Anatomy Chapters 6&8: The Skeletal System
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/108
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
1
New cards
support, protection, movement, storage, blood cell formation
functions of the skeletal system
2
New cards
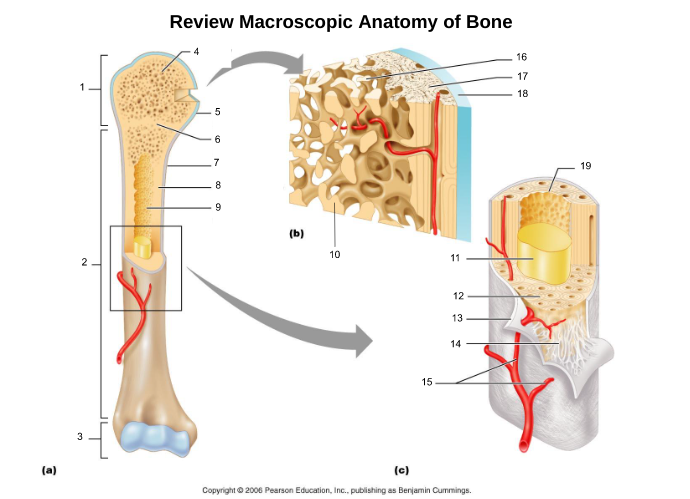
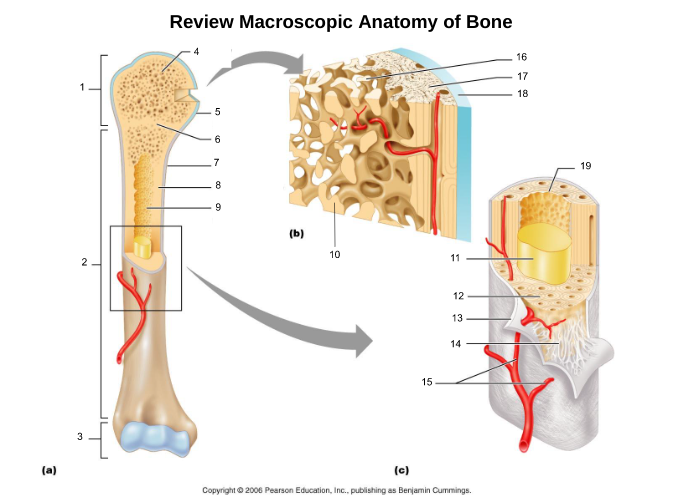
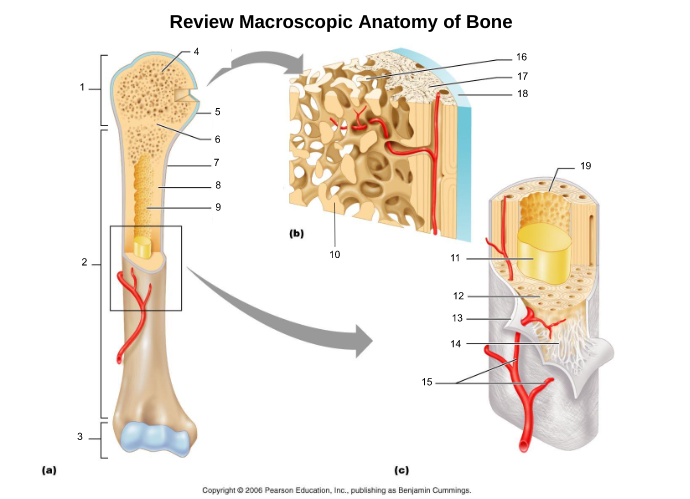
compact bone (8, 12, 17)
dense solid layer on the outside
3
New cards
spongy bone (4, 16)
porous bone with scaffolds called trabaculae, on inside of bone and end of bones
4
New cards
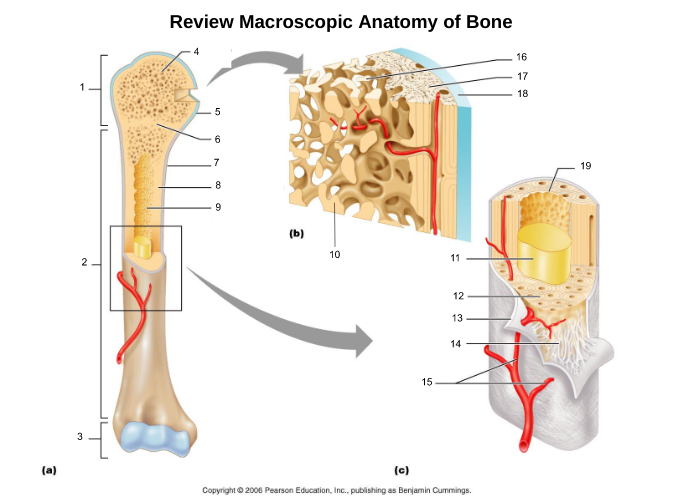
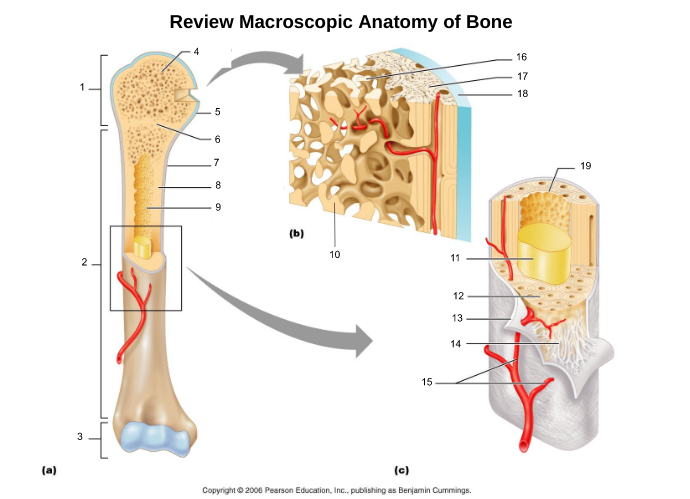
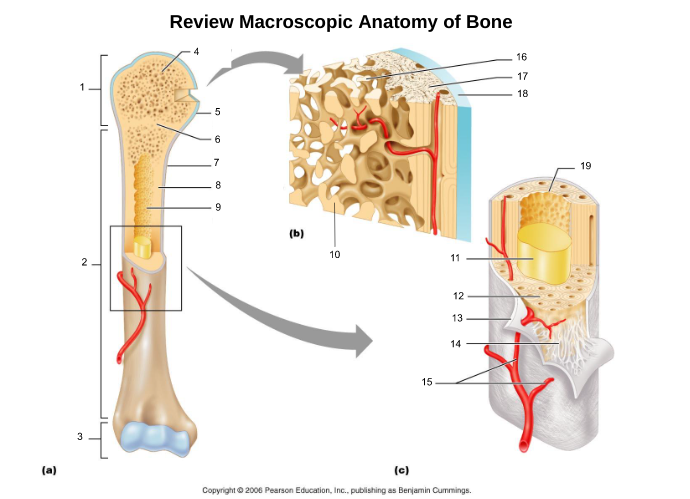
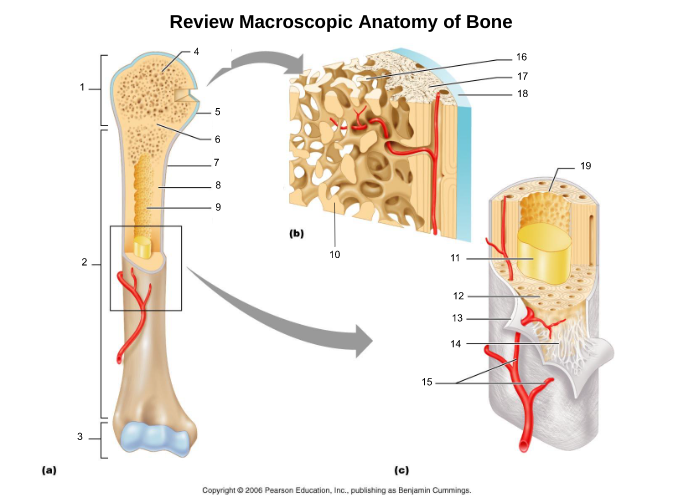
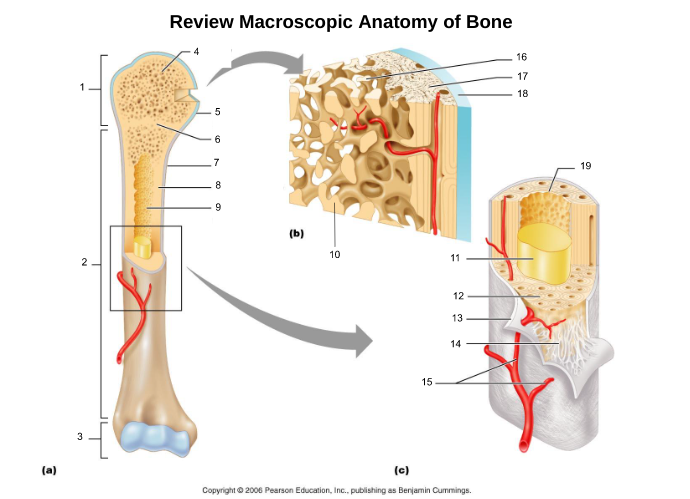
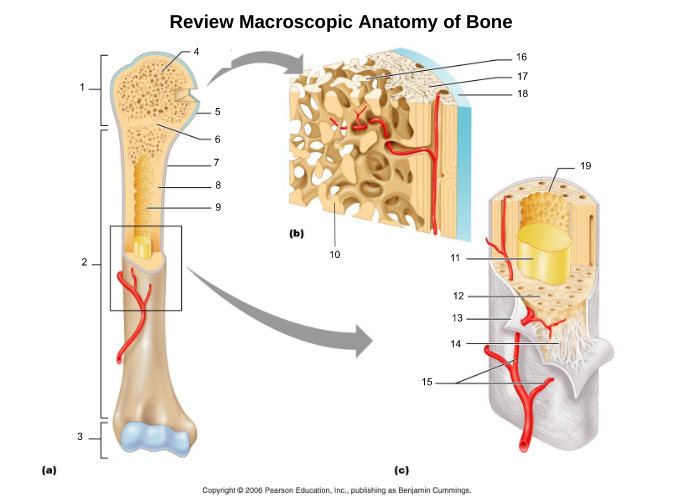
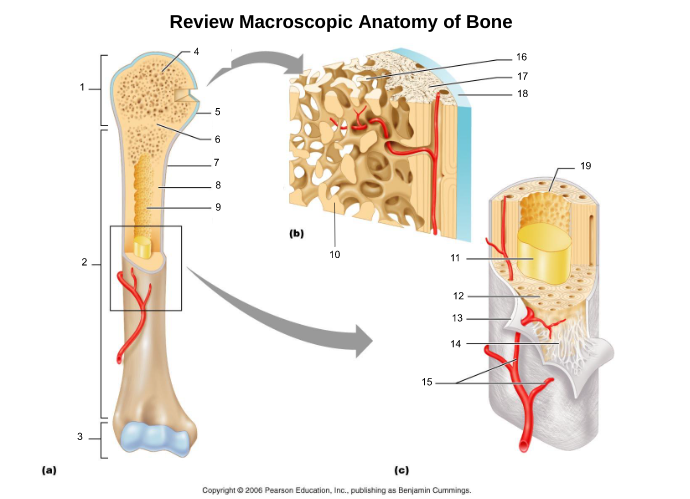
proximal epiphysis (1)
proximal end of bone
5
New cards
diaphysis (2)
long axis of bone
6
New cards
distal epiphysis (3)
distal end of bone
7
New cards
epiphyseal plate/line (6)
hyaline cartilage in middle of epiphysis where bone lengthening takes place, once lengthening ends leaves a line of compact bone
8
New cards
articular cartliage (5)
cartilage at end of bones
9
New cards
medullary cavity (9)
central cavity inside the diaphysis
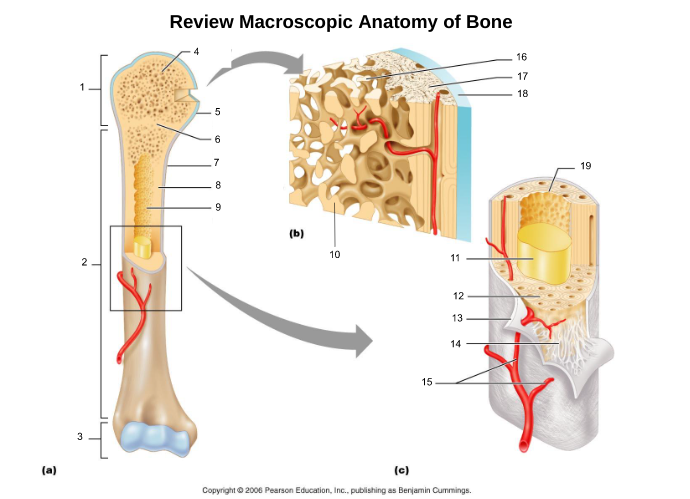
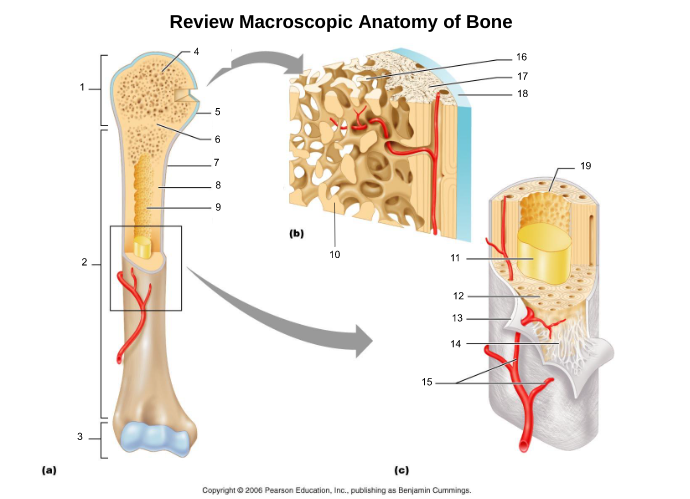
10
New cards
yellow bone marrow (11)
fat storage in medullary cavity of adults
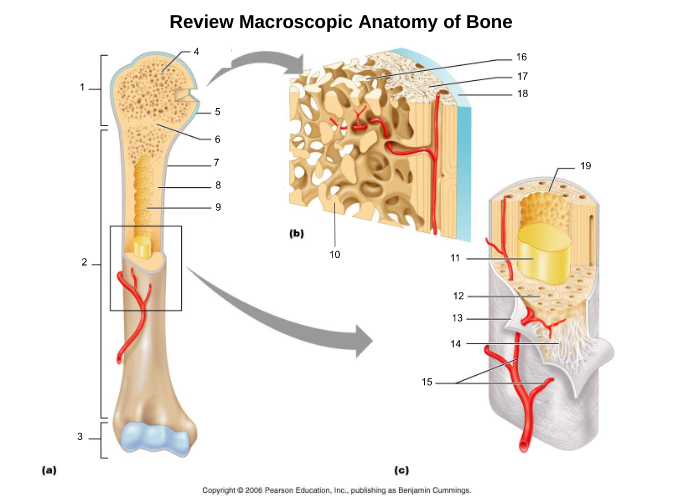
11
New cards
red bone marrow (9)
blood cell production in spongy bone and medullary cavity of children
12
New cards
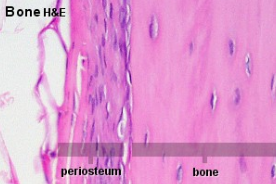
periosteum (7)
double layered membrane of connective tissue covering the outside of the bone that:
- Isolates the bone from surrounding tissues
- Contains blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves; enters bone through nutrient foramen
- Participates in bone growth and repair
- Connects tendons and ligaments to bones through the weaving of collagen fibers (Sharpey’s fibers) to outer fibrous layer (dense irregular) and then to the bone matrix
- Isolates the bone from surrounding tissues
- Contains blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves; enters bone through nutrient foramen
- Participates in bone growth and repair
- Connects tendons and ligaments to bones through the weaving of collagen fibers (Sharpey’s fibers) to outer fibrous layer (dense irregular) and then to the bone matrix
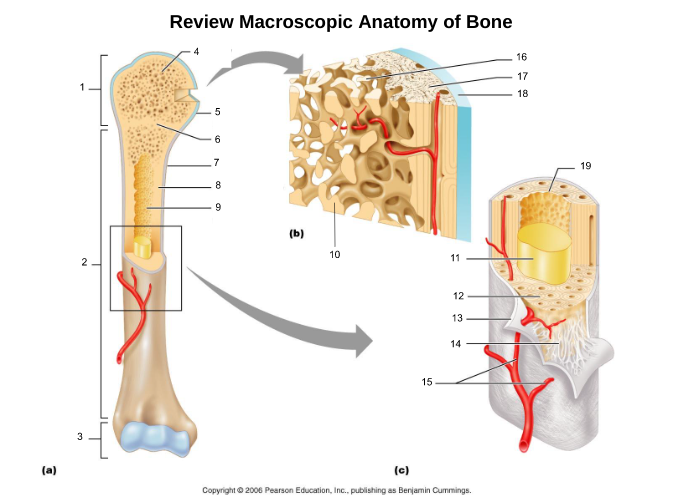
13
New cards
endosteum (19)
connective tissue cellular layer lining trabeculae of spongy bone, central canals, Volkmann’s canals, and the medullary cavity that aids in bone growth, repair, and remodeling; contains osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteoprogenitor cells.
14
New cards
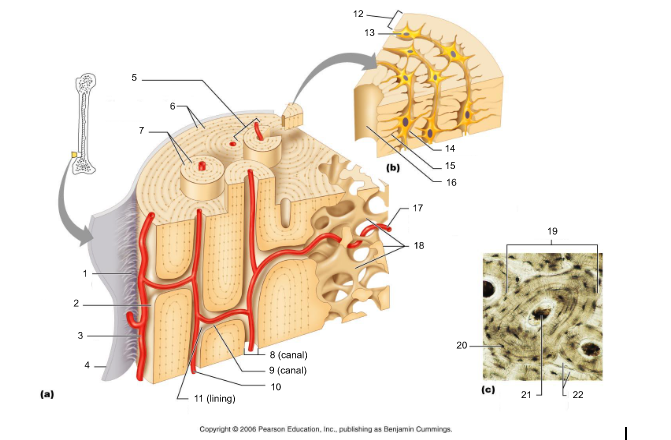
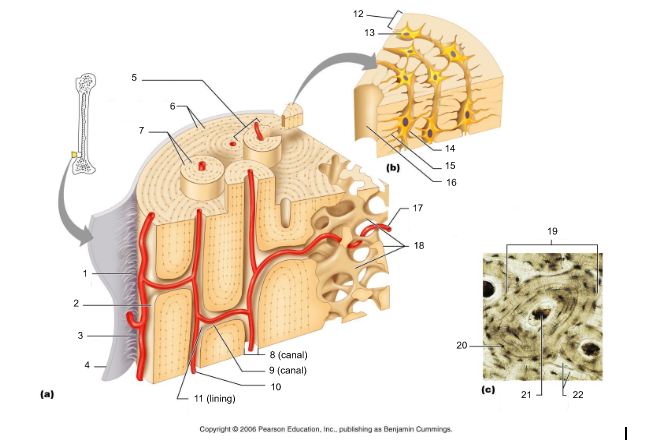
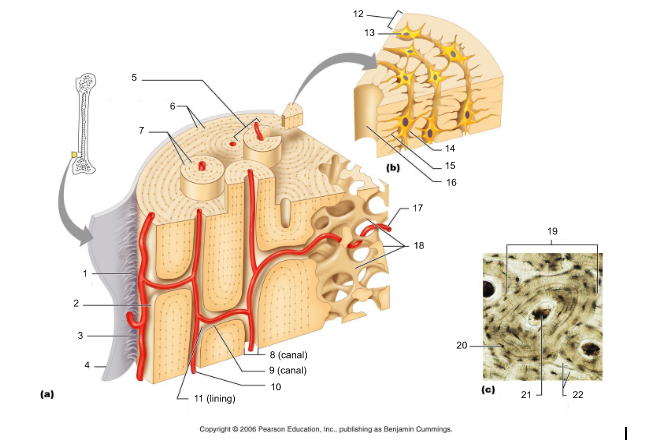
osteon (5, 19)
structural/functional unit of compact bone (cylinders or pillars tightly packed) composed of lamallae
15
New cards
central/Haversian canal (8, 16, 21)
tube in center of osteon that runs parallel with the surface of the bone and contains nerves and blood vessels to nourish bone cells
16
New cards
Volkmann's/perforating canal (9)
tubes that run perpendicular to the surface of the bone and contain blood vessels and nerves
17
New cards
lacuna (14)
cavities housing osteocytes that are sandwiched between lamellae, osteocytes can break down or build up extracellular matrix around them
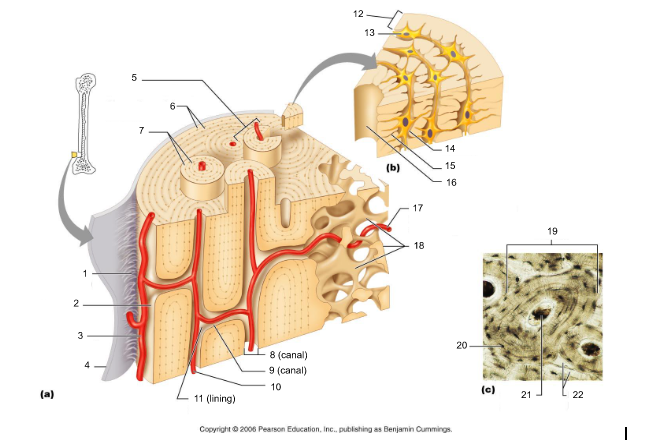
18
New cards
canaliculi (14, 20)
passageways between lacunae which permit the exchange of nutrients, gases, hormones, and wastes to pass between osteocytes (gap junctions) and ultimately to a central canal
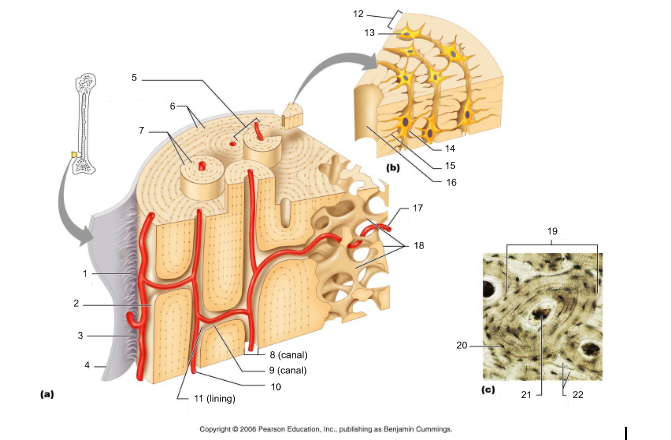
19
New cards
lamellae (cocentric) (7, 12)
hollow tubes made of inorganic hydroxyapatites around parallel collagen fibers. Collagen fibers of adjacent run in different directions to resist twisting
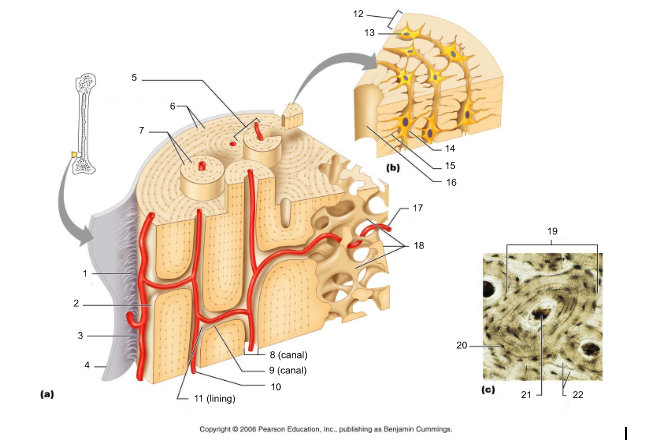
20
New cards
interstitial lamellae (22)
incomplete lamellae between osteons
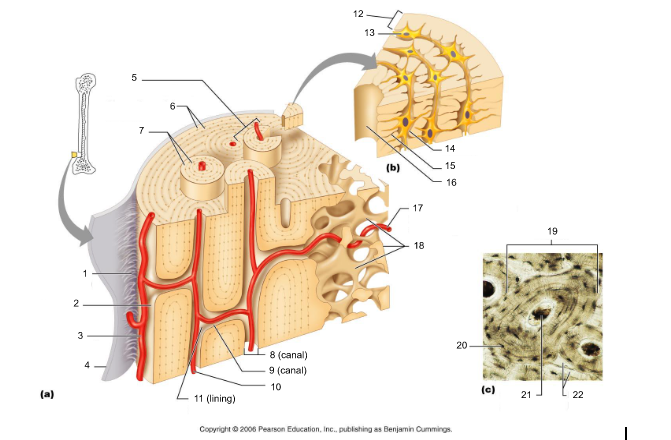
21
New cards
circumferential lamellae (6)
lamellae surrounding the entire outside of compact bone; under periosteum
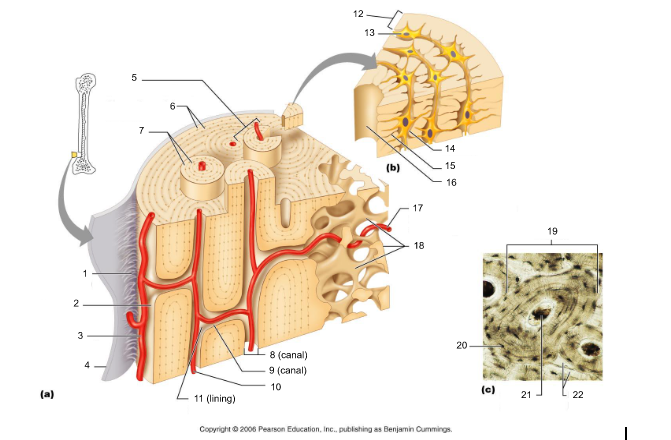
22
New cards
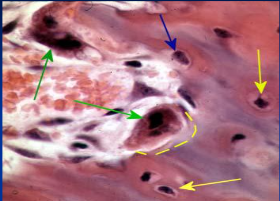
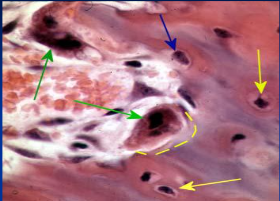
osteocytes (13) (yellow arrow)
mature bone cells within lacunae, maintain the protein and mineral content of surrounding matrix, when bone is damaged they are released from lacunae and convert to osteoblasts
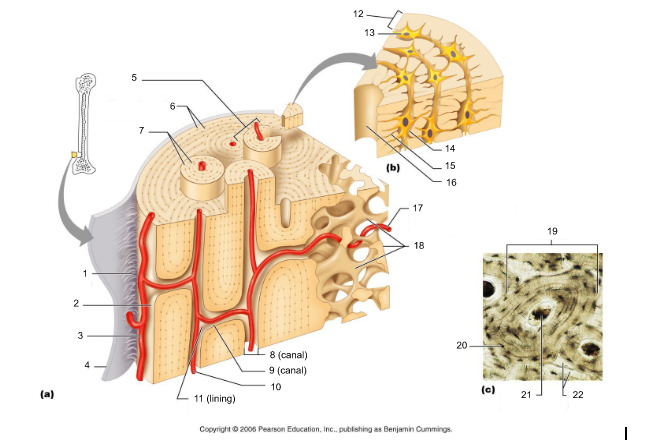
23
New cards
osteoblasts (blue arrow)
bone forming cells, produce osteoid and convert osteoid to bone by adding calcium salts to it; when trapped become osteocytes. Produce hormone Osteocalcin that plays a role in activating the fight-or-flight response by switching off the parasympathetic nervous system
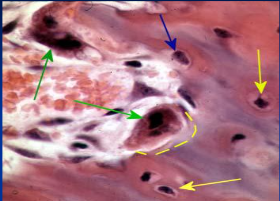
24
New cards
osteoprogenitor cells
stem cells which produce osteoblasts, located in periosteum and endosteum; become dormant in adult bone that is not growing or remodeling but provide nutrients to osteocytes via gap junctions
25
New cards
osteoclasts (green arrow)
giant multinucleated cells that break down and recycle bone matrix, located in periosteum and endosteum. Secretes lysosomal enzymes to digest organic matrix and dead osteocytes and hydrochloric acid to digest calcium salts
26
New cards
trabeculae (10)
plates that run in all directions forming branches with spaces between them. Made of lamellae that lack blood vessels, so nutrients diffuse between canaliculi that open onto the surface of trabeculae and blood vessels of the endosteum
27
New cards
Sharpey's fibers (14)
matrix of connective tissue consisting of bundles of strong collagenous fibers connecting periosteum to bone
28
New cards
long bone (a)
longer than wide (ex: humerous)
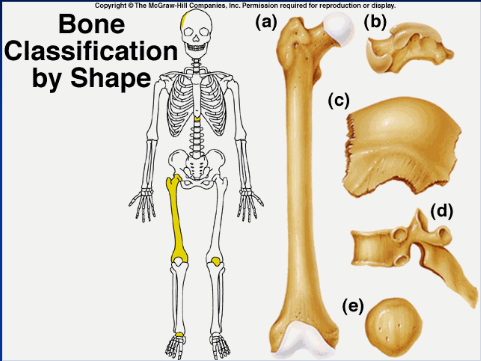
29
New cards
short bone (b)
more square shaped (ex: wrist or ankle bones)
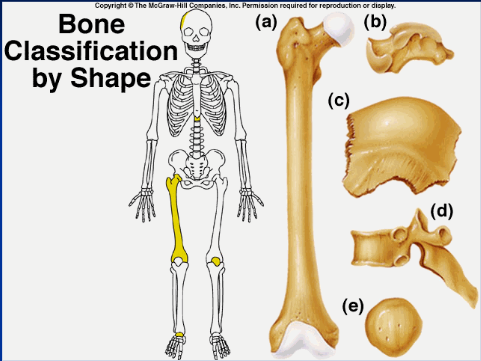
30
New cards
flat/sutural bone (c)
flatter bones (ex: ilium, skull)
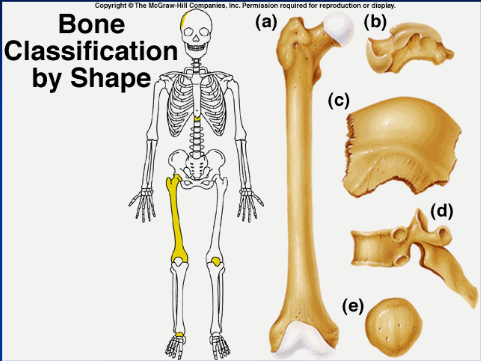
31
New cards
irregular bone (d)
weirdly shaped, doesn't fit into other classifications (ex: vertebrae, isonium)
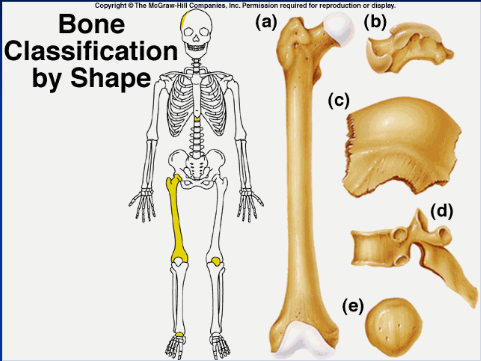
32
New cards
sesamoid bone (e)
upside down pyramid (ex: patella)
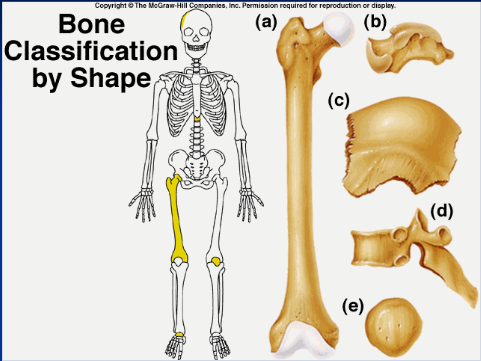
33
New cards
shape, location, formation
bones are classified by...
34
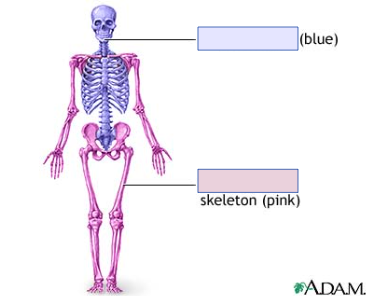
New cards
axial skeleton (blue)
longitudinal axis of body; skull, vertebrae, thoracic cage
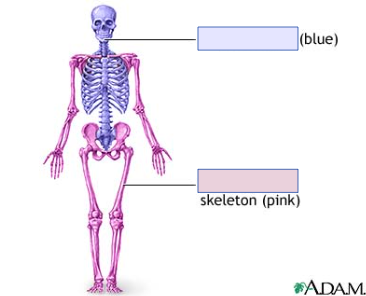
35
New cards
appendicular skeleton (pink)
bones of limbs and the girdles that connect them to the trunk
36
New cards
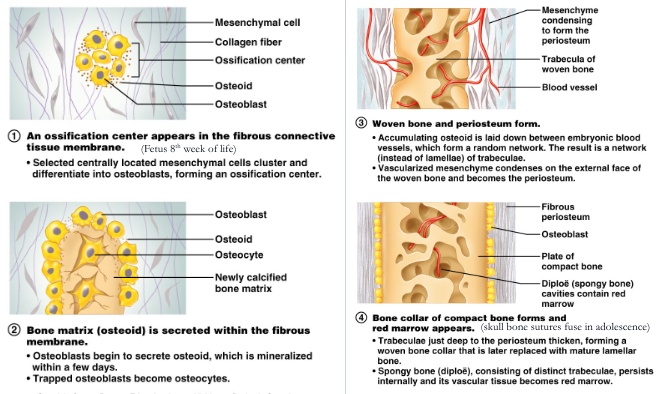
ossification
process of bone formation (osteogenesis)
37
New cards
calcification
deposition of calcium salts in cartilage, during ossification or in other tissues
38
New cards
intramembranous ossification
- forms flat bones: bones of skull, clavicles and the maxilla and mandible
- begins as sheet of fibrous connective tissue
- begins as sheet of fibrous connective tissue
39
New cards
fontanels
tough fibrous membrane where skull bones have not ossified (canvas). Fuse at 18 mo-2 yrs
40
New cards
endochondral ossification
- forms long, short, and irregular bones of the body below the base of the skull
- begins as pieces of hyaline cartilage
- begins as pieces of hyaline cartilage
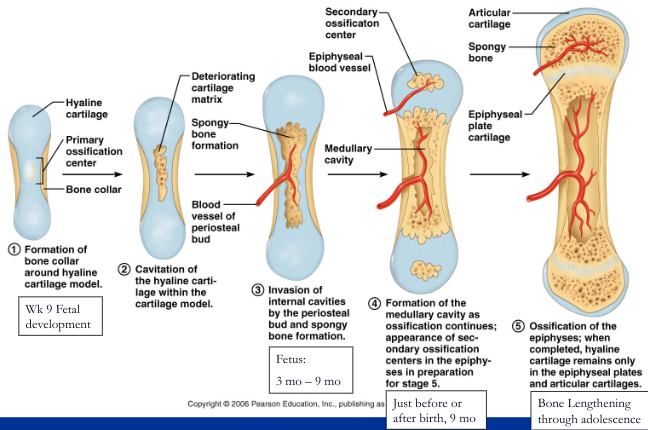
41
New cards
lengthening of bone at epiphyseal plate
- on the epiphysis side, chondroblasts divide adding new cartilage to lengthen bone
- on the diaphysis side, osteoblasts replace cartilage with spongy bone toward the epiphyseal side (both happen in the same direction which lengthens bone)
- osteoclasts digest spongy bone in the same direction as lengthening, forming a growing medullary cavity
- at puberty --> epiphyseal closure
- on the diaphysis side, osteoblasts replace cartilage with spongy bone toward the epiphyseal side (both happen in the same direction which lengthens bone)
- osteoclasts digest spongy bone in the same direction as lengthening, forming a growing medullary cavity
- at puberty --> epiphyseal closure
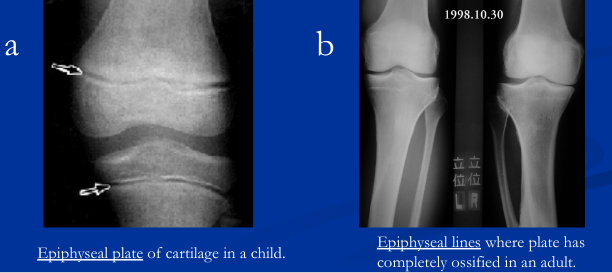
42
New cards
epiphyseal closure
Bone lengthening ends because at puberty, the sex, growth, and thyroid hormones stimulate osteoblasts to produce bone faster than the chondroblasts can make cartilage. Therefore, the epiphyseal plate gets thinner and thinner until it completely ossifies. The remnants of the epiphyseal plate can be seen as an ossified line called the epiphyseal line.
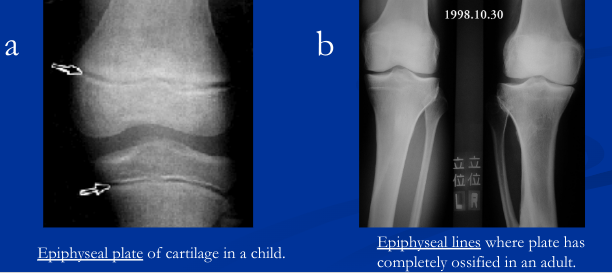
43
New cards
appositional growth
causes bones to grow larger in diameter (bones increase in diameter from birth through adulthood and can continue into adulthood when stressed by weight-bearing activities and muscle activity)
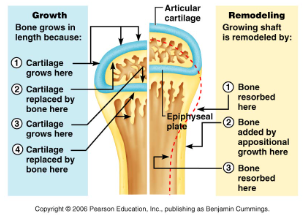
44
New cards
low levels of blood calcium
parathyroid gland secretes parathyroid hormone (PTH) which stimulates osteoclasts to break down bone, increasing blood calcium levels
45
New cards
high levels of blood calcium
thyroid gland secretes calcitonin which stimulates osteoblasts to take up calcium from blood and build up bone, lowering blood calcium levels
46
New cards
spongy bone
replaced every 3-4 years
47
New cards
compact bone
replaced every 10 years
48
New cards
after age 30, bone resorption outpaces bone deposition and bone density declines. A person could maximize peak bone density by regular weight-bearing activities and maintaining blood calcium levels (1000-1030 mg/day in adults)
at what age does bone density decline and what are things to do that maintain bone density?
49
New cards
joints
sites where two or more bones meet. Their two functions are securing bones together and allowing the skeleton to be mobile (consist of tendons, ligaments, and cartilage)
50
New cards
tendons
connect muscle to the bone
51
New cards
ligaments
connect bone to the bone
52
New cards
skeletal cartilage
consists of a perichondrium (membrane covering outside of cartilage made of dense irregular connective tissue; vascularized and cellular) and cartilage tissue (gel-like extracellular matrix with fibers and high water content, chondrocytes inside of lacunae, no nerves or blood vessels). The three types are hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage
53
New cards
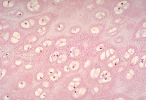
hyaline cartilage
Location: at ends of long bones, connect ribs to sternum, nose, larynx and trachea
Structure: circular chondrocytes in doublets and further apart with matrix filled with fine collagen fibers
Function: surface of bones glide with no friction, absorb, cushion
Structure: circular chondrocytes in doublets and further apart with matrix filled with fine collagen fibers
Function: surface of bones glide with no friction, absorb, cushion
54
New cards
elastic cartilage
Location: external ear, epiglottis, eustachian tubes
Structure: chondrocytes appear closer together and more elastic fibers than hyaline cartilage.
Function: make structure flexible
Structure: chondrocytes appear closer together and more elastic fibers than hyaline cartilage.
Function: make structure flexible
55
New cards
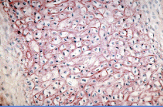
fibrocartilage
Location: Intervertebral discs, symphysis pubis, menisci of the knee
Structure: parallel rows of chondrocytes appear farther apart and in between is extracellular matrix filled with thick collagen fibers.
Function: withstand heavy pressure, compression, shock absorption
Structure: parallel rows of chondrocytes appear farther apart and in between is extracellular matrix filled with thick collagen fibers.
Function: withstand heavy pressure, compression, shock absorption
56
New cards
appositional growth
growing from the outside, chondroblasts in perichondrium secrete new matrix onto existing cartilage
57
New cards
interstitial growth
growing from the middle, chondrocytes in lacunae divide and secrete new matrix to expand cartilage from within
58
New cards
nose and ears
two locations cartilage continues to grow throughout lifetime
59
New cards
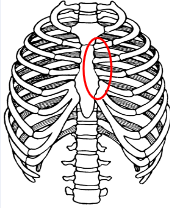
synarthroses or immovable joints
No active movement between bones
Bones secured together with fibrous connective tissue or cartilage
Ex. Sutures, Vertebrosternal ribs and sternum
Bones secured together with fibrous connective tissue or cartilage
Ex. Sutures, Vertebrosternal ribs and sternum
60
New cards
amphiarthroses or slightly movable joints
Limited amount of movement, designed for strength and flexibility
Bones joined by fibrocartilage discs or by ligaments
Ex. Intervertebral joints, Pubic symphysis, Sacroiliac joint, Interosseous membrane along radius and ulna
Bones joined by fibrocartilage discs or by ligaments
Ex. Intervertebral joints, Pubic symphysis, Sacroiliac joint, Interosseous membrane along radius and ulna
61
New cards
diarthroses or freely movable joints
Varying ranges of movement possible
Bones joined by fibrous articular capsule and ligaments with joint capsule in between
Ex: predominate in limbs, ends of long bones
Bones joined by fibrous articular capsule and ligaments with joint capsule in between
Ex: predominate in limbs, ends of long bones
62
New cards
synarthrotic joint
63
New cards
amphiarthrotic joint
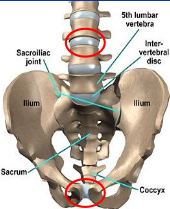
64
New cards
diarthrotic joint
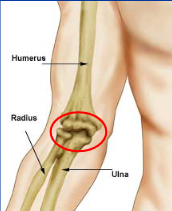
65
New cards
fibrous joints
bones joined by fibrous tissue (dense fibrous connective or ligaments), no joint cavity, immovable to slightly movable
66
New cards
sutures
fibrous joint: between skull bones; short dense fibrous connective tissue (later synostoses)

67
New cards
syndesmoses
fibrous joint: between tibia and fibula, radius & ulna; connected by long ligaments
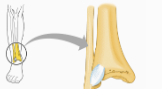
68
New cards
gomphoses
fibrous joint: connect teeth to sockets in jaw bones; connected by periodontal ligament
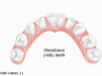
69
New cards
cartiliginous joints
bones joined by cartilage (hyaline and fibrocartilage), no joint cavity, immovable to slightly movable
70
New cards
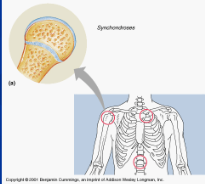
synchondroses
cartiliginous joint: epiphyseal plates, between first rib and sternum; plate of hyaline cartilage between bones (immovable)
71
New cards
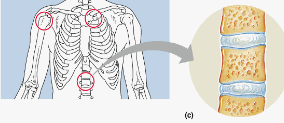
symphyses
cartiliginous joint: pubic symphysis, intervertebral discs; hyaline cartilage on ends of bones connected to fibrocartilage in the middle. (slightly movable)
72
New cards
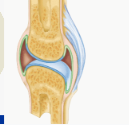
synovial joints
bones separated by a joint cavity and are freely movable; joints of the limbs
73
New cards
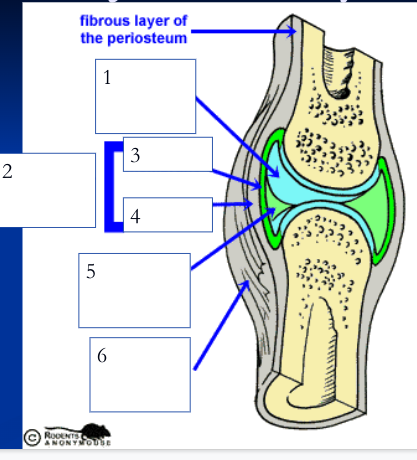
articular cartilage (1)
smooth hyaline cartilage covering ends of opposing bone surfaces of synovial joint
74
New cards
joint cavity (5)
space between bones filled with synovial fluid
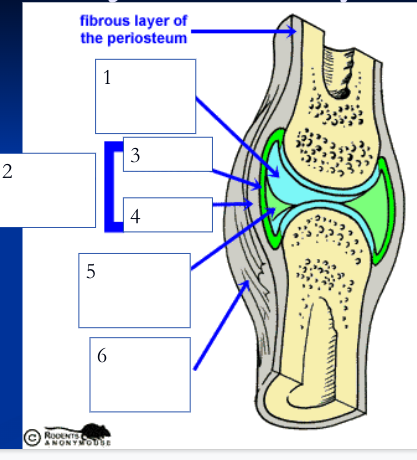
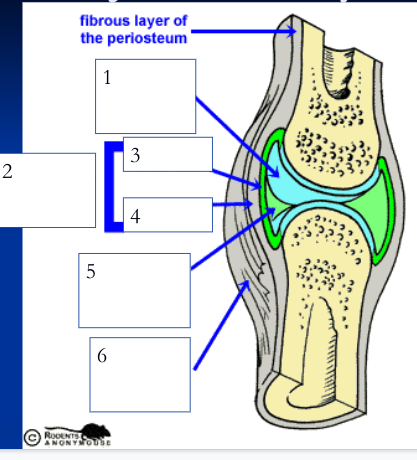
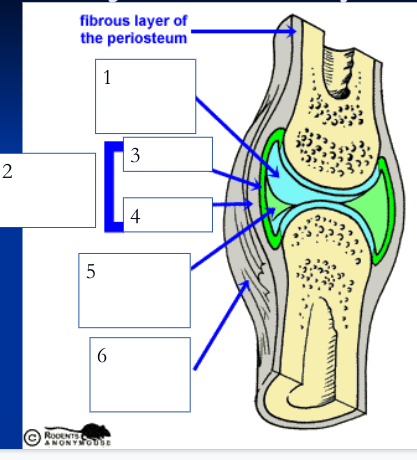
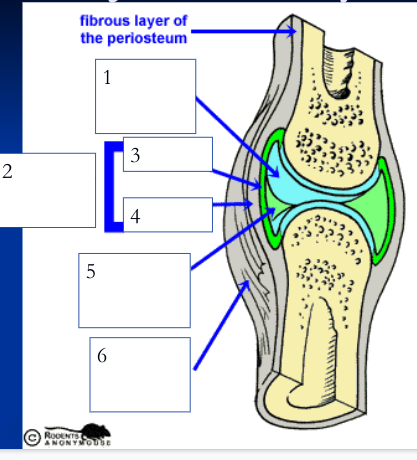
75
New cards
joint/articular capsule (2)
double layered capsule enclosing and connecting bones, composed of fibrous capsule and synovial membrane
76
New cards
fibrous capsule (4)
outer tough articular capsule (dense irregular connective tissue) that connects to periostea of bones, strengthens joint
77
New cards
synovial membrane (3)
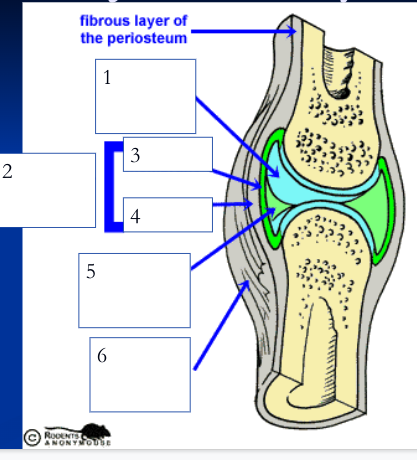
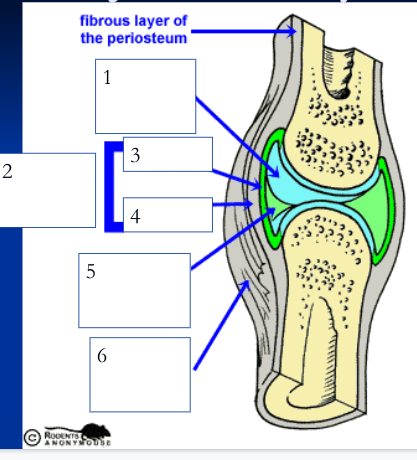
inner layer of articular capsule (loose areolar connective tissue) that lines the fibrous capsule internally and covers all internal joint surfaces that are not hyaline cartilage; secretes synovial fluid
78
New cards
synovial fluid (5)
viscous fluid with consistency of egg white that fills the joint cavity and inside of articular cartilage, less viscous when joint warms. Functions: lubrication, nutrient distribution, shock absorption, and contains macrophages to help digest microbes or cellular debris. Inside articular cartilage to aid in bearing pressure and nourish cartilage.
79
New cards
reinforcing ligaments (6)
(dense regular) strengthens joints, are either thickened parts of fibrous capsule or are independent structures; many nerves here and in the articular capsule sense position (proprioceptors)
80
New cards
menisci or articular discs
accessory structure found in some synovial joints: disc or wedge of fibrocartilage that subdivides the synovial cavity and is used for shock absorption and making the joint more stable (knee, jaw, sternoclavicular joints)
81
New cards
bursae
accessory structure found in some synovial joints: fluid filled sacs located between skin and bones that aid in movement of tendons, ligaments, muscle, or skin passing over bones; reduces friction and acts as shock absorbers.
82
New cards
tendon sheaths
accessory structure found in some synovial joints: bursae wrapped around a tendon that is subjected to friction when it crosses bony surfaces (shoulder joint)
83
New cards
fat pads
accessory structure found in some synovial joints: cushioning adipose pads located superficial to the joint cavity or between the fibrous capsule and the synovial membrane; which protect and act as packing material (hips and knees)
84
New cards
first factor that influences joint stability
Shape of articular surfaces
- Joints are more stable when two bone surfaces fit snugly into one another (hip)
- Joints are not stable when sockets are shallow or two bones do not fit together.
- Joints are more stable when two bone surfaces fit snugly into one another (hip)
- Joints are not stable when sockets are shallow or two bones do not fit together.
85
New cards
Number and positioning of ligaments
- The more ligaments the stronger the joint.
- Ligaments can only stretch 6% of their length before they break
- A joint is not stable when the main method of reinforcement is ligaments
- The more ligaments the stronger the joint.
- Ligaments can only stretch 6% of their length before they break
- A joint is not stable when the main method of reinforcement is ligaments
86
New cards
third factor that influences joint stability
Muscle tone
- Joints are stable when there is good muscle tone that allows the muscle tendons crossing the joint to be taught; most important factor in most joints (shoulder, knee, arches of foot)
- There are many sensory nerves around the articular capsule and ligaments, which quickly send signals to the muscles to regulate muscle tone (proprioceptors).
- Joints are stable when there is good muscle tone that allows the muscle tendons crossing the joint to be taught; most important factor in most joints (shoulder, knee, arches of foot)
- There are many sensory nerves around the articular capsule and ligaments, which quickly send signals to the muscles to regulate muscle tone (proprioceptors).
87
New cards
Shoulder joint because the bones fit more snugly together
is a shoulder joint or knee joint more stable?
88
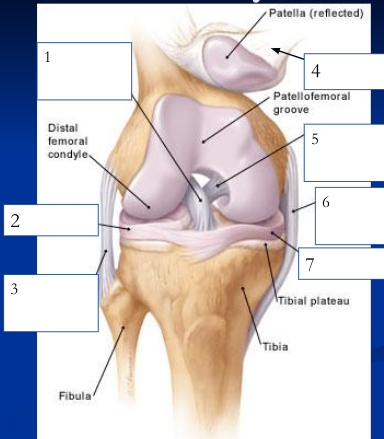
New cards
anterior cruciate ligament
1
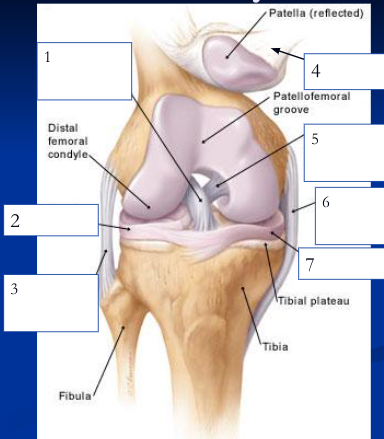
89
New cards
lateral meniscus
2
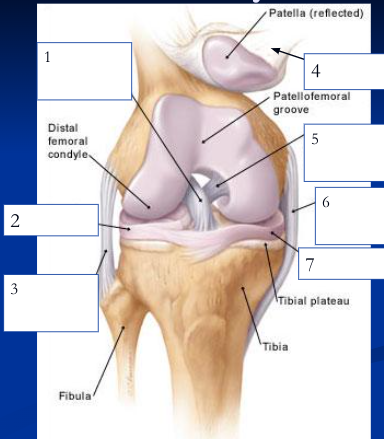
90
New cards
fibular collateral ligament
3
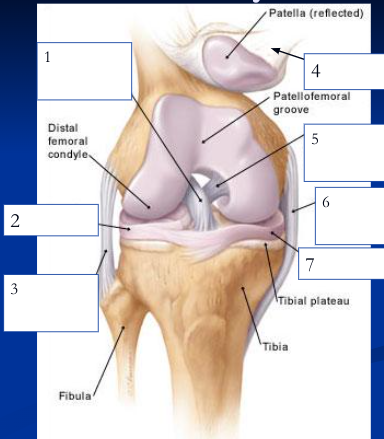
91
New cards
patellar ligament
4
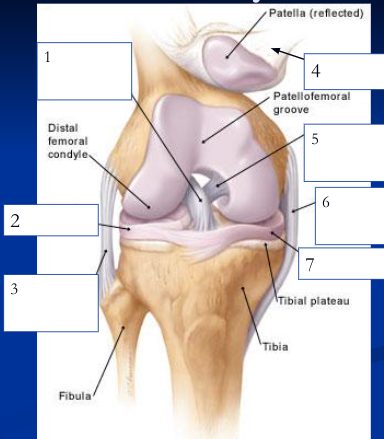
92
New cards
posterior cruciate ligament
5
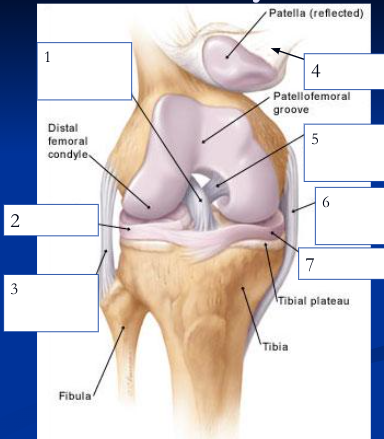
93
New cards
medial/tibial collateral ligament
6
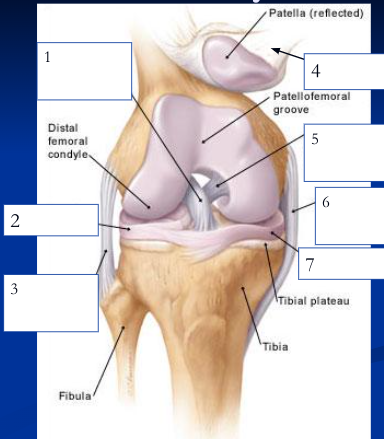
94
New cards
medial meniscus
7
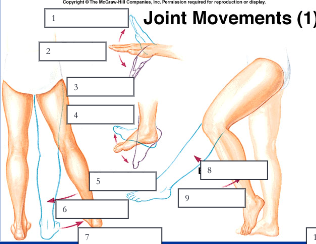
95
New cards
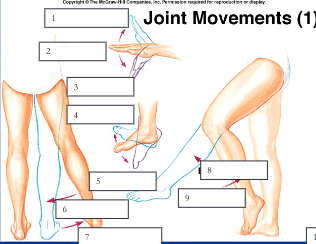
hyperextension, extension, flexion
1, 2, 3
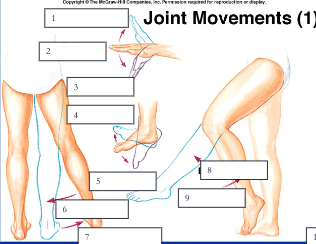
96
New cards
dorisflexion, plantar flexion
4, 5
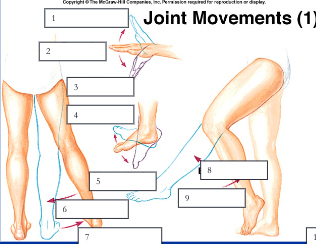
97
New cards
adduction, abduction
6, 7
98
New cards
extension, flexion
8, 9
99
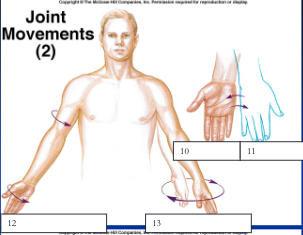
New cards
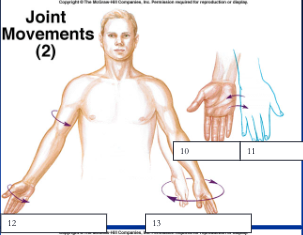
rotation, circumduction
12, 13
100
New cards
supination, pronation
10, 11