human systems and resource use
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
THE LAST ONE YIPPEEEEE
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
how to calculate crude birth/death rate
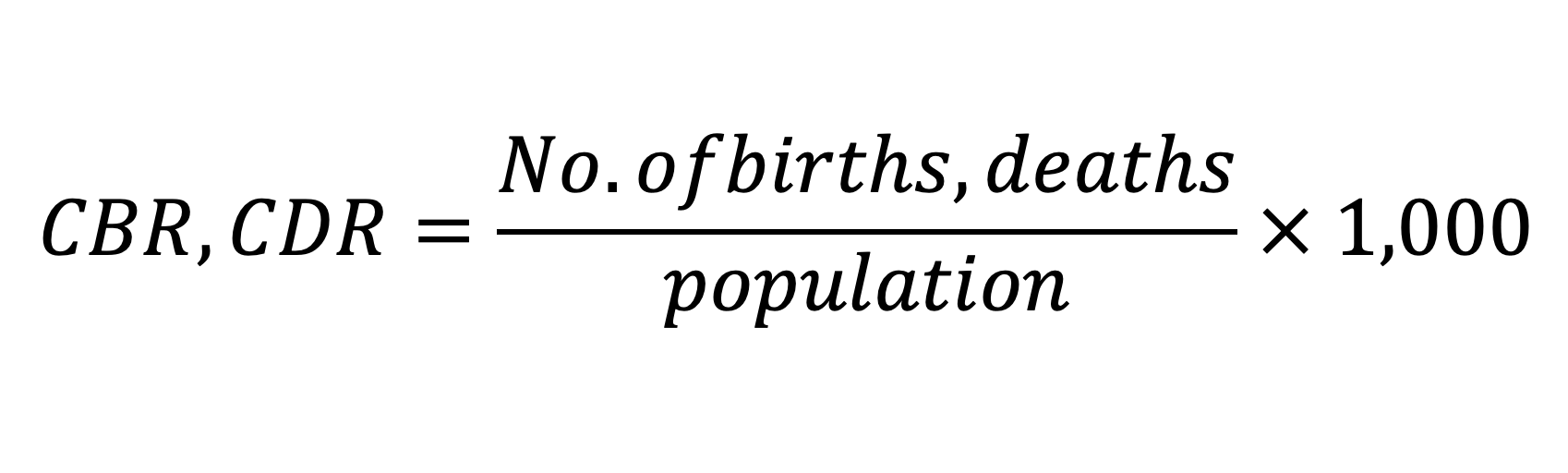
how to calculate natural increase rate
a percentage
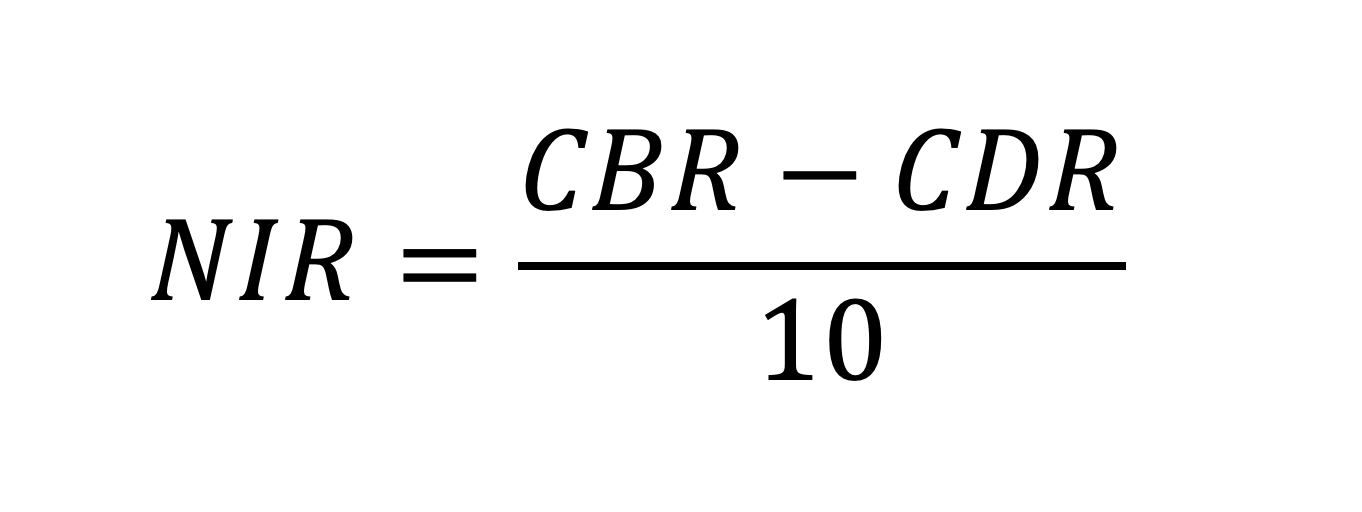
how to calculate doubling time
NIR of 1% means that pop doubles every 70 yrs

total fertility rate
average births per woman
replacement level
TFR at which pop replaces itself from one gen to the next = 2.1
renewable natural capital
can be replaced as fast as it is being used, e.g. solar-based species/ecosystems, groundwater, ozone layer
non-renewable natural capital
either irreplaceable or only over geological timescales: fossil fuels, soil, minerals
Use of valuation
Resources that have a price: marketable goods, ecological functions (renewable energy), recreational functions (ecotourism)
Non-use of valuation
Resources that have:
intrinsic value (right to exist)
future uses (medicines, gene pool)
extrinsic value (amazon rainforest)
How do cork forests show the dynamic nature of natural capital?
initially highly renewable, popular resource for bottles
but now plastic/screw caps are used, so losing value
Therefore loss of NATURAL INCOME reduces NATURAL CAPITAL
How does lithium mining show the dynamic nature of natural capital?
used to have little value; left alone in Cornish mines
but now used frequently in batteries = highly valuable
how do SDW volumes vary over time in the UK?
more garden waste in summer, more plastic, paper, food at Xmas
upsides of landfill sites
can be converted to green space once full IF properly managed
low start-up costs
technologically simple
little time/labour required
methane can be used as a power source
downsides of landfill sites
land prices: scarcity = cost
leachate can contaminate ground or surface water if not properly managed
gases can be dangerous (flammable) and contribute to the greenhouse effect
waste is non-renwable
odours, vermin, pests
upsides of incineration
reduces landfill disposal volume = increased lifespan
produces energy
ash converted to cinderblocks - renewable building material
downsides of incineration
difficult to start: strict legislation and resident protests
toxins released if not hot enough
produces CO2
recycling upsides
conserves energy and resources rather than producing new products
reduces landfill disposal volume = longer lifespan
creates new products to be sold = income
Creates lots of jobs and encourages local industry
downsides of recycling
energy-intensive
requires suitable collection/separation scheme
needs a large, steady supply to be viable
generally UNPROFITABLE
upsides of composting
aerobic process = no methane!! 🤩
produces fertiliser - useful product
reduces waste to other methods: organic waste a large proportion of total
downsides of composting
limited application: only organic waste
can smell/attract vermin if mismanaged
requires large plots of land
how can SDW be managed
alter human activity (mind control😈)
control pollutant release
restore damaged systems
how can human activity be altered
economic incentives/disincentives (GIVE THE PEOPLE MONEY)
legislation (bring back capital punishment for littering 🥰🥰)
community groups (☭)
education/awareness campaigns (propaganda..)

how can the release of pollutants be controlled?????
legislation for emission standards (make thames water shareholders swim in the Thames 😊🏊)
develop tech to extract pollutant from emissions
how can we restore the systems damaged by humanity to their former glory, forever curing them from the disease of human hubris?
extract/remove the pollutants (like from the Pacific garbage patch… teamseas..?.. MR BEAST🗣‼🔥)
reclaim landfill sites

what is carrying capacity
maximum no of a species or “load” (🤨) that can be sustainably supported by a given area
why is it difficult to estimate human carrying capacity (5 reasons)
constant efficiency improvements reduces EFs
technological developments demand different resources
different human populations have different lifestyles
difficult to identify any one limiting factor as there are so many
new resource pools are constantly discovered, e.g. peak oil was meant to be in the 80s but we discovered North Sea, tar sands, fracking etc
what is an EF
area of land and water required to support a defined human population at a given standard of living
what factors affect an EF
lifestyle choices (and EVSs)
productivity of food production systems
land use
industry
Why may an EF vary despite populations having the same consumption of food and energy? (8 reasons)
Any factors affecting land use or consumption:
Renewable vs fossil fuels
Efficiency of energy production
Located in more favourable climate for renewables like solar and wind
Plant-based vs animal products
Waste management system
May produce more products for exports
May employ more mitigation methods
Population density may vary leading to reduced land use
when does an EF become unsustainable???????
when it is bigger than the land area available to it - exceeds carrying capacity