Anti-Platelets, Anti-Coagulants
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
What are examples of Traditional NSAIDs?
Aspirin; ibuprofen; naproxen; naproxen sodium; indomethacin; ketorolac.

What is the prototypical antiplatelets and NSAIDs
Aspirin
What is the NSAID given parenterally?
Ketorolac (Toradol)
What common pain relievers are typically NOT included in the list of traditional NSAIDs (excluding aspirin)?
COX-2 specific or selective agents (Celebrex; Mobic); nor acetaminophen (Tylenol).
Which NSAID is the only one associated with cardiac protection? How does it do this?
Aspirin.
It has irreversible inhibition of platelet aggregation. The others reversibly inhibit
What risk is increased by taking traditional NSAIDs (excluding aspirin)
Increased risk of heart attack.
What is the difference between primary and secondary prophylaxis in cardiovascular care?
Primary Prophylaxis: Starting low-dose aspirin before a myocardial infarction (MI) to prevent the first episode. Controversial due to risk of bleeding in even healthy people.
Secondary Prophylaxis: Using aspirin after a first MI to prevent further episodes.
What are examples of COX-2 selective agents? What is their risk?
Celecoxib; meloxicam. All increase risk of heart attack
How does aspirin inhibit platelet aggregation?
Platelet activation (by thrombin, collagen, ADP) → releases arachidonic acid from membrane phospholipids.
Arachidonic acid → Prostaglandin H₂ (via COX-1) → converted to Thromboxane A₂ (TXA₂) which is released into plasma.
TXA₂ promotes platelet aggregation and plug formation.
Aspirin irreversibly inhibits COX-1, blocking TXA₂ synthesis → ↓ platelet aggregation for 7–10 days (platelet lifespan).
🔥 Aspirin is the only antiplatelet that irreversibly inhibits COX-1.
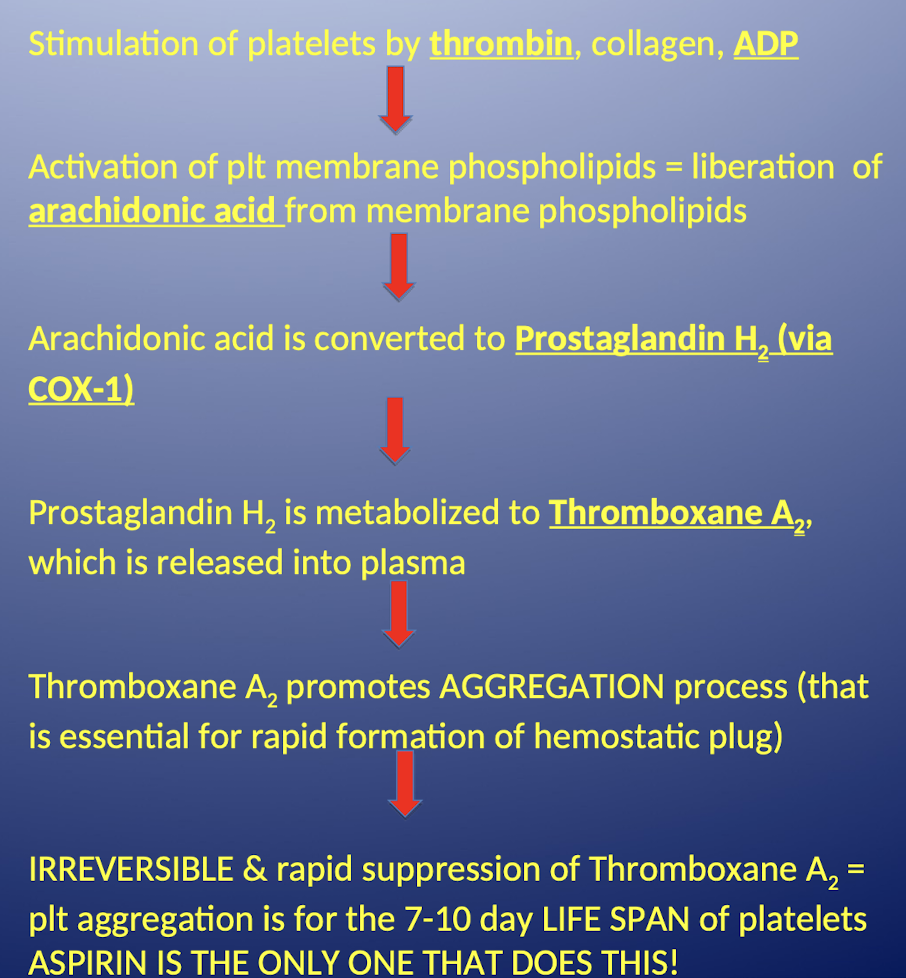
What is the role of Thromboxane A2 in hemostasis?
It promotes the AGGREGATION process that is essential for rapid formation of the hemostatic plug.
How long does the irreversible suppression of Thromboxane A2 caused by aspirin last?
For the 7-10 day LIFE SPAN of platelets.
What is the primary clinical difference in use between aspirin and anticoagulants?
Aspirin is primarily given to prevent arteriolar clots (mostly platelets); as opposed to anti-coagulants which are given to prevent VENOUS clots (mostly fibrin).
What is the pharmacokinetics of aspirin?
It is hydrolyzed to salicylic acid via the liver
What is the standard dosing range and administration tip for daily aspirin?
81 – 325 mg enteric coated tablets daily; take with the largest meal of the day (helps with local irritation).
For primary prevention of AMI, which demographic is typically recommended aspirin use?
men 45-79 yrs old
For primary prevention of ischemic stroke, which demographic is typically recommended aspirin use?
women 55-79 years old
When is aspirin recommended for men or women over 80 years old?
recommeded ONLY if they have high CV risks and no additional GI bleeding risks (other than age)
If they’ve had no cardiac events before 80 their risk of GI bleed is higher than risk of a cardiac event.
What are major adverse effects of Aspirin use?
Prolonged bleeding time (all antiplatelets do it) Increased risk for hemorrhagic stroke AND GI bleeding; CNS: tinnitus.
Why do you stop taking anti-platelets 7 days before surgery?
Due to risk of prolonged bleeding time.
Which drug classes are taken with food?
Steroids and NSAIDS
If you take ibuprofen within ___ hours prior to aspirin, what happens?
2 hours. It antagonizes aspirin’s platelet inhibition.
A patient needs to take both aspirin and ibuprofen; how should they manage the timing to avoid antagonism of aspirin’s platelet inhibition?
Take aspirin 1 hour BEFORE or ≥ 8 hours AFTER ibuprofen.
Why can we not give kids aspirin?
Salicylates in kids can cause rye syndrome. Its also tied to tinnitus
What is the alternative name for P2Y12 ADP Receptor Inhibitors?
Thienopyridine Derivatives.
Which P2Y12 ADP receptor inhbitor is no longer available in the U.S
Ticlopidine (Ticlid) big problem with thrombocytopenia
What are the three oral examples of P2Y12 inhibitors? Which is the most potent?
Clopidogrel (plavix)
Ticagrelor (Brilinta)
Prasugrel (Effient) - Effient most EFFicient at platelet inhibition
With more efficacy poses more risks
LIST is in order of least to most potent
all have grel in the name
Which P2Y12 inhibitor is given as an IV infusion and achieves maximum inhibition quickly?
Cangrelor; achieving MAX inhibition of platelet aggregation w/in 2 mins.
What is the mechanism of action of P2Y₁₂ (ADP) receptor inhibitors like clopidogrel, prasugrel, and ticagrelor? Which ones are reversible and irreversible? What is needed for rapid effect?
Block ADP (P2Y₁₂) receptors on platelets, preventing ADP from activating GP IIb/IIIa receptors → platelets cannot bind fibrinogen or each other ↓ platelet aggregation.
No effect on prostaglandins (no rye syndrome issue, etc).
Clopidogrel & prasugrel: bind irreversibly
Ticagrelor & cangrelor: bind reversibly
Oral (PO) agents usually need a loading dose for rapid effect.
Why is Ticagrelor taken twice a day?
Ticagrelor starts with T — just like the word Two.
It’s reversible, so it needs to be taken 2 times a day to maintain its effect.
🧠 Mnemonic: T for Ticagrelor = T for Two doses daily
What are the irreversible P2Y12 ADP receptor inhibitors?
Clopidogrel(Plavix) and Prasugrel (Effient) .
Why would you give a loading dose of the oral P2Y12 ADP receptor inhibitors?
7 days before theres full antiplatelet benefit
Which P2Y12 inhibitors bind irreversibly to the ADP receptor?
Clopidogrel and Prasugrel.
Which P2Y12 inhibitors bind reversibly to the ADP receptor?
Ticagrelor and cangrelor.
Why do PO P2Y12 inhibitors often require a loading dose?
For faster antiplatelet effect.
Describe the pharmacokinetics and metabolism of Clopidogrel (Plavix)
It is a PRODRUG; metabolized via the hepatic CYP450 system (specifically 2C19 isoenzyme); which results in ACTIVE METABOLITES.
How long does it take for Clopidogrel to reach maximum inhibition of platelet aggregation? What is the duration of its antiplatelet effect?
3-5 days.
7-10 days
What is the dosing of clopidogrel (plavix)?
75 mg daily alone or in combo with aspirin
Is clopidogrel a prodrug? How is it activated?
Yes, clopidogrel is a prodrug
Requires hepatic activation via CYP450 enzyme system, mainly CYP2C19
Converted to active metabolites that inhibit platelet aggregation
What is the clinical implication of a CYP2C19 "poor metabolizer" taking Clopidogrel?
Decreased efficacy of clopidogrel; increased chance of CV or cerebrovascular event.
What should be done if a patient is a poor CYP2C19 metabolizer?
Testing is available to detect CYP2C19 polymorphism
If poor metabolizer → use a different antiplatelet agent (e.g., prasugrel, ticagrelor)
Which common Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) should be avoided in patients taking Clopidogrel due to CYP450 2C19 inhibition?
Esomeprazole (Nexium) 2nd most common drug interaction; Omeprazole (Prilosec). → Both decrease activation of clopidogrel → ↓ antiplatelet effect
How long must Clopidogrel (Plavix) be held prior to a procedure or surgery?
5 days.
What is the MOA of Ticagrelor?

What unique risk does Ticagrelor pose during a bleed requiring platelet infusion?
Ticagrelor may inhibit new platelets that are infused because it binds reversibly.
What is the standard maintenance dosing for Ticagrelor (Brilinta)? what other dose is used?
90 mg twice a day.
Loading Dose of 180mg and take with 81mg (low dose) of aspirin
Why is aspirin dosing restricted when co-administered with Ticagrelor?
Aspirin doses greater than 100 mg will impair ticagrelor’s mechanism of action.
How quickly does Ticagrelor achieve maximum inhibition of platelet aggregation?
1-3 hours. (when given loading dose)
How long must Ticagrelor (Brilinta) be discontinued before surgery?
5 days.
What is the suggested antidote for severe bleeding due to Ticagrelor (Brilinta)?
No specific antidote; recombinant factor VIIa suggested.
What is the MOA and dosing of Prasugrel (Effient)?
Irreversibly inhibits ADP receptor
10 mg once daily (give LD of 60 mg) and take with 81-325 mg of aspirin
How quickly does Prasugrel achieve maximum inhibition of platelet aggregation?
2-4 hours.
What is a major contraindication for the use of Prasugrel (Effient)? Why/ Whats its ADR?
Patients with prior TIA or stroke.
BLEEDING (black box warning)
What are the drug interactions with Prasugrel?
Other drugs that increase bleeding risk (warfarin, NSAIDs)
How long must Prasugrel (Effient) be held prior to a procedure or surgery?
7 days. Because risk of bleeding
What is the antidote for Prasugrel (Effient)?
Platelet infusion.
Which P2Y12 ADP Receptor Inhibitors carry a Black Box Warning for BLEEDING?
Ticagrelor; Prasugrel; & Cangrelor.
What is the specific black box warning for Ticagrelor?

What serious haematological adverse reaction is associated with P2Y12 ADP Receptor Inhibitors? What are the more classic ones?
TTP (Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura).
Prolonged bleeding time and thrombocytopenia
What is the mechanism of action for Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors?
They target the platelet IIb/IIIa receptor complex; which is the final common pathway for platelet aggregation.
How are Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors typically administered, and why are oral forms avoided?
They are given IV (in emergency situations), PO forms have been shown to INCREASE mortality
Which class of antiplatelet agents is considered the most potent? Name examples?
GP IIb/IIIa inhibitors. Eptifibatide and Tirofiban

Rank the antiplatelet potencies from highest to lowest
GP IIb/IIa inhibitors > Thieonopyridine derivatives (Prasugrel (Effient) > Ticagrelor (Brilinta) > Clopidogrel (Plavix)) > aspirin.
Which antiplatelet drugs are classified as Pregnancy Category B?
Clopidogrel; Prasugrel; eptifibatide; tirofiban.
Which antiplatelet drugs are classified as Pregnancy Category C?
Aspirin (in some cases); ticagrelor.
How long must Aspirin, Clopidogrel, Ticagrelor, and Prasugrel be held prior to surgery?
.

What is the mechanism of action of Warfarin (brand name coumadin) (anticoagulant)?
Inhibits vitamin K dependent, hepatic coagulation factors: II (minor); VII; IX; and X; as well as protein C and S.
VITAMIN K = WARFARIN
Why is "bridging" often required when initiating Warfarin therapy?
PEAK EFFECTS are delayed for 72-96 hours; so patients may need to bridge with another anticoagulant (heparin or LMWH).
How does Warfarin affect clotting factor activity?
Warfarin leads to the production of clotting factors with reduced activity.
These factors function at only 10–40% of their normal activity.
🧠 Think: Warfarin = Weak Factors
IV warafrin not really used because it still takes time to inhibit factors
What happens if someone consumes a lot of vitamin K?
It inhibits warfarin. Specifically vitamin K1
What is the pregnancy category for Warfarin (Coumadin), and what is the risk?
Category X. Cant take when pregnant but breast feeding on warfain is fine because it doesn’t cross breastmilk

If a pregnant female requires anticoagulation, what agent is typically administered?
Heparin
What are the typical recommended starting doses for Warfarin?
5 mg daily for 2 – 5 days; then adjust dose according to INR (International normalized ratio).
DO NOT GIVE LOADING DOSES FOR COUMADIN
What primary CYP450 isoenzyme metabolizes Warfarin, leading to numerous drug interactions?
CYP450 2C9
What is the standard target therapeutic range for INR when monitoring Warfarin therapy?
2-3 or 2.5. typically try to hit right in the middle
Higher INR values indicate _____
a greater level of anticoagulation
How long must Warfarin be held prior to a procedure or surgery?
5 days.
What is a key dietary consideration for patients taking Warfarin?
Maintain a consistent amount of vit K in the diet and therefore avoid sporadic ingestion of foods high in vitamin K (beef liver; pork liver; green tea; green leafy vegs).
What is an almost guaranteed drug interaction with coumadin? What is the antidote?
Anti-bacterials. No speciifc antidote but vitamin K may be used as one
What is "purple toe syndrome" and what drug is it associated with?
A rare; painful; blue-tinged discoloration of the toe caused by cholesterol emboli from plaques; observed with warfarin therapy.
When a patient is on Warfarin therapy, which common OTC pain reliever should be recommended instead of NSAIDs or Aspirin (unless intentional)?
Acetaminophen (Tylenol
What is often used as an antidote or in conjunction with Ffresh Frozen Plasma to reverse Warfarin effects?
Vitamin K.
why is warfarin contraindicated in pregnancy?
It is teratogenic
What are the direct oral factor Xa inhibtors?
Rivarixaban (Xarelto)
Apixaban ( Eliquis)
Edoxaban (Savaysa)
What is the mechanism of action of Dabigatran (Pradaxa)? What is its cool fact and major inhibition?
Direct thrombin inhibitor (factor IIa).
1st PO anticoagulant approved in U.S in over 50 years but you miss you dose within 15 minutes increase your risk of an event.
Used in place of warfarin
When is dabigatran indicated?
for reducing the risk of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation
What is a specific contraindication for Dabigatran use related to cardiac implants?
Patients with mechanical prosthetic heart valves.
also not recommended for bioprosthetic valves
Unlike Warfarin, what monitoring parameter is not required for Dabigatran?
INR monitoring
How long must Dabigatran (Pradaxa) be held prior to a procedure or surgery?
24-72 hours.
What are the reversal agents for Dabigatran (Pradaxa)?
Activated charcoal and idarucizumab (Praxbind).
What ingredient in Dabigatran causes dyspepsia (indigestion) and why is it included?
Tartaric acid (cream of tartar); included to help with absorption.
What critical warning is associated with compliance for Dabigatran?
If a dose is missed; the effectiveness starts to wane within 15 minutes of the missed dose.
What are the three main Direct Oral Factor Xa Inhibitors listed?
Rivaroxaban (Xarelto); Apixaban (Eliquis); Edoxaban (Savaysa).
What is the mechanism of action of Direct Oral Factor Xa Inhibitors?
Factor Xa inhibitor; which reduces the production of thrombin (IIa) from prothrombin.
When are direct oral factor Xa inhibitors indicated?
Used in place of warfarin or low molecular weight heparin to prevent Venus thrombosis after hip or knee replacement surgery; just approved to prevent stroke in patients with afib.
What are the reversal agents for Rivaroxaban and Apixaban?
Andexxa (coagulation factor X).
Which CYP enzymes primarily metabolize Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)?
CYP 3A4/5 and CYP 2J2 isoenzymes.
Which CYP enzyme primarily metabolizes Apixaban (Eliquis)?
CYP 3A4.
Why should dosages of Factor Xa inhibitors sometimes be reduced or avoided when taken with drugs like clarithromycin; verapamil; and amiodarone?
Because the Factor Xa inhibitors are substrates of P-gp; and these listed drugs are P-gp inhibitors.
What class of drugs should be avoided with apixaban and rivaroxaban due to reduced efficacy risk?
Strong P-gp and CYP 3A4 inducers (for example; phenytoin; carbamazepine; rifampin; St. John’s wort).
What is the primary characteristic of Heparin as an anticoagulant?
Injectable; rapid-acting anticoagulant that is often used acutely.