A LEVEL BIOLOGY (year 2)
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is a gene
A sequence of bases on a DNA molecule for protein ( polypeptide)which results in a characteristic
What is an allele
Version of a gene
What is codominance
Both alleles are expressed in the phenotype when present
What is dihybrid inheritance
Patterns of inheritance of 2 different genes on a different pair of autosomes
What are autosomes
Normal non sex chromosome pair
Ratio of dihybrid inheritance for two heterozygous individuals
9:3:3:1
What is autosomal linkage
The loci of two different genes are on the same pair of autosomes so are extremely likely to be inherited together unless crossing over occurs
What is the hardy - Weinberg principle (equations)
P+q=1
P2 + 2pm + q2 = 1
What is a gene pool
All alleles of all genes within a population
What does the hardy - Weinberg principle predict
Frequency of specific alleles within each population gene pool
According to the Hardy-Weinberg principle the frequency of alleles will remain constant from one generation to the next provided…
No mutations occur
All individual are likely to pass on their alleles
Mating is random
No immigration/emigration/migration
No selection of alleles
Population is large
What is a sex linked gene
Only present on X (or Y) chromosome
What is epistasis
The interaction between two non linked genes which causes one gene to mask the expression of the other n the phenotype
What is evolution
The gradual change in a species over time (changes to the allele frequency in the gene pool )
What is speciation
When enough difference is accumulated that members of a population are no longer able to breed with the original population / species
What causes the production of new alleles
Mutations
What causes genetic variation between individuals
Meiosis + random fertilisation
Stages of evolution and speciation
Isolation
Variation caused by mutations
Different selection pressures
Breed and pass on advantageous alleles
Allele increases in frequency
Speciation
What are the three types of selection
Directional
Stabilising
Disruptive
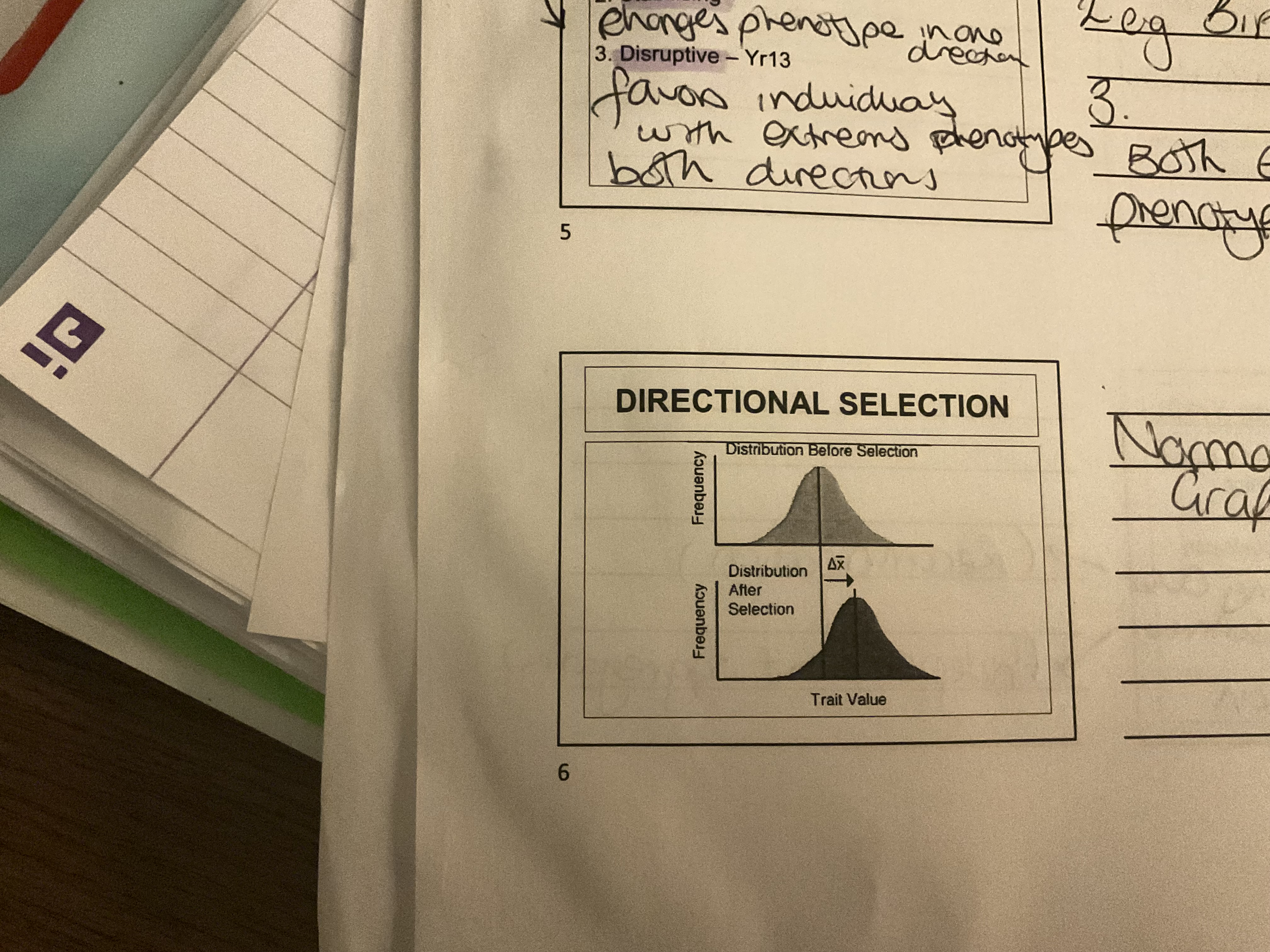
What is directional selection
Selection for 1 extreme phenotype e.g giraffe neck length
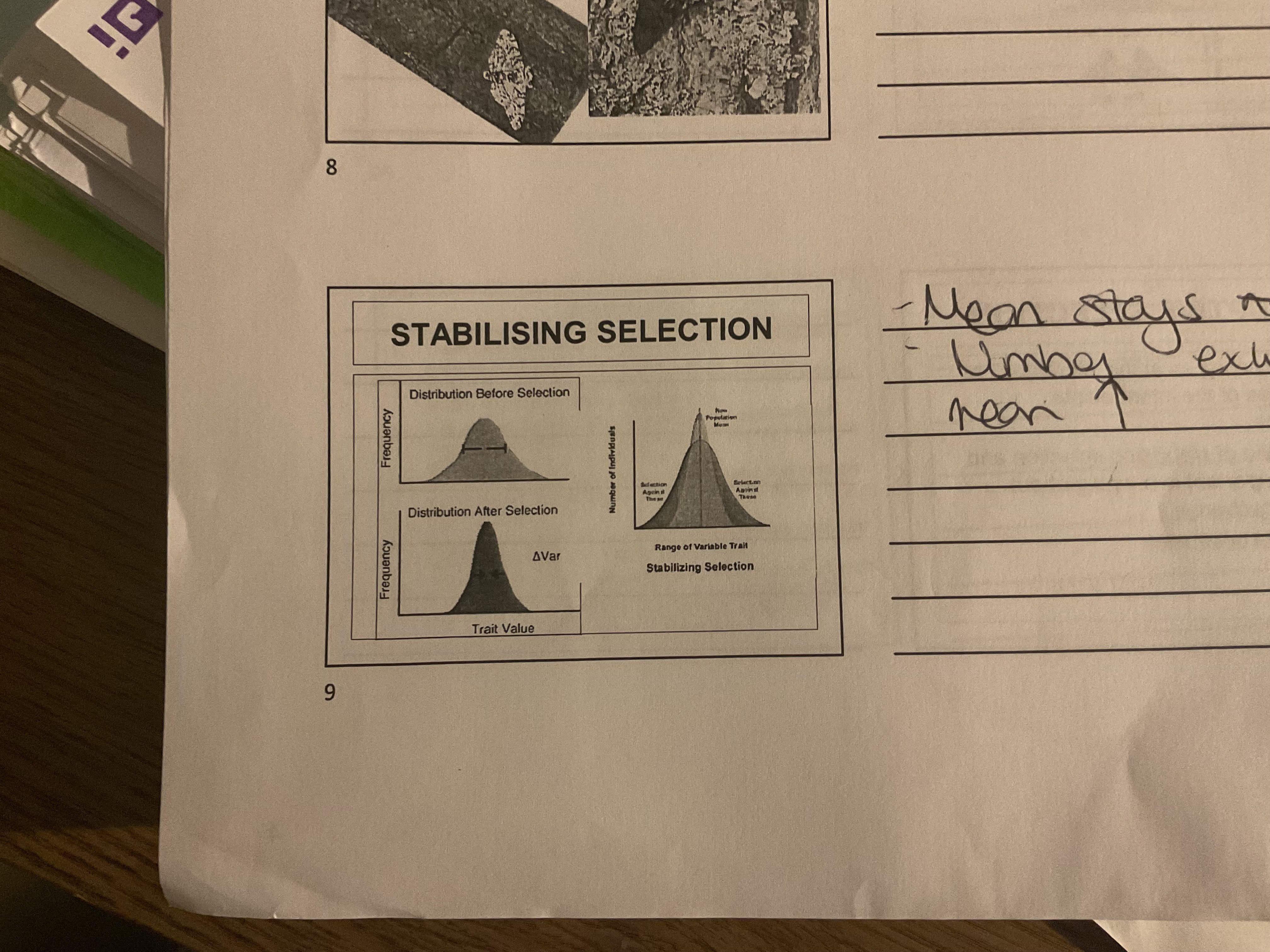
What is stabalising selection
Average phenotype is preserved eg birth weight
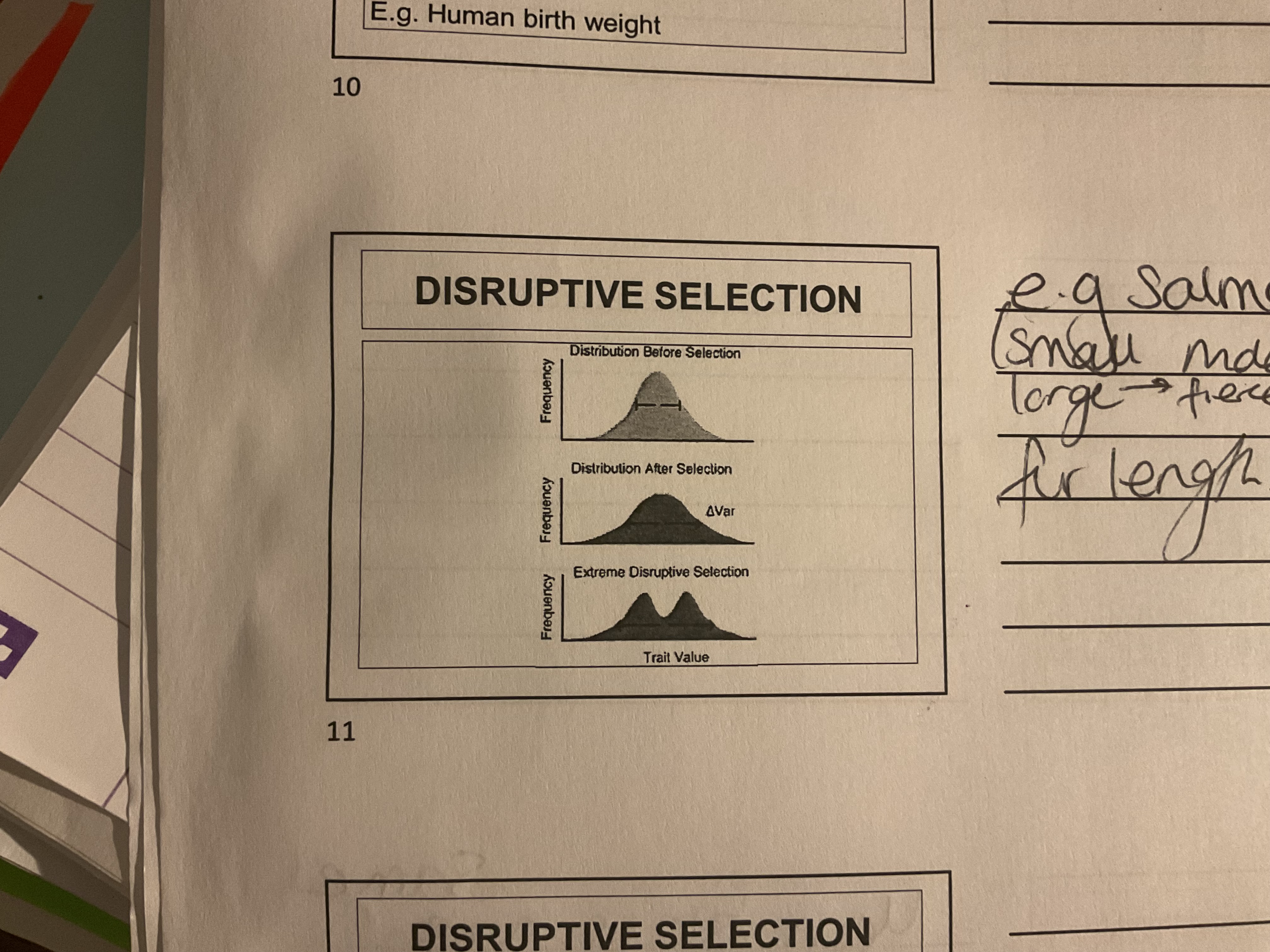
What is disruptive selection
Favours individuals with extreme phenotypes in both directions as both extremes confer to an advantage
Directional selection graph
Shifts left or right
Stabilising selection graph
Narrows
Disruptive selection graph
Splits in two
Two types of speciation
Allopatric and sympatric
What is allopatric speciation
Geographical physical barrier
What is sympatric speciation
Same area however reproductively isolated e.g different mating times
Types of sympatric speciation
Ecological
Temporal
Behavioral
Mechanical
Gametic
Hybrid
Why does anaerobic respiration produce far less ATP than aerobic respiration?
Anaerobic respiration relies on substrate level phosphorylation in the glycolytic pathway to produce a net 2 ATP per glucose.
Aerobic respiration produces 2 ATP from substrate-level phosphorylation in glycolysis, 2 ATP from substrate-level phosphorylation in the Krebs cycle and around 32 ATP from oxidative phosphorylation.