L23: Microanatomy of the Kidney
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
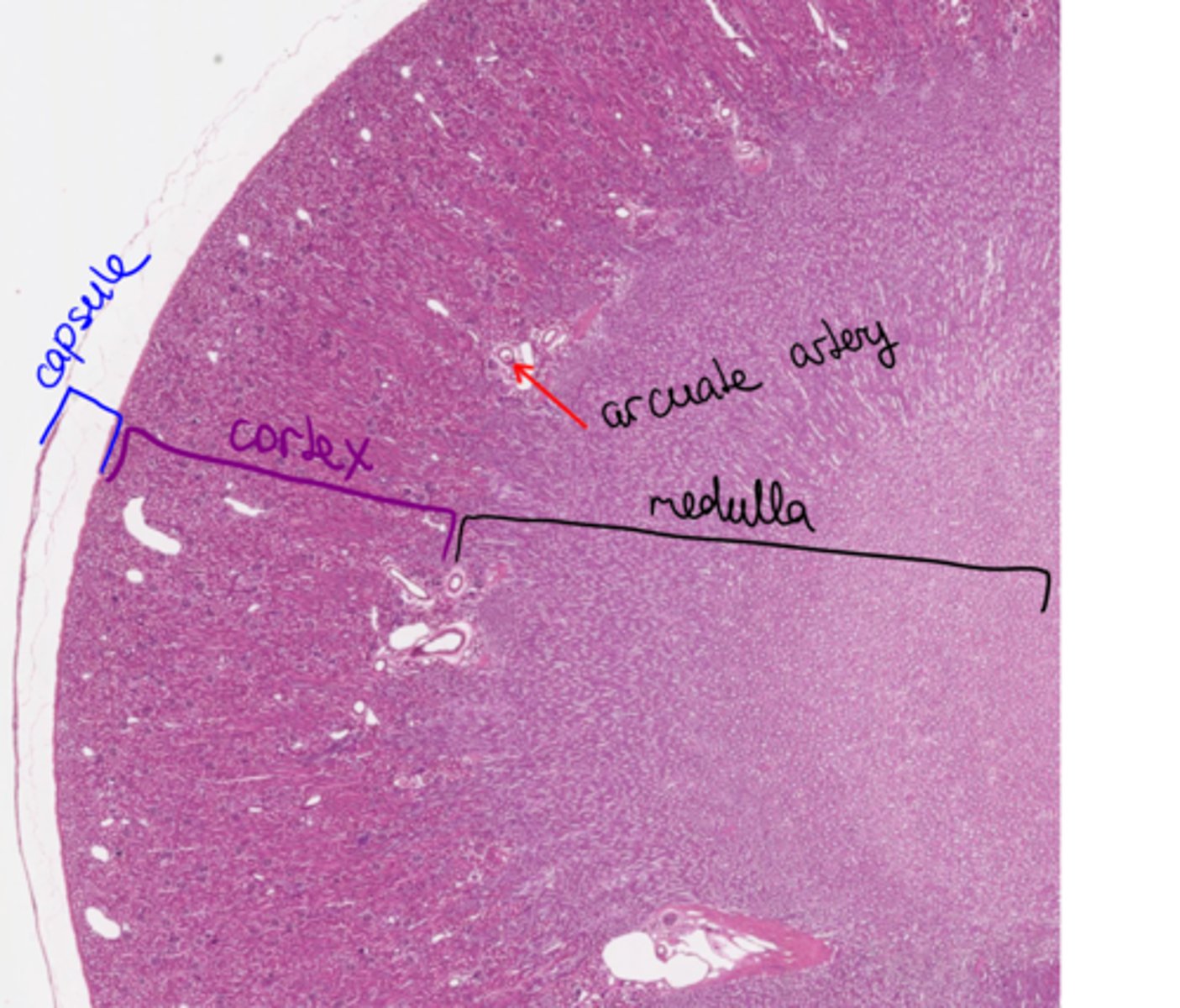
Microscopic structure of the outer cortex
- renal corpuscles with glomerulus
- pars convoluta with proximal and convoluted tubules
- pars radiata (medullary rays) collecting ducts
- blood vessels
Functional unit of the kidney
nephron/renal tubule
Renal corpuscle
blood-filtering component of the nephron
Glomerulus
capillary plexus which is enveloped by Bowman's capsule, responsible for blood filtration
Bowman's Space
surrounds the glomerulus creating the renal corpuscle
Proximal convoluted tubule
first & longest part of the proximal tubule
Proximal straight tubule
continues from the proximal convoluted tubule & descends into the medulla becoming the thin descending limb
Loop of henle
section of the nephron tubule that conserves water and minimizes the volume of urine
Distal convoluted tubule
shorter than the proximal convoluted tubule & no brush border/microvilli
Papillary duct
formed by the merging of several medullary collecting ducts
What is the functional unit of the kidney?
the nephron
Where is the proximal convoluted tubule located?
in the cortex
What is the area surrounding the glomerulus called?
Bowman's space
Kidney capsule is formed by
dense connective tissue
The outer cortex of the kidney appears
granular, uniform or lobated
The inner medulla of the kidney appears
smooth, mostly contains tubular parts of the nephron and collecting system
Kidney gross histology
Kidney cortex histology
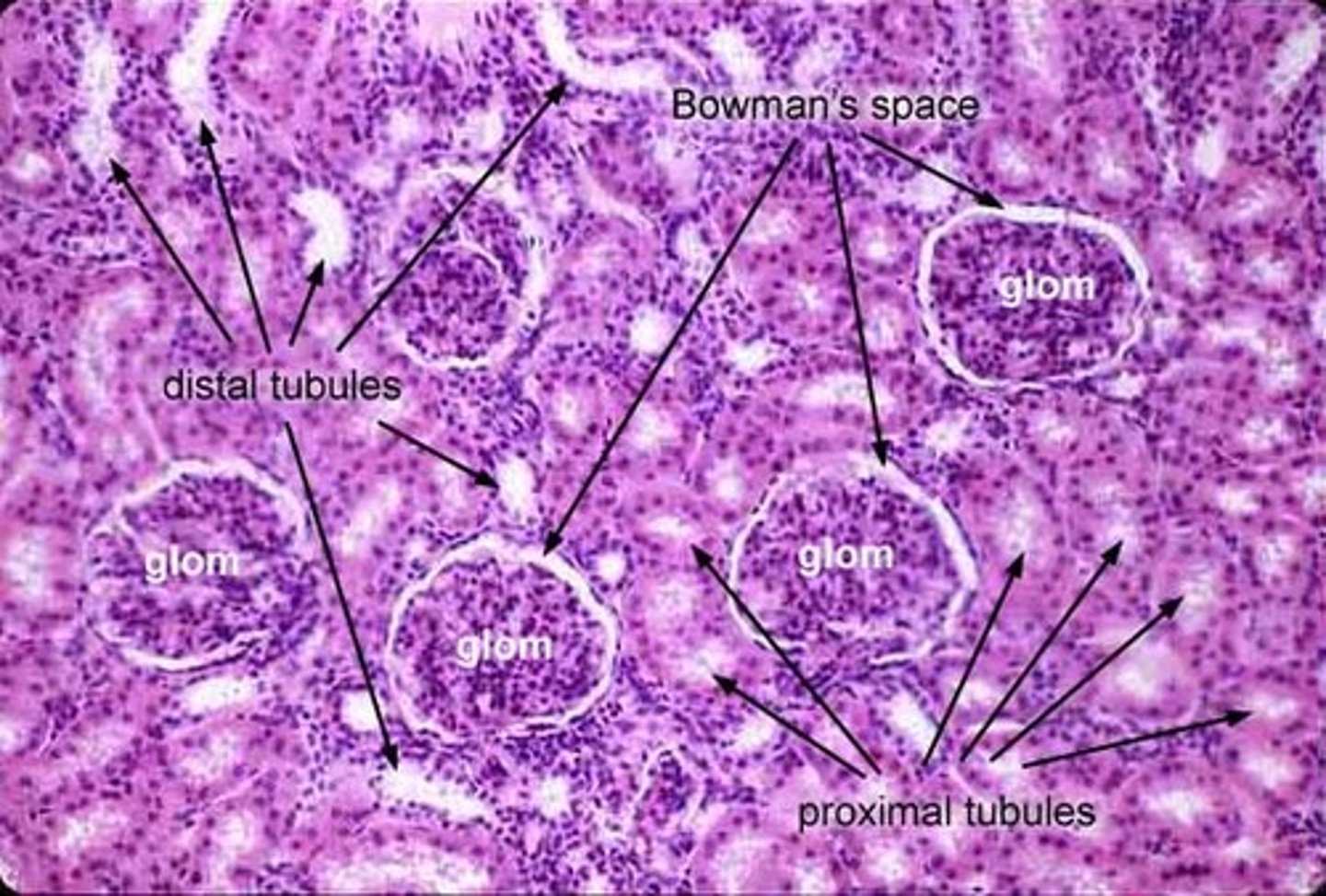
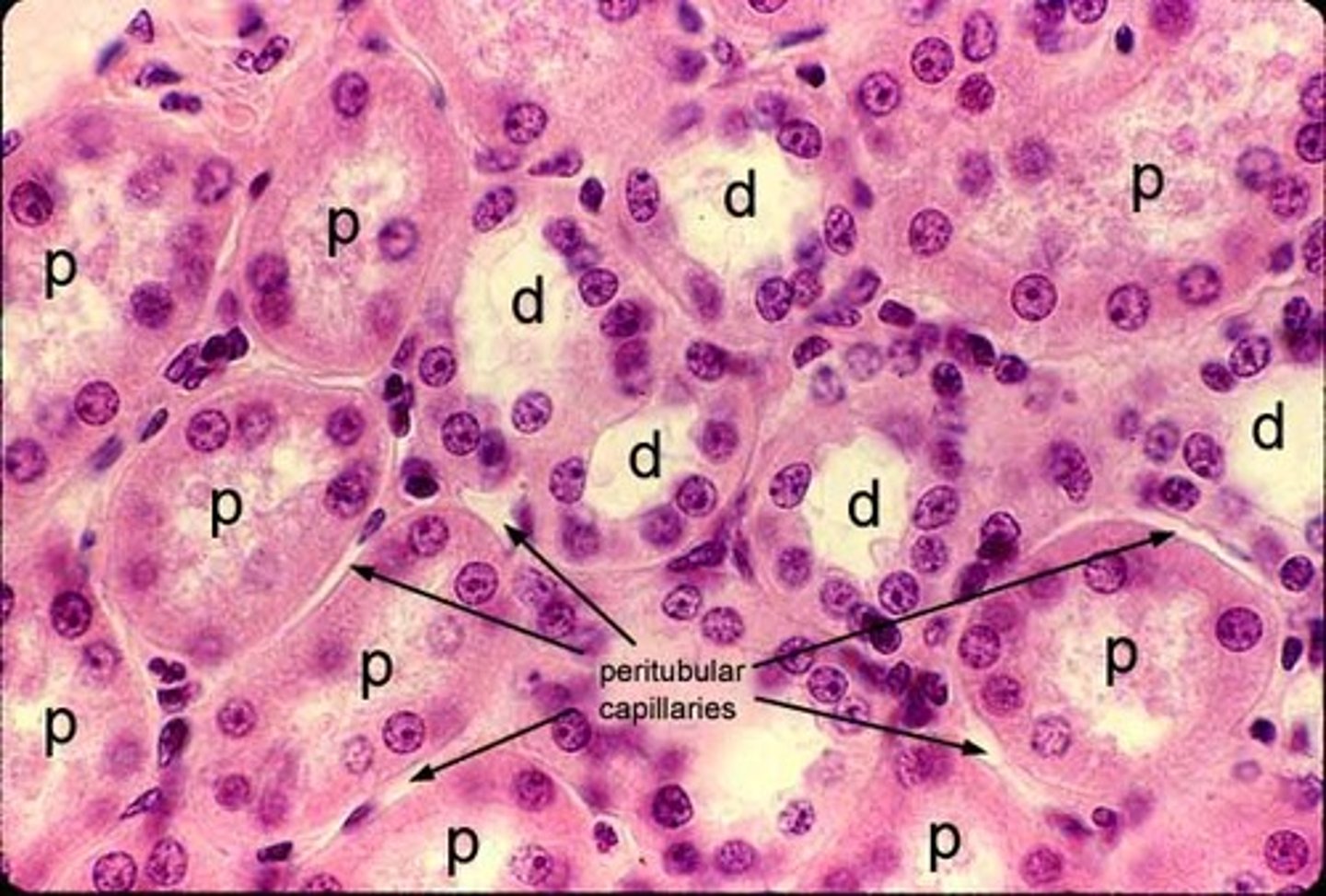
How can you differentiate proximal convoluted tubules from distal convoluted tubules?
proximal convoluted tubules: less distinct lumen, contains microvilli
distal convoluted tubules: more distinct lumen, does not contain microvilli
Kidney medulla histology
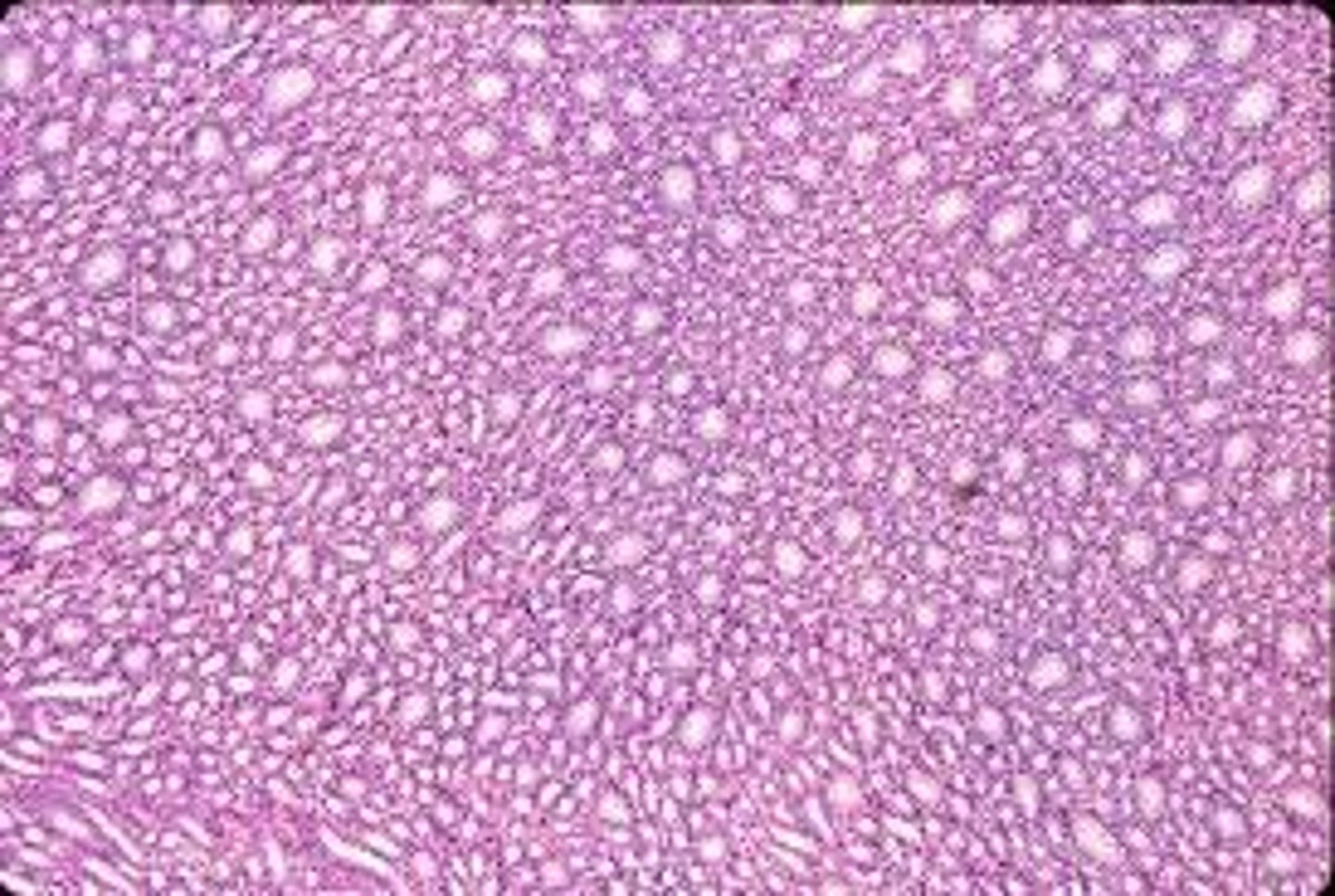
What is contained within the medulla of the kidney?
collecting ducts, descending thin & ascending thin segments of loop of Henle, ascending thick sengment, vasa recti, peritubular capillaries
Considering the structure of the nephron, which structure will appear only in the section through the medulla of the kidney?
thick limb of Henle's loop & thin limb of Henle's loop
Nephron anatomy
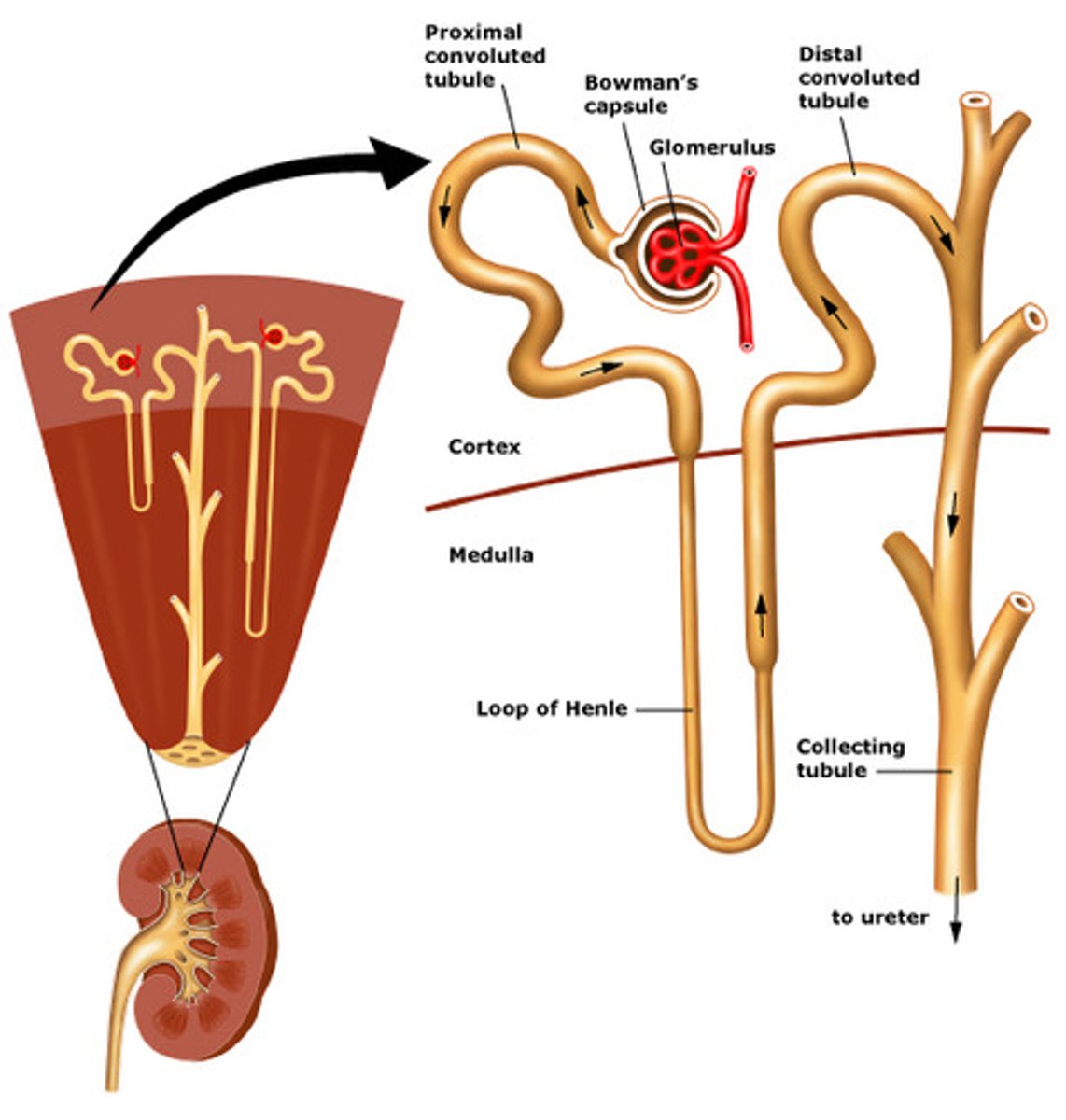
Juxtamedullary nephron
type of nephron located near the boundary of the cortex & medulla, concentrates urine
Cortical nephron
nephrons located almost entirely in the renal cortex, loop of Henle is shorter
What structure makes up the peritubular capillary network?
efferent arterioles
What makes up the parietal layer of the Bowman's capsule?
simple squamous epithelium
What makes up the visceral layer of the Bowman's capsule?
podocytes
What occurs in the Bowman's space?
pre-urine filtrate is collected in this space
Vascular pole of the Bowman's capsule
the side of the capsule where the afferent and efferent arterioles enter and exit the glomerulus
Urinary pole of the Bowman's capsule
the side of the glomerulus where the filtrate exits and enters the proximal convoluted tubule
What is the function of the Glomerulus?
filtration of the blood (20%), 99% is reabsorbed
What is in the filtrate from the Bowman's capsule?
water, glucose, nutrients, bicarbonates, amino acids, small proteins, lipids, electrolytes
What is the purpose of the porous capillaries in the glomerulus?
allows substances of certain sizes to pass through
Glomerulus composition
- porous capillaries
- basement membrane with collagen type 4 layer
- surrounded by podocytes
What is the function of the larger lumen of the afferent arteriole and the smaller lumen of the efferent arteriole?
creates a pressure gradient encouraging filtration into the bowman's space
Podocytes
form the visceral layer of the bowman's space, act as a filtration barrier to control amount of filtrate produced
- contain cell body, primary processes, secondary processes
What do the podocytes form?
filtration slits that allow for filtration
Mesangial/intercapillary cells
holds the capillary tuft in place, connects the distal convoluted tubule at the vascular pole
- help to maintain GFR
- produce extracellular matrix
- regulate capillary blood flow
- phagocytosis
- secrete growth factors
Renal corpuscle histology
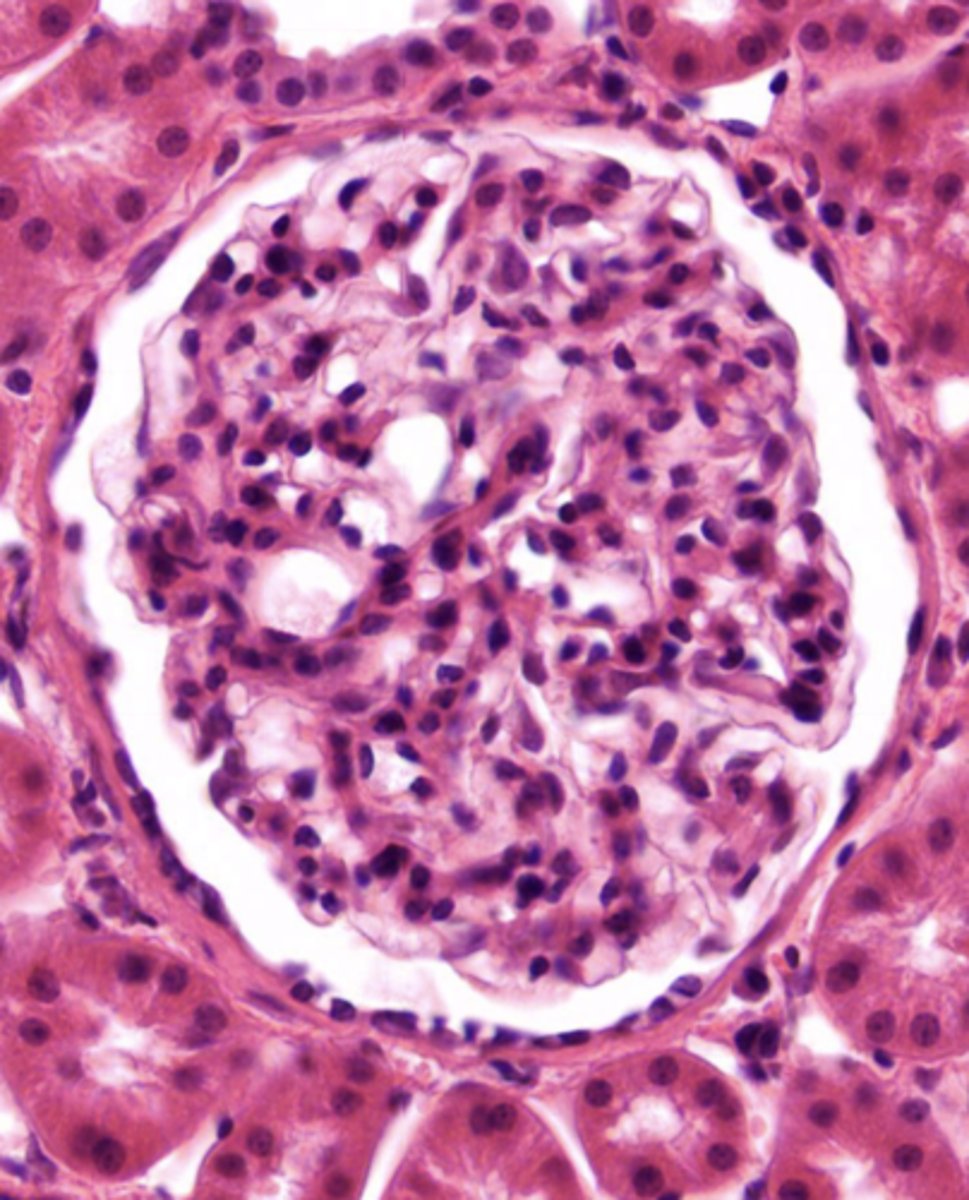
What epithelium is present in the parietal layer of the Bowman's capsule?
simple squamous epithelium
Proximal convoluted tubule & proximal straight tubule composition
- simple columnar epithelium with Acidophilic cytoplasm
- microvilli/brush border and basal striations
- microvilli less distinct in PST
Proximal convoluted tubule is responsible for how much reabsorption?
65%
Proximal convoluted tubule histology
Hele's loop: descending thin limb
simple squamous epithelium, nuclei are somewhat flattened & protrude into the lumen
Henle's loop: ascending thick limb
reabsorption of Na,Cl,K,Ca,Mg
What segment of the nephron reabsorbs most of the water from the glomerular filtrate?
the proximal convoluted tubule (65%)
Macula densa of the juxtaglomerular apparatus
modified cuboidal to columnar cells, sensitive to Cl ion and regulate filtration rate
Juxtaglomerular cells (JG) in afferent arteriole
modified smooth muscles, produce renin
Juxtaglomerular apparatus
specialized structure formed by the distal tubule & afferent arteriole, regulates blood pressure & glomerular filtration rate through the secretion of renin
The smaller collecting ducts are lined by
- simple cuboidal epithelium
- lateral borders are clear
The larger collecting ducts are lined by
simple columnar epithelium
The papillary duct is lined by
two epithelium layers & transitional epithelium
Calyces and renal pelvis are lined by
transitional epithelium and underlying loose connective tissue layer
What is responsible for the cloudy-like appearance of the urine in horses?
mucous glands present under the epithelium in the calyces and renal pelvis