Energy Transformations and Enzyme Function in Metabolism
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
What is energy in the context of biological systems?
Energy is the capacity to do work or the capacity for change.
What are the two categories of energy?
Potential energy (stored energy) and kinetic energy (energy of movement).
What is metabolism?
The sum total of all chemical reactions in an organism.
What are anabolic reactions?
Reactions that build complex molecules from simple ones, requiring an input of energy.
What are catabolic reactions?
Reactions that break down complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy.
What does the first law of thermodynamics state?
Energy is neither created nor destroyed; the total energy before and after conversion remains the same.
What does the second law of thermodynamics state?
Some energy becomes unavailable to do work during transformations, and disorder tends to increase.
What is entropy?
A measure of disorder in a system; it takes energy to impose order.
How is total energy in a system expressed?
Total energy = usable energy + unusable energy.
What is the relationship between enthalpy (H), free energy (G), and entropy (S)?
H = G + TS, where T is the absolute temperature.
How can changes in energy be measured?
In calories or joules.
What does ΔG represent in a chemical reaction?
The change in __________, calculated as ΔG = ΔH - TΔS.
What does a negative ΔG indicate?
Free energy is released.
What does a positive ΔG indicate?
Free energy is consumed.
What happens if free energy is not available for a reaction?
The reaction does not occur.
What factors influence the magnitude of ΔG?
ΔH (total energy added or released) and ΔS (change in entropy).
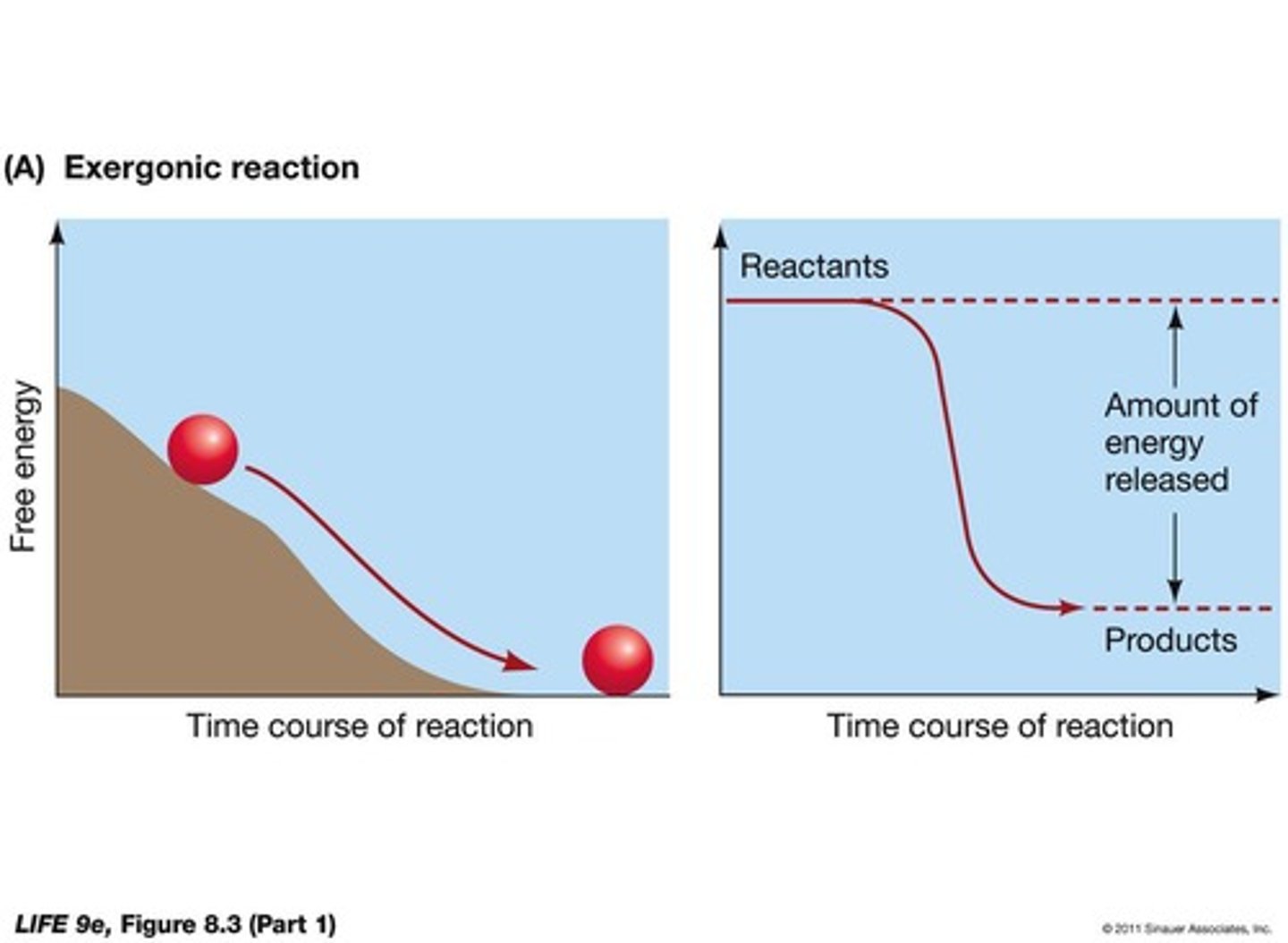
What is an exergonic reaction?
A reaction that releases free energy (-ΔG) and decreases complexity.
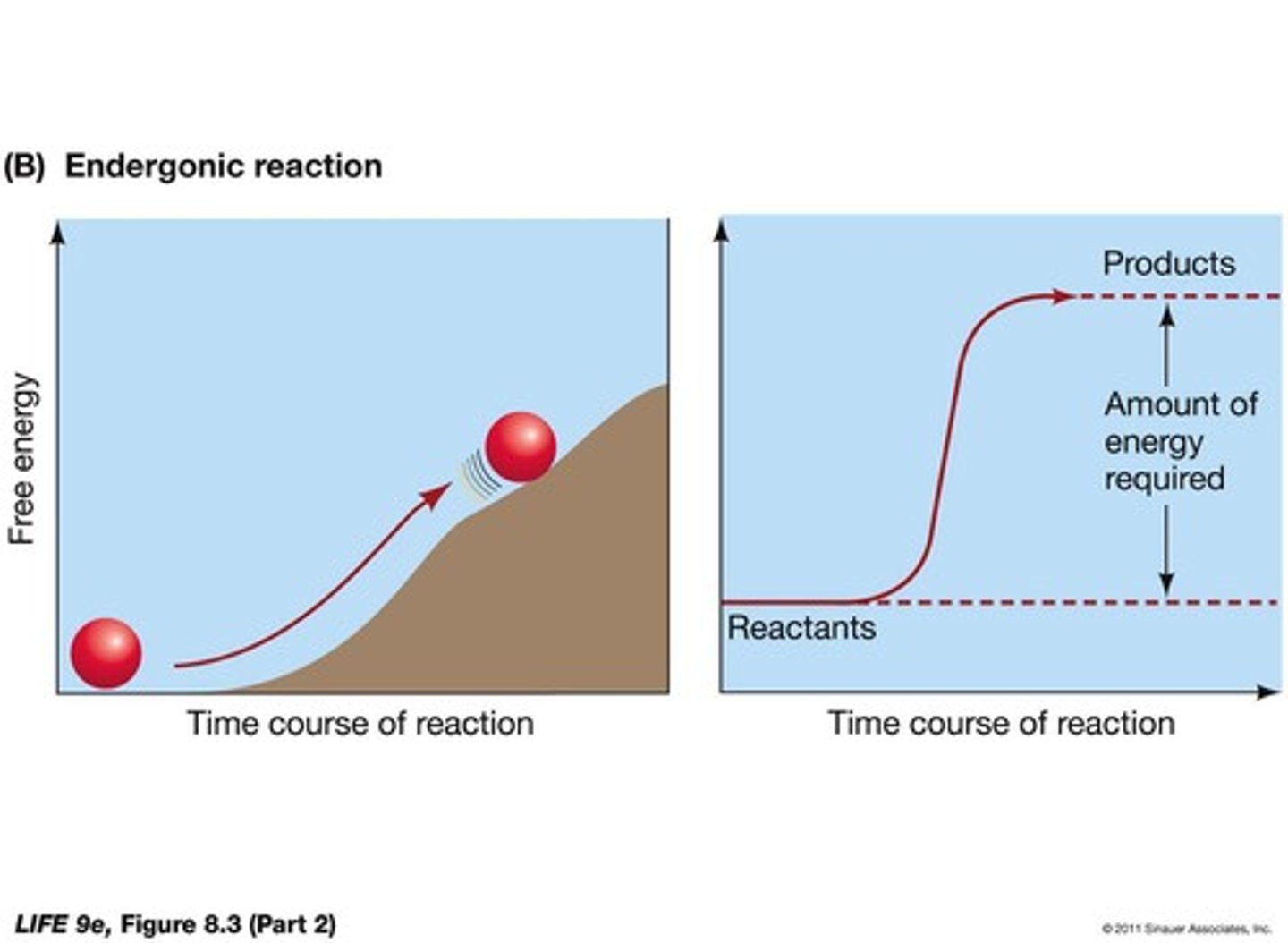
What is an endergonic reaction?
A reaction that consumes free energy (+ΔG) and increases complexity.
What occurs at chemical equilibrium?
ΔG = 0, meaning forward and reverse reactions are balanced.
What determines the favored direction of a chemical reaction?
The concentrations of the reactants and products.
What is an example of a reaction that increases entropy?
The hydrolysis of a protein into its component amino acids, resulting in a positive ΔS.
What is the significance of large changes in entropy?
They make ΔG more negative, favoring the occurrence of the reaction.
What is the role of energy transformations in living organisms?
They are essential for maintaining order and sustaining life.
What determines the direction favored in a reaction involving A and B?
The concentrations of A and B.
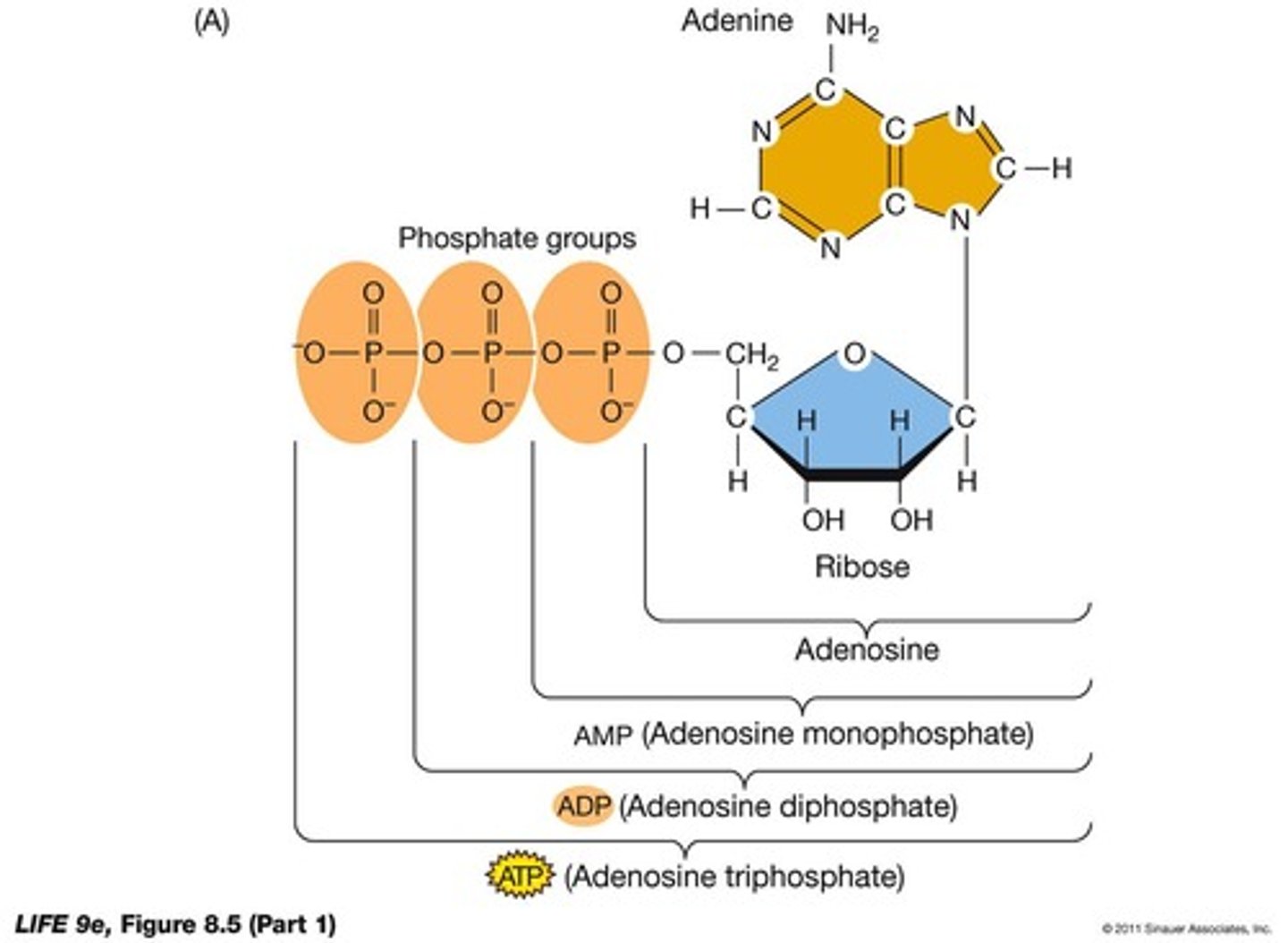
What is the role of ATP in biochemical energetics?
ATP captures and transfers free energy, releasing energy when hydrolyzed.
What type of reaction is ATP hydrolysis?
Exergonic.
What is the process of ATP formation?
ATP formation is endergonic, supplied by catabolic pathways or sunlight.
What is the free energy change (ΔG) for ATP hydrolysis?
ΔG = -7.3 to -14 kcal/mol.
What is bioluminescence in relation to ATP?
______ is an endergonic reaction driven by ATP hydrolysis.
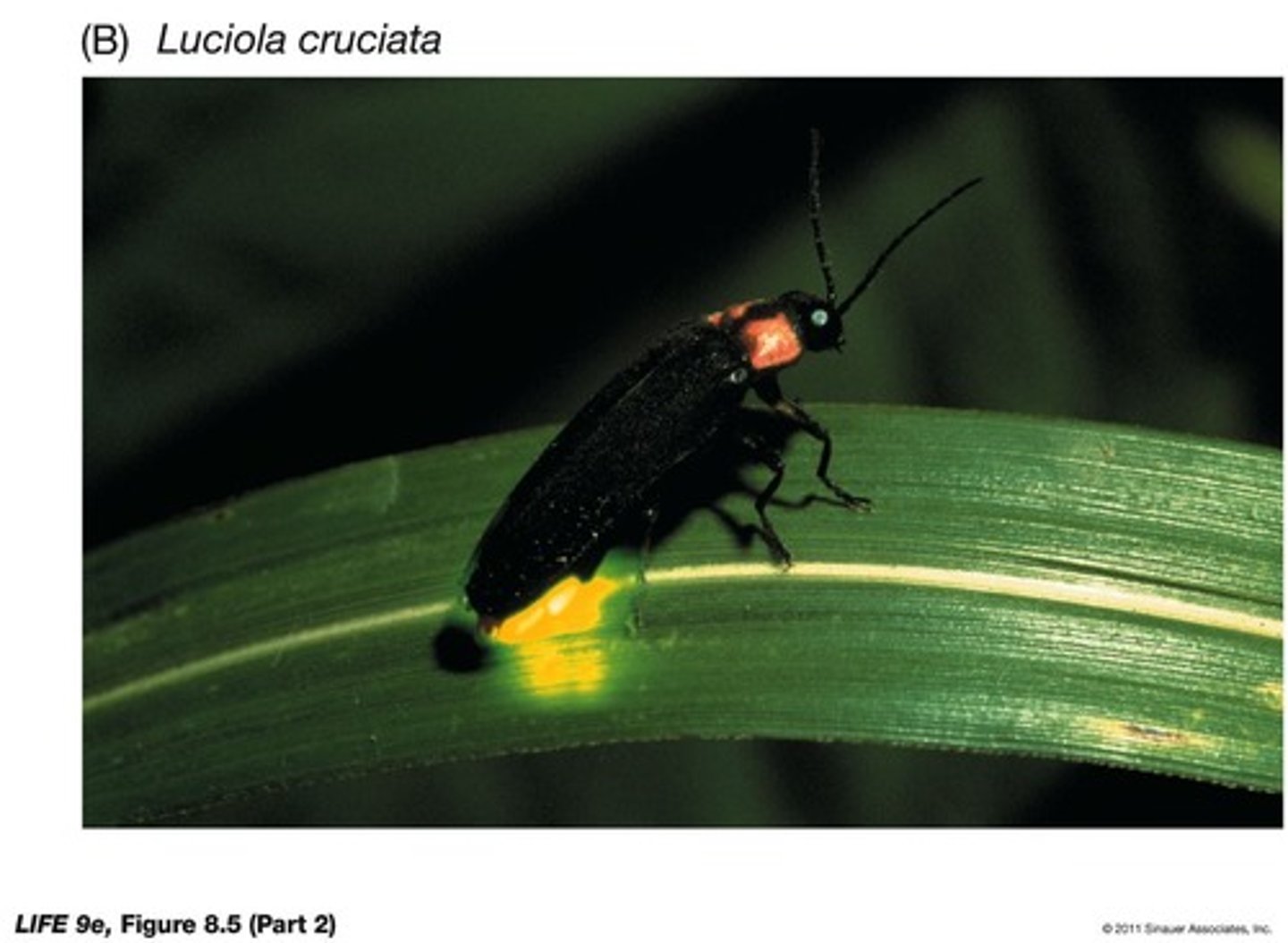

How are exergonic and endergonic reactions related?
They are coupled.
What is the role of catalysts in reactions?
What are most biological catalysts?
Most ________ are enzymes which are proteins.
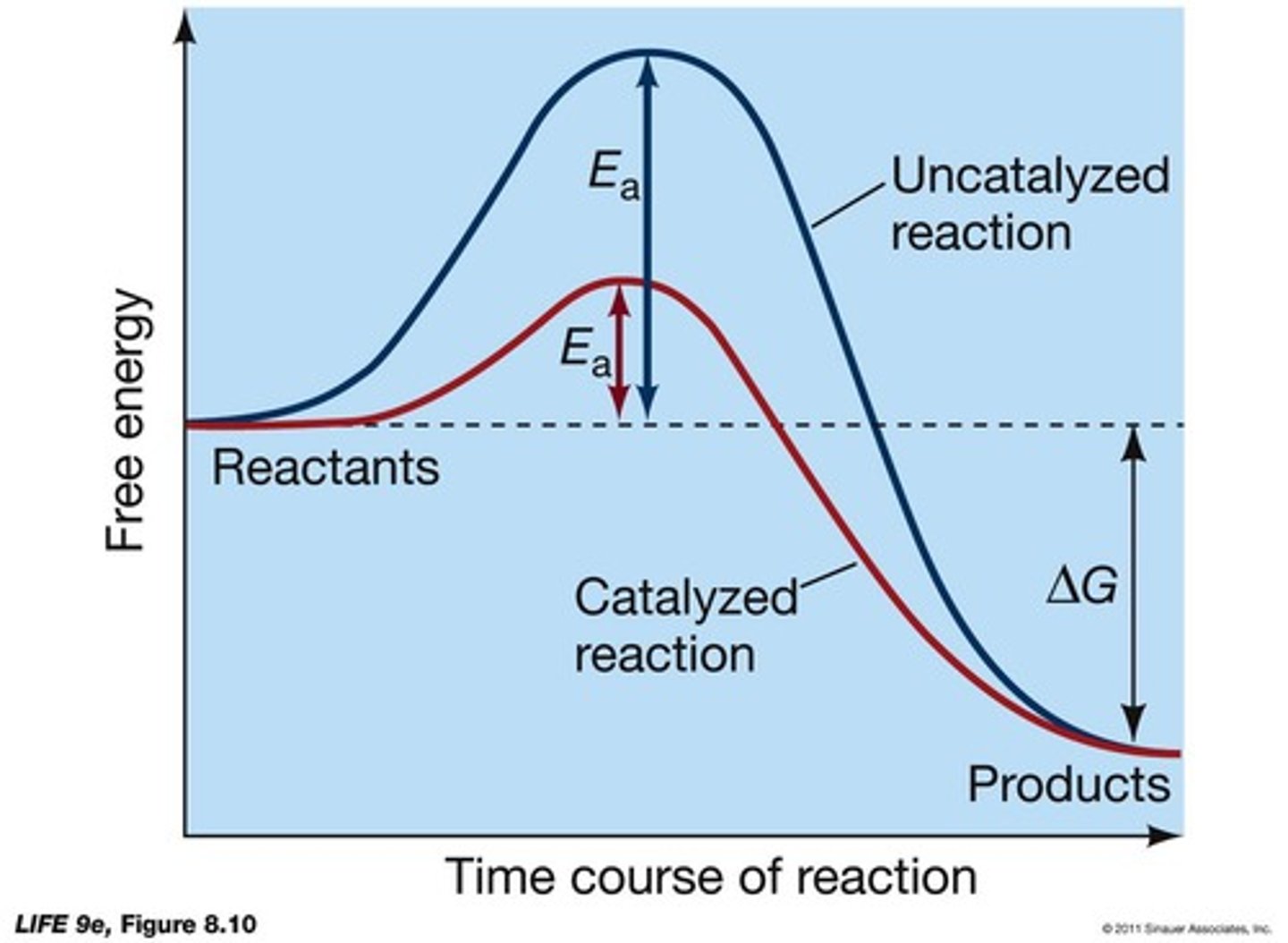
What is activation energy (Ea)?
The amount of energy required to start a reaction.
How do enzymes and ribozymes affect activation energy?
They lower the energy barrier by bringing reactants together.
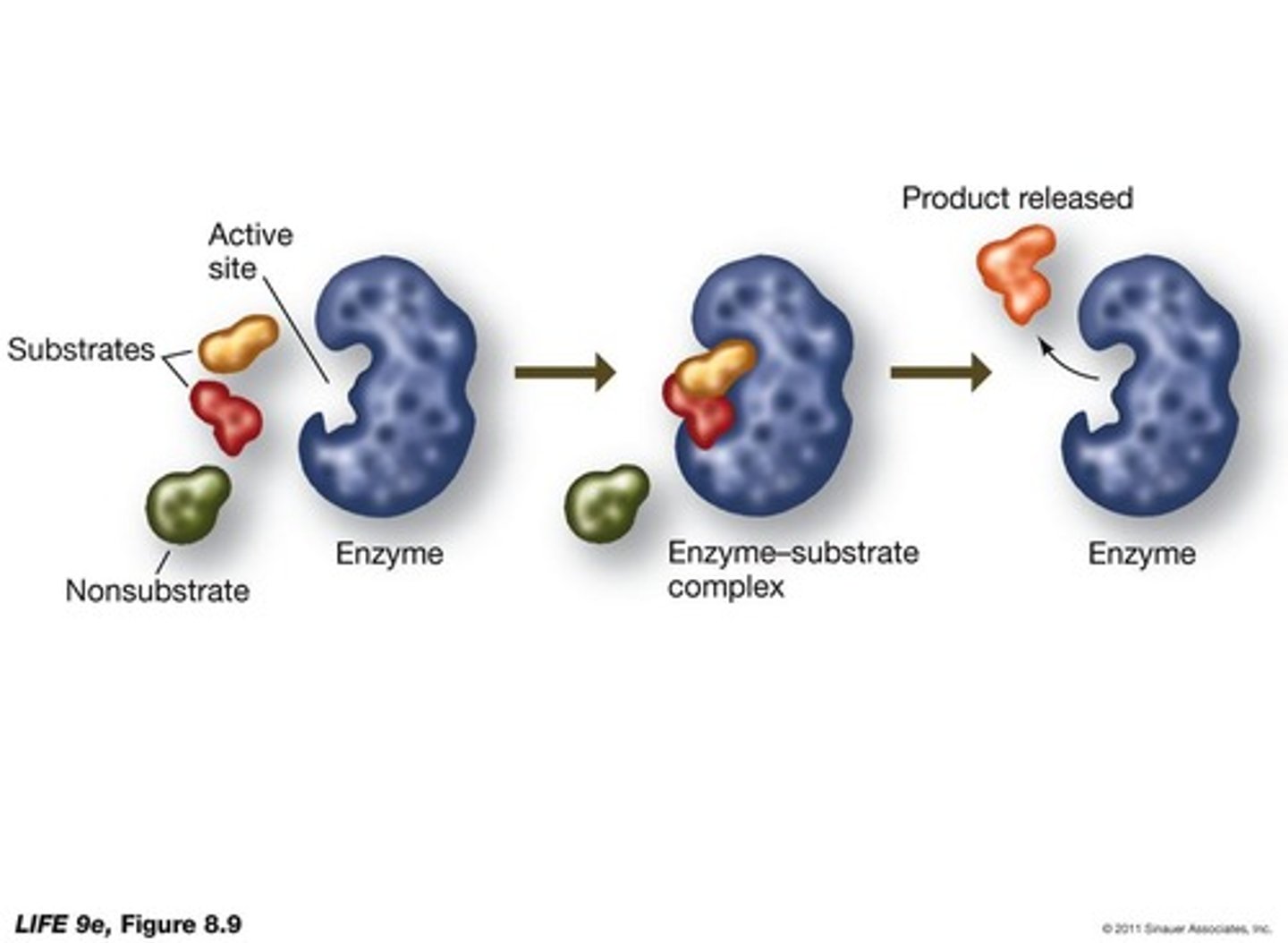
What is the specificity of biological catalysts?
(enzymes and ribozymes) are highly specific, with reactants called substrates.
What binds to the active site of an enzyme?
Substrate molecules.
How is the enzyme-substrate complex (ES) formed?
It is held together by hydrogen bonds, electrical attraction, or covalent bonds.
What happens to an enzyme after it catalyzes a reaction?
The enzyme may change when bound to the substrate but returns to its original form.
What does the final equilibrium of a reaction depend on when catalyzed by an enzyme?
The final equilibrium doesn't change, and ΔG doesn't change.
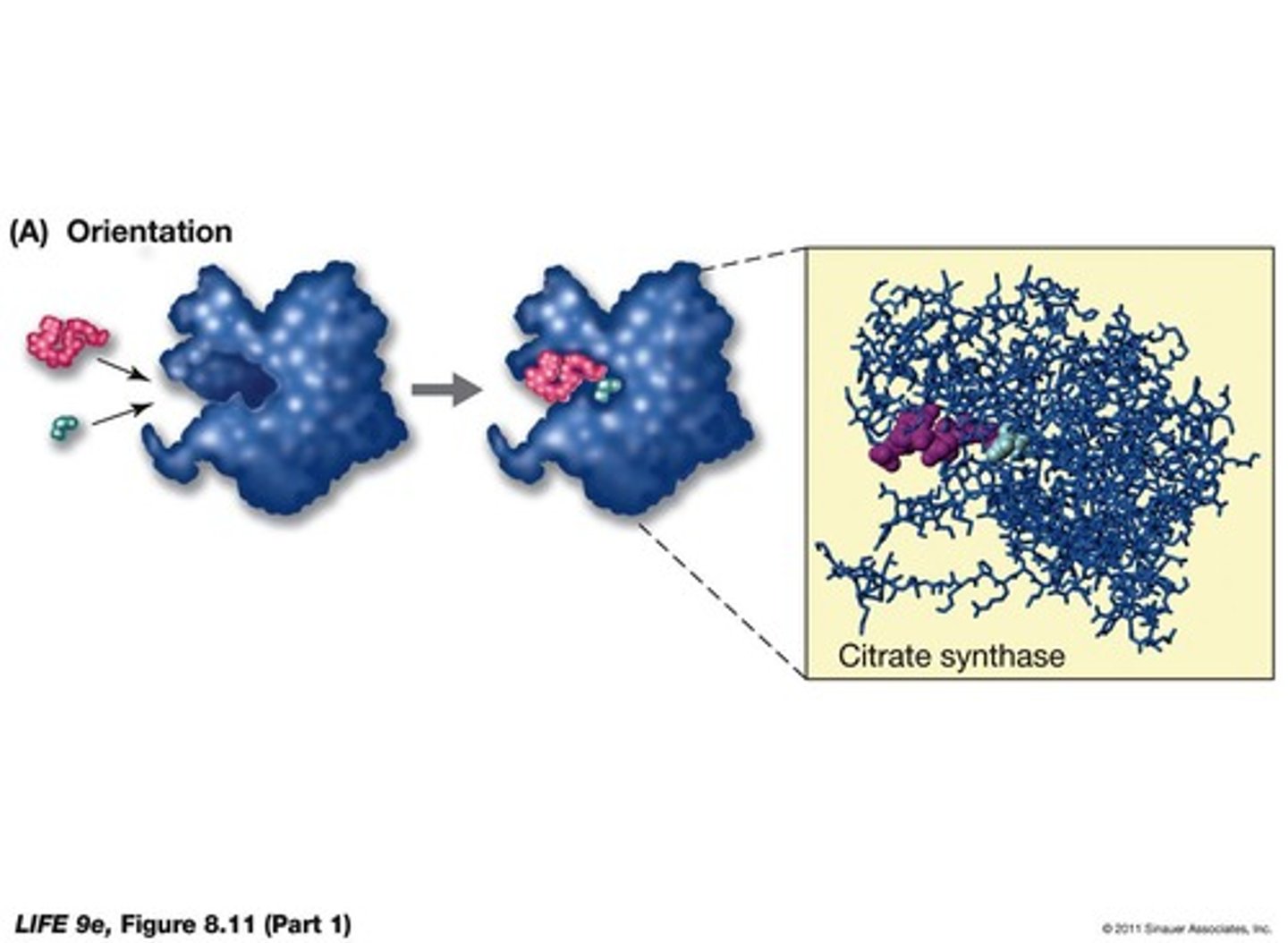
What mechanisms do enzymes use to catalyze reactions?
can orient substrates, stretch bonds, and temporarily add chemical groups.
What types of catalysis can enzymes perform?
Acid-base catalysis, covalent catalysis, and metal ion catalysis.
What is the 'lock and key' model in enzyme function?
The shape of the enzyme active site allows a specific substrate to fit.
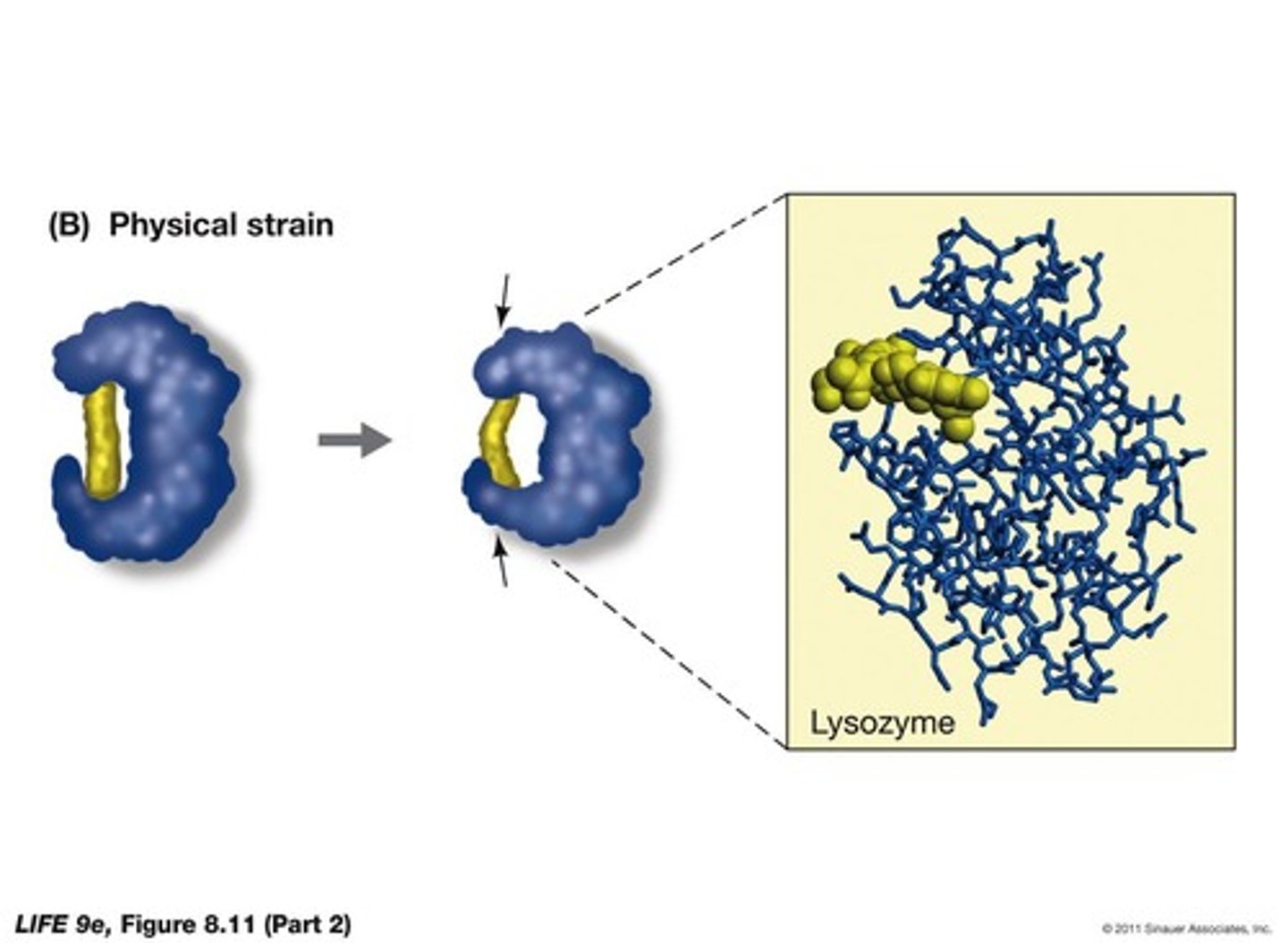
What is induced fit in enzymes?
Many enzymes change shape when they bind to the substrate.
What are prosthetic groups, cofactors, and coenzymes?
________ groups are non-amino acid organic groups; _________ are inorganic ions; _______ are small carbon-containing molecules not permanently bound to enzymes.
What factors influence the rate of a catalyzed reaction?
The ___________ depends on substrate concentration and enzyme efficiency.
What occurs at saturation in enzyme reactions?
At ________________________, all enzyme is bound to substrate, achieving maximum rate.
What is the maximum rate used to calculate enzyme efficiency?
The maximum rate is the number of substrate molecules converted to product per unit time, ranging from 1 to 1 million molecules per second.
What role do enzymes play in metabolic pathways?
Enzymes catalyze specific reactions within interconnected ___________________, helping to maintain internal homeostasis.
What are inhibitors in the context of enzyme regulation?
Inhibitors are molecules that bind to enzymes and slow reaction rates, which can be reversible or irreversible.
What is irreversible inhibition?
occurs when an inhibitor covalently bonds to the active site of an enzyme, permanently inactivating it.
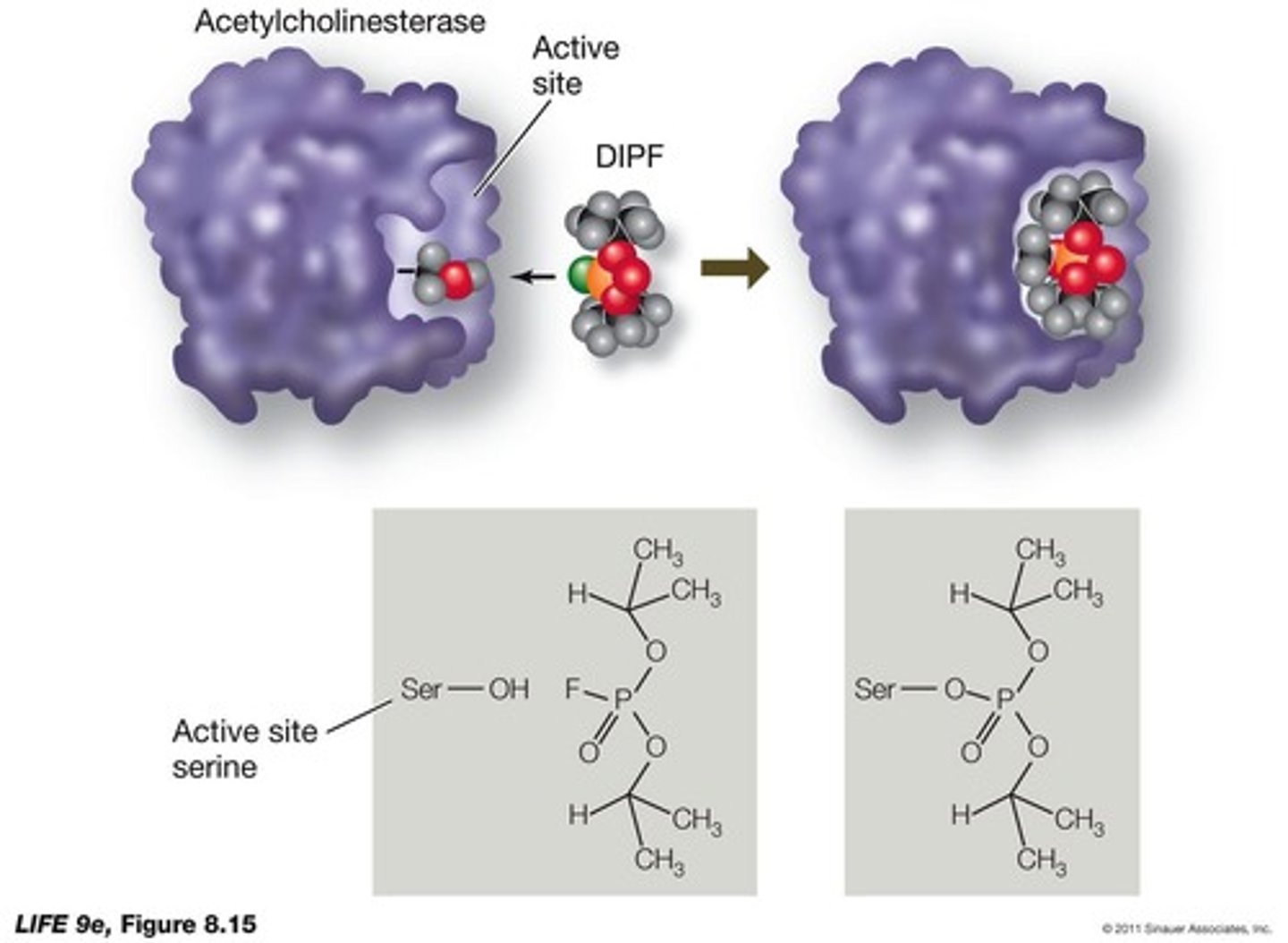
Give an example of an irreversible inhibitor.
DIPF or nerve gas.
What is reversible inhibition?
__________ involves an inhibitor that bonds noncovalently to the active site, preventing substrate binding.
What distinguishes competitive inhibitors from non-competitive inhibitors?
_______________________________ compete with the natural substrate for binding sites, while __________________ inhibitors bind to a different site, altering the enzyme's shape.
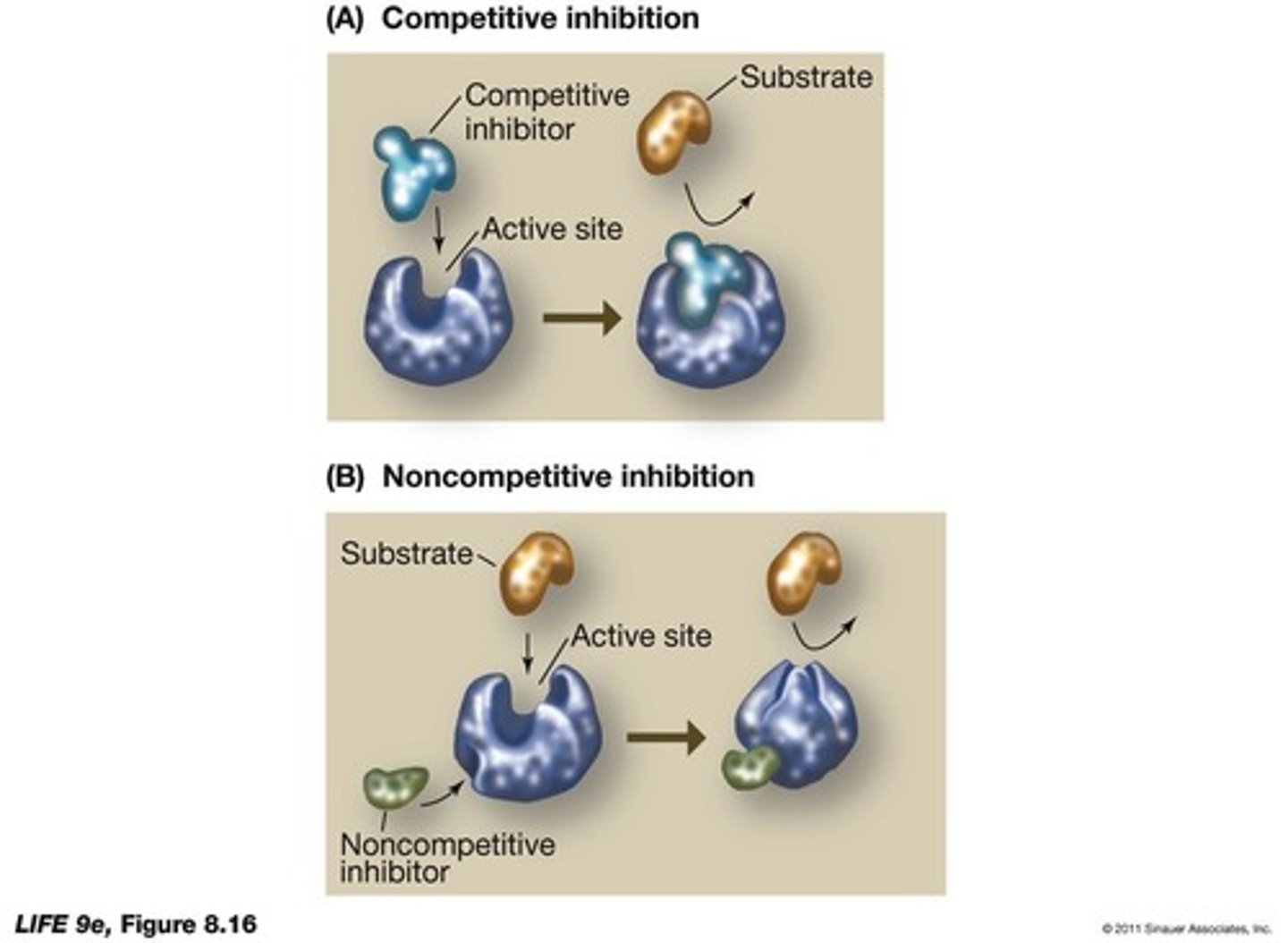
What is allosteric regulation?
occurs when an effector molecule binds to a regulatory subunit of an enzyme, inducing a change in the enzyme's shape and/or activity.
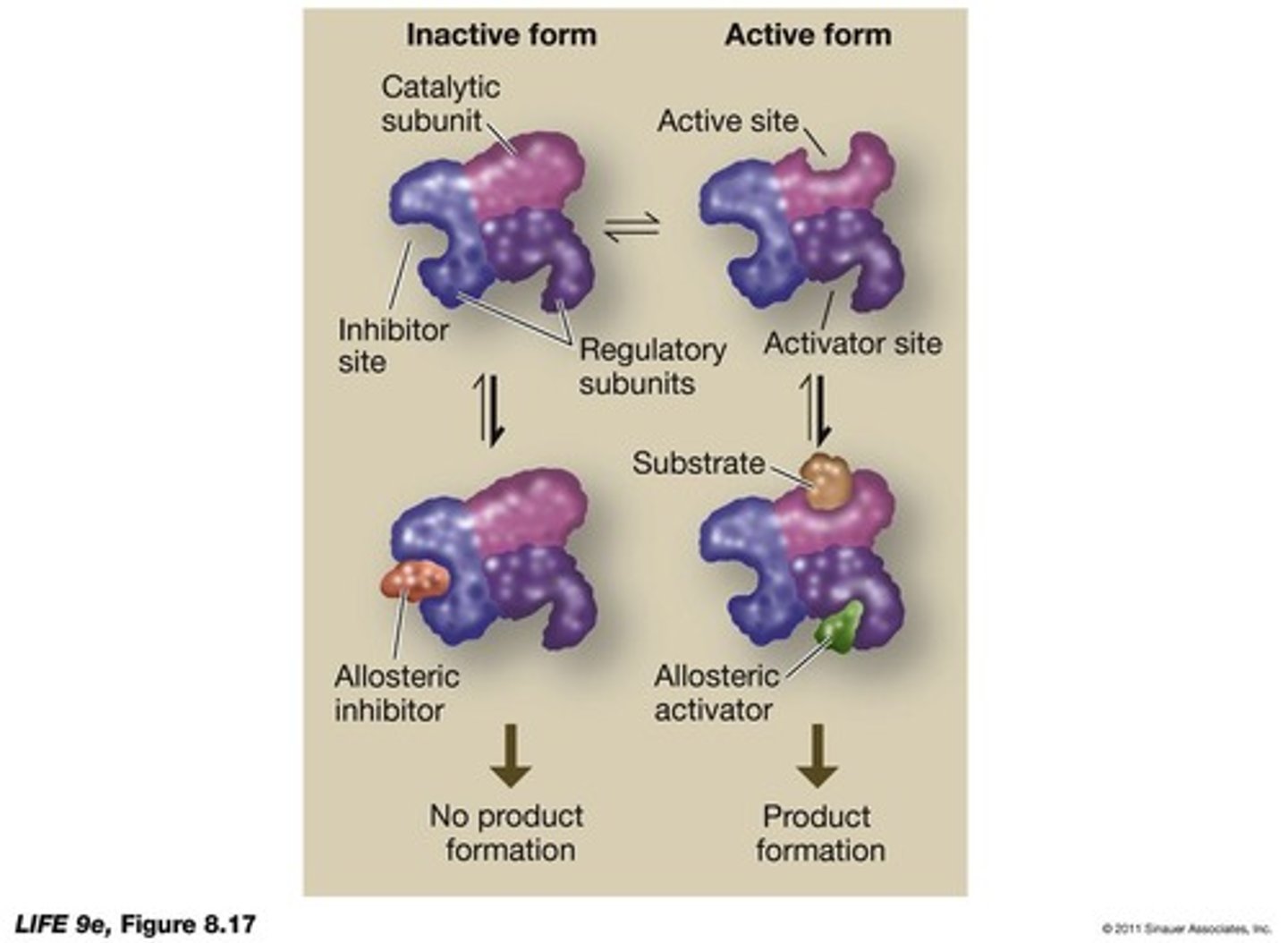
What are allosteric effectors?
are natural, noncompetitive, reversible inhibitors and/or activators of enzyme activity.
What is feedback inhibition?
_______________ is when the final product of a metabolic pathway acts as a noncompetitive inhibitor of an earlier enzyme, shutting down the pathway.
What is covalent modification in enzyme regulation?
_______ involves the addition of a functional group (usually phosphate) to an enzyme, which can either inhibit or activate the enzyme.
How does pH affect enzyme activity?
Every enzyme has an optimal pH at which it is most active; pH influences the ionization of functional groups, affecting enzyme folding and function.
What happens to enzymes at high temperatures?
At _____________, noncovalent bonds begin to break, causing the enzyme to lose its tertiary structure and potentially become denatured.
What are isozymes?
enzymes that catalyze the same reaction but have different properties, such as optimal temperature.
How do isozymes help organisms adapt to temperature changes?
Organisms can use ________ to adjust to temperature changes, as enzymes in humans have higher optimal temperatures than those in most bacteria.
What is the effect of temperature on enzyme activity?
Every enzyme has an optimal temperature; exceeding this can lead to denaturation.
What is the role of active and inactive forms of allosteric enzymes?
Allosteric enzymes can exist in an active form that binds substrate and an inactive form that cannot bind substrate but can bind an inhibitor.
What is the significance of the regulatory subunits in allosteric enzymes?
Regulatory subunits are where inhibitors and activators bind, influencing the activity of the catalytic subunit.
What is the importance of enzyme regulation in metabolic pathways?
Regulation of enzymes and reaction rates is crucial for maintaining homeostasis within cells.
What happens to enzyme activity when the concentration of a competitive inhibitor is reduced?
When the concentration of a competitive inhibitor is reduced, it detaches from the active site, allowing substrate binding to resume.
What is the relationship between enzyme structure and function?
The structure of an enzyme, including its active site and potential allosteric sites, directly influences its ability to catalyze reactions.
How do environmental factors influence enzyme function?
Environmental factors such as pH and temperature can affect the ionization of functional groups and the stability of the enzyme's structure, impacting its activity.