Unit 3: IMF, so small yet so important!
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
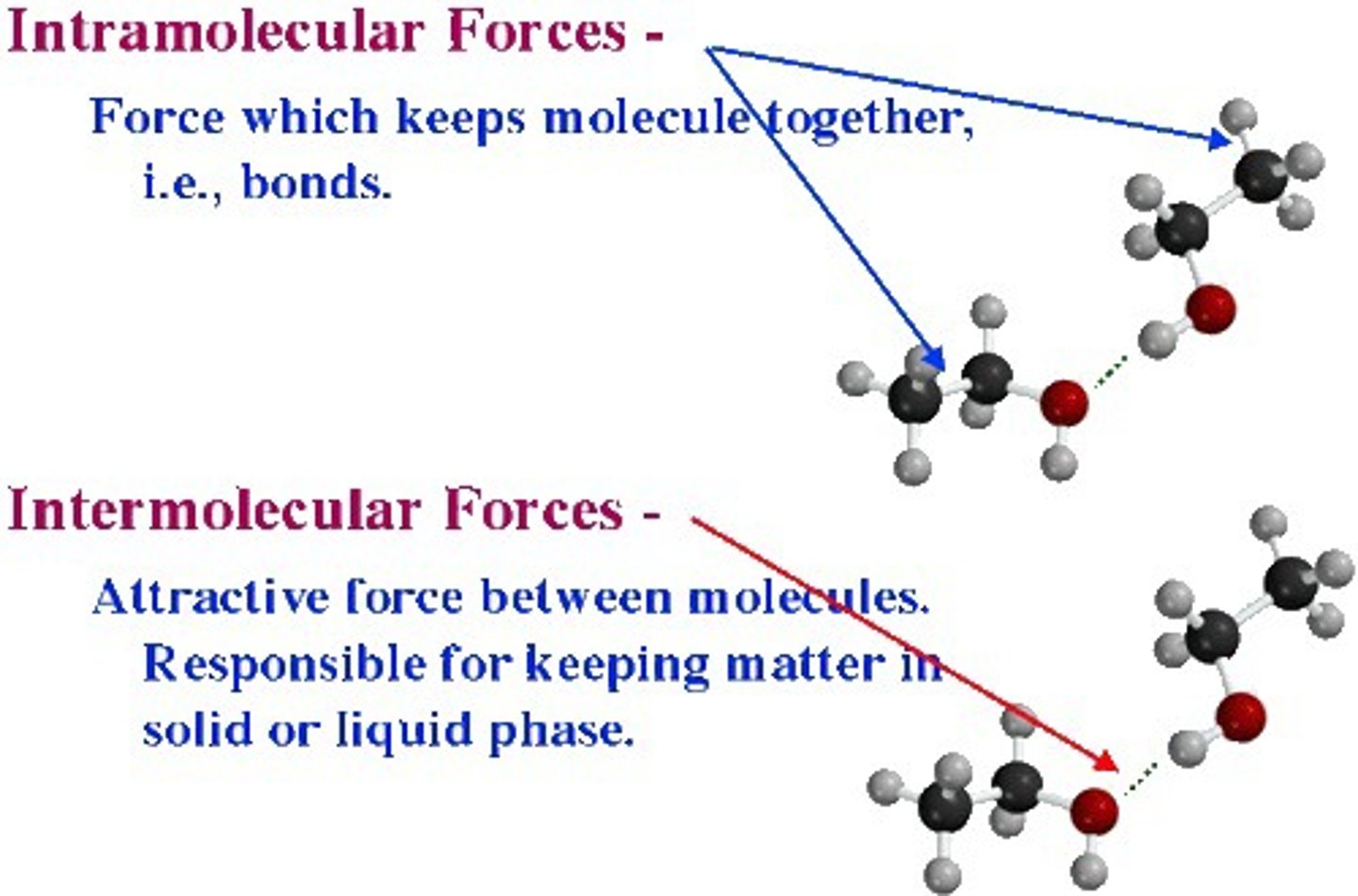
intermolecular forces
forces of attraction BETWEEN molecules
intramolecular forces
bonding forces that hold the atoms of a molecule together
ion-dipole interactions
Coulombic attractions between ions and polar molecules
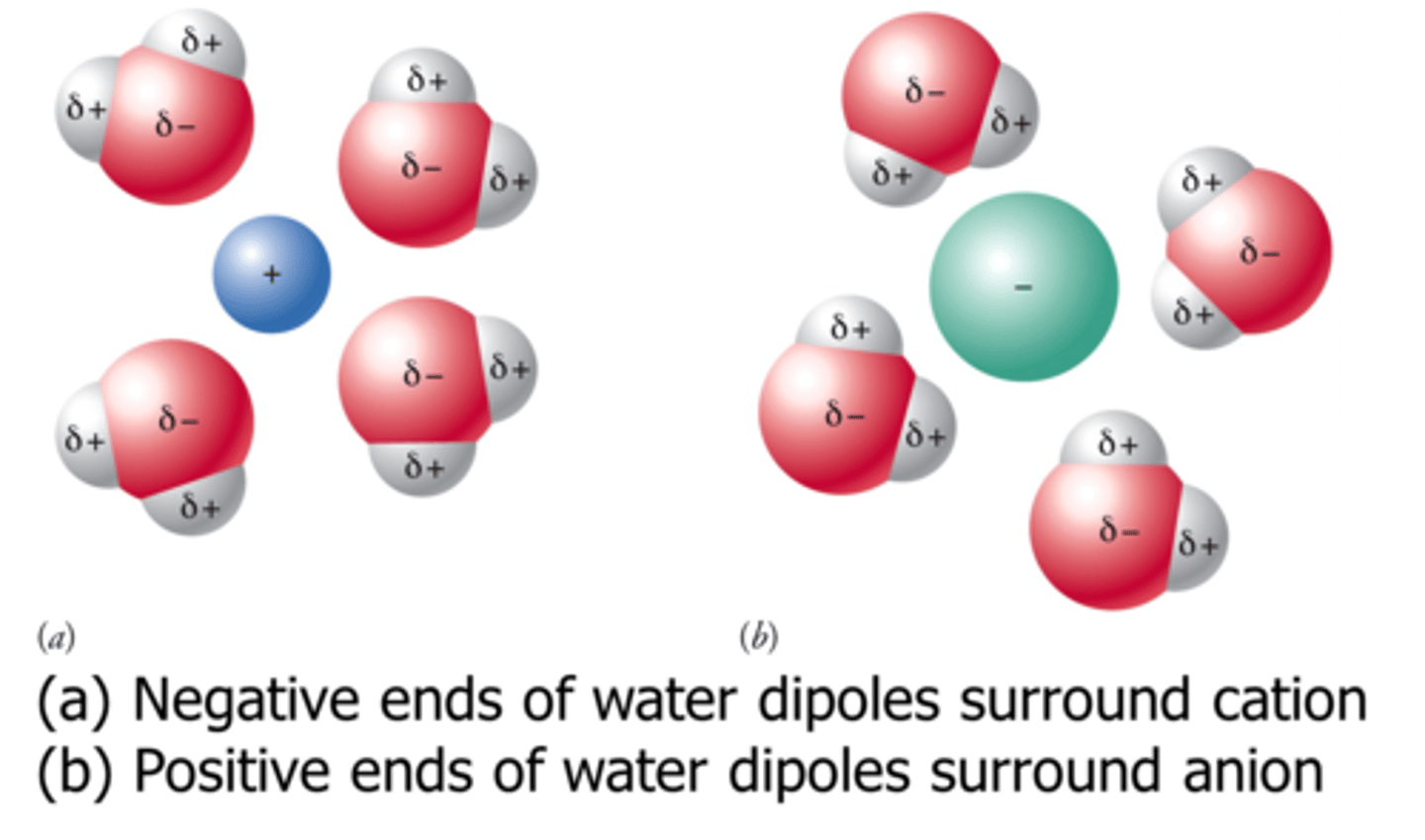
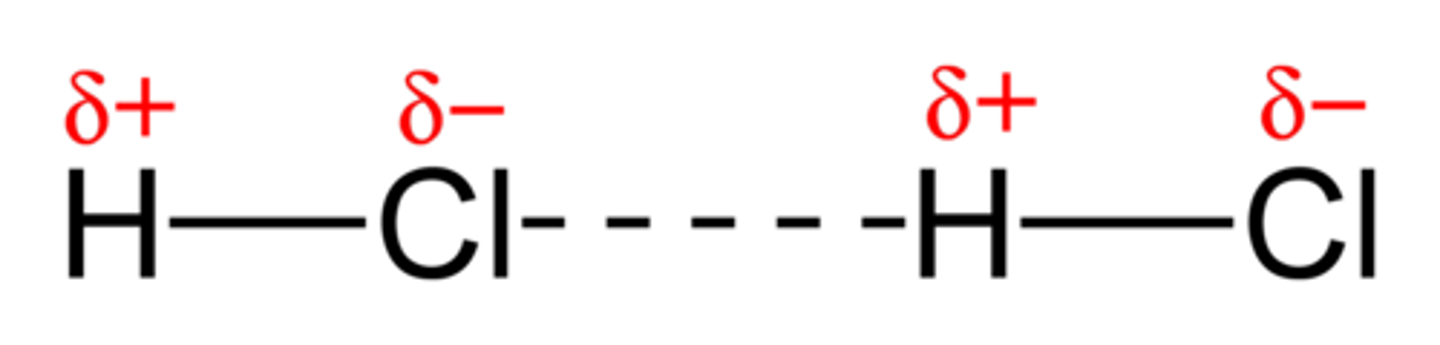
dipole-dipole interactions
Type of intermolecular force in which opposite poles of neighboring dipole molecules are drawn together.
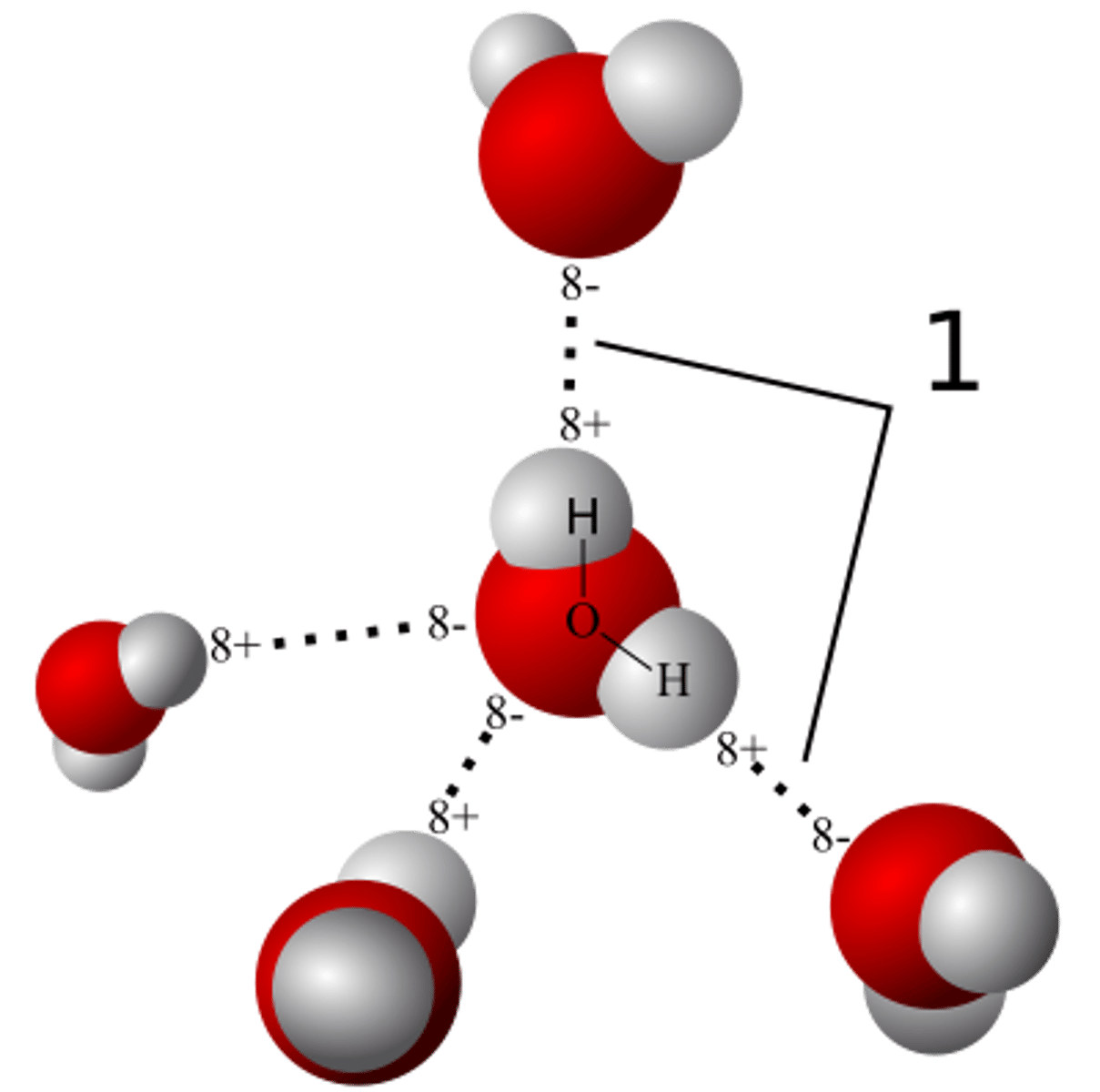
hydrogen bonding
strong type of intermolecular dipole-dipole attraction. Occurs between hydrogen and F, O or N
London dispersion forces
the intermolecular attraction resulting from the uneven distribution of electrons and the creation of temporary dipoles
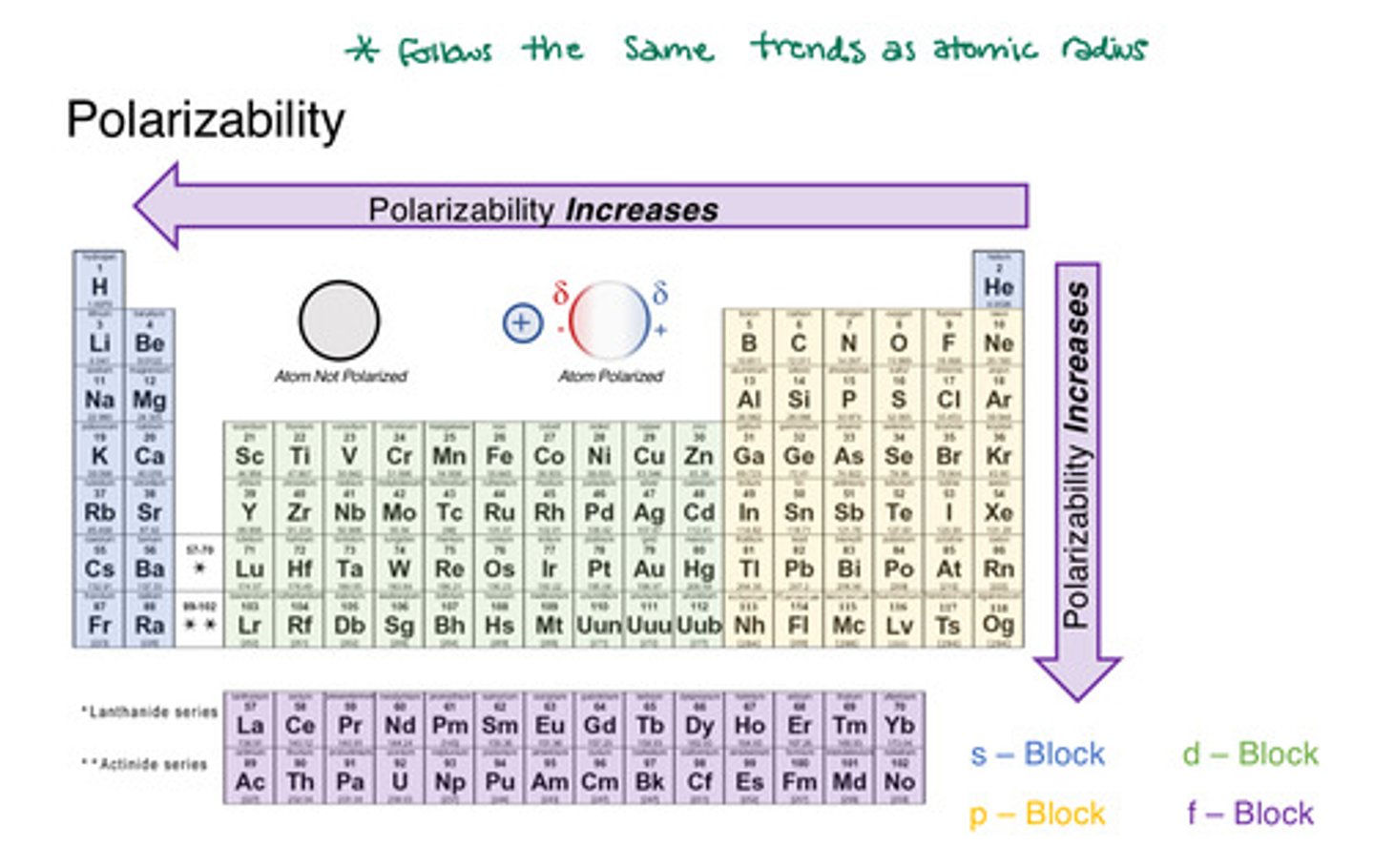
polarizability
the ease with which the electron distribution in the atom or molecule can be distorted
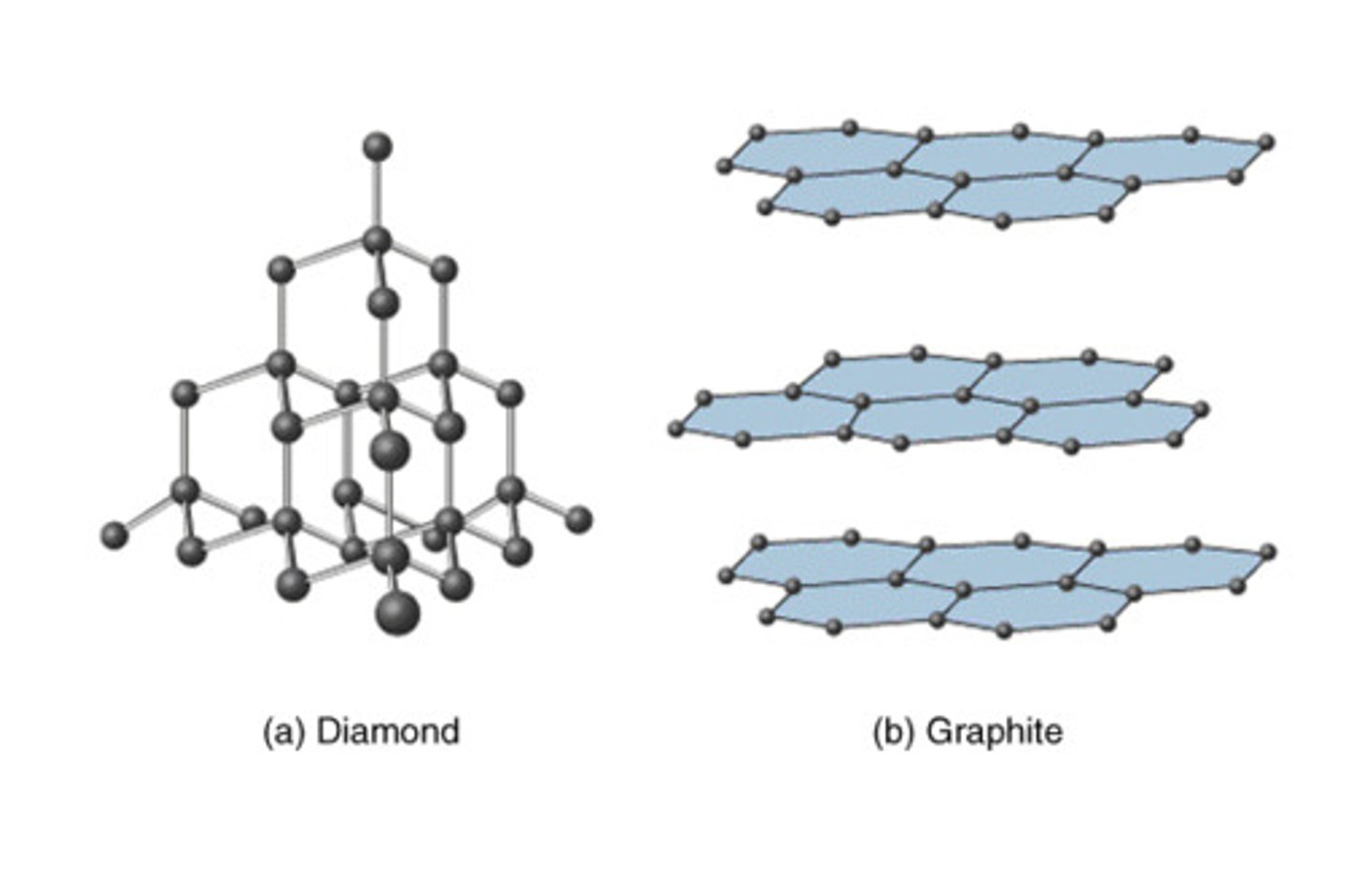
covalent network solids
have covalent bonds joining the atoms together in an extremely large crystal lattice
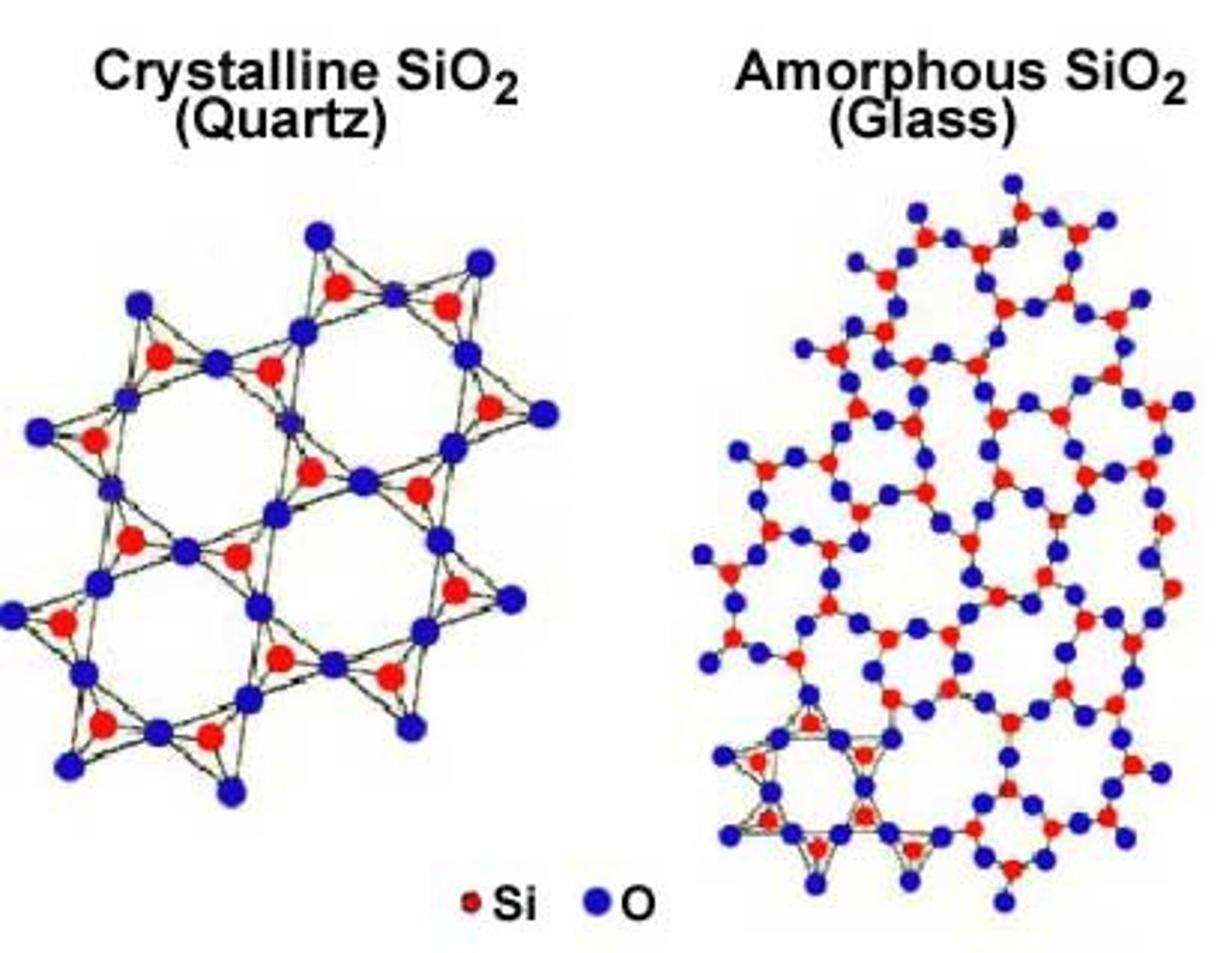
amorphous solid
describes a solid that lacks an ordered internal structure; denotes a random arrangement of atoms
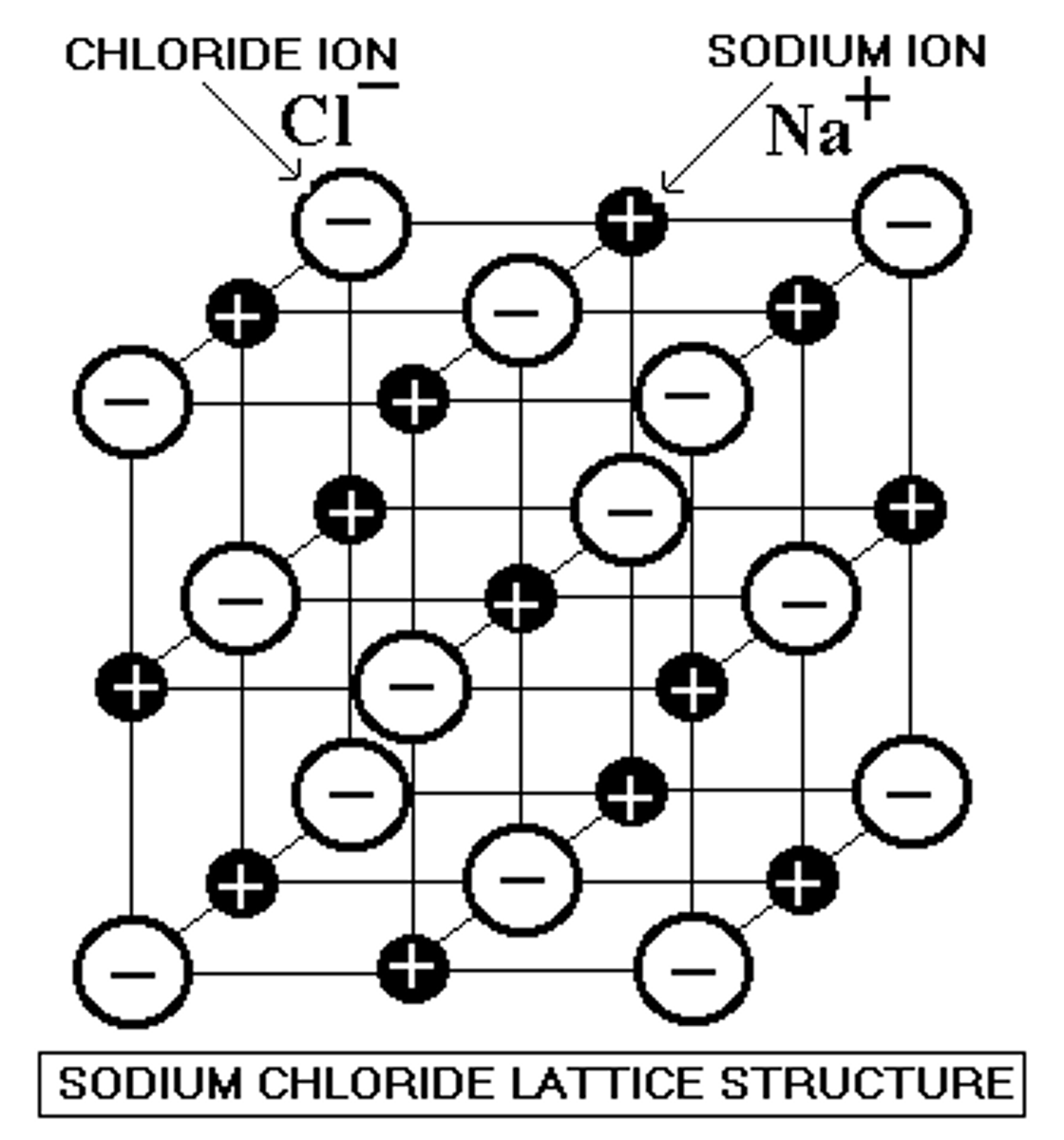
crystal lattice
A 3-dimensional geometric arrangement of the atoms or molecules or ions composing a crystal
unit cell
the smallest portion of a crystal lattice that shows the 3D pattern of the entire lattice
metallic solids
solids that have metal atoms occupying the crystal lattice and held together by metallic bonding
fluidity
ability for molecules to flow past each other
Compressability
The ability of a substance to be squeezed into a smaller volume or space.
surface tension
Occurs when molecules on the surface of a liquid experience a net inward force; the greater the IMF, the greater the surface tension
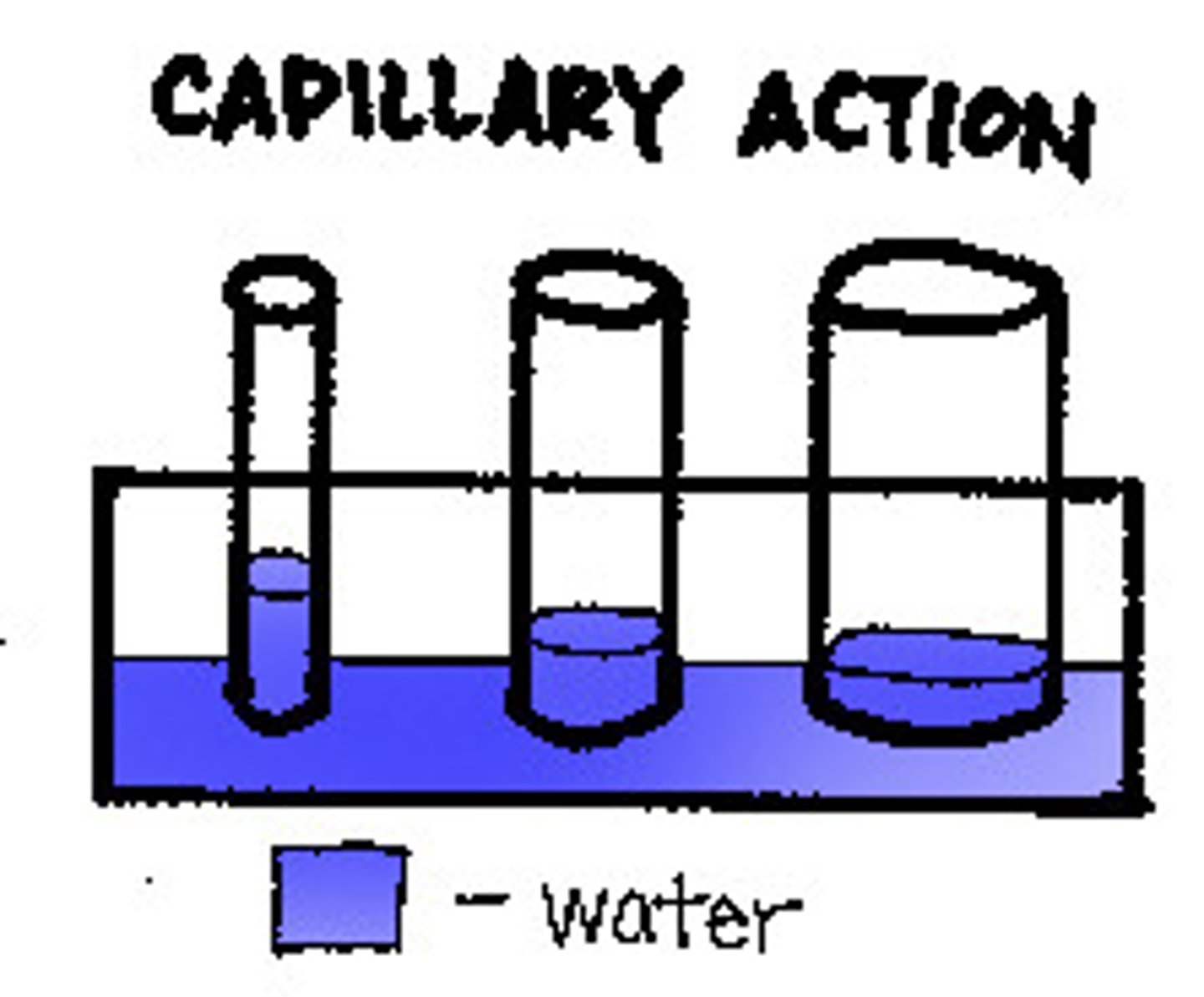
capillary action
the attraction of the surface of a liquid to the surface of a solid
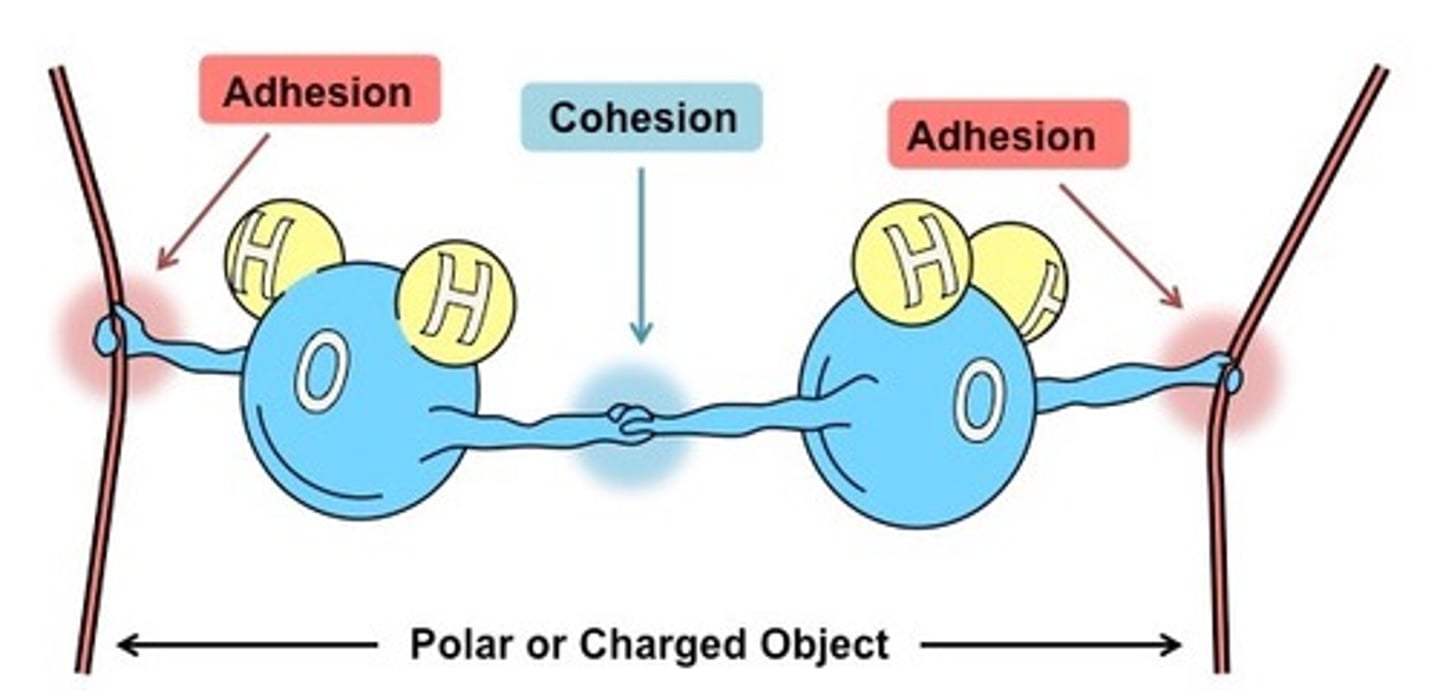
cohesive forces
intermolecular forces that bind similar molecules to one another
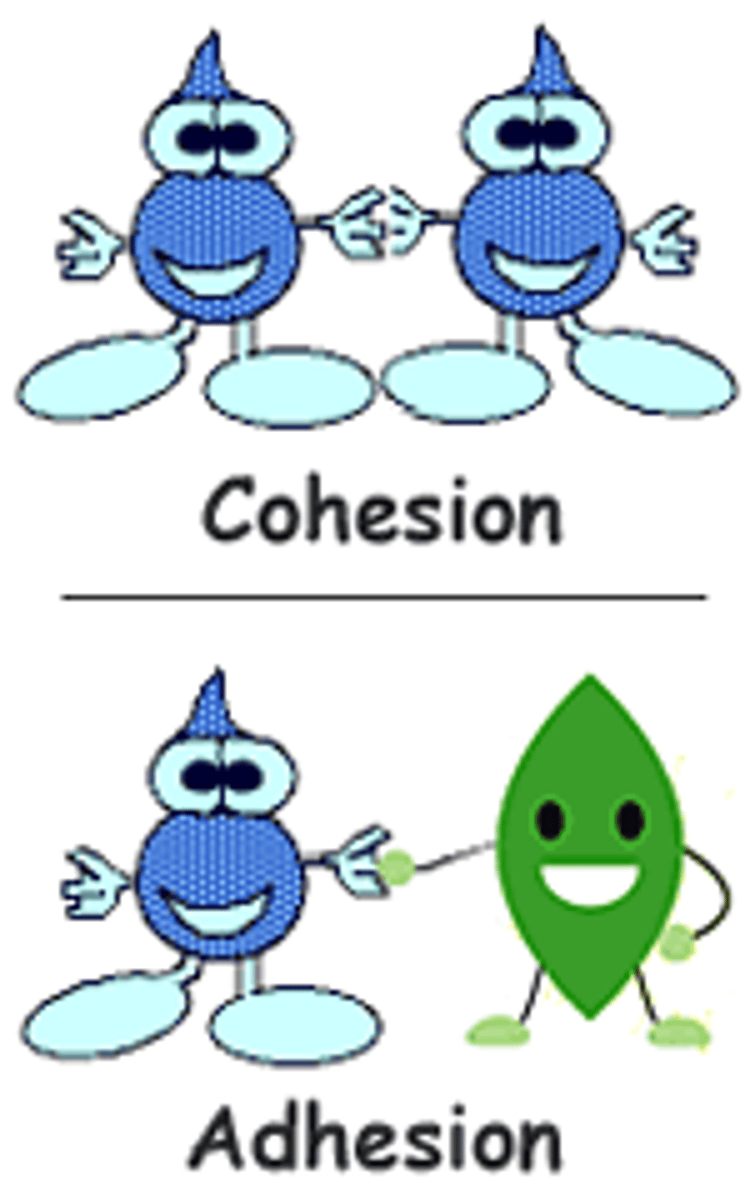
adhesive forces
intermolecular forces that bind a substance to its container
Viscosity
a liquid's resistance to flow

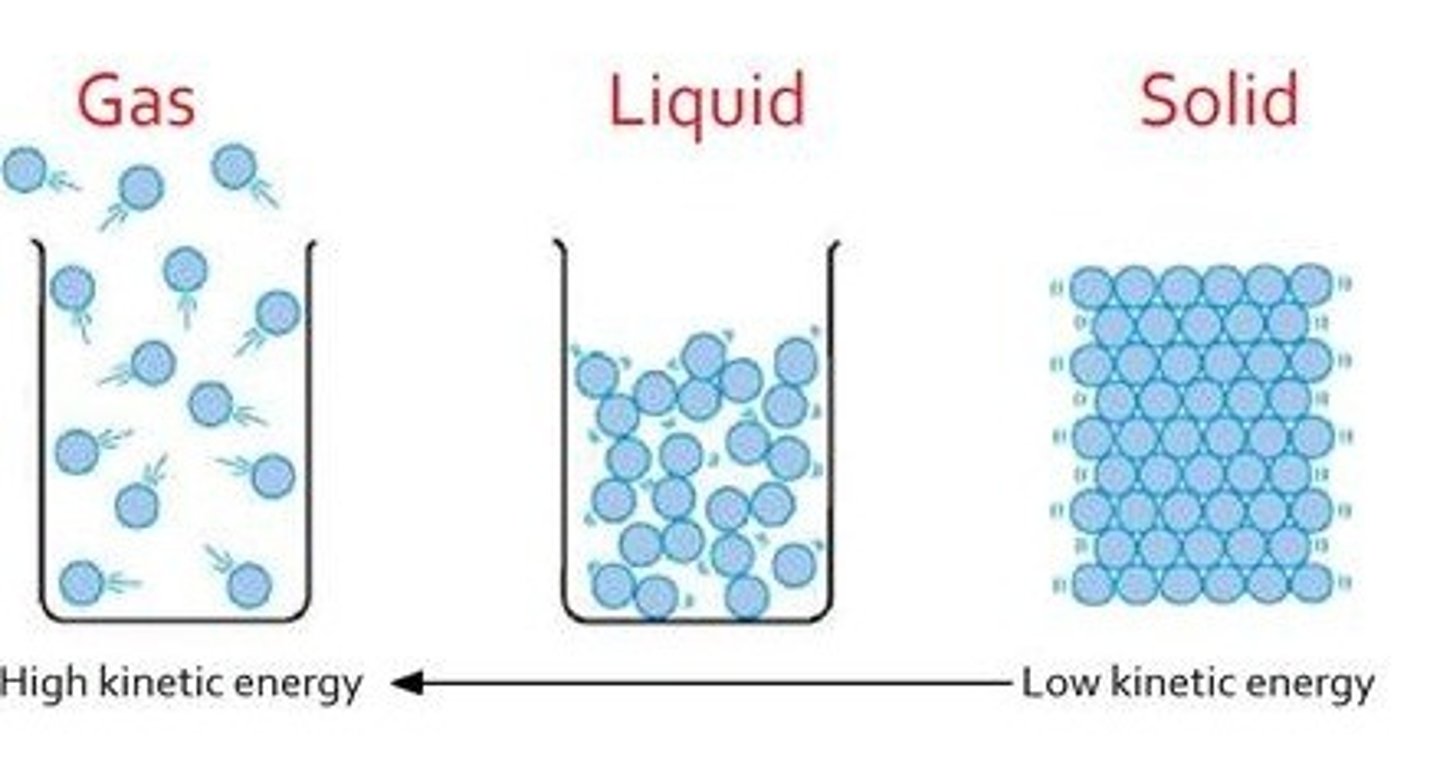
Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT)
a model that assumes an ideal gas is composed of tiny particles (molecules) in constant motion (1) which only experience elastic collisions (2), no attractive or repulsive forces (3), and have no volume (4)
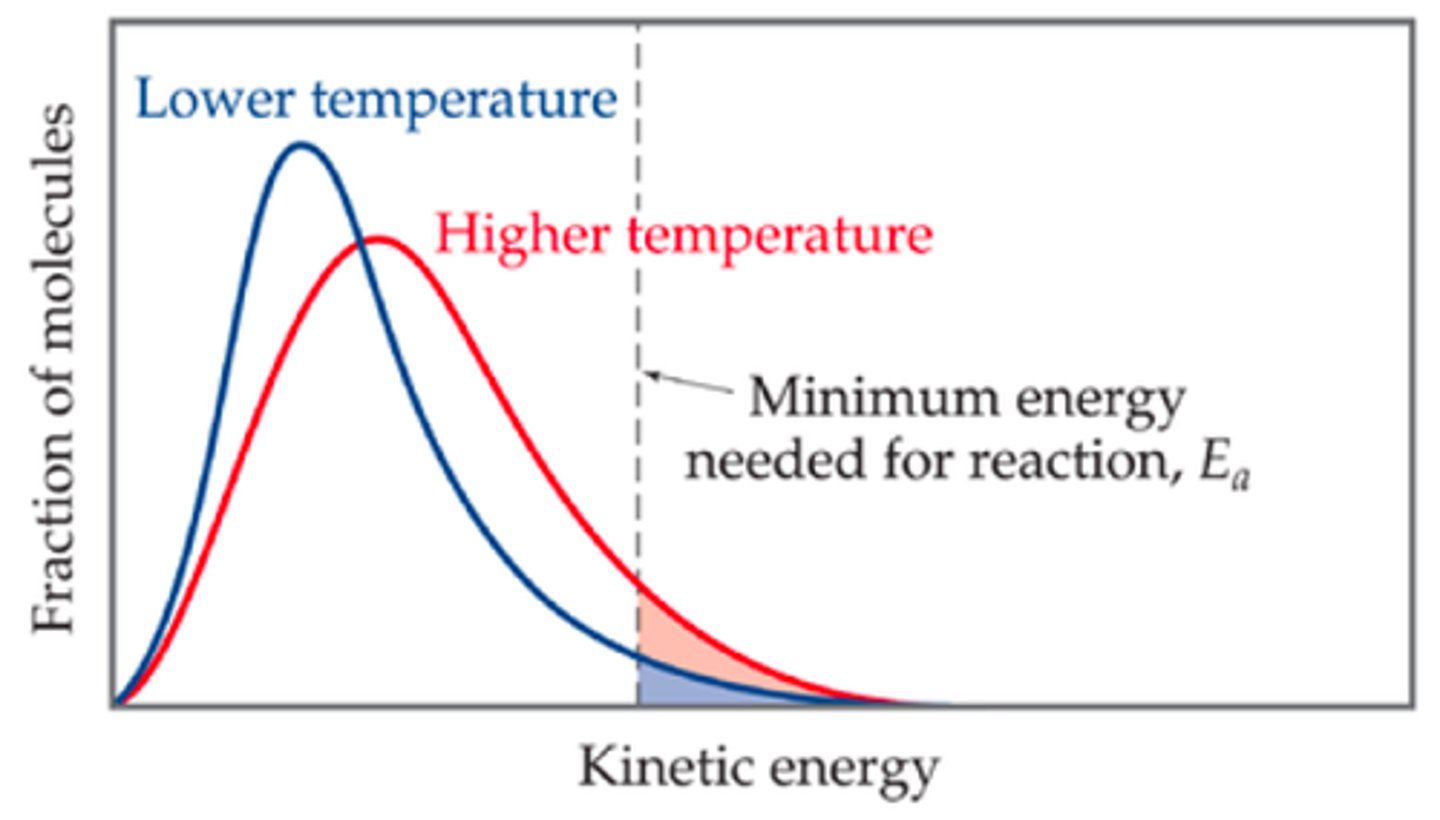
Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution
Shows the spread of energies that molecules of gas or liquid have at a particular temperature
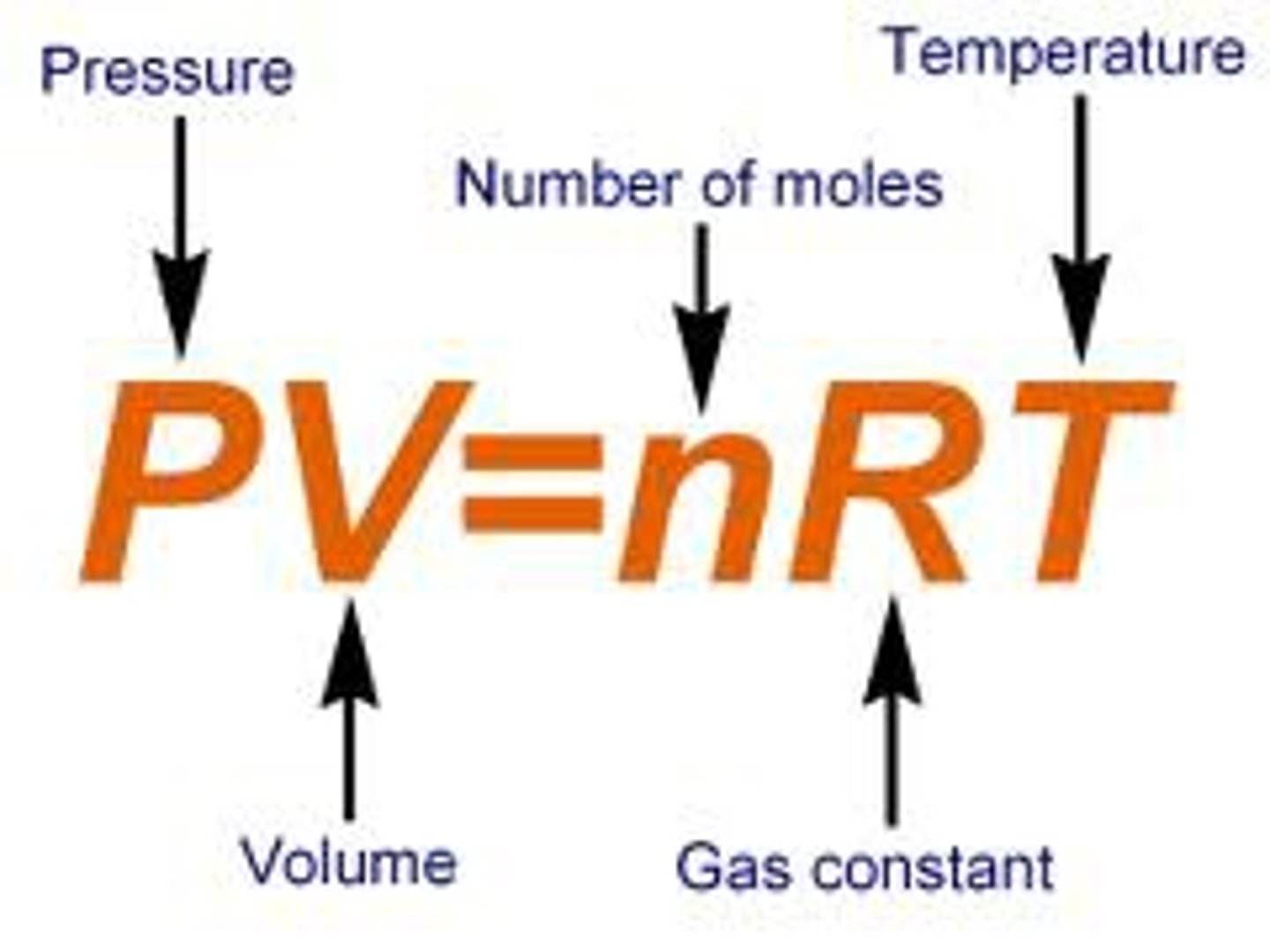
Ideal Gas Law
PV=nRT
Combined Gas Law
the relationship between the pressure, volume, and temperature of a fixed amount of gas
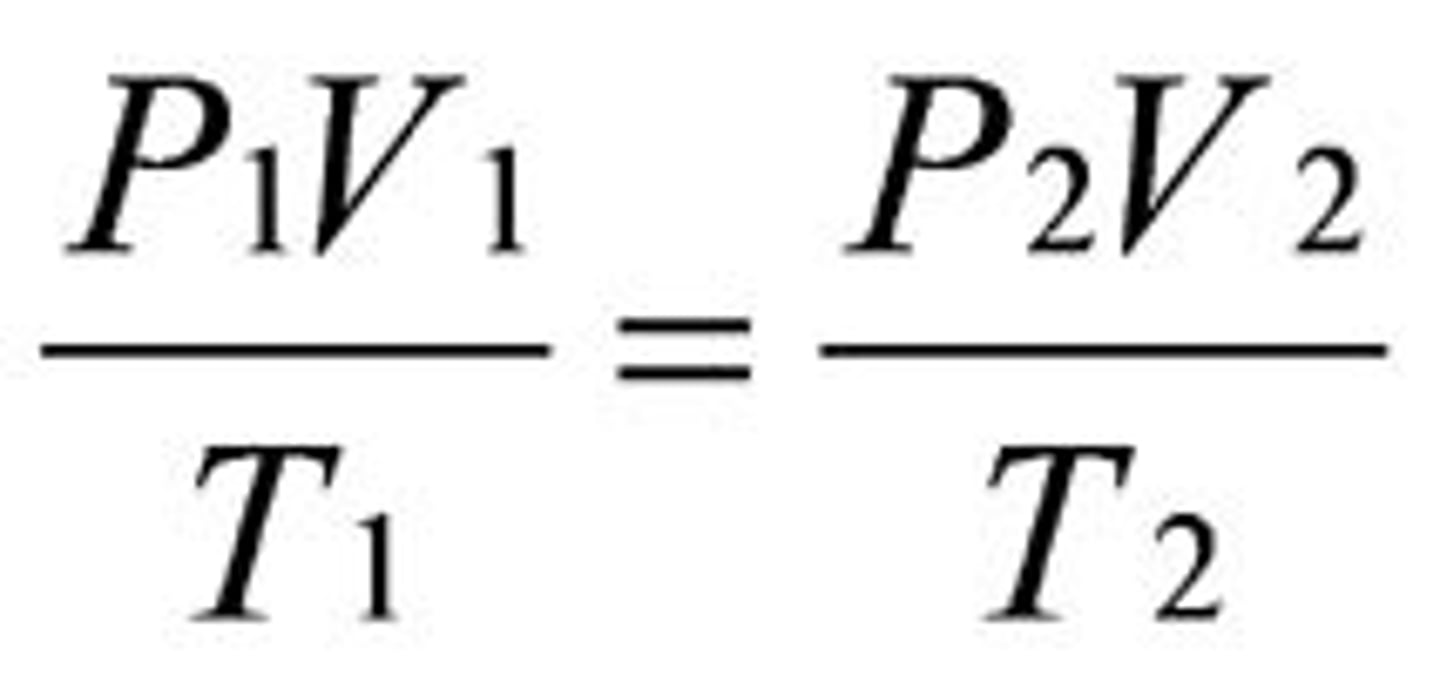
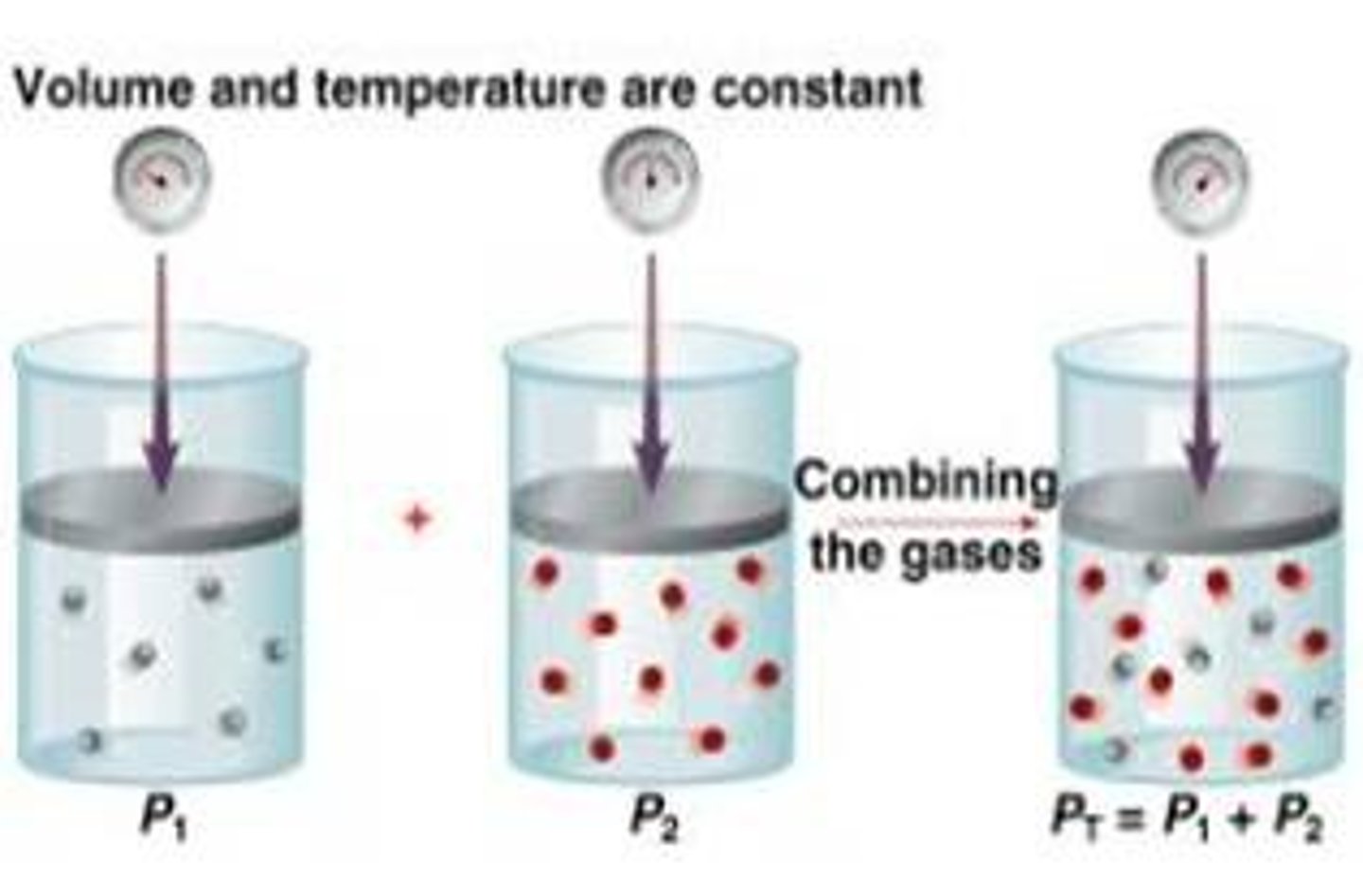
Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures
Total pressure of a gas is equal to the sum of the partial pressure of the component gases
mole fraction
the ratio of the number of moles of solute in solution to the total number of moles of solute and solvent
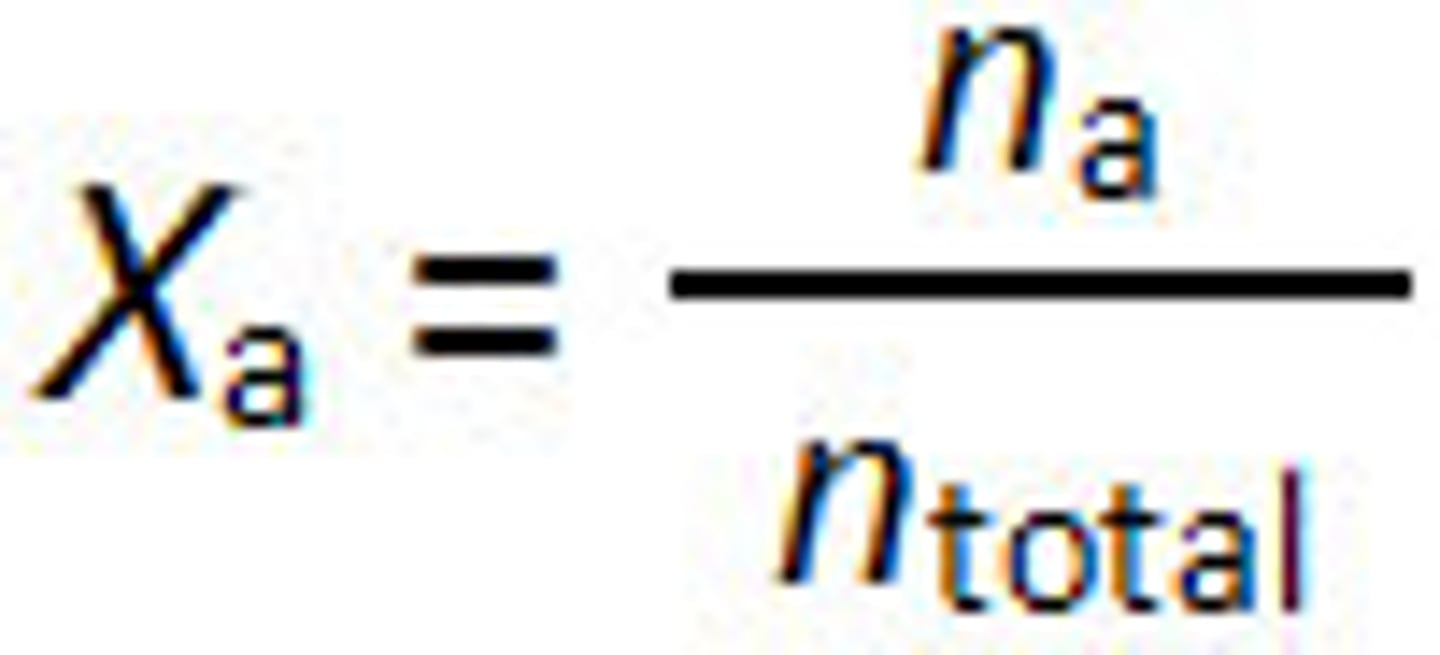
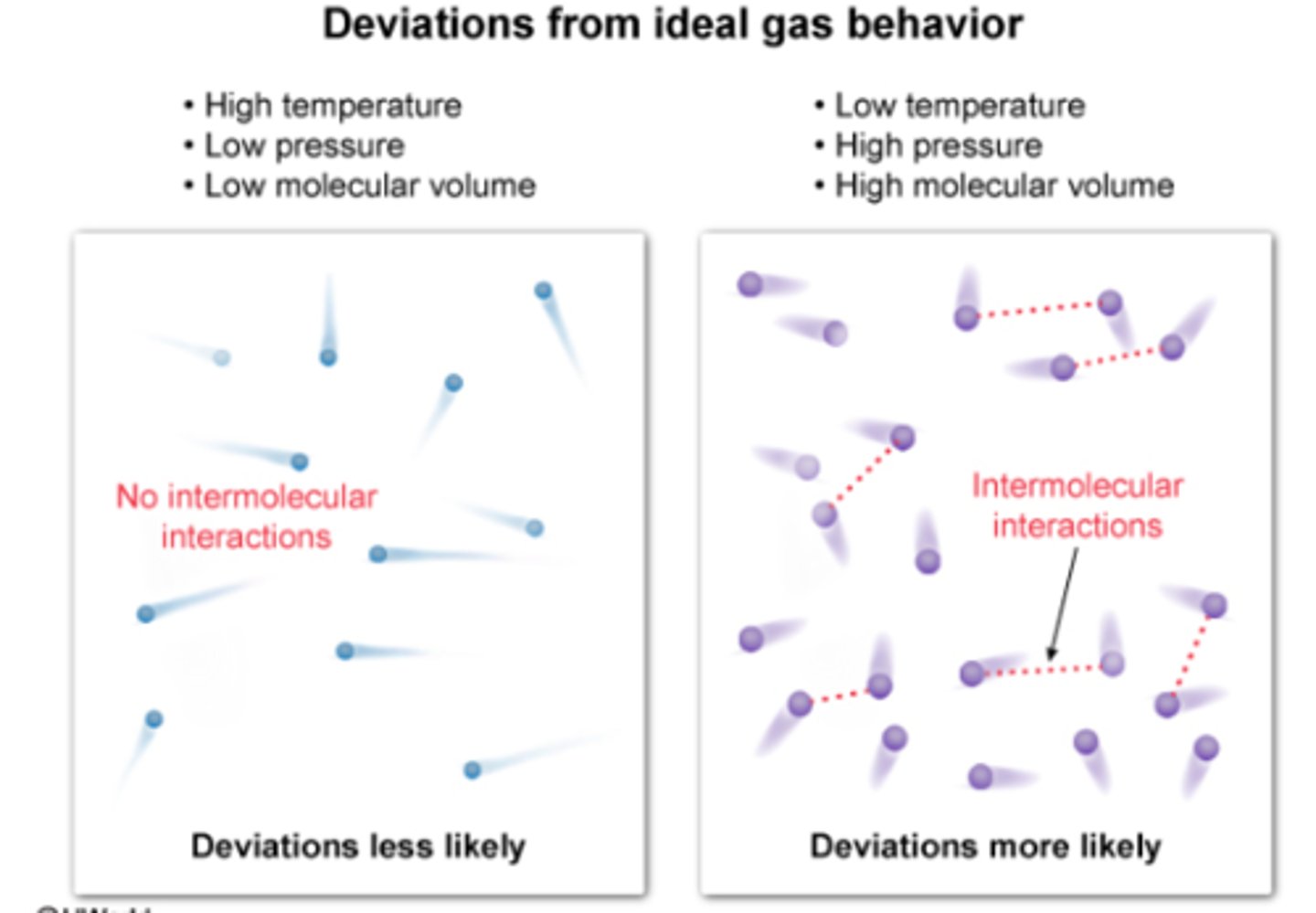
Deviations from Ideal Behavior
high pressure and low temperature
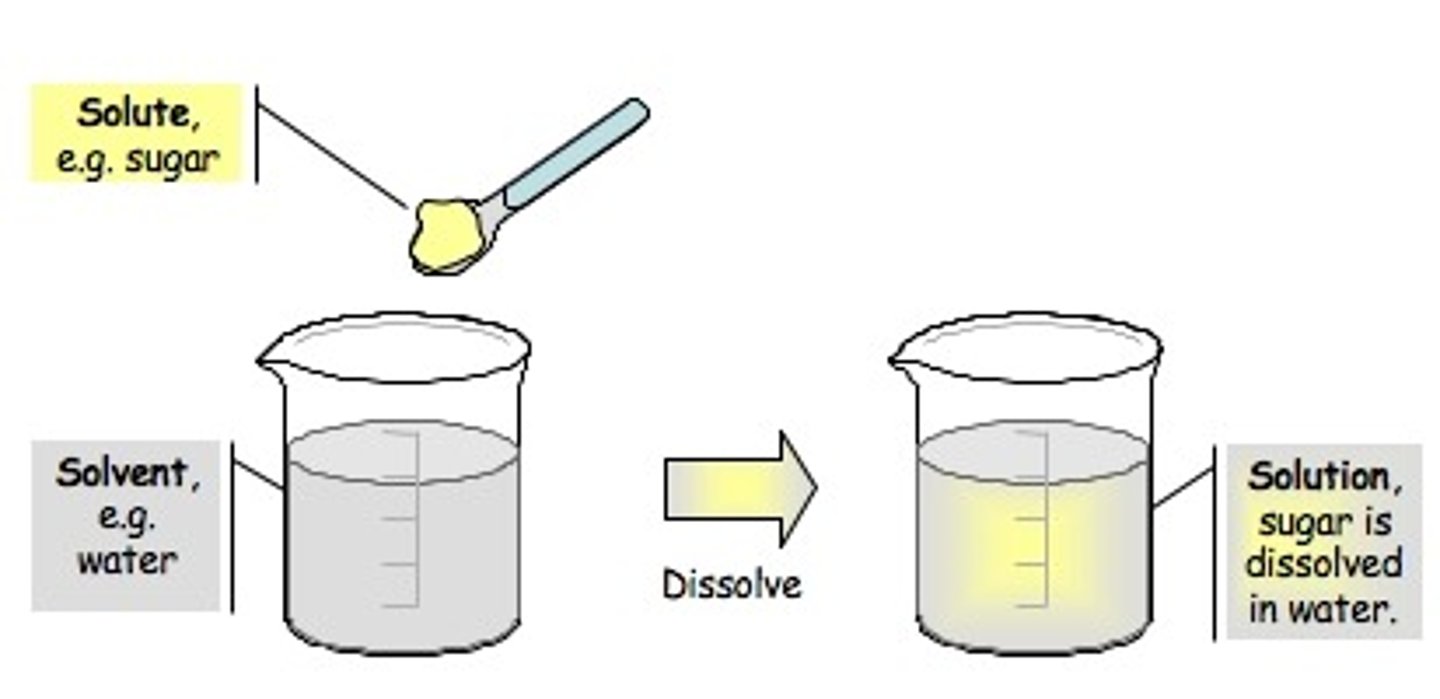
homogeneous mixture (solution)
A mixture in which substances are evenly distributed throughout the mixture
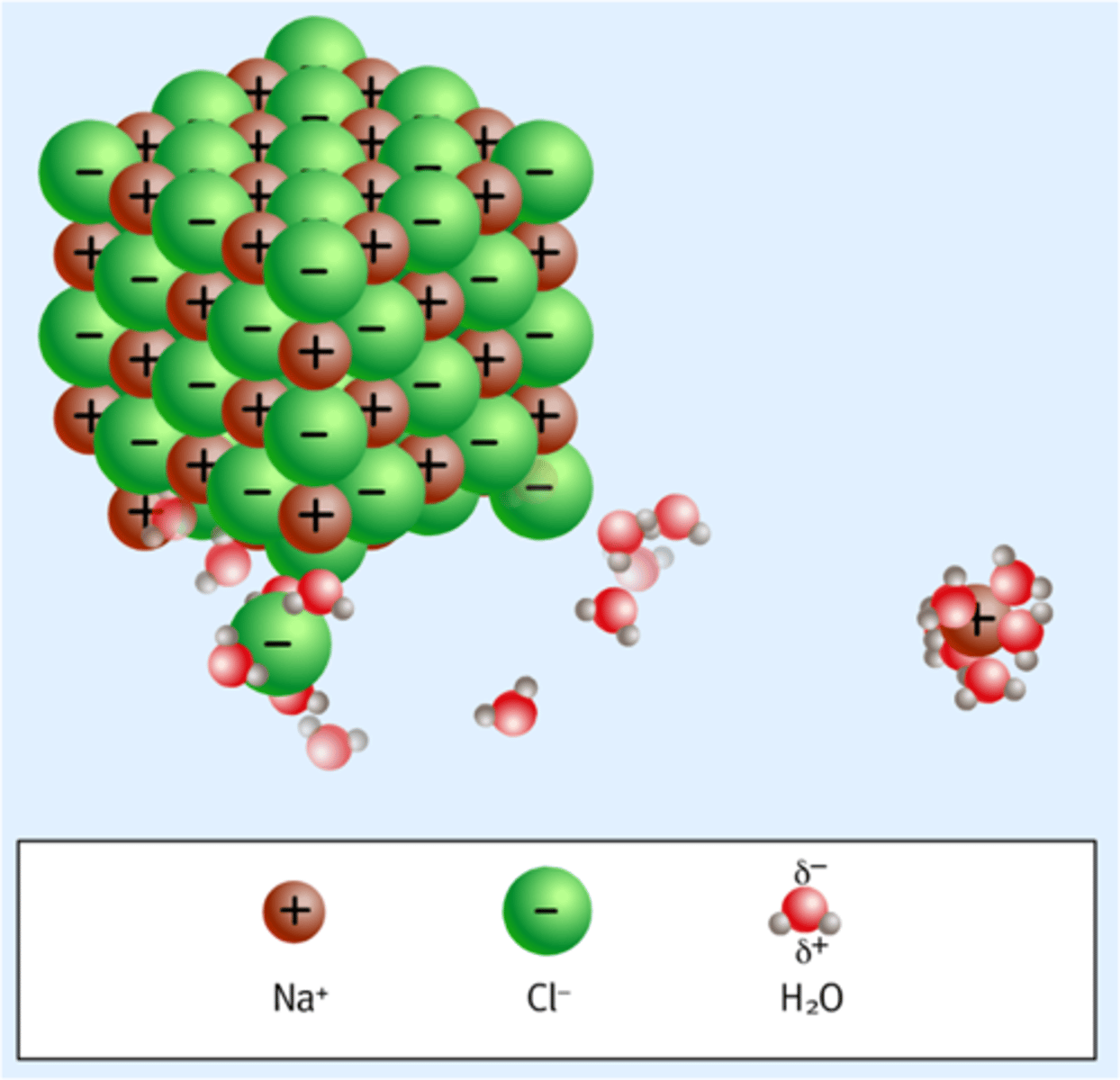
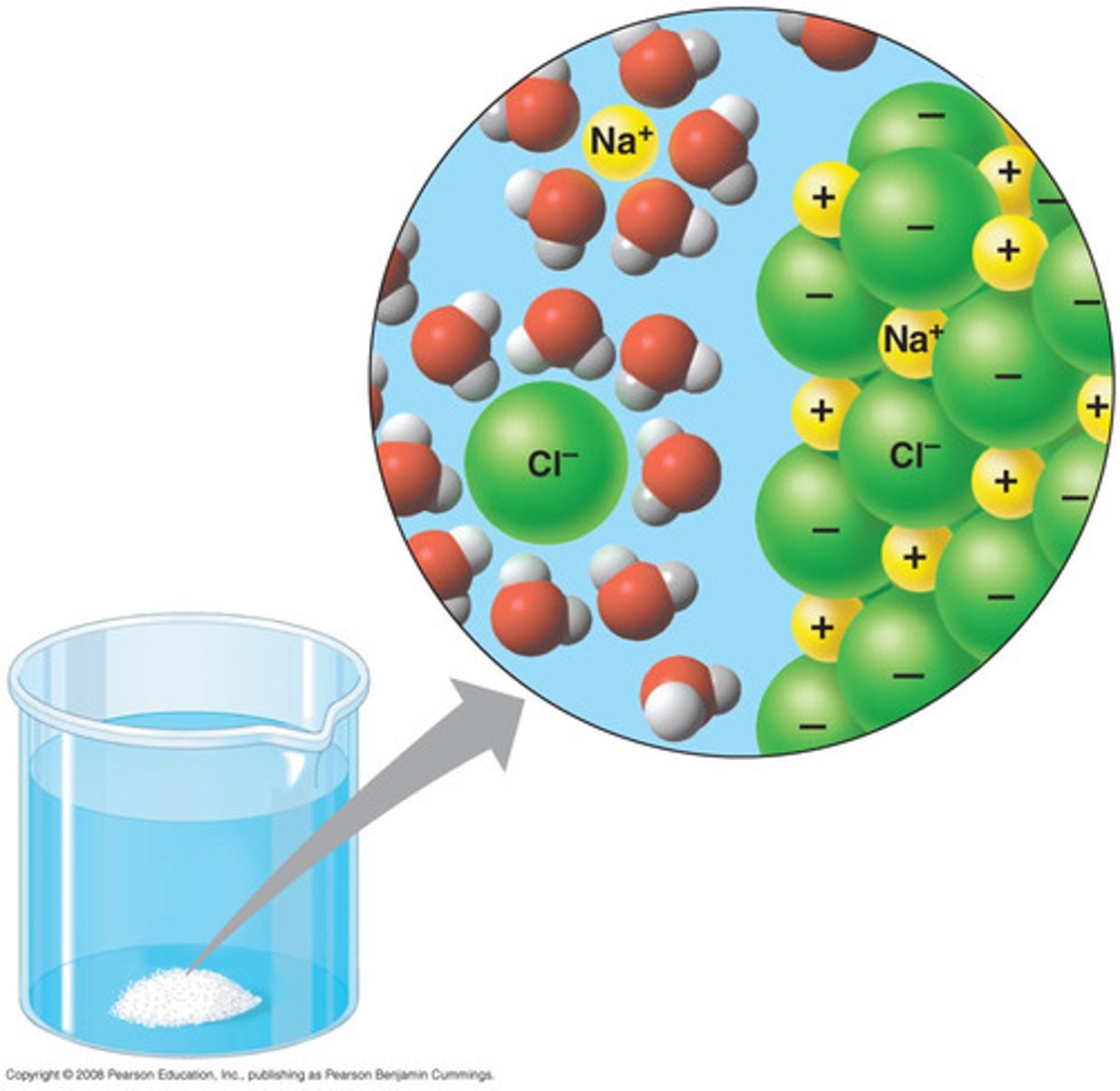
Solvation
a process that occurs when an ionic solute dissolves; in solution, solvent molecules surround the positive and negative ions
Hydration
solution process with water as the solvent
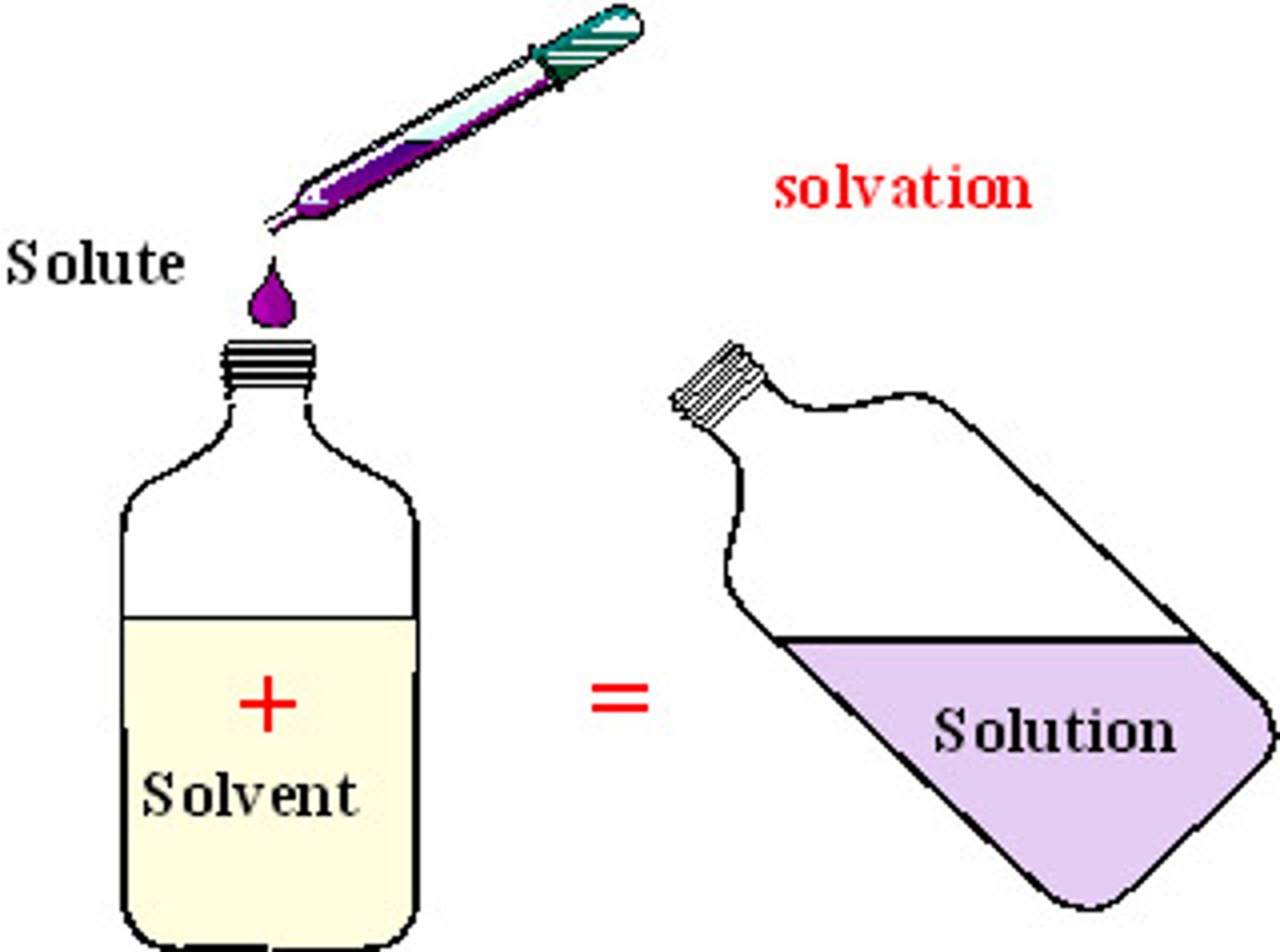
Solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
Solvent
the substance in which the solute dissolves
heterogeneous mixture
A mixture that is not uniform in composition; components are not evenly distributed throughout the mixture

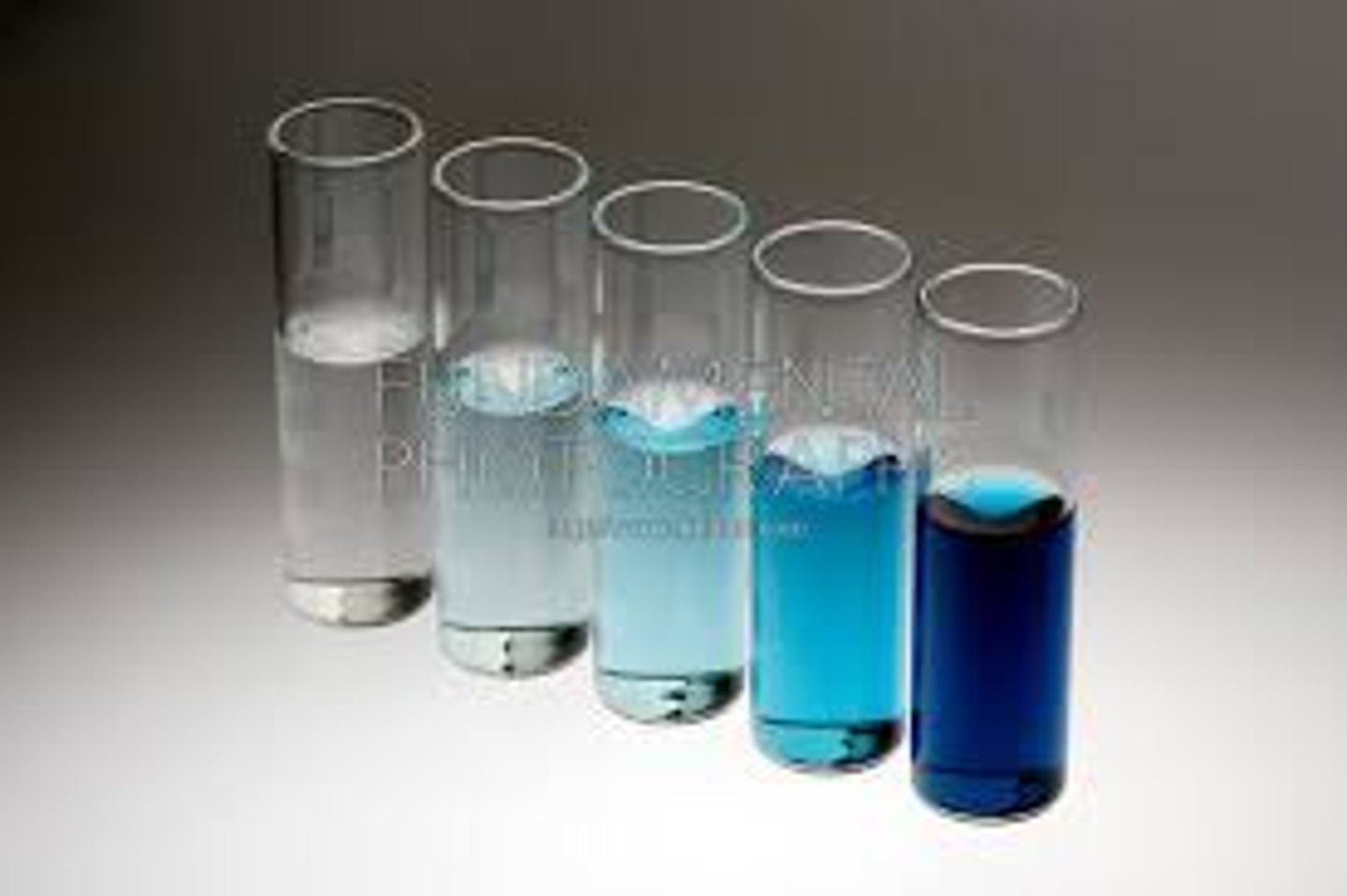
Concentration
the mass of solute in a given volume of solution, or mass/volume
Molarity
A common measure of solute concentration, referring to the number of moles of solute per liter of solution.
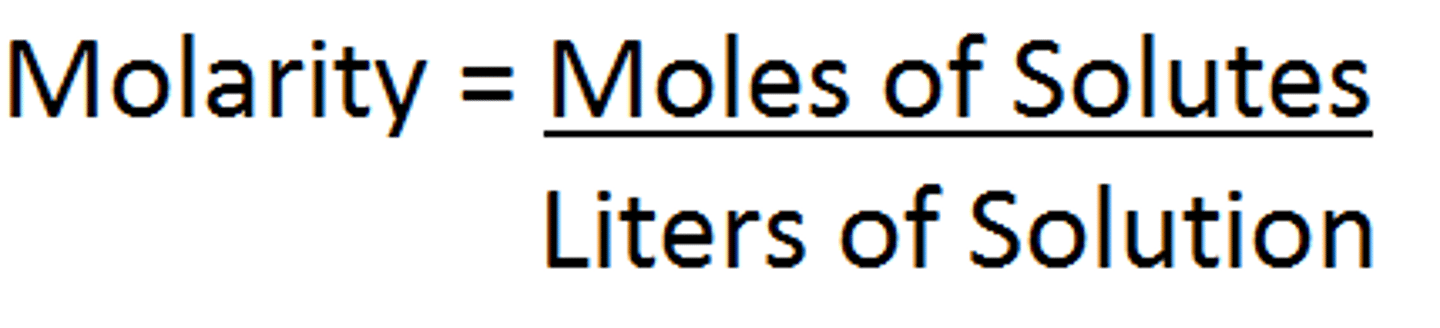
Dilution
Adding water to a solution in order to decrease the concentration

Dilution equation
M1V1 = M2V2

Beer's Law
explains the relationship between absorbance, at a given wavelength and concentration, A = εbc

Photon
A particle of electromagnetic radiation with no mass that carries a quantum of energy
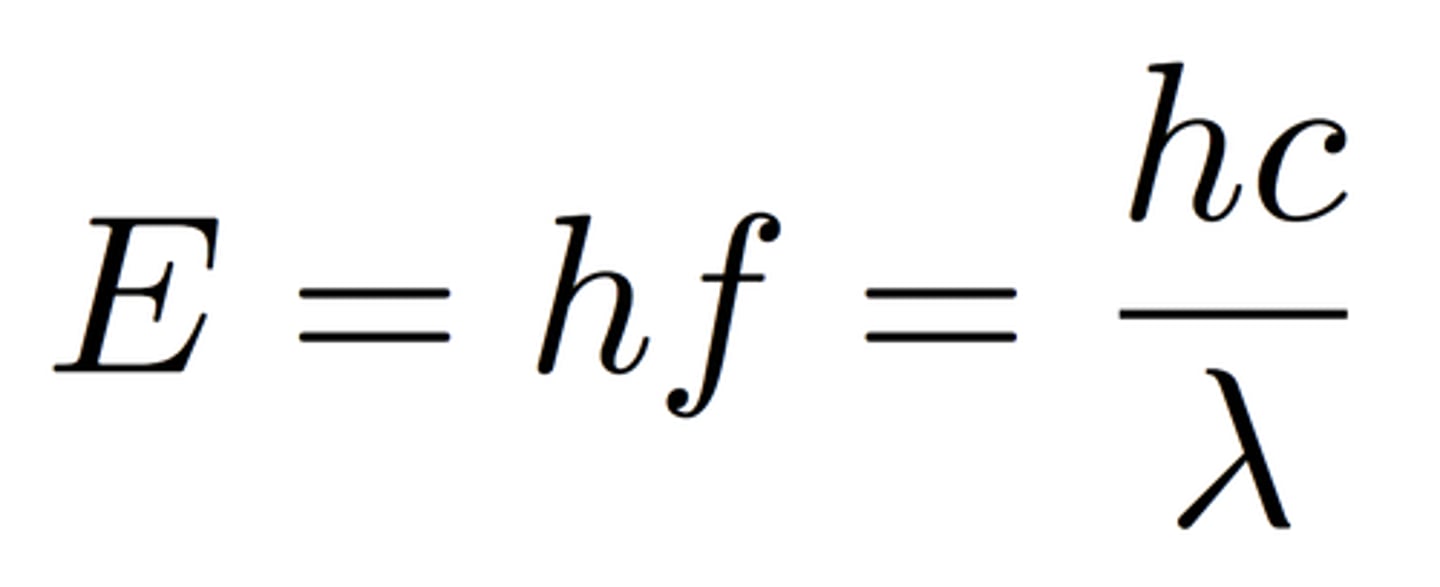
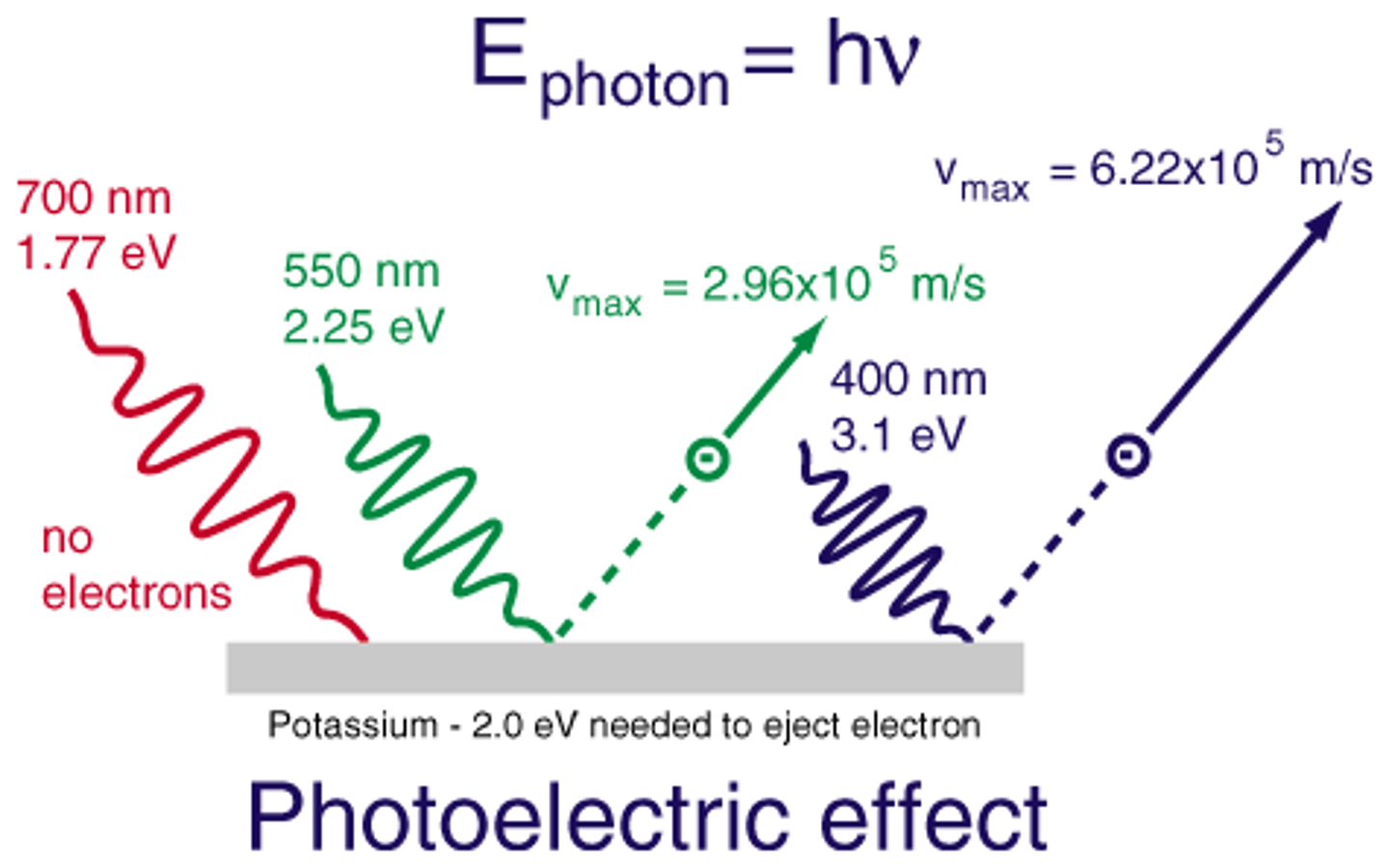
photoelectric effect
refers to the emission of electrons from a metal when light shines on the metal
emission
When an electron falls to a lower energy level, a photon is emitted
adsorption chromatography
solute adsorbed on surface of stationary phase
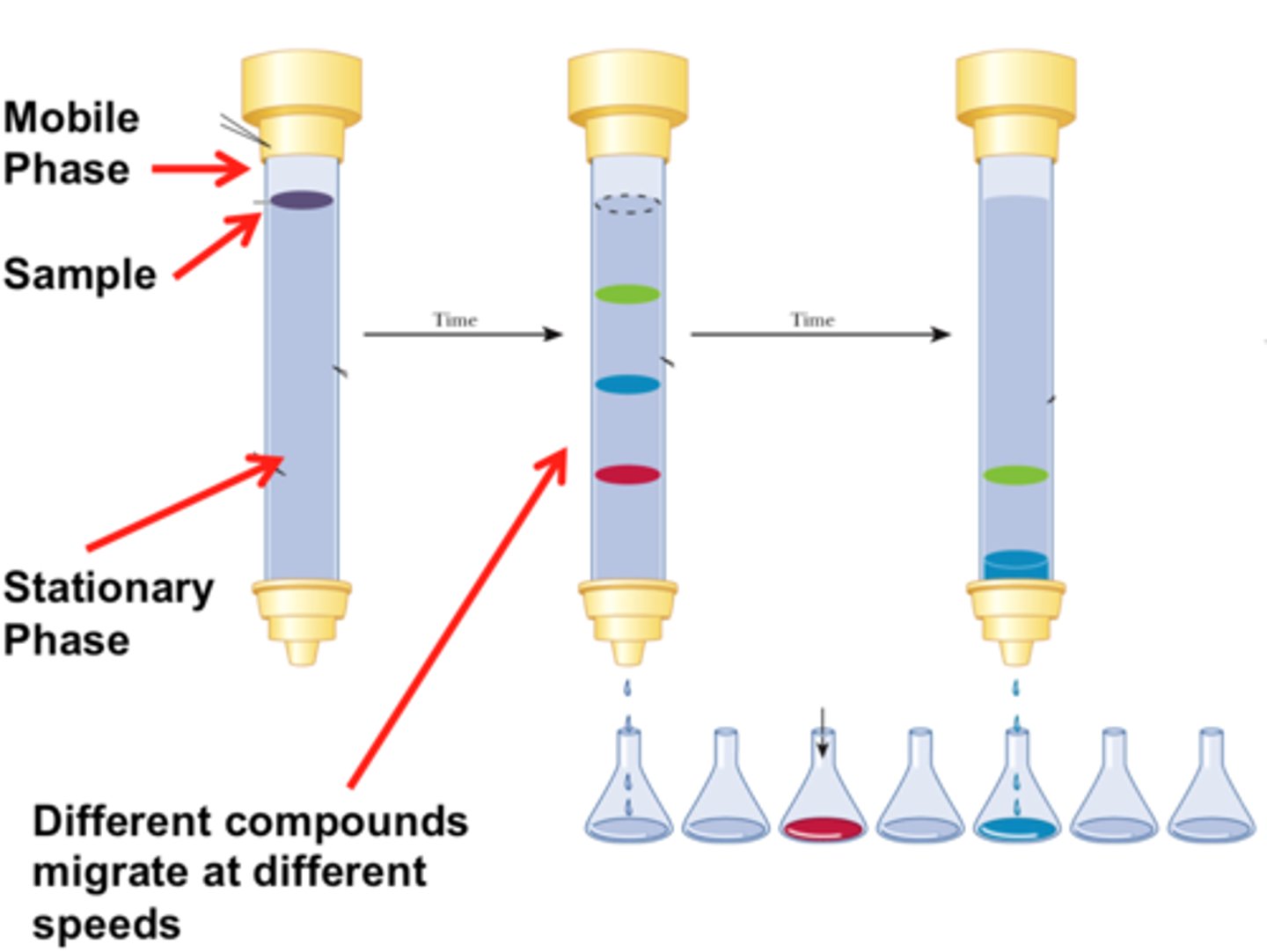
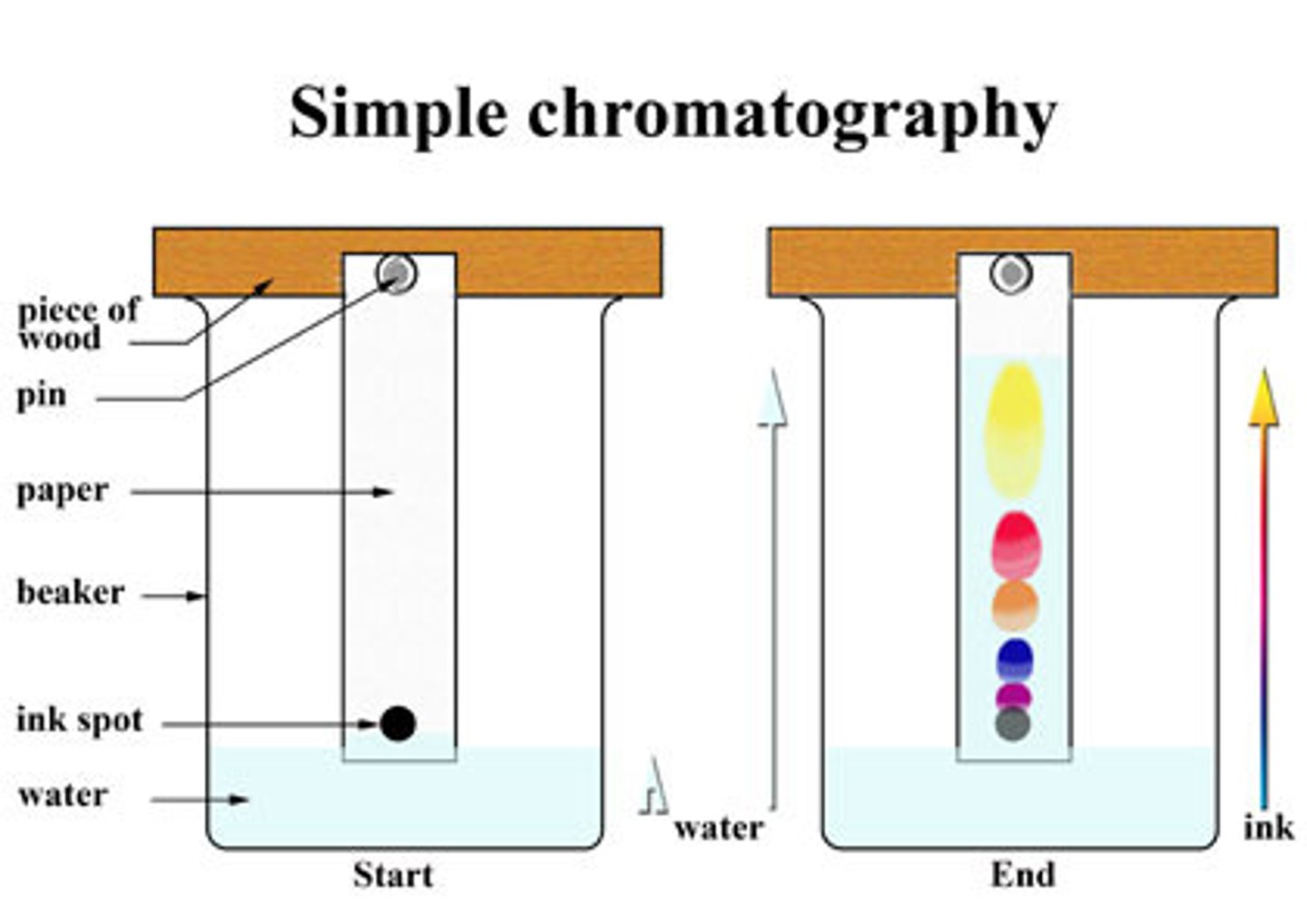
Chromatography
A technique that is used to separate the components of a mixture based on the tendency of each component to travel or be drawn across the surface of another material.
electromagnetic radiation
a form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels through space
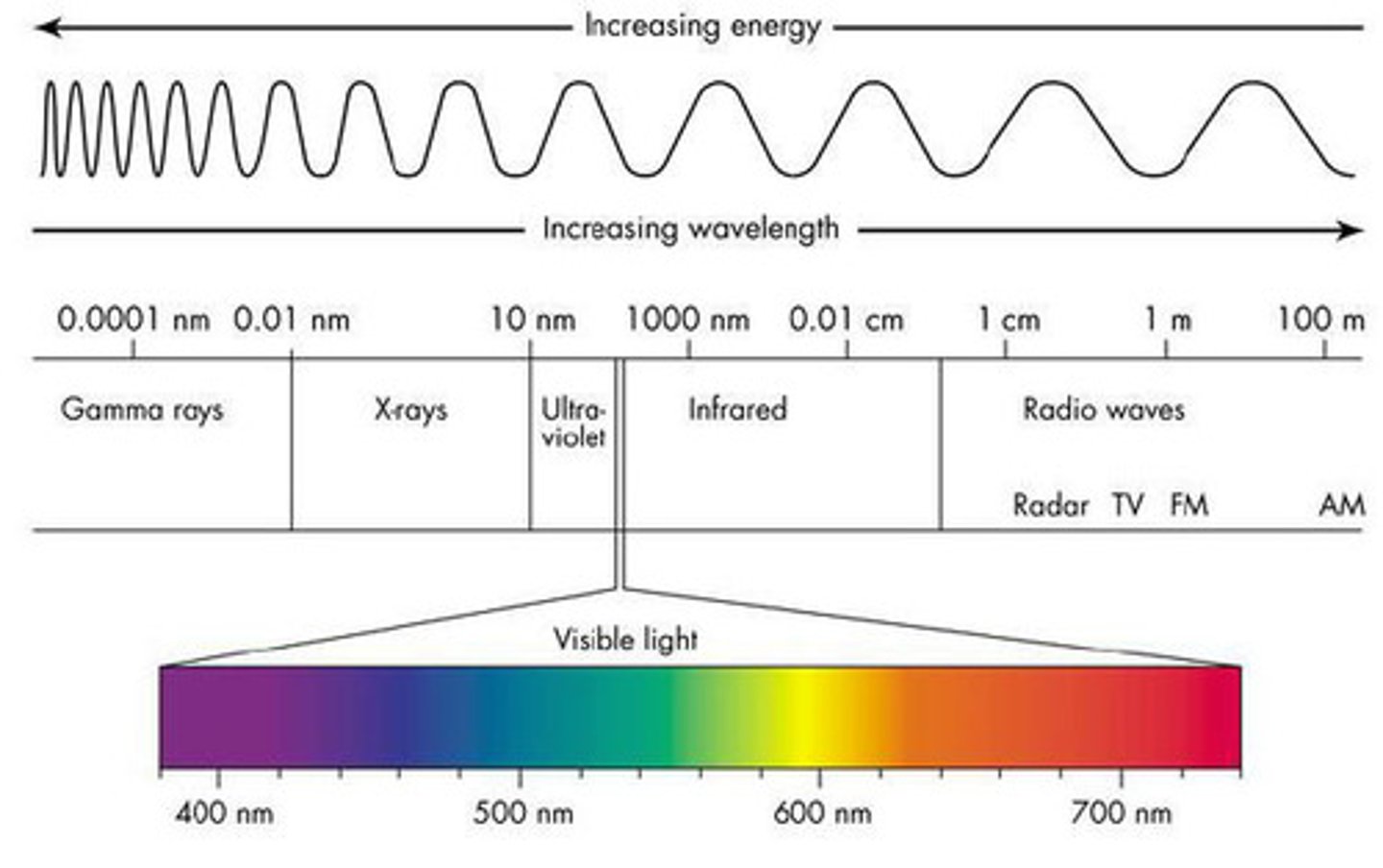
Wavelength
The distance between two corresponding parts of a wave

particle-wave duality
light can behave as a particle and a wave
spectroscopy
the study of the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter
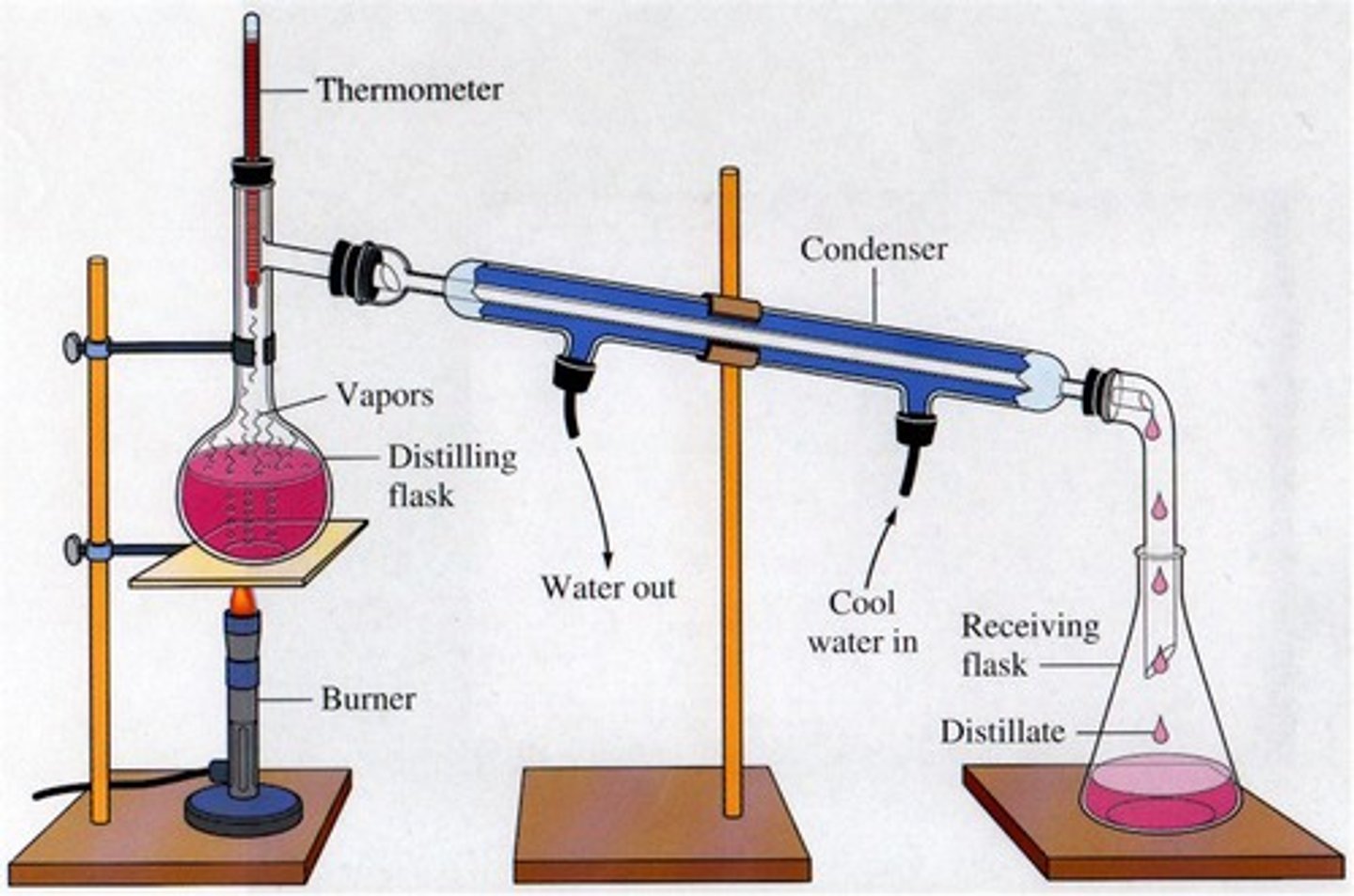
Distillation
A process that separates the substances in a solution based on their boiling points
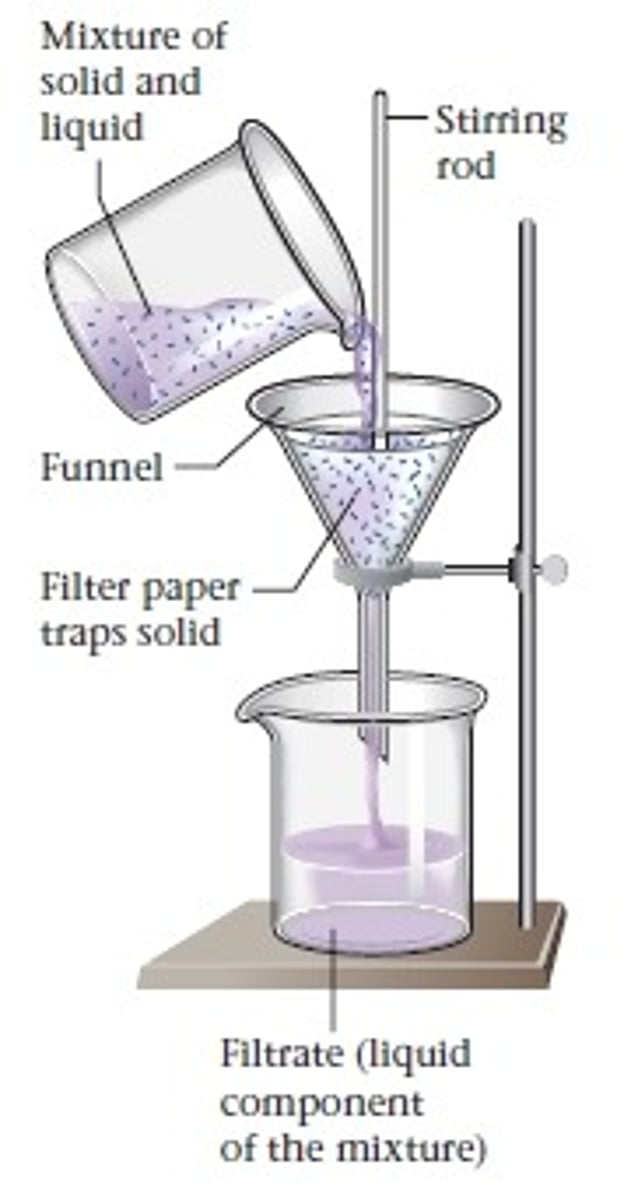
Filtration
A process that separates materials based on the size of their particles.
Fractional distillation
separation of a liquid mixture into fractions differing in boiling point (and hence chemical composition) by means of distillation, typically using a fractionating column.
porous barrier
Any medium through which ions can slowly pass
