history of the print final study guide
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
relief print
The actual surface from which the printing is derived stands raised above the areas that have been cut away. Ink is applied only to this raised surface and transferred to paper by applying vertical pressure. Important examples include woodcut, linocut, and wood-engraving.

intaglio print
Involves making incisions into a metal plate, usually copper, but occasionally iron, steel, or zinc. The surface of the plate is wiped clean so that the ink is left only in the incisions. Printing requires great pressure to force the paper into the grooves to pull out the ink. A physical characteristic of this print is the plate-mark.

impression
An individual print taken from a plate or block. The quality of ____ from copper intaglio plates often deteriorates due to the repeated wiping and pressure necessary for printing, which is why early ______ are highly valued.
state
A specific stage in the development of a plate. A print may exist in a preparatory 'etched ___' before additional work, such as engraving, is added to create a 'later ___'.
letterpress printing
A relief printing technique where raised, inked surfaces like movable type or carved blocks are pressed onto paper to create an impression.

surface tone
Films of ink intentionally left on the surface of an intaglio plate, which the printer leaves during the wiping process to create artistic or atmospheric effects.
embossment
The physical texture impressed onto the paper from the block during printing, such as the texture of the wood block often visible on the background of a woodcut.
registration
The precise alignment of multiple printing elements, such as different colors or plates, on a single sheet of paper to create a final image.
woodcut
A relief technique using side grain wood (softer than wood used for wood engraving). Often shows wood pattern and texture. Generally less precise, rougher than engravings and etchings.

wood engraving
A relief technique using end grain wood blocks (cut across the grain), creates a harder surface that is good for high levels of detail.

cross hatching
A system of parallel or intersecting lines used for shading and tonal effects. In woodcut, the cutter must meticulously clear all the material between the hatchings
gouge
A cutting tool used along with chisels to remove large, unwanted areas of wood from a woodcut block.

engraving
The principal and oldest manual technique within the intaglio class. It requires highly skilled cutting of lines directly into a metal plate, traditionally copper, using a specialized tool called a burin.

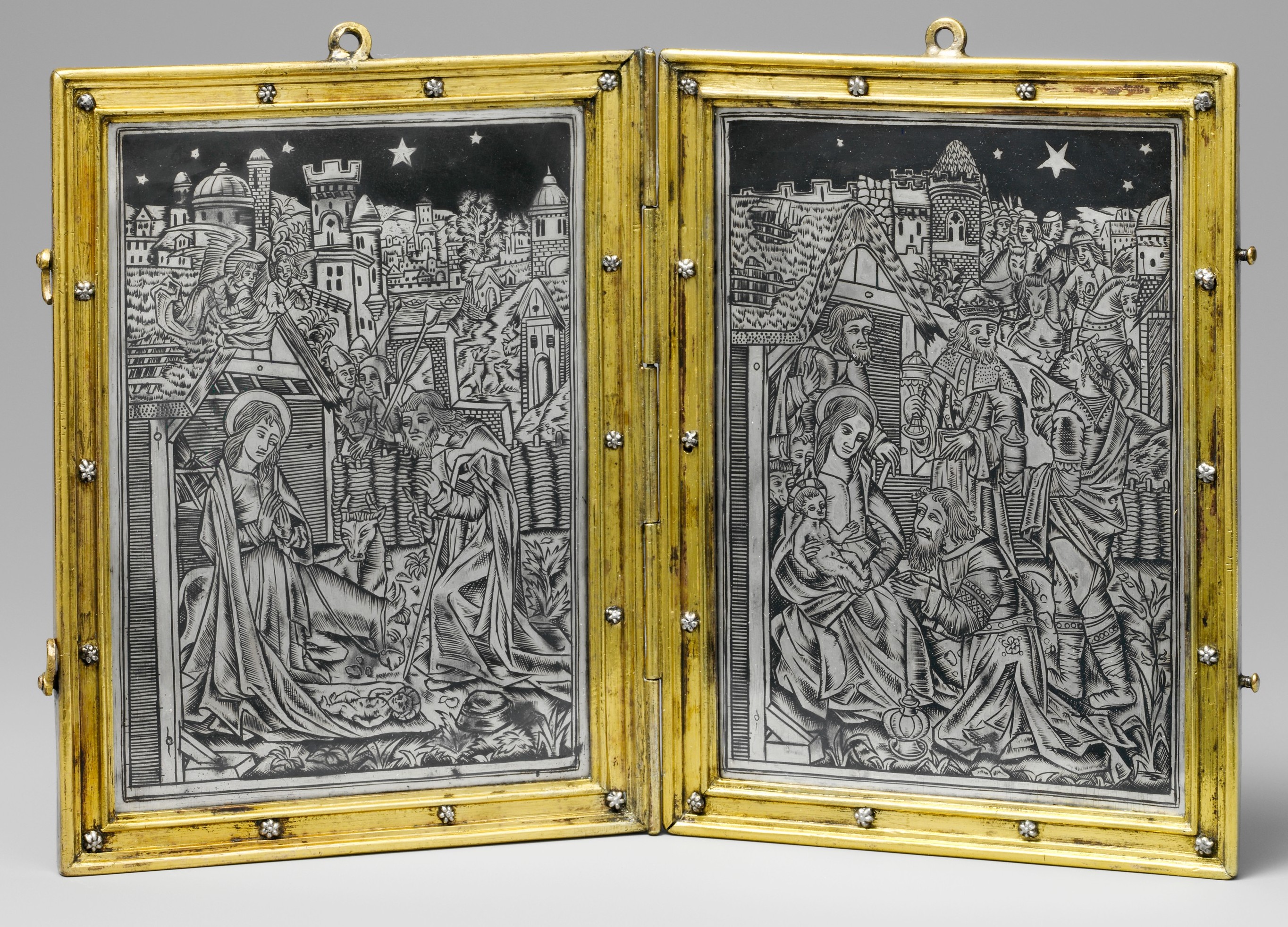
niello print
A specific type of print developed in Florence around the late 1440s. Originally created to decorate the lids of small boxes. Involves engraving a design into a metal surface, then filling the engraved lines with a black, metallic alloy made of sulfur and other metals like silver, copper, and lead. The piece is heated, causing the niello to melt and flow into the grooves. After it cools, the excess is polished off, leaving a black inlay that provides a sharp contrast with the surrounding polished metal.

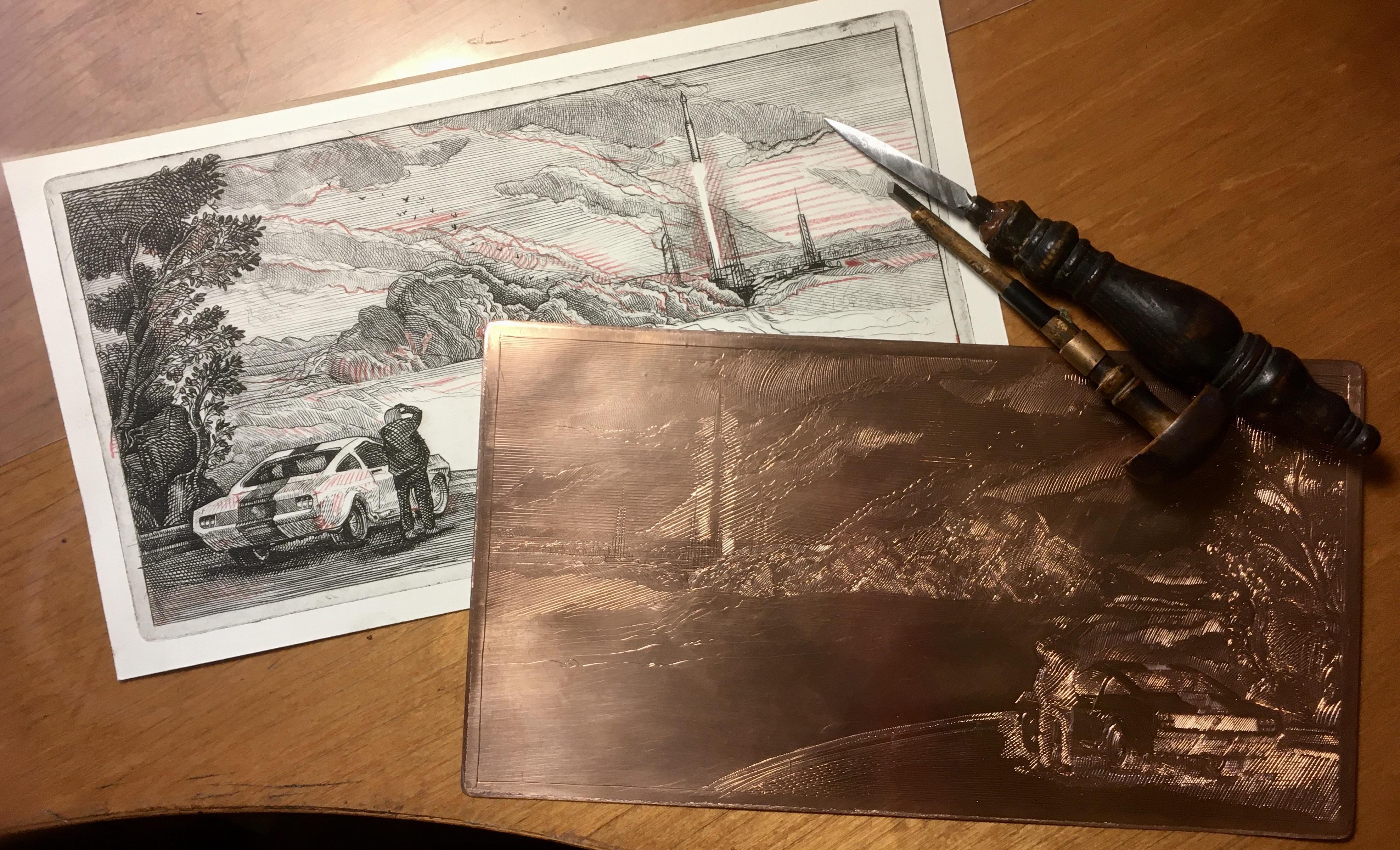
etching
The most important intaglio technique after engraving, defined by the essential principle that the metal of the plate is removed by being eaten into by acid rather than being manually cut by a tool. Different types include hard ground, soft ground, and aquatint.

hard ground
Intaglio etching technique that involves a protective coating, impervious to acid, applied to the etching plate. The artist draws lines through this ground to expose the metal. The metal is then put in an acid bath to etch lines into it. Sharp lines.
soft ground
Intaglio etching technique that involves specialized etching ground containing tallow that prevents it from hardening. Drawing on paper placed over this ground lifts the ground, transferring the drawing design to the plate, and allowing the print to resemble a chalk or pencil drawing. Softer lines.
stop out
A varnish used by etchers to cover specific areas of the plate that have been sufficiently bitten by the acid. This allows the rest of the plate to be put back into the acid bath for further, deeper biting.
foul biting
A damaging outcome in etching resulting from the acid indiscriminately attacking the plate due to an imperfect etching ground
drypoint
The simplest intaglio process, where a line is scratched directly into the copper plate using a sharp metal point. This action raises a ridge of metal called the burr, which holds ink and produces the characteristic rich, feathery smudge in the print.

burin/graver
The main tools used for engraving, pushed forward to cut a sharp, V-shaped groove in the metal.

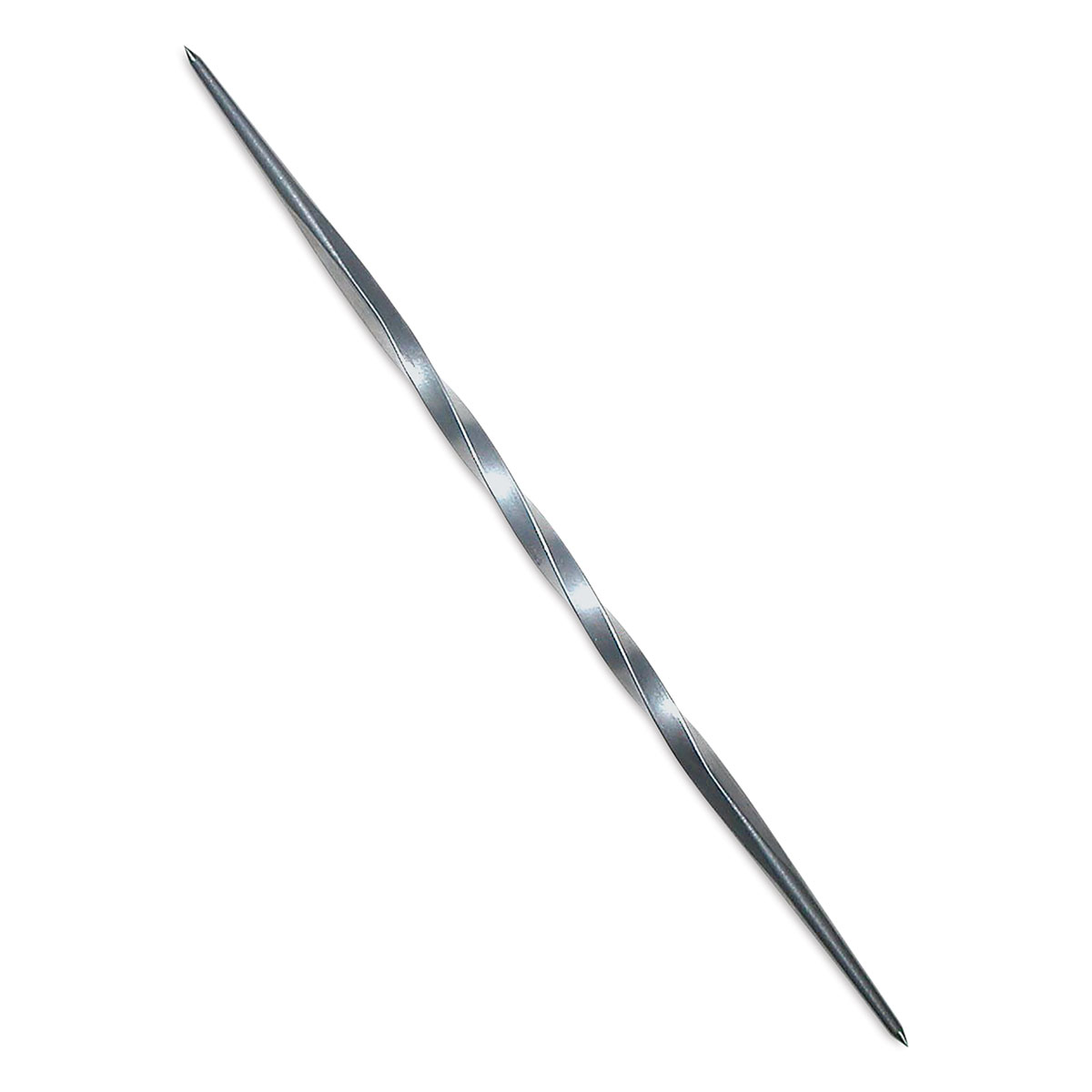
stylus
A simple metal point, also referred to as an etching needle, used to draw lines through the hard ground on an etching plate.

scraper
Used in engraving to remove metal from the plate before burnishing. It is also used in tonal processes like mezzotint and drypoint to clear away the roughened surface or burr.

burnisher
Used in conjunction with the scraper by smoothing the plate surface. In mezzotint and aquatint, this is used to rub down parts of the plate to achieve lighter tones and highlights.

aquatint
An intaglio technique specializing in tonal effects, created by using a resin dust ground that forms a network of exposed copper areas when fused to the plate. Gradation of tone is achieved through successive acid baths and the application of stop-out varnish.

aquatint box
Equipment used in the aquatint technique where resin dust is blown into a cloud and allowed to settle onto the plate in an even film before being fixed.

mezzotint
A complex intaglio dot process specifically intended to achieve dense tonal effects by roughening the entire surface of the plate using a rocker tool. The image is created by scraping and burnishing this roughened surface to generate lighter tones, effectively working from dark to light.

monotype
A printmaking process invented by Giovanni Benedetto Castiglione in the seventeenth century. Print is created by applying ink or paint directly to a smooth, non-absorbent surface like glass or metal, then pressing it onto paper to transfer the image




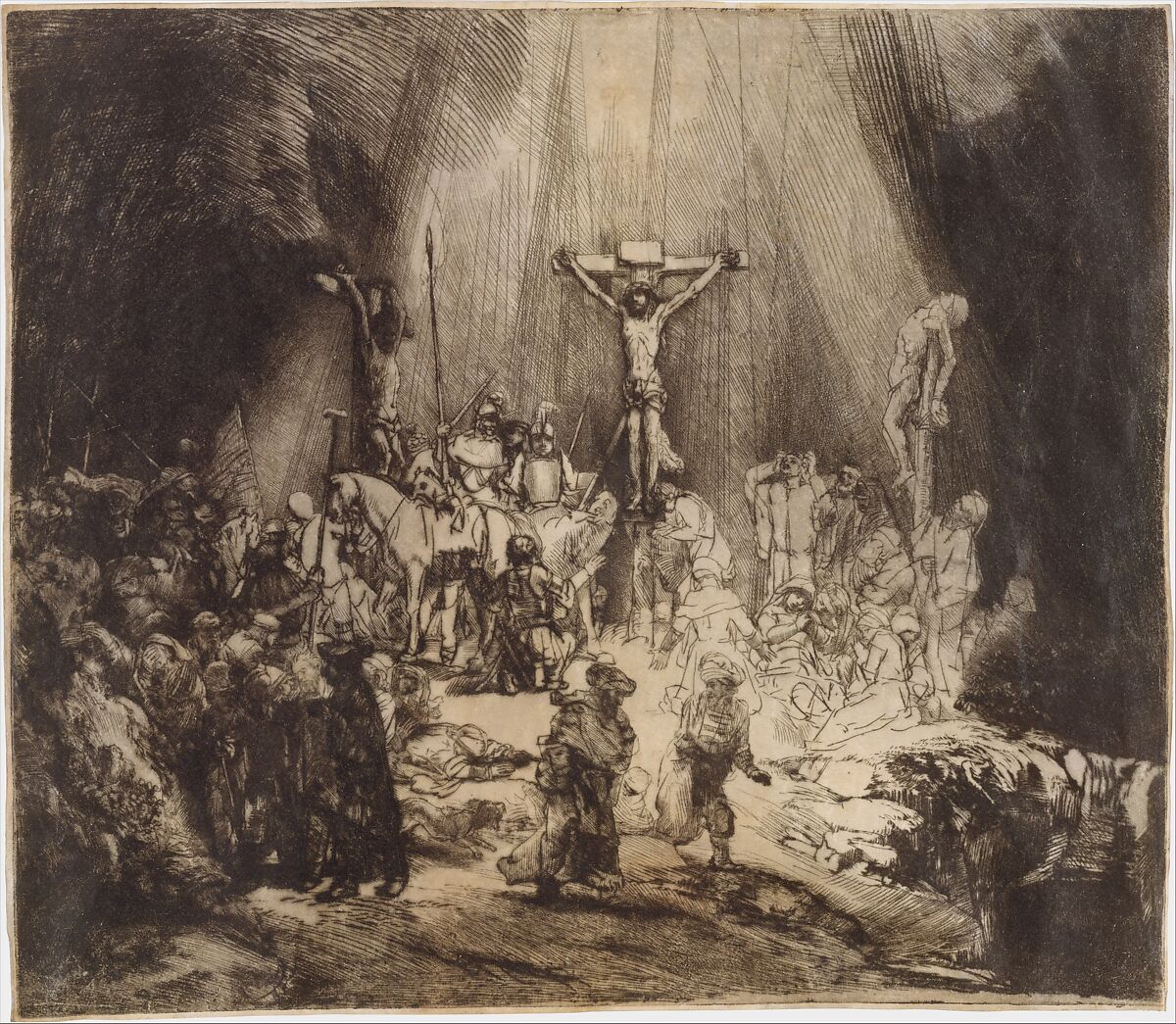
17th century Dutch known for intaglio work(etching/drypoint), dramatic use of light/shadow (chiaroscuro), deep psychological portraits, prolific output (paintings, etchings, drawings), and realistic portrayal of human emotion, important works include The Hundred Guilder Print (Christ Healing the Sick) and The Three Crosses


