day 3 exams kms
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
whats a gene
How a gene is represented in the chromosome
whats an allele
different version of a gene
what’s a genome
the complete set of all genetic information in an organism, contained in its DNA
difference between autosomes and sex chromosomes
autosomes - found in both male and female individual
sex chromosomes - 23rd pair of chromosomes, contains sex chromosomes
what is the nature of a pair of homologous chromosomes carrying the same gene loci
same gene loci have the same genes at the same locations, one inherited from each parent
whats the significance in the crossing over if chromatids and independent assortment for genetic diversity
prophase I - crossing over = creates genetic diversity
Anaphase II, sister chromatids separate = daughter haploid cells, not identical
process of meiosis to make haploid gametes
IPMAT I, PMAT II
interphase, prophase metaphase, anaphase, telophase
codominance
both alleles for a trait are expressed in the offspring, phenotype that displays both traits
incomplete dominance
one allele doesn't completely mask the presence of another allele in a heterozygous individual
how does genetic material, environmental and epigenetic factprs affect phenotypes
changes which genes are turned on, therefore which phenotype is present
dna methylation- turns certain nucleotides off
histone modification- packaging of dna is either too tight or too loose
whats a test cross
a genetic cross used to determine the unknown genotype of an organism that displays a dominant trait
whats a monohybrid cross
studies the inheritance of a single trait, such as flower color or height, by tracking the alleles of one gene
whats a dihybrid cross
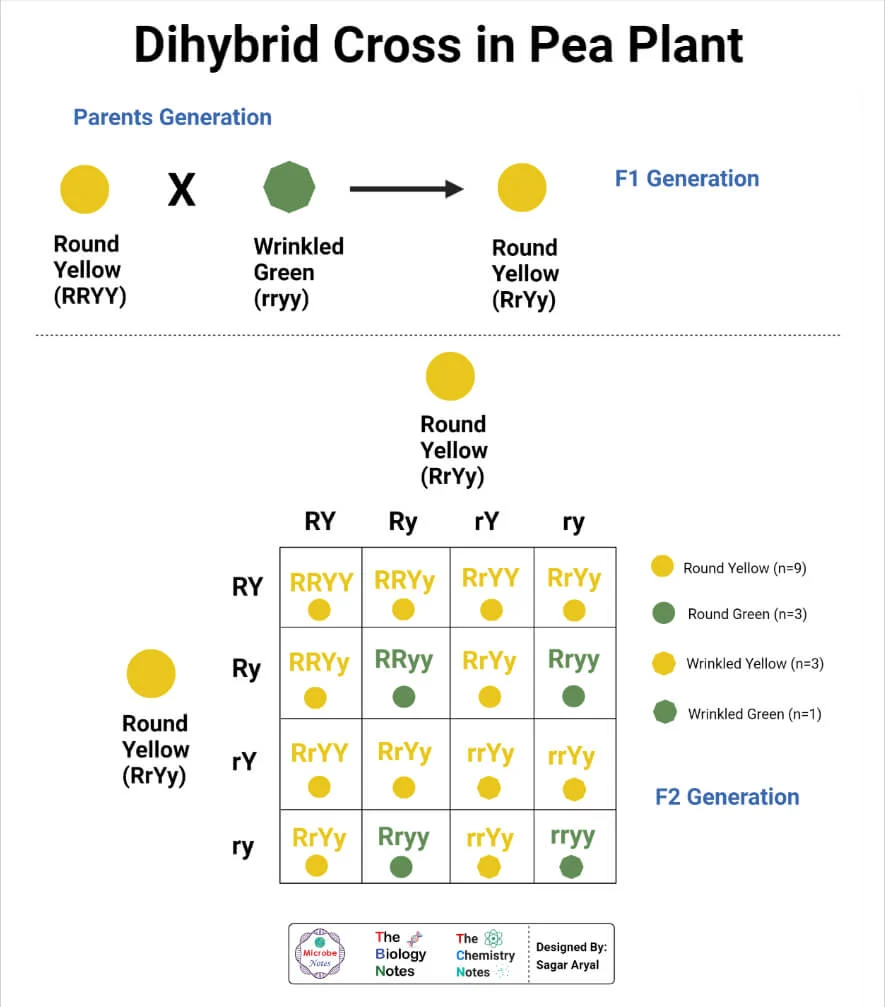
meiosis 1
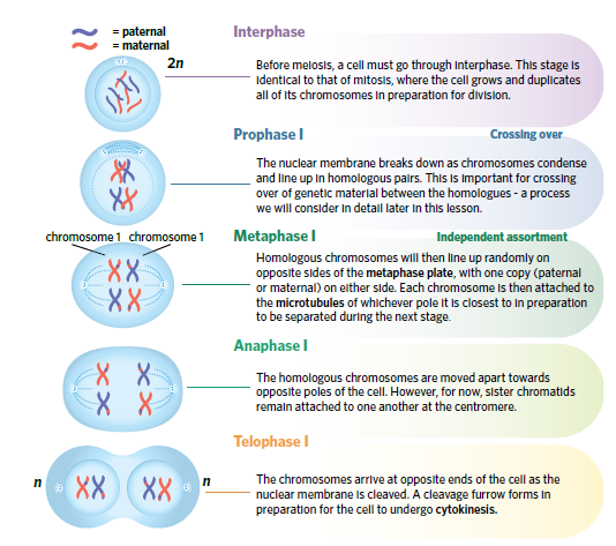
meoisis 2
bioethical issue
moral conflict/question that arises from advances in sciences, medicine and biotech
approaches to bioethics
consequence-based approach-
- aims to maximize positive outcome, minimize negative outcomes
rule-based approach
- promotes decision maker to follow a rule/procedure without questioning it reguardless of individual circumstances or context
virtue based approach
- decison making based on moral compass, expected to act good, honest, kind
ethical concepts
integrity
commitment to truth
consistent behavior
refers to openness to scrutiny and criticism
justice
emphasizes fair distribution of resources and equal access to benefits of an action, treats everyone the same, how they should be treated
beneficence
seeking to maximize benefit of others
non-maleficence
commitment to minimizing harm
sometimes the cost of restricting features
respect
upholding value of others (beliefs, freedoms, autonomy)
what is klinefelter's syndrome
an extra X chromosome in individuals who are genetically male (47,XXY).
Common features: Tall stature, long limbs, learning disabilities, and a broad range of other health issues that may appear later in life.
what is down syndrome
An extra, full copy of chromosome 21
'Common features: A range of physical characteristics at birth (like a flat face and upward-slanting eyes) and a higher risk of certain health problems, such as heart defects, hearing and vision issues, and gastrointestinal defects.
The components of Australia's current food system include:
Primary productio
The design brief is important in the process of product development as it
Defines the aims and intentions of a few product and its specifications
One of the main responsibilities of the state government in food safety is to
Approve all food safety auditors
Why has there been an increase in the amount of food imported into Australia
A period of drought of many years has meant farmers have not been able to produce enough food to meet demand
How do we detect the aroma of food
The chemical molecules in the food are drawn into the olfactory cells of the nose
Two current economic trends or issues in Australian farming and fisheries production
Aquaculture & Organic food production
Aquaculture
An increasing trend to the production of fish through aquaculture production 43 per cent of all fish produced in Australia
Organic food production
An increasing demand for organic food amongst Australian consumers. Has grown by 15 per cent
Why is signing a "free-trade" agreement an advantage to Australian farmers
A free-trade agreement gives Aussie farmers the potential to significant increase the amount of food they expert because tariffs have been removed. Increase demand doe Aussie produce
Describe the role of the federal government in ensuring a safe food supply for all Aussies
Responsibility of ensuring a safe food supply for all consumers in Aus. It develops and reviews all legislation in relation to the food supply through food standards Aus new zealand
When food is imported into Australia it is subjected to biosecurity protocols. Identify 2 strategies used by the staff of the department or agriculture and water resources to ensure that food imported into Australia is safe
X Ray machines & detector dogs
What is large scale cropping
Is a highly mechanised production system that uses large scale machinery eg computer operated systems
Two areas in Australia where wheat is grown
South west Australia & north west Victoria
Two reasons there has been a rapid increase in poultry production in Australia
- Chicken cuts and offal are also widely exported to Asian countries within our region
- Chicken is considered to be an economical meat for Aus consumers and is cheaper than many red meats such as beef or lamb
Two leading Aus food processing companies & identify two main types of food
- Devondale- tasty cheese
The difference between proprietary products and private label products
The proprietary brand is a product that the manufacturing company will sell using a brand name eg tip top bread
A private label product sells under the name of a super market eg Coles
The food service sector influences the food choices that consumers make
Ready to cook meals for time poor consumers
And components of a meal that only require the additional of a protein ingredients such as curry base
Consumer rights organisations use the media to influence consumers food shopping habits.
Consumers rights organisations such as RSPCA provide animal welfare. Eg hens need more space for having eggs
Consumer rights organisations "choice" has run a campaign to have plan oil specially identified on food labels on food labels rather then under the generic title "vegetable oil"
- replacing rain forests which are the natural home of orangutan
- orangutan becoming endangered
- affecting the environment
- identifying palm oil of the label allows consumer to become informed about the product
One type of information that could be obtained by undertaking market research when designing a new food product
New trends in society such as the demand for foods that provide a health benefit
Three reasons why the development of a prototype or product testing is a value component of the design process
- Determine the best ingredient combination
- calculate the shelf life of the product
- determine the most efficient production processes
Quantitative analysis- definition
Involves scientific tests that can be used to measure the physical features of food products
Qualitative analysis- definition
Involves sensory tests that are used to rate or sensory properties of food
Quantitative analysis- important for the manufacturer in the development of new food products
Meets the standards in the food standards code
Qualitative analysis- important for the manufacturer in the development of new food products
Appealing to consumers and helps guarantee the quality of the product
Facial hedonic descriptors preference test
- Used with children
- describe if u liked it or not
Three strategies to follow when setting up a tasting panel to compare food products
Maximum five products
Each person takes the same test
Water or small fry biscuit taken in between to cleanse palate
Reasons why food is wasted
Buying to much
Not stored properly
Letting food go out of date
Two strategies a family could use to reduce the amount of fat in recipes and meals prepared in the home
Increase veggies in meals
Avoid frying or roaring food
Use non-sticking frying pan
Radiation- no direct contact
Rays of heat eg. Toaster no direct contact
Convection
Occurs when the molecules in liquids or gases move from a warmer area to a cooler one. Eg baking roasting simmering
Conduction- direct conduct
Occurs when heat is transferred from one molecule to another by collision or movement eg shallow frying
Microwaving
In microwave cooking energy is transferred to the food by electromagnetic radiation
What is sodium
Salt
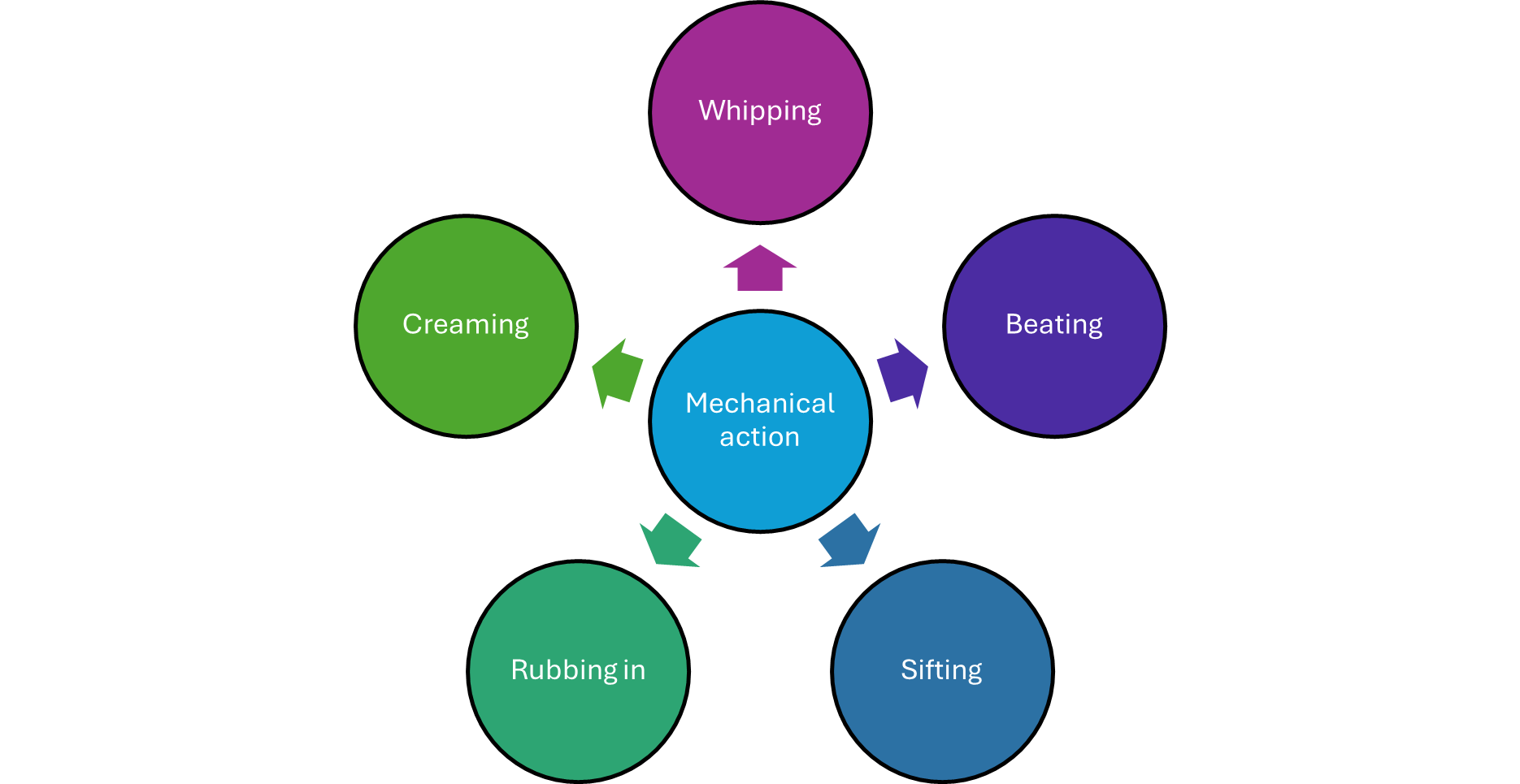
Aeration
incorporating air into food using biological or mechanical means
biological - yeast/fermentation emitting co2
mechanical - mixing/whisking
coagulation
permanent change
proteins change because of heat or addition of acid
liquid → thick mass
e.g thickening of egg white and yolk when cooked
milk turning into cheese or yogurt
dextrinization
breakdown of starch into dextrins when exposed to dry heat
results in change in colour to golden brown
e.g toasting bread
gelatinisation
thickening process
occurs when starch granules absorb liquid and swell in the presence of heat
forms a gel
e.g making a white sauce by heating flour and milk together
Carmelisation
heating of sugar or foods containing sugar
produces a golden-brown colour and distinct flavor
e.g toffee
Denaturation
permanent structural change of protein molecules
occurs though application of heat, mechanical action or addition of acid
Emulsification
process of mixing two liquids which don’t usually combine
e.g oil and water
Maillard reaction
chemical reaction between a protein and a sugar
produces a golden-brown colour when dry heat is applied
Examples of starch
flour, cornflower, rice, potato flour, rice flour, pasta
reactions:
milliard reaction
dextrinization
gelatinization
Examples of sugar
granular, caster, raw, brown, golden syrup
reactions:
Millard reaction
caramelization
aeration
Examples of Fats and Oils
butter, canola oil, lard, olive oil, rice bran oil, coconut oil
reactions:
emulsification
aeration
examples of protein
meat, eggs, fish, poultry, diary
reactions:
denaturization
coagulation
emulsification
aeration
Millard reaction
Examples of chemical raising agents
Bicarb soda- alkali, requires acid to work, needs to be mixed with an acid (vinegar, golden syrup, honey, sugar
Baking powder- contains bicarb soda with an acid powder, can be mixed with water
Yeast- biological raising agent, moisture, warmth, sugar (food)
Examples of mechanical raising agent
physical movement to create air pockets
what is conduction
touching the pan - direct heat
what is convection
circulation of heat - oven
what is radiation
chemical air
what are the macro nutrients
Carbohydrates
Protein
Fats
What does the CHOICES acrynum mean
C- cultural restrictions (in season, cutlery, geographic location)
H- health conditions (allergies, intolerances, diseases)
O- obtaining nutrients for life span stage (life span stages)
I- individual tastes and preferences (balance food preferences, meals will need adaptations)
C- considering activity levels (age, higher = more food intake)
E- ethical restrictions (vegans, vegetarians)
S- spiritual/religious restrictions (religions, faith, elimination of some foods)
atmospheric polution
contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by any chemical, physical or biological agent that modifies the natural characteristics of the atmosphere
terrestrial pollution
contamination of soil and land components with harmful substances that can adversely affect human health and the environment
water pollution
the contamination of a water body, such as a river, lake, or ocean, by harmful substances that degrade its quality and can be toxic to the environment and human health.
light polution
the inappropriate or excessive use of artificial light at night, which disrupts ecosystems, affects human and wildlife health, and obscures the night sky
noise pollution
noise above 65 decibels (dB)
thermal pollution
the degradation of water quality by any process that changes the ambient water temperature
heavy metal pollution
the contamination of the environment by high concentrations of metals like lead, mercury, and cadmium, caused primarily by human activities such as industrial processes, mining, and agriculture
waste
unwanted or unusable materials that are discarded after use, including household trash, hazardous materials, and wastewater
contaminant
a polluting or poisonous substance that makes something impure.
pollutant
any substance or energy introduced into the environment that causes harm or contamination.
how can pollutants be transported
water - Water soluble pollutants and non water soluble pollutants enter streams rivers and lakes
air - Still warm conditions can trap air pollution around urban areas/ When it rains some air pollutants dissolve into the rain becoming acid rain
what are the sources for pollution
Direct pollution - eg factory discharging effluent into a creek
Indirect pollution - Agricultural runoff (Nitrogen rich fertilisers)
point sources emissions
Release from on point, such as industry - can be controlled by scrubbers etc
diffuse source emissions
harder to control
Fugitive - difficult to control (eg mining)
Mobile - eg Cars (Pollution controls on engine)
pollution sinks
Nitrite (NO₂-) Produces Acid rain when removed from the atmosphere via rain
Nitrate (NO₃-) Plants uses this pollutant to make proteins
Oceans trap CO₂ (Carbon Dioxide) via photosynthesis of seagrass and algae
Land plants trap CO₂ via photosynthesis and store the carbon in their body mass
Heavy metals settle out in wetlands remaining trapped in the sediments
bioaccululation
The accumulation over time in an organism of substances. These substances can be beneficial such as vitamin A, D and K or toxic such as mercury.
bioconcentration
is a type of bioaccumulation when a substance that is not food accumulates in the body of the individual
biomagnificagtion
is the process by which toxic substances are magnified the further up the food chain you go.
scale of environmental impacts
Local (a few square kilometers - chemical spill/ contamination of a block of land
Regional (Large distinct area) - photochemical smog soil salinity
Global (international impact) - greenhouse effect, ozone depletion and acid rain
hazards
defined as factors that threaten or impair human health
epidemiology
try to find cause and effect of factors and population illness
how can we manage environmental health
Health in Australia is under the jurisdiction of Federal and state governments of Health
Environment in Australia is under the jurisdiction of Federal and state government of Environment
That is two separate departments
Exposure
Measure of how much pollutant a person is exposed to
Ingested via food or drink
Inhaled into lungs and then into the blood
Dermal absorption
persistant chemicals
(not break down) this increases the possibility of exposure
environmental indicators
Physical
The measurement of a physical feature such as sunlight reaching the forest floor or the creek bottom and temperature.
Chemical
The measurement of the present of chemical factors such as carbon monoxide or the amount of oxygen, nitrogen or phosphate in a creek.
Biological
The measure of the presence or absence of a particular species of plant, animal or microbe.
Social-economic
Measures the cost relating to people and society around health and wellbeing, regeneration projects and environmental regulation.
Read Environmental indicators for air quality
ecological niche
he ecological niche of an organism tells us what the organism does in the ecosystem (producer/herbivore/carnivore, links in the food web and how it fits into the biogeochemical cycles)
Generalists - species that occupy a broad ecological niche and feed on many things
Specialist - a species that has a specialized ecological niche and may only feed on a few types of organisms
range of tolerance
Species can only survive within the tolerance range of different factors (physical or chemical).