Protein Extraction & Quantitation
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
western blot
used to detect specific proteins in a qualitative or semi-quantitative manner
consists of gel electrophoresis + immunoblotting
1. load samples
2. gel electrophoresis
(electrophoresis part)^^
3. transfer
4. detect
(immunoblot part)^^
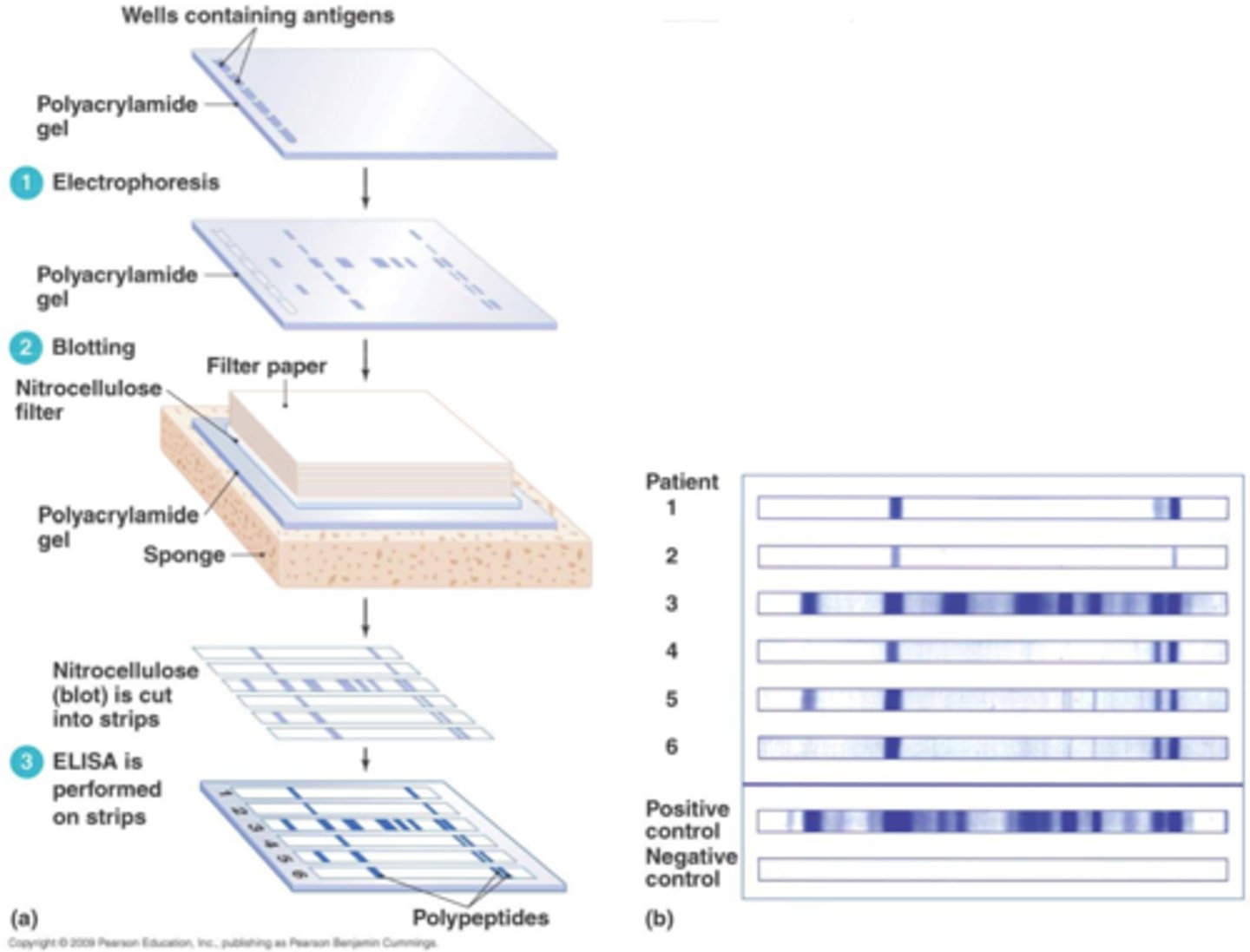
blotting
molecular technique of transferring biological specimens to a membrane for detection
1. cell disruption
2. protein solubilization
3. contaminant removal
4. quantitation
protein extraction methods
- mechanical
- liquid homogenization
- sonication
- freeze-thaw
- manual grinding
- solution-based cell lysis
mechanical extraction
rotating blades grind and disperse cells and tissues
waring blender polytron
liquid homogenization extraction
cell or tissue suspensions are cheared by forcing them through a narrow space
ex. dounce homogenizer
sonication extraction
high frequency sound waves shear cells
sonicator
freeze-thaw extraction
repeated cycles of freezing and thawing disrupt cells through ice crystal formation
ex. freezer or dry ice with ethanol
manual grinding extraction
grinding plant tissue, frozen in liquid nitrogen
mortar and pestle
solution-based cell lysis
ex. uses relatively mild detergents to lyse cells allowing solubilization of molecules
ex. ripa buffer
ripa buffer
A lysis buffer used to extract proteins from cells
"Radioimmunoprecipitation assay"
solubilizing samples
- must choose right detergent/buffer system
- generates protein extracts of cells
components of lysis buffer
- buffer
- detergent
- salt
- protease and/or phosphatase inhibitors
what do detergents do in lysis buffers?
disrupt membranes
ionic = harsher, disrupt all membranes
non-ionic = mild, keep nuclear membrane in tact
ionic detergents
- will disrupt all membranes
- harsher detergents
- good for protein extractions
- keep proteins in solution
- lyse nuclear membrane
ex. SDS
nonionic detergents
- milder
- good for protein extraction
- will not lyse nuclear membrane
- solubilize membrane protein
- protein maintain native state
ex. Tritor X
protein quantitation methods
- absorbance at 280 nM
- HPLC analysis
- copper-based protein analysis (BCA assay, Lowry assay)
- dye-based protein analysis (Bradford assay)
absorbance at 280 nM
Amino acids containing aromatic side chains (i.e., tyrosine, tryptophan and phenylalanine) exhibit strong UV-light absorption. Thus, proteins and peptides absorb UV-light in proportion to their aromatic amino acid content and total concentration
HPLC analysis
after labeling all primary amines (i.e., N-terminus and side-chain of lysine residues) with a colored or fluorescent dye such as ninhydrin or o-pthlaladehyde (OPA)
copper-based protein assay
Based on protein-copper chelation and secondary detection of the reduced copper
• BCA Protein Assays
• Lowry Assay
dye-based protein assay
Protein-dye binding and direct detection of the color change associated with the bound dye
Bradford Assay: positive amine groups in proximity with the negative charge of the dye
- Inhibited by detergents
- low uniformity
BCA assay
-used to determine total concentration of protein in a solution using colorimetric reaction and spectrophotometry
-standards and unknowns are prepared with working reagent
-generate a standard curve that can calculate unknown concentration of protein
centrifugation
goals: - to collect
- to fractionate cellular and sub-scellular componnent,
- in rpm: revolutions per minute, regardless of rotor size
RCF: relative centrigugal frorce --> depends on the size of the rotor
RCF is more accurate than RPM because RCF takes size of rotor into account
- separation is primarily based on the size of particles
when a cell homogenate is centrifuged at 1,000g for 10 mins ..
unbroken cells and heavynuclei pellet to the bottom of the tube.
when a cell homogenate is centrifuged at 10,000g for 20 mins ..
pellet subcellular organelles of intermediate velocities such as mitochondria, lysosomes, and microbodies to partial purity
rate-zonal (size) separation
Takes advantage of particle size and mass instead of particle density for sedimentation.
Density of particles > density of gradient
ex. blood separation
which is better, RPM or RCF?
RCF! takes size of rotor into account for force
Isopycnic (density) separation
Particles migrate to where the density of the surrounding solution is exactly the same as the density of the particle.
Density of gradient > density of particles
distinguishing properties of proteins
1. Mass: determined by the # and types of amino acids
2. Shape: contributed most by 3° and 4°structure
3. Charge: determined by amino acid composition and conditions
electrophoresis can separate proteins according to any of these properties
general electrophoresis overview
(Electrophoresis)
1. cast a gel
2. prepare and load samples
(immunoblot)
3. apply current
4. detection
common matrices used for casting gels
agarose and polyacrylamide
agarose
polysaccharide of agarobiose held together by both inter-and intra molecular hydrogen bonds
polyacrylamide
polymerized acrylamide; increased resolution + separation relative to agarose
polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE)
PAGE: used to separate and analyze macromolecules (i.e. proteins, nucleic acids) based on size and charge.
1. gel matrix is formed from polyacrylamide
2. gel is porous; pore sizes can be adjusted to separate molecules of different sizes.
3. macromolecule samples are loaded into gel
4. electric field is applied, causing the negatively charged macromolecules to migrate towards the positive electrode.
5. Smaller molecules move faster through, larger molecules are impeded by the pores
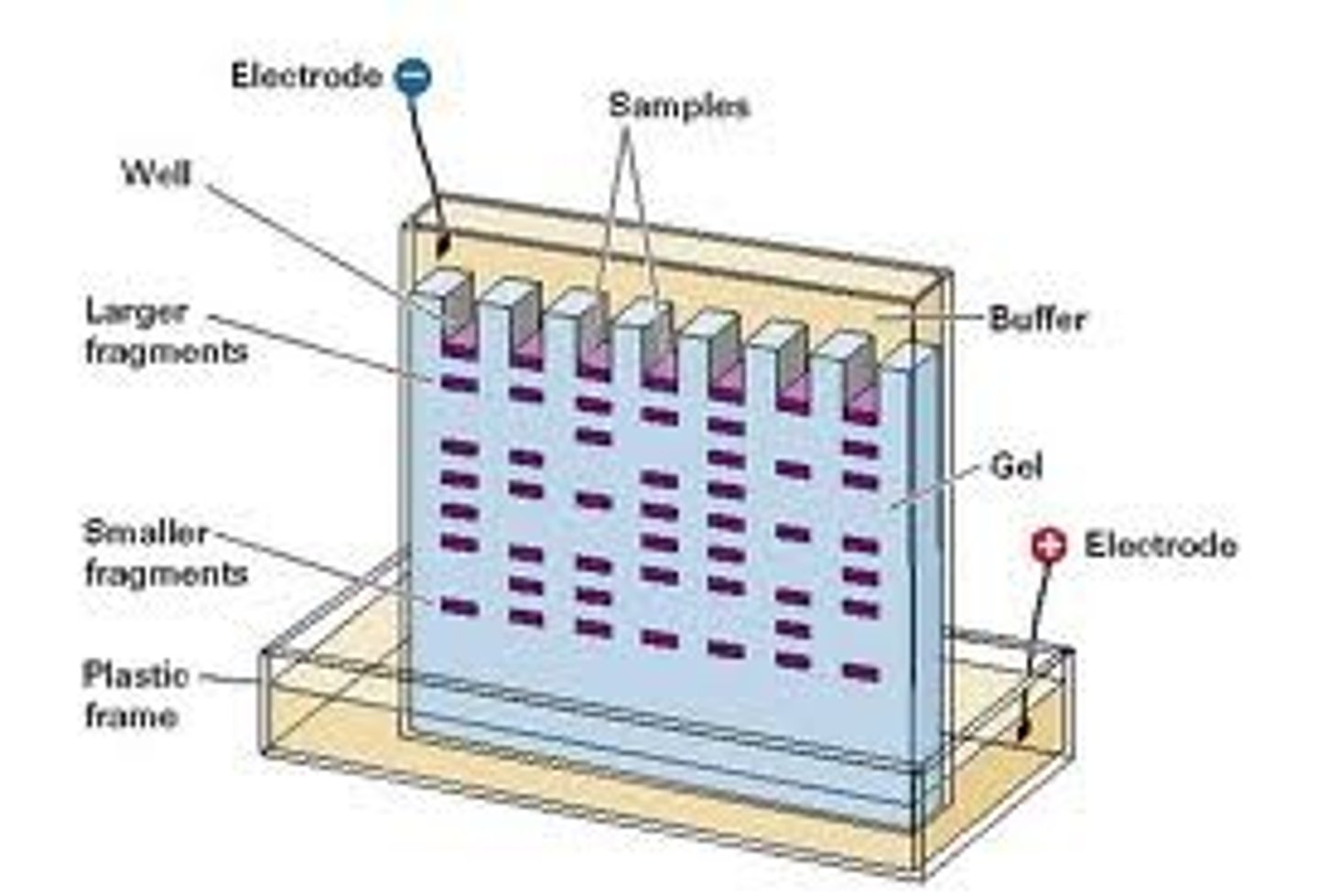
the size of the pores is________related to the amount of acrylamide used
inversely
reducing SDS-PAGE
►The gel is cast in buffer contain sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS).
►Protein samples are heated with SDS before electrophoresis so that the charge-density of all proteins is made roughly equal.
►A reducing agent [dithiothreitol (DTT) or beta-mercaptoethanol] is also added to sample buffer to cleave disulfide bonds and destroy quaternary or tertiary protein structure.
►Proteins separate according to mass
buffer: SDS + DTT/β-ME + sucrose/glycerol +bromophenol blue
non-reducing SDS-PAGE
►The gel is cast in buffer contain sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS).
►Protein samples are heated with SDS before electrophoresis so that the charge-density of all proteins is made roughlyequal
.►No reducing agent is added. Disulfide bonds remain and affect size and shape of proteins.
►Proteins separate according to mass but are more influenced by shape than reducing gels and mass will depend onpresence or absence of disulfide bonds
buffer: SDS + sucrose/glycerol + bromophenol blue
native page
► No SDS, no reducing agent is used in either the gel or the sample buffer.
►The higher the negative charge density (more charges per molecule mass), the faster a protein will migrate.
►Proteins stay in native form including their shape and interactions with other proteins
►Some proteins retain their enzymatic activity (function)
►Proteins separate based upon both their charge and mass and the shape of the protein or protein complex plays abigger role
buffer: sucrose/glycerol + bromophenol blue
stacking gel
A stacking gel is usually set on top of the resolving gel. The stacking gel has a lower concentration of acrylamide (and larger pores), a lower pH (e.g., 6.8) and a different ionic content. This allows the proteins in a loaded sample to be concentrated into a tight band during the first few minutes of electrophoresis before entering the resolving portion of a gel
what do you want to run your gel at?
constant voltage
V = IR
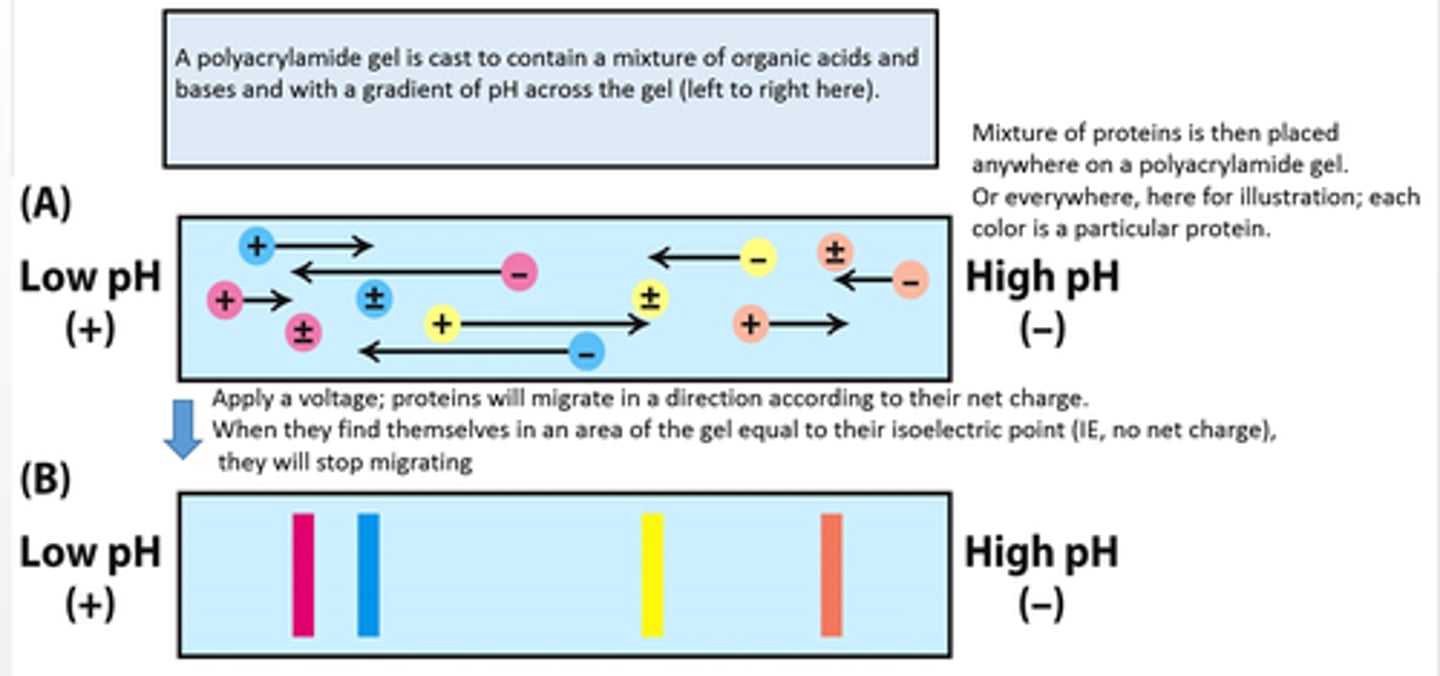
isoelectric focusing
A specialized method of separating proteins by their isoelectric point using electrophoresis; the gel is modified to possess a pH gradient
separate proteins based on net charge vs. molecular weight using a pH gradient within the gel
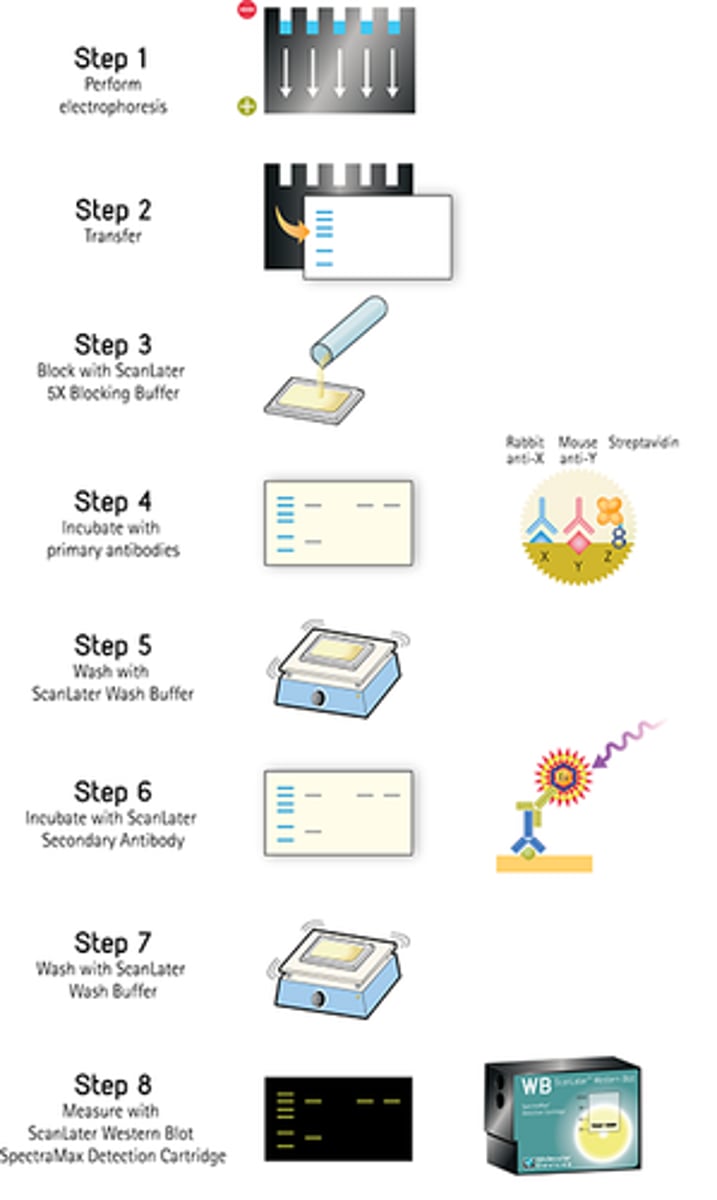
western blot steps
1. Perform gel electrophoresis
2. Transfer to nitrocellulose membrane or PVDF --> either wet or semi-dry)
3. Block membrane with neutral protein (BSA or milk casein)
4. Incubate with primary antibody - specific to the target protein
5. Incubate with secondary antibody -> labelled secondary antibody specific to primary antibody, conjugated with HRP
6. Develop and analyze results - detect via chemiluminescent
semi dry trasnfer
a lot quicker than wet transfer of membrane for western blot
goat anti-mouse HRP
seocondary antibody made in goat that recogne primary antipudy
HRP
horseradish peroxidase; an enzyme used to stimulate the conversion of the colorless substrate into a colored product in this exercise
what does band size indicate in western blot?
indicates amount of protein present
--> run same blot with a gifferent antibody trhat will serve as nagative
antibody structural characteristics
.1 150 kDa globular plasma protein
2. 4 polypeptide chains: 2 light (~25 kDa) and 2 heavy (~50 kDa)
3. Each chain has a variable (Fab) and a constant (Fc) region
considerations for selecting antibodies:
1. Raised in compatible species
2. Monoclonal vs polyclonal
3. Referenced in publications for western blot
monoclonal antibody binding
only one antibody binds to protein
polyclonal antibody
A mixture of antibodies that all recognize the same antigen, but different epitopes
immunoprecipitation basic steps
1.