Biochemistry: Macromolecules and Their Functions
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
Carbohydrates
Provide short and long term energy storage for organisms. They provide energy for the body's metabolism.
Lipids
One of the four major classes of large, complex organic macromolecules.
Proteins
One of the four major classes of large, complex organic macromolecules.
Nucleic acids
One of the four major classes of large, complex organic macromolecules.
CHNOPS
The six important elements that most biological molecules are made from: Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur.
Covalent Bonds
Bonds that can either be non-polar (ie. lipids) or polar (ie. water).
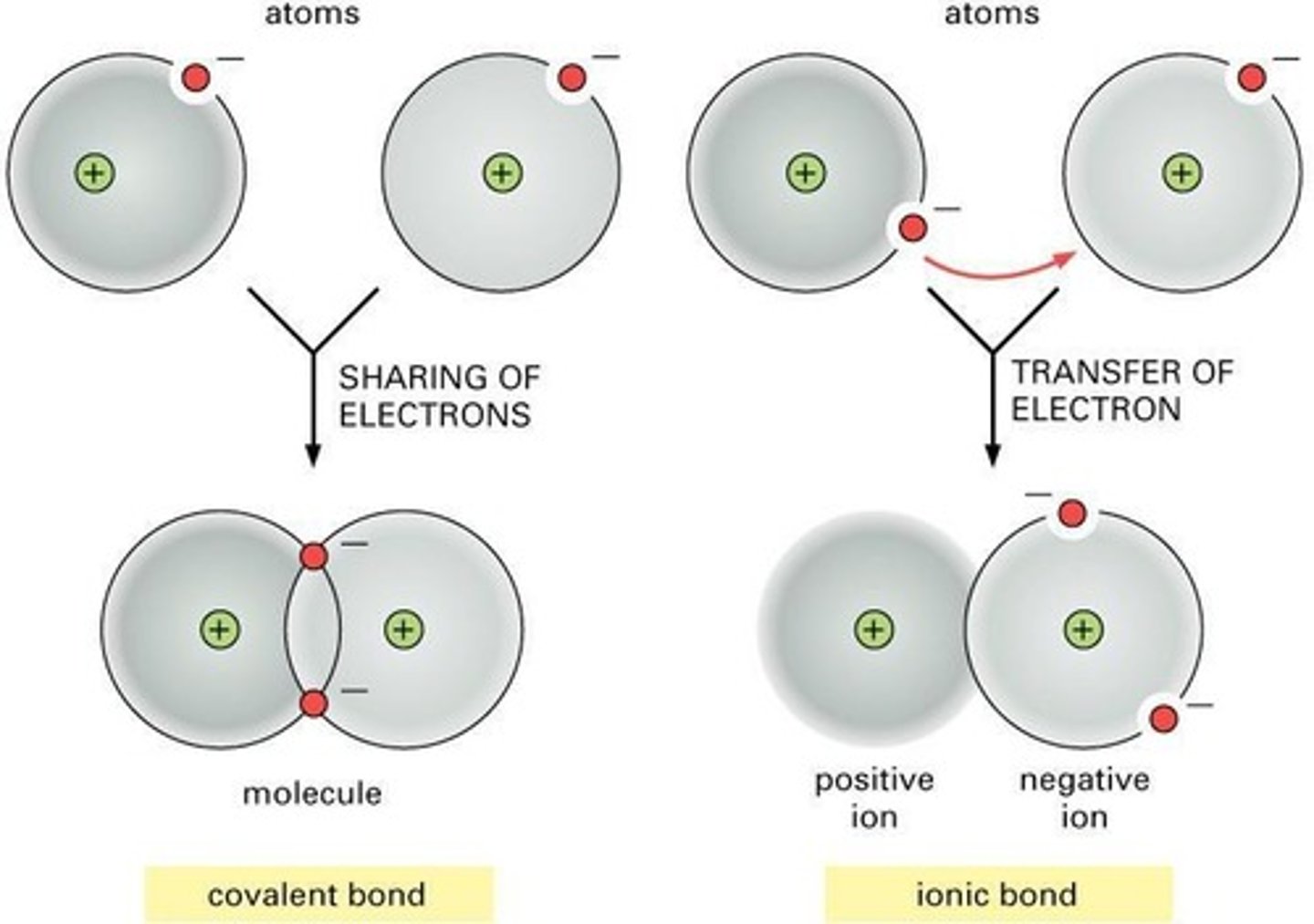
Ionic Bonds
Bonds that are always polar (ie. charged).
Polymers
Long molecules formed by covalently linking many subunits.
Monomers
Each repeating subunit of a polymer.
Dehydration Synthesis
A reaction through which macromolecules are assembled.
Hydrolysis
A reaction through which macromolecules are broken down into their individual subunits.
Carbohydrate Composition
Almost always have two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen for every atom of carbon. The general formula is (CH2O)n.
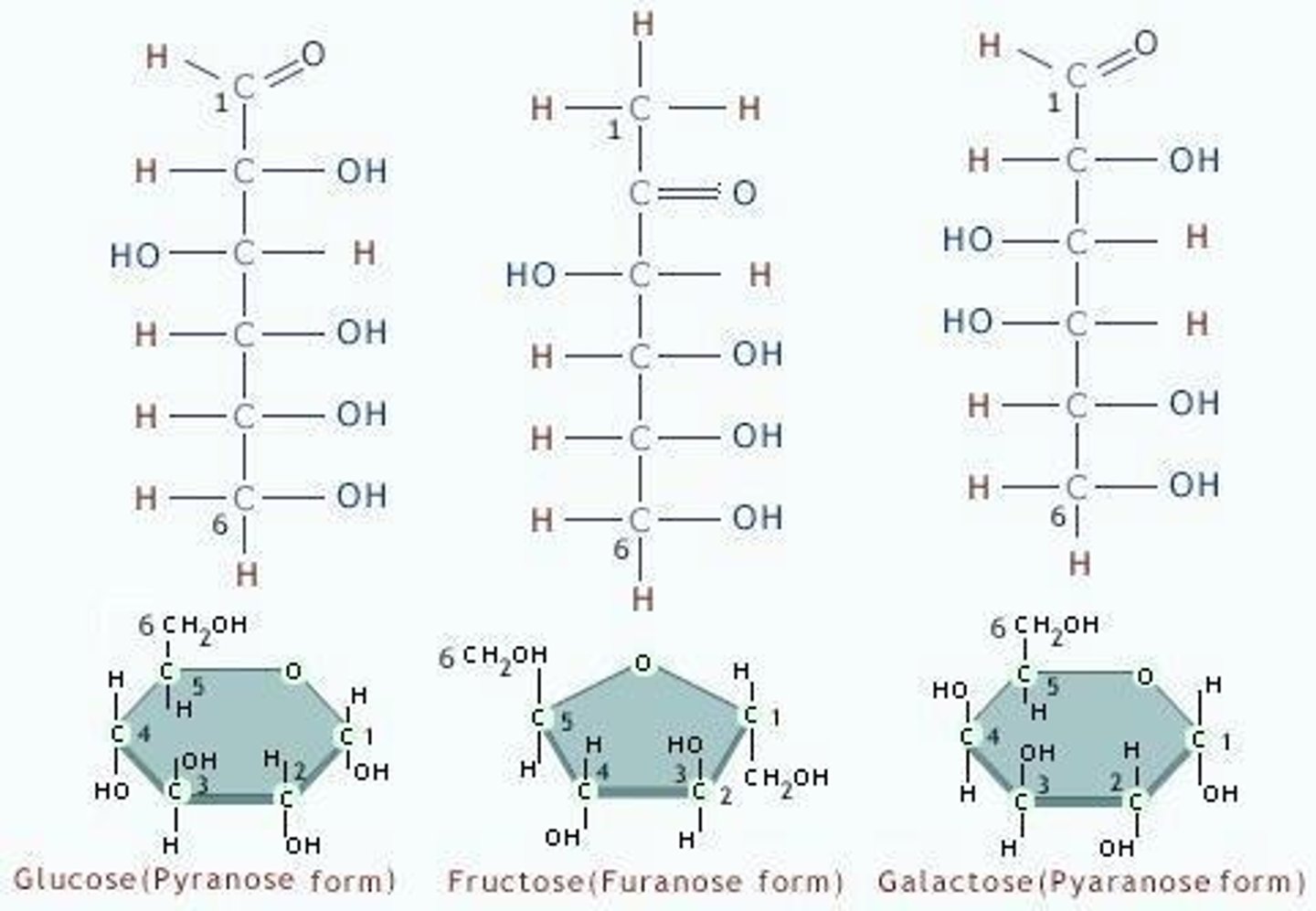
Monosaccharides
Carbohydrates with three to seven carbon atoms, known as simple or energy sugars.
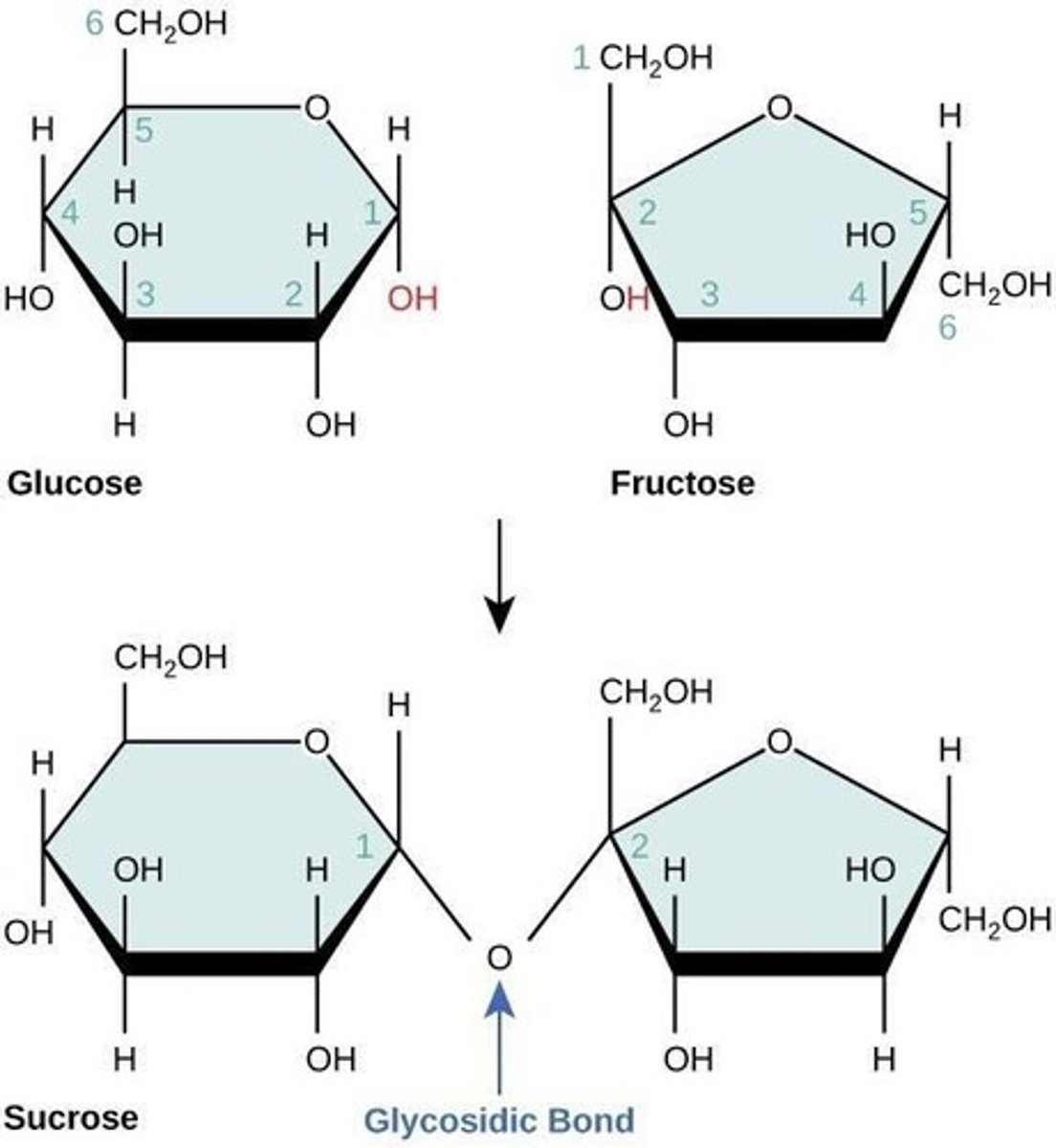
Disaccharides
Also known as double or transport sugars, made up of two monosaccharides through dehydration synthesis.
Polysaccharides
Carbohydrates that consist of many linked simple sugars, also known as complex, storage or structural sugars.
Trioses
Monosaccharides with 3 carbon atoms.
Tetroses
Monosaccharides with 4 carbon atoms.
Pentoses
Monosaccharides with 5 carbon atoms.
Hexoses
Monosaccharides with 6 carbon atoms.
Heptoses
Monosaccharides with 7 carbon atoms.
Isomers
Compounds that have the same chemical formula but different molecular shapes.
Sucrose
A disaccharide formed from glucose and fructose.
Maltose
A disaccharide formed from glucose and glucose.
Lactose
A disaccharide formed from glucose and galactose.
C12H22O11
The formula for disaccharides like sucrose, maltose, and lactose.
Starch/Amylose
Stores energy in plants.
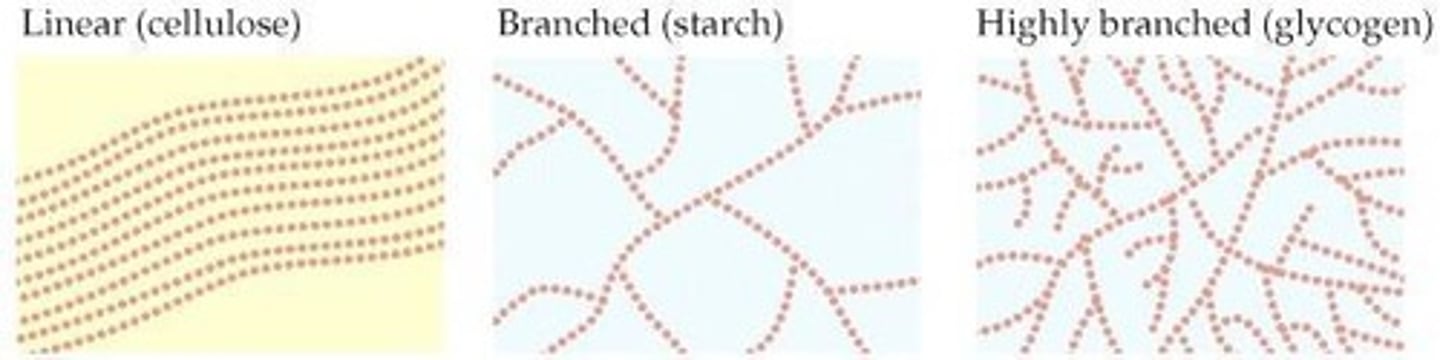
Glycogen
Stores energy in animals.
Cellulose
Makes up cell walls in plants.
Chitin
Found in arthropod exoskeletons and cell walls in fungi.
Polysaccharide Structure
Determines function.
Glycogen Molecules
More branched than amylose or cellulose, packing more glucose units into a single cell.
Energy Storage in Animals
Glycogen is the main storage form of glucose in the body, particularly in the liver and muscles.
Cellulose Molecules
More linear, storing less glucose but providing more structural support for plants.
Cellulose-Digesting Bacteria
Herbivores need these in their digestive tract to obtain more nourishment from their diets.
Monosaccharides
Simple or energy sugars.
Disaccharides
Double or transport sugars.
Polysaccharides
Complex or storage sugars.
Glucose
Example of a monosaccharide.
Fructose
Example of a monosaccharide.
Galactose
Example of a monosaccharide.
Maltose
Example of a disaccharide.
Sucrose
Example of a disaccharide.
Lactose
Example of a disaccharide.
Triglycerides
Fats/Oils that store 2.25 times more energy per gram than any other biological molecule.
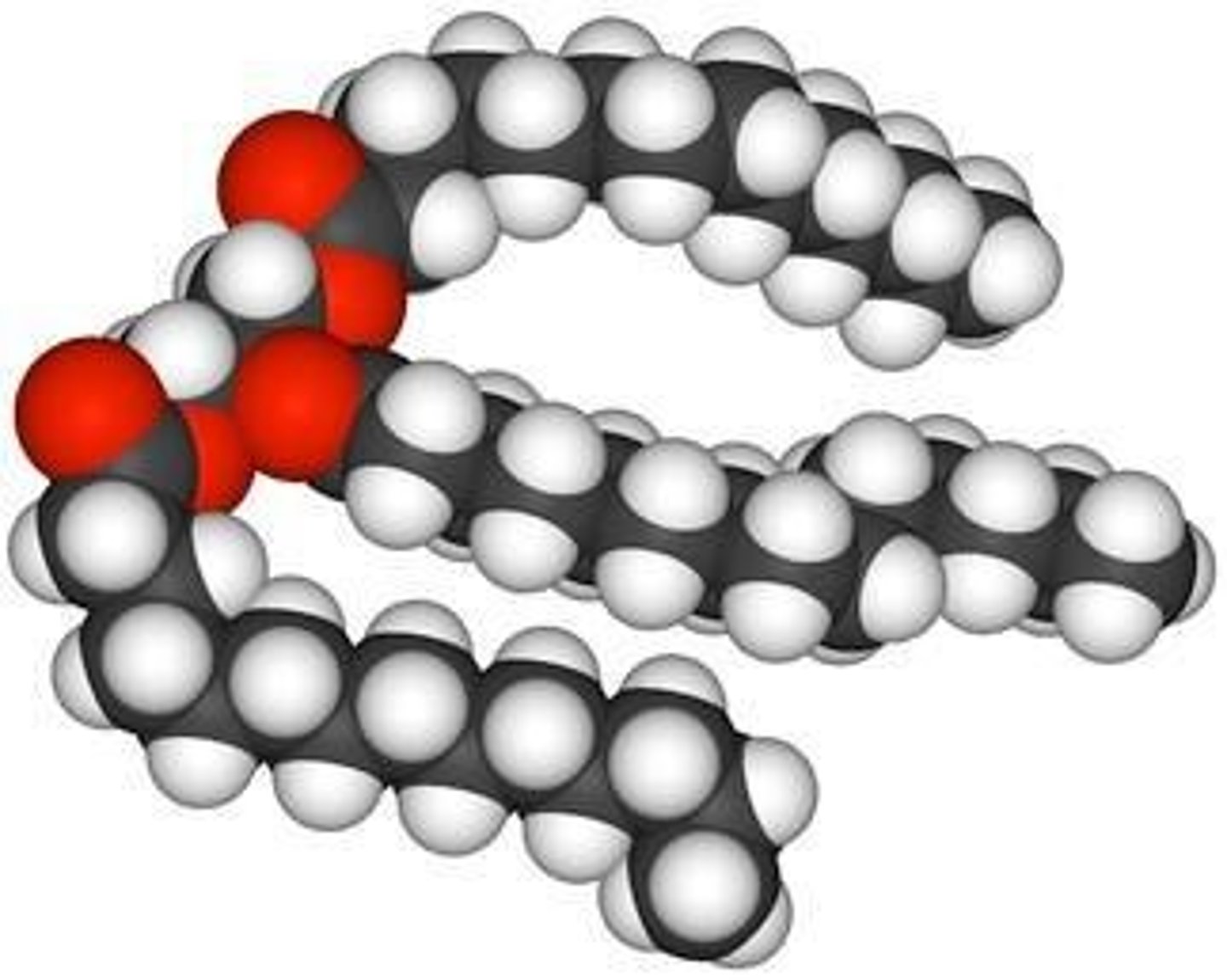
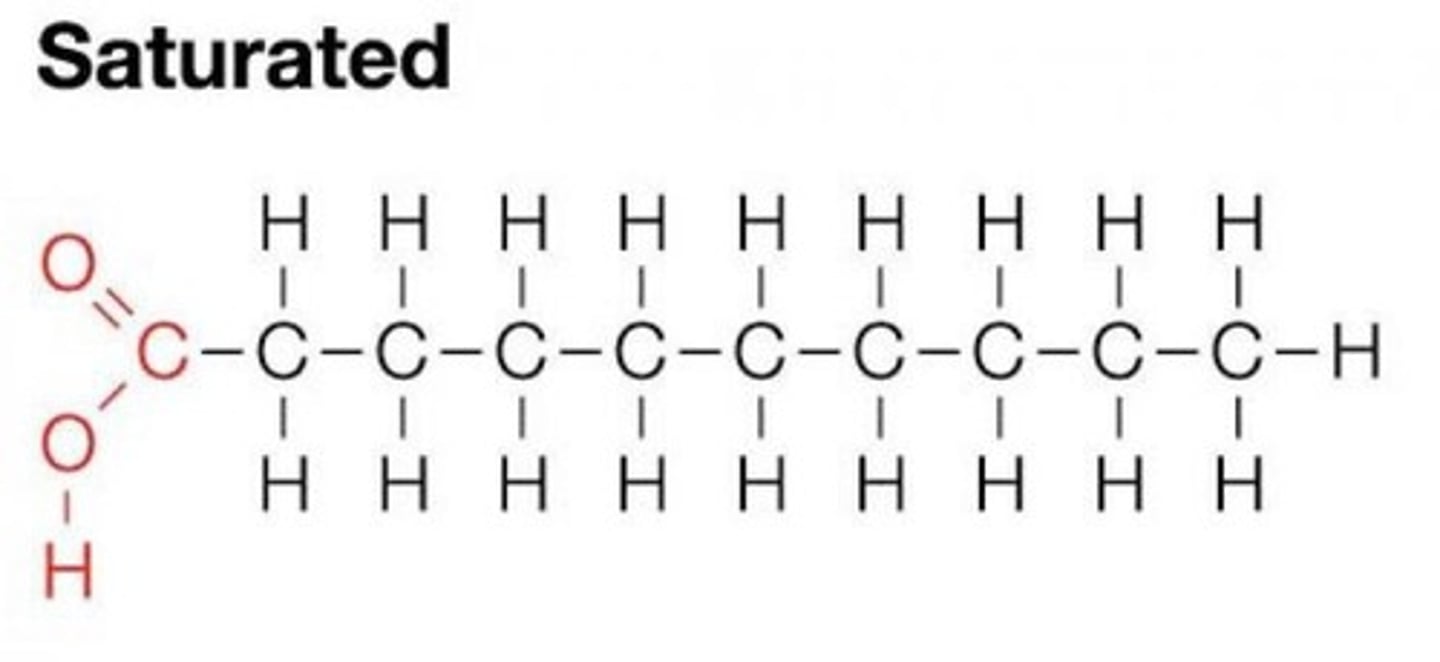
Saturated Fatty Acids
Contain the maximum number of hydrogen atoms, solid at room temperature, and harder to digest.
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Have double bonds between some carbon atoms, liquid at room temperature, and easier to digest.

Dietary Perspective on Unsaturated Fats
Healthier as they increase HDL (good cholesterol) and decrease LDL (bad cholesterol).
Dietary Perspective on Saturated Fats
Increase LDL in the body, leading to a greater risk of heart disease.
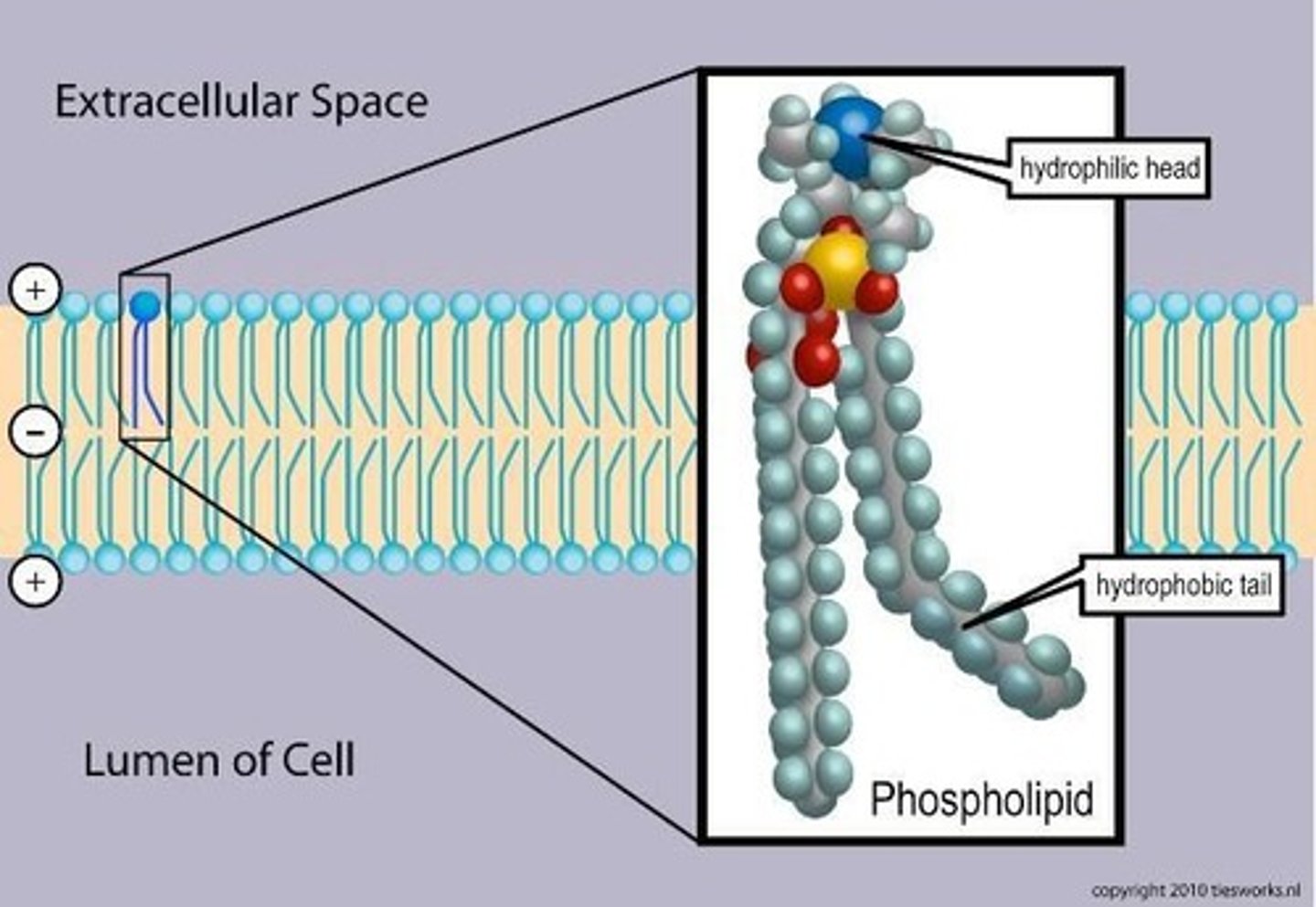
Phospholipids
Structural lipids found in most animal membranes, including cell membranes.
Phospholipid Bilayer
Formed by phospholipids butting up tail to tail.
Steroids
Lipids consisting of four interconnected carbon rings, serving as components of membranes or as vitamins and hormones.
Cholesterol
One of the most abundant steroids, serving as a major component of membranes that wrap around & insulate many nerve fibers and a chemical precursor of several important animal hormones.
Insolubility of Cholesterol
Like other lipids, it is insoluble in water and may settle out of solution when present in high concentrations, which can cause gallstones and atherosclerosis.
Triglycerides
Stores energy.
Phospholipids
Major component of cell membrane structure.
Steroids
Function as hormones.
Glycerol
A component of triglycerides, connected to two fatty acids.
Fatty Acids
Can be unsaturated (oils) or saturated (fats).
Cholesterol Structure
Composed of interconnected carbon rings.
Protein Functions
Proteins serve essential functions including structural support, enzymatic catalysis, transport & storage, movement, immune protection, hormonal regulation, and sensory perception.
Structural Support
Major component of bone, cartilage, feathers, fur, hair, biological membranes, and chromosomes.
Enzymatic Catalysis
All enzymes are proteins that play unique roles in growth and function.
Transport & Storage
Proteins serve as carriers of important small molecules and ions, such as iron atoms carried in mammalian blood by transferrin.
Movement
Muscle fibers are composed primarily of protein filaments.
Immune Protection
Immunoglobulins are a group of highly specific protein molecules.
Hormonal Regulation
Several hormones are proteins and others are transported throughout the body by proteins.
Sensory Perception
Responses of nerve cells to specific stimuli are often mediated by specific receptor proteins.
Amino Acids
The subunits of proteins, consisting of a central carbon atom bonded to a hydrogen atom, an amino group, a carboxyl group, and an R group.
Essential Amino Acids
Nine amino acids that cannot be synthesized and must come from diet: threonine, tryptophan, valine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, histidine, isoleucine, and leucine.
Peptide Bonds
Amino acids bond together in strands to form proteins, connected by peptide bonds via dehydration synthesis.
Dipeptide
Formed when two amino acids are connected together.
Tripeptide
Formed when three amino acids are connected together.
Polypeptide
A chain of many amino acids.
Protein Structure
Different amino acids along the strand attract and repel each other, causing the strands to coil and twist, resulting in a complex 3D structure.
Denaturation
The loss of tertiary and secondary structures of proteins due to external stress or compounds, such as cooking.
Deamination
The loss of tertiary and secondary structures by the removal of amine group(s), usually facilitated by enzymes called deaminases.
Hemoglobin
Oxygen-transport protein in red blood cells.
Cell Membrane Proteins
Relay signals between the cell's internal and external environments; move molecules and ions across the membrane; allow cells to identify each other and interact.
Catalase
Catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen, preventing the build-up of carbon dioxide within the blood.
Keratin
Key component of skin, hair, and nails.
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
A double-stranded nucleic acid molecule that governs the processes of heredity in the cells of organisms.
RNA (ribonucleic acid)
Plays a role in gene expression and protein synthesis.
Nucleotides
Subunits that make up nucleic acids, including adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, and uracil.
Enzymes
Specialized protein molecules that function as biological catalysts.
Carbonic Anhydrase
An enzyme produced by red blood cells that enables carbon dioxide and water to react to form about 600,000 molecules of carbonic acid each second.
Lock and Key Approach
A model for how enzymes work, where the enzyme's active site is specifically shaped to fit the substrate.
Optimal Temperature
The temperature range at which specific enzymes function best.
Inhibitors
Molecules that attach to the enzyme and reduce its ability to bind substrate.
Competitive Inhibitors
Inhibitors that compete with the substrate to occupy the active site of the enzyme.
Non-Competitive Inhibitors
Inhibitors that attach elsewhere on the enzyme, changing its shape and reducing its ability to bind substrate.
Chemical Reactions
Processes that occur in the body, such as the oxidation of glucose, which releases energy.
Catalysts
Substances that speed up chemical reactions and lower the energy required for the reaction without being consumed.
Macromolecules
Large molecules discussed earlier that can be used for chemical reactions in the body.
Temperature Effects on Enzymes
Enzymes are affected by temperature and pH, with specific enzymes having an optimal functioning range.
Denaturation
The process by which proteins lose their structure and function due to high temperatures.
Substrate
The reactant molecule that an enzyme acts upon.
Chemical Energy
Energy released from chemical reactions, such as the oxidation of glucose.
Biological Catalysts
Substances that increase the rate of biological reactions, primarily enzymes.
Phosphate Group
A component of nucleic acids, along with a nitrogenous base and a five-carbon sugar.
Five-Carbon Sugar
A component of nucleic acids, which can be either deoxyribose or ribose.