Properties of carboxylic acids
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What are carboxylic acids?
Organic acids which contain the carboxyl functional group - COOH
A carboxyl group contains both a carbonyl group and a hydroxyl group
Show the functional group of a carboxylic acid
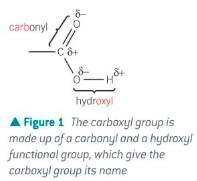
How is a carboxylic acid named?
Adding the suffix -oic acid to the stem of the longest carbon chain
Describe the solubility of carboxylic acids
The C=O and O-H bonds in carboxylic acids are polar, allowing carboxylic acids to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules
Carboxylic acids with up to four carbon atoms are soluble in water
As the number of carbon atoms increases, the solubility decreases as the non-polar carbon chain has a greater effect on the overall polarity of the molecule
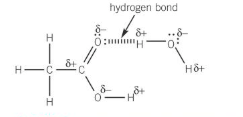
Describe thee strength of carboxylic acids
Carboxylic acids are weak acids which partially dissociate / ionise
In which reactions do carboxylic acids form salts?
Redox reactions with metals
Neutralisation reactions with bases (alkalis, metal oxides, carbonates)
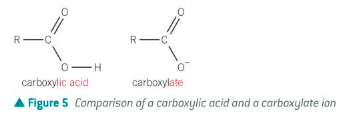
Describe the salts formed by carboxylic acids as well as how they are named
Carboxylic acids form carboxylate salts
The carboxylate ion in the salt is named by changing the ‘-ic acid’ to ‘ate’
Carboxylic acid + metal
Carboxylic acid + metal → salt + hydrogen
Write the symbol equation for the reaction of propanoic acid with magnesium?
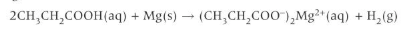
Carboxylic acid + metal oxide
Carboxylic acid + metal oxide → salt + water
Give the formula for the reaction between aqueous ethanoic acid and calcium oxide
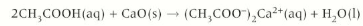
Carboxylic acid + alkali
Carboxylic acid + alkali → salt + water
Give the formula for the reaction between ethanoic acid and sodium hydroxide
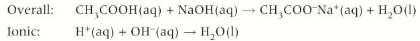
Carboxylic acid + carbonates
Carboxylic acid + carbonates → carbon dioxide + salt + water
Give the formula for the reaction between ethanoic acid and aqueous sodium carbonate
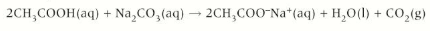
How are carboxylic acids distinguished from phenols?
Neutralisation of the carboxylic acid with carbonates - phenols are not acidic enough to react with carbonates