Carbohydrates and Lipids Quiz
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

15 Terms
carbohydrate monomer and polymer
monomer: monosaccharide, polymer: polysaccharide
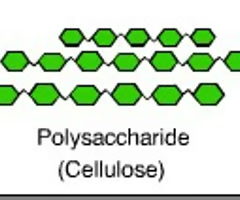
linear carbohydrate
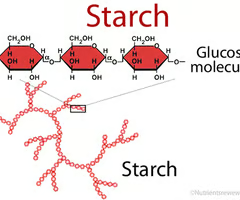
branched carbohydrate
lipid monomers
glycerol and fatty acids
lipid structure
hydrophilic (polar) head and hydrophobic (non-polar) tail
What elements make up all organic macromolecules?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorous (CHONP)
What does structure equals function mean?
what a molecule can do is determined by it's shape and composition
lipid functions
long energy storage, phospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane, steroids (hormones), thermal insulation
glucose
the form of sugar that circulates in the blood and provides the major source of energy for body tissues
cellulose
carbohydrate component of plant cell walls, has a linear structure
starch
storage form of glucose in plants, has a branched structure
glycogen
storage form of glucose in animals, has a highly branched structure
hydrolysis
breaks down complex molecules into individuals molecules by adding a water molecule
dehydration synthesis
puts together molecules to make a more complex molecule by removing a water molecule
atherosclerosis
the build up of fatty deposits in arteries caused by eating too much saturated fats and cholesterol, can lead to a heart attack or stroke