topic 7: mycology pt2
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What are the three mechanisms involved in fungal diseases?
Tissue invasion (mycosis) toxin production (mycotoxicosis), and induction of hypersensitivity.
How are fungal diseases categorized based on lesion sites?
Superficial mycoses, subcutaneous mycoses, and systemic mycoses.
What are dermatomycoses?
Opportunistic infections of skin or mucocutaneous junctions resulting from overgrowth of fungi.
What examples of fungi cause dermatomycoses?
Candida species and Malassezia pachydermatis.
What are dermatophytoses?
Clinically important infections that are communicable and zoonotic, caused by dermatophytes invading keratinized structures.
What are examples of dermatophytes?
Microsporum species and Trichophyton species.
What characterizes subcutaneous mycoses?
Localized fungal invasion of the dermis and subcutis, often following penetration by a foreign body.
What is phaeohyphomycosis?
An infection caused by pigmented fungi.
What are mycetomas?
Tumor-like granulomatous lesions caused by fungal infections.
What are systemic mycoses?
Fungal infections that often originate in the respiratory or digestive tracts and usually follow opportunistic infections.
What factors predispose individuals to systemic mycoses?
Alteration in normal microbial flora, immunosuppression, exposure to high doses of spores, and poor nutrition.
What are mycotoxicoses?
Diseases resulting from ingestion of fungal toxins that are pre-formed in stored food or standing crops.
What is aflatoxin and its source?
A toxin from Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus that mainly affects poultry, pigs, and cattle.
What are the effects of aflatoxin?
Liver damage, decreased feed intake, poor growth, and immunosuppression.
What is ochratoxin A and its source?
A toxin from Aspergillus and Penicillium that mainly affects swine and poultry.
What are the effects of ochratoxin A?
Nephrotoxicity, weight loss, and reduced productivity.
What is fumonisin and its source?
A toxin from Fusarium verticillioides that mainly affects horses and pigs.
What condition does fumonisin cause in horses?
Leukoencephalomalacia (ELEM).
What is the significance of hypersensitivity to fungi in domestic animals?
Hypersensitivity reactions are rare but can occur in chronic pulmonary disease in cattle and horses.
What precautions should be taken during mycological cultural procedures?
They should be performed in a biohazard cabinet due to the risk of human infection from spore aerosols.
What specimens are used for diagnosing dermatophytosis?
Hair and skin scrapings and biopsy.
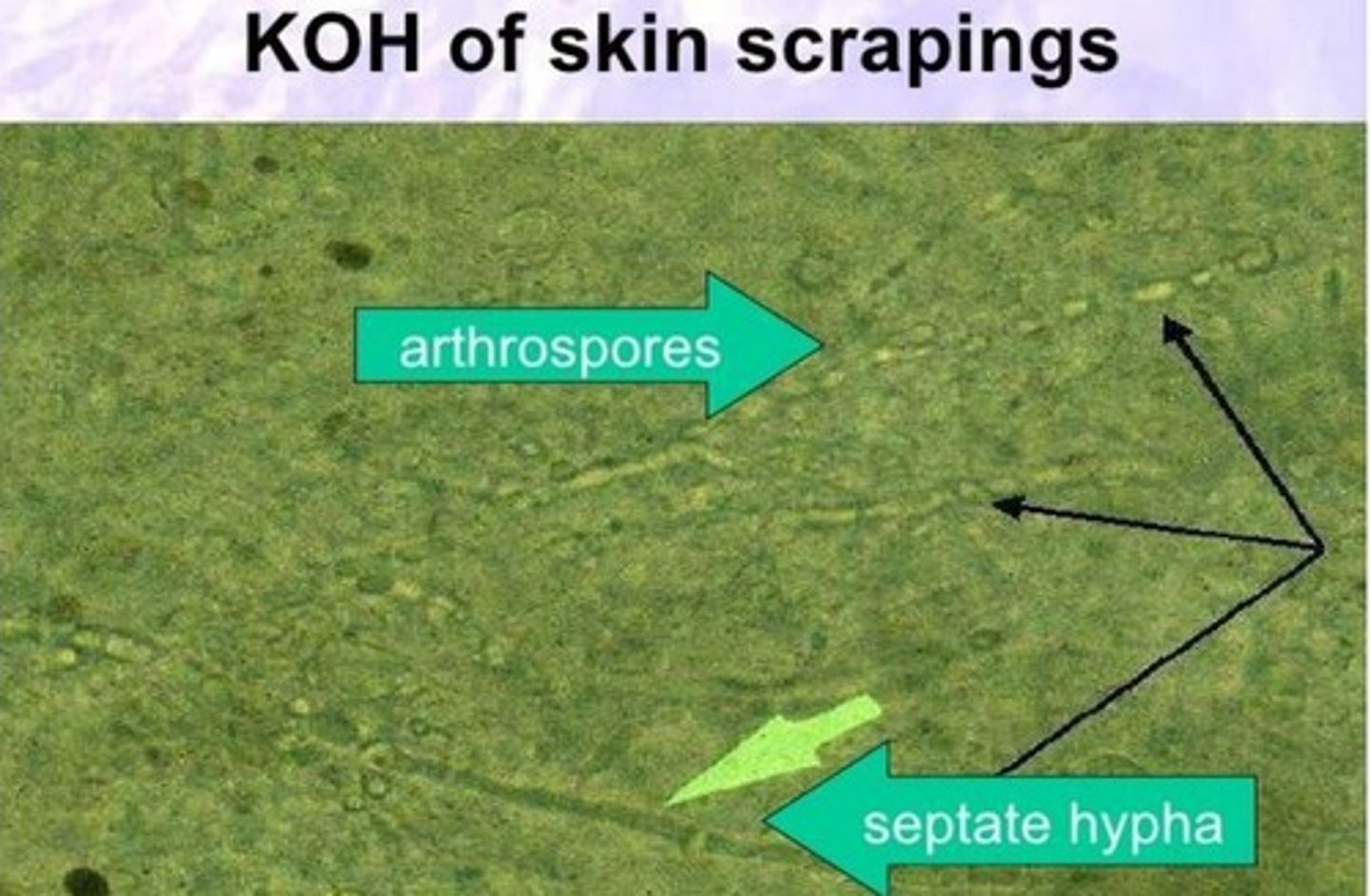
What is the role of KOH in the microscopic identification of fungi?
It clears specimens to demonstrate ringworm arthrospores surrounding infected hairs.
How is Cryptococcus neoformans detected?
In cerebrospinal fluid using India ink or nigrosine to visualize budding cells with wide capsules.
What is the primary target for antifungal chemotherapy?
Ergosterol in fungal membranes.
What are polyenes and give an example?
Antifungal drugs that bind to ergosterol; examples include Amphotericin B and Nystatin.
What is the mechanism of azoles?
They inhibit ergosterol synthesis by blocking 14 alpha demethylase.
What are echinocandins and their mechanism?
They inhibit beta glucan synthesis in the fungal cell wall.
What is the significance of dimorphic fungi?
They have two forms: mold at 25°C and yeast at 37°C, which aids in identification.
What is a conidiophore?
A specialized hypha that supports conidia.
What is a pseudohypha?
A chain of elongating yeast cells with constriction at septa but not true hypha.