JMU BIO 103 Final Exam - McMullen
1/223
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
224 Terms
What are the 5 characteristics of protists?
1. they are eukaryotic
2. they are either a unicellular or multicellular species
3. they are either a nonmotile or motile species
4. they are either aquatic or terrestrial species
5. they are either autotrophic (photosynthetic) or heterotrophic (non-photosynthetic)
What is a protist?
a protist is a eukaryote that is not a plant, fungus, or animal
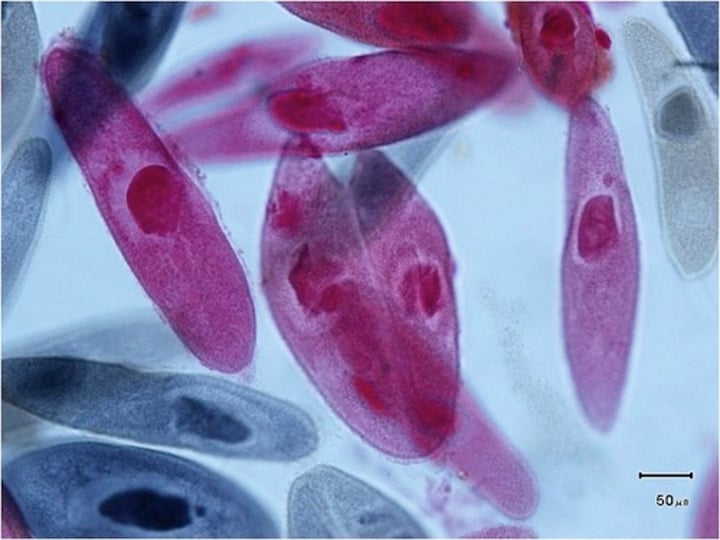
What does a paramecium look like?
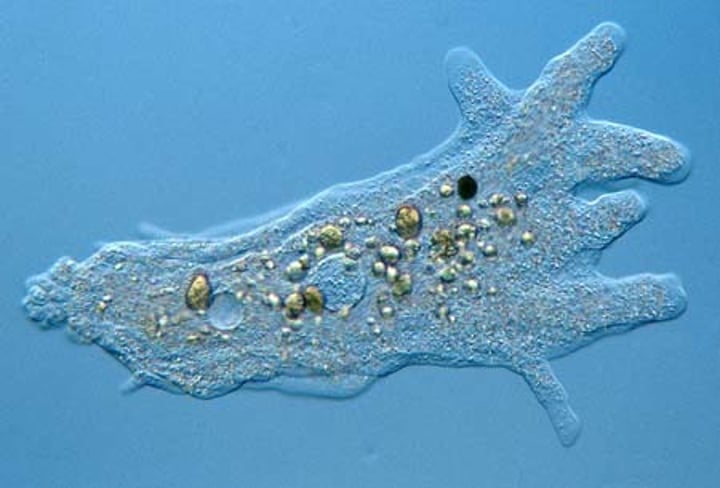
What does a amoeba look like?
What does a slime mold look like?
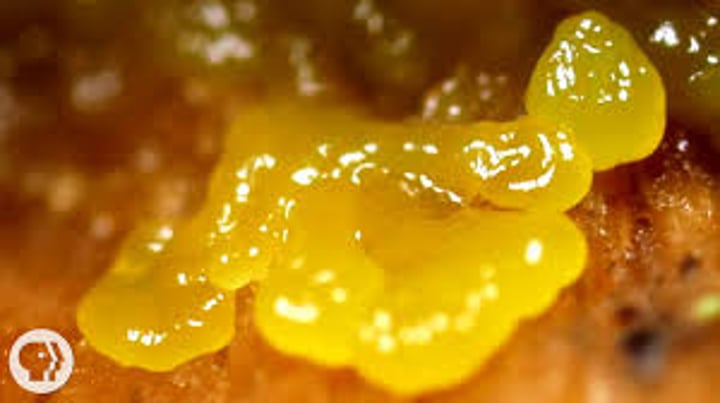

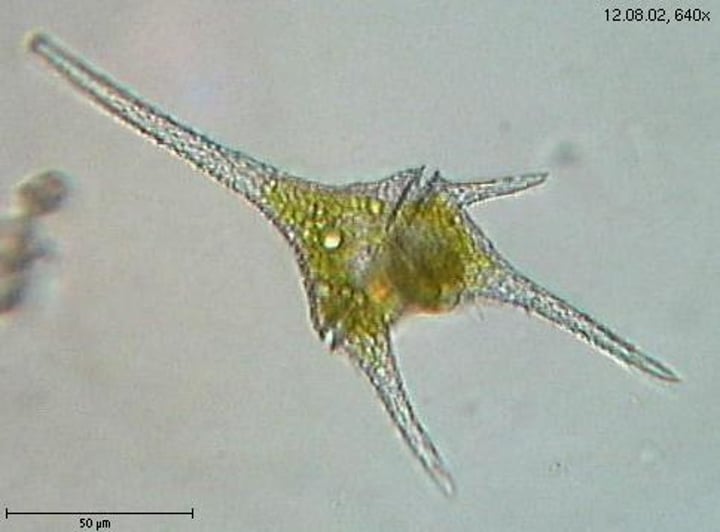
What does a euglena look like?
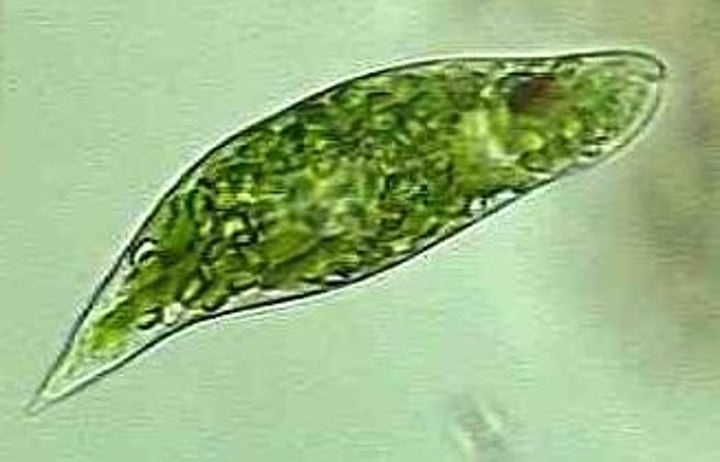

What do dinoflagellates look like?
What does brown algae look like?
ex. kelp
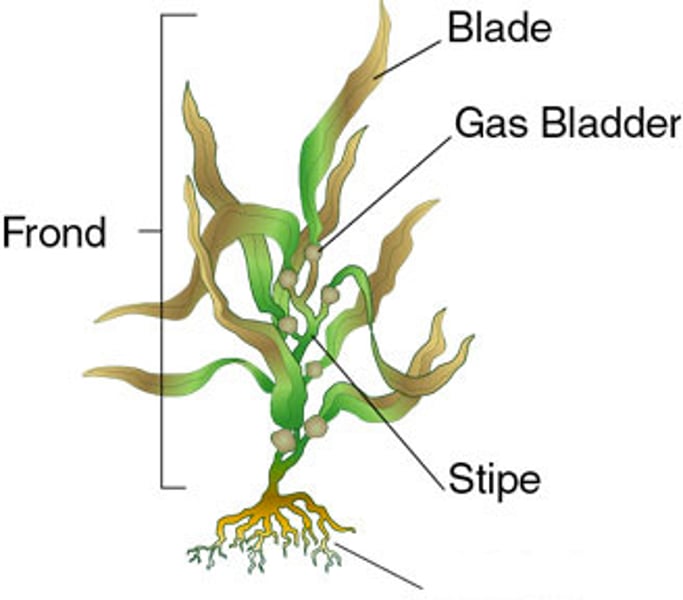
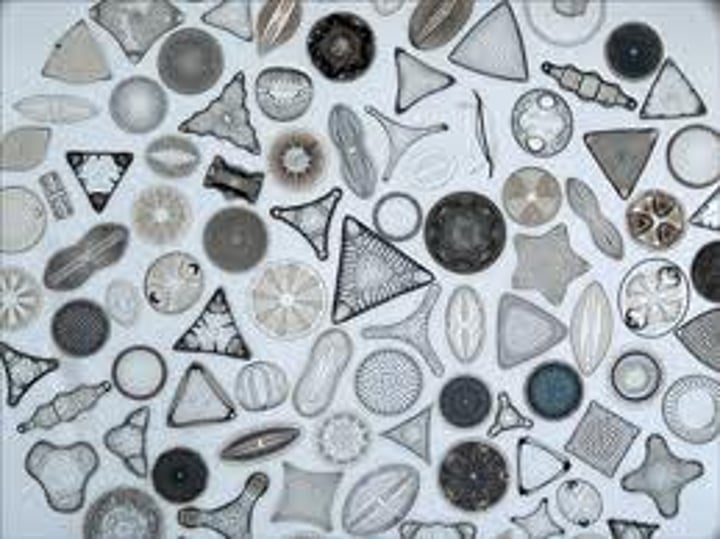
What do diatoms look like?

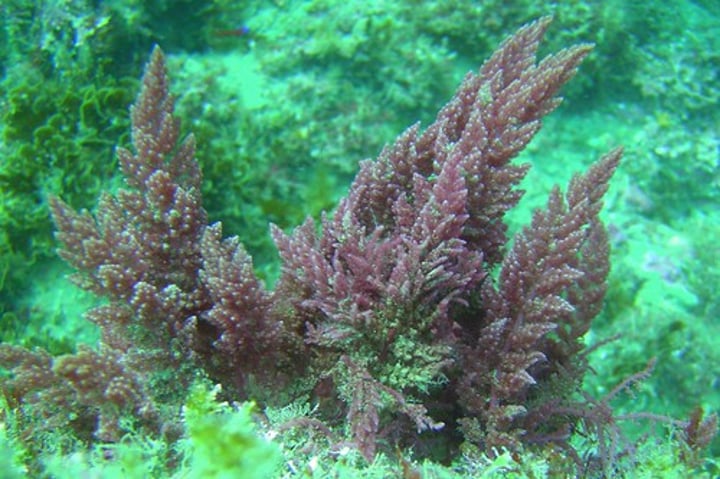
What does red algae look like?

Do protists have any unique synapomorphies that distinguish them from other eukaryotes?
no
Are protists a monophyletic group?
no, they contain a common ancestor and some, but not all descendants
What group are protists from?
they are from paraphyletic groups which means they have ancestors from all over
What is the ecological importance of protists?
marine photosynthetic protists help with carbon fixation
Define carbon fixation
this is when living things turn carbon dioxide in the atmosphere into food for themselves
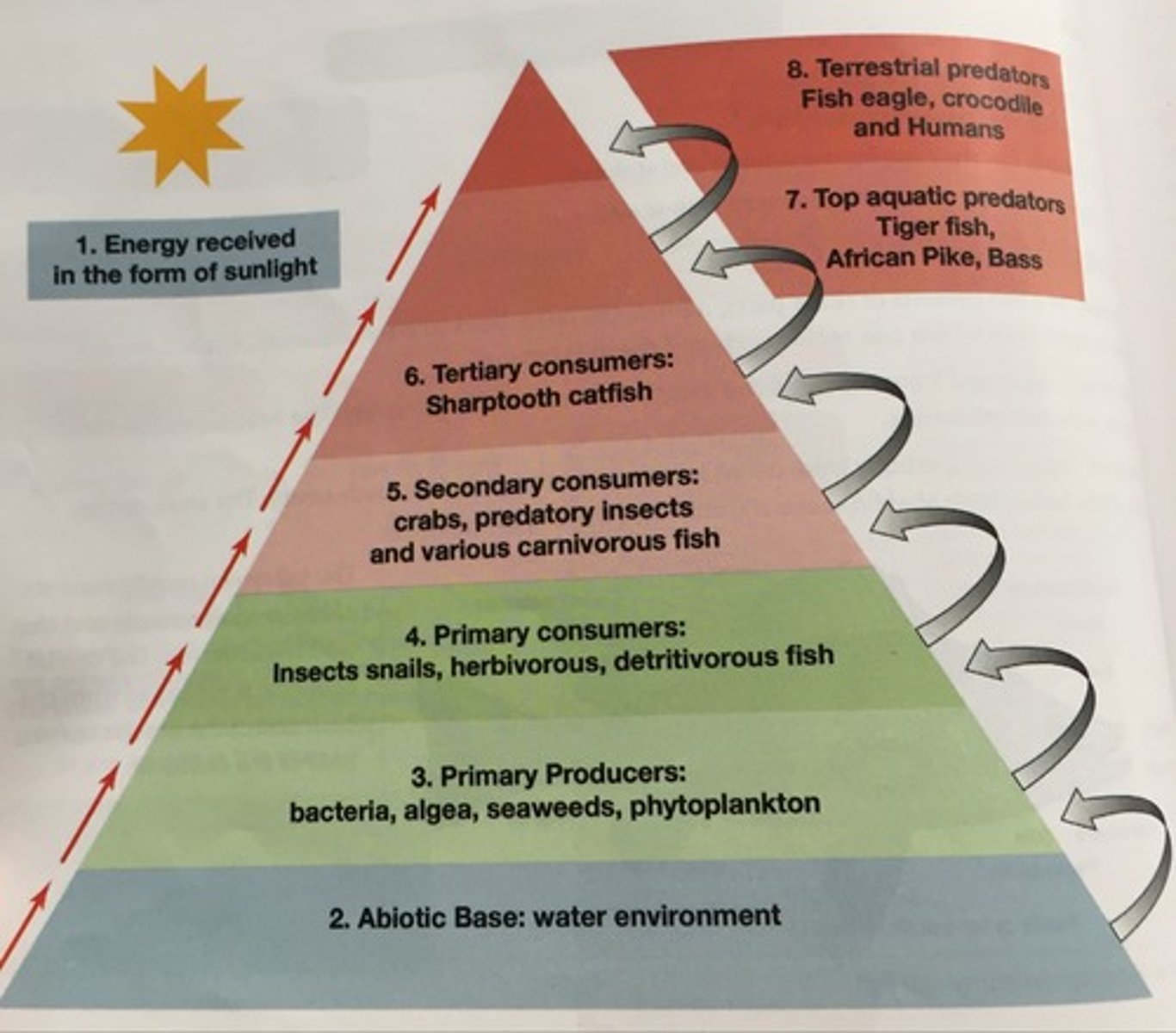
Diagram of the aquatic food pyramid
1. humans (top)
2. big fish
3. crustaceans
4. grazing protists
5. photosynthetic protists (bottom)
What does plasmopara viticola cause?
it causes downy mildew of grapes
Describe the beginning of downy mildew of grapes
in the 1870s, it was accidentally introduced to France and nearly destroyed the grape and wine industries. A professor from the University of Bordeaux noted that leaves with copper sulfate and lime were healthy and not infected
Define a foliar fungicide
it is a chemical that can be used to kill fungi. The first foliar fungicide was used to control the downy mildew of grapes in France
Does plasmopara viticola make leaves more or less photosynthetic?
less photosynthetic
What foods does the disease phytophthora affect?
it causes diseases in avocados, onions, tomatoes, strawberries, apples, and many other plants.
What is the most famous member of the phytophthora disease?
phytophthora infestans
What does phytophthora infestans affect?
it is a disease to potatoes. This caused a potato famine in Ireland from 1846-1847. Approximately 800,000 people starved to death and many more emigrated (about 1.2 million) to other countries
What is another name for this potato disease?
a potato blight
How many pounds of potatoes did Irish adults used to eat per day?
9-13 pounds
Describe reproduction in protists
single-celled protists use simple cell division (mitosis) as a means of asexual reproduction
ex. euglena and paramecium
What are thought to be the first organisms to have sexually reproduced?
single-celled protists
Do most protists have a haploid or diploid dominant life cycle?
haploid dominant life cycle; but some do have a diploid dominant life cycle, while others exhibit an alternation of haploid and diploid multicellular generations
In protists that have a haploid dominant life cycle, what is the only diploid cell that is produced?
the zygote
What is this type of meiosis called?
zygotic meiosis
In protists that have a diploid dominant life cycle, what is the only haploid cell that is produced?
gametes
What is this type of meiosis called?
gametic meiosis
What type of meiosis do humans have?
gametic meiosis
What type of meiosis do protists have with an alternation of generations?
sporic meiosis
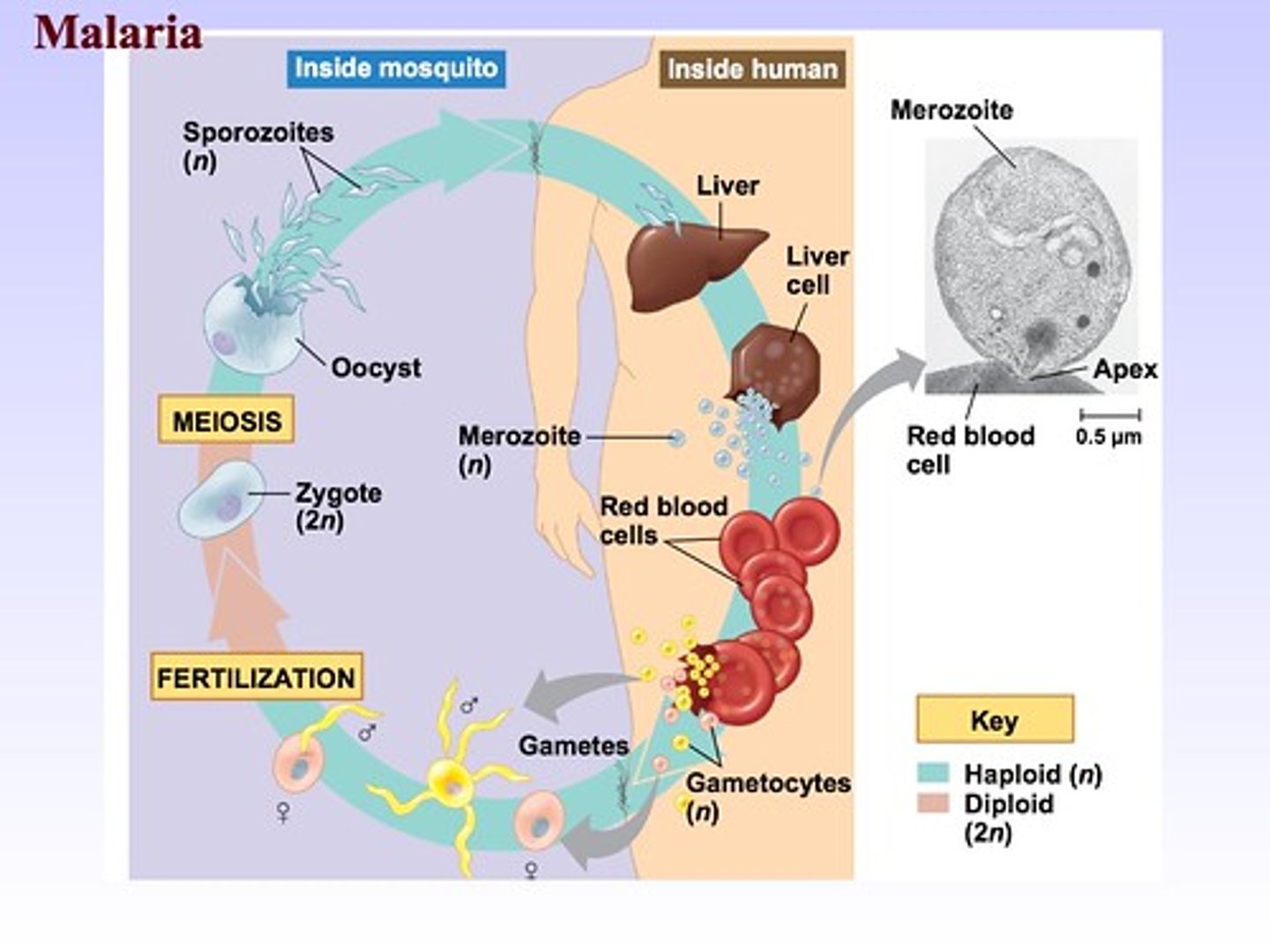
Diagram of a haploid dominant protist
ex. plasmodium - malaria
Define isogamy
these are identical gametes, both in looks and size
Define anisogamy
these are gametes that are different in appearance and size
Define oogamy
sexual reproduction involving a small motile male gamete and a large much less motile female gamete
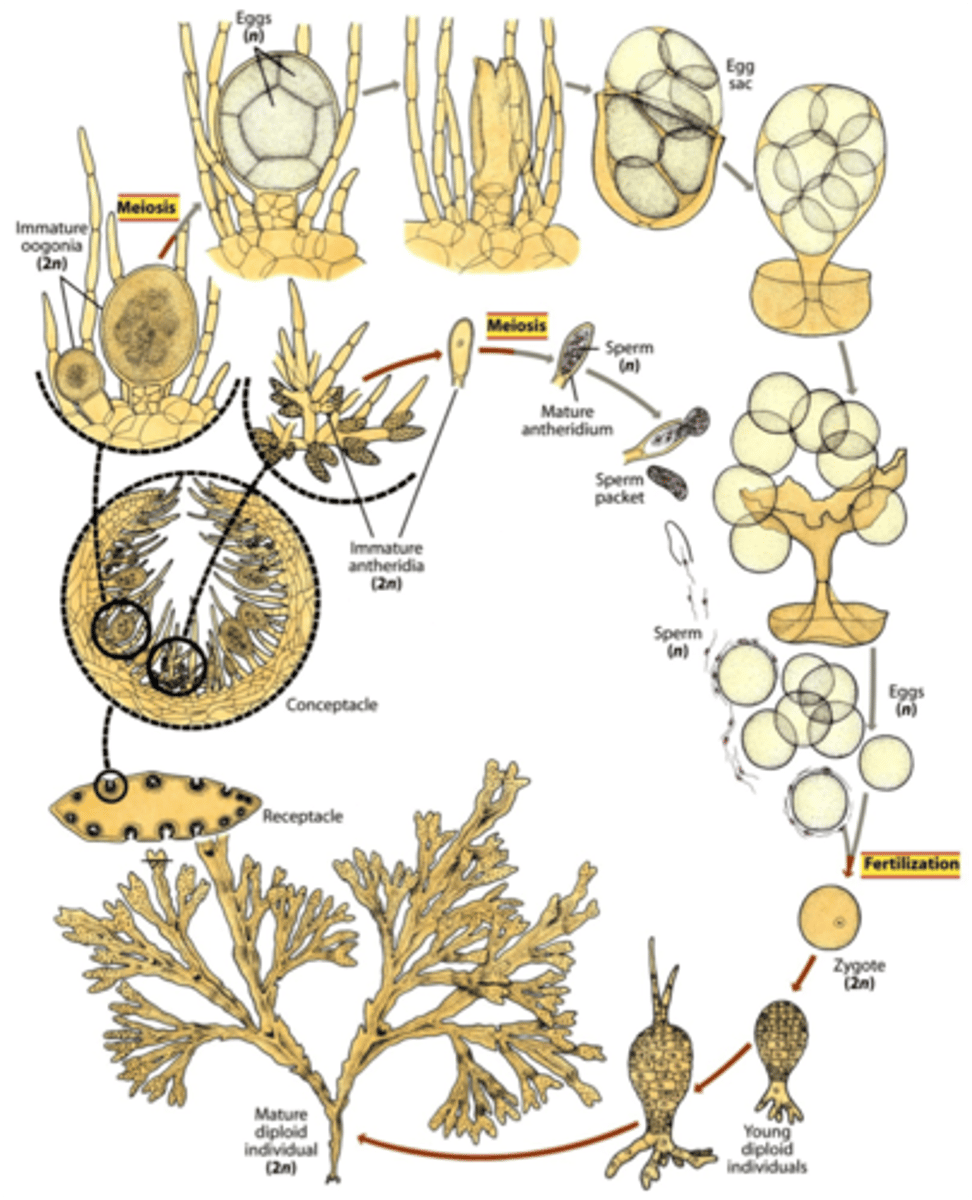
Diagram of a diploid dominant protist
ex. fucus - brown alga
What type of meiosis does brown alga have?
gametic meiosis
What is oogonia?
it is the brown alga gametangia
What is oogamy?
this refers to the sperm and egg
Diagram of an alternation of generations
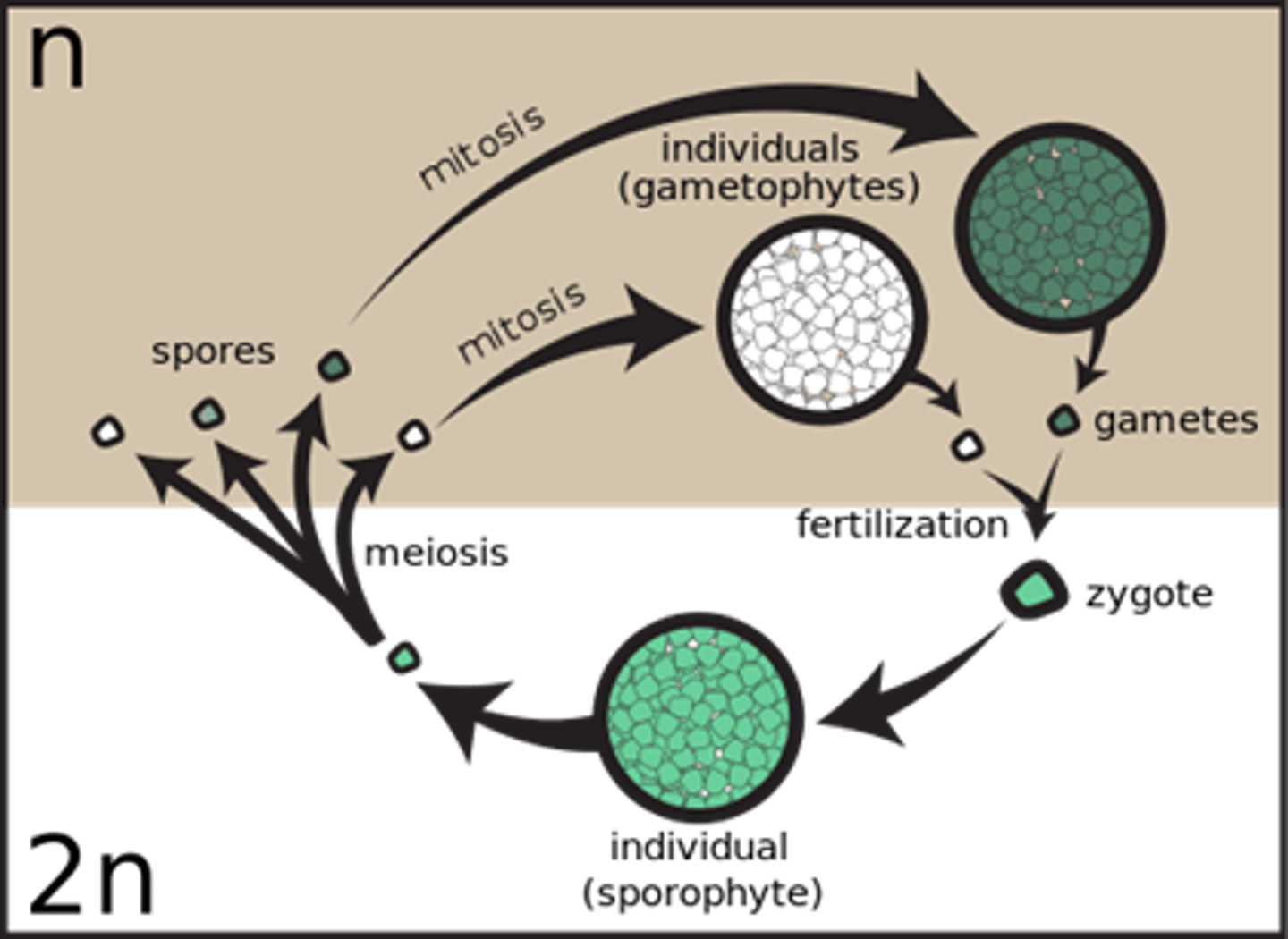
Diagram of the life cycle laminaria (brown alga)
it has alternation of generations
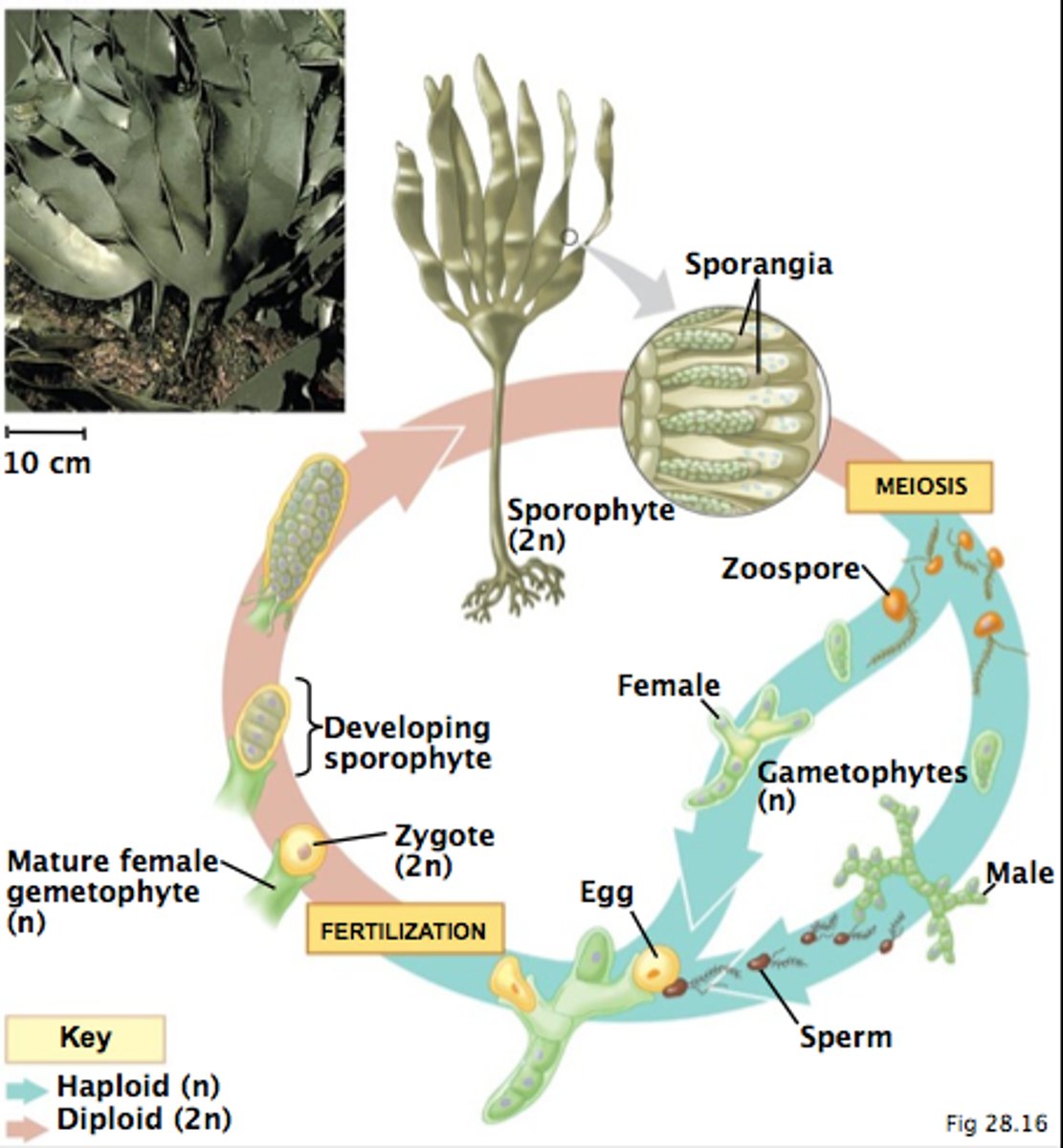
What are the 4 similarities between some fungi and some animals?
1. DNA sequence data
2. Chitin
3. Flagella of chytrids are similar to those of animal sperm cells in that they are both single, attached at the back (posterior), and whiplash
4. Glycogen is the form in which food is stored
Define chitin
this is the main matter that is found in all fungi cell walls and what is in the exoskeletons of some animals like insects and crustaceans
Characteristics of fungi (5)
1. they are eukaryotic
2. they can be unicellular or multicellular
3. they can be motile or nonmotile
4. they are mainly terrestrial
5. they are heterotrophic (non-photosynthetic)
ex. yeast = unicellular fungi
What is the only motile fungi?
chytrids, and they are also aquatic which is not very common
Describe morels
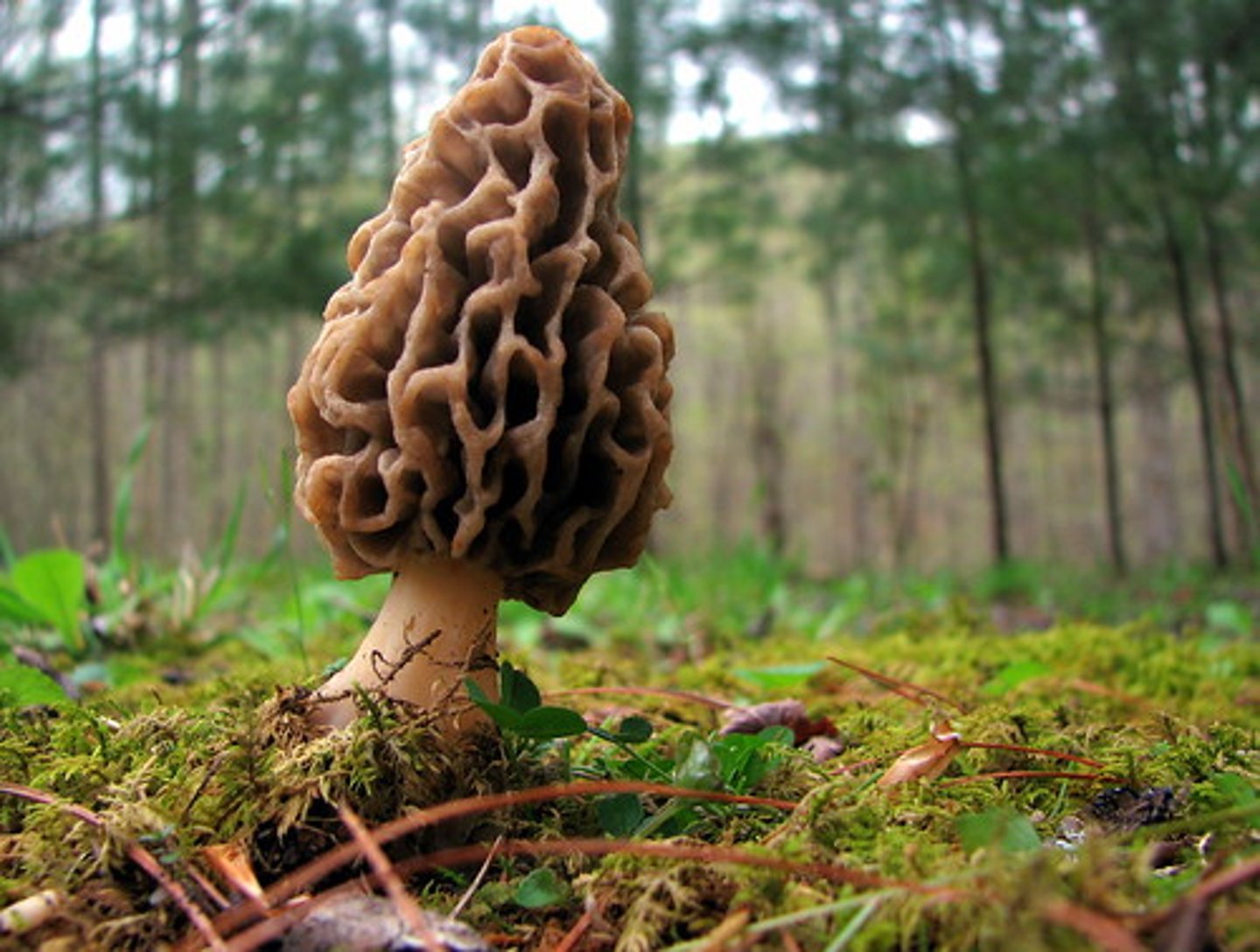

Describe molds
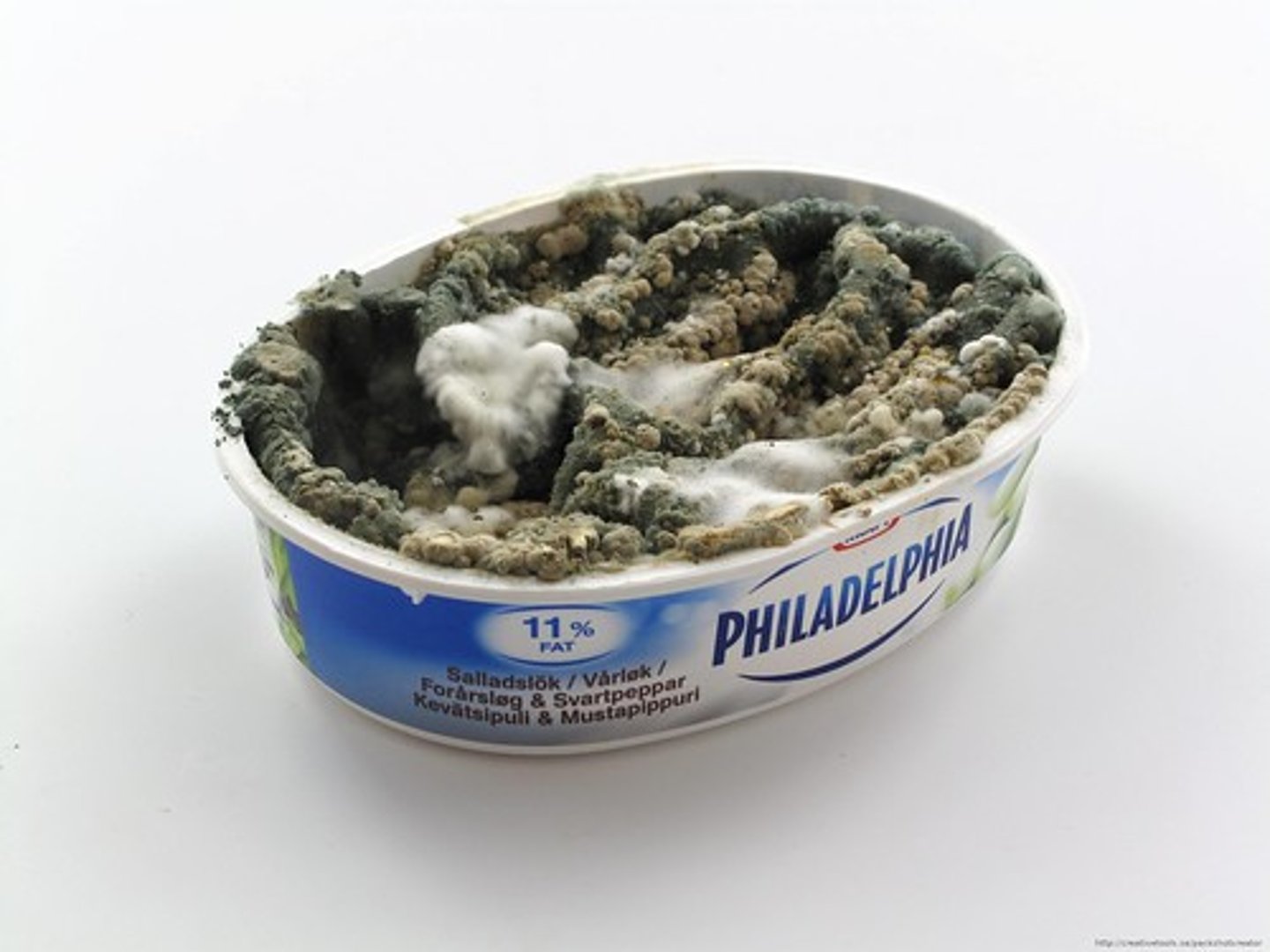

Describe jelly fungi
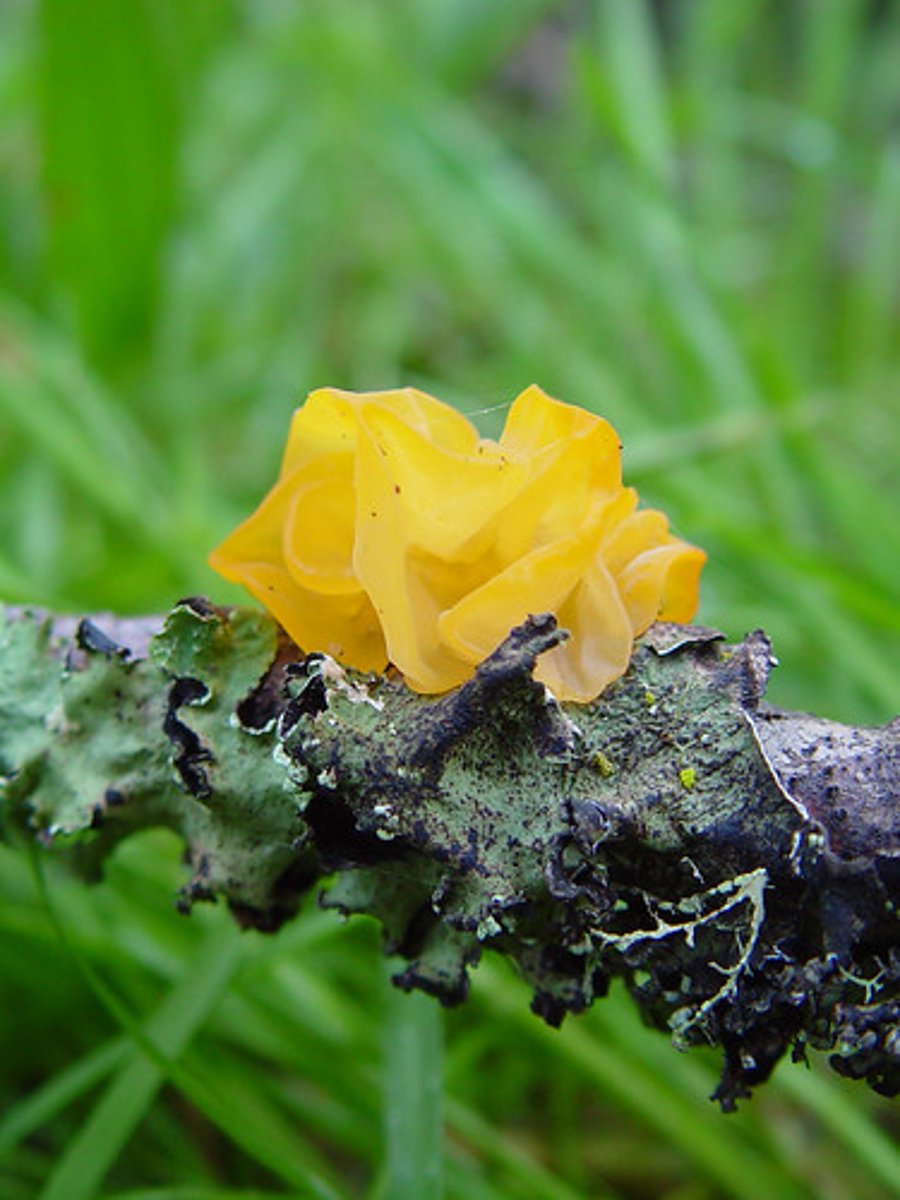

Describe mushrooms
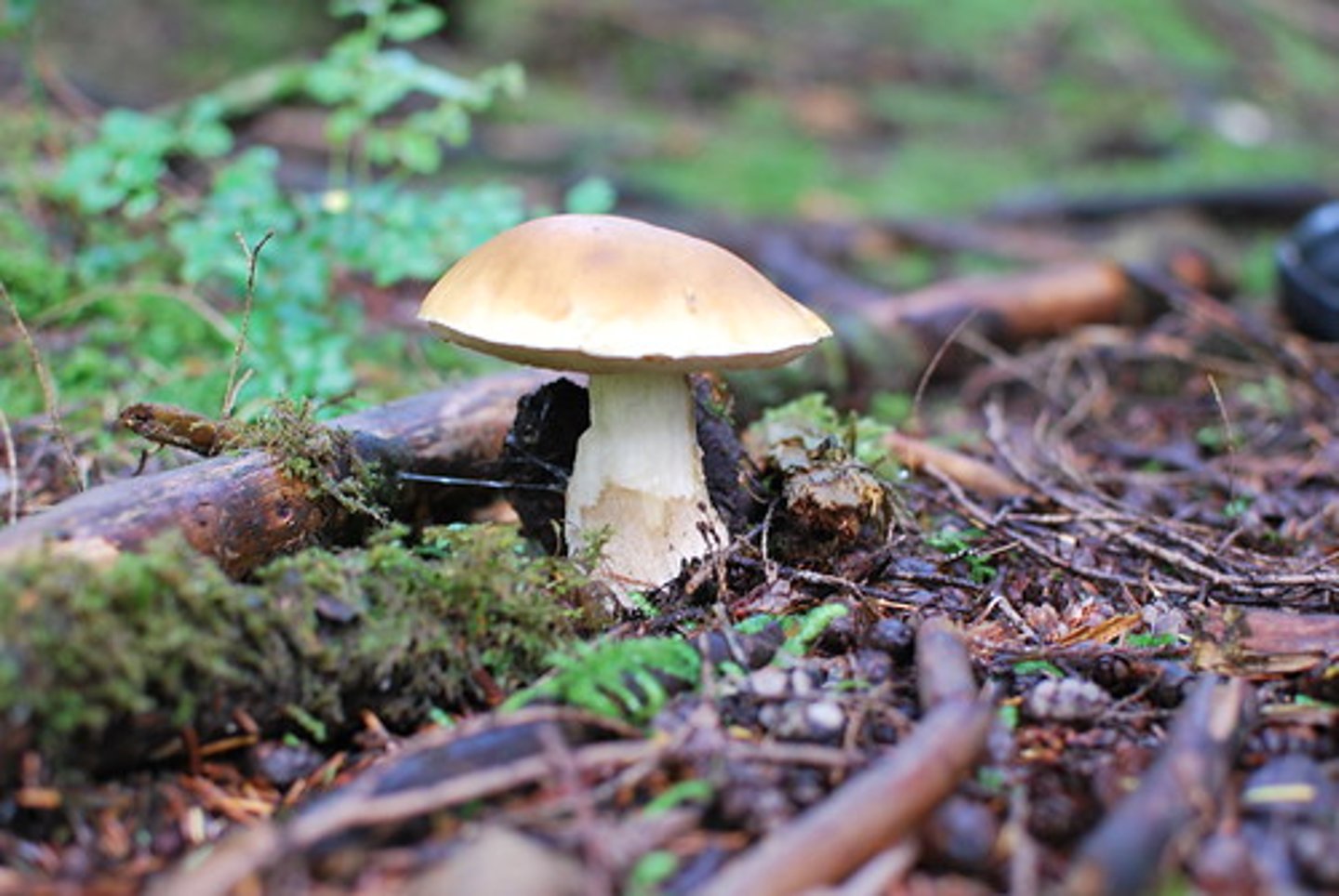

Describe puffballs
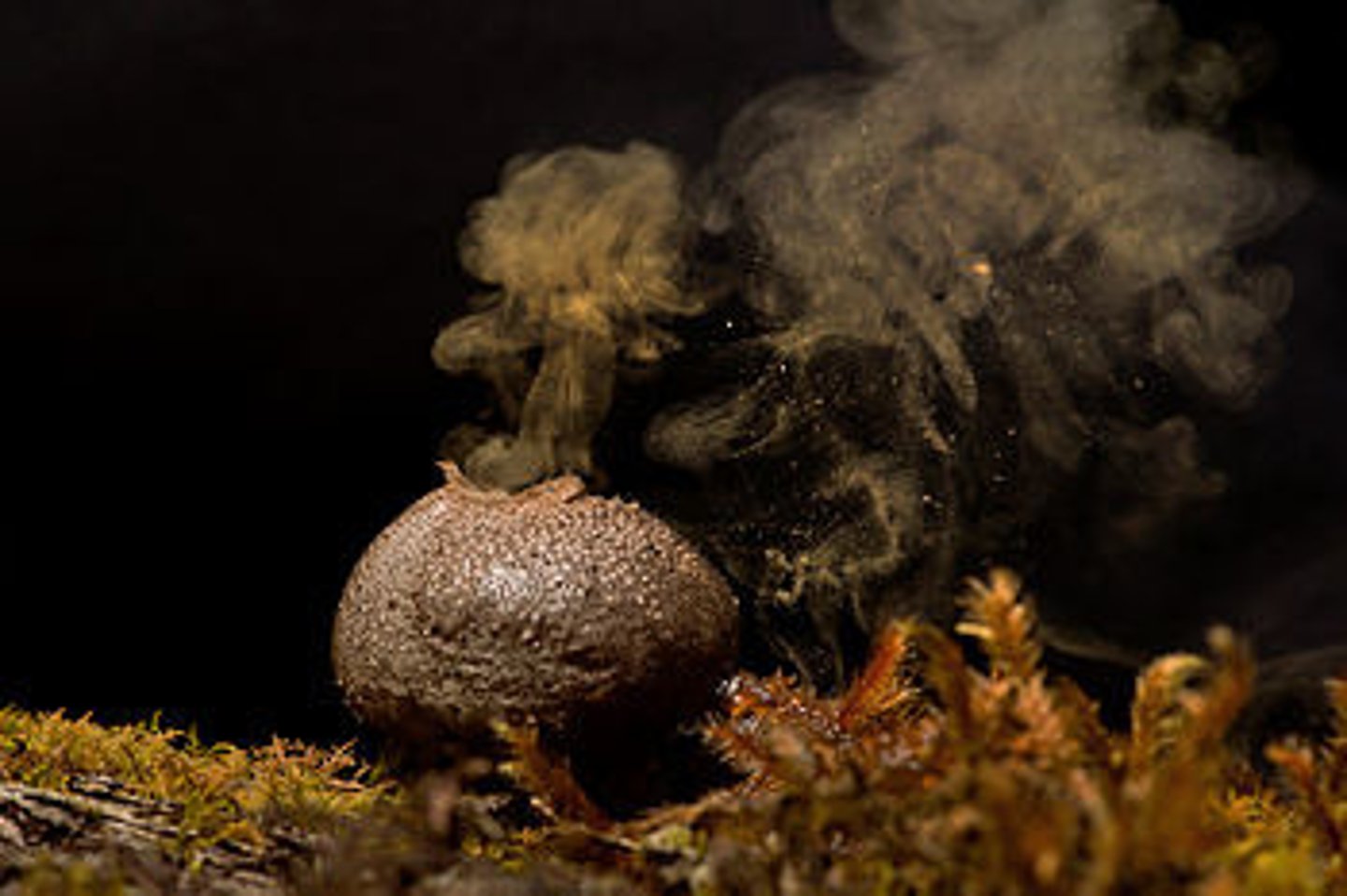

Describe dog stinkhorn
they smell bad and their spores are dispersed by insects like flies
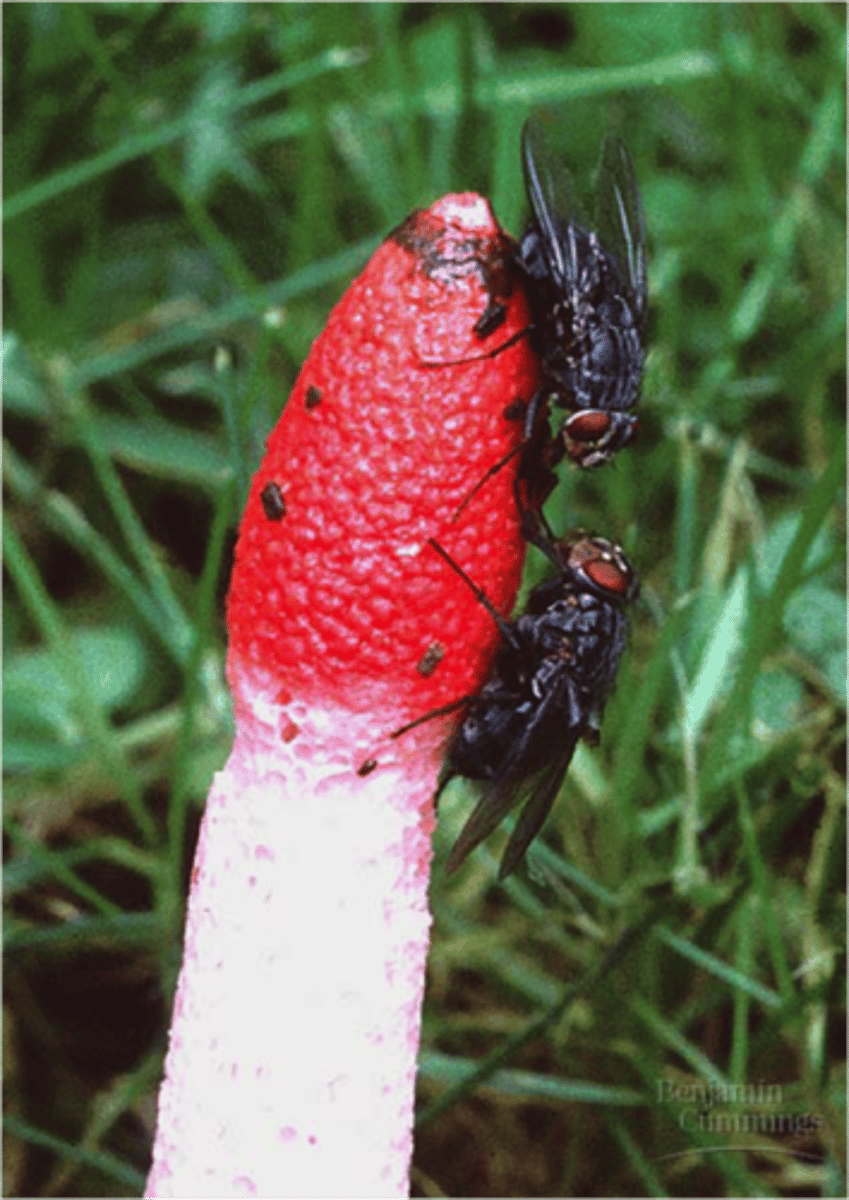

Describe bridal veil stinkhorn
they also smell bad and their spores are dispersed by insects like flies

What are fungi considered when it comes to getting their energy?
they are organoheterotrophs
Define organoheterotrophs
this means that their energy source and carbon source are both reduced carbon compounds
their energy and carbon source both come from other organisms (ex. food)
What special thing do fungi hyphae do?
they secrete digestive enzymes; they then absorb their necessary nutrients after extracellular digestion has taken place
Define mycelium
it is a big mass of hyphae
In fungi, when does nutrient distribution occur?
when small molecules are passed along the hyphae by diffusion. Nutrients flow to the growing tips, which elongate quickly
Are fungi usually saprophytic?
yes
Define saprophytic fungi
this type of fungi lives on dead things and gets its nutrients from dead things
Other than saprophytic, what else can fungi be?
they can be parasites like noose fungi and oyster fungi or crop pests like corn smut and plant rust
Are most fungi multicellular or unicellular?
most are multicellular but some are single-celled
Where does mycelia usually grow?
underground and can cover thousands of acres with their reproductive parts coming to the surface every so often
Define mycorrhizae
relationship between plant roots and fungi that extend the root surface area. This helps the plant absorb more
nutrients from soil
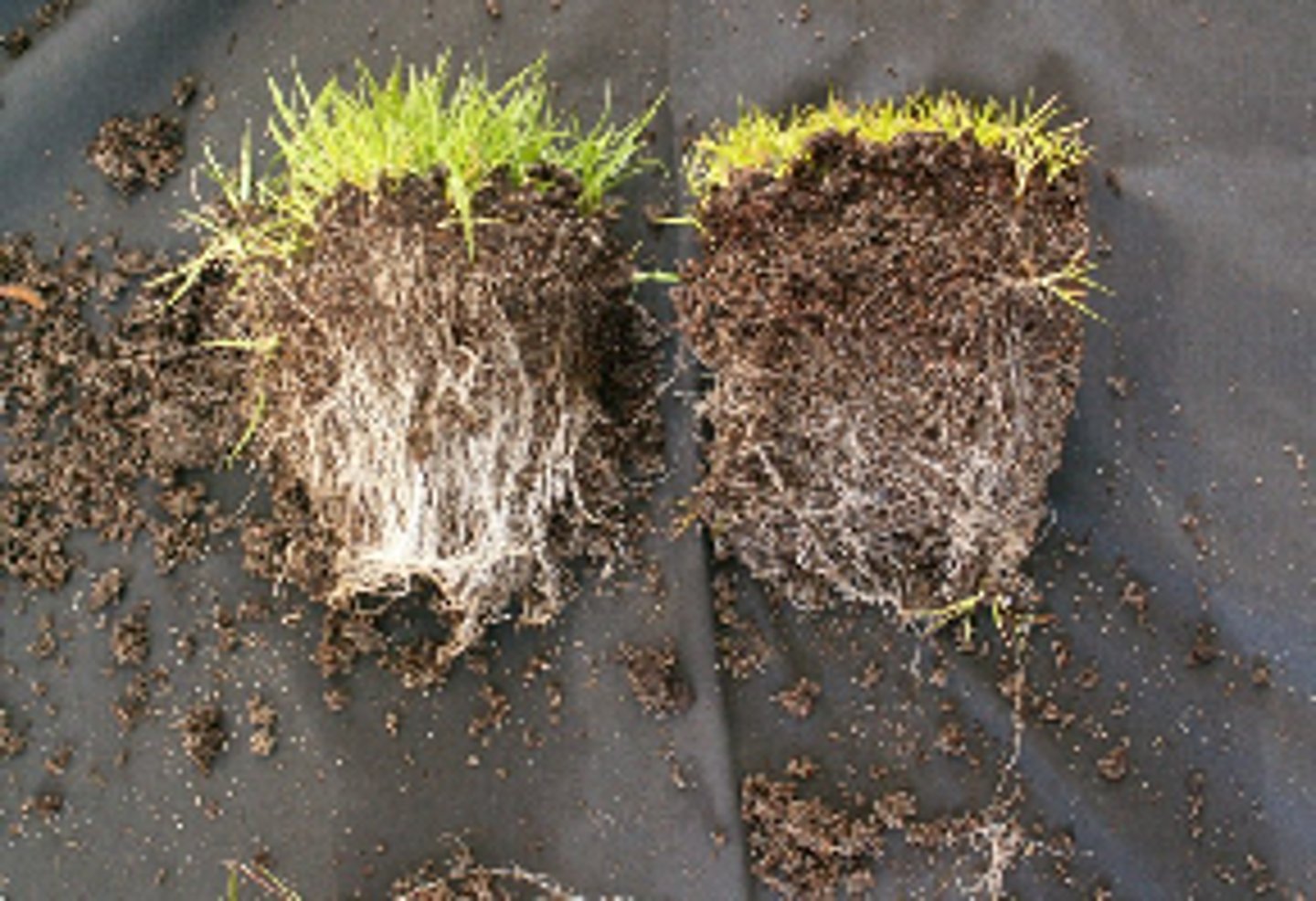

Who do plant roots need help from?
they need help from fungi to absorb water and minerals; fungi gain sugar and amino acids from the plant
How many nuclei do fungi cells have?
typically 1, 2, or more nuclei
What is it called when a fungi has 1 nucleus
monokaryotic
What is it called when a fungi has 2 nucleus
dikaryotic
What is it called when a fungi has 2 or more nuclei
coenocytic
Is each nuclei diploid or haploid?
haploid
Define plasmogamy
this is the fusion of hyphae from two fungi
Define karyogamy
this is the fusion of nuclei from the fused cells
Is there usually a big seperation in time between plasmogamy and karyogamy?
yes
Define homokaryotic
when there is only 1 type of nucleus
Define heterokaryotic
haploid nuclei from 2 genetically distinct individuals
What are the fundamental reproductive cells of the fungi?
spores
During what reproduction are spores produced?
asexual and sexual
What is the primary dispersal stage for fungi?
spores
How are fungi spores dispersed?
by the wind and in very large numbers, so they are very common to find in the air
Describe the reproduction of fungi
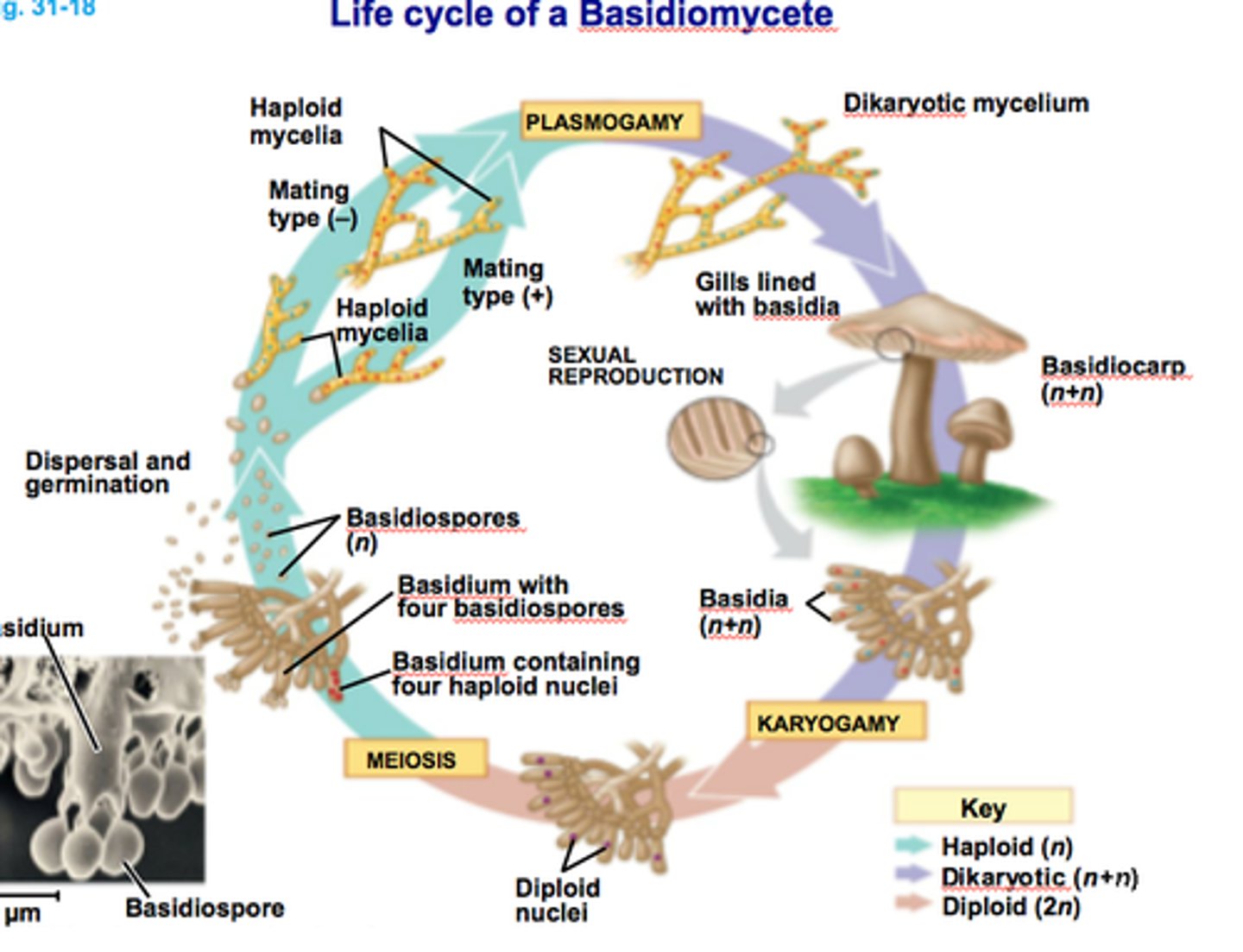
Do mushrooms have haploid or diploid dominant reproduction?
haploid dominant
What is the primary mycelium?
it is when each cell has just 1 nuclei
What is the secondary mycelium?
it is when each cell has 2 nuclei
What are the characteristics of animals (7)
1. eukaryotic
2. most are motile
3. aquatic and terrestrial
4. multicellular
5. heterotrophic and ingest food
6. no cell walls
7. multicellular organism that ingests food (a unique combination)
What is considered to be the earliest ancestor of animals?
choanoflagellates, which are single-celled organisms
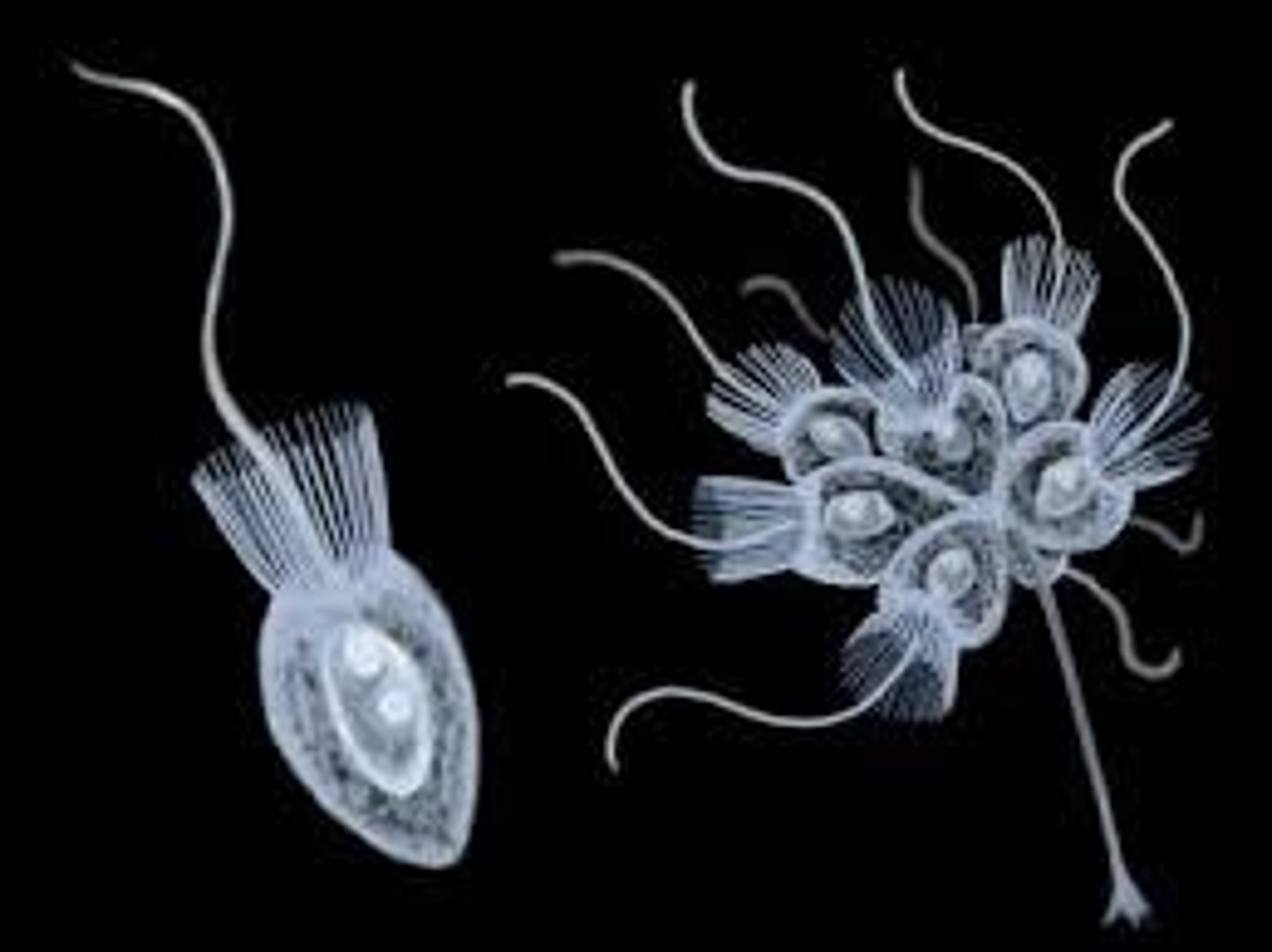

Describe the colonial hypothesis
this suggests that the ancestors of animals were colonial, flagellated protists that evolved specialization and dependence upon one another until they became multicellular animals
Can the cells of multicellular organisms survive individually?
no
What did choanoflagellates evolve into?
the first sponge
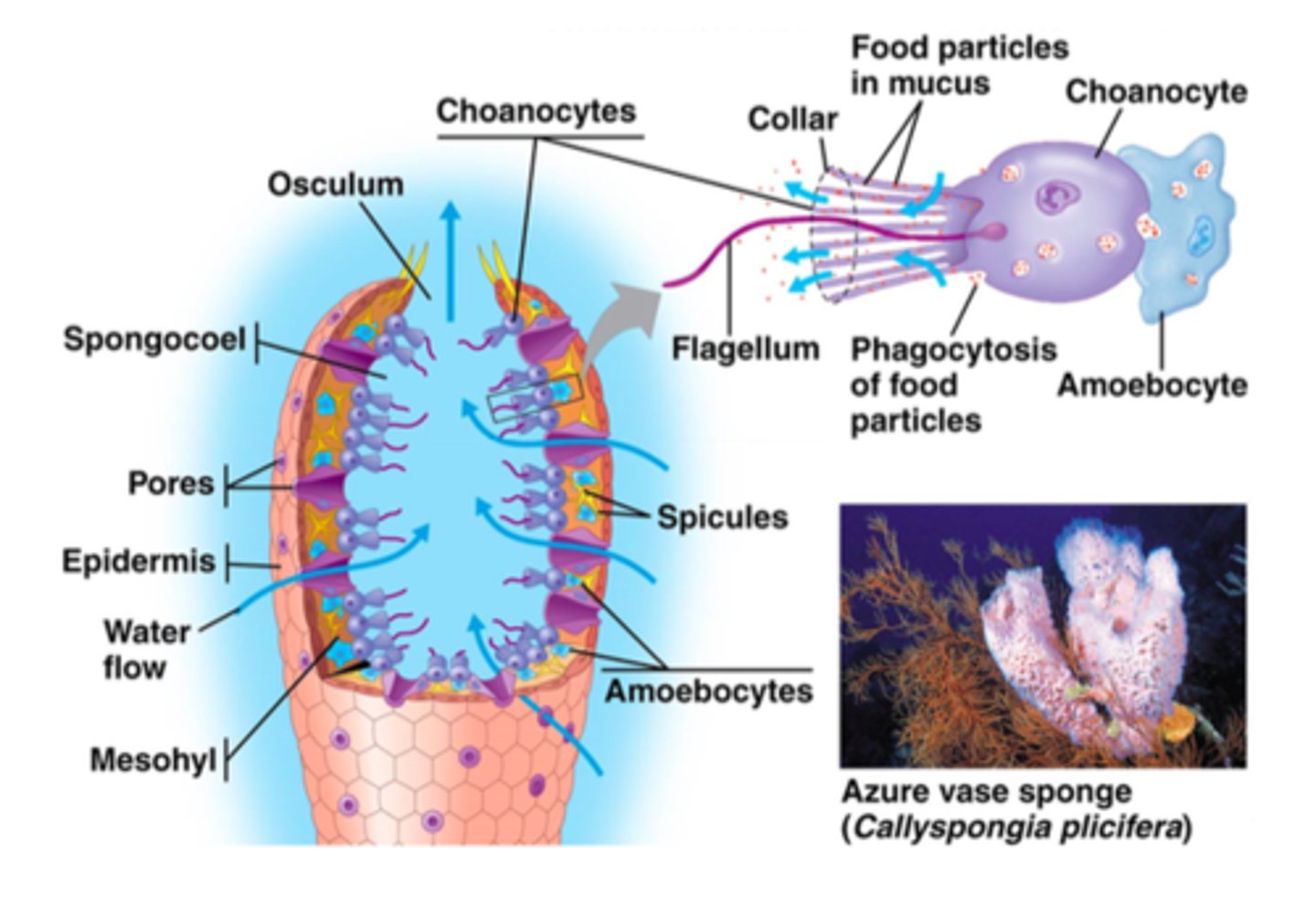
What is the purpose of the flagella?
it is to beat the water and bring food in closer to the organism
What is some evidence that supports that choanoflagellates later became animals as we know then today?
1. flagellates tend to form colonies today, so it is assumed that they did so long ago too
2. Since sperm is flagellated in most animals, it is assumed that the protist ancestor was too or else it would have taken a long time for the flagella to become what they are today in most all animal species
What is the most primitive of all animals?
porifera
What are porifera?
sponges
Are sponges multicellular or unicellular?
multicellular
What do sponges not have?
they don't have tissue
Define tissues
they are groups of cells organized into a functional unit, like muscle tissue for contraction
Are sponges symmetrical or asymmetrical?
asymmetrical
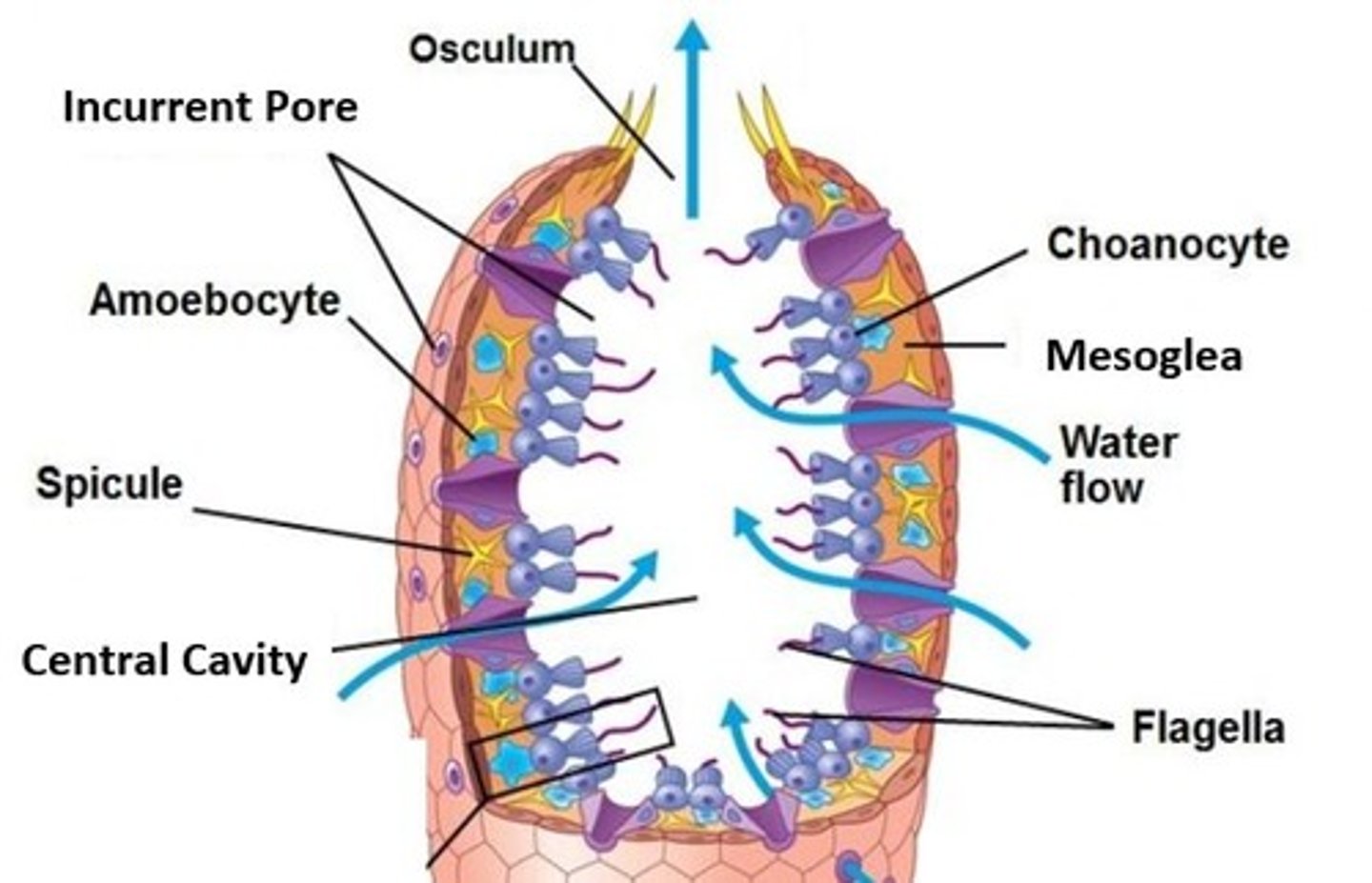
What are the two major cell types of sponges?
choancytes and ameobocytes
Describe the choancytes of sponges
they are the "feeding cells" that line the interior