Antigen Receptors
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
antigen receptor (AgR)
-BCR or TCR used by the lymphocyte to survey its environment for unfamiliar mlcs that could represent dangerous non-self
-B lymphocyte: when activated via its BCR, it can convert its antigen receptor into a secreted form (antibody- done by an RNA splicing change)
antigen recognition by lymphocytes
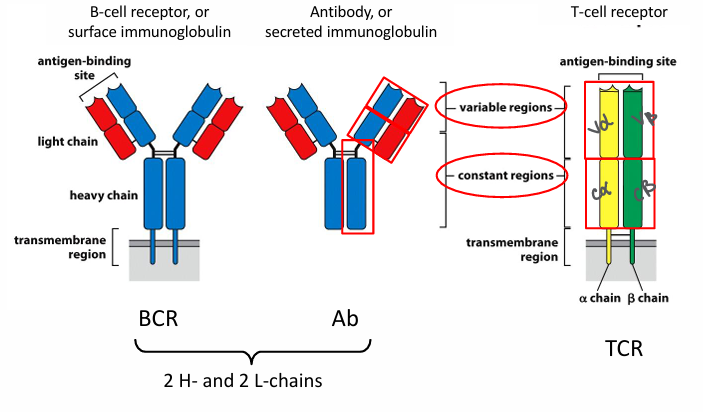
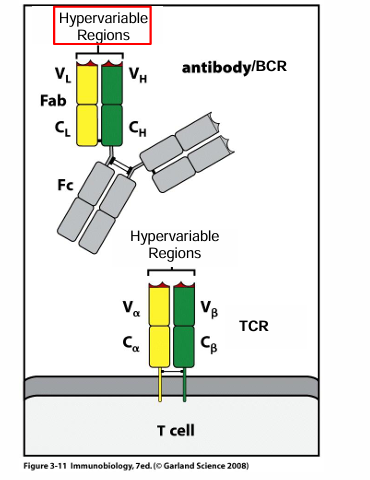
similarity between antibody and TCR
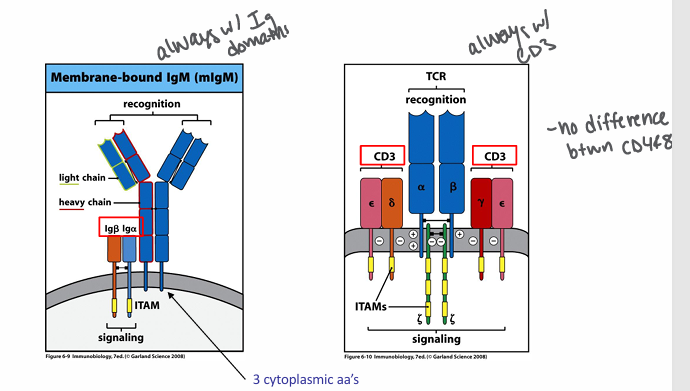
antigen receptor signaling
-ITAM = immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activating motif
-tyrosine within conserved sequence gets phosphorylated → phosphotyrosines bind to kinases
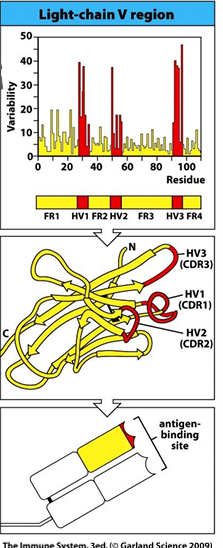
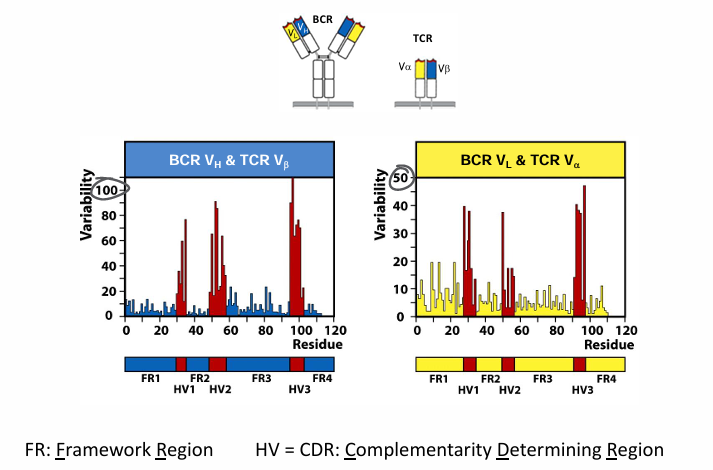
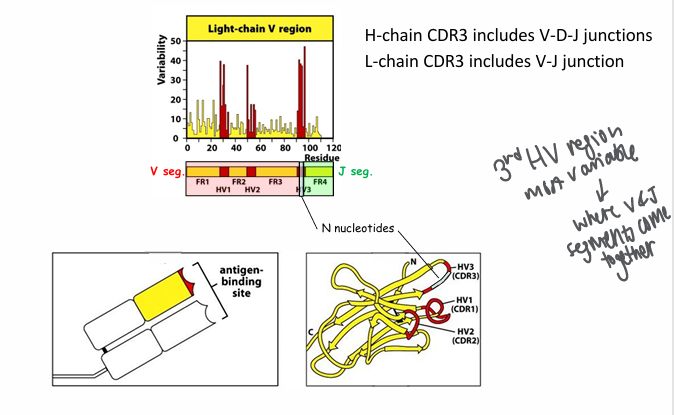
discovery of hypervariable regions
-variability at any given aa position: # distinct aa/frequency of most common aa
-discovered hypervariable loops contributing to the specificity of the antigen-binding site (no 2 antibodies will have the same specificity)
hypervariable regions in B and T cell receptors
**note different y-axis scales between graphs
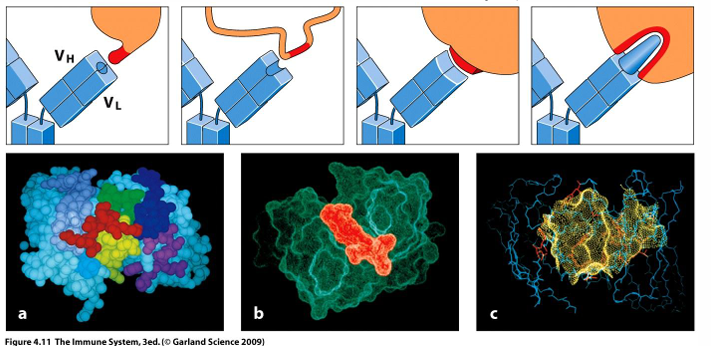
BCR antigen-binding sites
-diverse structures
-epitopes of antigens can bind to pockets, grooves, extended surfaces, or knobs in antigen-binding sites
-very high specificity match
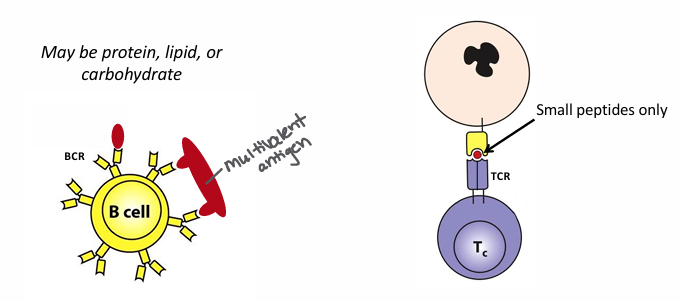
difference between B and T cell receptors
-BCR or antibody can bind native, unprocessed, free-floating antigen that may be a protein, lipid, or carbohydrate
-TCR can bind only processed Ag peptides presented by another cell (small peptides only)
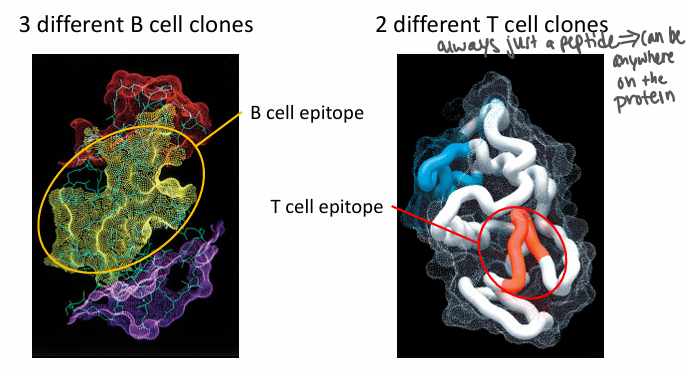
difference in cell clones between B and T cell receptors
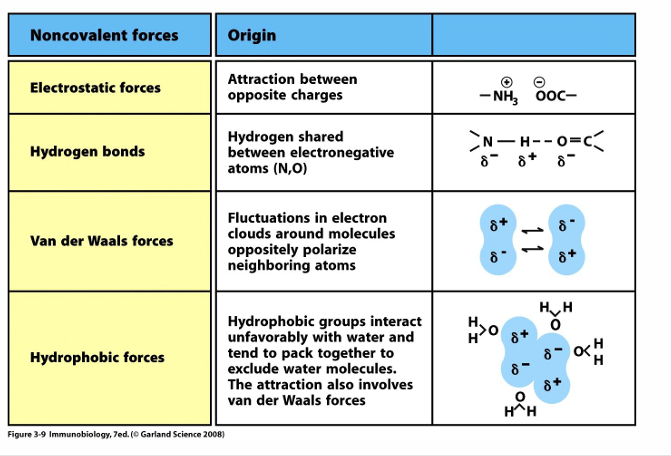
non-covalent forces contributing to receptor:antigen binding
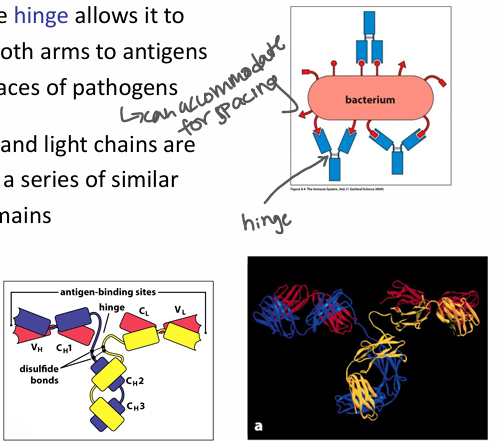
features of immunoglobulin molecule
-flexible hinge allows it to bind with both arms to antigens on the surfaces of pathogens
-heavy and light chains are made from a series of similar protein domains
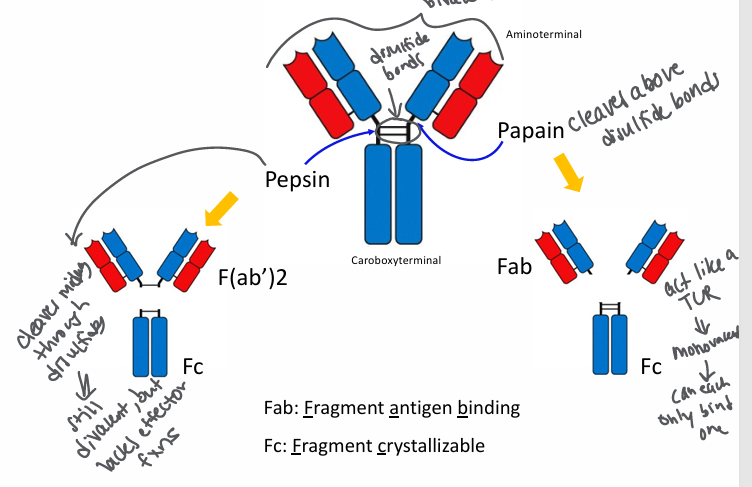
useful immunoglobulin fragments
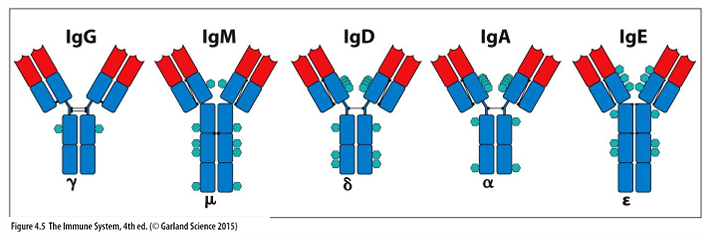
structure of human immunoglobulin classes (isotypes)
-newly generated, antigen-inexperienced or “naive” B cells express IgM and IgD on their cell surface (first to come out of bone marrow)
-IgG, IgE, or IgA expressed on cell surface of antigen-activated B cells following Ig class switch
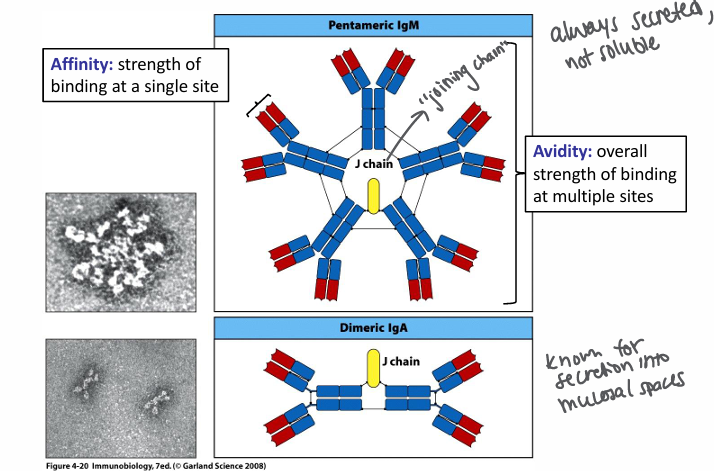
IgM and IgA molecules
-can form multimers
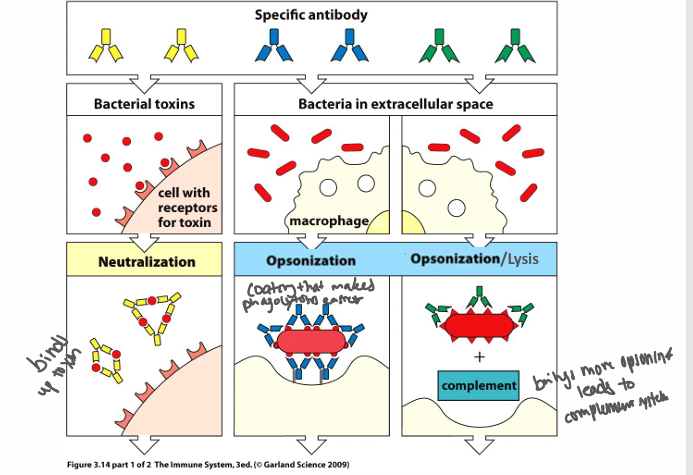
mechanisms by which antibodies combat infection
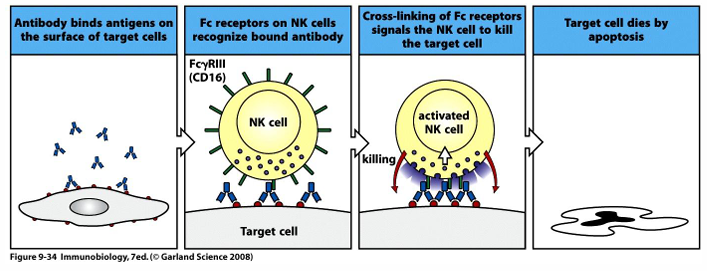
antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
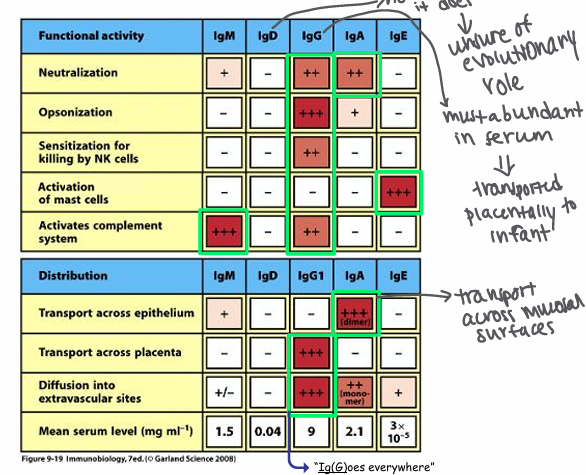
Ig isotypes- different functions and distributions
importance of antibodies as clinical tools
-monoclonal antibody: preparation of antibody secreted by a single clone of plasma cell- a soluble protein, available in unlimited quantities, with exquisite specificity and high affinity for any ligand chosen
-could: neutralize toxin or pathologic protein of choice (biologic “sponge”), neutralize viral infection after exposure, target pathologic cells, identify cells using antibody “tags” specific for surface proteins (“markers”)
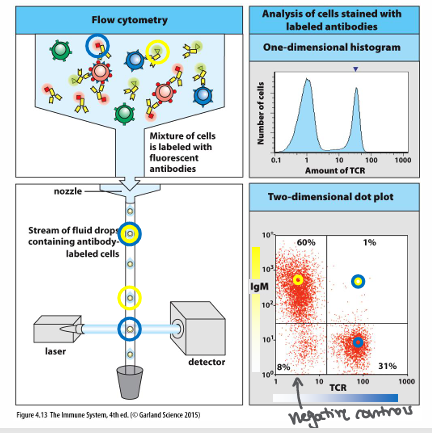
ID/quantification of cells by flow cytometry
-antibodies as reagents
adaptive system’s challenge
-pathogen: HUGE variety- millions of potential invaders to be recognized
-genome encodes 20-30k genes- if antigen receptors are to be specific, will need to generate millions of unique receptors (limited genome)
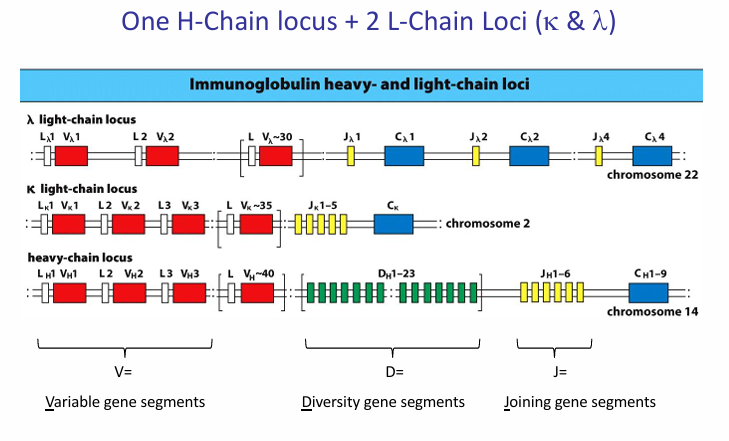
germline organization of BCR
diversity of B and T cell receptors generated by
-gene rearrangement through somatic DNA recombination
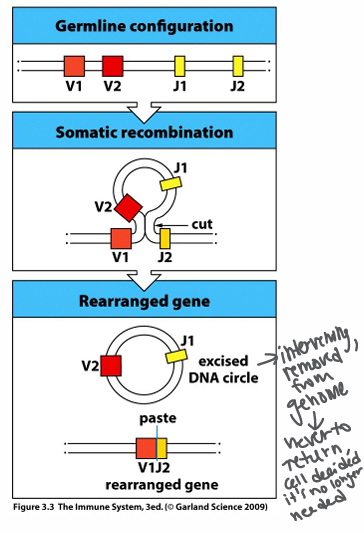
______ encode the BCR V-domain
-V(D)J segments
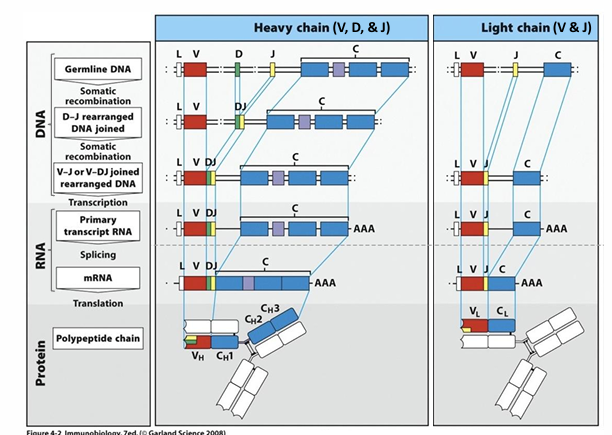
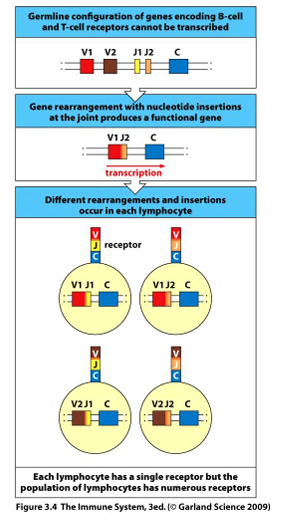
combinatorial diversity
-gene rearrangement produces huge variety in antigen receptors
-millions of lymphocytes = millions of receptors, but 1 new lymphocyte = 1 unique receptor
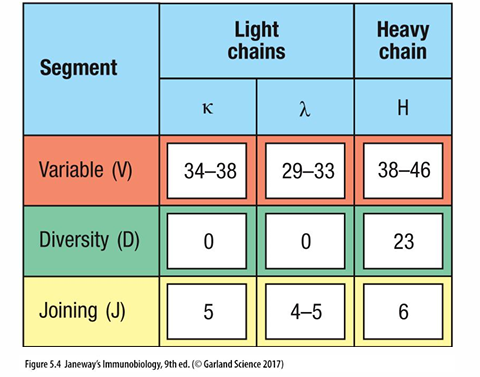
number of functional gene segments in human immunoglobulin loci
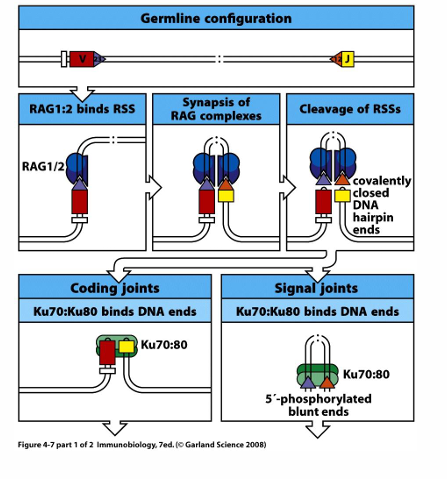
each V/D/J gene segment is flanked by
-recombination signal sequences (RSS)
-must be 12-23 → 12-23 rule ensures a D will always be inserted between V & J (12-12 and 23-23 won’t work)

enzymatic steps in RAG-dependent V(D)J recombination
coding joints and signal joints continuation
-recombination excision circles (TRECs and BRECs): generated with every TCR & BCR, remain in lymphocyte (tiny episome), TRECs routinely assayed in newborns via heel stick to rule out SCID
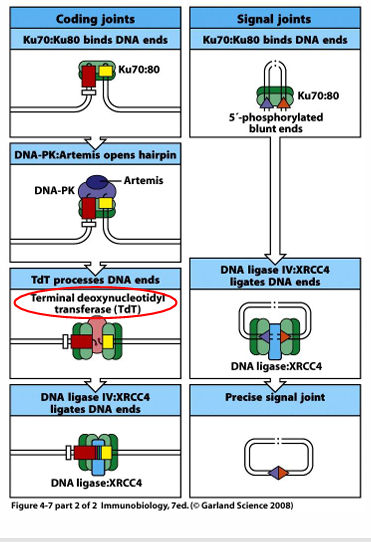
addition of non-germline encoded nucleotides
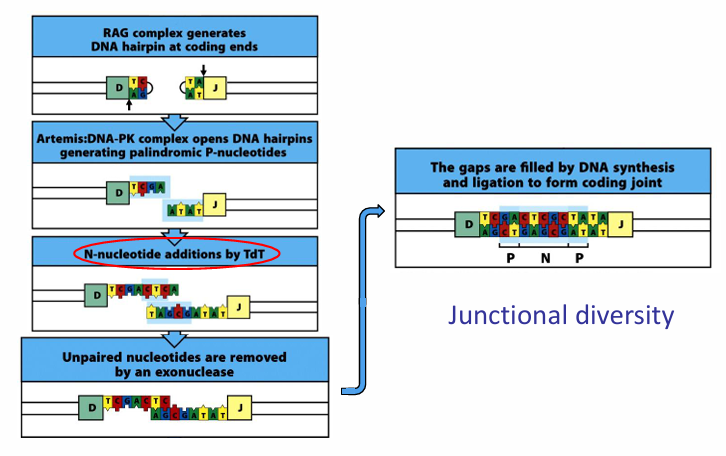
junctional diversity is hardwired in the
-hypervariable loops
3 processes establish diversity of the pre-immune repertoire
1) combinatorial diversity (Vh, Dh, Jh & Vl, Jl assortment)
2) junctional diversity (TdT and non-templated bp addition)
3) combinatorial diversity through HC and LC combinations