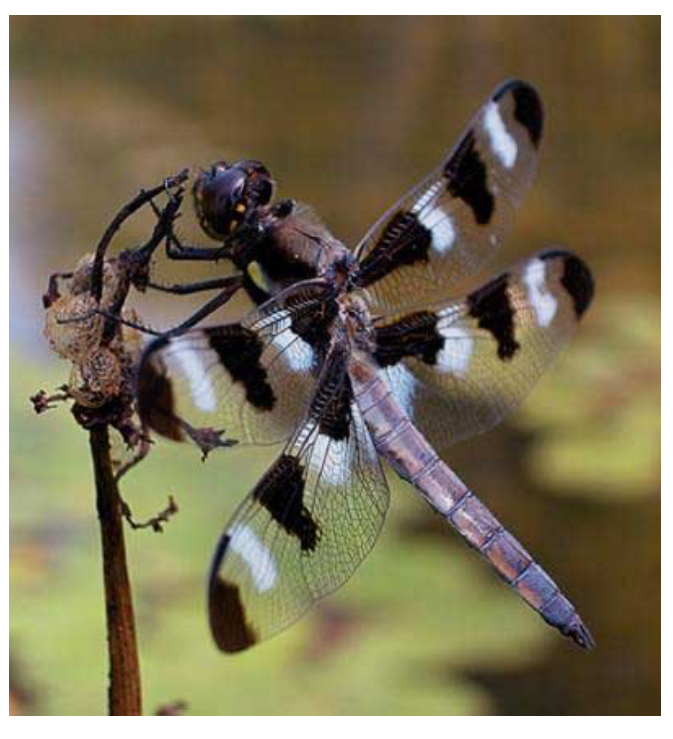

Membranous Wings
Thin, flexible, and often translucent with veins for nutrient transport and gas exchange. Most efficient type, most winged insects will have at least one pair(hindpair)
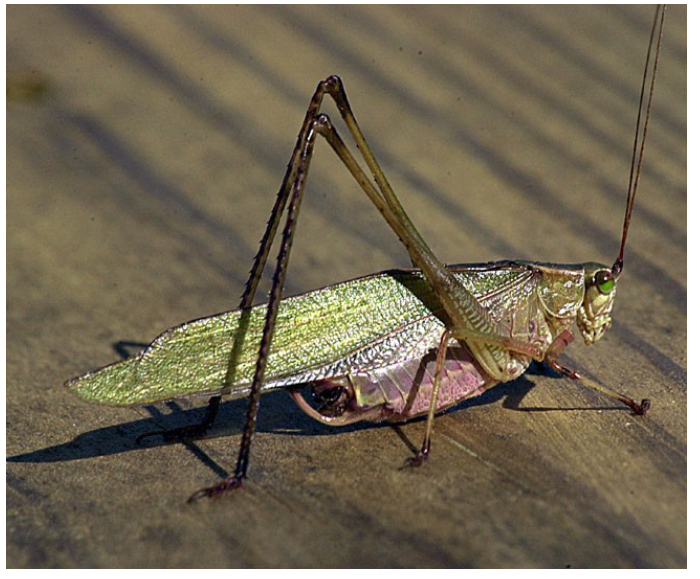

Tegmina Wings
Leathery, parchment-like, durable but flexible. serve as primarily as protection for hindwings and steering during flight. In some insects its modified for sound production
Elytra wings
Not used for flight, Hardened, protective forewings
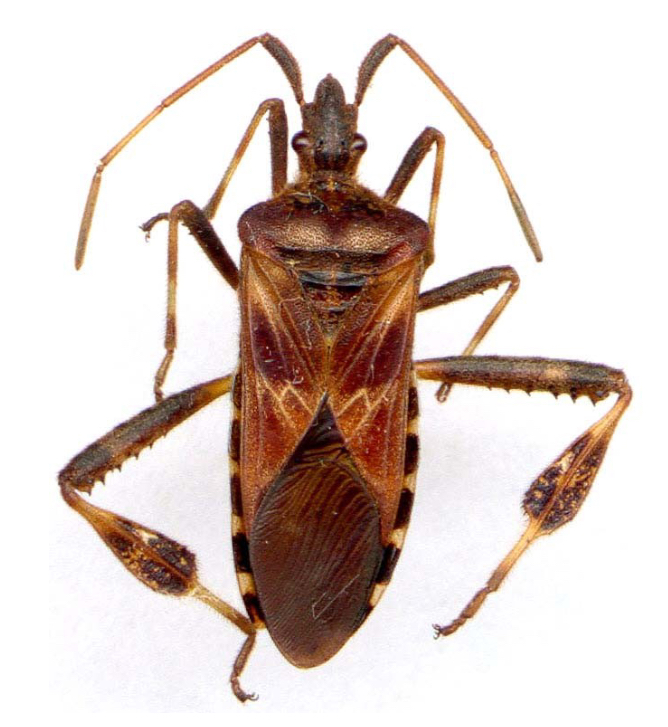

Hemelytra wings
Partially hardened/leathery with membranous tip, found in true bugs
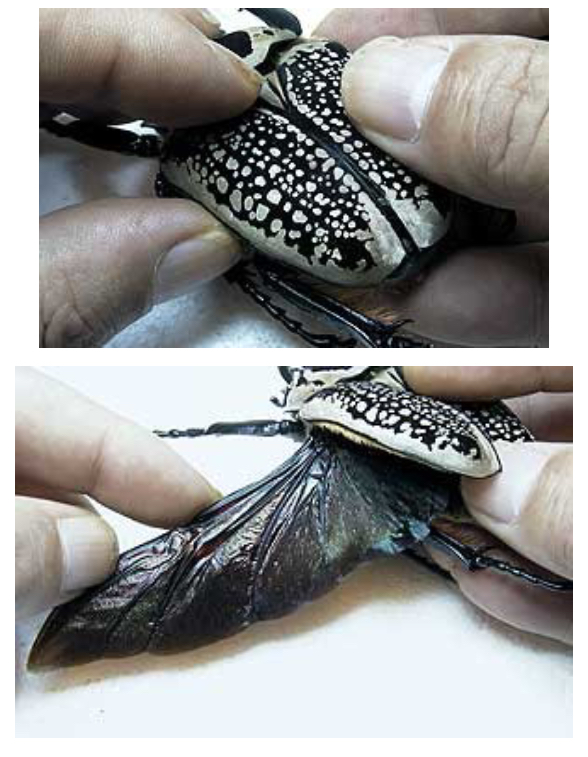
Which is female and which is male
A is Female and B is Male
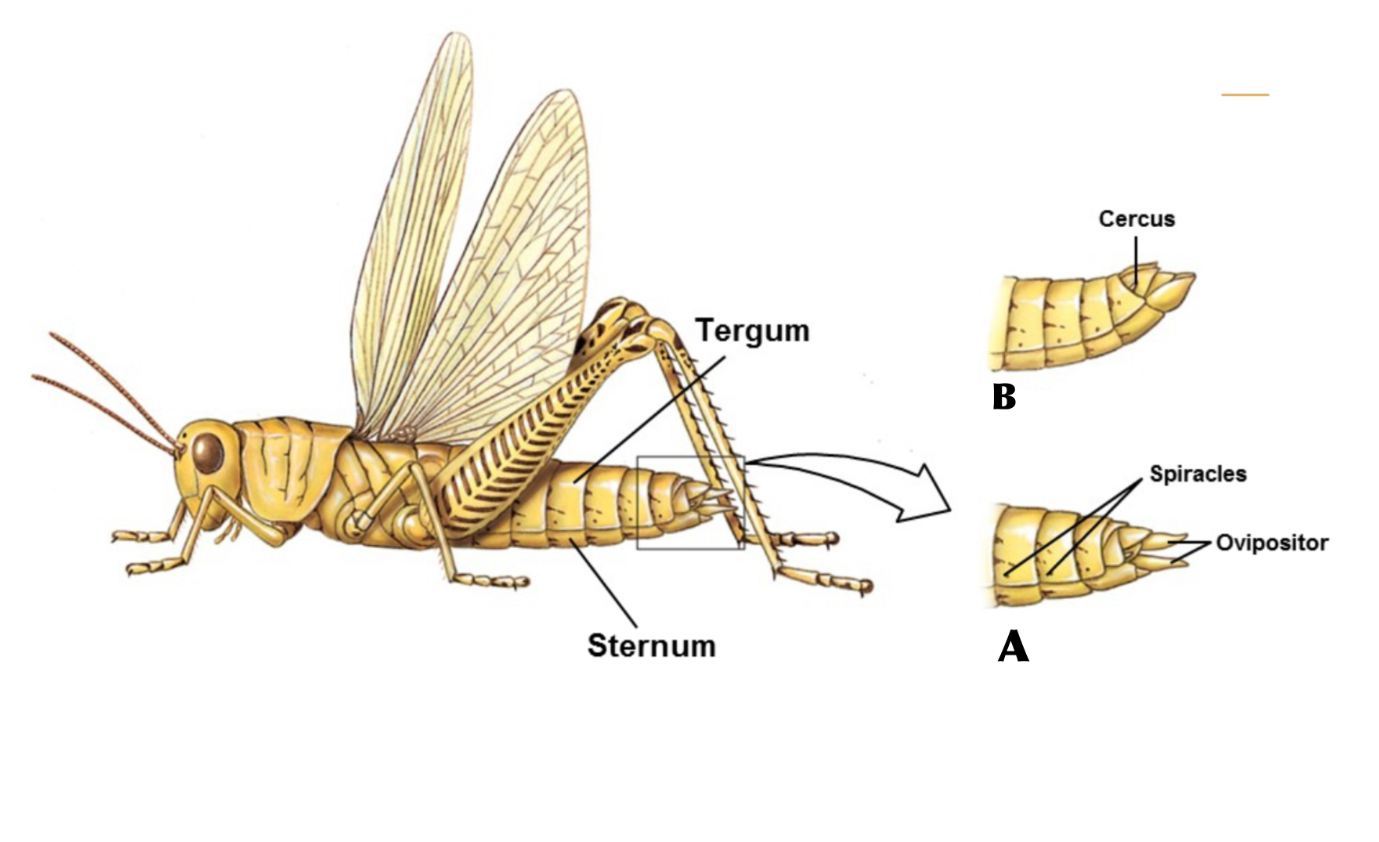
What is A
Tergum
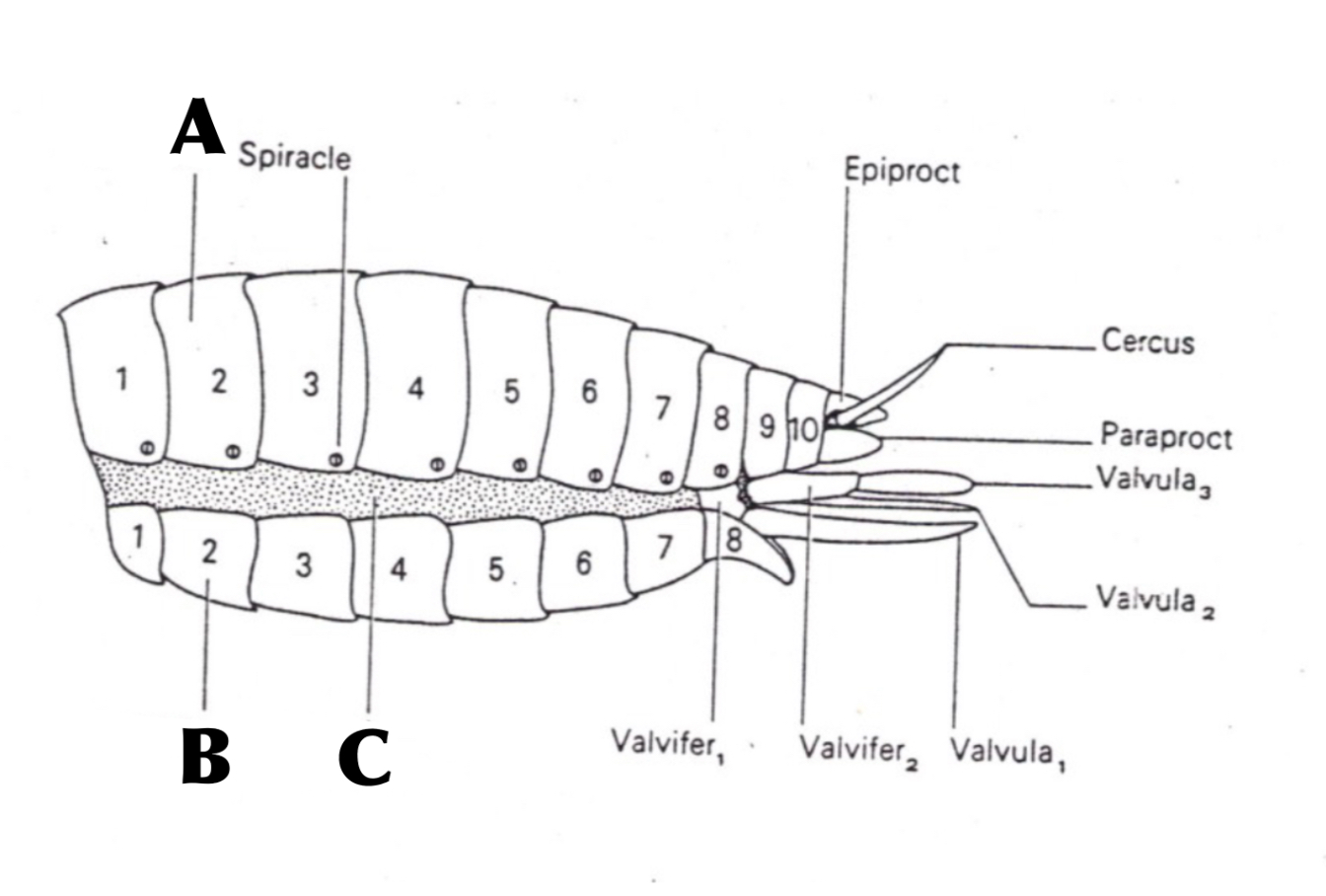
What is B
Sternum
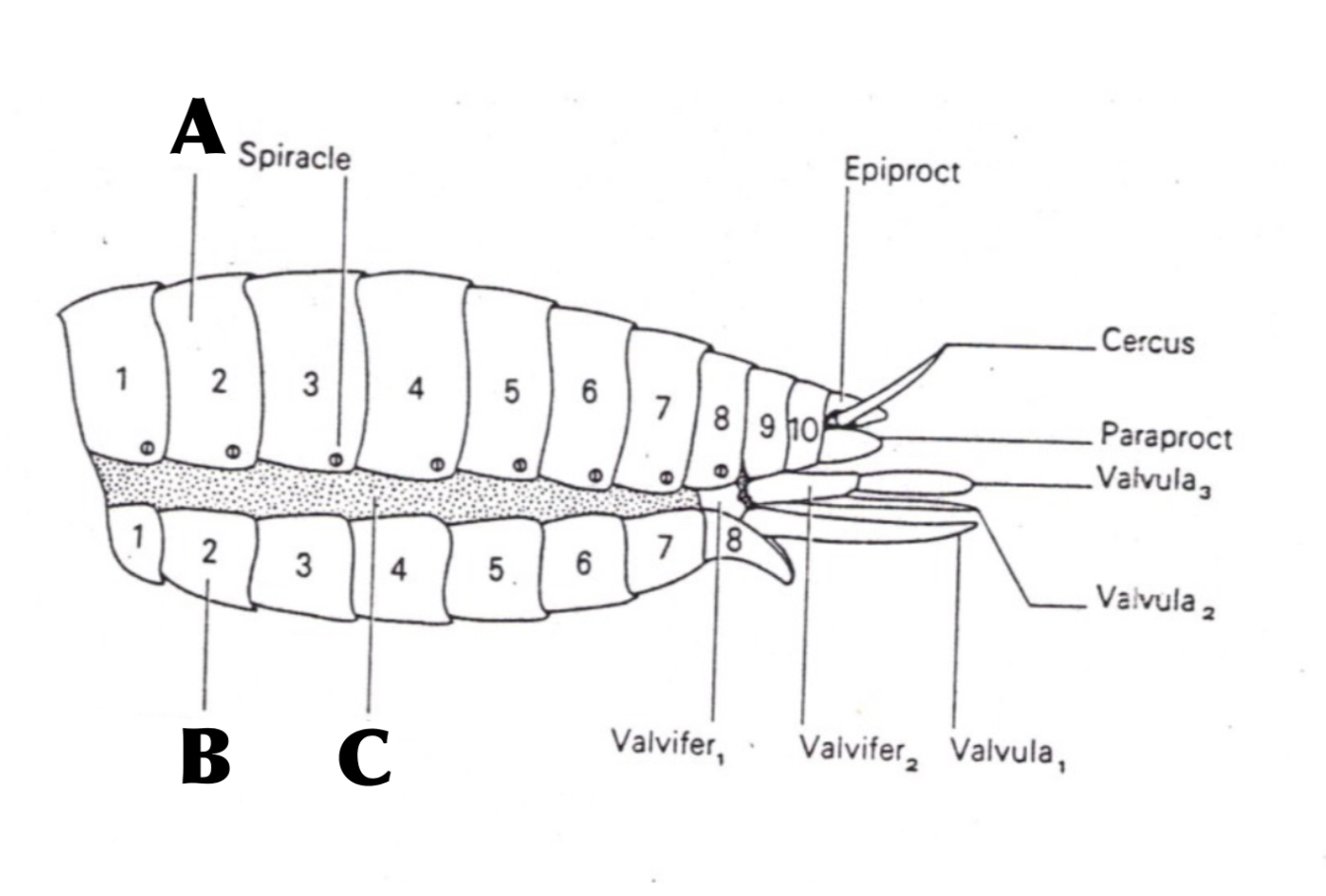
What is C
Pleural Membrane
Pleural Membrane
Membranous joint between Tergum and Sternum, that allows abdomen to stretch for feeding and space for unborn young
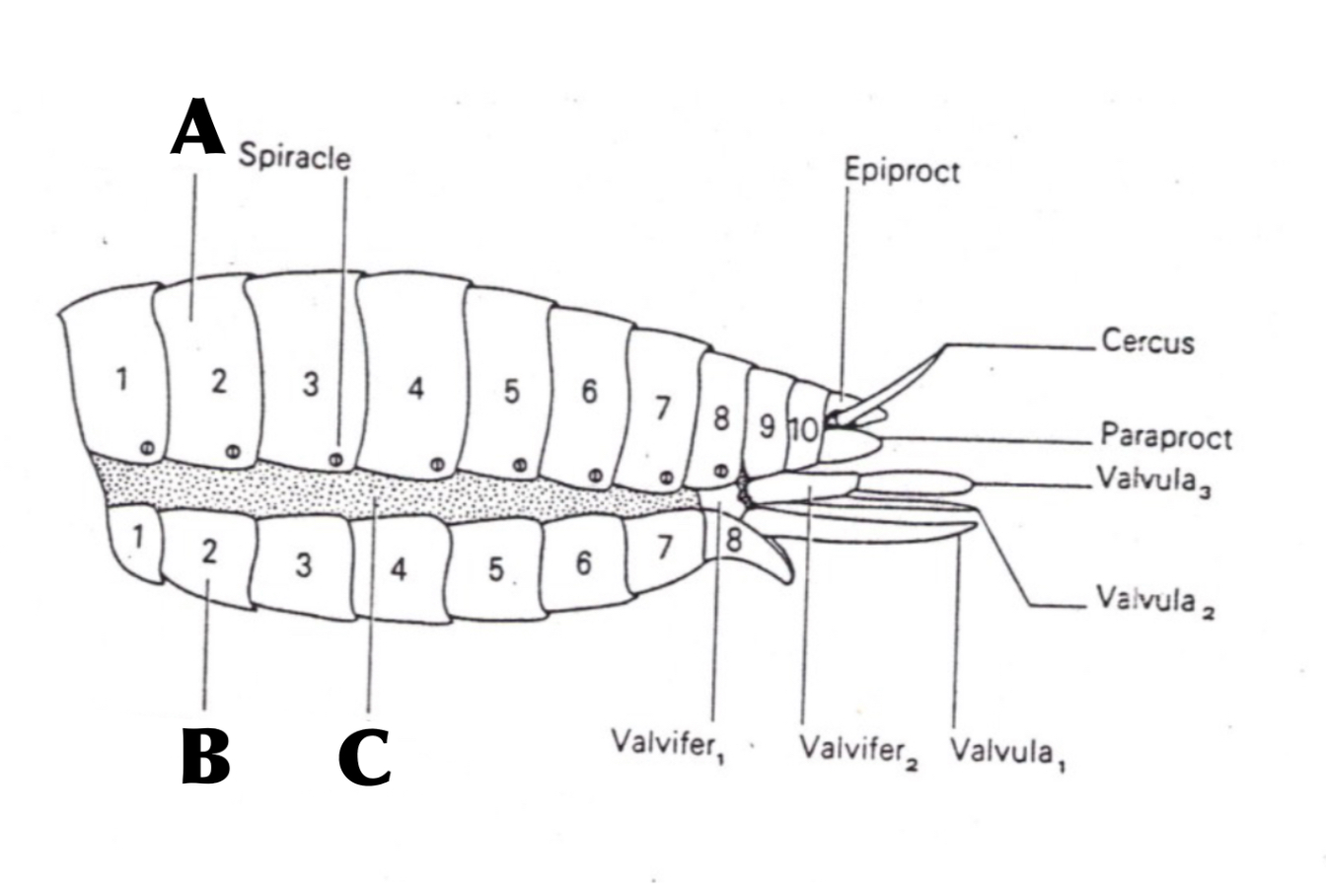
Ovipositor
a specialized organ in many female insects, and some other animals, that is used for laying eggs
Cercus
a small appendage at the end of the abdomen of some insects and other arthropods used to detect air currents and vibrations, which helps insects sense danger and escape predators

Capitate Antennae
knob/club at tip, sensory organ with a strong emphasis on smell
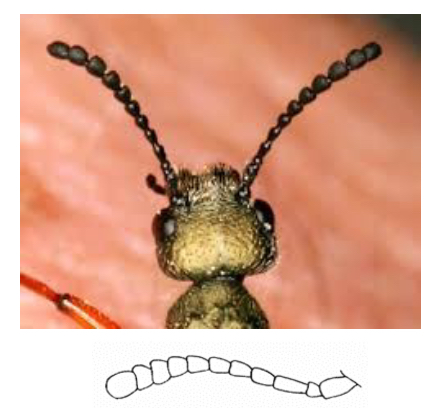

Clavate Antennae
Club like swelling at tip, sensory organ used to detect stimuli like smells, humidity, and vibrations
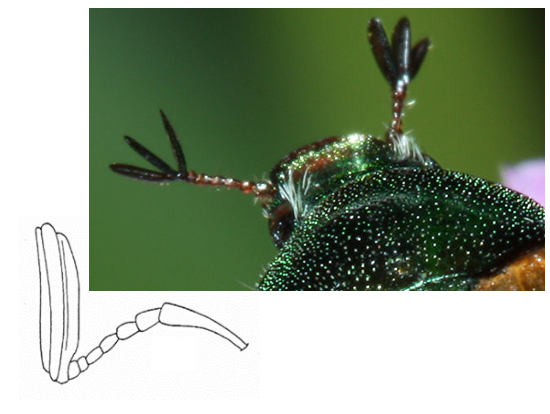

Lamellate Antennae
Consists of flattened, plate-like segments used for enhanced chemoreception