Biochemistry II Lesson 5: Hormones and Metabolism
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
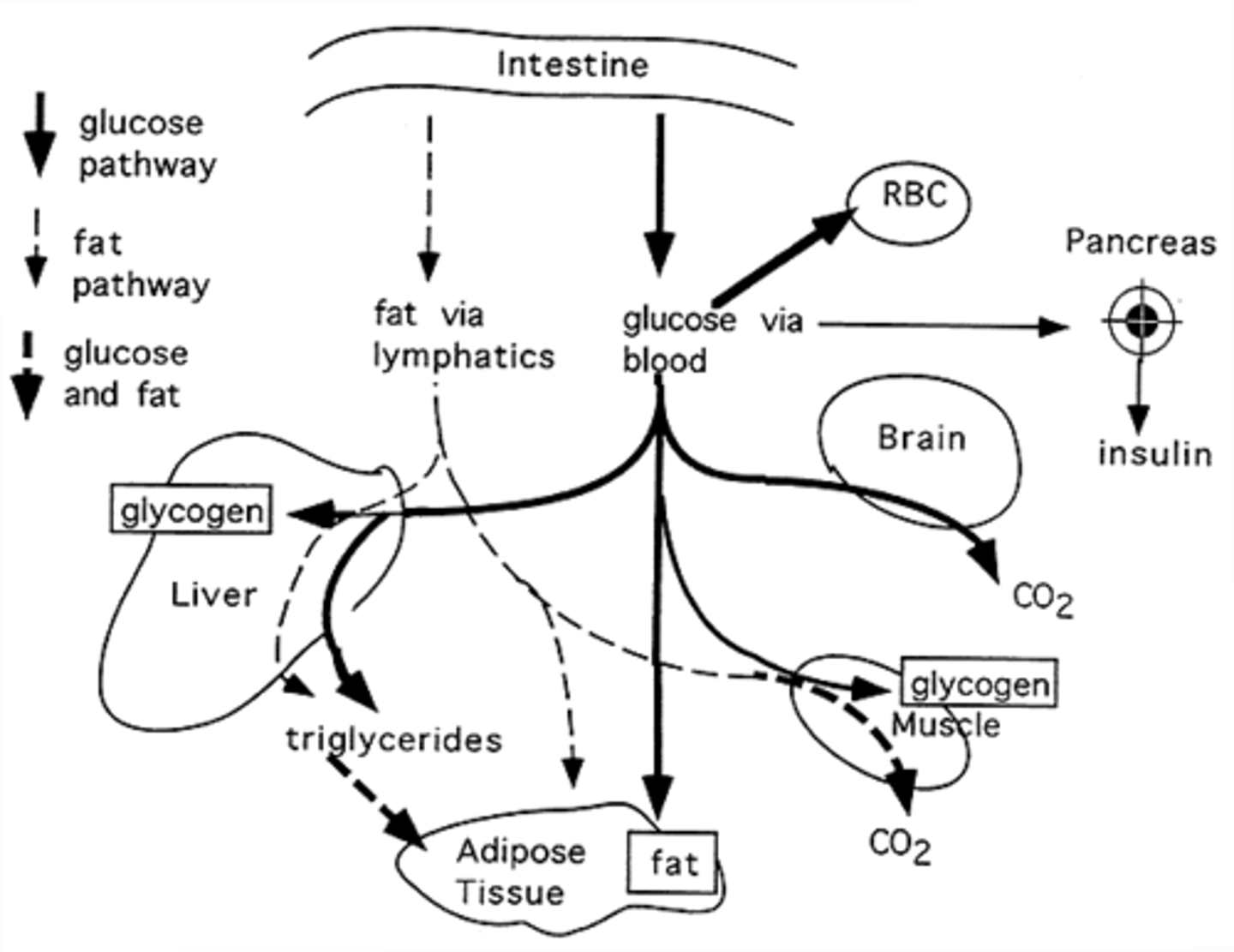
When excess glucose enters the liver, the liver may do which of the following in order to store it for later use?
I. Convert the glucose into glycogen.
II. Convert the glucose into triglycerides and then package them into HDLs for transport to the adipose tissue.
III. Convert them into amino acids for storage in the muscles.
(A) I Only
(B) II Only
(C) I and II Only
(D) I, II, and III
(A) I Only
When excess glucose enters the liver, the liver may:
(1) Convert the glucose into glycogen.
(2) Convert the glucose into triglycerides and then package them into VLDLs (NOT HDLs) for transport to the adipose tissue.
CRB Which of the following is the threshold for blood glucose that, above this threshold, would trigger Insulin release?
(A) 100mg/L
(B) 100mg/dL
(C) 10mg%
(D) 10mg/dL
(B) 100mg/dL
[Note that 100mg/dL is equal to 100mg%]
When blood glucose levels are above 100mg/dL, or 5.6mM, then insulin release will occur proportional to the blood levels of glucose.
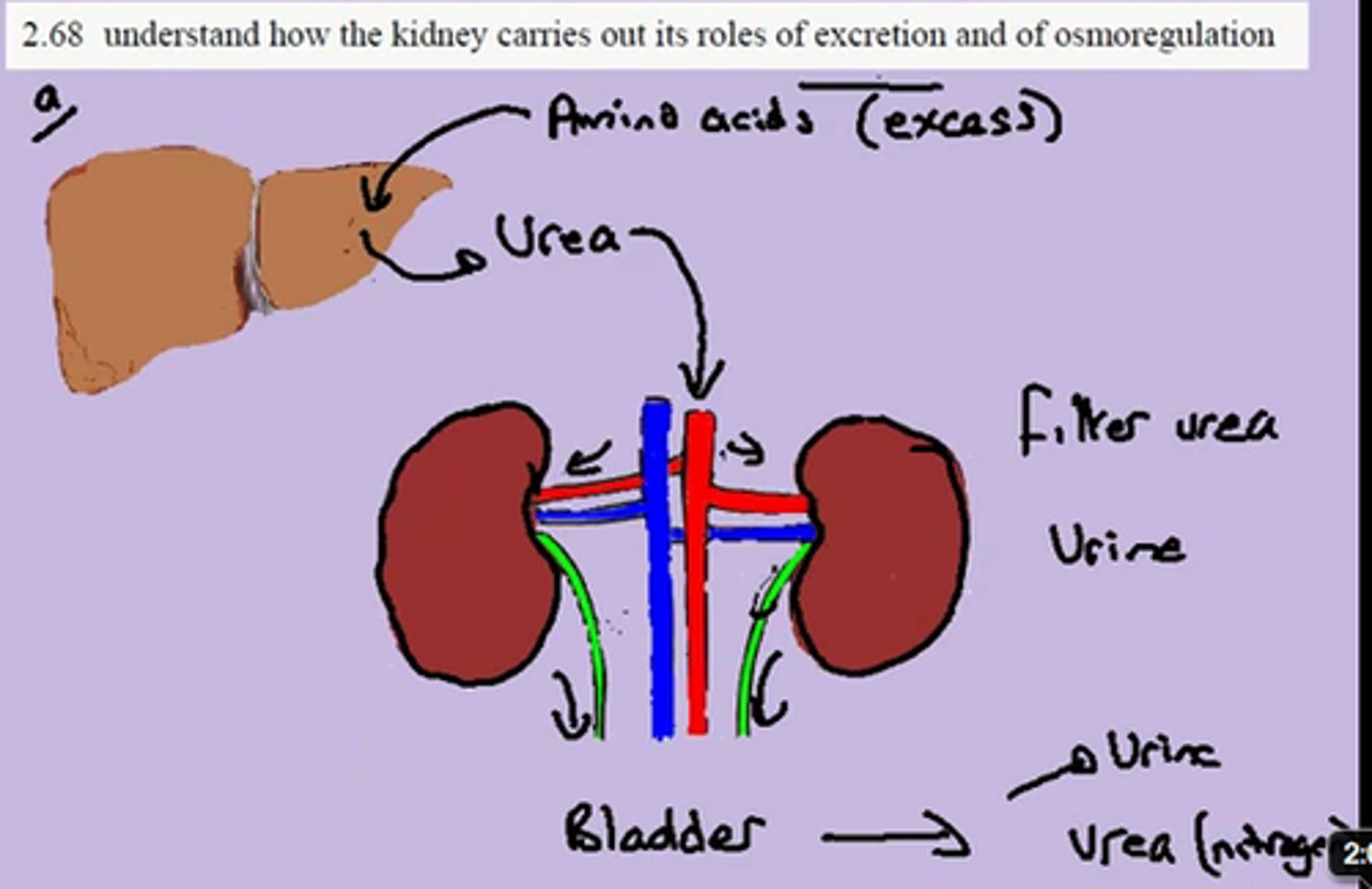
In the liver, amino acids are broken down into α-keto acids. NH3 is produced in this reaction. The NH3 will then travel to which vital organ?
(A) Spleen
(B) Thyroid
(C) Hypothalamus
(D) Kidney
(D) Kidney
The NH3 will travel to the Kidney and get excreted as Urea.
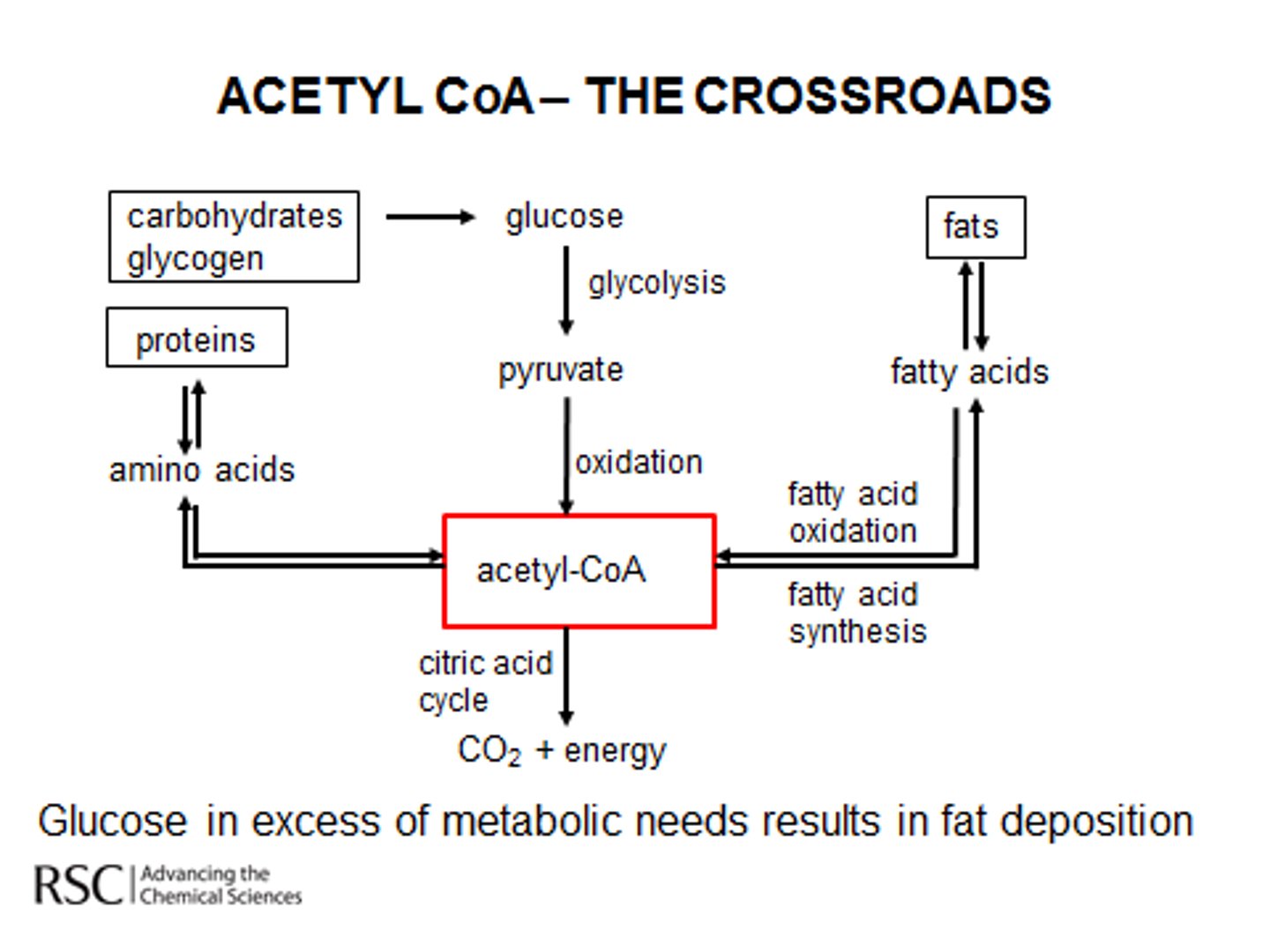
During the Absorptive state in the liver, amino acids may be broken down into α-keto acids. If these are then designated for immediate energy use, they will be converted into:
(A) Acetyl CoA
(B) Fatty Acids
(C) Glycogen
(D) Pyruvate
(A) Acetyl CoA
In the liver, amino acids may be broken down into α-keto acids. If these are then used for energy, they will first be converted into Acetyl CoA.
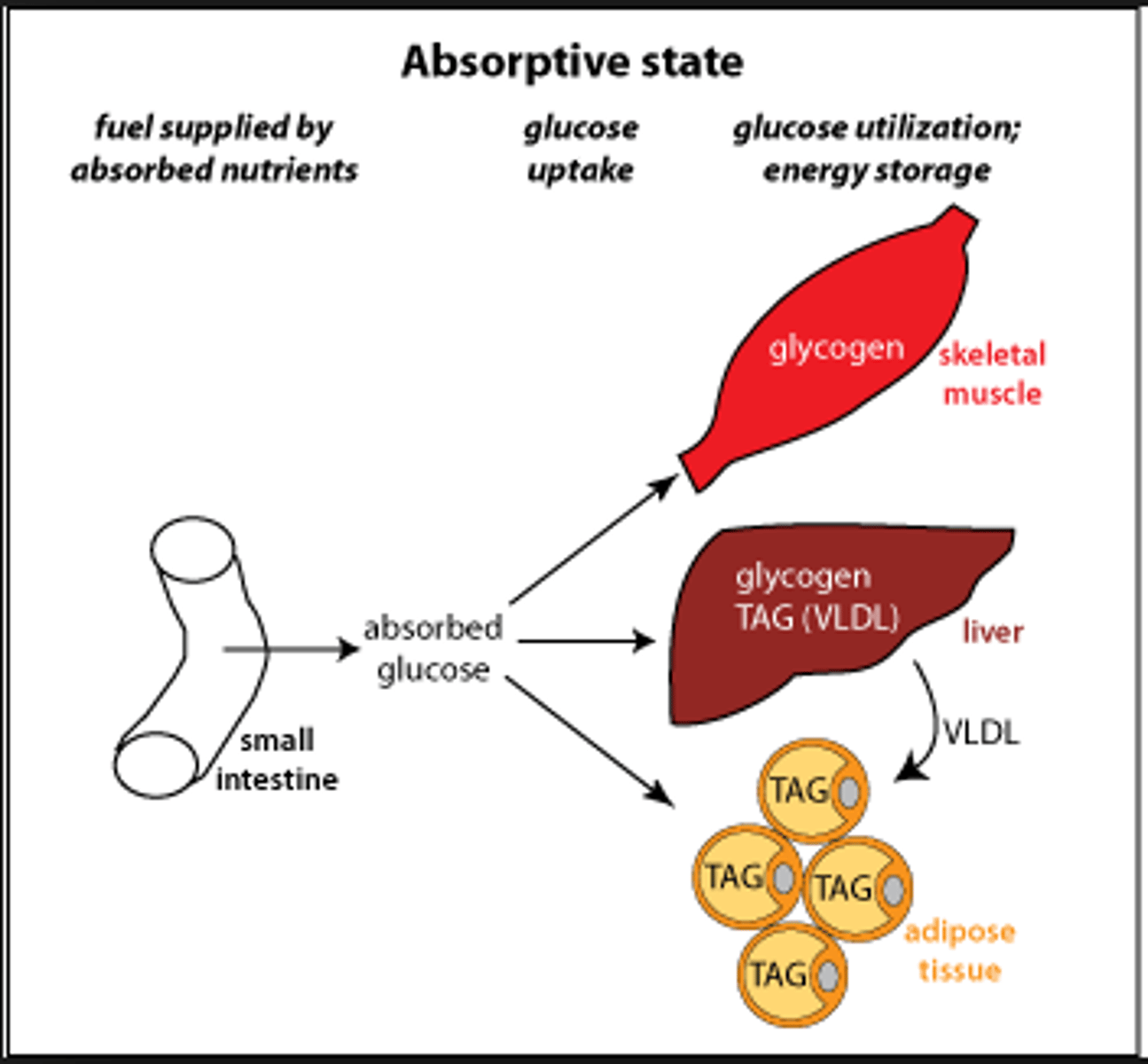
CRB Which of the following are also names for the Absorptive State?
I. Postprandial State
II. Well-Fed State
III. Counterregulatory State
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) II and III
(D) I, II and III
(B) I and II only
The Absorptive State can also be called the Well-Fed State and the Postprandial State.
CRB How long does the Postprandial State last for after eating a meal?
(A) 1-2 hours
(B) 3-5 hours
(C) 6-8 hours
(D) 30 minutes - 2 hours
(B) 3-5 hours
The Postprandial State lasts for 3-5 hours after eating a meal.
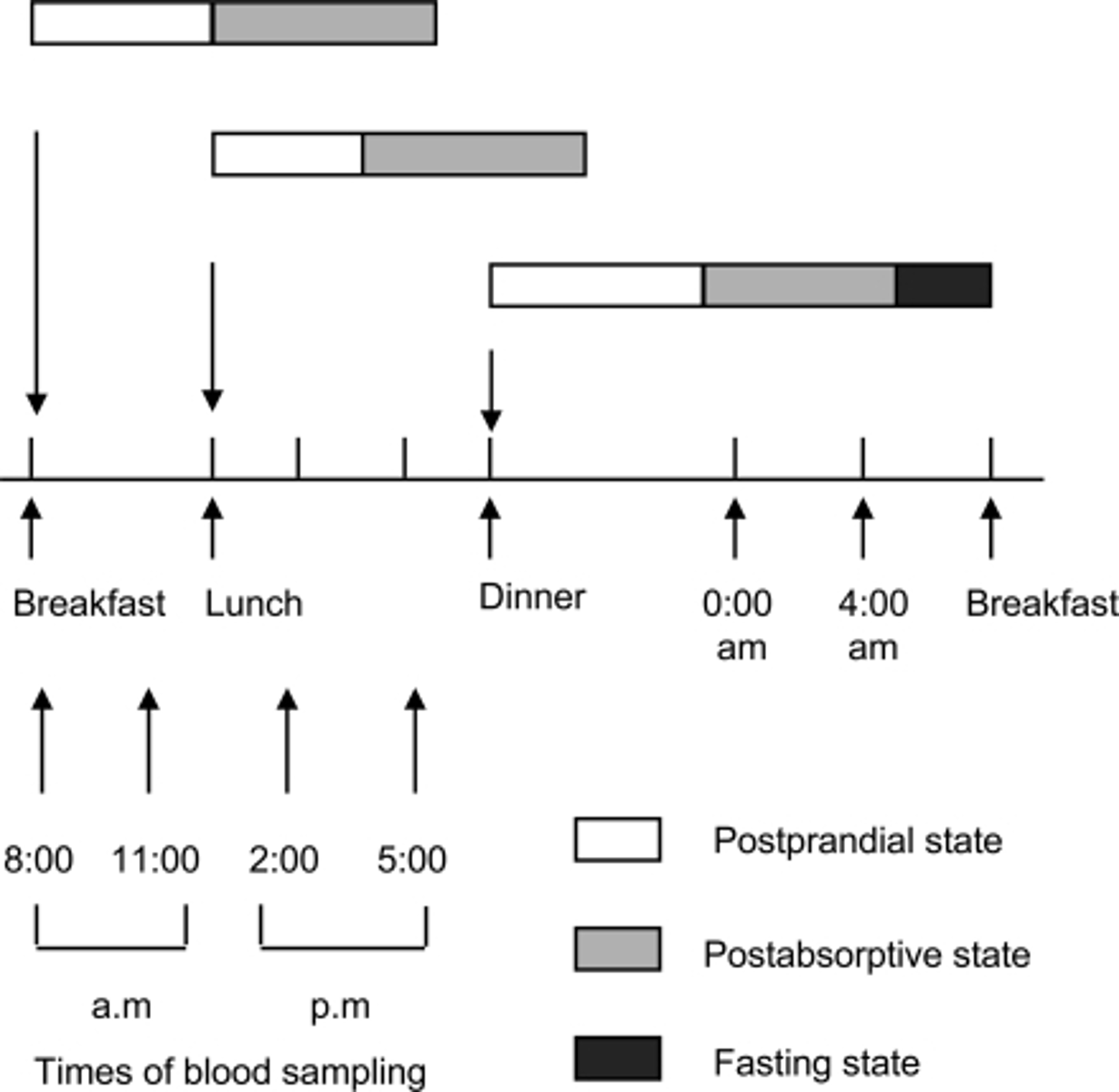
During the Absorptive state in the liver, amino acids may be broken down into α-keto acids. If these are designated for energy storage, they will be converted into:
(A) Acetyl CoA
(B) Fatty Acids
(C) Glycogen
(D) Pyruvate
(B) Fatty Acids
In the liver, amino acids may be broken down into α-keto acids. If these are then stored for energy, they will be converted into Fatty Acids.
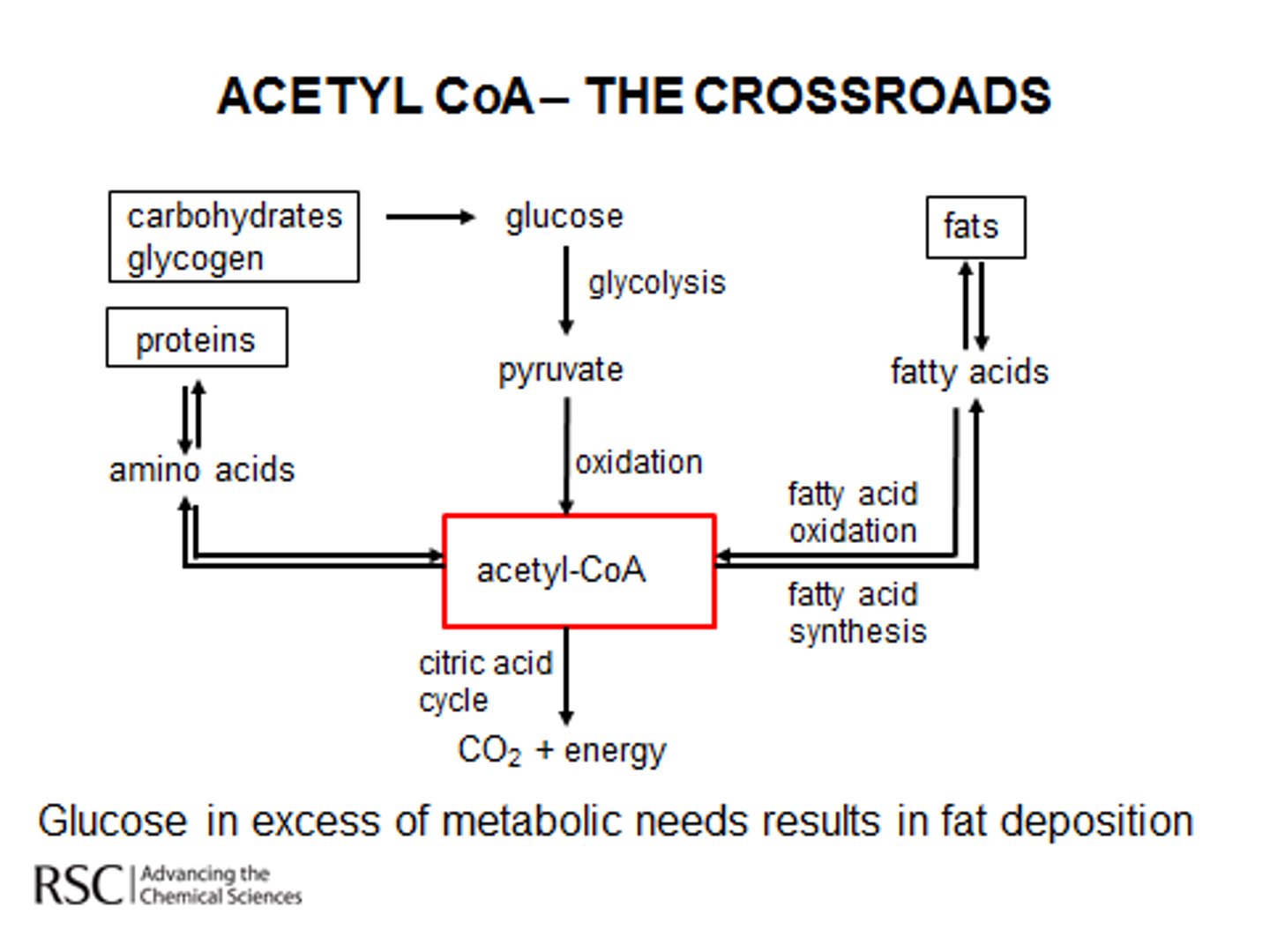
Adipose Tissue can receive which of the following for subsequent energy storage?
I. Triglycerides
II. Fatty Acids
III. Glucose
(A) I Only
(B) I and II Only
(C) II and III Only
(D) I, II, and III
(D) I, II, and III
Adipose Tissue can receive Triglycerides from VLDLs. It can also receive glucose, which it will then convert into Fatty Acids and subsequently Triglycerides.
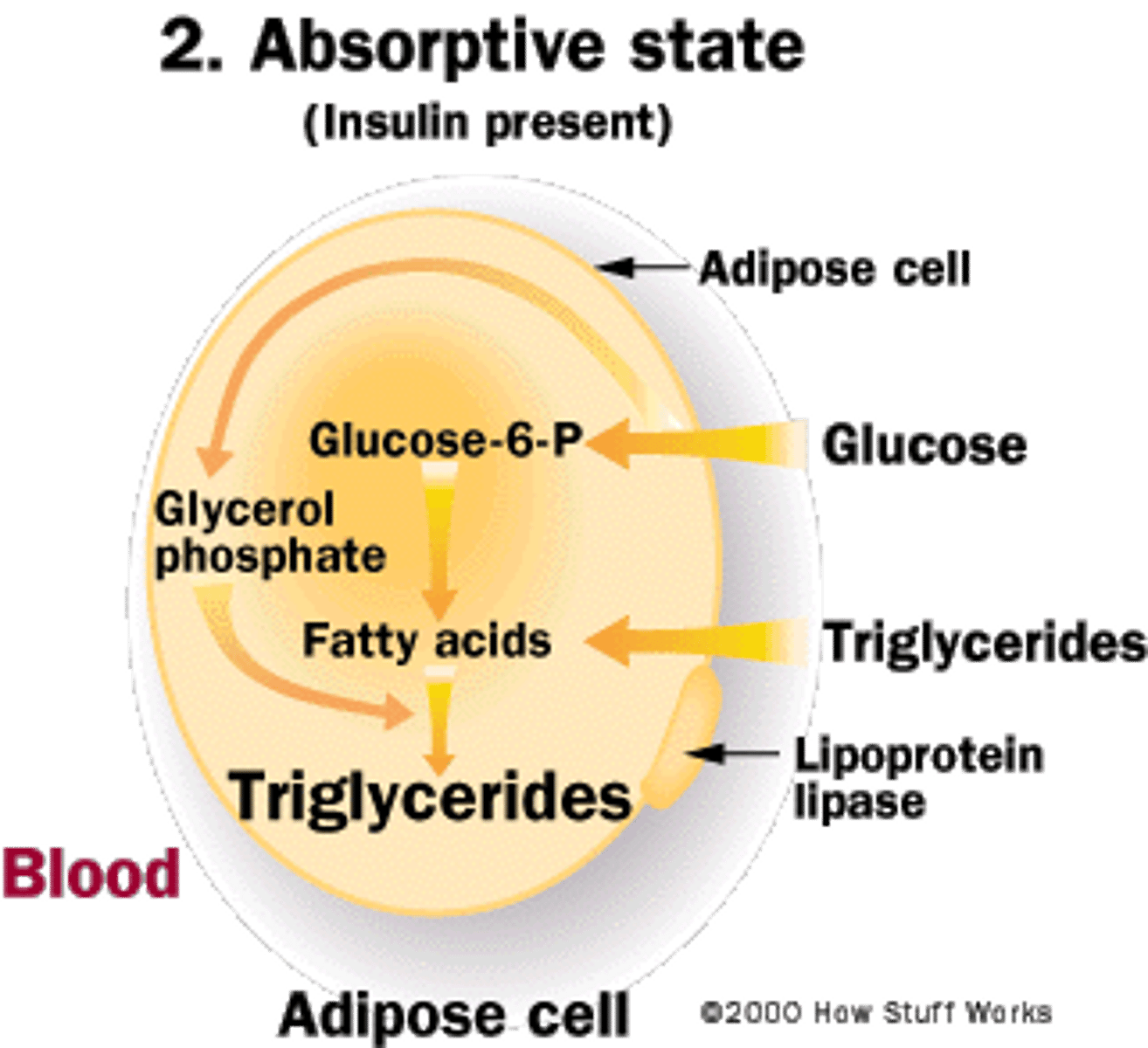
True or False? Glucose can be stored as glycogen in both adipose tissue and skeletal muscle.
False. Glucose can be stored as glycogen in the skeletal muscle but not adipose tissue.
Mike just ate a big Thanksgiving feast. Which state is Mike likely in?
(A) Absorptive
(B) Post-absorptive
(C) Excretion
(D) Filtration
(A) Absorptive
The absorptive state is also known as the "well-fed state" and is characterized by energy storage.
The Post-absorptive State is also known as the "fasting state" and is characterized by energy utilization.
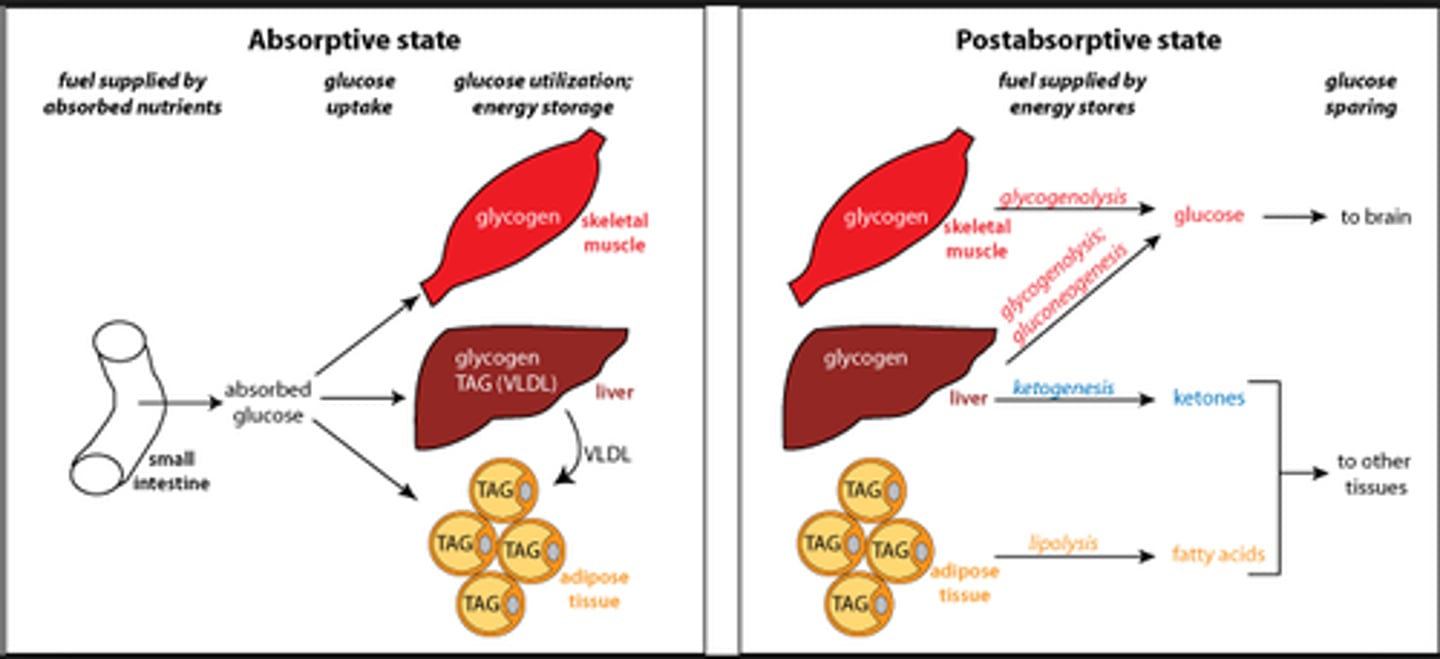
CRB How long after the last meal would it take to transition from the Postabsorbtive "Fasting state" to the Prolonged Fasting "Starvation" state?
(A) 1 day
(B) 1 hour
(C) 12 hours
(D) 3 days
(A) 1 day
After 1 day (24 hours) since the last meal, the Starvation State will start.
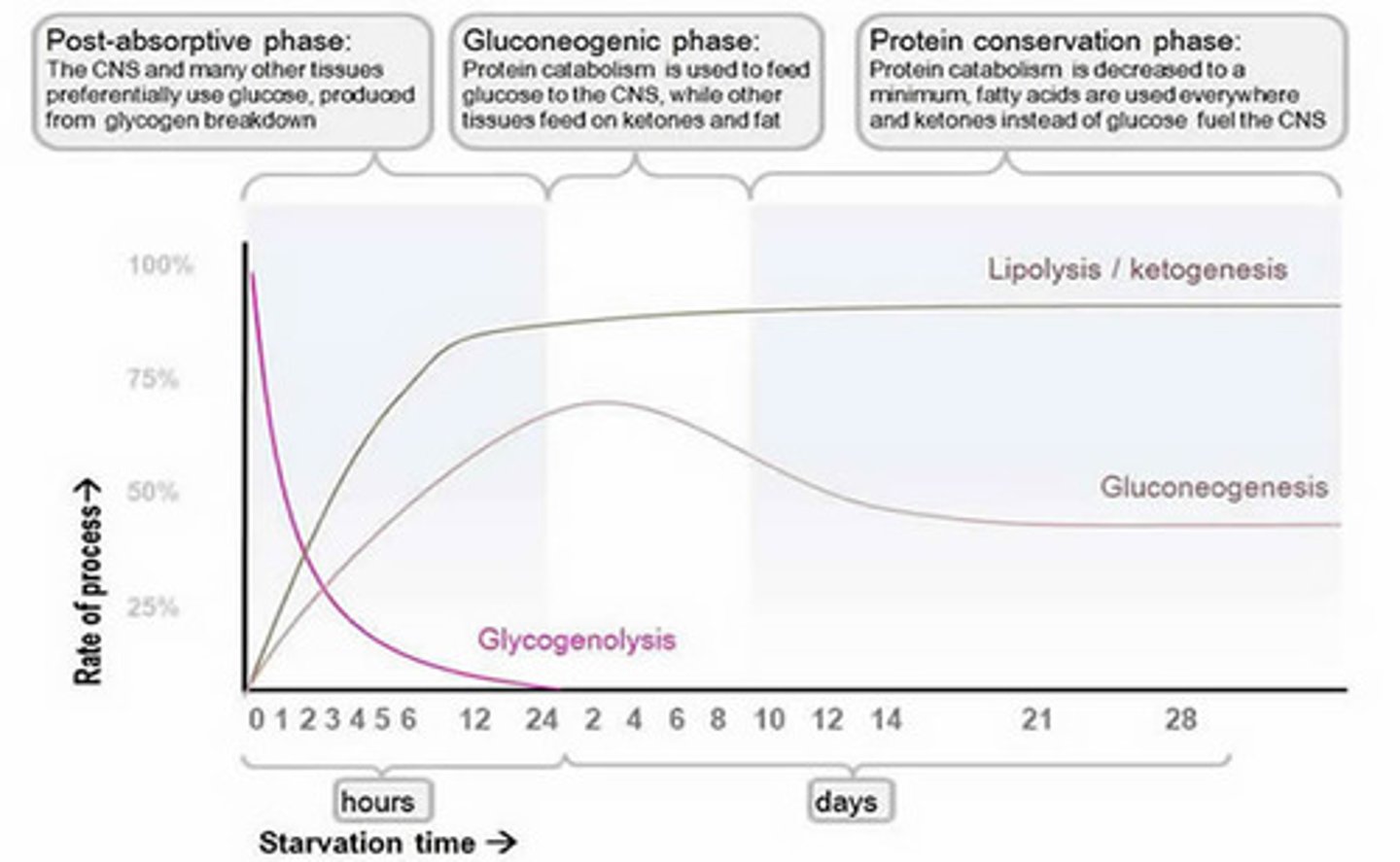
CRB Which of the following statements about the Starvation state is FALSE?
(A) Gluconeogenesis is the dominant form that glucose in the body comes from.
(B) Lipolysis is rapid, and the Acetyl-CoA is used to make Ketone Bodies.
(C) Muscles and the Brain will start using Ketone Bodies as their primary source of fuel.
(D) The shift to using primarily Ketone Bodies by the brain spares proteins and amino acids from gluconeogenesis, allowing vital proteins to keep functioning.
(C) Muscles and the Brain will start using Ketone Bodies as their primary source of fuel.
The Brain will use primarily Ketone Bodies, but Muscle Cells will use Fatty Acids circulating in the blood.
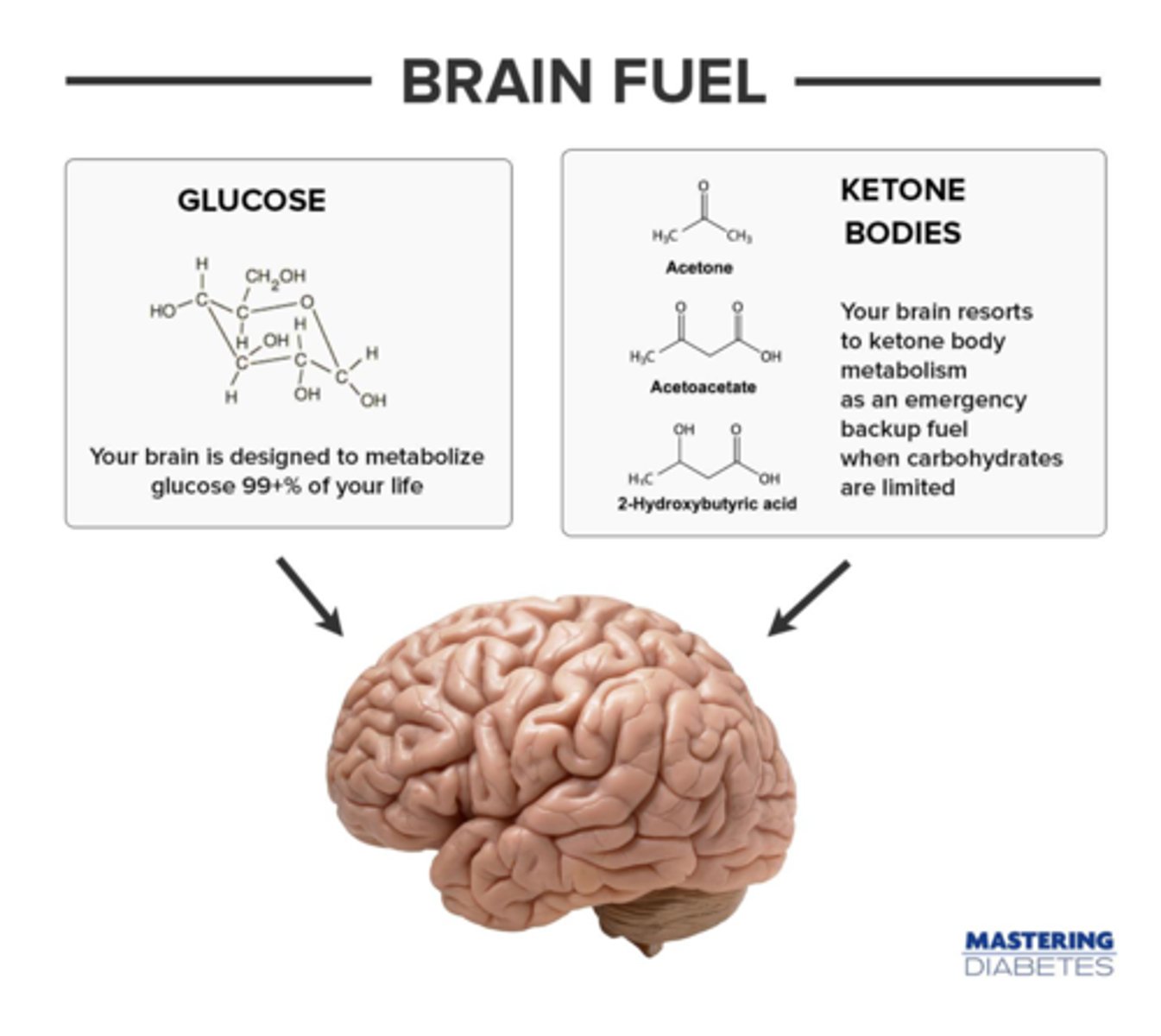
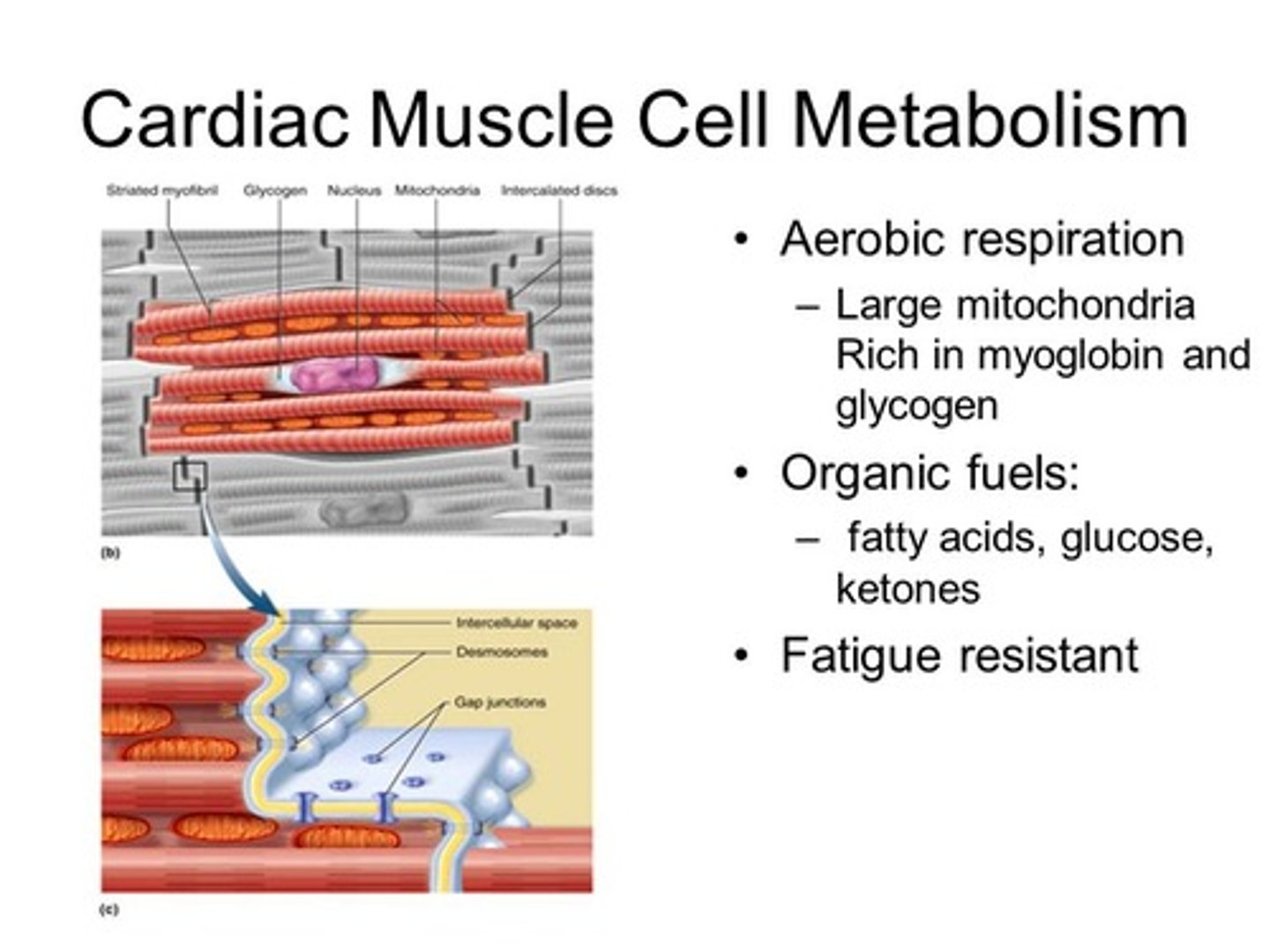
CRB True or false? Even under Fed or Fasted conditions, Cardiac myocytes still prefer Fatty Acids as their primary fuel source.
True. Even under Fed or Fasted conditions, Cardiac myocytes still prefer Fatty Acids as their primary fuel source.
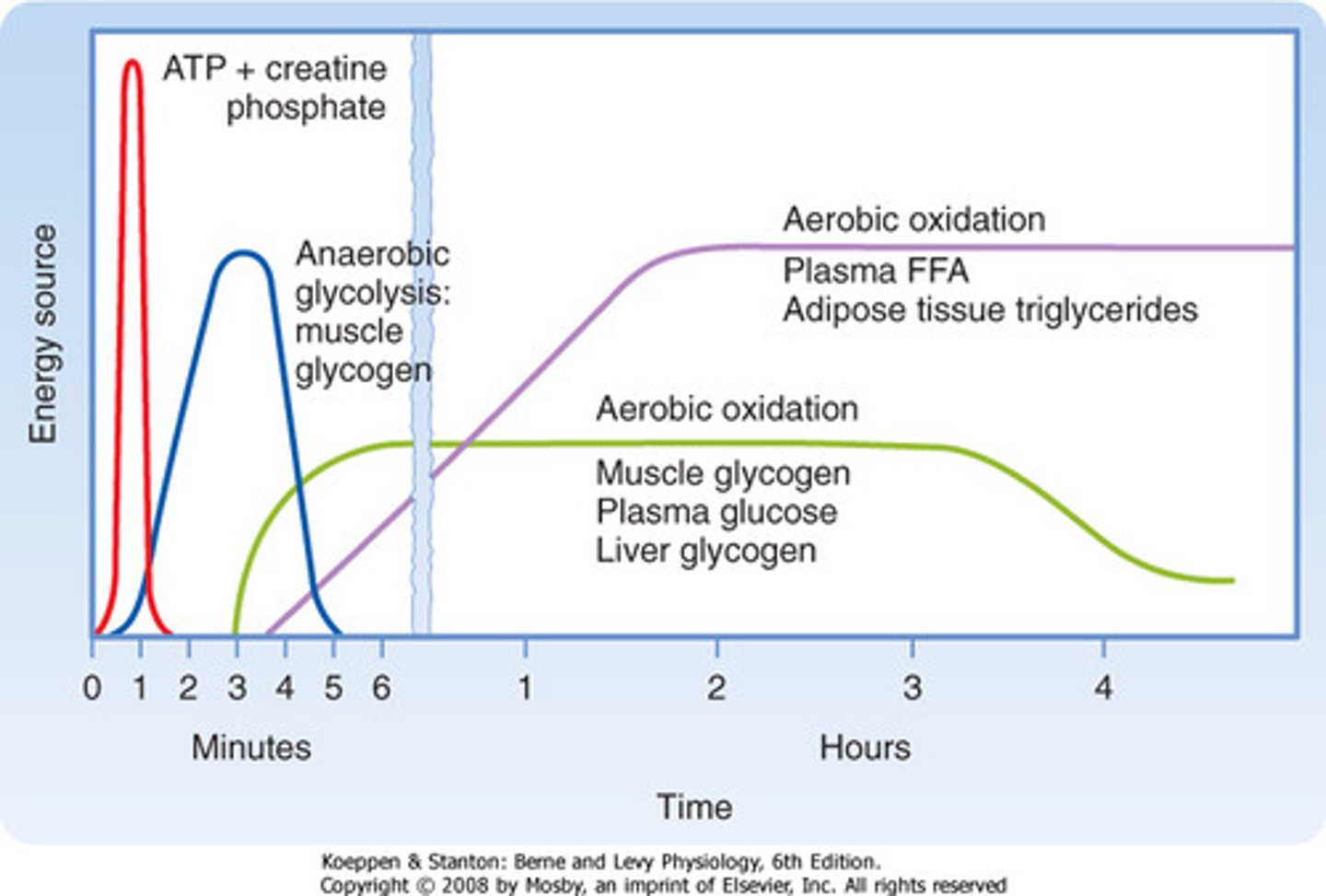
CRB Fill in the blanks: In continuous, moderately intense exercise, the muscles will use _______________ as their primary energy source. For short-burst activities, the muscles rely upon _______________ as their primary energy source.
(A) Creatine Phosphate and Glycogen, Anaerobic Glycolysis.
(B) Oxidation of Fatty Acids, Anaerobic Glycolysis
(C) Oxidation of Fatty Acids and Glucose, Anaerobic Glycolysis and Creatine Phosphate and Glycogen Stores
(D) None of the above.
(C) Oxidation of Fatty Acids and Glucose, Anaerobic Glycolysis and Creatine Phosphate and Glycogen Stores
In continuous, moderately intense exercise, the muscles will use Oxidation of Fatty Acids and Glucose as their primary energy source. For short-burst activities, the muscles rely upon Anaerobic Glycolysis and Creatine Phosphate and Glycogen Stores as their primary energy source.
Although B's choices are technically right, they are far from the best answer.
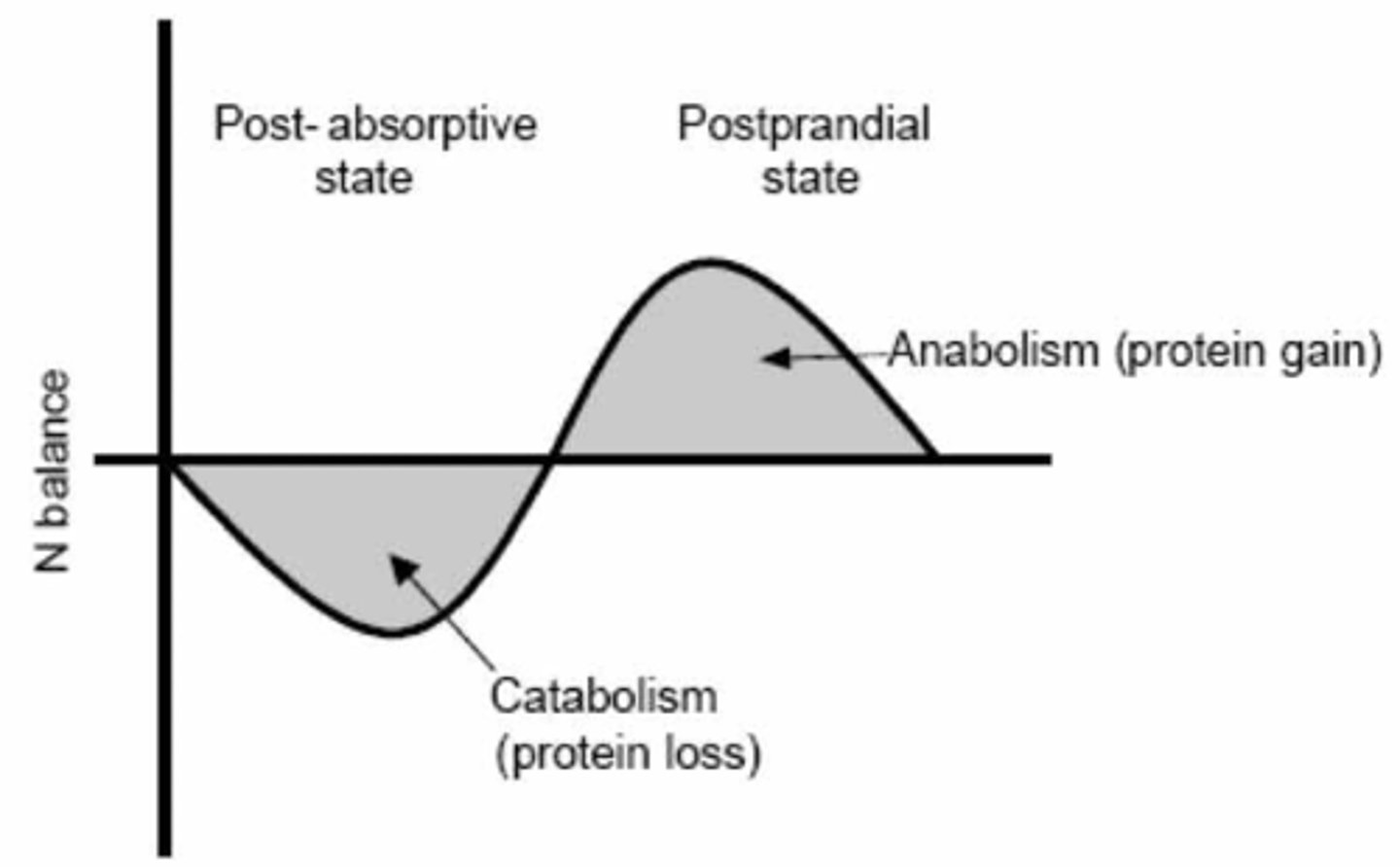
The Absorptive State is most closely associated with _____________. The Post-absorptive State is closely associated with ___________.
(A) catabolism, catabolism
(B) catabolism, anabolism
(C) anabolism, anabolism
(D) anabolism, catabolism
(D) anabolism, catabolism
The Absorptive State is most closely associated with anabolism (macronutrient storage). The Post-absorptive State is closely associated with catabolism (macronutrient breakdown).
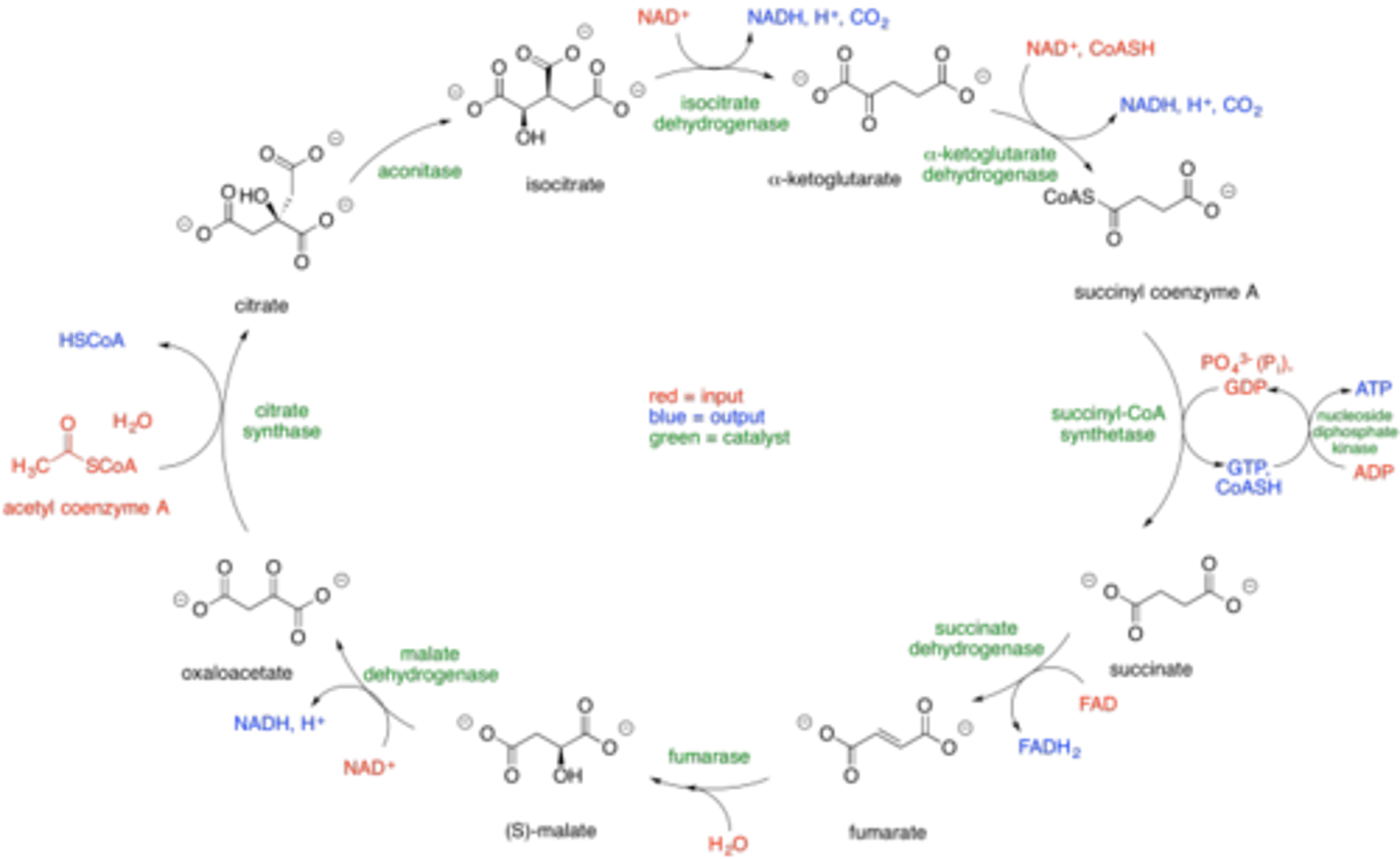
During the Post-absorptive State in the liver, amino acids may be broken down into α-keto acids. Which of the following is NOT an α-keto acid?
(A) Acetyl CoA
(B) α-ketoglutarate
(C) Oxaloacetate
(D) Pyruvate
(A) Acetyl CoA
During the Post-absorptive State in the liver, amino acids may be broken down into α-keto acids. Many α-keto acids can easily enter the Krebs Cycle, including:
1. α-ketoglutarate
2. Oxaloacetate
3. Pyruvate
During the Post-absorptive State in the liver, Triglycerides may be broken down into Fatty Acids and Glycerol, which can then be converted into which of the following for energy throughout the body?
I. Amino Acids
II. Glucose
III. Ketones
(A) I and II Only
(B) II and III Only
(C) I and III Only
(D) I, II, and III
(B) II and III Only
During the Post-absorptive State in the liver, Triglycerides may be broken down into Glycerol and Fatty Acids, which can then be converted into glucose (Glycerol) and Acetyl CoA and ketones (fatty acids) for energy throughout the body
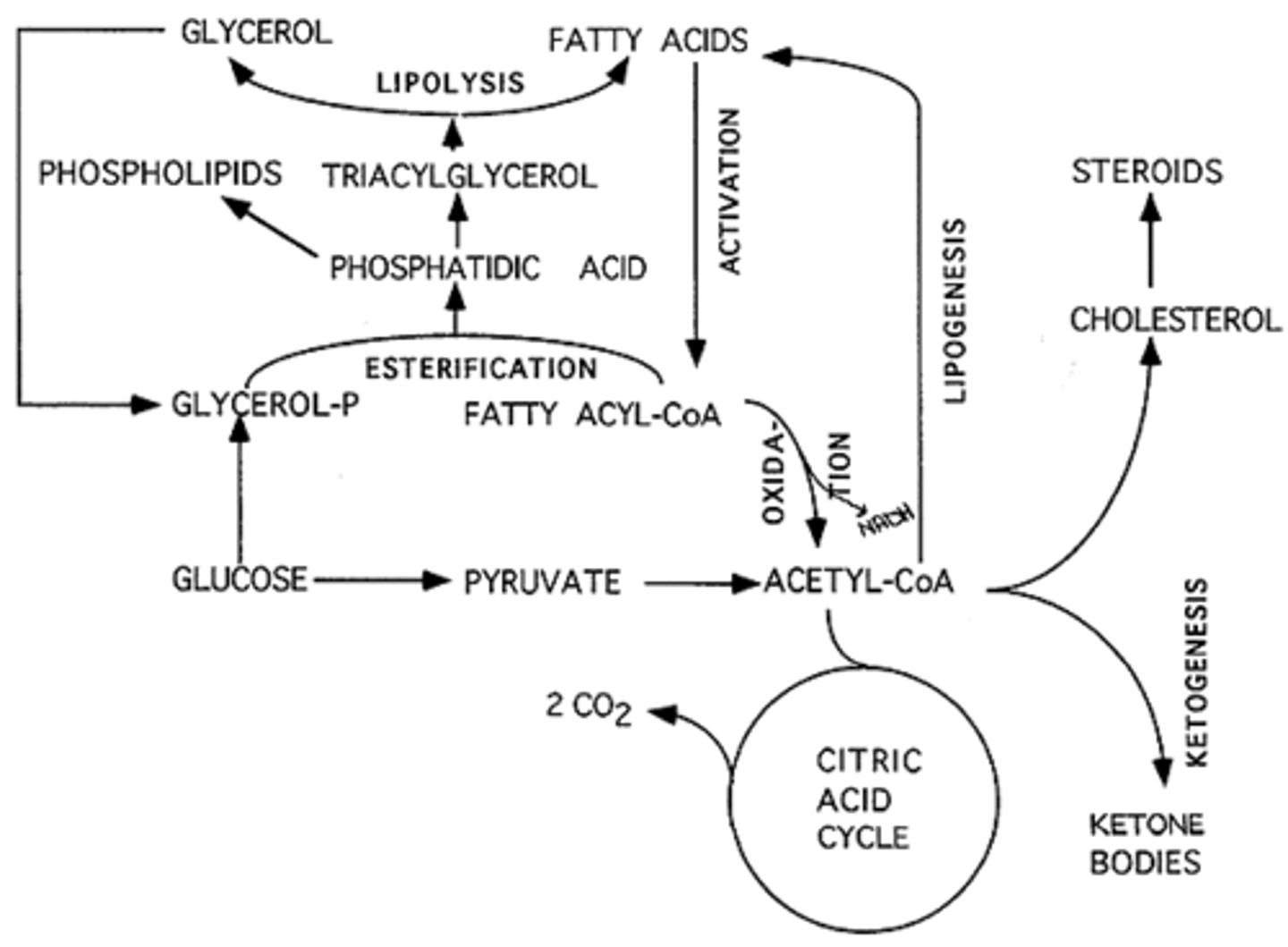
True or False? During the Post-absorptive State in the Adipose Tissue, Triglycerides may be broken down into Fatty Acids, which can then immediately be converted into glucose and ketones for energy throughout the body.
False. The Fatty Acids must be transported to the liver where they can be broken down into ketone bodies for energy.
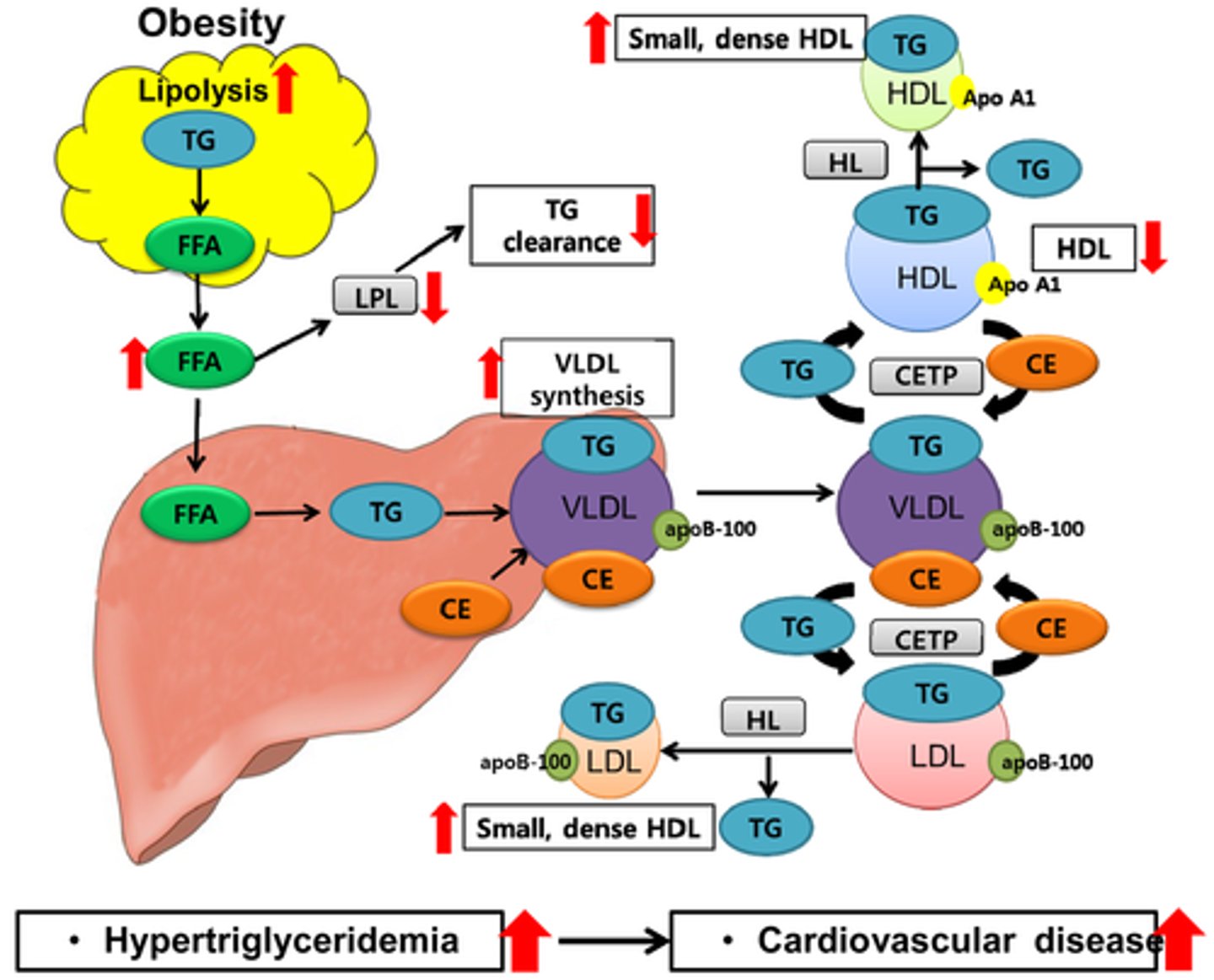
If breaking down glucose into lactate can generate energy in the muscles at a faster rate than aerobic respiration, why don't we do this all the time?
Breaking down glucose into lactate (anaerobic respiration) is a very inefficient process, producing way less ATP per glucose molecule than aerobic respiration. Also, lactate is acidic, which will disturb the local environment.
True or False? The Brain is generally characterized by Catabolism during both the Absorptive State and the Post-absorptive State.
True. The Brain is generally characterized by Catabolism during both the Absorptive State and the Post-absorptive State.
In the Post-absorptive State, which of the following are generally used for energy in the brain?
I. Glucose
II. Ketones
III. Fatty Acids
(A) I Only
(B) II Only
(C) I and II Only
(D) I and III Only
(C) I and II Only
In the Post-absorptive State, glucose and ketones are generally used for energy in the brain
Which area of the body will typically utilize most of the glucose that you consume on a normal day?
(A) The Liver
(B) Skeletal Muscle
(C) The Integument
(D) The Brain
(D) The Brain
The Brain utilizes about 20-25% of all the glucose you consume in a single day.
Chronic Hyperglycemia (Diabetes) may result in which of the following?
I. Eye damage
II. Lethargy
III. Kidney Disease
(A) I Only
(B) II Only
(C) I and III Only
(D) I, II, and III
(C) I and III Only
Chronic Hyperglycemia (Diabetes) may result in eye, nerve, and kidney disease/damage.
Hypoglycemia will result in lethargy, coma, or even death!
Insulin will be released in periods of ______________, and glucagon will be released in periods of ___________.
(A) hypoglycemia, hypoglycemia
(B) hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia
(C) hyperglycemia, hyperglycemia
(D) hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia
(D) hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia
Insulin will be released in periods of hyperglycemia, and glucagon will be released in periods of hypoglycemia.
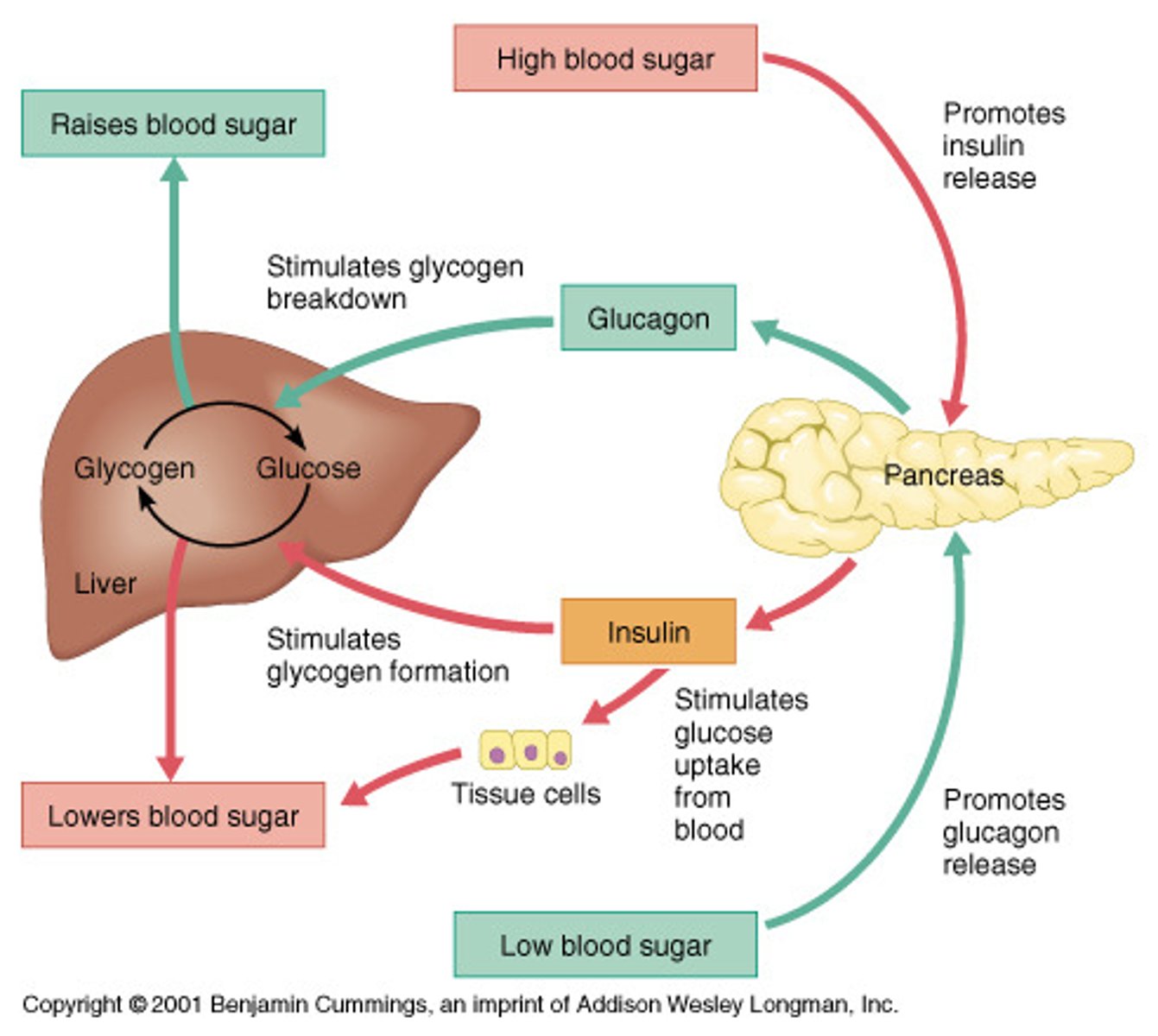
CRB What is the main inhibitor of Glucagon release?
(A) Hyperglycemia
(B) Insulin Release
(C) Basic amino acids
(D) Increased blood Osmolarity
(A) Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia is the main inhibitor of Glucagon release.
Basic amino acids in the blood actually trigger Glucagon release!
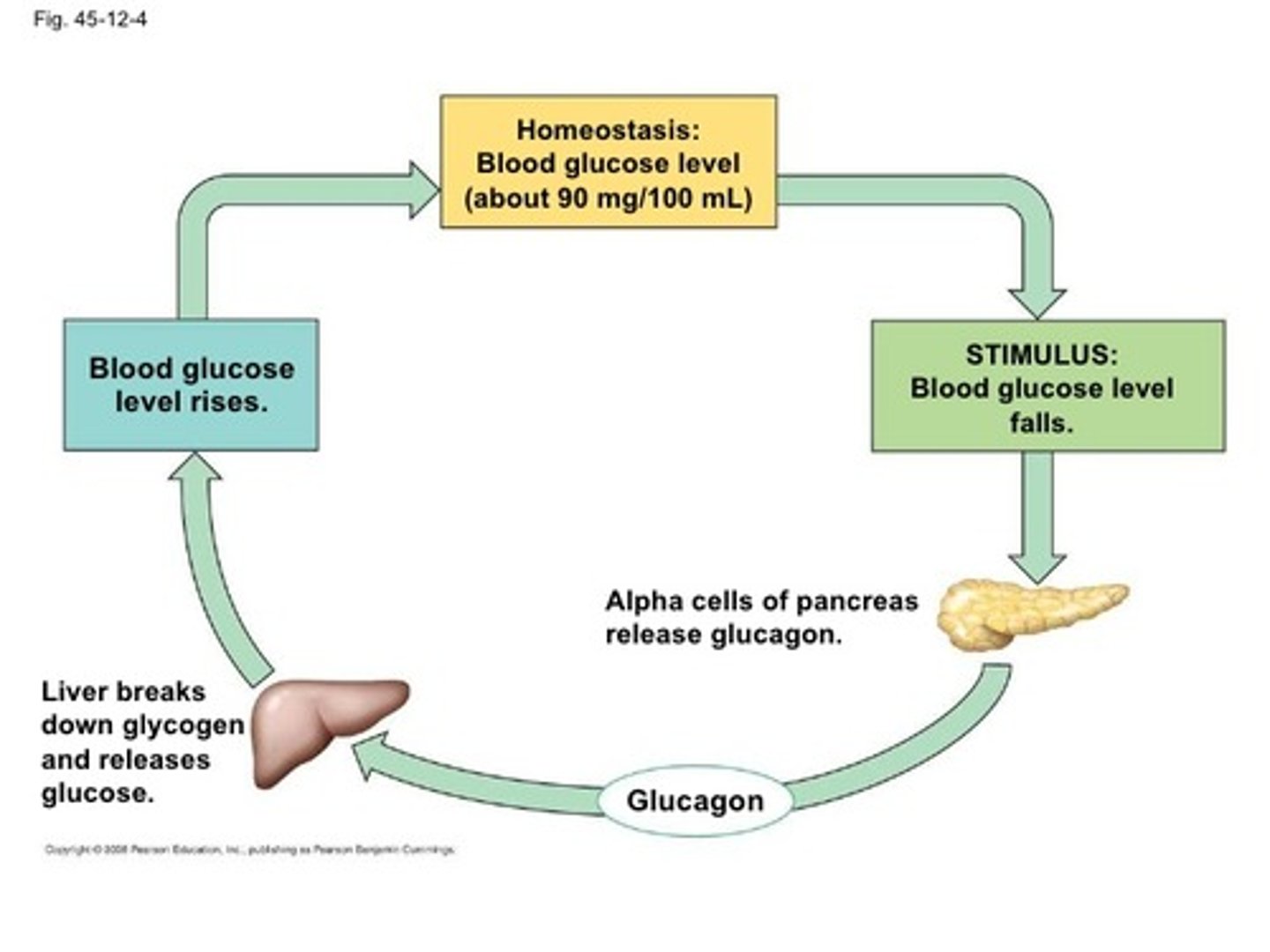
CRB Which of the following statements best describes the structure of Glucagon and Insulin?
(A) Both Glucagon and Insulin are Peptide Hormones.
(B) Glucagon is a Peptide Hormone and Insulin is a Steroid.
(C) Glucagon is a Steroid and Insulin is a Peptide Hormone.
(D) Both Glucagon and Insulin are Steroid Hormones.
(A) Both Glucagon and Insulin are Peptide Hormones.
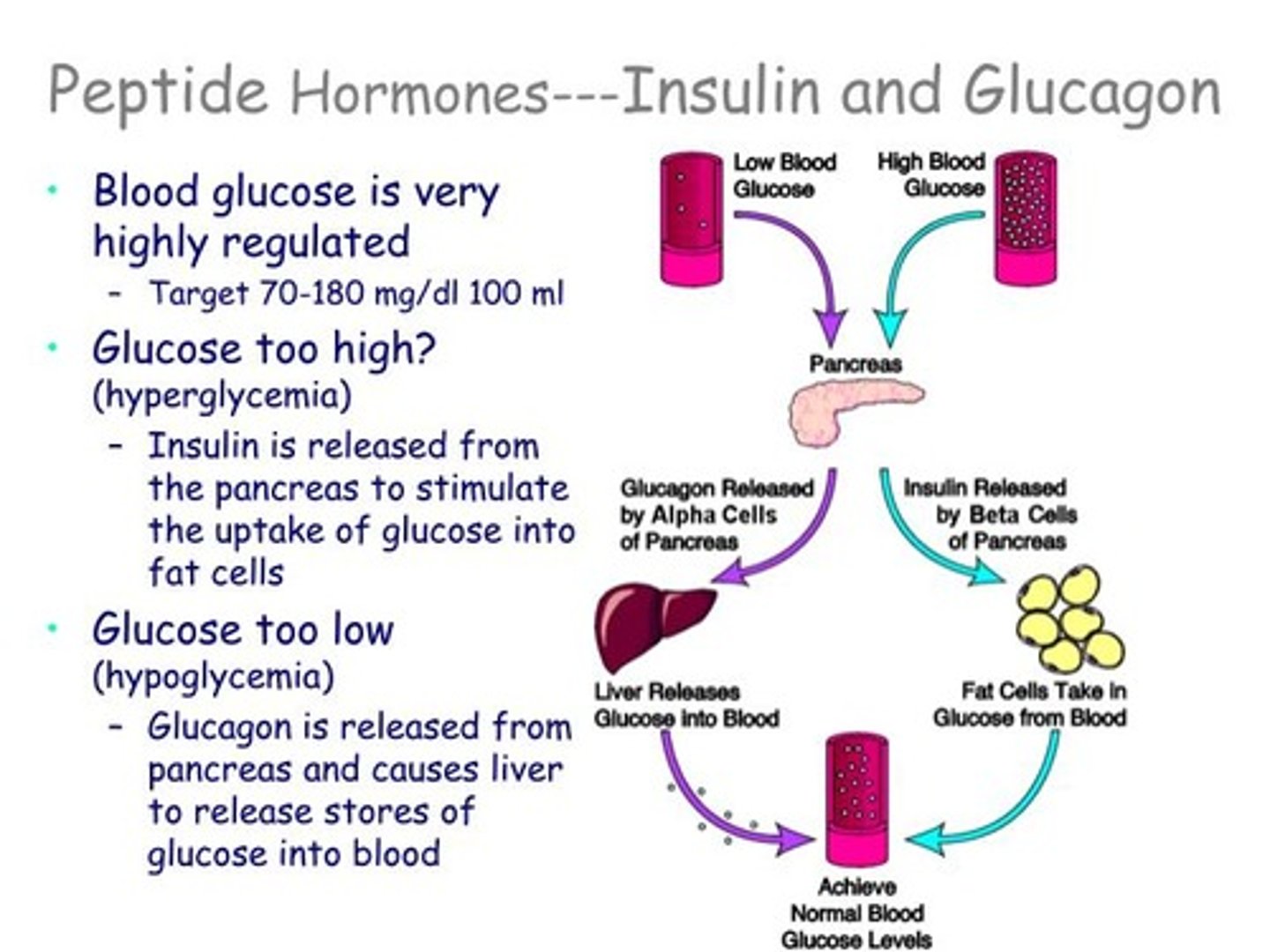
CRB Which of the following statements about Insulin release are true?
I. As a Peptide Hormone, Insulin is stored in β-cells in vesicles normally.
II. When increased glucose triggers Insulin release, there is a response within a few minutes because of vesicle secretion of already-made Insulin.
III. About half an hour after the first release of insulin, if blood glucose levels are still above threshold, then new Insulin that has just been synthesized is ready to be released.
(A) III only
(B) I and II only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II and III
(D) I, II and III
Each of the following statements about Insulin release are true:
I. As a Peptide Hormone, Insulin is stored in β-cells in vesicles normally.
II. When increased glucose triggers Insulin release, there is a response within a few minutes because of vesicle secretion of already-made Insulin.
III. About half an hour after the first release of insulin, if blood glucose levels are still above threshold, then new Insulin that has just been synthesized is ready to be released.
Insulin causes glucose ___________, and glucagon causes glucose _____________.
(A) storage, storage
(B) storage, release
(C) release, release
(D) release, storage
(B) storage, release
Insulin causes glucose storage, and glucagon causes glucose release.
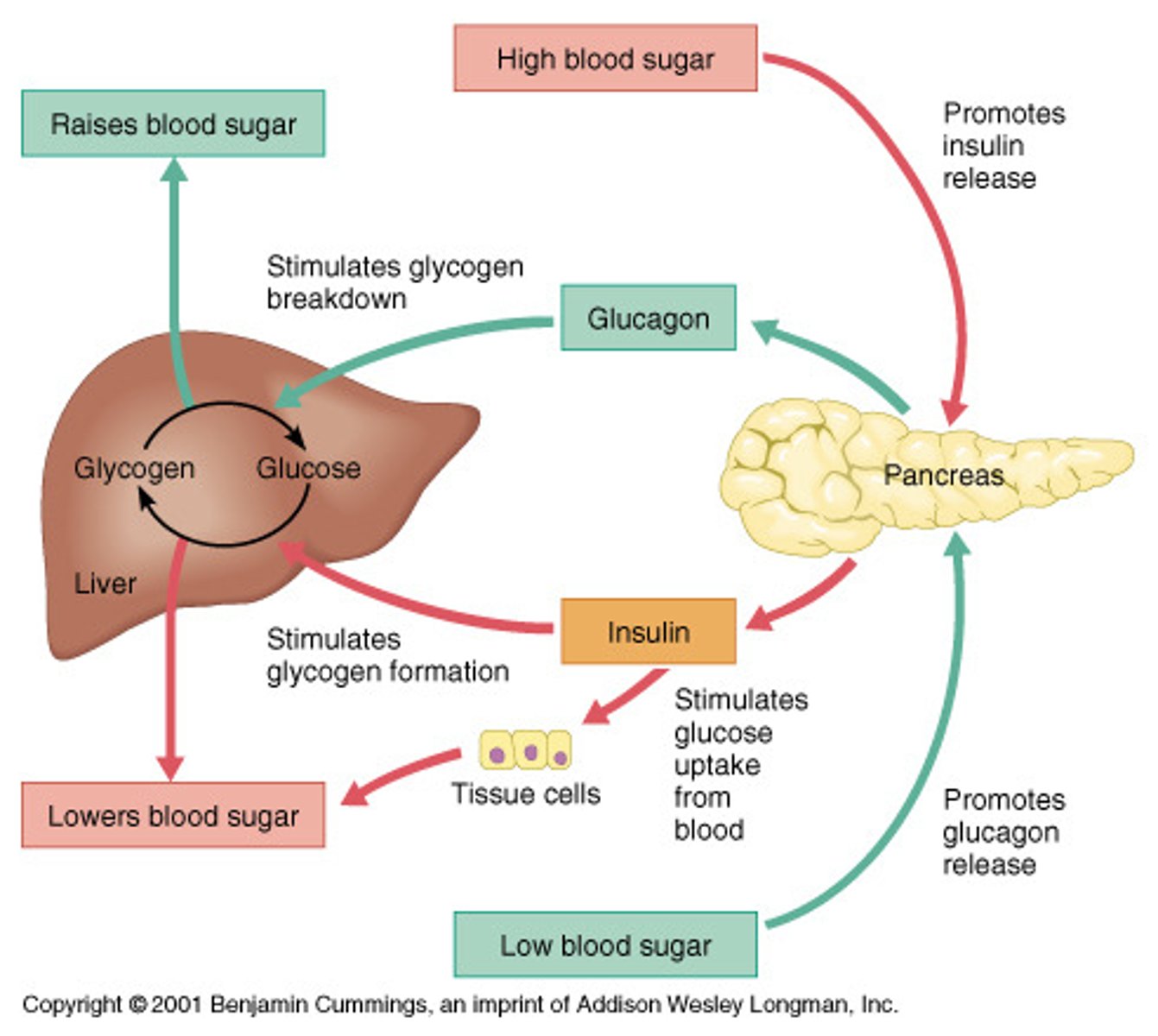
CRB Glucagon can be considered a Counterregulatory Hormone because its actions oppose insulin. Which of the following is NOT another Counterregulatory Hormone?
(A) Cortisol
(B) Growth Hormone
(C) Prolactin
(D) Epinephrine and Norepinephrine
(C) Prolactin
Cortisol, Growth Hormone, Epinephrine and Norepinephrine are all considered Counterregulatory Hormones.
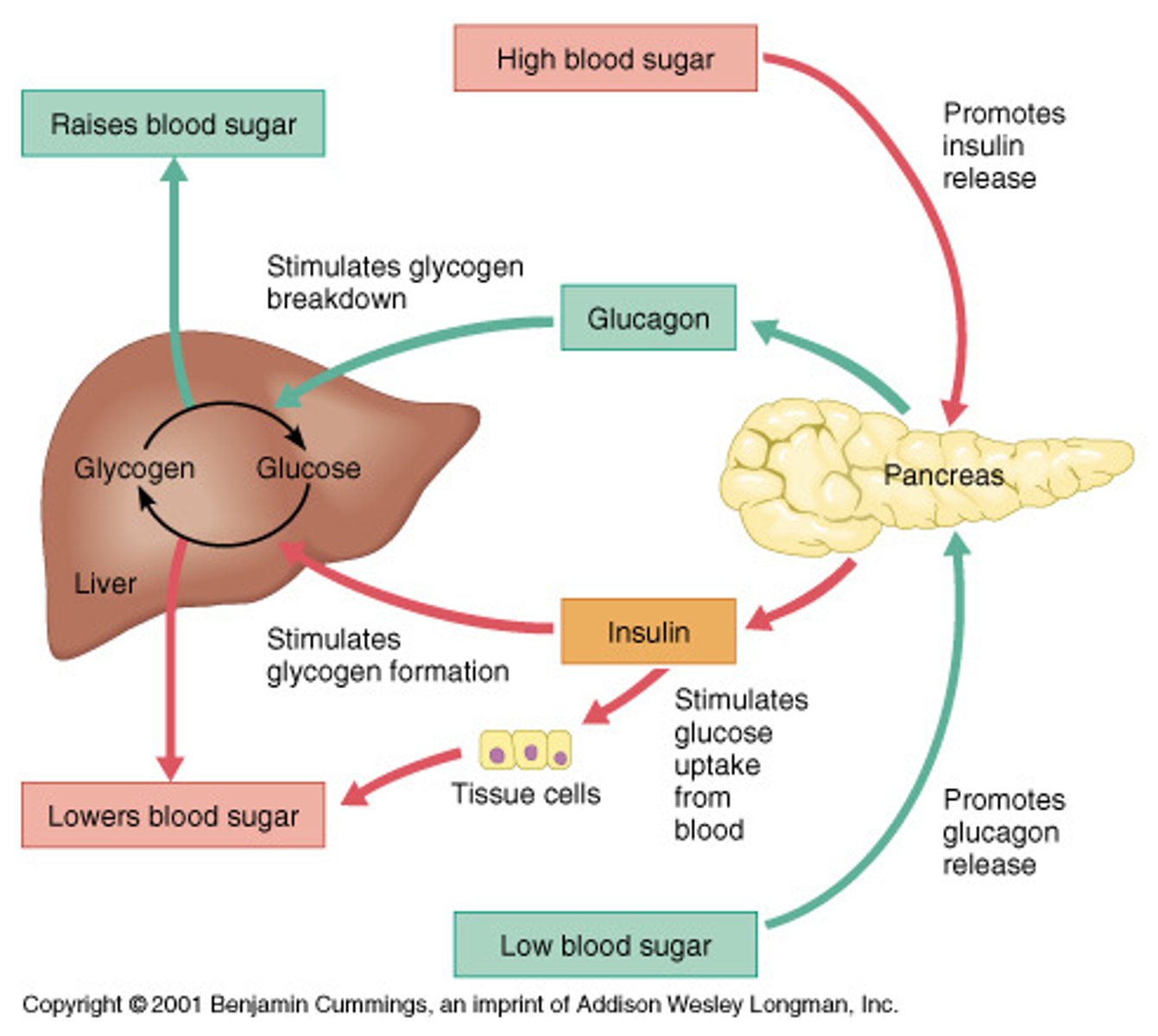
Insulin will stimulate:
Gluconeogenesis or Glycolysis?
Glycogenesis or Glycogenolysis?
Lipogenesis or Lipolysis?
Insulin will stimulate:
- Glycolysis
- Glycogenesis
- Lipogenesis
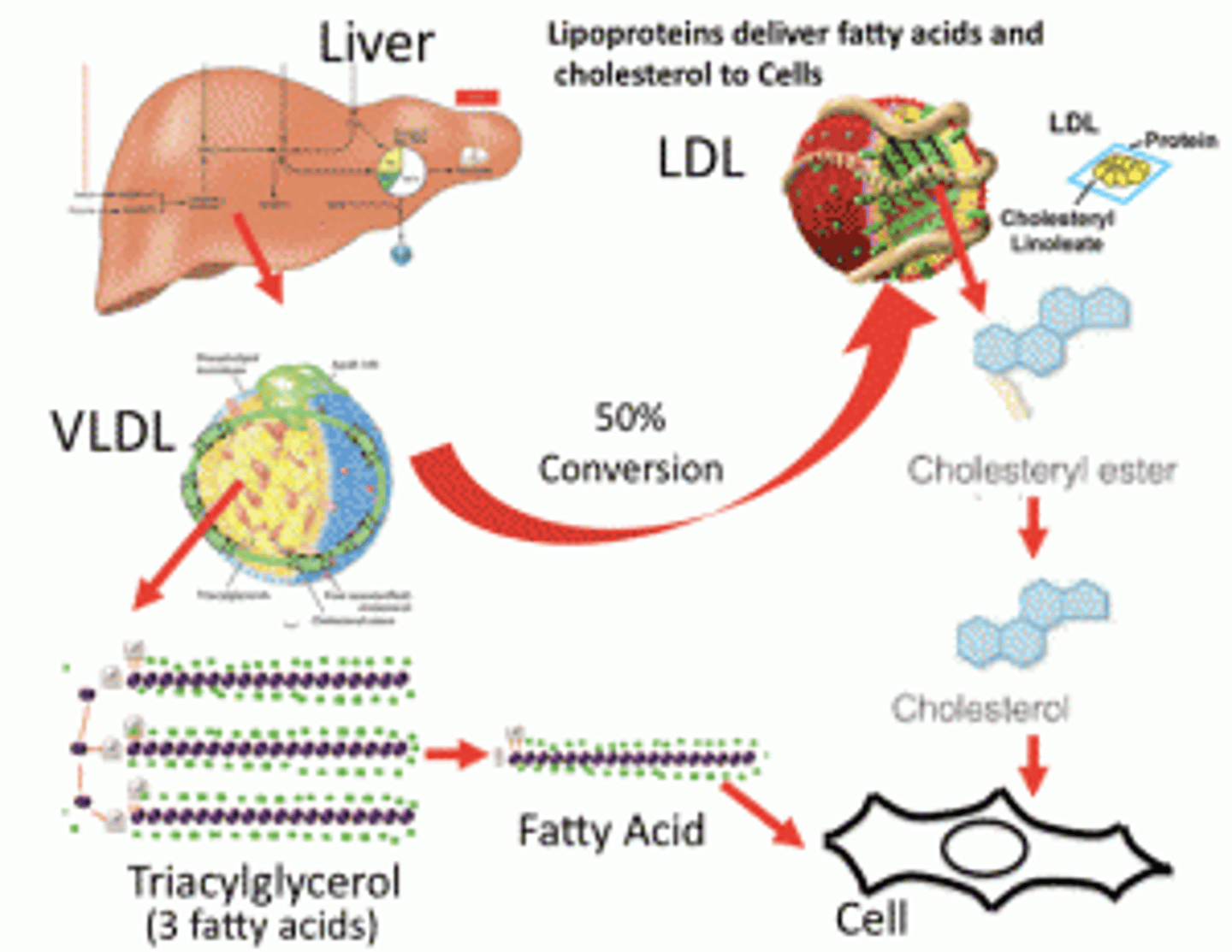
CRB After Insulin has stimulated Lipogenesis in the liver, how are the Fatty Acids stored?
(A) They are converted to Triacylglycerols and stored in the liver.
(B) They are converted to Triacylglycerols and released into the blood as VLDL.
(C) They are converted to Triacylglycerols and released into the blood as LDL.
(D) They are converted to Triacylglycerols and released into the blood as HDL.
(B) They are converted to Triacylglycerols and released into the blood as VLDL.
Triacylglycerols are often called Triglycerides, and VLDL stands for Very Low Density Lipoprotein.
CRB Which of the following is NOT one of the three major target tissues for Insulin?
(A) Liver
(B) Brain
(C) Muscle
(D) Adipose Tissue
(B) Brain
The three major target tissues for Insulin are the Liver, Muscle and Adipose Tissue.
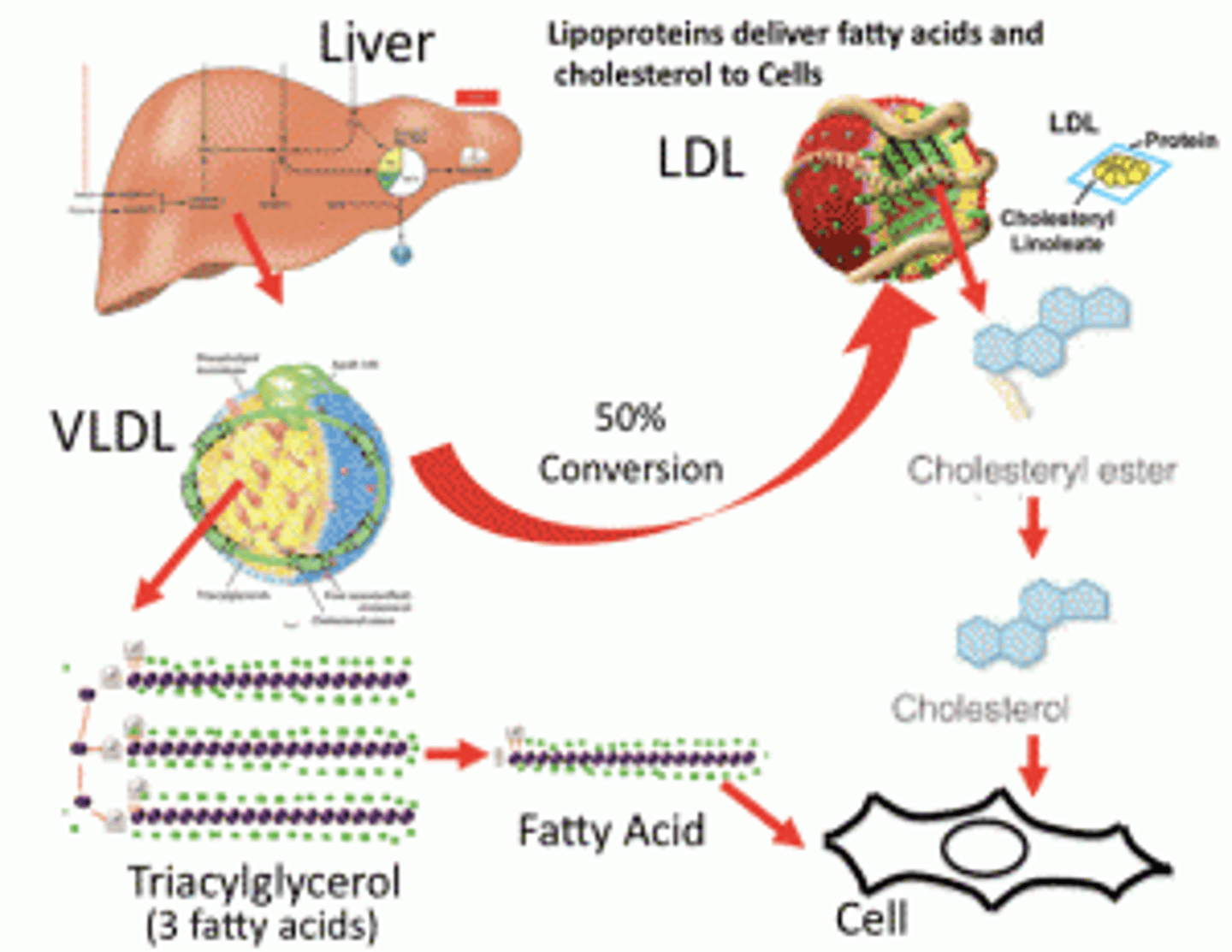
CRB True or false? The red blood cells and nervous tissue are particularly Insulin-resistant.
True. The red blood cells and nervous tissue are particularly Insulin-resistant.
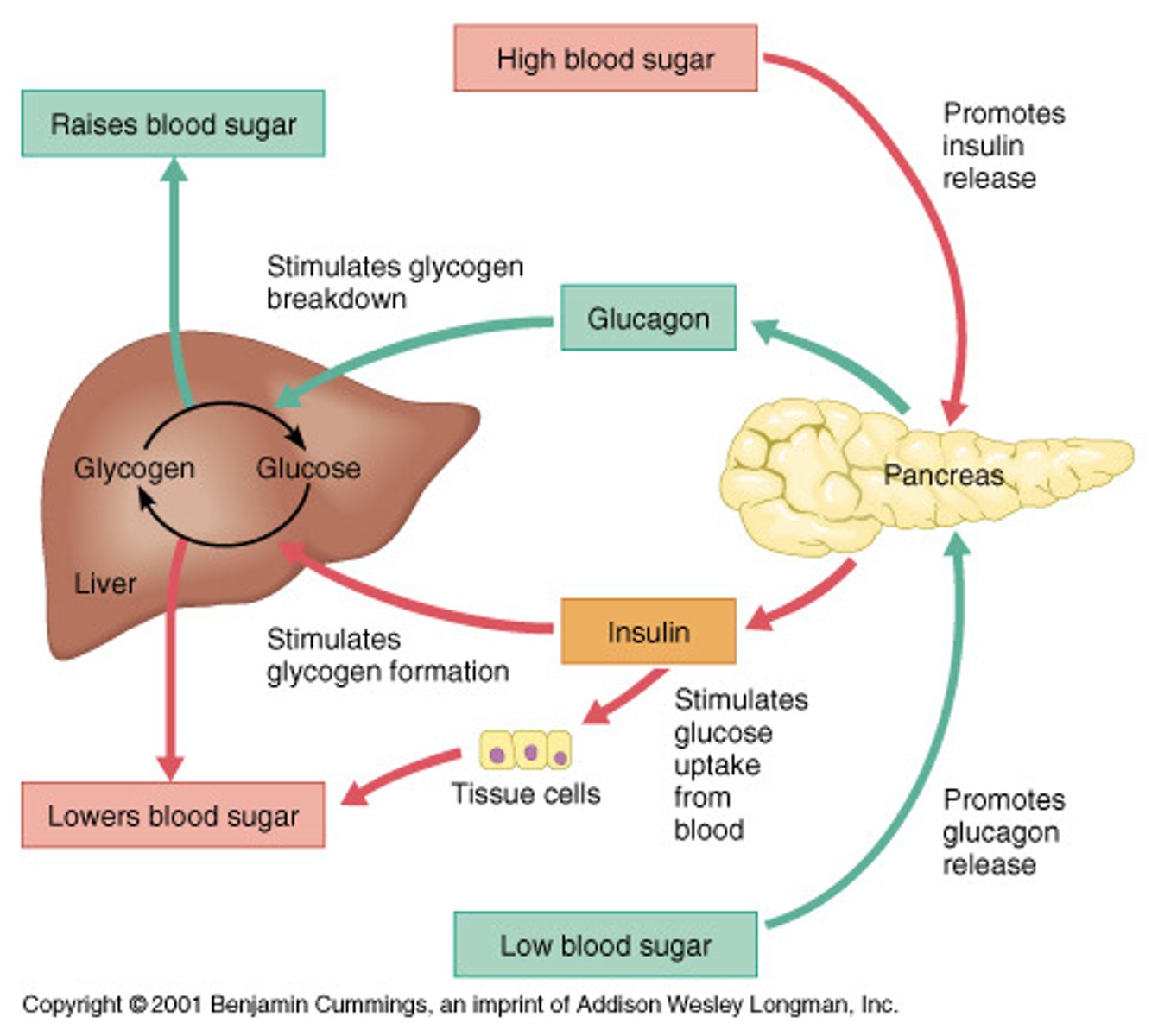
Glucagon will stimulate:
Gluconeogenesis or Glycolysis?
Glycogenesis or Glycogenolysis?
Lipogenesis or Lipolysis?
Glucagon will stimulate:
- Gluconeogenesis
- Glycogenolysis
- Lipolysis
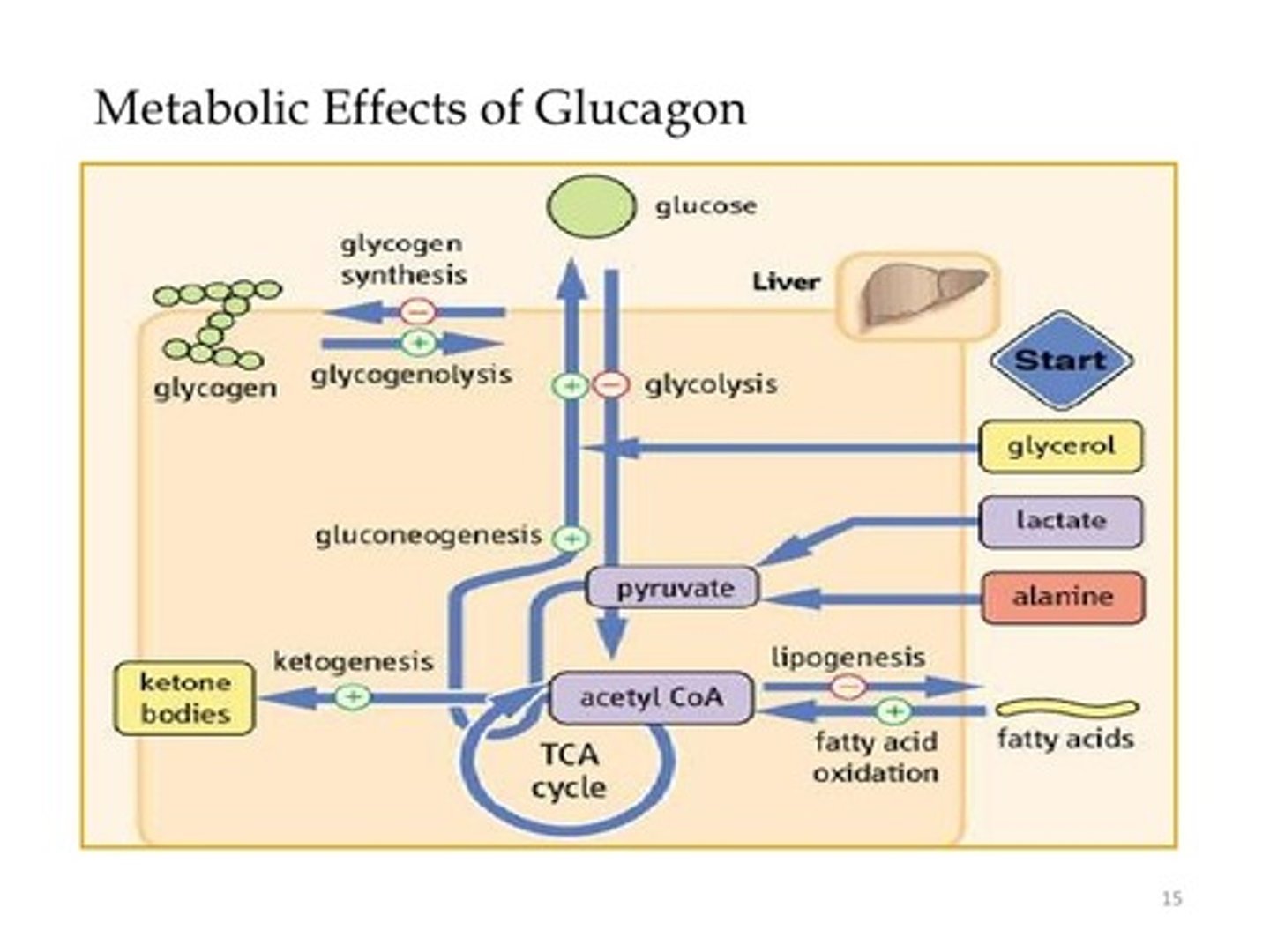
True or False? Insulin will stimulate Ketogenesis in order to store more energy.
False. GLUCAGON will stimulate Ketogenesis in order to produce more energy that can be utilized by the heart and the brain during periods of hypoglycemia.
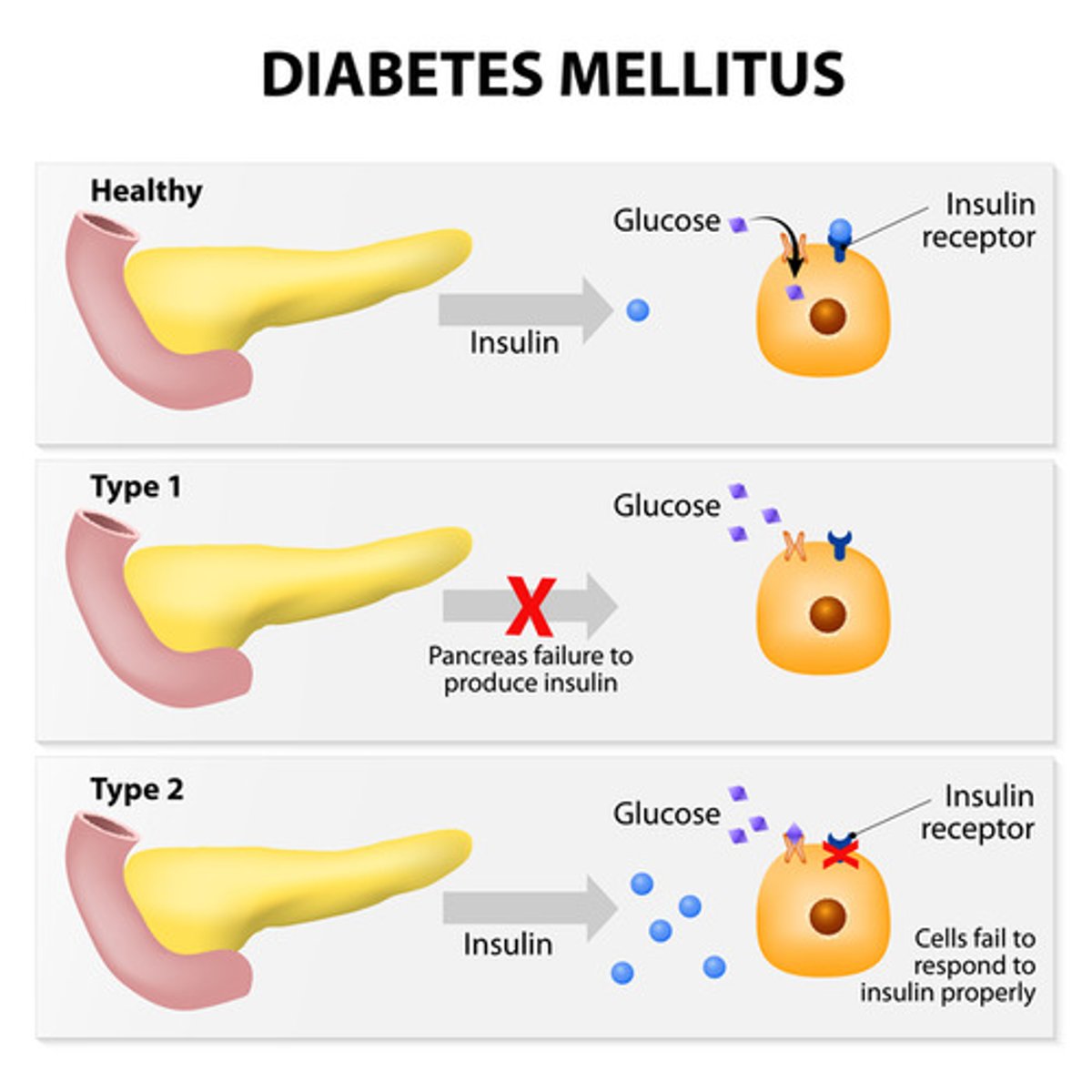
Compare the cause of Type I versus Type II Diabetes.
Type I Diabetes results from an inability of the pancreas to produce insulin. This usually occurs early on in life.
Type II Diabetes results from desensitized insulin receptors and usually occurs later in life.

Compare the treatment for Type I versus Type II Diabetes.
Insulin may be injected in either case, but will be much more effective for Type I Diabetes.
Treatment of Type II Diabetes seeks to re-sensitize the receptors either through drugs or lifestyle changes (diet, exercise, etc).
CRB Fill in the blanks: Because treatment with insulin is the only effective treatment for ______________ Diabetes, it is called Insulin-Dependent. ____________ Diabetes can be treated also with drugs to re-sensitize the insulin receptors or increase insulin production, making it non-insulin dependent.
(A) Type I, Type II
(B) Insipidus, Mellitus
(C) Mellitus, Insipidus
(D) Type II, Type I
(A) Type I, Type II
Because treatment with insulin is the only effective treatment for Type I Diabetes, it is called Insulin-Dependent. Type II Diabetes can be treated also with drugs to re-sensitize the insulin receptors or increase insulin production, making it non-insulin dependent.
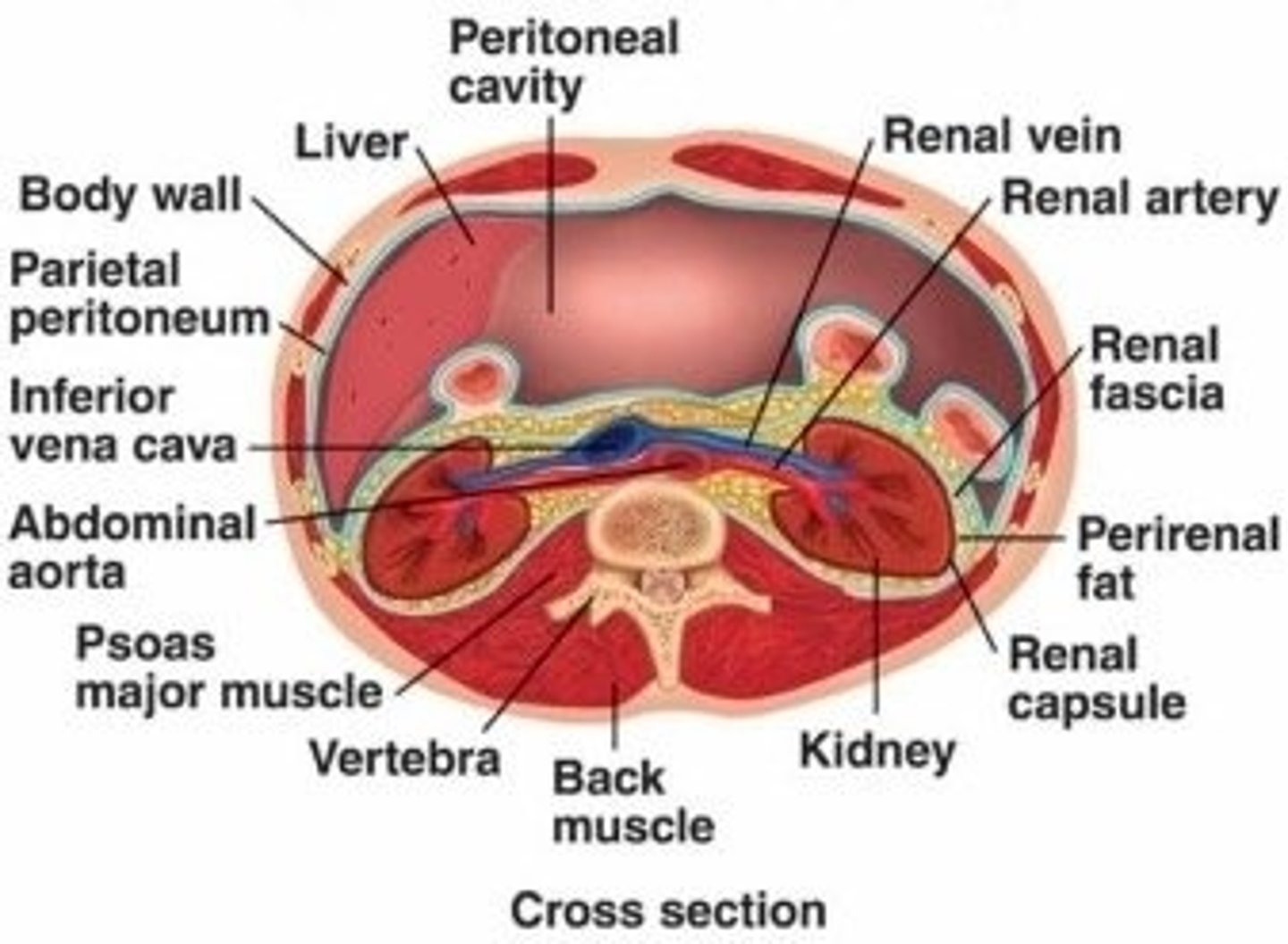
The Liver sits in the:
(A) Retroperitoneum
(B) Anteroperitoneum
(C) Peritoneum
(D) Central Peritoneum
(C) Peritoneum
The Liver sits in the Peritoneum.
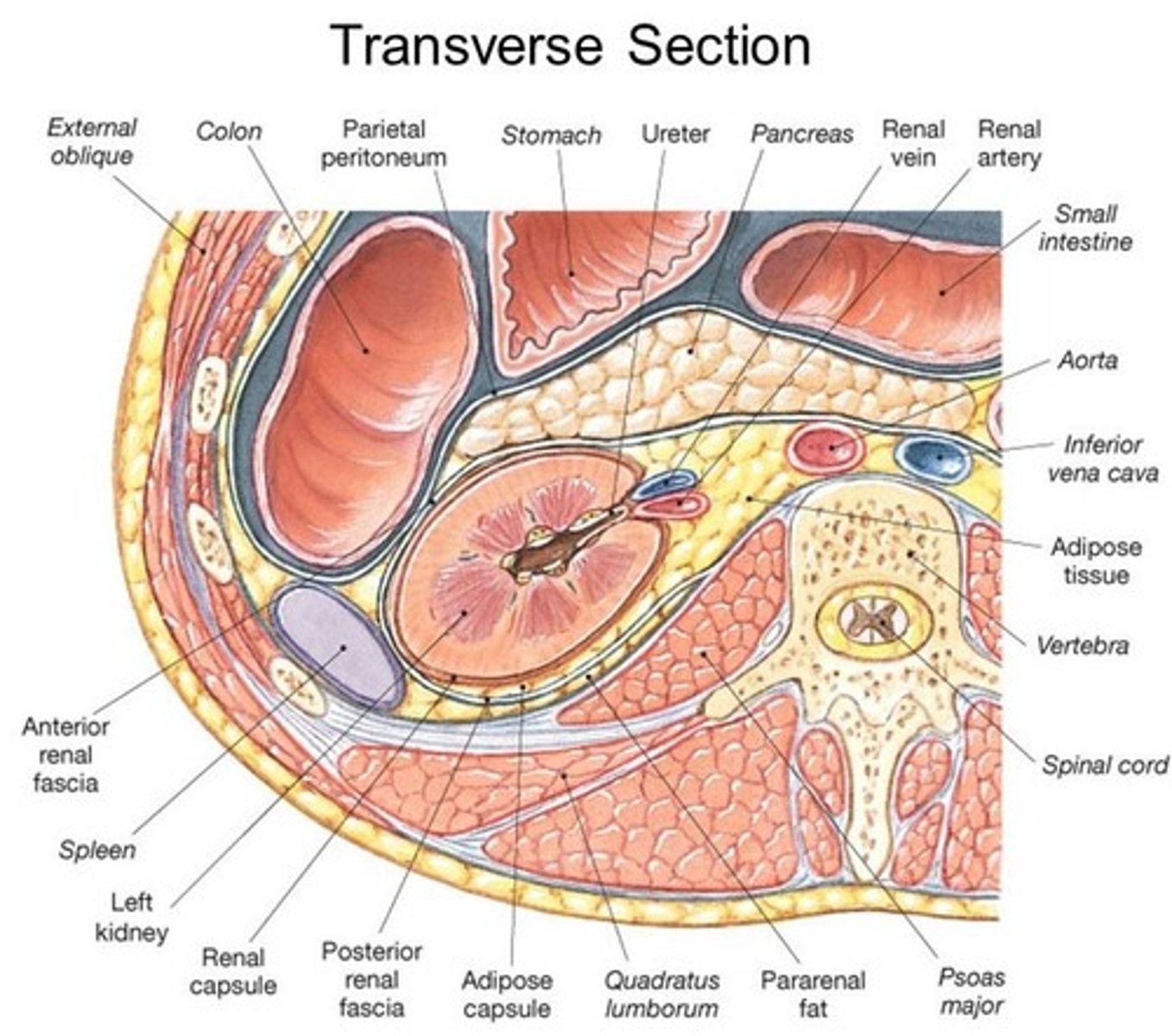
The Pancreas sits in the:
(A) Retroperitoneum
(B) Anteroperitoneum
(C) Peritoneum
(D) Central Peritoneum
(A) Retroperitoneum
The Pancreas sits in the Retroperitoneum (to the back and to the left, behind the parietal peritoneum).
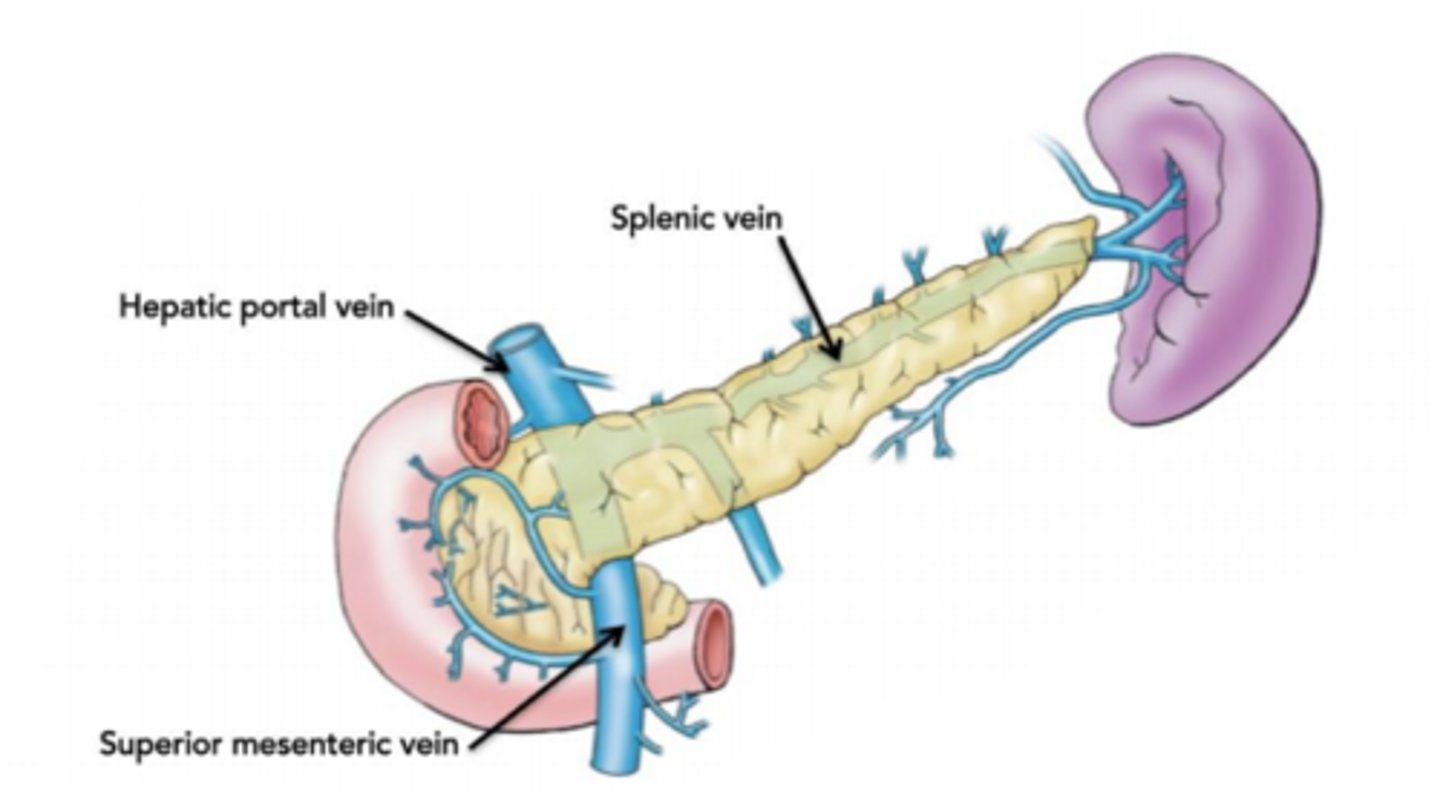
The Hepatic Portal System carries blood from the Small Intestines to the Liver. Why might the portal veins pass through the pancreas on their way to the Liver?
The portal veins pass through the pancreas in order to give it signals regarding food intake so that it knows what hormones to produce.
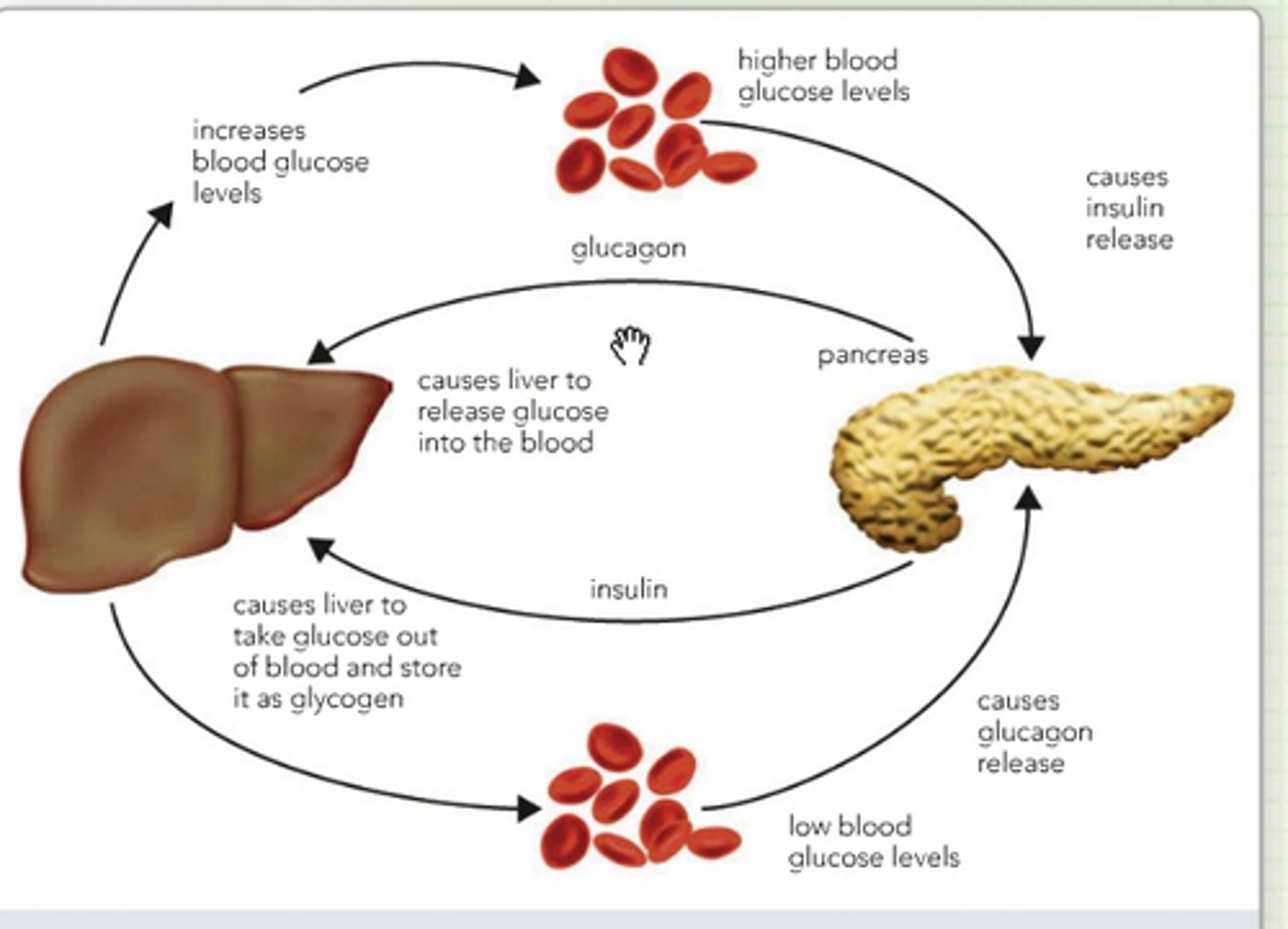
The Pancreatic Endocrine Glands will release hormones. These hormones will exert their greatest effect on which organ?
(A) The Brain
(B) The Pancreas
(C) The Liver
(D) The Kidneys
(C) The Liver
These hormones will have an effect that is 4x greater at the Liver than anywhere else in the body.
__-cells within the Islet of Langerhans are responsible for producing Insulin. __-cells within the Islet of Langerhans are responsible for producing Glucagon.
(A) α, α
(B) α, β
(C) β, β
(D) β, α
(D) β, α
β-cells within the Islet of Langerhans are responsible for producing Insulin. α-cells within the Islet of Langerhans are responsible for producing Glucagon.
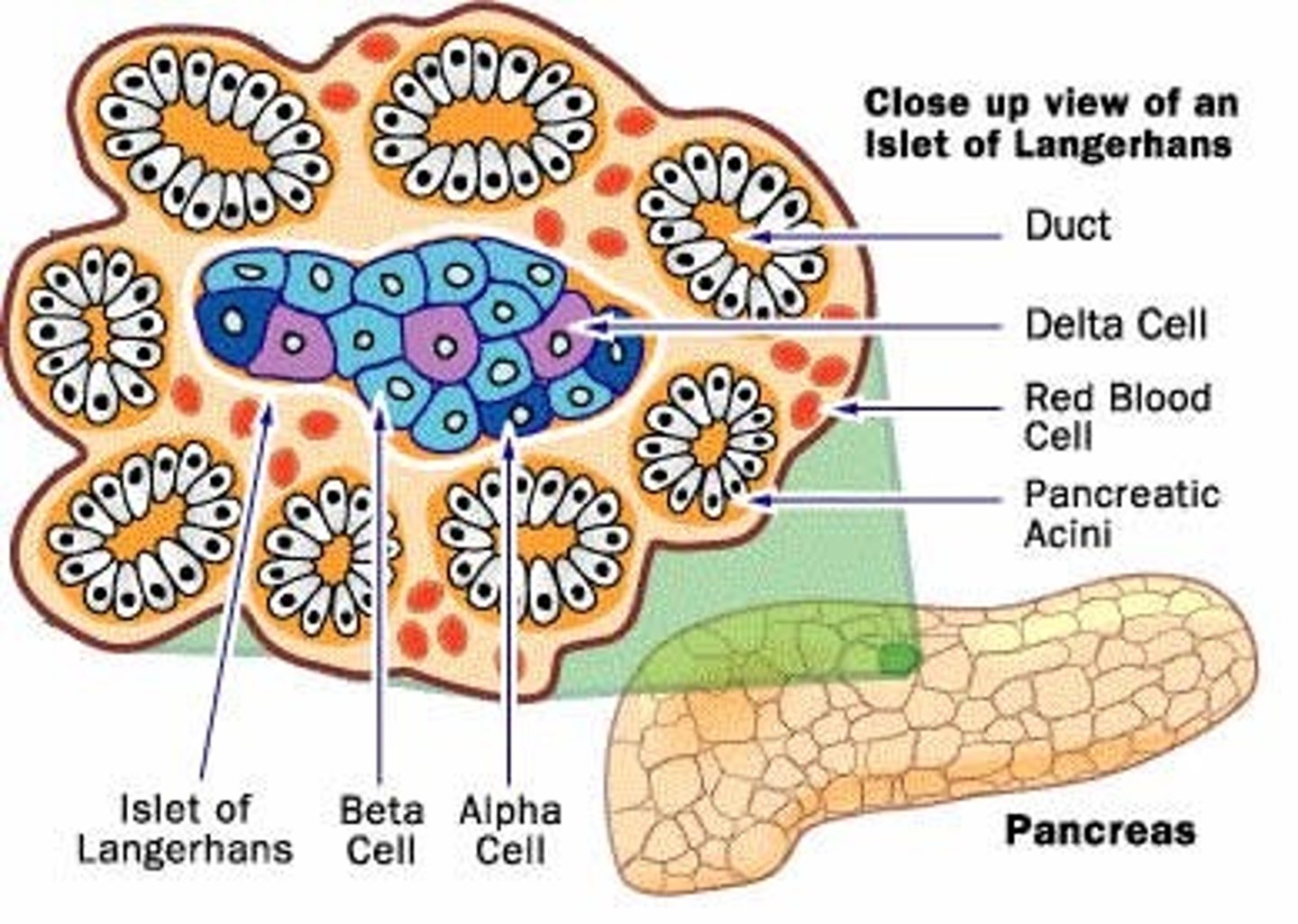
β-cells are equipped with which glucose transporter?
(A) GLUT1
(B) GLUT2
(C) GLUT3
(D) GLUT4
(B) GLUT2
β-cells are equipped with GLUT2.
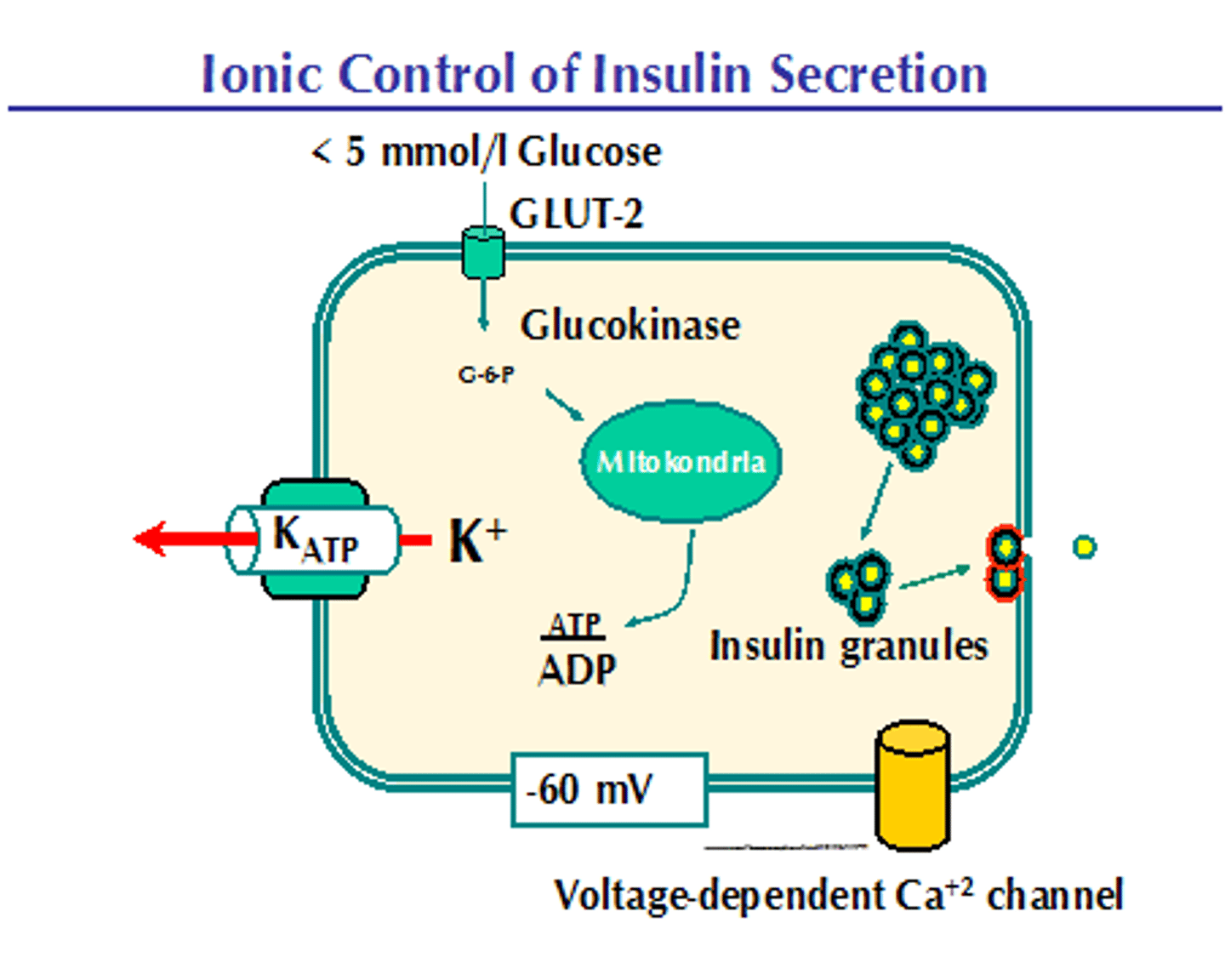
CRB Adipose Tissue and Muscles are equipped with which glucose transporter?
(A) GLUT1
(B) GLUT2
(C) GLUT3
(D) GLUT4
(D) GLUT4
Adipose Tissue and Muscles are equipped with GLUT4.
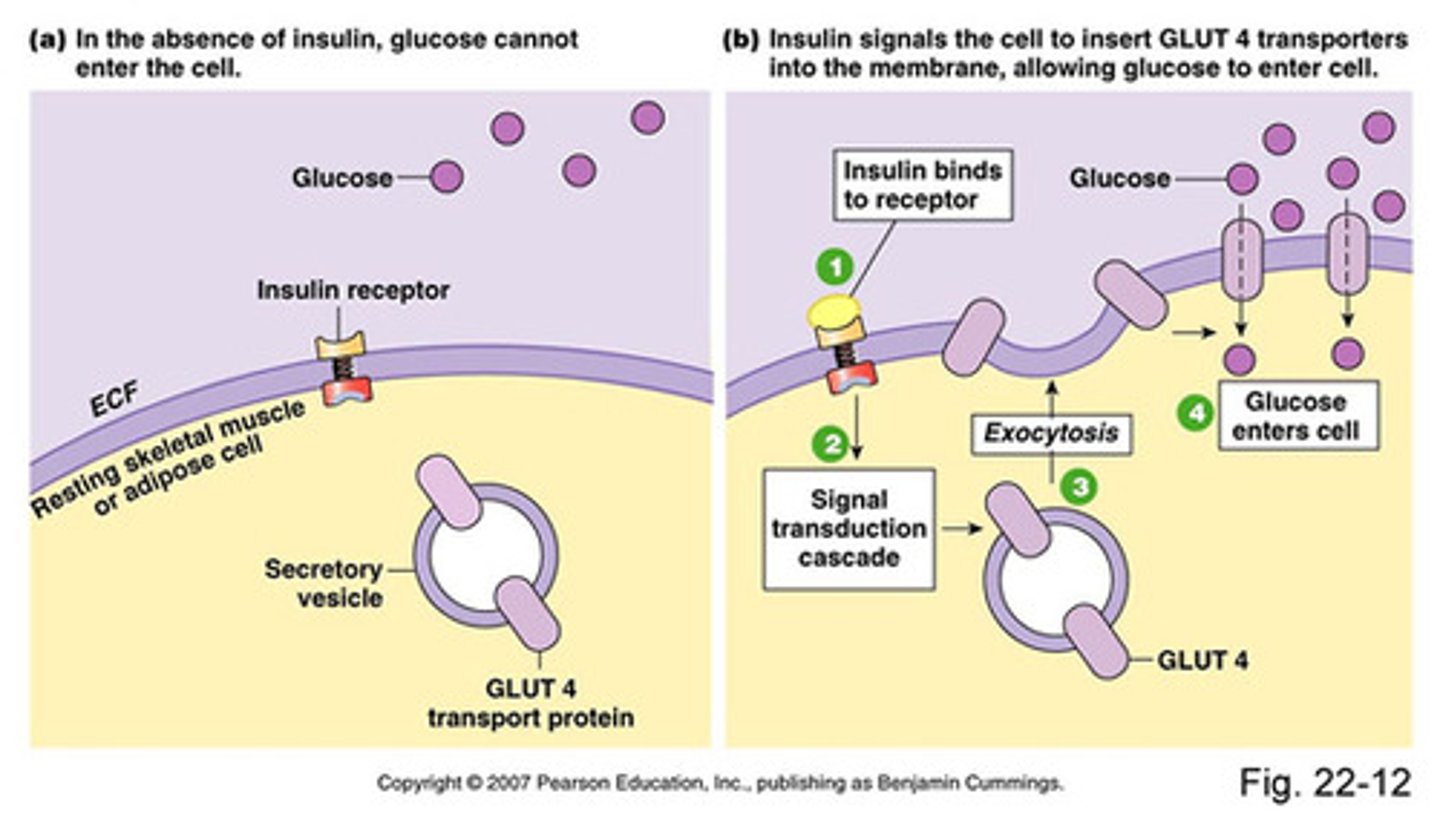
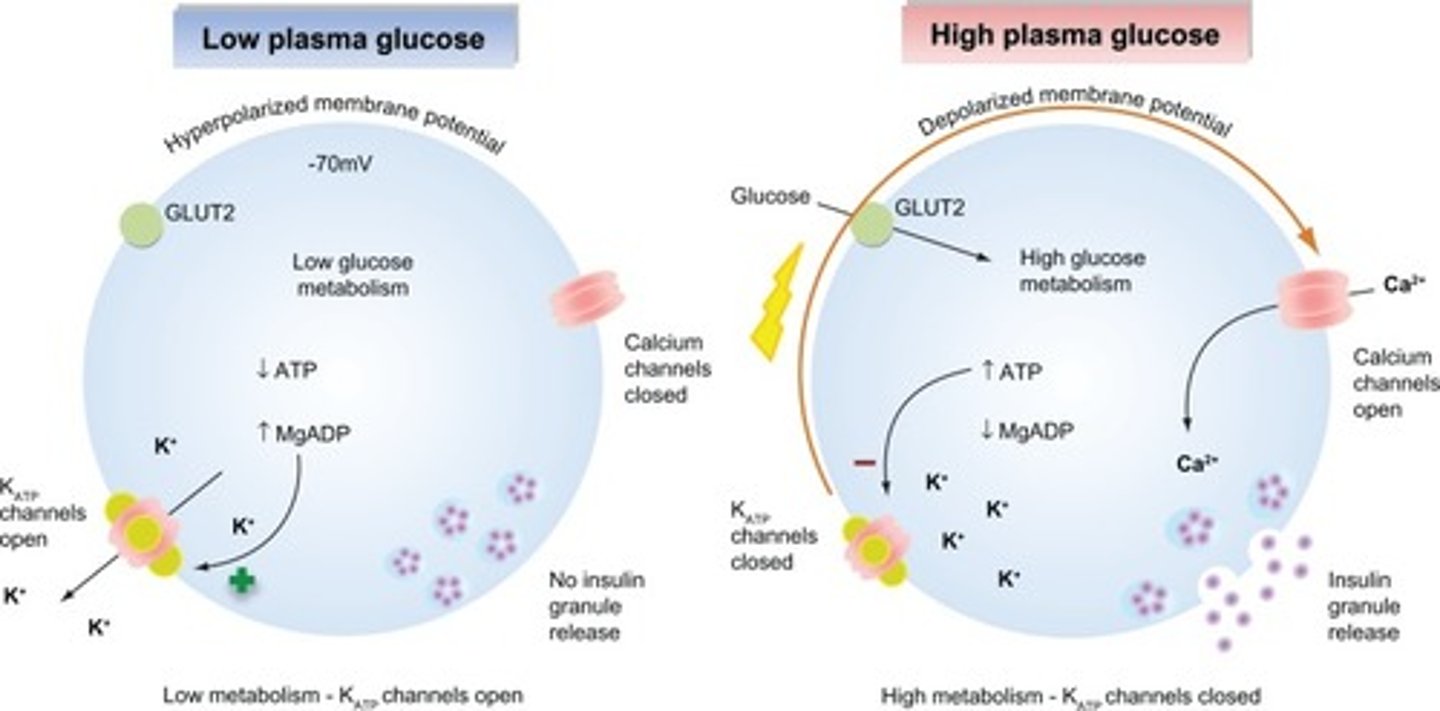
A large amount of glucose enters the GLUT2 transporter. Describe each step that will eventually result in this β-cell releasing Insulin.
1. Glucose enters the β-cell via the GLUT2 transporter.
2. The glucose undergoes glycolysis, Kreb's cycle and ETC, resulting in ATP production.
3. This ATP binds to a Potassium Channel, inhibiting it from causing K+ export.
4. K+ builds up in the cell, resulting in a change to the voltage potential, which causes a voltage-gated Ca2+ channel to be activated, resulting in the influx of Ca2+ ions.
5. Ca2+ ions bind to vessicles containing insulin, giving them the signal to fuse with the cell membrane and release insulin into the blood stream.
CRB Because GLUT2 will only take up glucose if its at high concentrations, and GLUT4 will take up glucose even at lower concentrations, which is a higher affinity transporter?
(A) GLUT2, since concentrations are higher when it is transporting.
(B) GLUT2, because the lowest number GLUTs are higher affinity.
(C) GLUT4, since it does not need as high concentrations to transport glucose.
(D) GLUT4, because the higher number GLUTs are higher affinity.
(C) GLUT4, since it does not need as high concentrations to transport glucose.
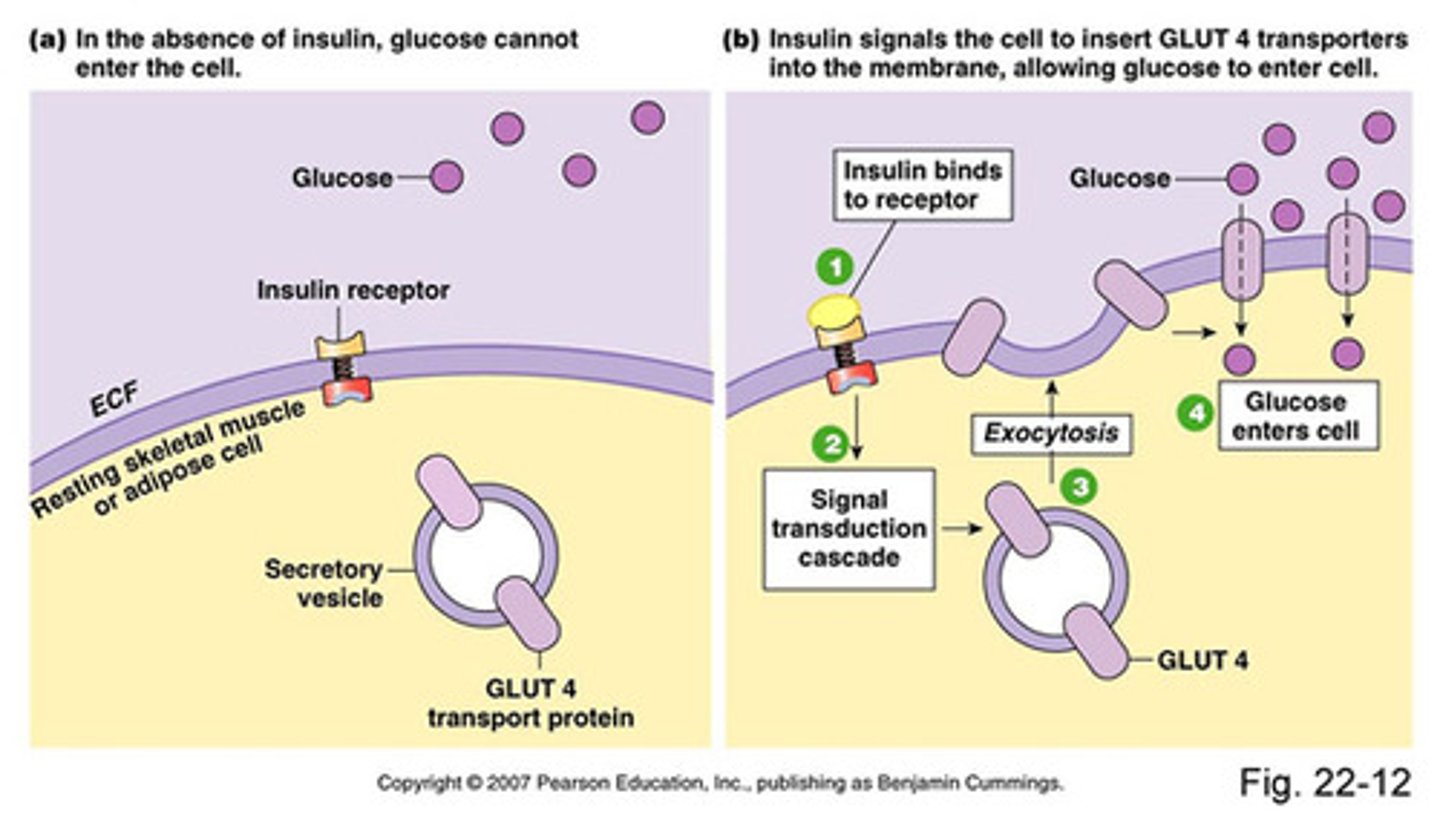
CRB True or false? Insulin's primary effect on Muscle is to take the GLUT4 transporters, typically found in endosomes, and have them inserted into the plasma membrane, so that more glucose will be uptaken.
True. Insulin's primary effect on Muscle is to take the GLUT4 transporters, typically found in endosomes, and have them inserted into the plasma membrane, so that more glucose will be uptaken.
CRB True or false? Many of the enzymes that insulin secretion will phosphorylate will be dephosphorylated by Glucagon Secretion.
True. Many of the enzymes that insulin secretion will phosphorylate will be dephosphorylated by Glucagon Secretion.
Although we know relatively little regarding the mechanism of glucagon release from α-cells, we do know that it is triggered by:
(A) Glucose
(B) Glycogen
(C) Lipids
(D) Amino Acids
(D) Amino Acids
Although we know relatively little regarding the mechanism of glucagon release from α-cells, we do know that it is triggered by amino acids.
Which brain area is primarily responsible for the regulation of hunger?
(A) The Pituitary Gland
(B) The Pineal Gland
(C) The Hippocampus
(D) The Hypothalamus
(D) The Hypothalamus
The Hypothalamus is primarily responsible for the regulation of hunger

Billy is extremely hungry so he eats ten candy bars (c'mon Bill...). After finishing his candy bars, he realizes that he is no longer hungry. What happened at the receptors in his Hypothalamus that regulate hunger during the time he was hungry versus when he felt full?
When Billy was hungry, there was no insulin acting on and inhibiting the receptors at his hypothalamus.
Then Billy ate candy bars, which are high in glucose, he began to feel full because insulin began inhibiting these receptors, telling the Hypothalamus that there is no more need for eating.
Jack is also really hungry. He, however, decides to eat ten sticks of butter (gross...). After finishing his buttery feast, he realizes that he is no longer hungry. What happened at the receptors in his Hypothalamus that regulate hunger during the time he was hungry versus when he felt full?
When Jack was hungry, there was no leptin acting on and inhibiting the receptors at his hypothalamus.
Then Jack ate sticks of butter, which are high in fats/lipids, he began to feel full because leptin began inhibiting these receptors, telling the Hypothalamus that there is no more need for eating.
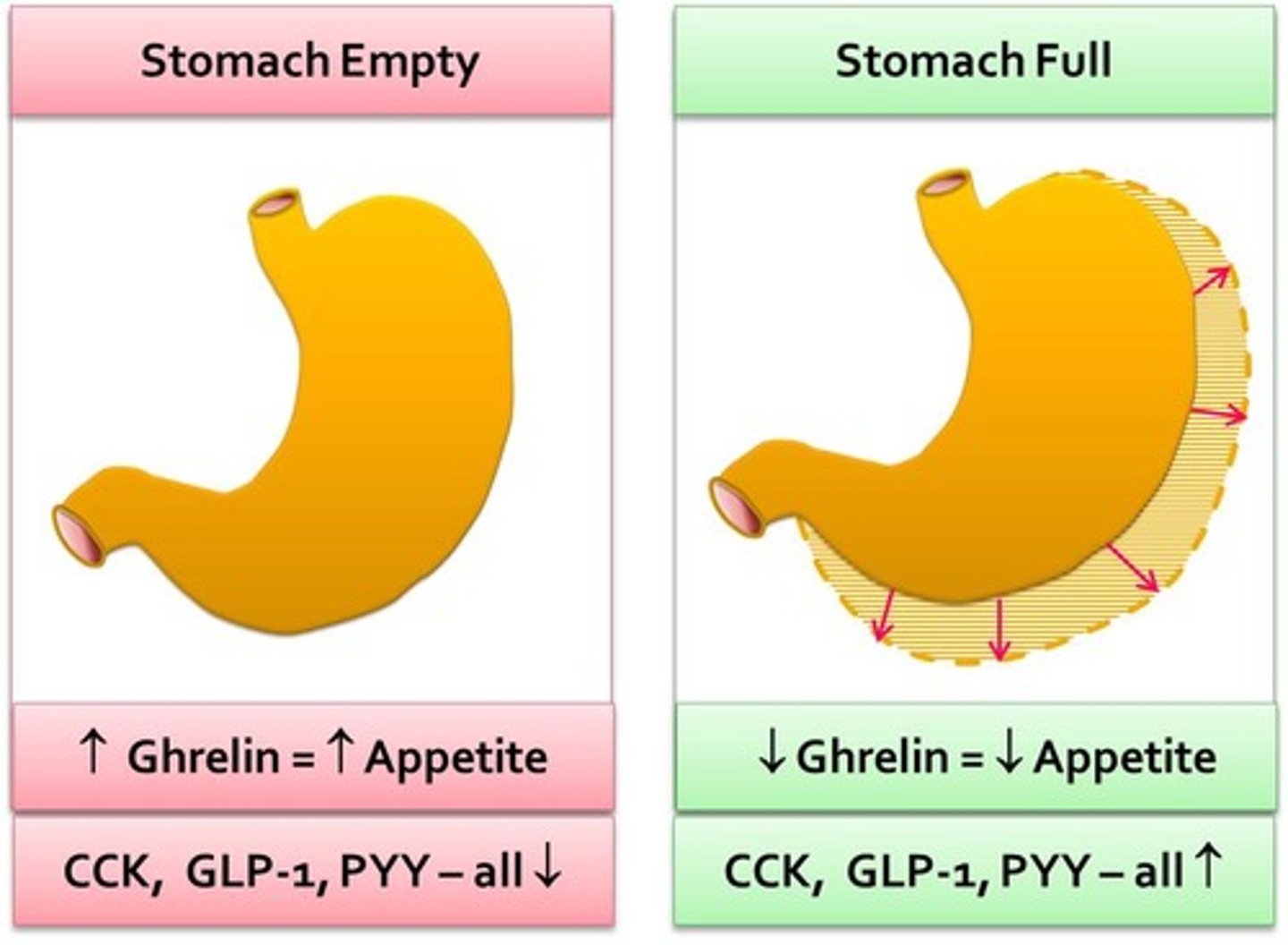
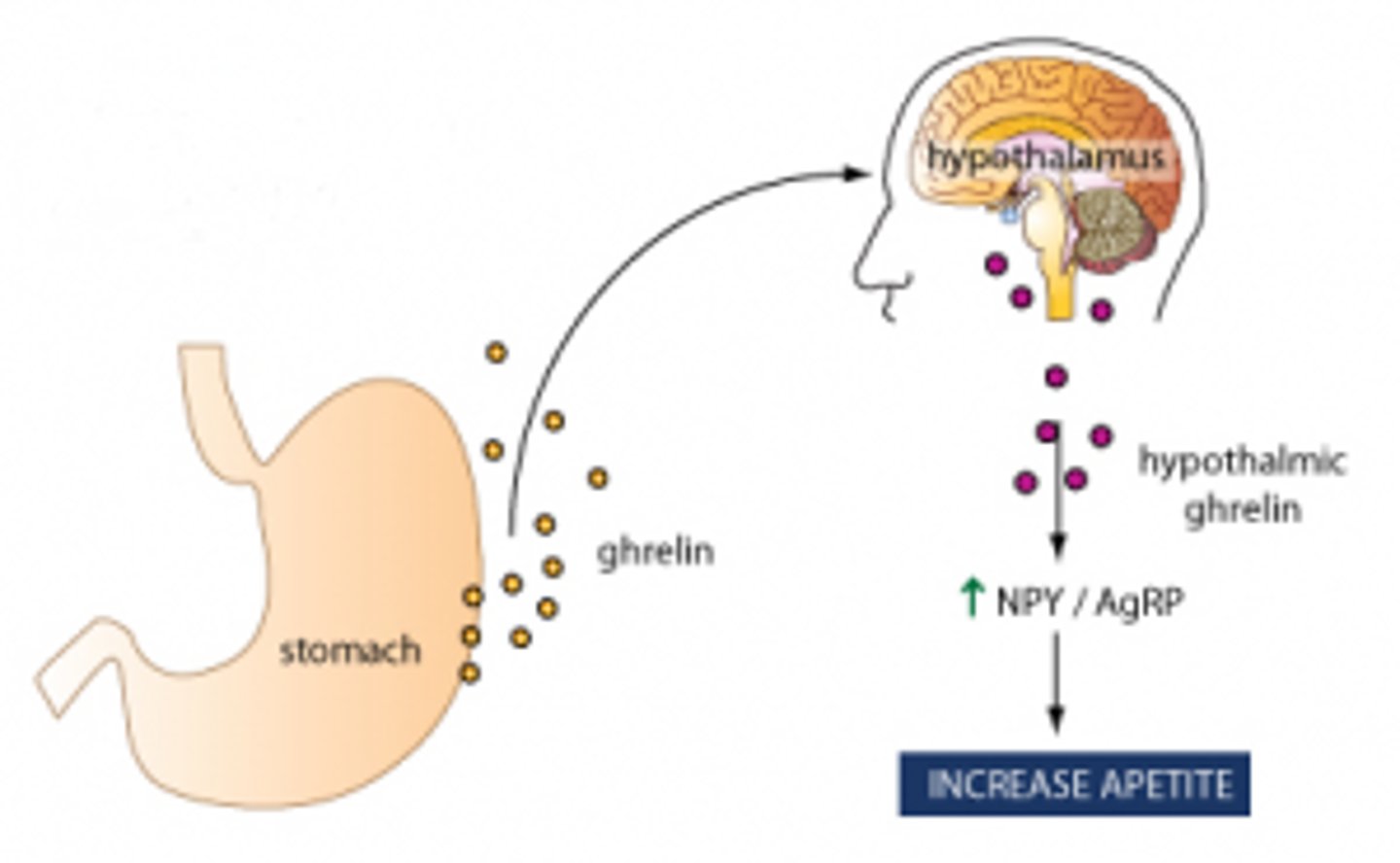
Samantha is also really hungry. What hormone will tell her hypothalamus that her stomach is empty?
(A) Insulin
(B) Glucagon
(C) Leptin
(D) Ghrelin
(D) Ghrelin
Ghrelin is produced when your stomach is "growling."
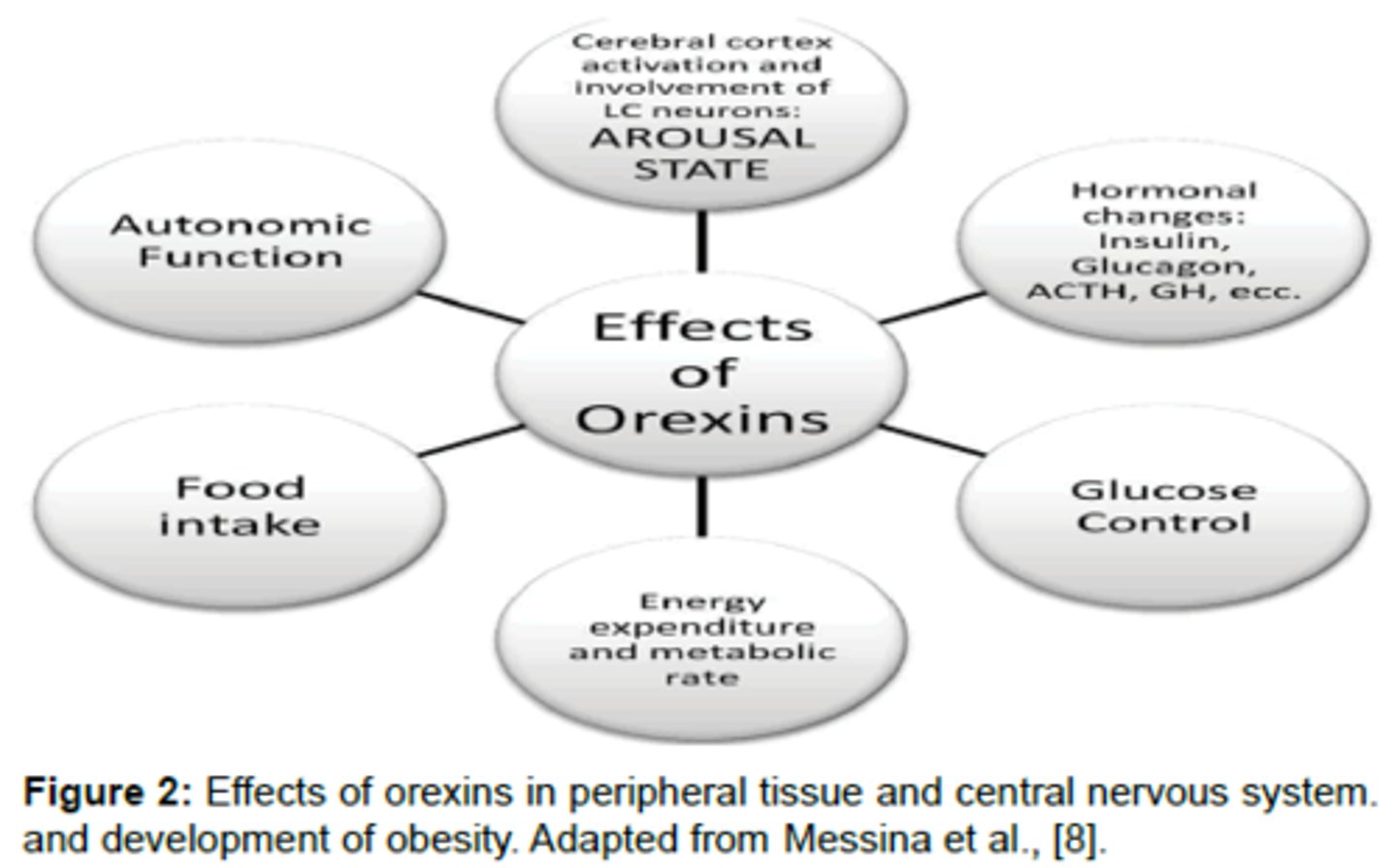
CRB Which of the following are functions of Orexin?
I. Increasing Appetite
II. Influencing Awareness and the Sleep-Wake Cycle
III. Decreasing Appetite
(A) II only
(B) III only
(C) I and II only
(D) II and III only
(C) I and II only
Orexin increases Appetite and influences Awareness and the Sleep-Wake Cycle.
Why is it that Leptin levels do not vary very much over time?
Leptin levels are more dependent on the amount of adipose tissue you have (something that is fairly constant day-to-day).
The amount of energy that you expend each day is dependent on your basal metabolic rate, your activity level, and diet-induced thermogenesis. Compare each of these three factors.
Your basal metabolic rate is the amount of energy that you need to burn in order to maintain the act of living. It would be the amount of evergy you would burn if you just sat still all day. This energy is used to run internal processes such as cell development, digestion, etc.
Your activity level is the amount of energy you expend by moving or exercising.
Diet-induced Thermogenesis is the energy that is given off as heat as we store the food that we eat for energy.

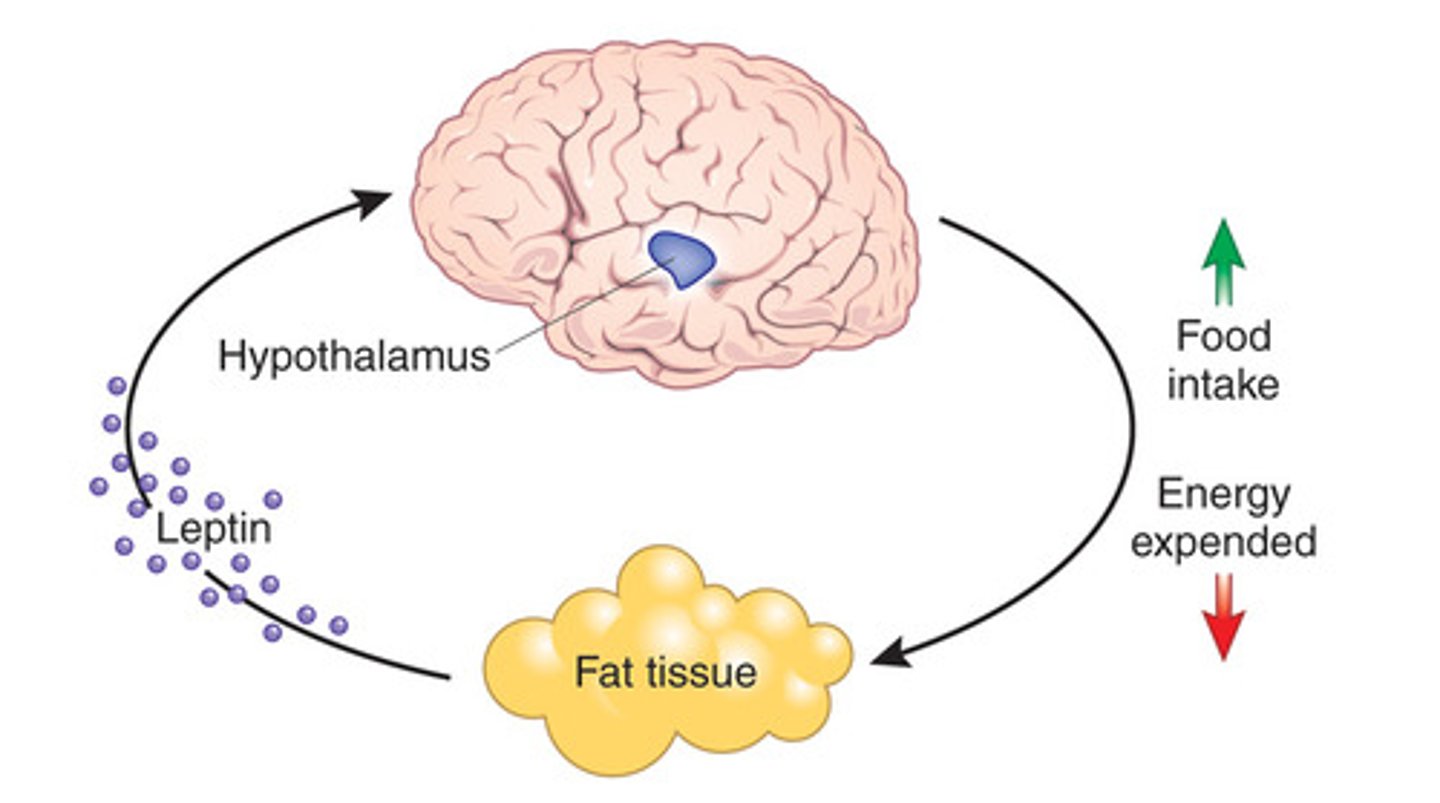
In an experiment with mice, researchers knocked out a gene in mice, which resulted in these mice becoming obese very quickly. Which hormone's genes did they knock out?
(A) Insulin
(B) Ghrelin
(C) Glucagon
(D) Leptin
(D) Leptin
Leptin is what signals your hypothalamus that you are full. Without this hormone, the mice never felt full.
What do you suppose would have happened to the mice had the researchers knocked out Ghrelin?
The mice would have gotten thinner as they wouldn't have received hunger signals upon having an empty stomach.
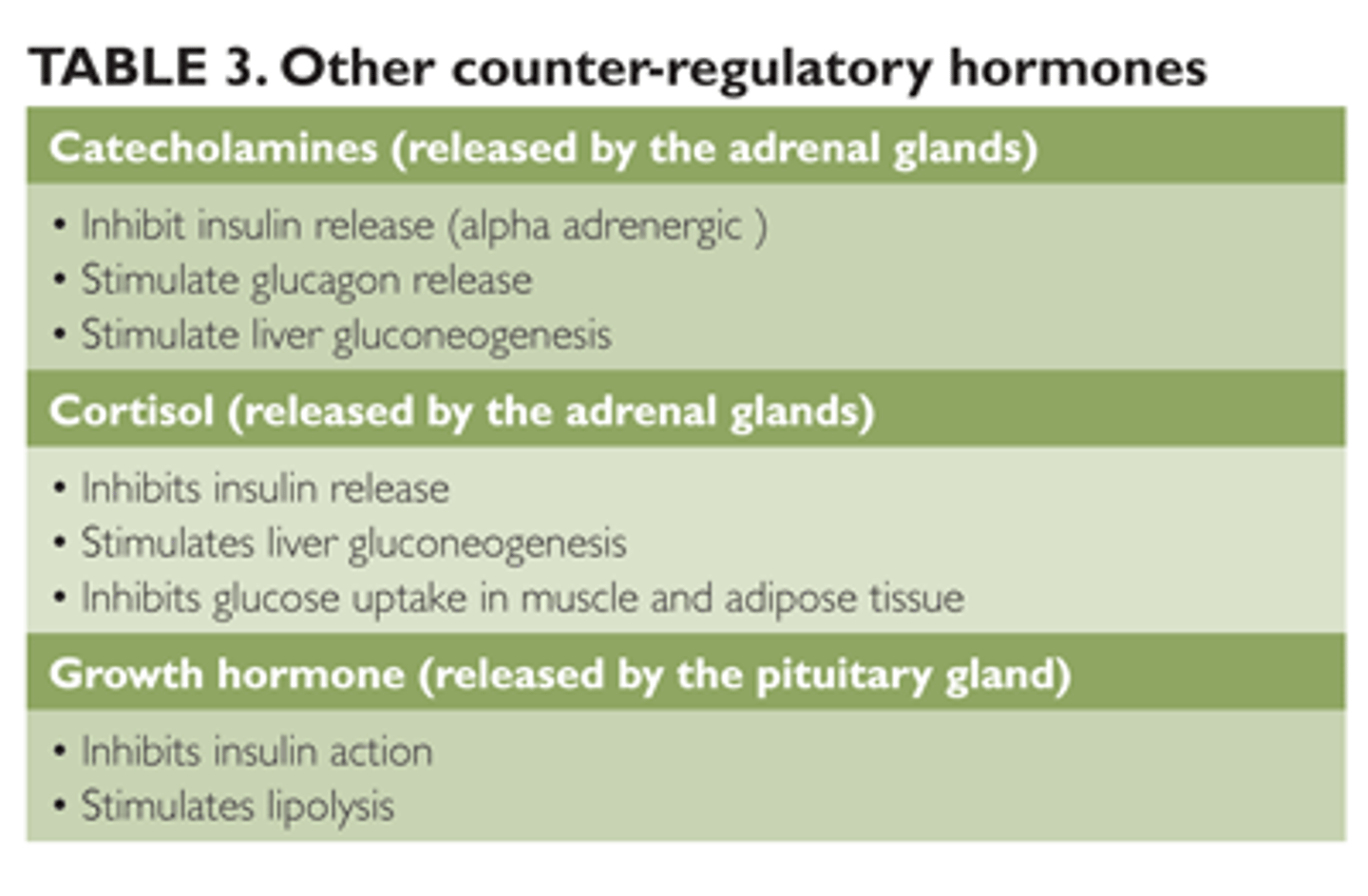
CRB Which of the following are Catecholamines and Counterregulatory Hormones?
I. Epinephrine
II. Noradrenaline
III. Cortisol
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) I and III only
(D) II and III only
(B) I and II only
Epinephrine/Adrenaline and Norepinephrine/Noradrenaline are Catecholamines and Counterregulatory Hormones.
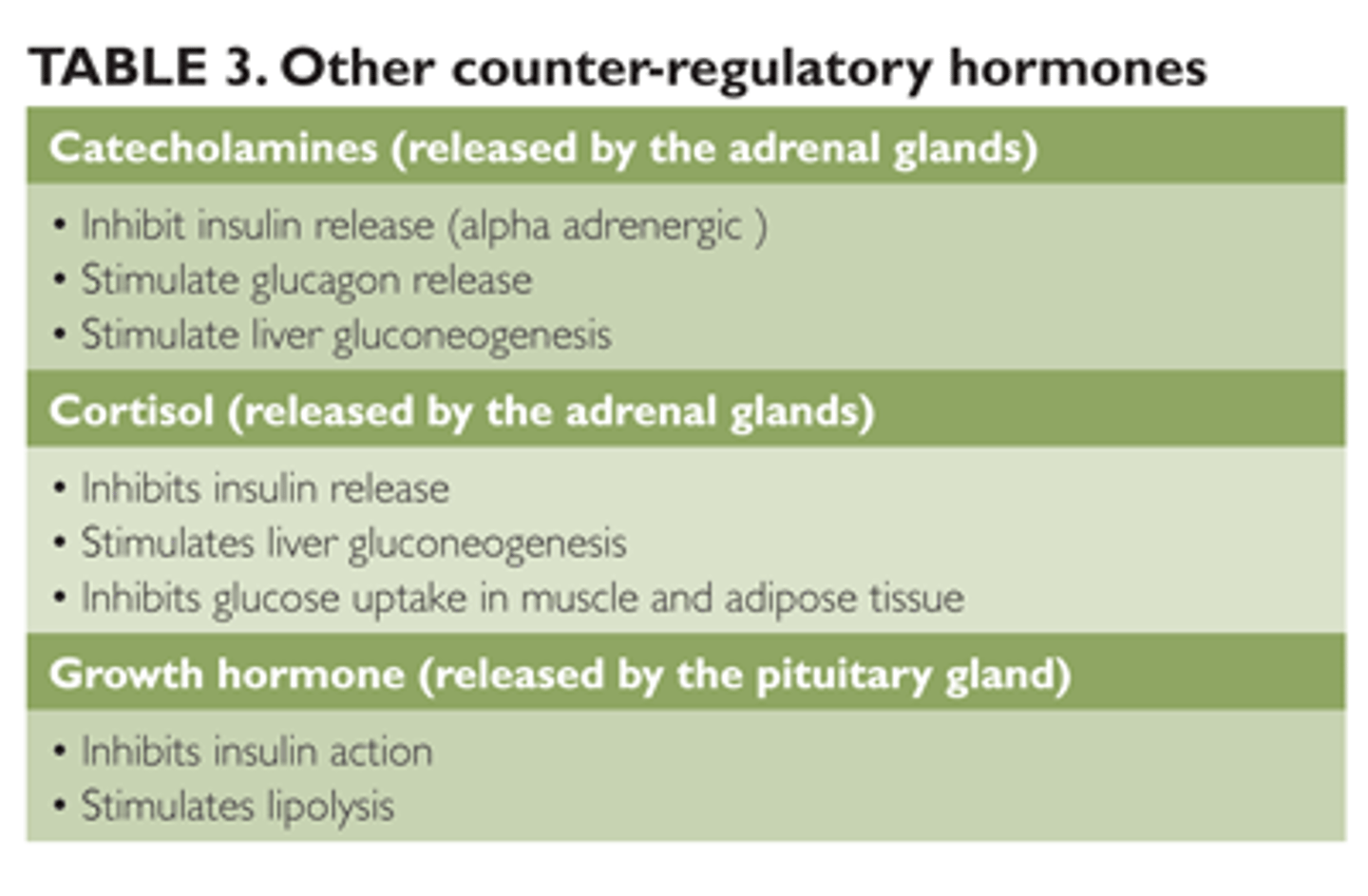
CRB Recall that Cortisol is also a Counterregulatory Hormone. Which of the following statements about Cortisol is incorrect?
(A) Cortisol is a glucocorticoid that will be released in response to various stresses.
(B) Cortisol elevates blood glucose levels by decreasing glucose uptake by Muscle and Adipose tissue.
(C) Cortisol can directly inhibit the the glucose uptake of GLUT2 transporters.
(D) Cortisol has a permissive effect, enhancing the effects of other Counterregulatory Hormones.
(C) Cortisol can directly inhibit the the glucose uptake of GLUT2 transporters.
Cortisol has no effect on the GLUT2 tranpsorters in the liver.
CRB True or false? Thyroid hormones are also involved in glucose regulation, but mainly as a permissive hormone that can widely vary to limit effects of Counterregulatory Hormones.
False. Thyroid hormones are also involved in glucose regulation, but mainly as a permissive hormone. Thyroid hormones are also kept relatively constant, in order to not alter the basal metabolic rate too drastically.