2.21 Developmental Abnormalities of Bones
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What are examples of developmental bone abnormalities?
Angular limb deformity (ALD)
Physitis
Physeal fractures (Salter-Harris fractures)
Defects of the spine
Digit malformation
Rickets
Inward/medial.
Outward/lateral.
Valgus. Often grow out of it.
Which ALD is more severe?
Varus.
What types of factors may cause ALD?
Perinatal factors
Developmental factors
Premature birth, twin pregnancy, placentitis, perinatal soft tissue trauma, and poorly calcified bone.
What type of dalric shoes are used for valgus vs. varus?
Valgus: medial extensions
Varus: lateral extensions
Valgus: Enhance growth on lateral side (needle into growth plate).
Varus: Hoof extension and screw into lateral side to enhance growth on the medial side.
What are more invasive surgical methods for treatment of ALD?
Periosteal stripping of radius, transphyseal bridging, transphyseal screw placement, corrective osteotomy or ostectomy
What is the prognosis for severe angular limb deformities?
Poor without treatment, but favourable with early detection and proper surgery.
Which growth plates are more commonly affected by physitis at which ages?
Nursing foals: P1
Post-weaning: Radius (also, metacarpus/metatarsus)
Trauma, overfeeding (grow too fast), obesity, mineral imbalances, and genetic predisposition, Salter-Harris fractures.
What is the pathological result of physitis?
Disturbance of endochondral ossification.
X-ray, calcium:phosphorus ratio (1:1), and increased alkaline phosphatase (ALP).
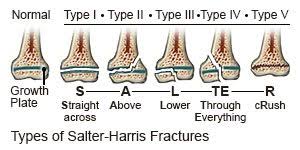
What are the types of Salter-Harris fractures?
I: Straight across
II: Above
III: Lower
IV: Through Everything
V: cRush
What is the pathological result of physeal fractures?
Disruption of the bone in growth plate.
What is the treatment of physeal fractures?
Important to use a locking technique - Locking compression plate (for long bones) + lag screws + cast. (metal plates and screws on each side of the bone).
What are defects of the spine?
Scoliosis: S-shaped spine.
Lordosis: Sway-back /downward curved spine.
Kyphosis: Upward curving of the spine.
Synostosis: fusion of a vertebra with the next vertebra
How common are defects of the spine?
Uncommon.
What is digit malformation?
2nd or 4th splint bone develops into a complete lower limb and foot.
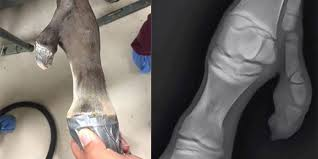
Which is rickets?
Rare. Nutritional deficiency of vitamin D. Results in metaphyseal flaring and bowing of extremities.
What age are radial fractures more common?
4 months.
What age are cannon bone fractures more common?
18 months.
Which joints are most affected by ALD?
Front: carpal joint with radius
Hind: tarsal/hock with tibia.
What is the prognosis of cuboidal bone malformation?
Bad. No real treatment as is due to prematurity.