Class 7 - Aging & Dementia
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
(Normal Aging) Language remains intact:
Slight decline in word-finding abilities
No change in comprehending everyday discourse (e.g., television newscast)
Syntactic complexity in discourse declines with aging
(Normal Aging) Sustained attention remains mostly intact:
Slightly decline in selective attention skills
(Normal Aging) Divided attention skills intact during simple tasks:
Divided attention begins to break down in complex tasks
Normal Aging Continued:
Reaction time is slowed
LTM & procedural memory remain intact
STM is reduced
What is Mild Cognitive Impairment?
Changes that are significant enough to not be within the normal spectrum of changes w/ age, but not severe enough to affect ADLs
MCI may increase the risk of later progressing to dementia, caused by Alzheimer’s disease or other neurological conditions
In some people, MCI never gets worse
And in some other people, MCI eventually gets better
What is the 3 criteria for diagnosing MCI?
Self-report of memory problems, w/ corroboration from a family member or caregiver
Measurable memory impairment on standardized testing, outside the range expected for age- & education-matched healthy older adults
No impairments in reasoning, general thinking skills, or ability to perform ADLs
What are the etiologies of MCI?
Arises from a lesser degree of the same types of brain changes seen in Alzheimer’s disease or other forms of dementia
Small strokes or reduced blood flow through brain blood vessels
Shrinkage of the hippocampus, a brain region important for memory
Enlargement of the brain’s fluid-filled spaces (ventricles)
What symptoms are included in Mild Cognitive Impairment?
Decreased sustained attention
Decreased word-finding abilities
Decreased STM, episodic memory, semantic memory
Difficulty w/ executive functions
Difficulty following detailed heavy conversations/writings
No functional impairment
No significant impairment in occupation & social function
What are the 2 types of MCI?
Amnestic
Non-amnestic MCI
Amnestic MCI:
Single-domain: Most common; Majority of client amnestic MCI progress to AD
Multiple-domain
Non-amnestic MCI:
Single-domain: Relatively isolated impairment in a single non-memory domain such as EF or visuospatial processing
Multiple-domain: Slight impairment in multiple non-memory domains, not enough to constitute dementia
(DSM-5 Criteria for Neurocognitive Disorders) Mild Neurocognitive Disorders:
Mild cognitive impairment or MCI
Evidence of modest cognitive decline
Does NOT interfere w/ independent completion of ADLs
(DSM-5 Criteria for Neurocognitive Disorders) Major Neurocognitive Disorders or Dementia:
Evidence of significant cognitive decline
Cognitive decline must be severe enough to disrupt independence in ADLs
What are the cognitive domains affected by dementia?
Memory
EF
Attention
Language
Visuospatial function
Instrumental Activities of Daily Living
What are the progressive dementia types?
Alzheimer’s disease
Frontotemporal dementia
Lewy Body dementia
What are the potentially reversible or stoppable dementia types?
Medication-induced dementia
Metabolic / endocrine/ nutritional / systemic disorders
Vascular dementia / hydrocephalus / tumors / hematoma
Depression
Dementia Image:
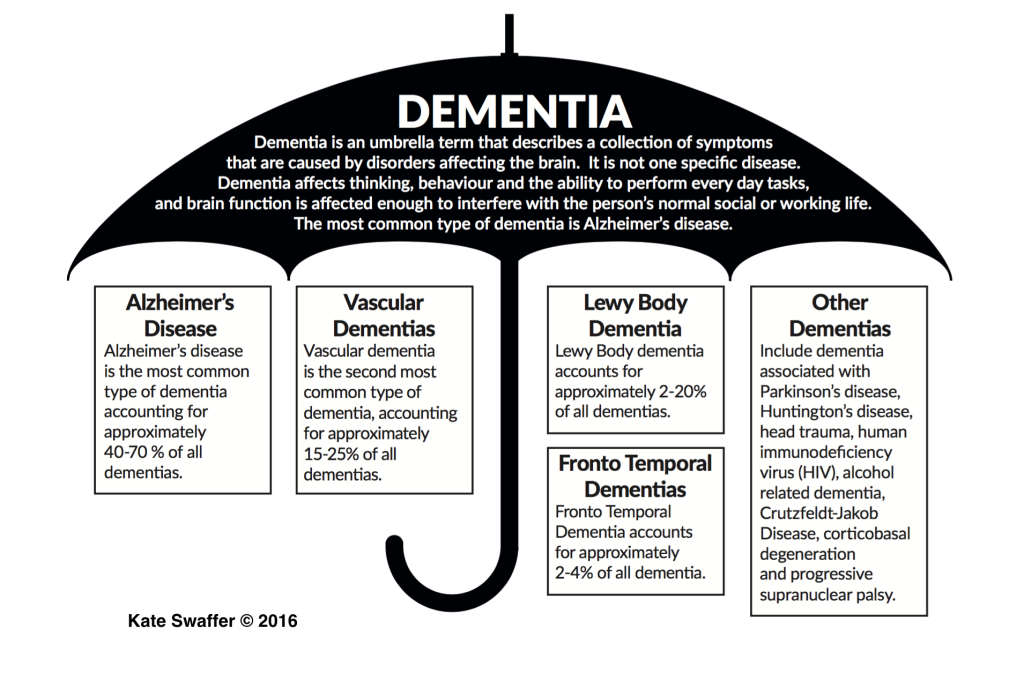
Alzheimer’s Disease:
Single most common cause of dementia
Currently affects nearly 5.7 million Americans (Alzheimer’s Association, 2018)
In the U.S., AD affects more women than men
What does neuropathology in AD include the presence of?
Beta-amyloid plaques: Dense protein deposits that accumulate outside & around neurons
Neurofibrillary tangles: Twisted fibers of tau protein that build up inside neurons
General neuronal atrophy-shrinkage of cortex & widening of ventricles
What are the modifiable risk factors of AD?
Heart-healthy diet
Social & cognitive engagement
Regular physical activity
Controlling cardiovascular risk
Preventing TBI
What are the nonmodifiable risk factors of AD?
Older age
Positive family history of AD (esp in first-degree relatives)
Carrier status for the e4 allele of APOE gene
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Continuum:
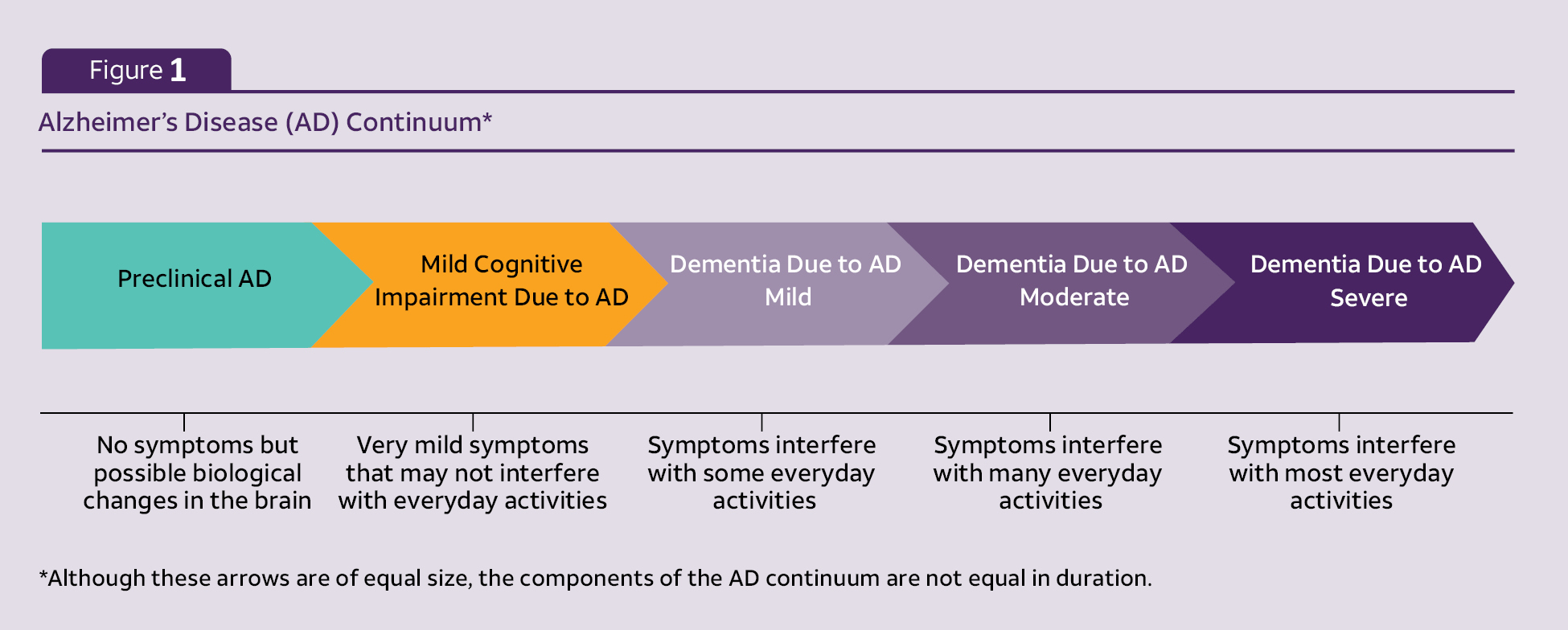
What are the earliest symptoms of AD?
Episodic memory deficits
Working memory deficits
Attention & EF impairments
Language & communication impairments adversely affecting lexical retrieval & discourse
AD Middle Stage:
Negative impact on ADLs & reliance on others
More severe memory loss, attention deficits, dramatic personality changes, visuospatial & visuo-constructive deficits, & expressive language deficits
May experience wanderlust, sundowner syndrome, disorientation, & confusion
AD Late Stage:
Loss of motor function
May become non-ambulatory, bedridden, incontinent, & unresponsive
Memory, cognition, & expressive language deficits are profound
May cause muteness & dysphagia
Vascular Dementia (VaD):
Considered the second most common cause of dementia
Caused by ischemic or hemorrhagic cerebrovascular disease, cardiovascular disease, or circulatory disturbances that damage brain areas vital for memory & cognitive functions
Risk factors are similar to AD
On average, people w/ vascular dementia may progress faster than those w/ AD
Vascular Dementia (VaD):
Sudden onset of any of the following symptoms
Confusion & episodic memory impairments
Slowed processing
Wandering or getting lost in familiar places
Rapid, shuffling gait (history of unsteadiness &/or falling)
Loss of bowel or bladder control
Emotional lability
Difficulty following instructions
Problems handling money
A Diagnosis of VAD Requires:
Objective evidence of cardiac &/or systemic vascular conditions
Evidence of cerebrovascular disease etiologically tied to onset of dementia symptoms
Focal neurological s/s (e.g., difficulties in movement, sensation, or speech-language)
Brain imaging evidence for ischemic, hemorrhagic, or white matter lesions on CT or MRI scans
What is frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTD or FTLD)?
FTD is a heterogeneous group of rare neurodegenerative disorders that result in significant impairments of behavior, personality, & distinct types of language impairment
Most FTDs are diagnosed before the age of 65 years, usually between the age of 35-75 years
Rapidly progressive; has a 2 to 10 year disease course
Strong genetic component; positive family history in 20-40% of cases
Hallmark symptom: Progressive decline in behavior &/or language
FTD → Neuropathology:
FTDs are characterized by:
Progressive, focal atrophy of the frontal & anterior temporal brain regions
Spongiform changes in the cortex
Abnormal tau protein inclusions
What is Primary Progressive Aphasia (PPA)?
_____ is a specific type of a more general frontotemporal dementia
It is also an unusual dementia since episodic memory functions remain largely preserved for many years
The language impairment constitutes the most salient symptom that impacts the ADLs in the initial stages
The cognitive decline follows the language symptoms
In contrast to Alzheimer’s dementia, where patients tend to lose interest in recreational & social activities, some patients w/ PPA maintain & even intensify involvement in complex hobbies such as gardening, carpentry, sculpting & painting
What is the diagnostic criteria for PPA?
Gradual onset of language problems, isolated in initial stages of disease
Impaired ADL related to language deficit
No initial prominent visuospatial or episodic memory deficits
No initial behavioral disturbances
Impairment NOT explained by stroke, tumor, TBI, or other neurological or psychiatric condition
PPA Subtypes:
Diagnosis of PPA subtype should follow PPA diagnosis:
Semantic variant
Logopenic variant
Nonfluent variant
Consensus criteria for diagnosis of PPA subtypes developed by international panel of experts
What is semantic PPA?
loss of semantic knowledge d/t anterior temporal lobe atrophy, greater in the language dominant
What are the core clinical features of semantic PPA?
Picture naming deficit
Single-word comprehension deficit
What are the supporting features of semantic PPA?
At least 3 of the following:
Loss of object knowledge
Surface dyslexia/dysgraphia
Relatively preserved repetition
Intact grammar & motor speech
What is the disease progression of semantic PPA?
Atrophy spreads throughout semantic network, eventually affecting frontal & parietal lobes as well
Progressively empty speech
Behavioral symptoms may emerge
Compulsions
Disinhibition
Personality changes
Altered eating preferences
Worsening dysexecutive symptoms
What is logopenic PPA?
Impaired phonological processing d/t temporoparietal atrophy, greater in language dominant hemisphere
What are the core clinical features of logopenic PPA?
Both of the following:
Difficulty w/ single-word retrieval in spontaneous speech & picture naming
Phrase & sentence repetition deficit (b/c of phonemic paraphasias!)
What are the supporting features of logopenic PPA?
At least 3 of the following:
Phonemic paraphasias in spontaneous speech & picture naming
Relatively preserved comprehension of single words & intact object knowledge
Lack of motor speech impairments
Spared syntactic processing
What is the disease progression of logopenic PPA?
Atrophy begins to extend anteriorly into anterior temporal lobes, eventually
What is nonfluent PPA?
impaired grammatical processing &/or apraxia of speech d/t frontoinsular atrophy, greater in the language dominant hemisphere
What are the core clinical features of nonfluent PPA?
At least 1 of the following:
Agrammatism (difficulty using correct grammar & syntax)
instead of saying "The cat is sitting on the mat," someone with agrammatism might say, "Cat...sit...mat".
Apraxia of speech (difficulty planning and coordinating the movements needed for speech
What are the supporting features of nonfluent PPA?
At least 2 of the following:
Syntax comprehension deficit, particularly for complex syntax
Relatively preserved comprehension of single words
Relatively preserved object knowledge
What is the disease progression of nonfluent PPA?
May develop generalized movement disorder, including dysphagia
Increasingly unintelligible & agrammatic
Mutism