Chapter 22: Carbonyl Condensation and Alpha Substitutions of Carbonyl Compounds.
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What is an enolate ion?
The O is willing to take on 1 pair of e in the double bond of the carbonyl.
The pair of electrons in the carbanion can double bond with the carbonyl carbon, creating an enolate ion, stabilized by resonance.
Through resonance these electrons can attack to form carbon-carbon bonds.
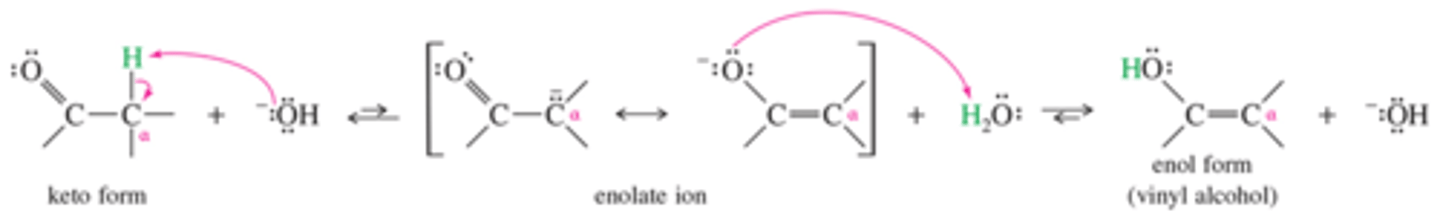
What is the mechanism for base catalyzed tautomerism? Which form is favored?
Here we see Keto to Enol, but the reserve reaction is the dominant. This is the form of the reaction that allows for alpha carbon activity. The reaction funnels to the product in this way.
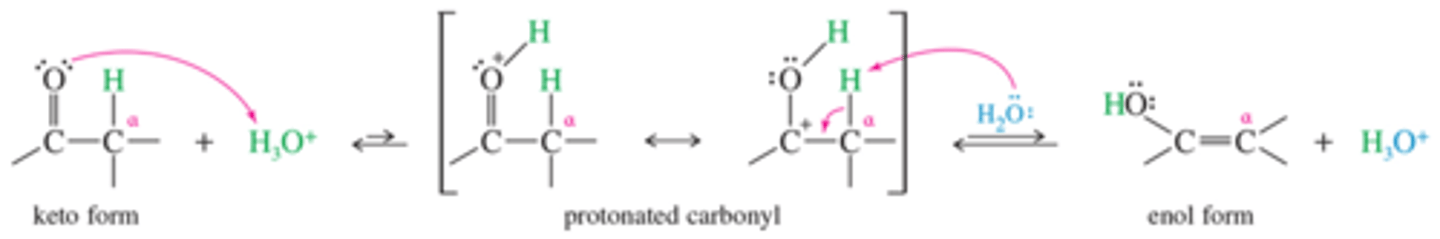
What is the mechanism for acid catalyzed tautomerism?
Which form is favored?
Here we see Keto to Enol, but the reserve reaction is the dominant. This is the form of the reaction that allows for alpha carbon activity. The reaction funnels to the product in this way.
What is the racemization of keto-enol conversion
If a chiral a carbon has an enolizable hydrogen atom, a trace of acid or base allows that carbon to invert its configuration, with the enol serving as the intermediate. This is called racemization.
50/50 mixture of both sterochemical form made
What is the mechanism for the formation of enolate ion?
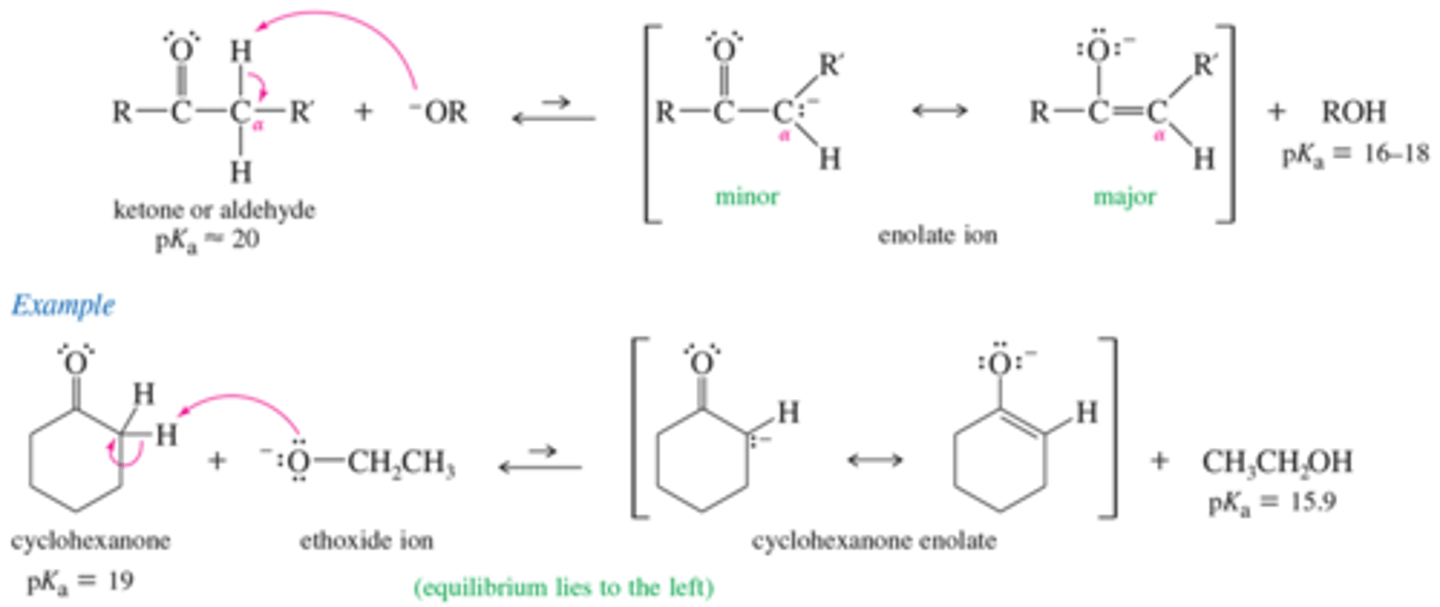
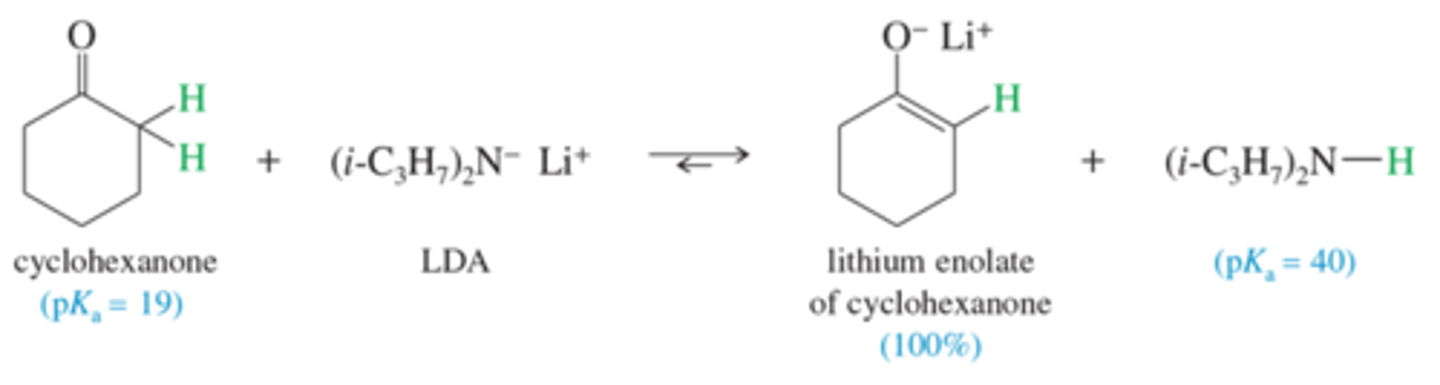
What base do we use to convert a carbonyl compound completely to its enolate?
LDA
Very basic with a PKa of 50
Produce the enolate of cyclohexanone?
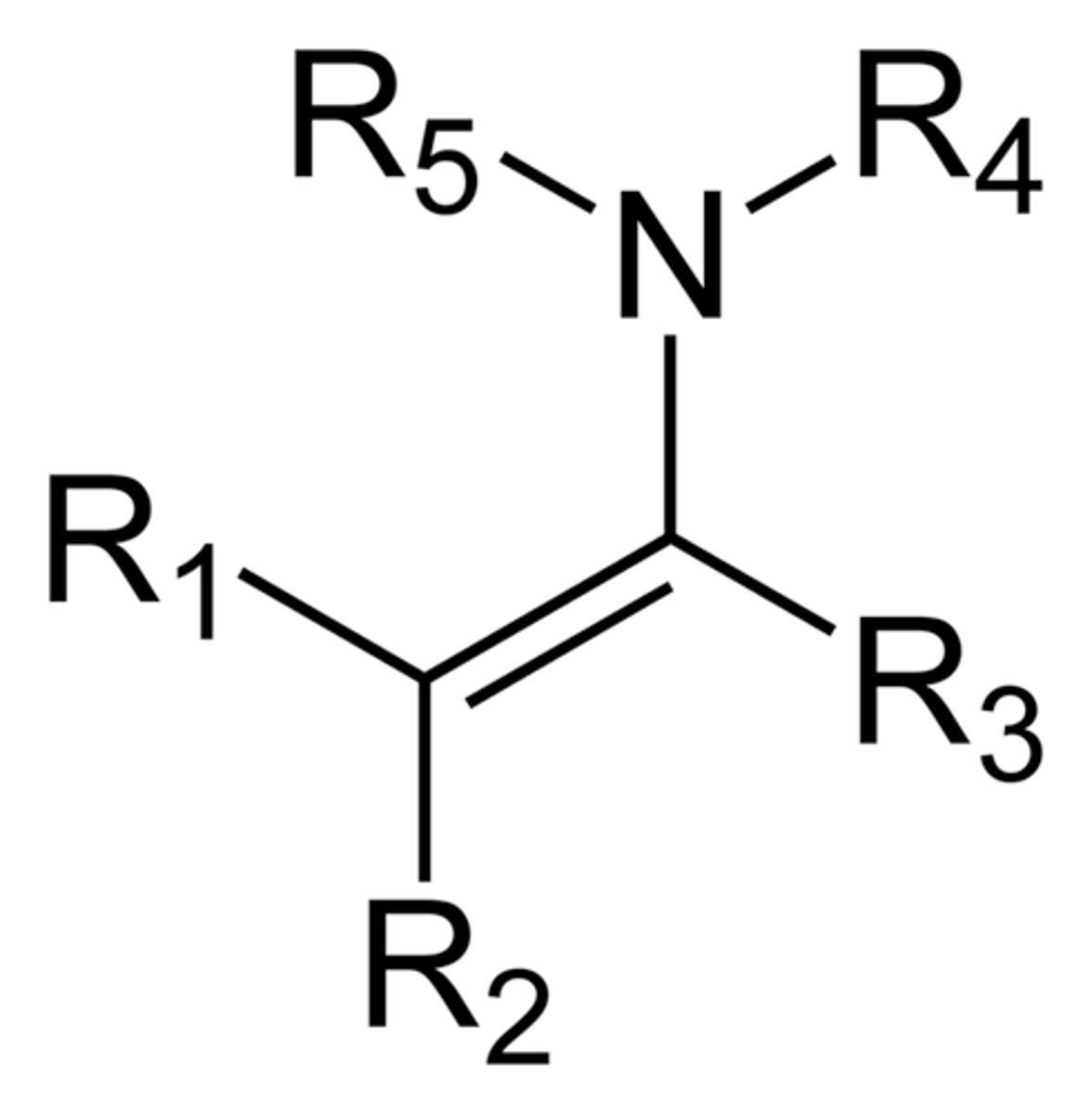
What is an enamine?
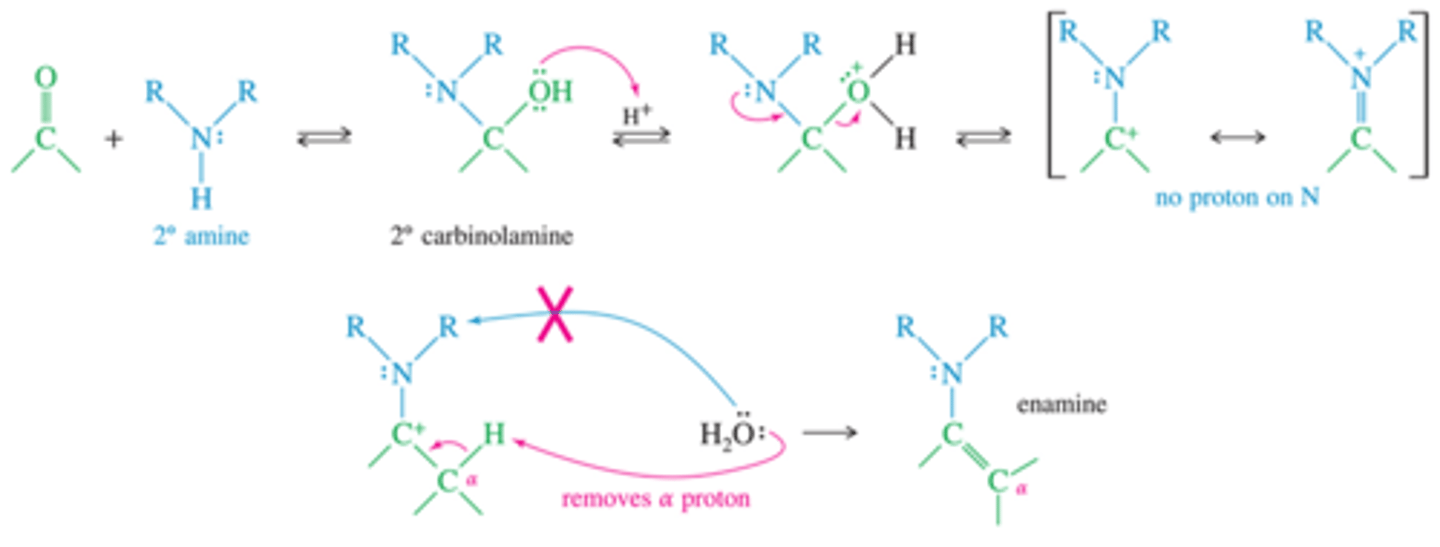
An enamine is an unsaturated compound derived by the condensation of an aldehyde or ketone with a secondary amine.
What is the mecahnism for the formation of an enamine?
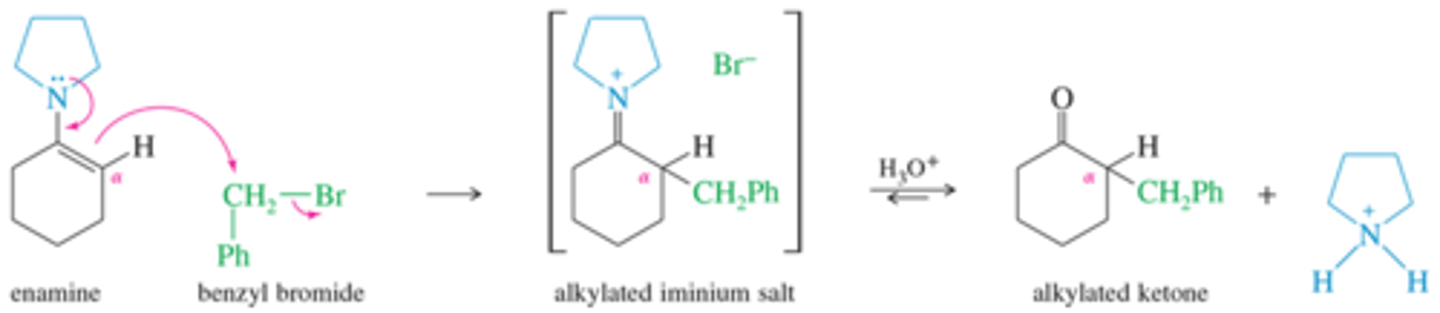
What is the mechanism for the alkylation of an enamie
What reagents can be used to halogenate keytones
Take keytone/carbonyl containing group.
Add base -OH with X2
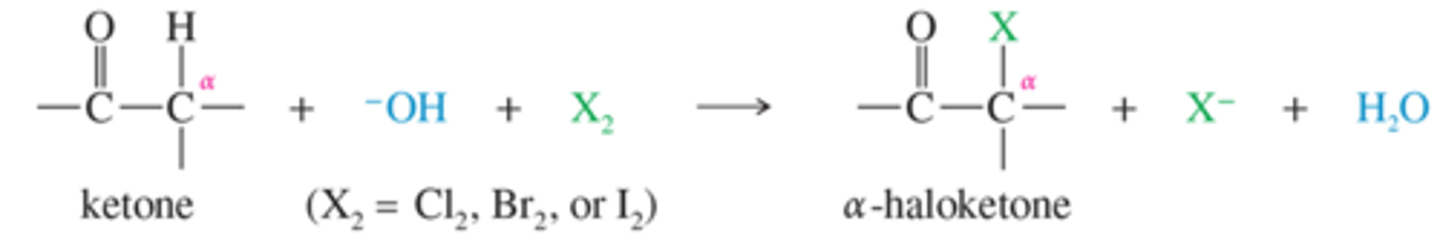
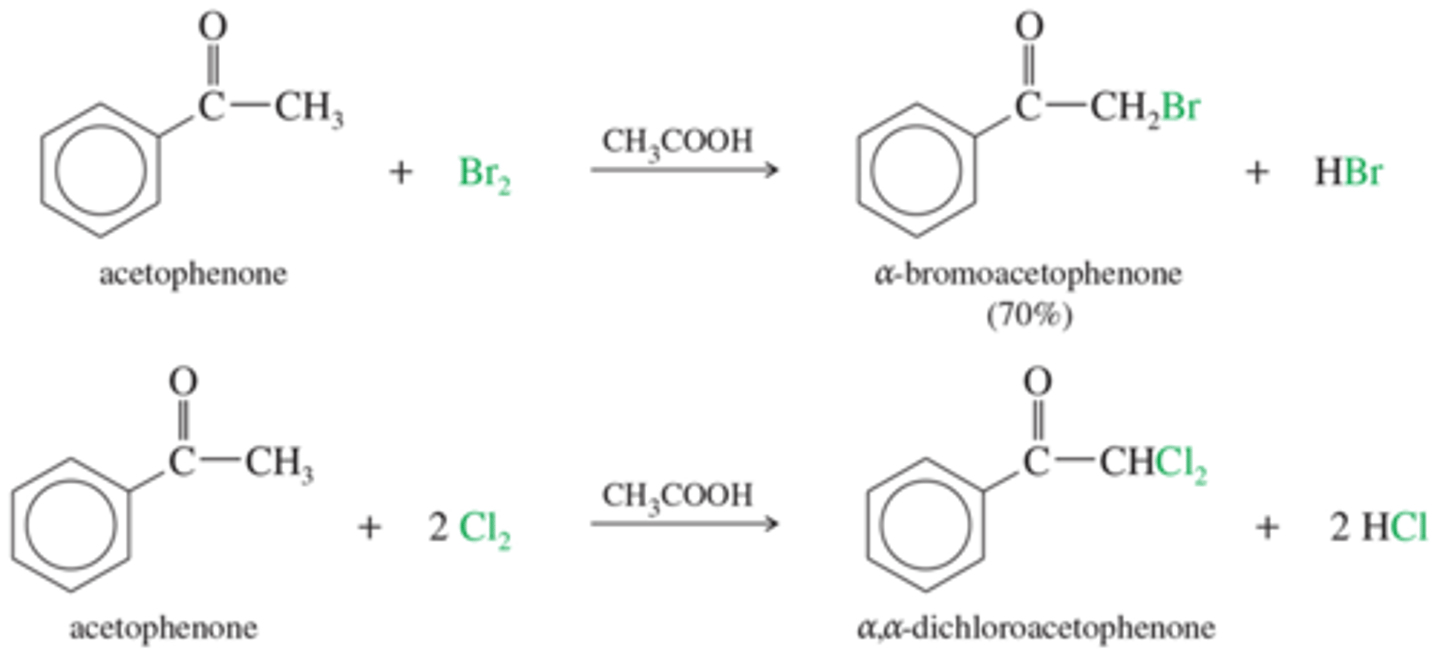
What is the haloform reaction?
Converts methyl ketones (ketone with a methyl on the end) into carboxylic acids. Reagents = I2, Br2, or bleach (NaOCl), then a neutralizer.
Need to exhaustively halogenate
What is the mechanism for acid catalyzed a-halogenation
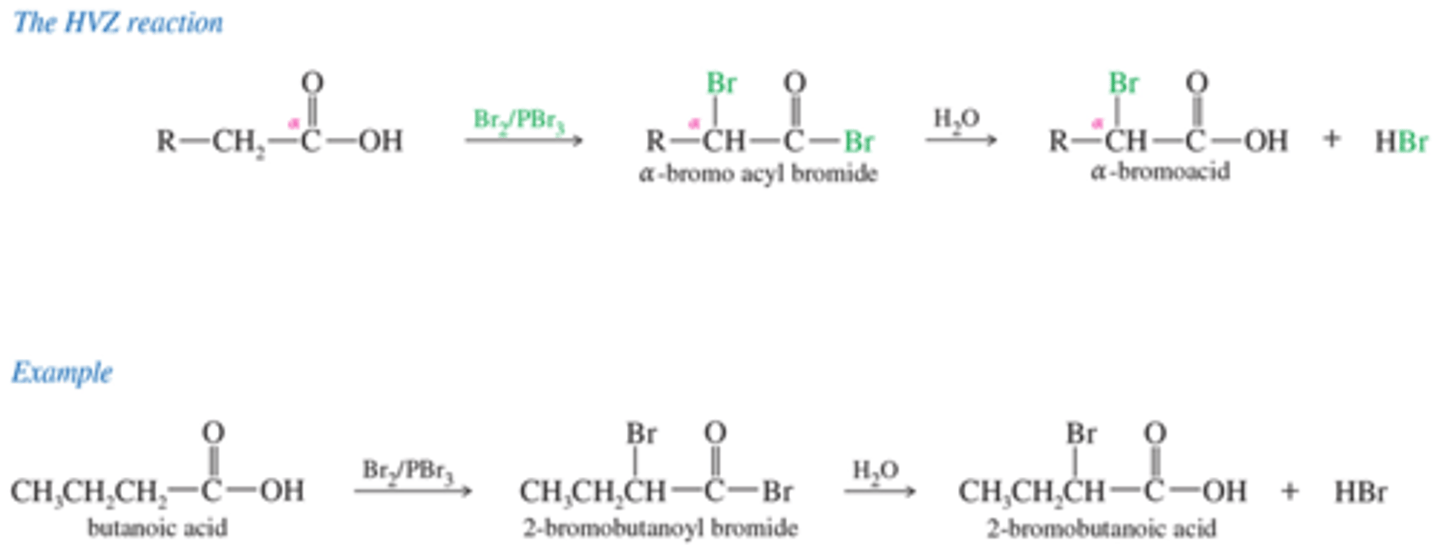
What are the mechanism for Hell-Bolhard-Zelinsky (HVZ) Reaction?
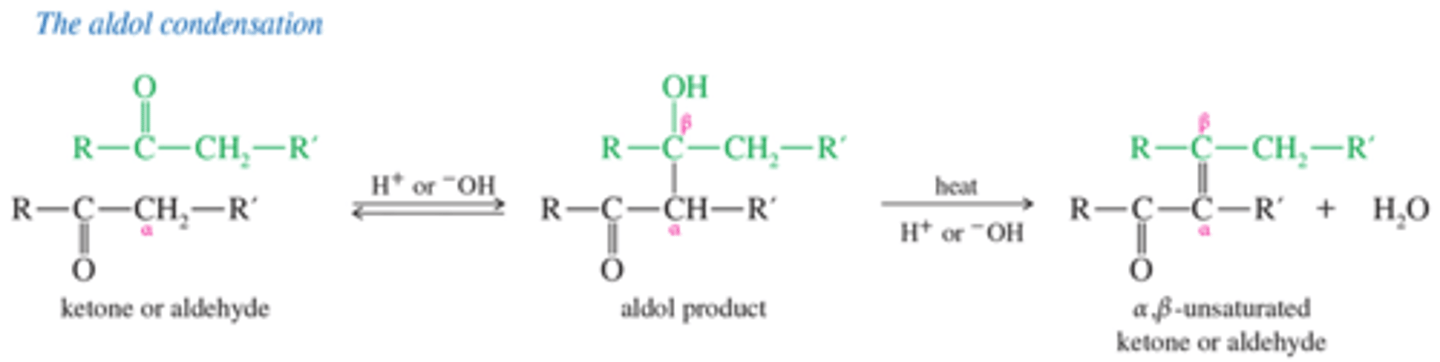
What is the mechanism for Aldol condensation?
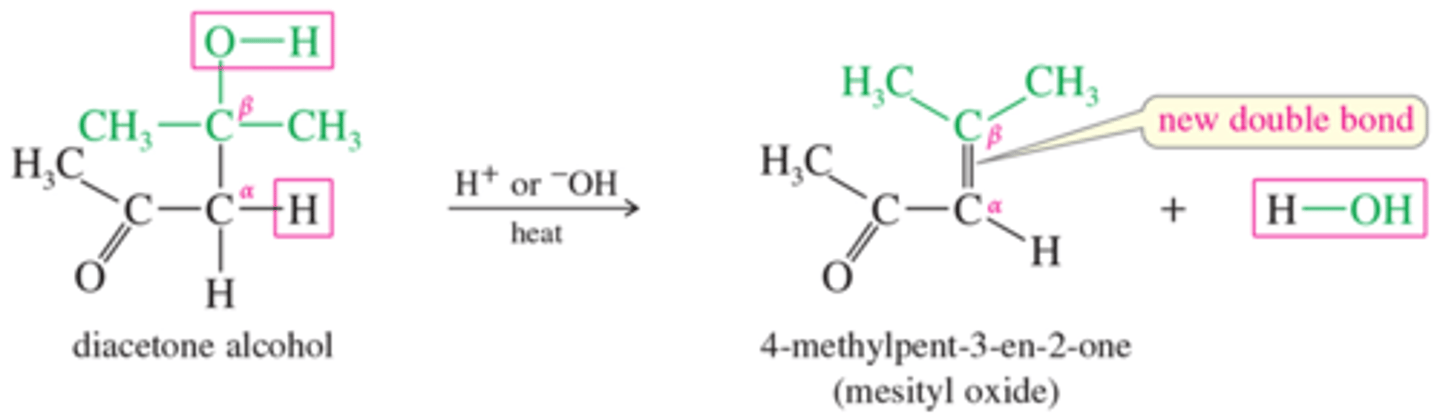
How do you dehydrate aldol products producing a new double bond?
Acid of base
Heat
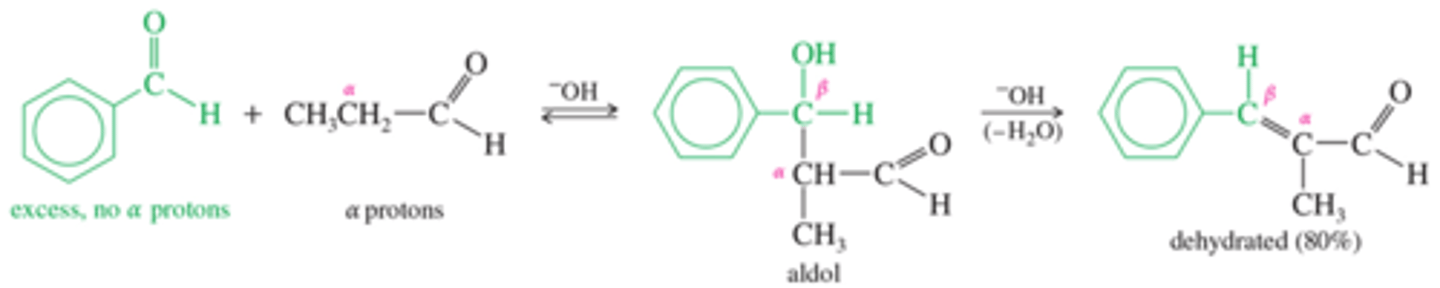
What are crossed aldol condensations? Is this a limitation?
When the enolate of one aldehyde (or ketone) adds to the carbonyl group of a different aldehyde or ketone, the result is called a crossed aldol condensation.
Can be a limitation in controlling product
How do you control for crossing in aldol condensation?
A crossed aldol condensation can be effective if it is planned so that only one of the reactants can form an enolate ion.
Phenols are good at this
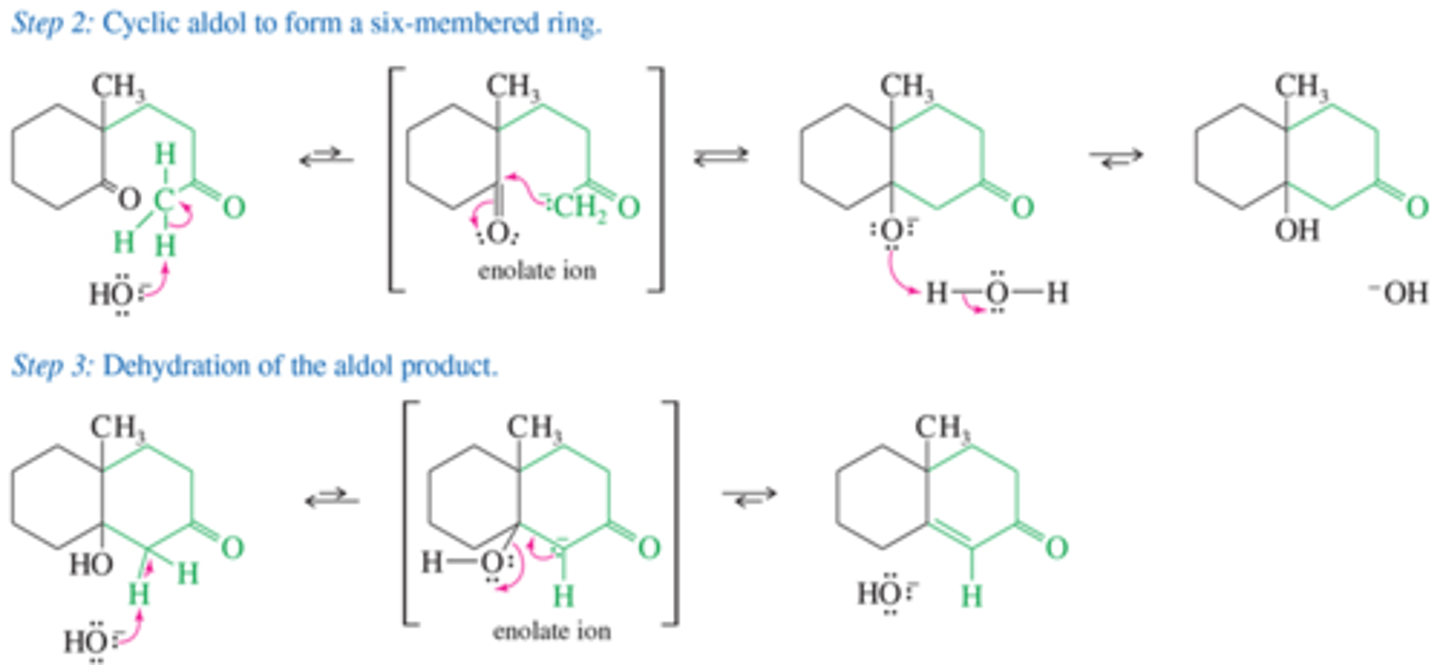
What is the mechanism for aldol cyclization?
hint: Driven by intramolecular reactions think electon donating and accepting components
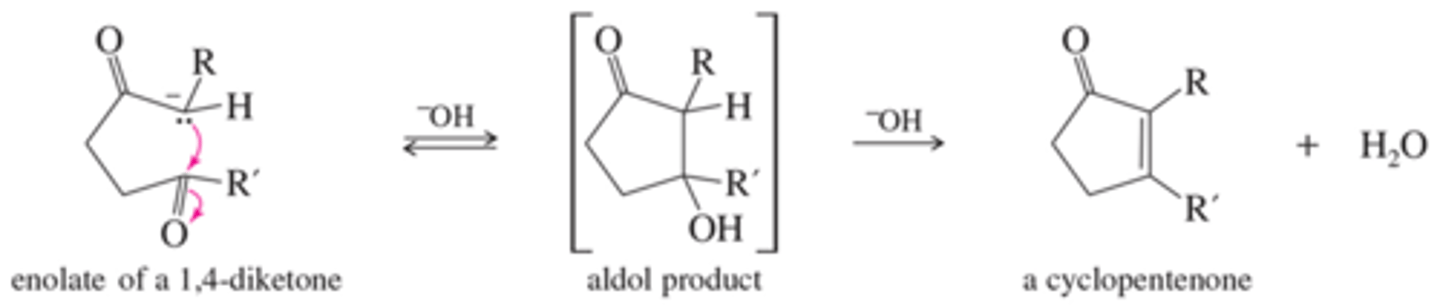
What ring size is favored for aldol cyclization reactions?
How do I prompt the creation of larger rings?
5-6 membered rings
to make larger rings remove H2O to cause forward reaction
What is adol condensation? What type of addition is it?
the addition of an enolate ion to another carbonyl group.
alpha-beta addition.
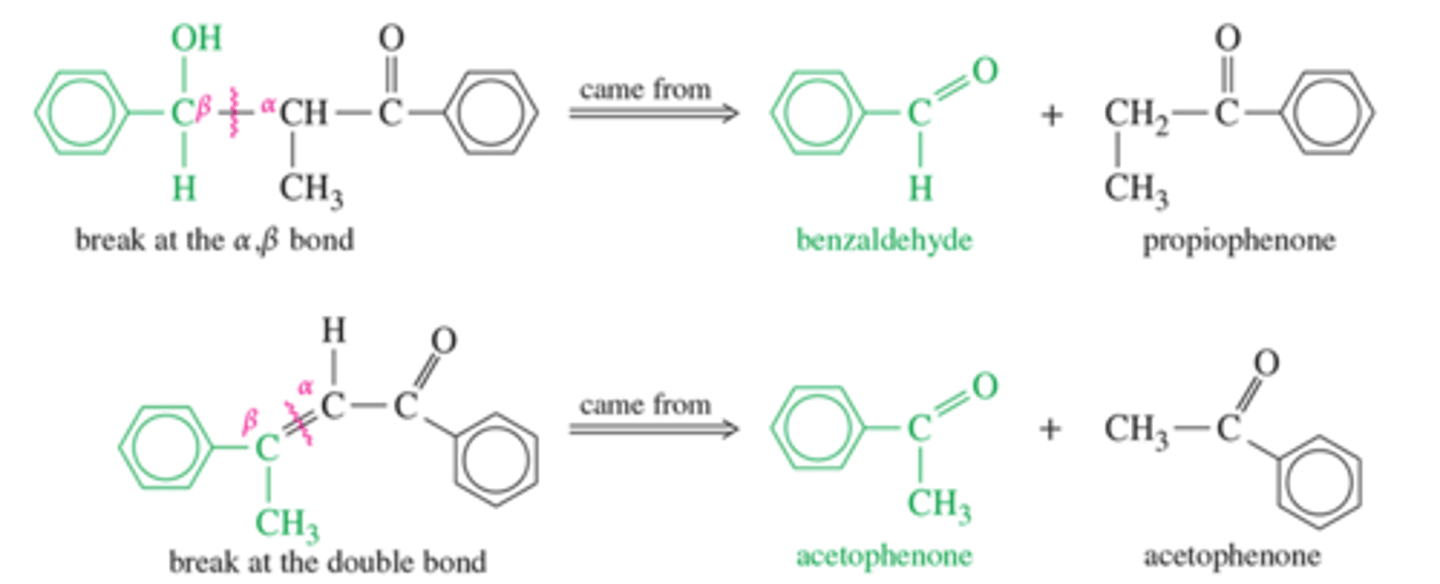
How can you determine the retosynthetic addition of aldol condensates?
Look for double bonds or single bonds near alcohol where an alpha-beta carbon linkage occured?
What is the mechanism for Claisen Ester Condensation?
The Claisen condensation results when an ester molecule undergoes nucleophilic acyl substitution by an enolate.
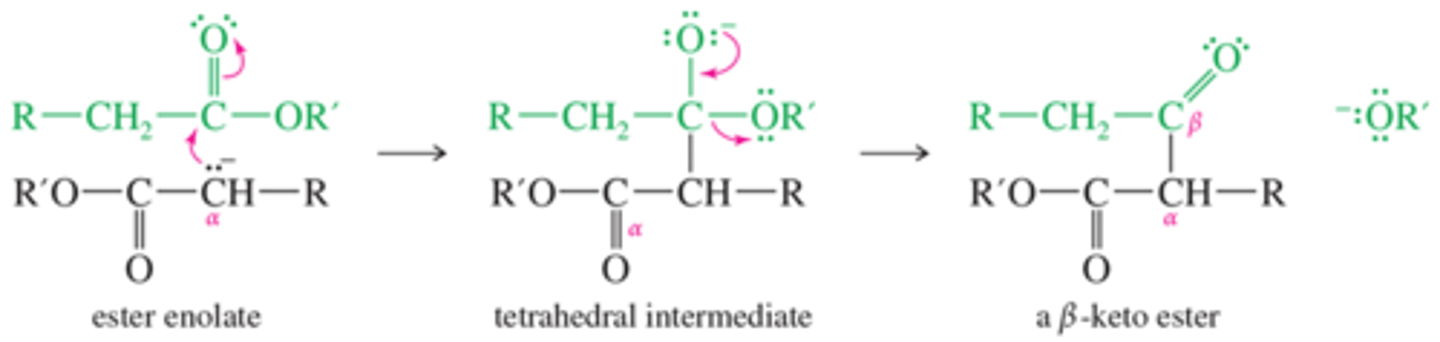
What are internal Clalisen reactions called?
Dieckmann Condensation
When doing a crossed claisen can you have two different enolates
No.
Make the following
(Flip card to see final product)
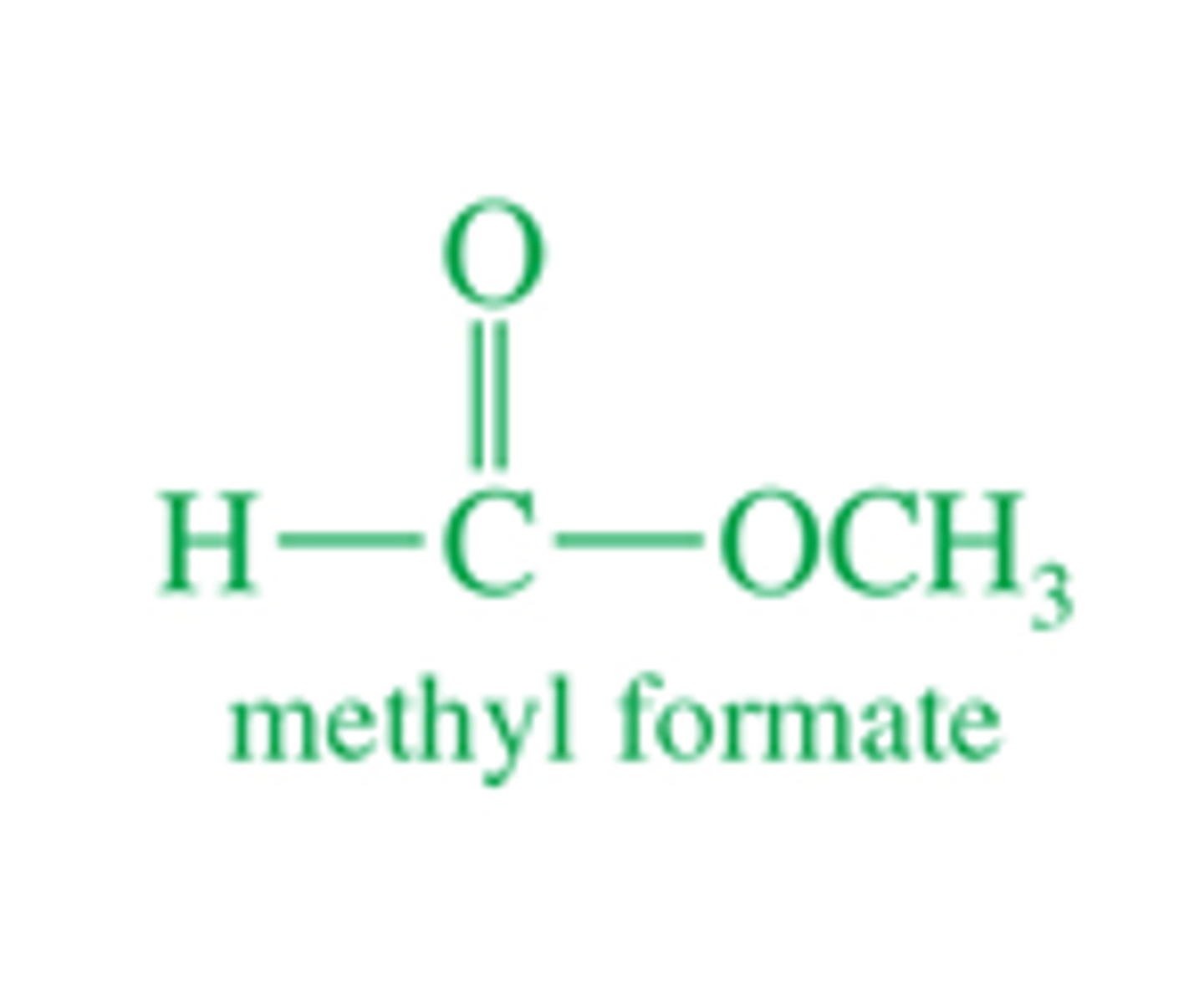
What is the crossed claisen mechanism.
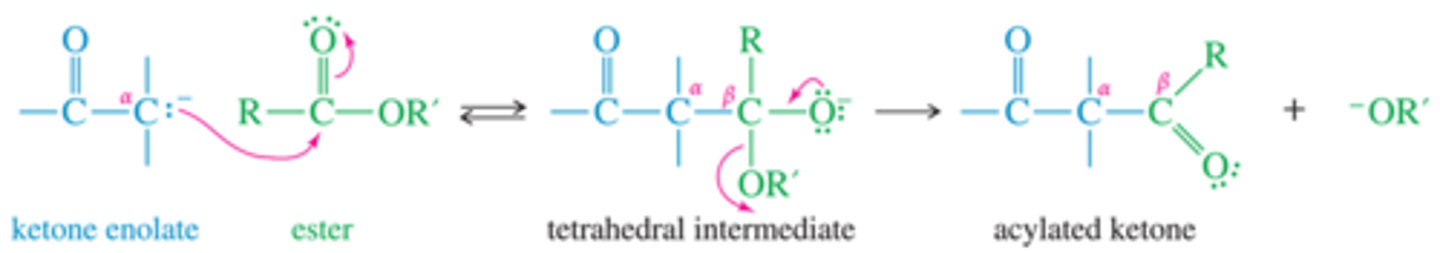
What is Michael Reaction donors and acceptors
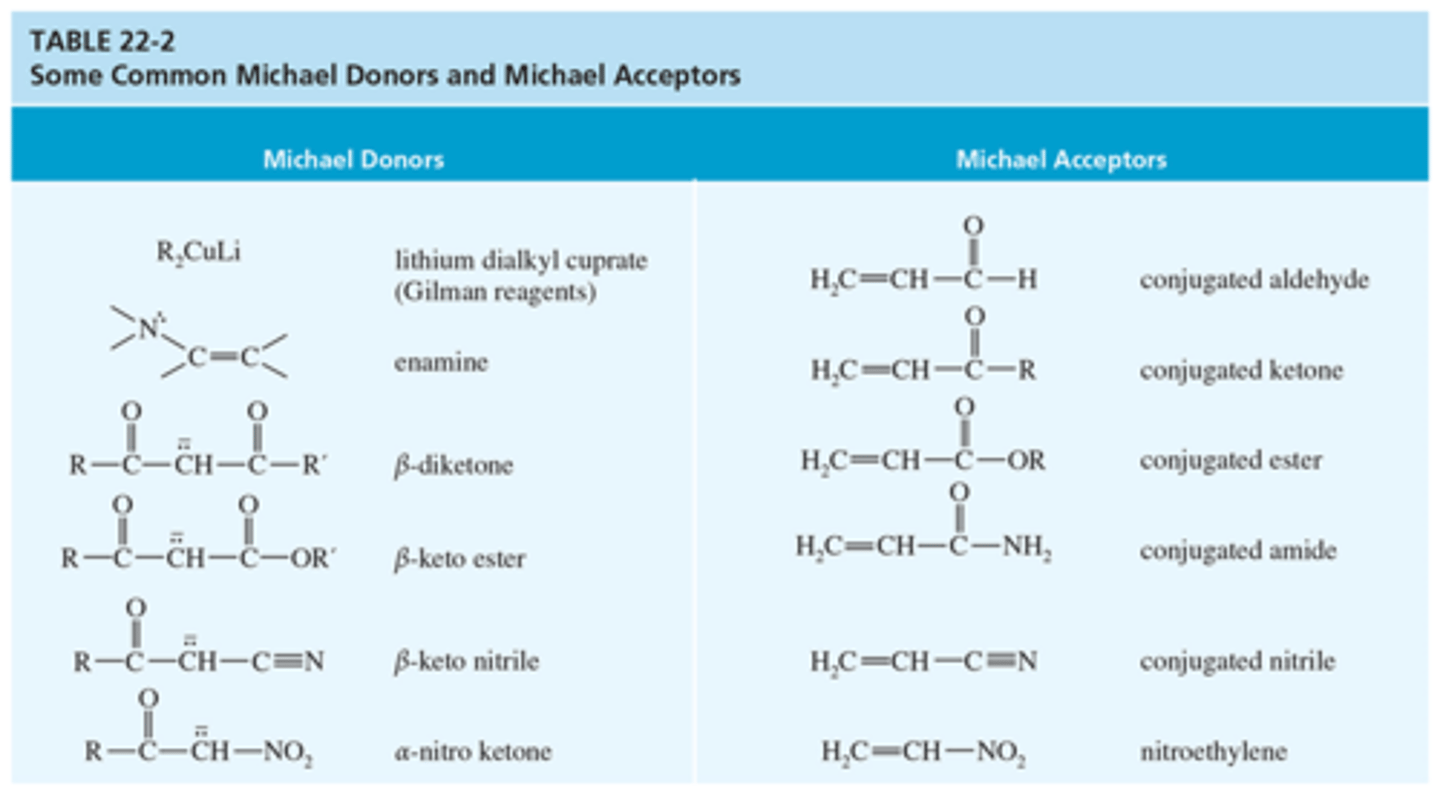
What is the mechanism for Malonic Ester Synthesis
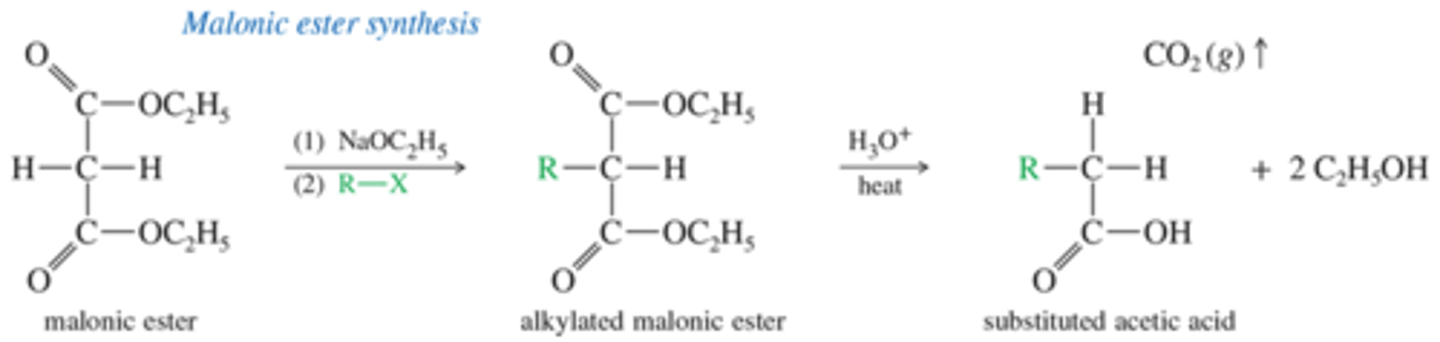
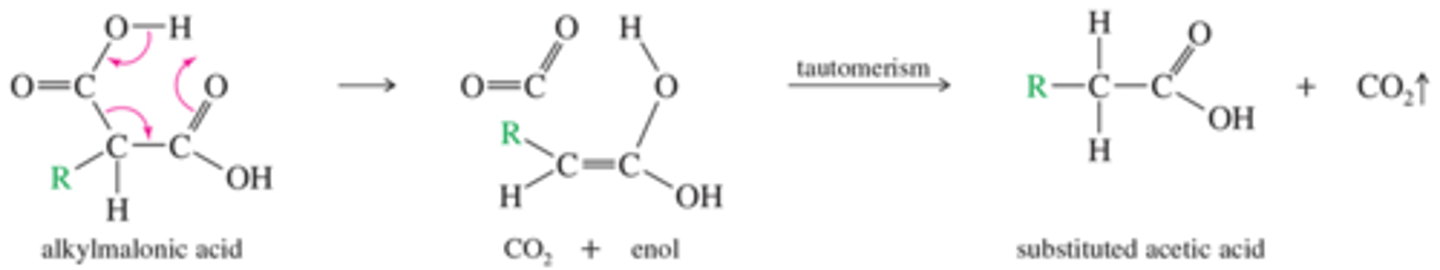
What is the mechanism of Decarboxylation of the Alkylmalonic Acid
What type of addition is michael reaction
1-2 to 1-4
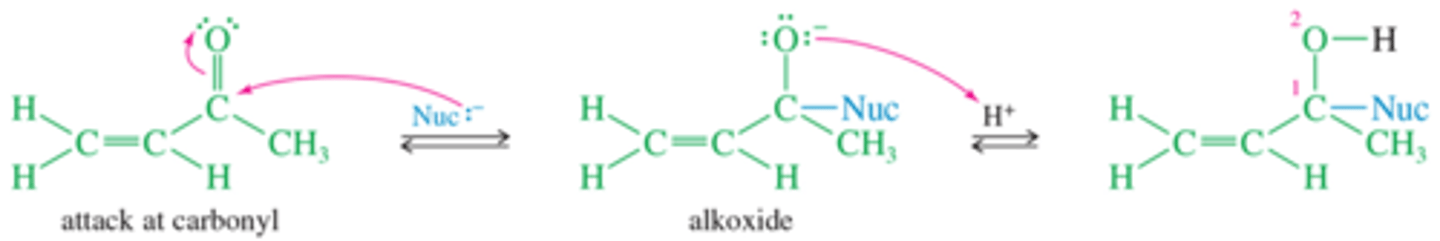
What is Michael Reaction mechanism for 1-2?
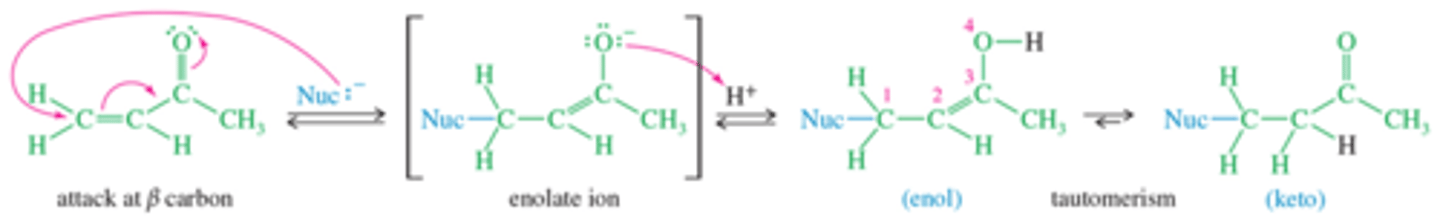
What is Michael Reaction mechanism for 1-4?
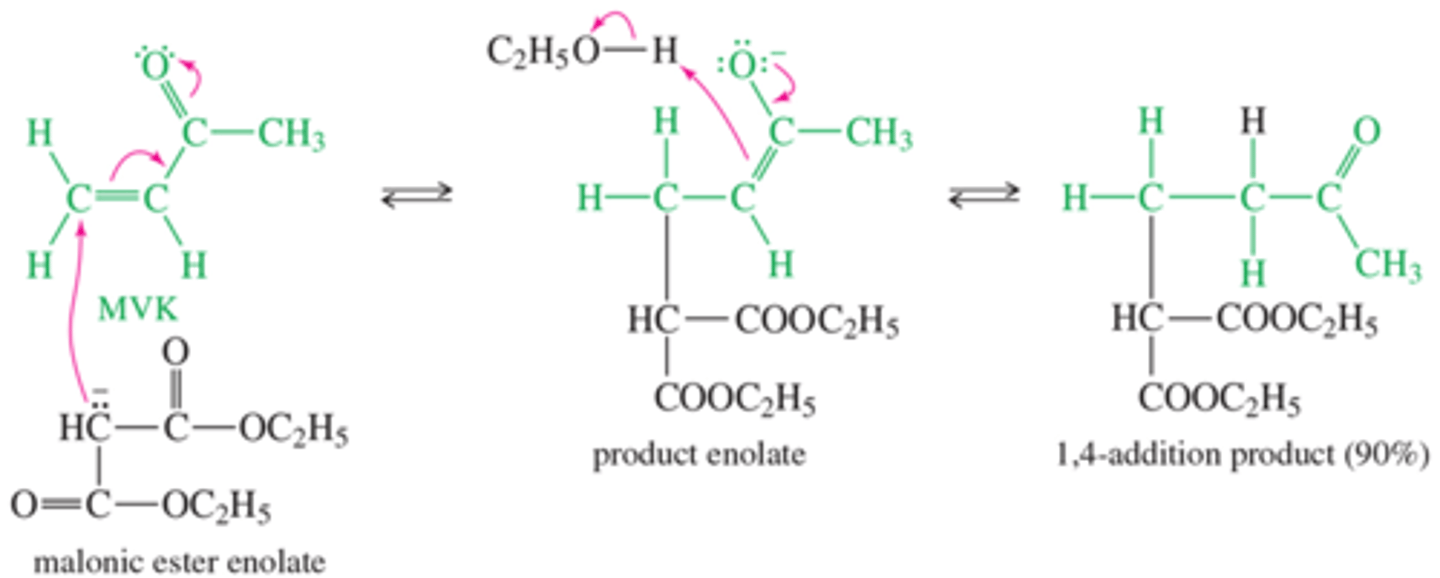
What is the Methyl Vinyl Ketone Reaction?
1-4
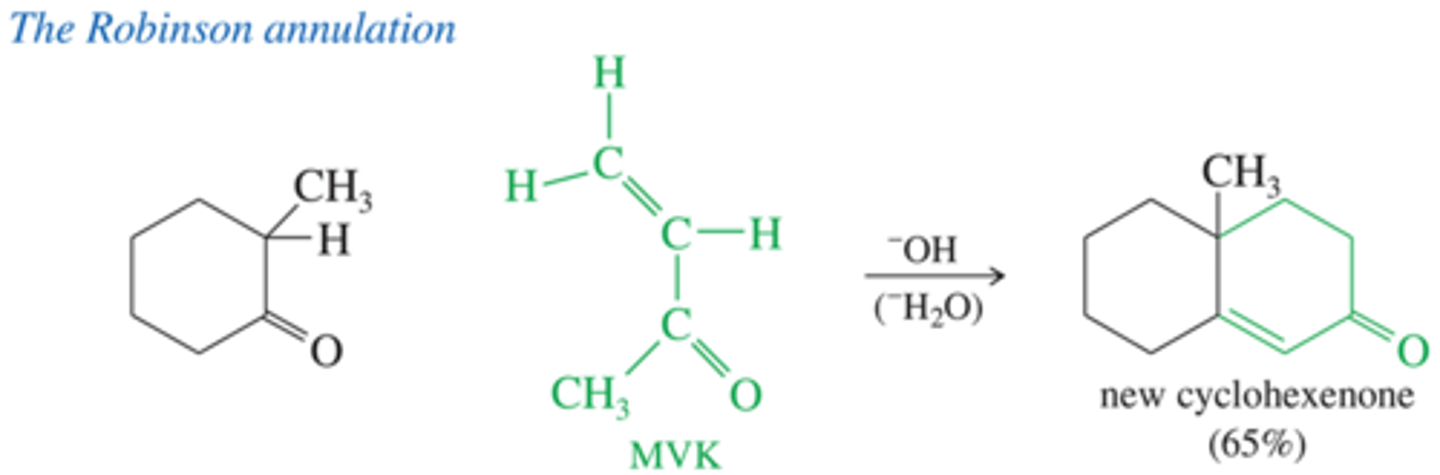
What is Robinson annulation?
What is the mechanism for Robinson Annulation?