Lower Extremity Venous Abnormalities
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What are the symptoms of venous disease?
Pain
Swelling or edema
Rubor, redness, or hyperpigmentation (brawny disolorization)
Warmth
Venous HTN
Ulcers
What is the Homan sign?
Pain experienced with quick dorsiflexion of foot seen in those with DVT
What is a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) of the lower extremity?
Thrombosis of deep veins that most commonly originate at calf in soleal sinuses
What is the most reliable finding for a DVT diagnosis?
Lack of compressibility
What is the sonographic appearance of an acute DVT?
Grayscale shows a non-compressible and dilated vessel lumen
Grayscale shows an anechoic structure with poor wall attachment filling lumen
Color shows no color fill
PW shows no or minimal venous flow
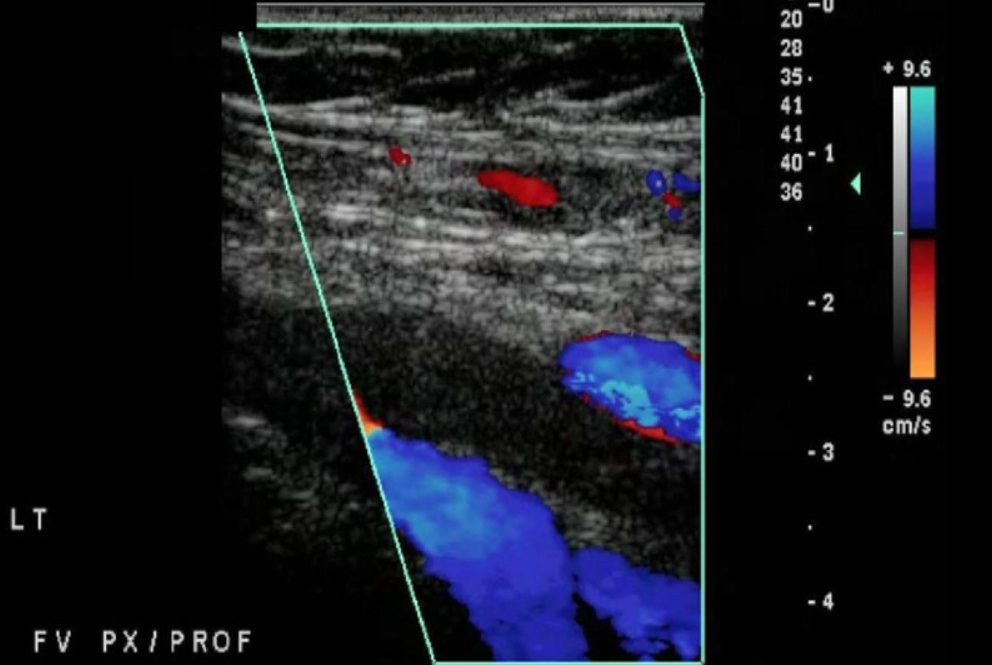
Identify this image.
Acute DVT
What is the sonographic appearance of a chronic DVT?
Grayscale shows a non-compressible and retracted vessel lumen
Grayscale shows an echogenic or hyperechoic structure with strong wall attachment lining lumen
Grayscale shows echogenic vein walls
Color shows partial color fill
PW shows continuous or normal venous flow
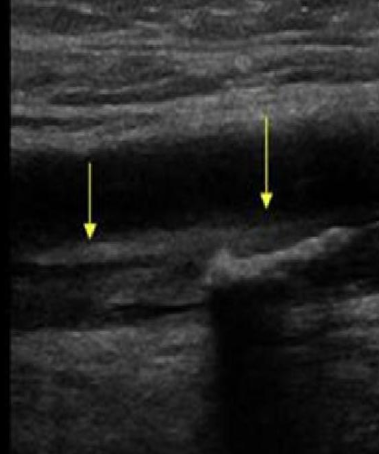
Identify this image.
Chronic DVT
What is Virchow’s Triad?
Main factors contributing to DVT that include
Trauma due to injury or drug usage
Stasis due to bed rest or pregnancy
Hypercoagulability due to cancer, oral contraceptive use, or polycythemia vera
What is the treatment for DVT?
DVT in deep leg veins veins are treated aggressively
Bedrest
Lovenox shot
IV heparin to stop clot progression
Coumadin, Warfarin, Xarelto, or Eliquis therapy for 3-6 months
What is a Greenfield filter?
Umbrella-like device inserted in IVC below renal veins to prevent embolisms from reaching lungs in patients with history of multiple DVTs
What is venous bypass?
Procedure used to treat ilio-femoral venous obstruction
Left obstruction: Flow moves left to right in graft
Right obstruction: Flow moves right to left in graft
What lab values are associated with DVT?
D-dimer > 500 ng/ml
What is D-dimer?
Test that can indicate DVT
What can cause increased D-dimer levels?
Pregnancy
Malignancy
Recent surgery
Trauma
What are the characteristics of a venous ulcer?
Not painful
Shallow ulceration
Wet and oozing
Located near medial malleolus or GAITER ZONE
What is May Thurner syndrome?
When right iliac artery compresses left iliac vein and causes extensive DVT
What is superficial phlebitis or thrombophlebitis?
Inflammation of vein walls with or without thrombus
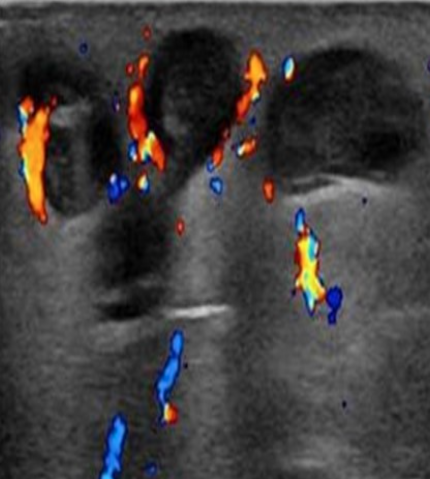
Identify this image.
Superficial phlebitis or thrombophlebitis seen as increased vascularity around vessel walls
What is superficial venous thrombosis?
Thrombosis of superficial vein due to valvular insufficiency or patient inactivity
What is the treatment for a superficial venous thrombosis?
Less aggressive
Anti-inflammatory drugs
Support stockings
Warm compress
Limb elevation
What is phlegmasia cerulea dolens?
Extensive thrombosis occluding deep AND superficial system due to MALIGNANCY
What are the symptoms of phlegmasia cerulea dolens?
Cyanotic skin due to high concentration of deoxygenated blood
Severe limb swelling
Edema
What is phlegmasia alba dolens?
Extensive thrombosis that ONLY affects deep system due to PREGNANCY
What are the symptoms of phlegmasia alba dolens?
Milky white skin due to reduction in arterial flow
Swelling
Pallor
Pain
What is cellulitis?
Bacterial infection of skin that causes skin to be red and warm
What is a Baker’s cyst?
Encapsulated synovial fluid in medial popliteal fossa due to chronic knee joint dysfunction
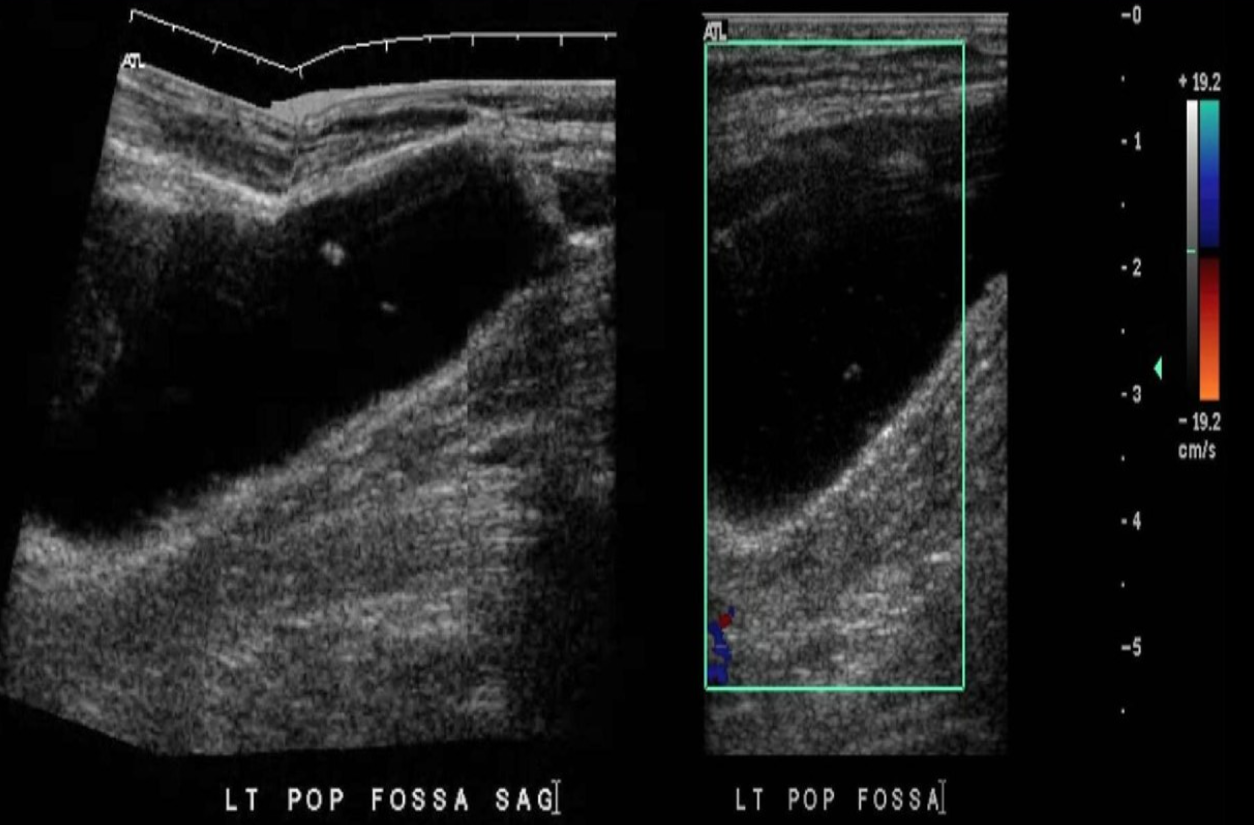
Identify this image.
Baker’s cyst
What is the most common complication of DVT?
Post phlebitic syndrome (80%)
What is post phlebitic syndrome?
When DVT resolves, but there is damage to vein and valves causing reflux
What is the most significant complication of DVT?
Pulmonary embolism
What is a pulmonary embolism (PE)?
When thrombus breaks loose and travels through heart to lungs