ATC Class Modules 8-14
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
The definition of "wake turbulence" includes a number of phenomena affecting flight safety. Which of the four choices are not included in the definition?
Mach Buffet
Wingtip vortices are generated by an airliner ________.
when the nosewheel lifts off the runway (rotates) during takeoff.
Which three aircraft characteristics represent the greatest generated wake turbulence? When an aircraft is ____________.
heavy, clean, and slow
Which factor has the greatest impact on wake turbulence?
Weight
During calm wind conditions, vortices near the ground will travel laterally (i.e. out to the side) at a speed of ___________ knots.
2 to 3
Vortices from large aircraft will sink (descend) at a rate of approximately _____ to _______ feet per minute.
300; 500
The ability of an aircraft to counteract the effects of induced roll is based on the ________ and ________ of the aircraft.
wingspan; counter control capabilities
A helicopter generates wingtip vortices similar to a fixed-wing aircraft while
in forward flight.
Wake turbulence / wingtip vortices are a by-product of
lift
A dirty configured wing (flaps, slats, spoilers, etc.) ___________ the total wing area and ___________ wing loading.
increases; decreases
Which of the following is NOT one of three factors that govern the strength (rotational force) of a vortex?
The Coriolis Effect
Vortices from large aircraft normally level off ____ to ____ feet below that aircraft's flight path.
500; 1,000
How will a surface crosswind of 3 knots affect wake turbulence generated from a departing aircraft?
It will stall the upwind vortex while increasing the movement of the downwind vortex.
_________ is the mechanical force a wake vortex has on an aircraft encountering wake turbulence. With no counter control (roll control), the aircraft encountering a wingtip vortex would roll completely, spinning on its longitudinal axis until the vortex sufficiently weakened.
Induced Roll
During a helicopter's stationary hover or slow hover taxi, the outward vortices generated by the rotors will spread out to a distance of approximately ___ times the diameter of the rotor.
three
The greatest impact wake turbulence has on ATC is __________.
increased separation.
Why is a controller not responsible for anticipating the existence or effects of wake turbulence?
Because wake turbulence is unpredictable.
When viewed from behind, vortex circulation from a fixed-wing aircraft's left wing rotates in a _________ direction, while the vortex off the right wing rotates in a _______ direction.
clockwise; counterclockwise
Wingtip vortices diminish in strength with _______ and _______.
time; distance
As an airfoil moves through the air in sustained flight, an area of _____ pressure is created above it.
low
The minimum vertical separation required for aircraft above FL600 is ____ feet.
5,000
The absolute minimum vertical separation allowed between two IFR aircraft at and below FL410 is _____ feet.
1,000
Two thousand feet minimum vertical separation is always required for aircraft above ______ and FL600.
FL410
To apply lateral non-radar departure divergence separation, departing aircraft must be assigned specified headings which diverge by at least
45 degrees.
En route radar separation at or above FL600 requires a minimum of ____ miles between aircraft.
10
The standard minimum en route radar separation between two aircraft at FL270 is ___ miles.
5
The minimum vertical separation below an aircraft dumping fuel is ____ feet.
2,000
In a non-radar environment, to clear aircraft to hold over different fixes at the same altitude, the controller must ensure:
holding pattern airspace areas do not overlap.
Clearing aircraft to hold at different fixes at the same altitude is utilizing:
lateral separation.
In the NAS, all aircraft operating at or above 18,000 MSL shall set the altimeter to _____, regardless of the local altimeter settings at stations they fly over.
29.92 inches of mercury (inHg)
What does the term "RVSM" stand for?
Reduced Vertical Separation Minima
What is the minimum IFR vertical separation from a Military Operations Area (MOA) with a floor of 7,000 feet MSL and a ceiling of FL 230?
500 feet above and 500 feet below.
The spacing of aircraft at the same altitude by requiring operation on different routes or in different geographical locations defines:
lateral separation.
The spacing of aircraft at the same altitude by a minimum distance expressed in units of time or miles is a definition of:
longitudinal separation.
The standard minimum longitudinal non-radar separation between two aircraft using DME is:
10 minutes or 20 miles.
In a non-radar environment, N23806, a Beech Baron, crosses the Dublin VORTAC (DBN) at 1634Z northeast-bound on V-5 at an assigned altitude of 5,000 feet MSL. N225SH, a Piper Archer, is flying the same route and is behind N23806. Applying the appropriate non-radar longitudinal separation minima, what's the earliest time N225SH can cross DBN on V-5 at 5,000 feet MSL?
1644Z
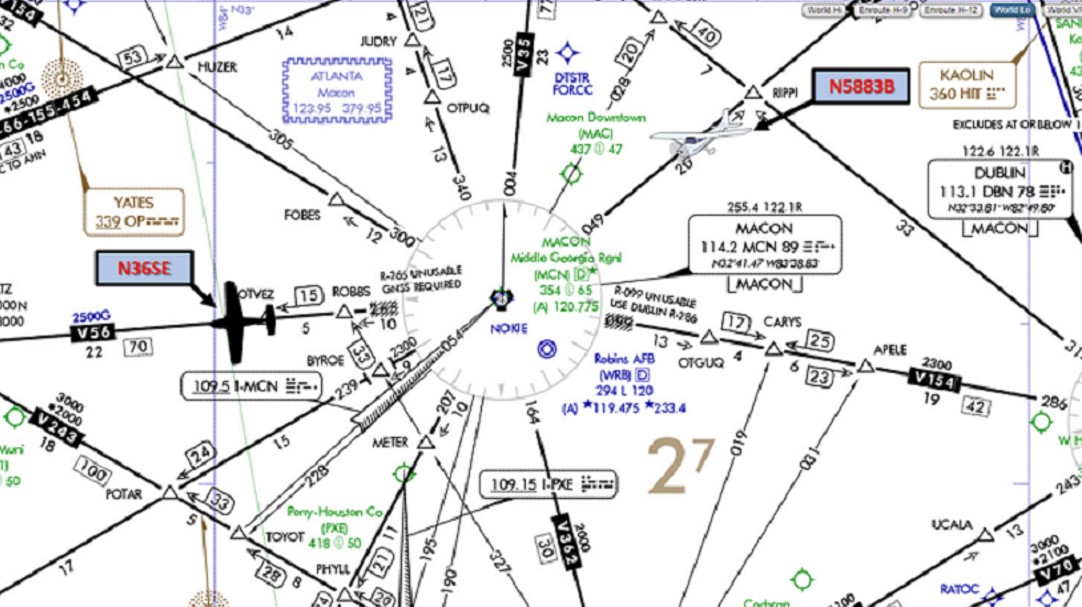
In a non-radar environment, N36SE, a Beechcraft Bonanza, is 6 DME west of the Macon VORTAC (MCN) westbound on V-56 at 8,000 feet MSL. N5232E, a Cessna Skyhawk, is approaching MCN southwest-bound on V-56 at 8,000 feet. How many DME from MCN can N5232E proceed without violating the appropriate non-radar longitudinal separation minima?
14 DME
Complete the following sentence: In a terminal radar facility, when radar data is received from a single radar antenna, use the following minima:
When two aircraft are _____________ from the antenna, 3 miles separation is required.
less than 40 miles
Complete the following sentence: In a terminal radar facility, when radar data is received from a single radar antenna, use the following minima:
When two aircraft are ____________ from the antenna, 5 miles separation is required.
40 miles or more
________ refers to the time a pilot can expect to receive a clearance beyond a clearance limit.
Expect Further Clearance (EFC) time
Which item is always included in any clearance?
Aircraft Identification or Call Sign
The purpose of an ATC clearance is to
prevent a collision between known aircraft.
The pilot-in-command of an aircraft shall comply with all provisions of an ATC clearance unless an amended clearance has been obtained, ____________, or the pilot is responding to a TCAS resolution advisory.
an emergency exists
A controller shall use the prefix phrases ATC CLEARS, ATC ADVISES, or ATC REQUESTS at the time that a clearance, advisory, or request is relayed:
through a non-ATC facility, such as an FBO, Airline Dispatcher, or another aircraft.
_________ allows a pilot on an IFR flight plan to make intermediate stops while en route to a final destination.
A Through Clearance
An authorization for a pilot to conduct flight at any altitude from the Minimum IFR Altitude (MIA) up to and including the altitude specified in the clearance is a/an ____________.
Cruise Clearance
______________ authorizes a pilot to proceed from the point of origin (i.e. the departure airport) to the destination airport on an IFR flight plan and under IFR conditions.
A Departure Clearance
The word ___________ is used only when expeditious compliance is required to avoid an imminent situation.
immediately
The word _________ is used only when prompt compliance is required to avoid the development of an imminent situation.
expedite
A re-route due to Special Use Airspace (SUA) going active or severe weather along an aircraft's filed route will result in the issuance of:
an Amended Clearance.
A tailwind can be hazardous during both takeoff and landing because
aircraft will require a longer takeoff or landing roll.
According to the NTSB, which condition is responsible for the most weather-related accidents?
Adverse Wind
A sudden wind shift, even at low speeds, can be hazardous during takeoff and landing because it can
quickly become a crosswind or tailwind.
What is the effect on an aircraft when departing from an airport with a high density altitude?
A longer takeoff roll is required.
Light aircraft are more susceptible to icing than commercial jet aircraft because light aircraft typically fly
at lower altitudes where they are more susceptible to freezing conditions.
This level of turbulence causes occupants to be forced violently against seat belts or shoulder straps, unsecured objects to be tossed about, and makes food service and walking impossible.
Severe
Which airplane would be at the most risk when landing with a 25-knot crosswind?
A small single-engine tailwheel-equipped general aviation aircraft.
Severe damage can occur if _________ is ingested into a jet engine.
volcanic ash
Convective currents are most active
on warm summer afternoons when winds are light.
Thunderstorm cell formation requires what three ingredients?
Sufficient water vapor, unstable air, and lift
__________________ is/are the single greatest cause of fatal general aviation aircraft accidents.
Continued visual flight into IFR weather
The most common and persistent weather hazard in aviation is
fog.
Ice that sticks to the outside of an airplane is called
structural icing.
Turbulence caused by obstructions, such as trees, buildings, or mountains is called
mechanical turbulence.
Any wind more than 90 degrees to the longitudinal axis of the runway is called a
tailwind.
During landing, a headwind gust ______________ airspeed, which _________ lift, and may cause an aircraft to briefly ______.
increases; increases; rise
IFR weather is primarily a hazard during
takeoff and landing.
A change in wind speed and/or wind direction in a short distance resulting in a tearing or effect is called
wind shear.
Three types of structural icing are
rime; clear (or glazed), and mixed icing.
A thunderstorm cell undergoes three distinct stages during its life-cycle, which are
towering cumulus, mature, and dissipating.
The purpose of a Pilot Weather Report (PIREP) is
to report meteorological conditions in flight.
Controllers are required to solicit PIREPs when
moderate turbulence is forecast.
Every PIREP must include the type of aircraft, altitude/flight level, location, and _______, along with at least one other element.
time in Zulu
How is an Urgent PIREP coded?
UUA
Towers and TRACONs use PIREPs to expedite traffic flow in the vicinity of the airport and to provide
hazardous weather avoidance procedures.
Which in-flight advisory would provide a forecast of occasionally severe Clear Air Turbulence (CAT) over Colorado?
SIGMET
Which in-flight advisory would be used to forecast a line of severe thunderstorms over Nebraska and Kansas?
Convective SIGMET
Which in-flight advisory would provide a forecast of moderate icing over West Virginia and Pennsylvania?
AIRMET Zulu
Which product might the Kansas City Center Weather Service Unit (CWSU) issue in response to pilot weather reports of severe clear icing in the Kansas City area below 6,000 feet that was unscheduled?
Center Weather Advisory (CWA)
A Meteorological Impact Statement (MIS) is
an unscheduled discussion product that summarizes anticipated weather conditions with potential impact on air traffic flow control and flight operations in an ARTCC's area of responsibility.
True or False: In an in-flight emergency requiring immediate action, the pilot-in-command may not deviate from any Federal Aviation Regulation or Air Traffic Clearance.
False
When in communication with an aircraft in distress, a controller should transfer responsibility to another facility only if better handling can be provided.
True
The minimum required information for ATC handling an emergency is
Aircraft Identification and Type, Nature of the Emergency, and Pilot’s Desires
_______ has the final authority as to the course of action to be followed in an emergency situation.
The Pilot-in-Command
An aircraft threatened by serious and/or imminent danger which requires immediate assistance is considered as
a distress condition.
The pilot of an aircraft experiencing radio failure can be expected to squawk code
7600.
When a bomb threat has been received involving an aircraft, the air traffic controller should inform the pilot of the threat and
comply with pilot requests.
__________ is a condition of being concerned about safety and requires timely, but not immediate assistance, and could lead to a potential distress condition.
Urgency
If an aircraft is experiencing a cargo fire (a distress condition) what word(s) will the pilot say, preferably repeating three (3) times?
Mayday
If an aircraft declares an emergency while on a controller's frequency, that controller should normally
leave the aircraft on that frequency.
When properly installed and maintained, __________ can expedite Search & Rescue operations and save lives. Additionally, they are designed to operate continuously for a minimum of _____.
an Emergency Locator Transmitter (ELT); 48 hours
Who can declare an emergency for an aircraft?
The Pilot, Aircraft Owner / Operator, or air traffic control personnel.
An interagency agreement that provides for the effective utilization of all available facilities during search and rescue missions is called
the National Search and Rescue Plan.
The Rescue Coordination Center (RCC) is operated by the
military.
Under the SAR plan, providing emergency services to an aircraft in distress is the primary responsibility of the
FAA.
An aircraft on an IFR flight plan is estimated over the Vienna VORTAC at 2032Z and has failed to report. At what time is this aircraft is considered overdue?
2102Z
When a VFR aircraft becomes overdue, who initiates the Information request (INREQ) message?
FSS personnel
The Alert Notice (ALNOT) search area is generally described as
50 miles either side of the route of flight from the last reported position to destination.
The transfer of search responsibility to the Rescue Coordination Center (RCC) is done
when the ALNOT search has been completed with negative results.
An aircraft on a VFR flight plan is considered overdue when it fails to arrive ______ after its ETA and communications or location cannot be established.
30 minutes