Biochemistry & Biophysics: Macromolecules, Bonds, and Interactions
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Life
Composed almost entirely of molecules made from six types of atoms.
Atoms
Form molecules by making strong covalent bonds that have specific lengths and geometry.
Structures of macromolecules
Determine their functions.
Biological macromolecules
Long chains containing many freely-rotating single bonds, allowing tremendous conformational flexibility.
Non-covalent interactions
Four types cause macromolecules to fold into specific conformations.
Reversible binding
The same four non-covalent interactions allow macromolecules to reversibly bind specific substrates.
Chemical bonds
About 10-10 M long=1 Ångstrom.
Single bonds
Allow free rotation.
Double bonds
Do not allow free rotation.
Ionic bonds
Result from attraction between opposite charges and are nondirectional.
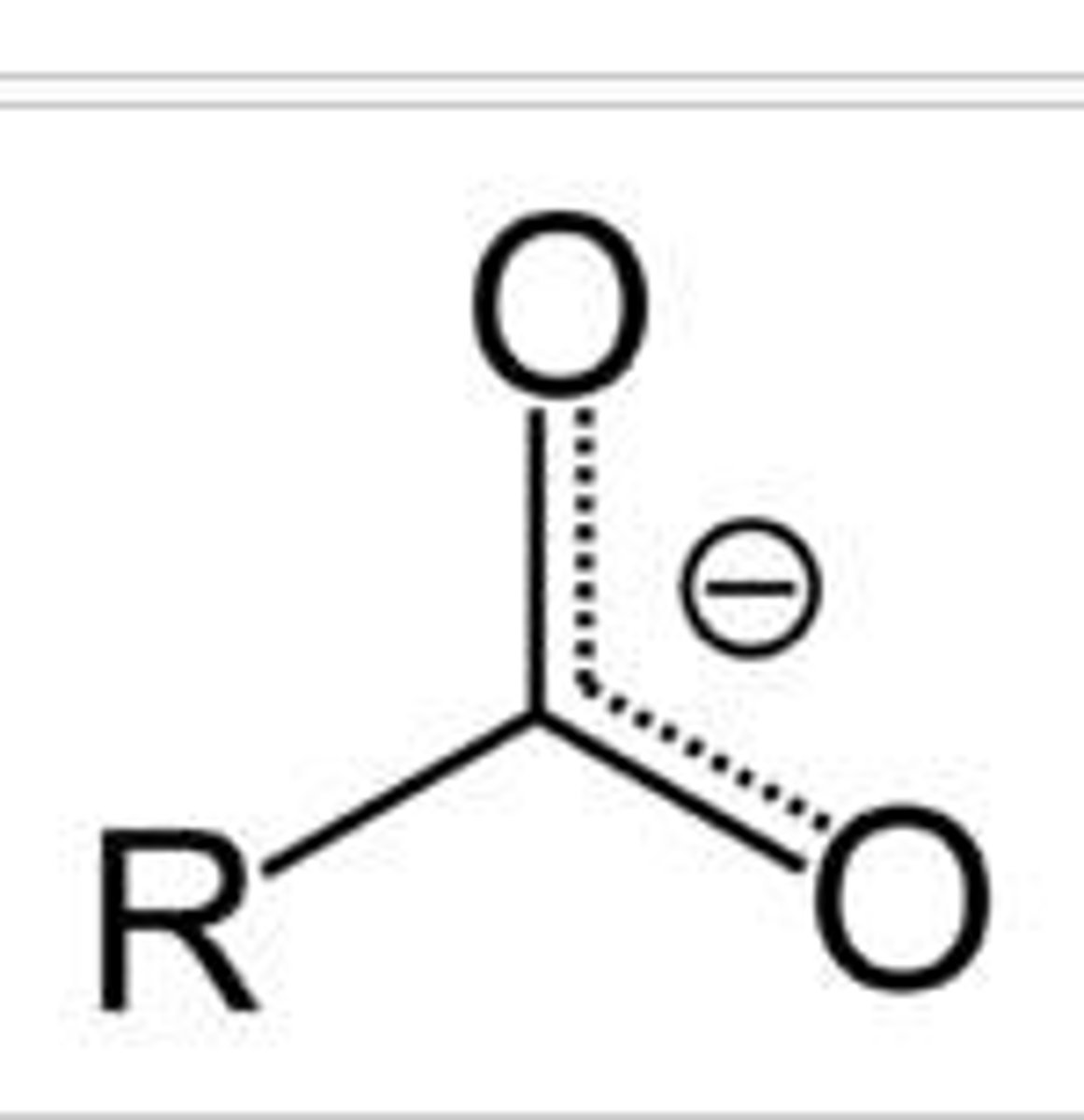
Ionized carboxyl group
-COO-.
Hydrogen bonds
Result when a partially positive charged H bond donor shares a proton with a partially negatively charged H bond acceptor; they are directional and have a specific length.
Hydrophobic interaction
Within a macromolecule, it is driven by maximizing H bonding of the surrounding water.
van der Waals interactions
Occur between nonpolar surfaces due to synchronized transient electric dipoles.
Single bond
A type of chemical bond that allows free rotation.
Double bond
A type of chemical bond that does not allow free rotation.
Bond rotation
The ability of a bond to rotate, applicable to single bonds.
Space-filling model
A model that represents the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule.
Conformation
The three-dimensional shape of a macromolecule.
Ångstrom
A unit of length equal to 10^-10 meters.
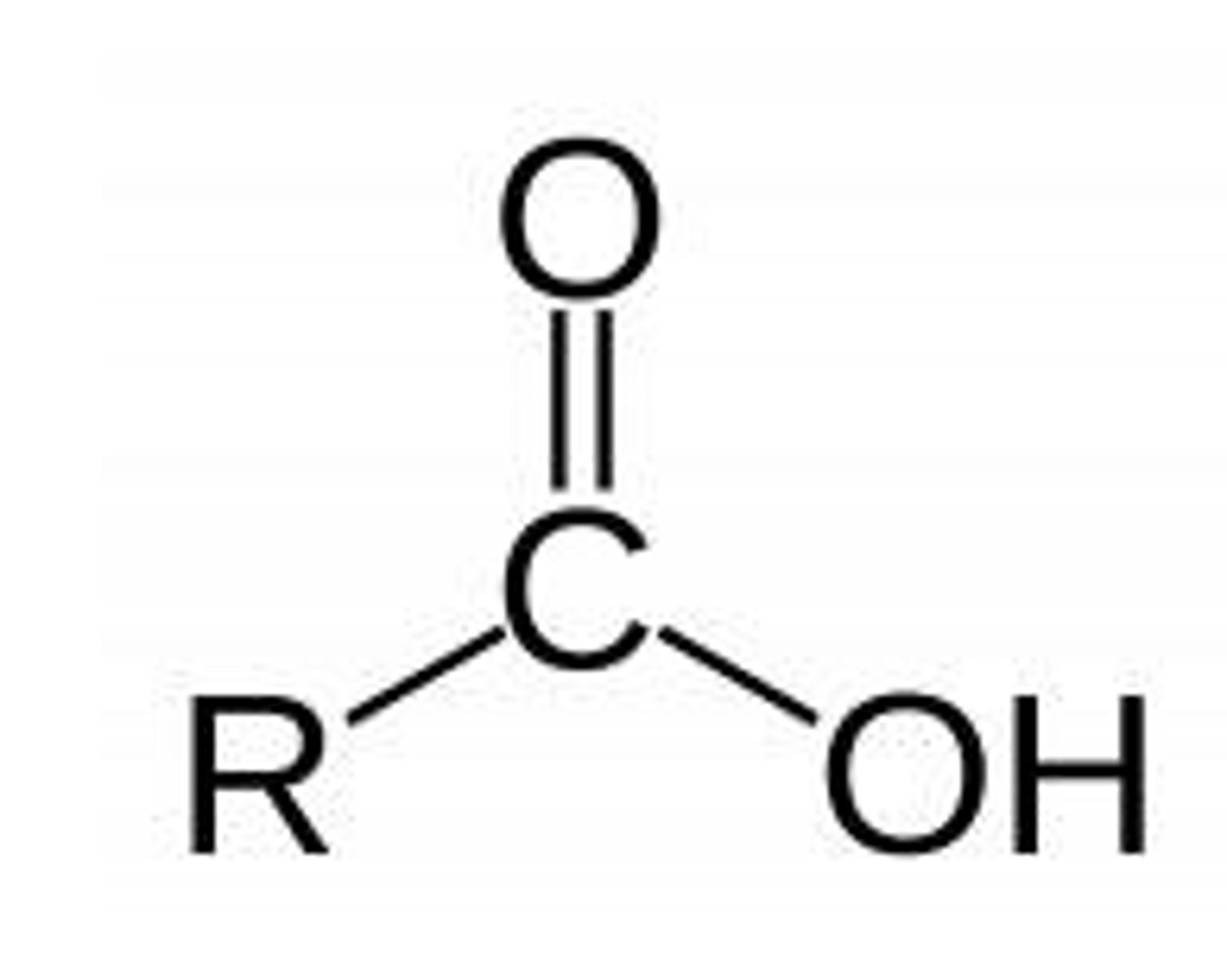
Carboxyl group
A functional group characterized by -COOH.
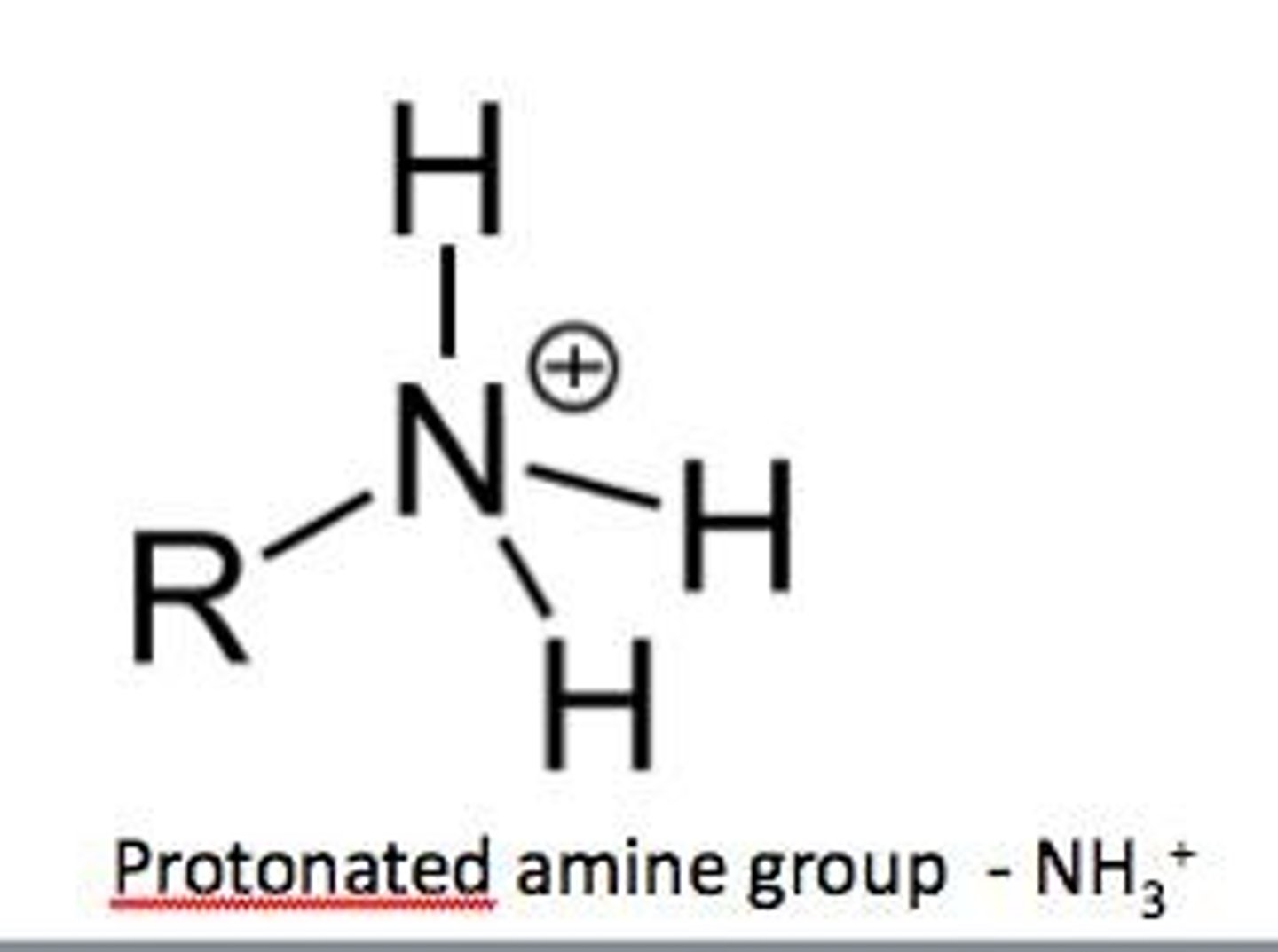
Amine group
A functional group characterized by -NH2.
Hydrophobic
Describes molecules that do not interact favorably with water.
Hydrophilic
Describes molecules that interact favorably with water.
Polar
Describes molecules with a distribution of electrical charge leading to partial positive and negative regions.
Non-polar
Describes molecules that do not have distinct positive and negative regions.
Substrate
The substance on which an enzyme acts.