Biochem Lab Midterm 1
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
The closer the R2 value is to 1.0, the better the linear regression fits your data points, and the more precise and accurate you’re pipetting (T/F)
True
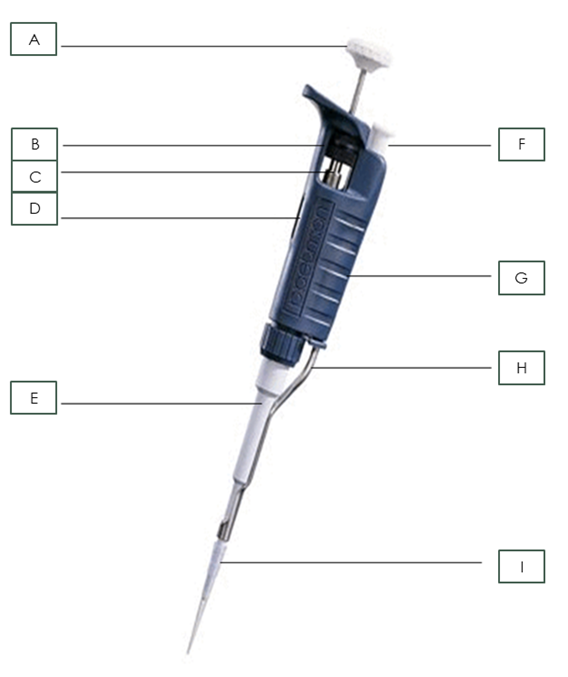
Name the pipette part: A
Plunger
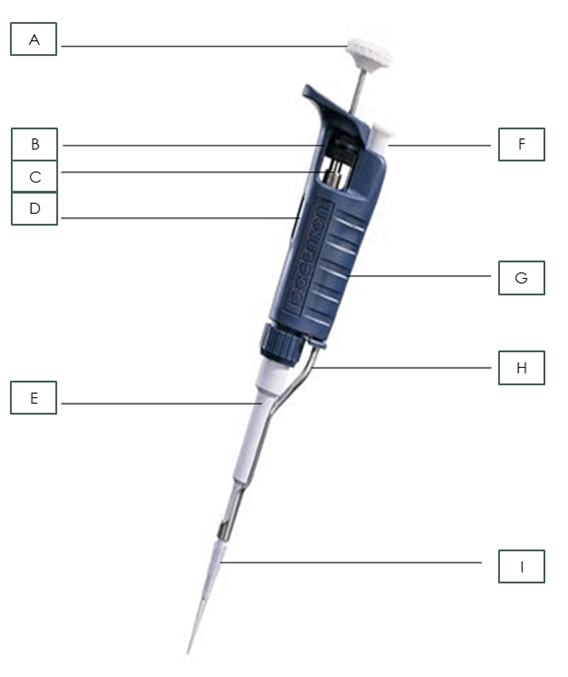
Name the pipette part: B
Friction Ring
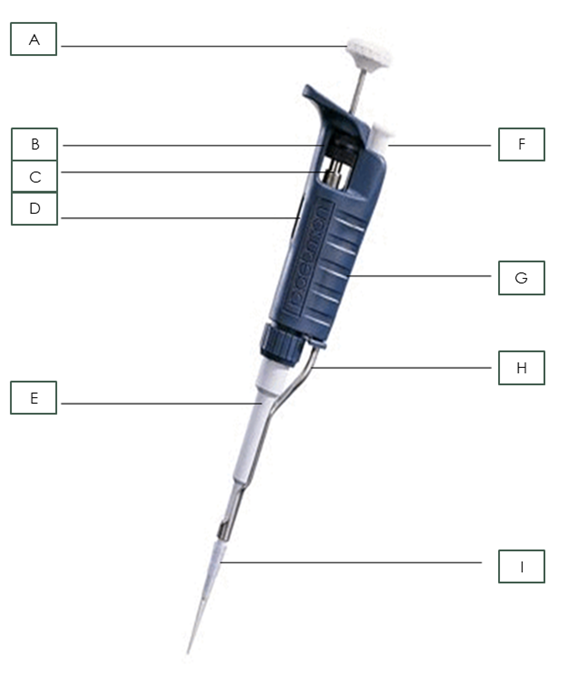
Name the pipette part: C
Micrometer
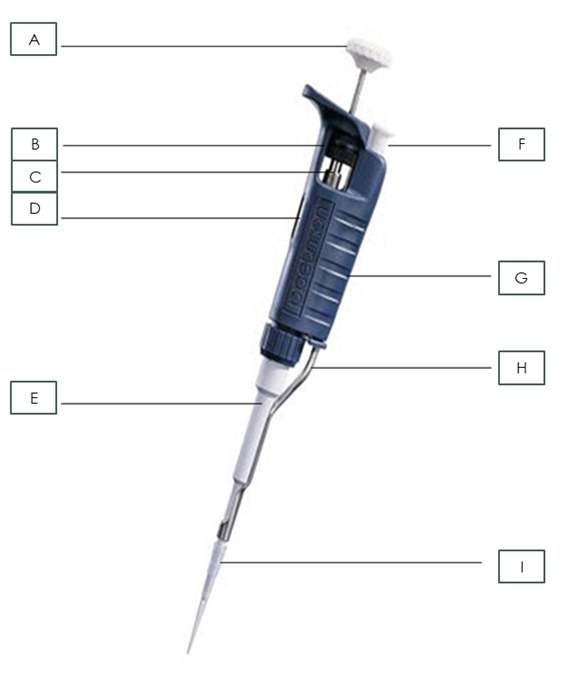
Name the pipette part: D
Volumeter
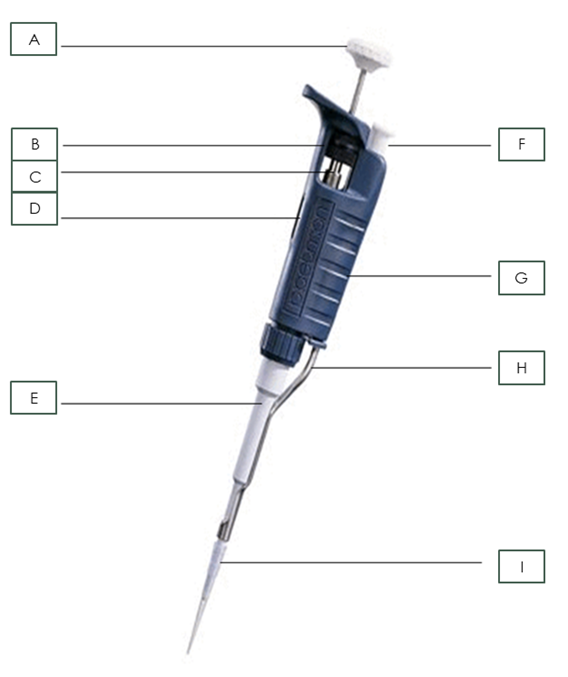
Name the pipette part: E
Shaft
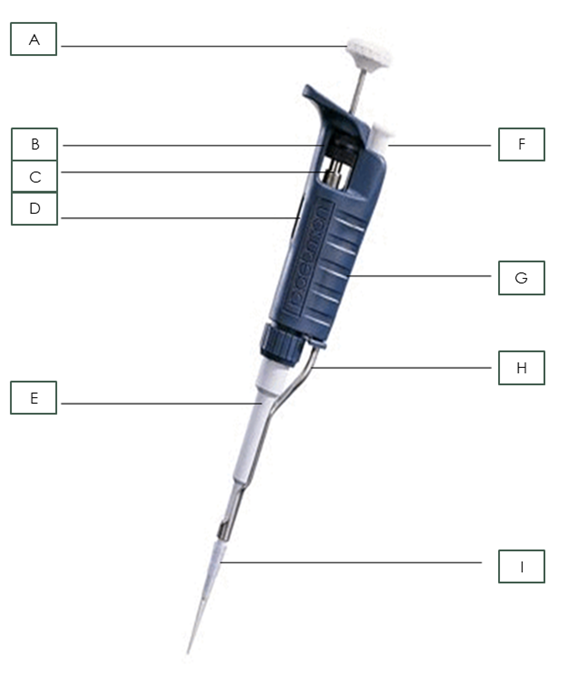
Name the pipette part: F
Tip Ejector Button
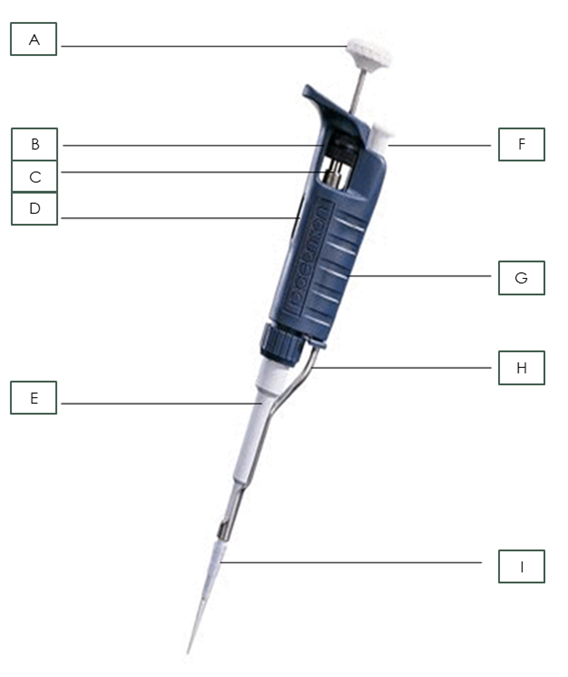
Name the pipette part: G
Body
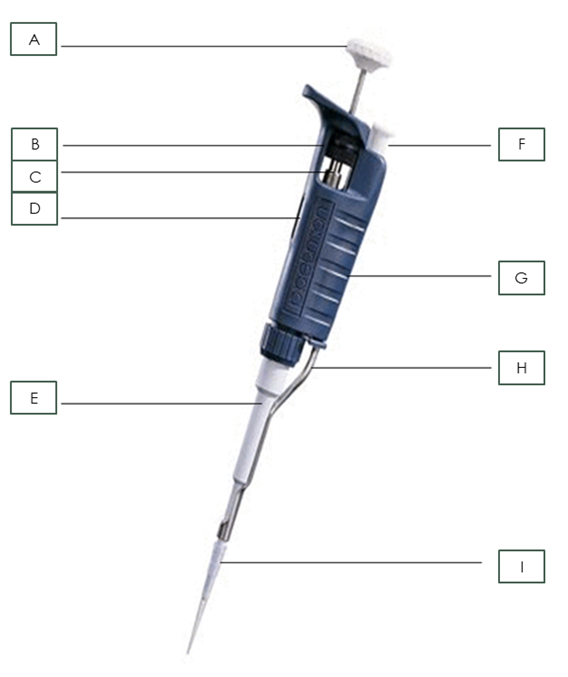
Name the pipette part: H
Tip Ejector
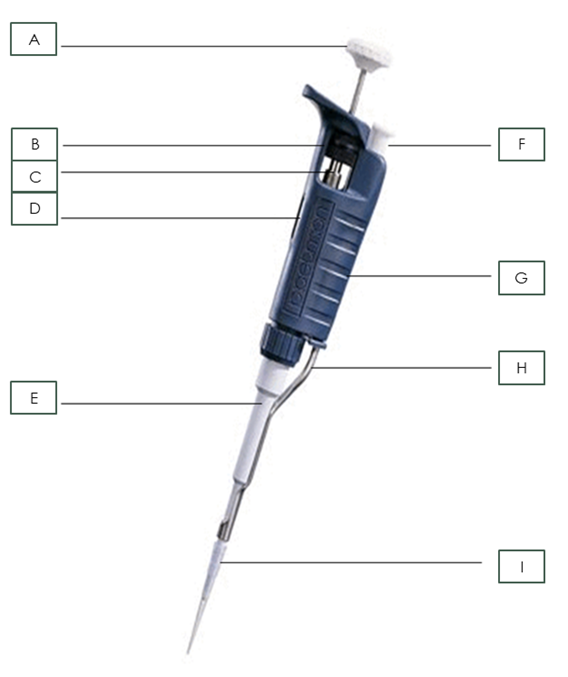
Name the pipette part: I
Pipette Tip
Gel filtration chromatography
Also known as size exclusion chromatography (SEC), When a mixture of molecules is dissolved in a liquid and then applied to a chromatography column that contains porous beads, large molecules pass quickly around the beads, whereas smaller molecules enter the tiny holes in the beads and pass through the column more slowly.
Affinity Chromatography
a biomolecule (often an antibody) that will bind to the protein to be purified is attached to the beads. A mixture of proteins is added to the column and everything passes through except the protein of interest, which binds to the antibody and is retained on the solid support. To get the protein to elute from the column, another buffer is used to disrupt the bond between the protein of interest and the antibody. Often this elution buffer contains high concentrations of salt or acid.
Ion Exchange Chromatography
the glass beads of the column have a charge on them (either + or −). A mixture of protein is added to the column and everything passes through except the protein of interest
Anion Exchange
If the charge of the beads is positive, it will bind negatively charged molecules
Cation Exchange
If the beads are negatively charged, they bind positively charged molecules
Beads (SEC)
Microscopic porous spheres that as has traps to filter small molecules that are temporarily trapped within the pores, also known as the stationary phase
Mixture of molecules dissolved in liquid (SEC)
The mobile phase
Column Bed (SEC)
The mass of beads within a column
Exclusion Limit (SEC)
Molecules greater than 60,000 pass around the beads and are excluded from the columns
The smaller the molecules, the slower they move through the column in size exclusion chromatography (T/F)
True
Buffer (SEC)
The liquid used to dissolve the biomolecules to make the mobile phase
Sample (SEC)
The mixture of biomolecules dissolved in the buffer
Identify the type of chromatography described by each statement.
A positively charged bead interacts with the protein to be purified, which carries a negative charge. A high salt buffer is used to elute the protein to be purified.
Ion-Exchange Chromatography
Identify the type of chromatography described by each statement.
Beads are linked to a biomolecule that interacts with the protein to be purified. The protein to be purified is sometimes eluted using a buffer containing a high concentration of salt or acid.
Affinity Chromatography
Identify the type of chromatography described by each statement.
Beads containing small pores are used to separate biomolecules based on their size. Large biomolecules have little interaction with the beads and elute first, whereas small biomolecules have a lot of interaction with the beads and elute later.
Size Exclusion Chromatography
Identify the type of chromatography described by each statement.
A negatively charged bead interacts with the protein to be purified, which carries a positive charge. A high salt buffer is used to elute the protein to be purified.
Ion-exchange chromatography
Imagine you have a mixture containing two proteins, untagged green fluorescent protein (GFP) and His-tagged GFP (His-GFP). Which type of chromatography would be useful to separate these proteins?
Affinity Chromatography
What type of chromatography is being used in this lab?
Size Exclusion chromatography to separate haemoglobin and vitamin B12
How does the type of chromatography being used in this lab function?
proteins are separated by…?
Size
What gives hemoglobin and myoglobin their distinctive colors?
Iron-containing heme
If athletes wanted to increase their endurance by increasing their oxygen-carrying capacity, how might they accomplish this increase?
Training at high Altitudes
How could gene-therapy, where a normal gene is substituted for a defective copy of a gene, help individuals who have vitamin B12 carrier protein disease?
By providing a working copy of the gene
Range of P1000
100-1000uL
Tip colour of P1000
Blue
Range of P200
20-200 uL
Tip colour of P200
Yellow
Range of P20
2-20 uL
Tip colour of P20
Clear
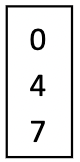
A micropipette is used to pipette specific, small volumes. What is the volume pipetted if the dial reads the following for a P200?
47uL
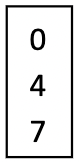
A micropipette is used to pipette specific, small volumes. What is the volume pipetted if the dial reads the following for a P1000?
470uL
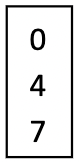
A micropipette is used to pipette specific, small volumes. What is the volume pipetted if the dial reads the following for a P20?
4.7uL

If a P20 micropipette has the pictured setting, what volume of liquid will be dispensed?
14.6uL

If a P200 micropipette has the pictured setting, what volume of liquid will be dispensed?
72uL

If a P1000 micropipette has the pictured setting, what volume of liquid will be dispensed?
530uL
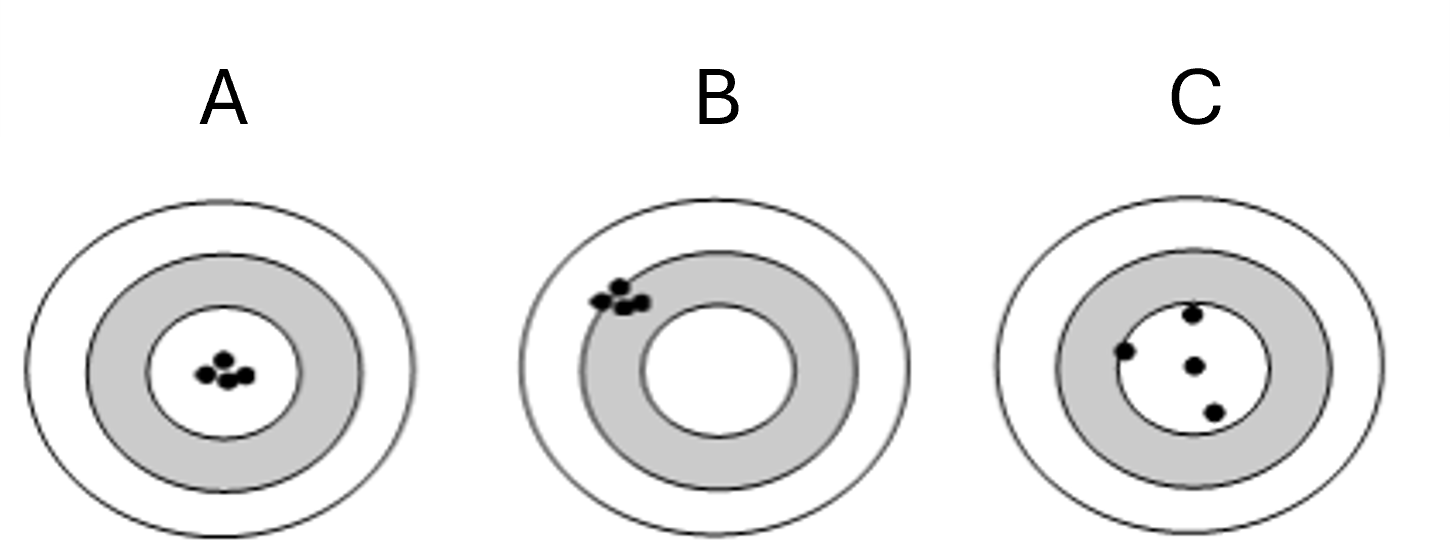
Target A
Precise and Accurate
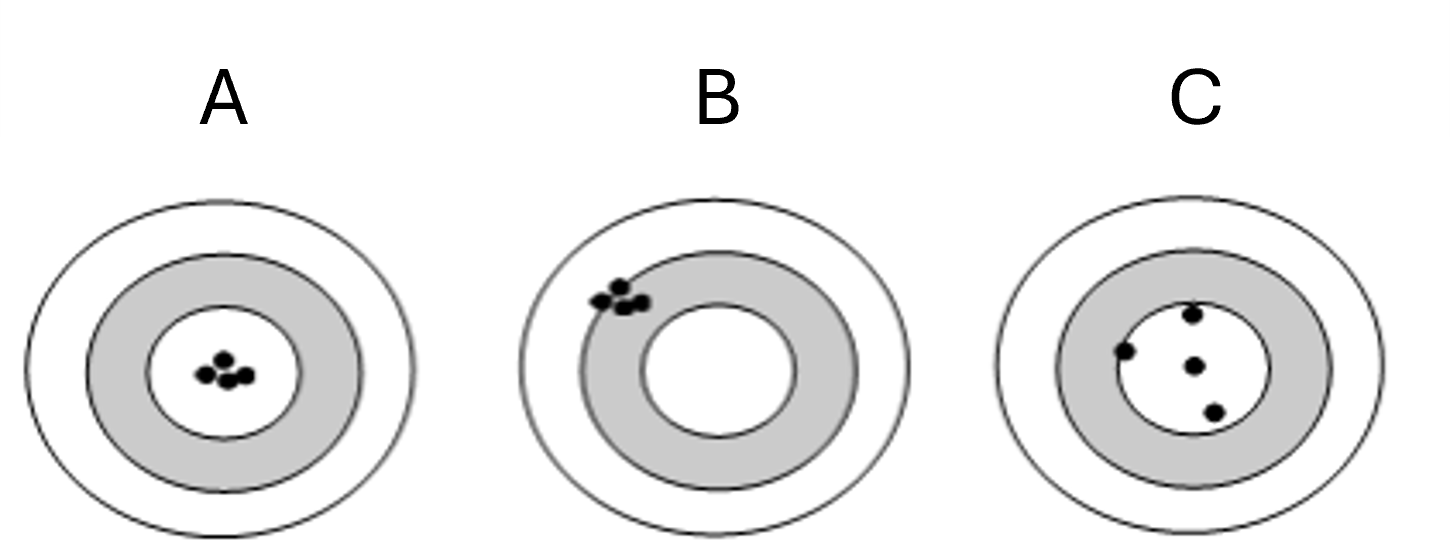
Target B
Precise but not Accurate
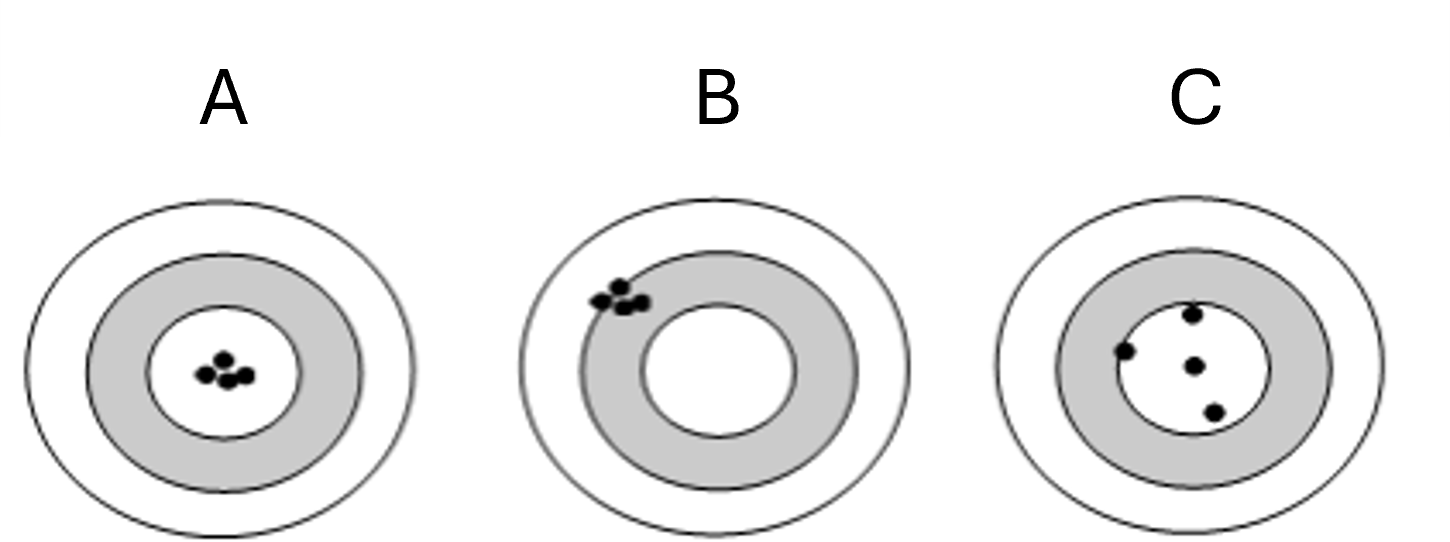
Target C
Accurate but not precise
a protein found in red blood cells, functions to transport oxygen to the tissues of the body
Hemoglobin
The body can not adapt to environmental changes which require increased amounts of oxygen delivery to tissues (TF)
False
Immunology
study of the immune system
Innate immunity
A person is born with certain immunological defenses against pathogens, includes circulating macrophages and natural killer cells
Passive immunity
the acquisition of antibodies from an external source, for example, antibodies passed from mother to infant, or certain postexposure vaccines such as that for rabies.
Passive immunity lasts only a few weeks, and also does not change with multiple exposures (T/F)
True
Acquired/Adaptive immunity
Specific response to specific foreign substances, split into 2categorties: humoral immunity and cell-mediated immunity
Humoral Immunity
involves production of antibodies that circulate in the bloodstream and lymph and bind specifically to foreign antigens
Cell-mediated immunity
involves the production of T lymphocytes (T cells) that bind and destroy infected cells
Antigen
In an immune response, an invasion by something foreign to the body generates antibody production by B lymphocytes (B cell)
Epitope
Each B lymphocyte generates a unique antibody that recognizes a single shape on an antigen
Antigens
can be microorganisms (e.g., viruses and bacteria), microbial products (e.g., toxins produced by some bacteria, or protein components of the microbes), foreign proteins, DNA and RNA molecules, drugs, and other chemicals
Antibodies
Proteins also called immunoglobulins (Ig), that are produced by B cells and can remain attached to B cells or become free floating
5 classes of immunoglobulins
IgG, IgM, IgA, Ig E, and IgD
IgE is the most abundant immunoglobulin (T/F)
False, IgG is the most abundant 15% (parham)
Immune cells
soldiers of the acquired immune response
Macrophages two primary functions
1) Removing foreign cells and molecules from the blood / 2) Processing antigens and presenting them on their cell surfaces
Disease can result from… (3)
Infection, genetic defect, or environmental toxins
Infections can be…
Transmitted from person to person, Transmitted from animals to people, or contracted from the environment
Pathogen Spread Through: Exchange of body fluids
Sexually transmitted diseases
Pathogen Spread Through: Food
Mad cow disease
Pathogen Spread Through: Water
Cholera and Giardiasis
Pathogen Spread Through: Inhalation
Flu and Tuberculosis
Pathogen Spread Through: Absorption through the skin
Hookworms
Pathogen Spread Through: Vector transfer
Malaria
Primary Response
When immunized with a foreign substance (either by vaccination or through natural exposure), an individual mounts an immune response
Secondary Response
The second time that the individual is exposed to the antigen, be it weeks or years after immunization, the immune response is larger and much more rapid
Antibody production may continue for a couple days or weeks (T/F)
False, months or even years
Problems with the immune system (3)
Hypersensitivity, Immunodeficiency, and autoimmune diseases
Hypersensitive Reactions
occur when the immune system overreacts to an antigen
Four types of hypersensitive reactions
1) anaphylactic reactions, allergies
2) Cytotoxic Reaction, transfusion reactions
3) Immune complex reactions, Farmer’s lung
4) Delayed-type hypersensitivity, Dermatitis
Immunodeficiency
an individual is unable to mount an effective immune response, resulting in increased vulnerability to opportunistic infections
Two types of immunodeficiency
1) Genetic basis (“bubble boy” disease)
2) External cause (HIV/AIDS)
Autoimmune disease
results from the immune system making a mistake and mounting an immune response against one’s own body
Immunofluorescence assay (IFA)
Specific microorganisms detected with fluorescently labeled antibodies
Agglutination
Visible precipitates appear when antibodies and specific antigens come in contact
Immunochromatography tests
Card or dipstick-based immunoassays
Microplate tests
ELISA or RIA
Molecular methods
Detection of microbial RNA or DNA; also used to detect microbial drug resistance (AST); may use PCR
Microscopy
Visual identification based on staining with specific reagents or on physical characteristics
Live attenuated vaccines
are weakened (attenuated) microbes, that are non-pathogenic. Ex. Measles and smallpox
Killed or inactivated vaccines
are made of microbes killed by heat or chemicals. Ex. Rabies
Subunit Vaccines
are made from pieces of microbes. They consist of one or more antigens from either the disease agent or a microbial product, and they may be derived from the organisms or engineered using molecular biology. Ex. Tetanus
DNA Vaccines
DNA that codes for microbial antigens is cloned into a vector, and the naked DNA is injected into the patient. The DNA is taken up by cells, transcribed, and translated, and the resulting antigenic protein elicits an immune response. Not available yet.
mRNA Vaccines
The molecules are made of mRNA bases which carry chemical modifications that increase the mRNA's stability and immunogenicity. The mRNA molecules are taken up by cells and translated to produce the antigen, which is then used to produce an immune response. Ex. COVID-19
Antibody Vaccines
The ability to construct human monoclonal antibodies using recombinant DNA technology means that antibodies prepared against specific antigens may be used safely in humans.
Postexposure Vaccines (immunotherapy)
are used to treat a disease
Two types of traditionally produced antibodies
Polyclonal Antibodies and Monoclonal Antibodies
Polyclonal antibodies
generated by immunizing an animal (usually a rabbit, goat, or sheep) and obtaining serum. The product is antiserum towards gp120, and the antiserum can be used directly or the antibodies can be purified from it.
Advantage/Disadvantage of Polyclonal antibodies
Simple, inexpensive but no batches will be the same
Monoclonal Antibodies
B cell clones producing single antibodies can be isolated from the spleens of immunized mice, but these cells die after a few weeks in the laboratory, limiting production of the large amounts of antibody generally needed for research and commercial applications. However, B cells can be made to live (and produce antibodies) indefinitely if they are fused with tumor-like immortal cells
Genetic engineering antibody methods (2)
Hybridoma Immortalization and Phage Display
Hybridoma Immortalization
Recombinant DNA technology allows the antigen recognition site from a known mouse monoclonal antibody to be camouflaged within a human antibody by combining part of the mouse gene with the human antibody gene