Visual Literacy Final Exam
1/217
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
218 Terms
Romanticism
an art movement whose works were marked by intense colors, turbulent emotions, complex composition, soft outlines, and sometimes heroic or exotic subject matter
Realism
art in which the goal is to portray forms in the natural world in a highly faithful manner
Impressionism
art movement that emphasized an accurate depiction of light in its changing qualities, ordinary subject matter, unusual visual angles, and inclusion of movement
Post-Impressionism
art movement that moved artists to create individualistic style
Expressionism
art movement that claimed the right to distort visual appearances to express psychological or emotional states, especially the artists' own feelings
Cubism
art movement developed by Picasso and George Braque that abstracts the forms of the visible world into fragments or facets drawn from multiple points of view
Abstract Expressionism
an American art movement of the mid-20th century, characterized by large scale and nonrepresentational imagery
Assemblage (combine)
the technique of creating a sculpture by grouping or piecing together distinct elements, as opposed to casting, molding, or carving
Happenings
an event staged or directed by artists and offered as art
Pop Art
an art style of the 1960s, deriving its imagery from popular, mass-produced culture
Minimalism
a broad tendency during the 60s and 70s toward simple, primary forms
Appropriation
a postmodern practice in which one artist reproduces an image created by another artist and claims it as their own
The Starry Night
Vincent Van Gogh, 1889

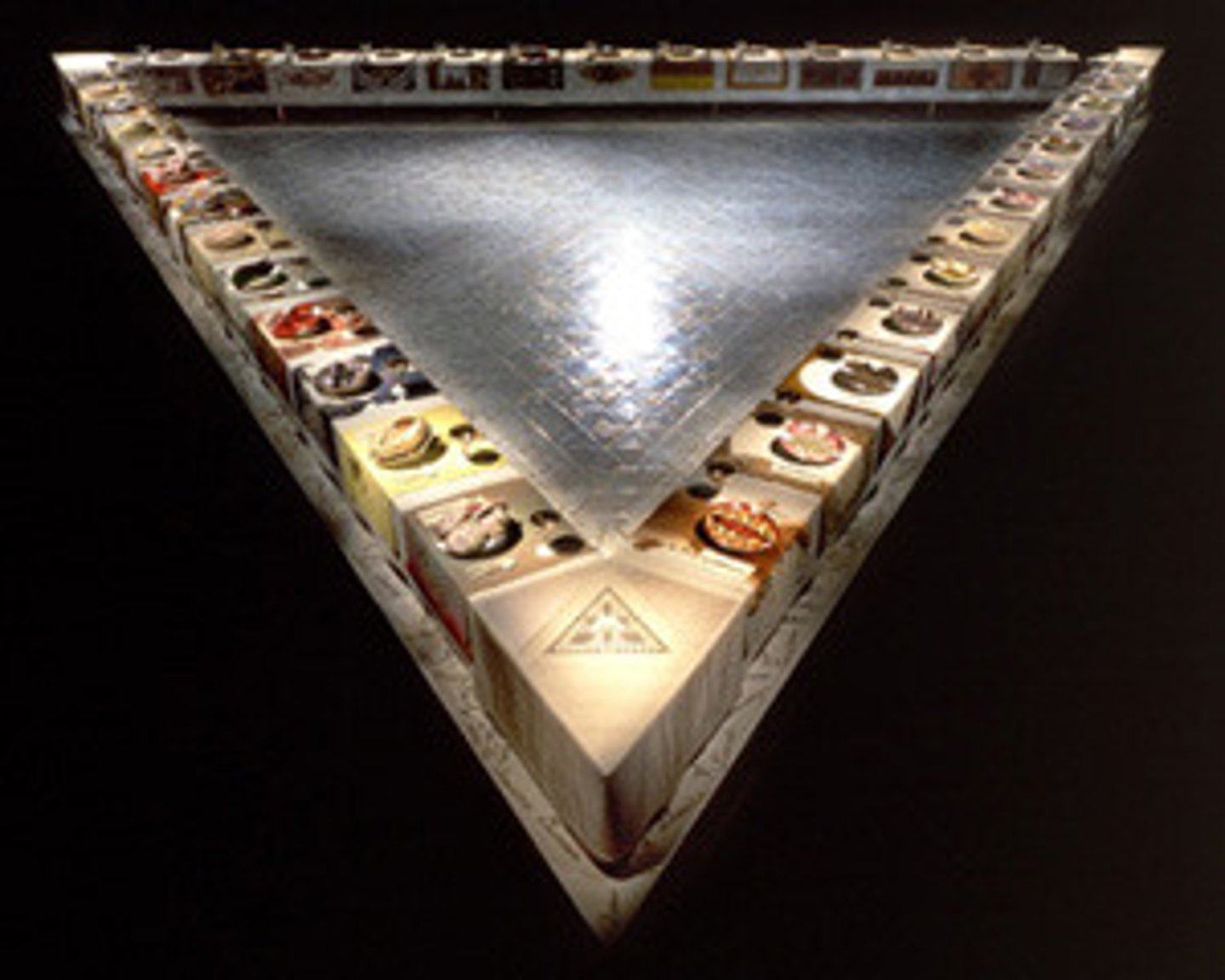
Dinner Party
Judy Chicago, 1979

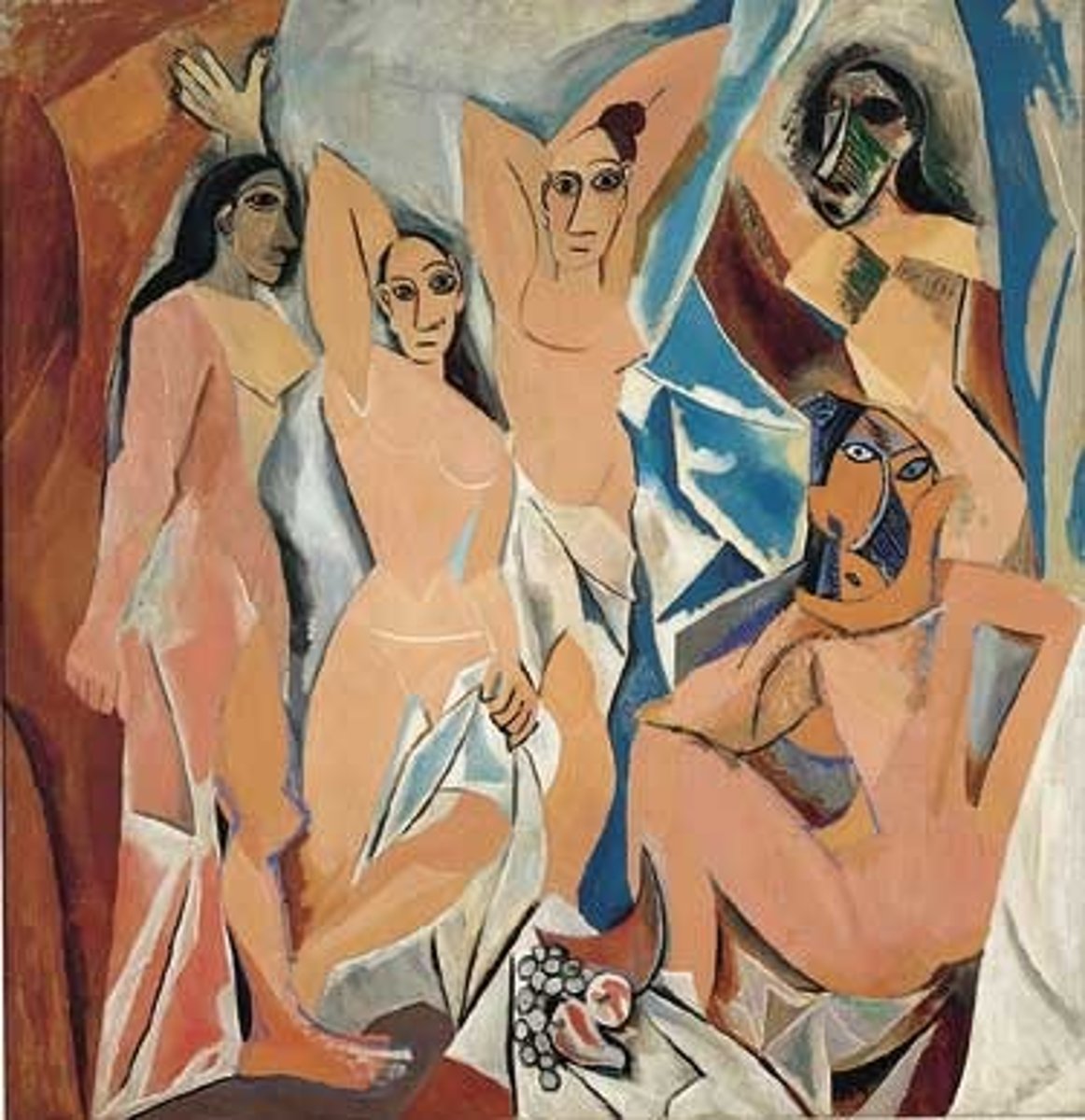
Les Demoiselles d'Avignon
Pablo Picasso, 1907

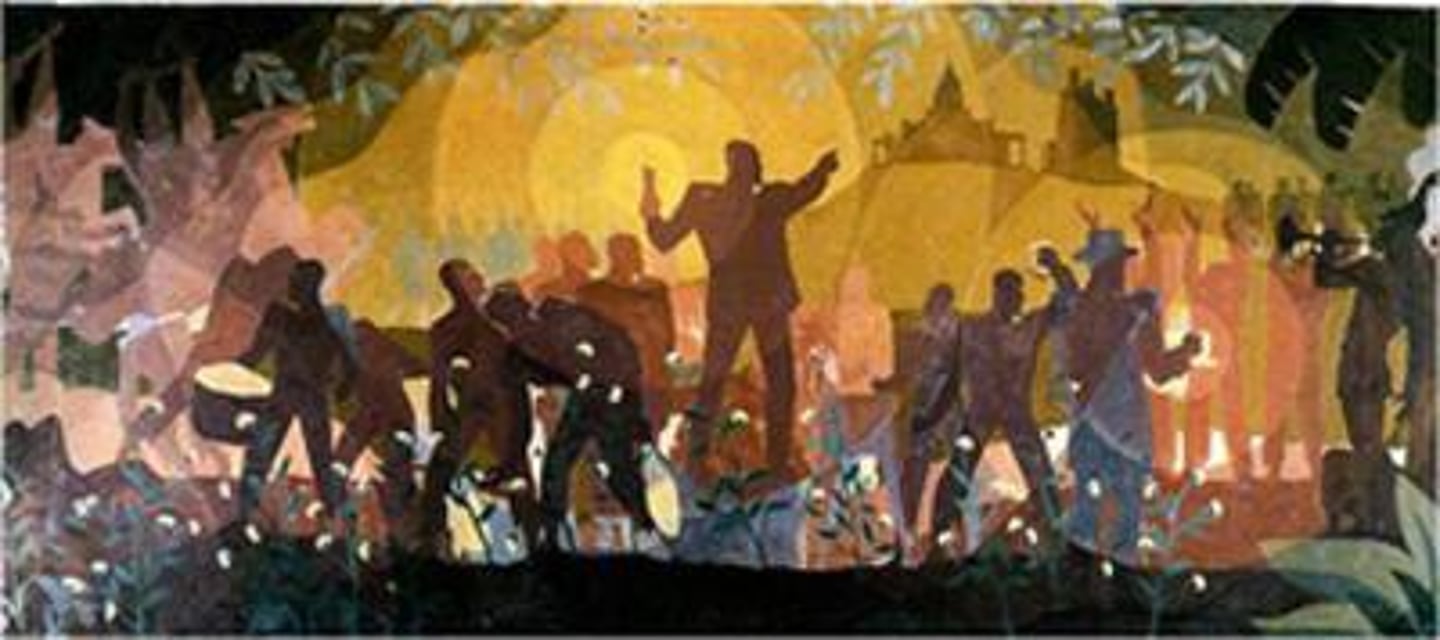
Aspects of Negro Life: From Slavery through Reconstruction
Aaron Douglas, 1934

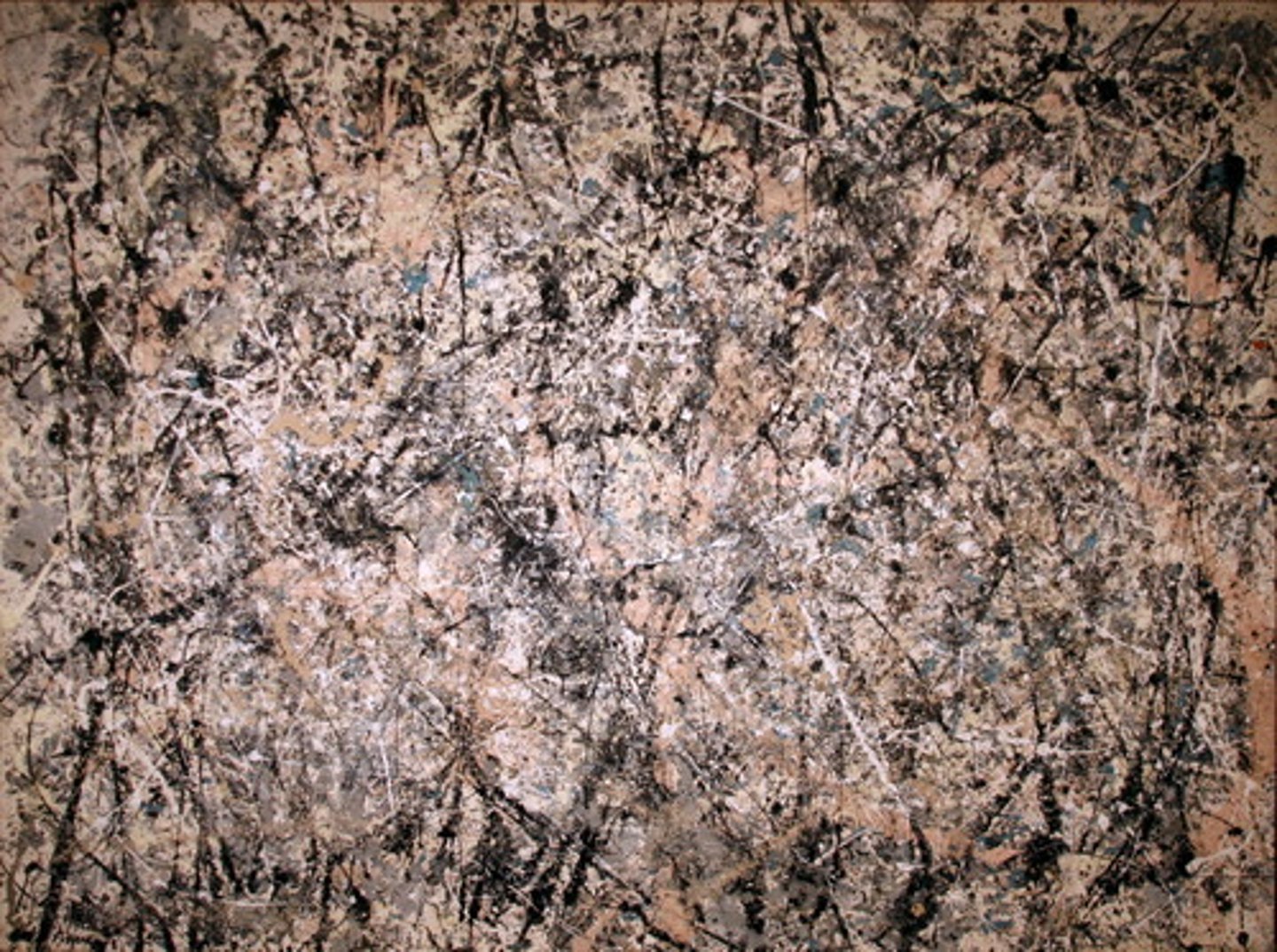
Number 1
Jackson Pollock, 1949

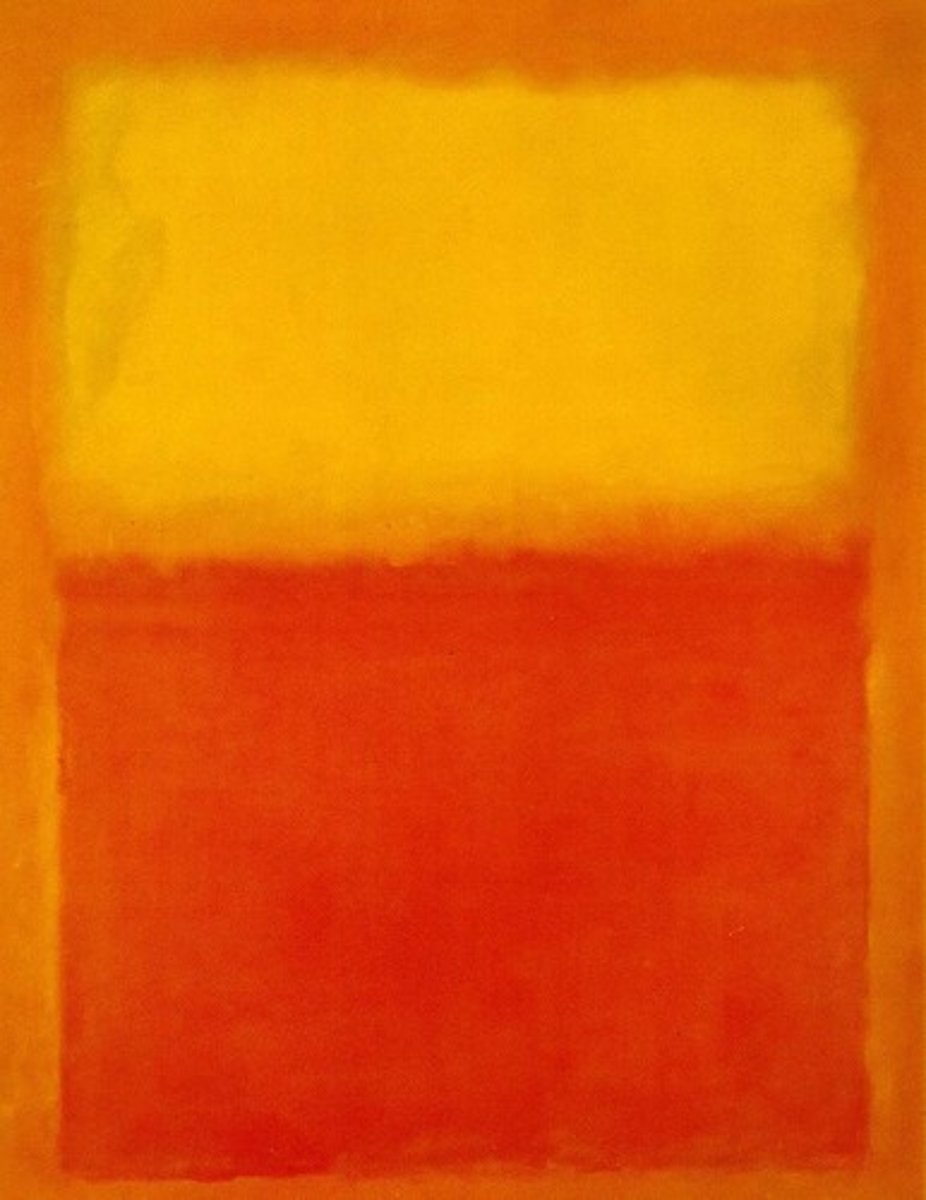
Orange and Yellow
Mark Rothko, 1956

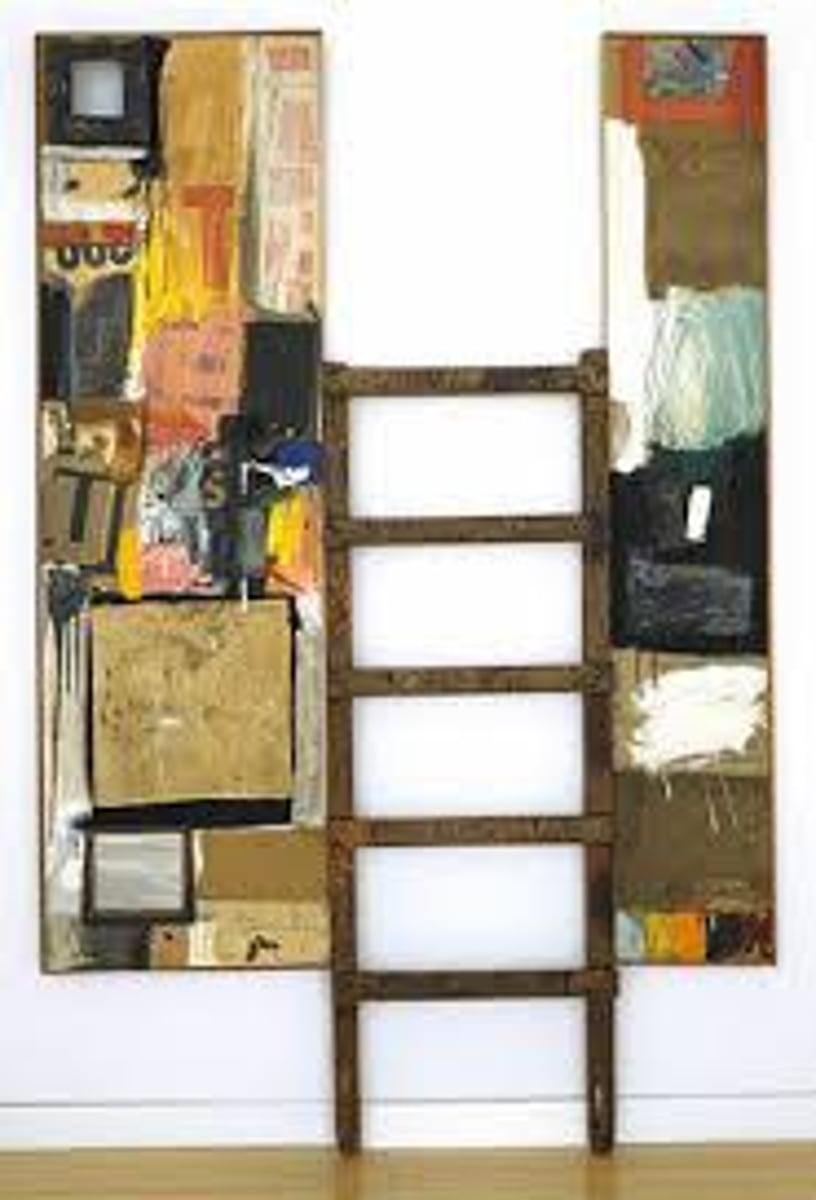
Winter Pool
Robert Rauschenberg, 1959

Blam
Roy Lichtenstein, 1962

One and Three Chairs
Joseph Kosuth, 1965

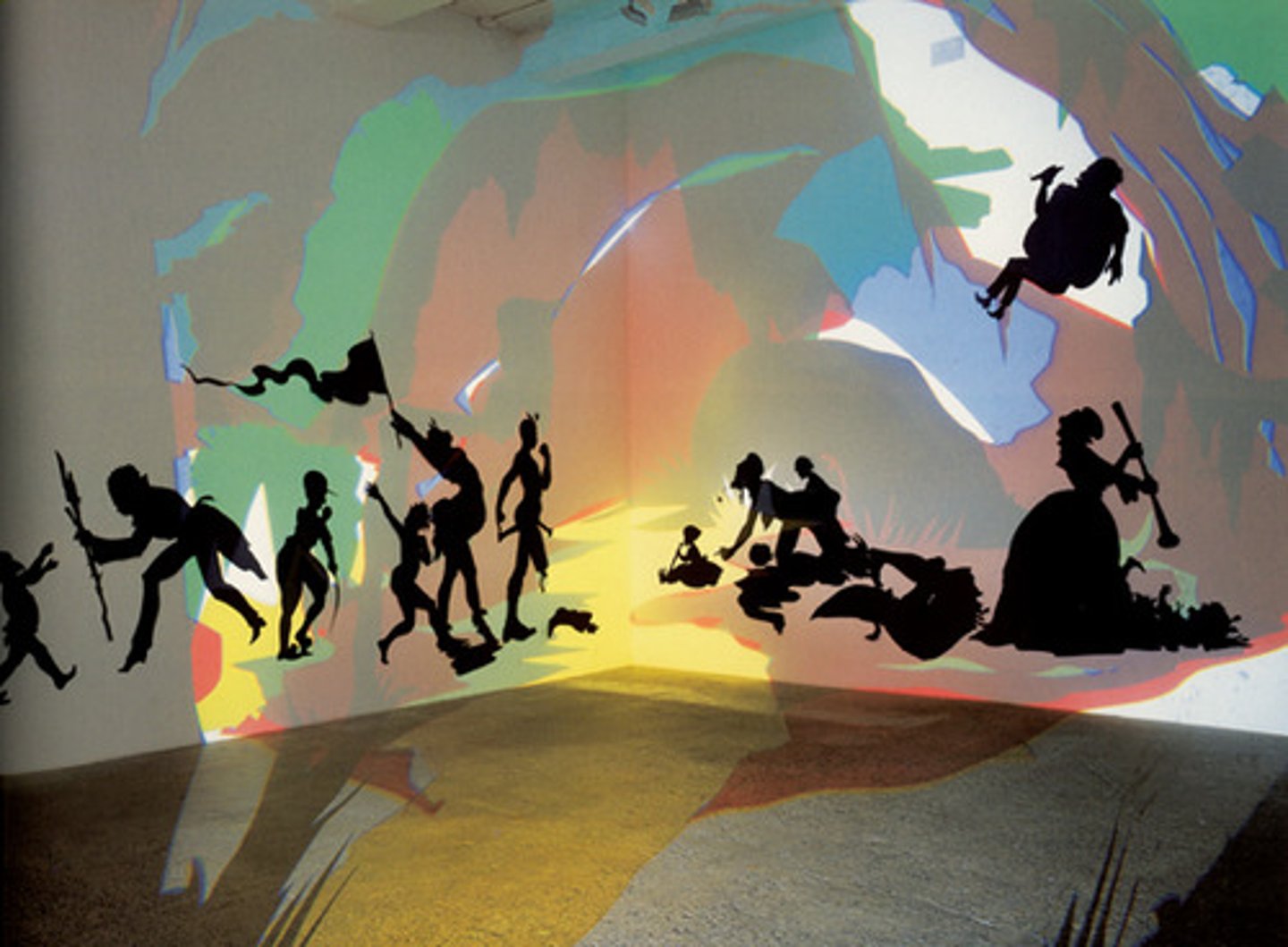
Darkytown Rebellion
Kara Walker, 2001

Architecture
the category of art that we live with the most; satisfies a basic, universal human need for a roof over one's head
Lascuax Cave
architecture example; cave in France where over 600 prehistoric paintings were discovered (15,000-13,000 BC)
Pyramids of Giza
architecture example; The three pyramids near Giza that were Built by Khufu, Cheops, and Cheops' son. Their the oldest and largest of the three pyramids in the Giza Necropolis bordering what is now Cairo, Egypt, and is the only one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World
Parthenon
architecture example; A large temple dedicated to the goddess Athena on the Acropolis in Athens, Greece. It was built in the 5th century BCE, during the Athenian golden age.
Panthenon
architecture example; A large, domed temple built in ancient Rome to honor many gods and goddesses.
Colosseum
architecture example; A large stadium in ancient Rome where athletic events took place
Palace of Versailles
architecture example; a palace built in the 17th century for Louis XIV southwest of Paris near the city of Versailles
Chartres Cathedral
architecture example; Finest example of French-Gothic architecture
University of Cathedral
architecture example; Gothic Revival skyscraper that's a landmark listed in the National Register of Historic Places and houses humanities departments
University of Chicago's Mansueto Library
architecture example; striking architectural design, including a soaring elliptical glass dome.
Structural Systems
provide basic framework and transport system for the body: Load-Bearing Construction + Post-and-Lintel Construction
Load-Bearing Construction
one of the basic ways to construct, where rows of loads are piled on top of others to build the walls
Post-and-Lintel Construction
a fundamental way of building by means of having vertical beams (posts) stabilized by horizontal beams (lintels) on top
Arch
a structure that evenly distributes the weight of the top, reliving stress a the point the vertical meets the horizon
Vault
roof support: Groin Vault, Barrel Vault, + Dome
Groin Valut
the creation of two barrel vaults that are crossed in the center at a right angle. Groin vaults are made from stone or brick. These vaults were first used in Europe and were later adopted by the Romans, the Byzantine, and Islamic people.
Barrel Vault
a vault forming a half cylinder
Dome
a rounded vault forming the roof of a building or structure, typically with a circular base.
Prehistoric
the period before written documentation
Classical
in connection with western civilization refers to ancient Greece and ancient Rome
Renaissance
the revival of interest in ancient Greek and Roman culture
Humanism
the stance which affirms that human beings have the right ad responsibility to give meanings and shape to their own lives
Triptych
a work of art (usually a panel painting) that is divided into three sections, or three carved panels
Mannerism
late Renaissance trend that suggests certain painters practiced an art of grace and sophistication
Sofonisba Anguissola
first woman artist known to have achieved celebrity among her contemporaries
Baroque
art full of emotion, energy, and movement
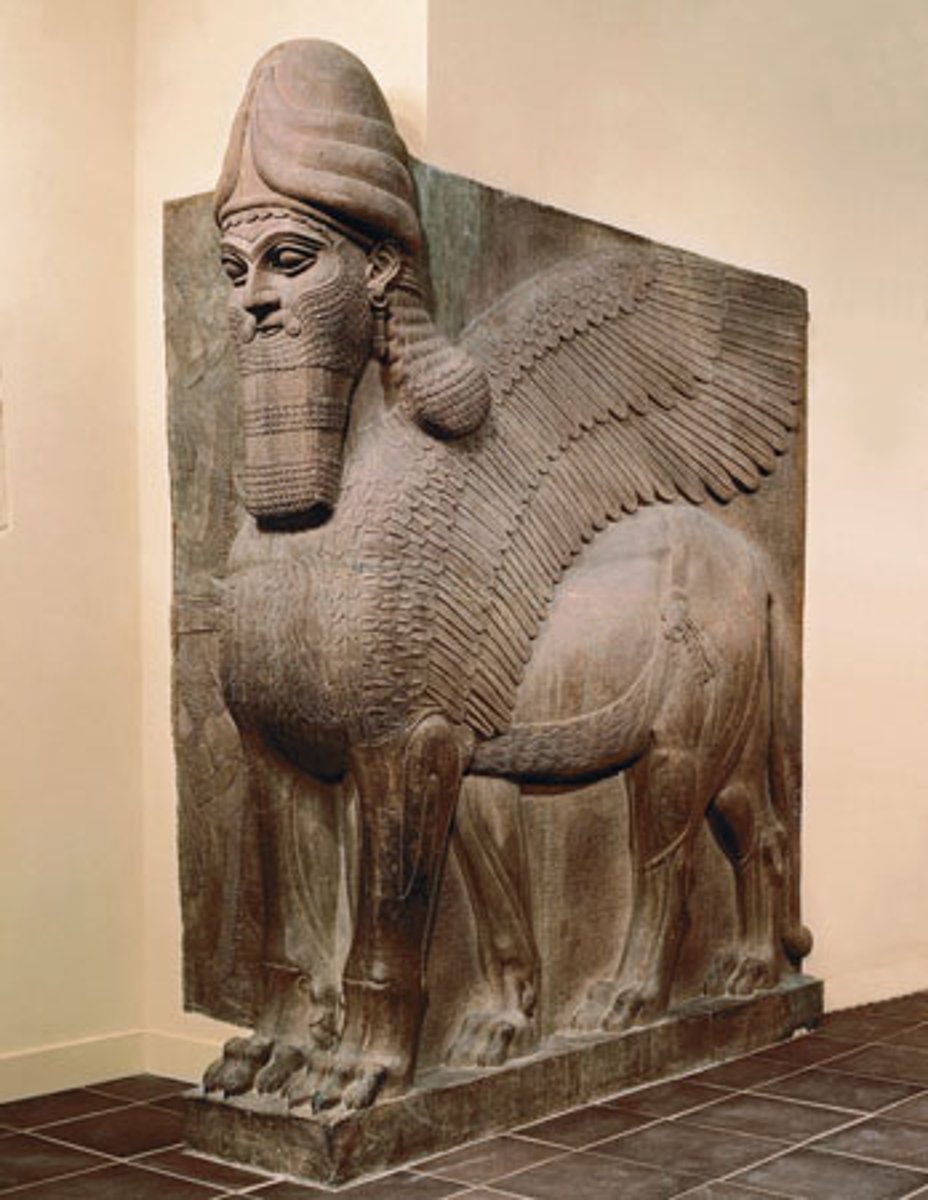
Assyrian, from Nimrud
Human-Headed Winged Lion

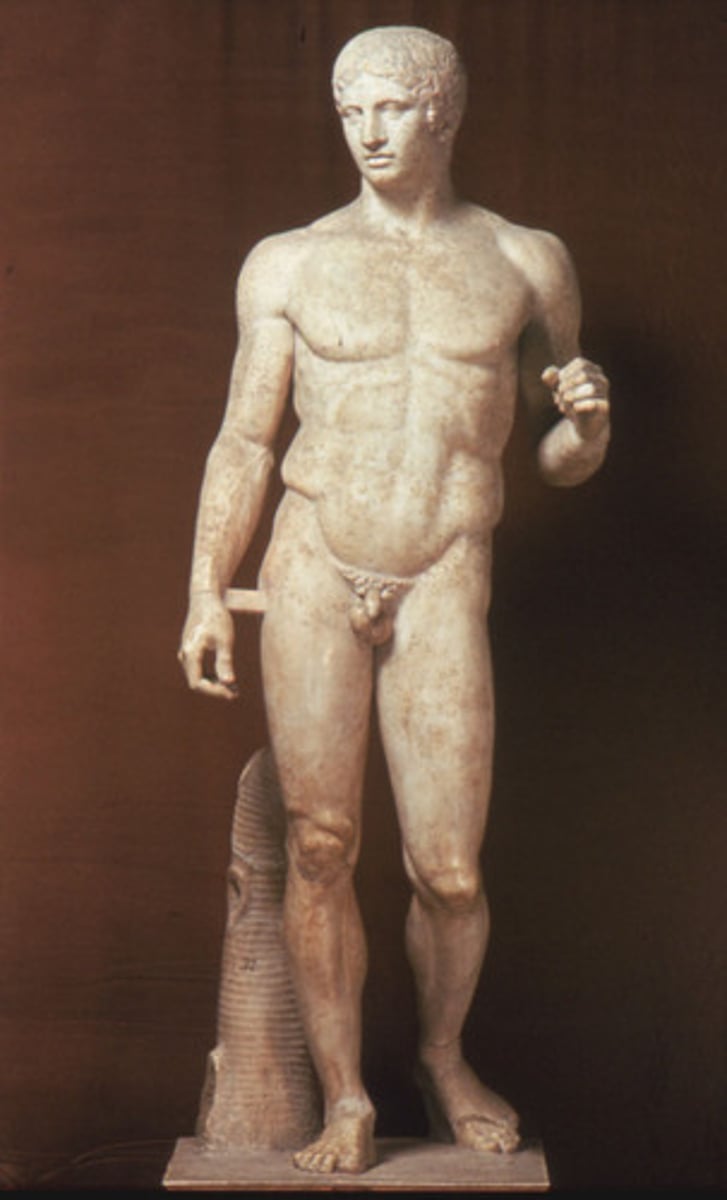
Polykleitos
Spear Bearer (Doryphorus)

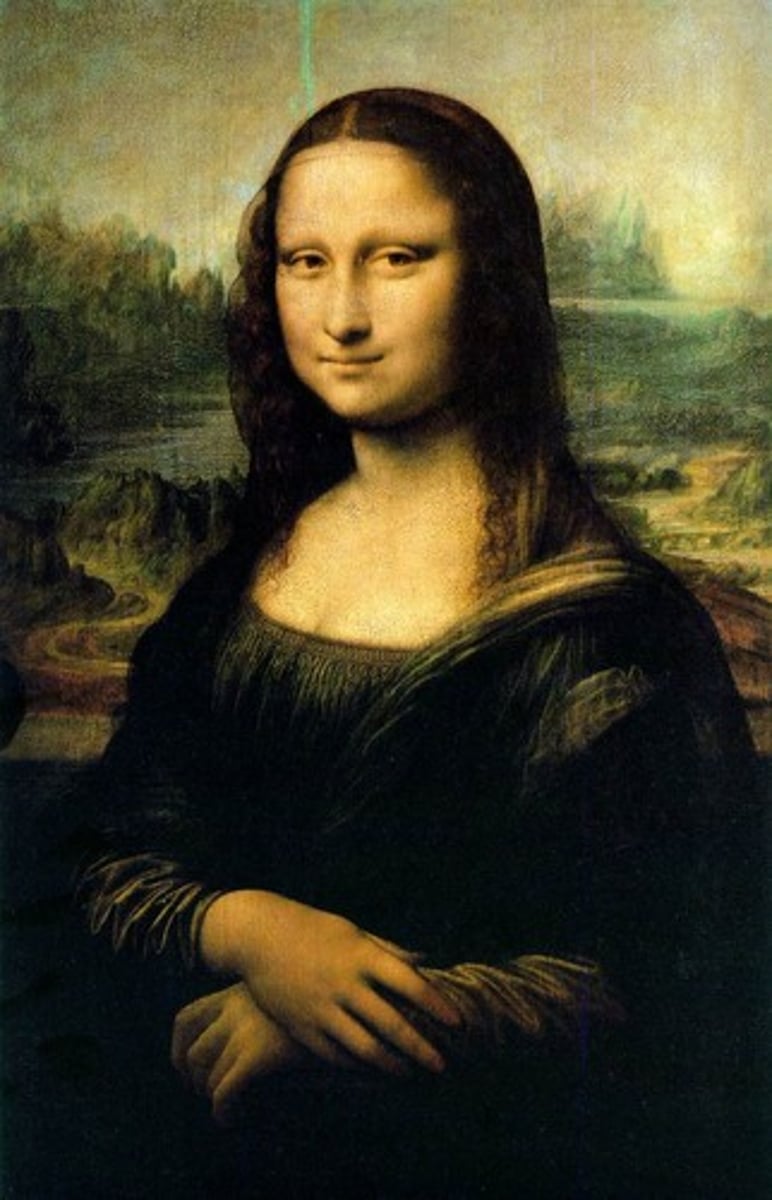
Leonardo di Vinci
Mona Lisa

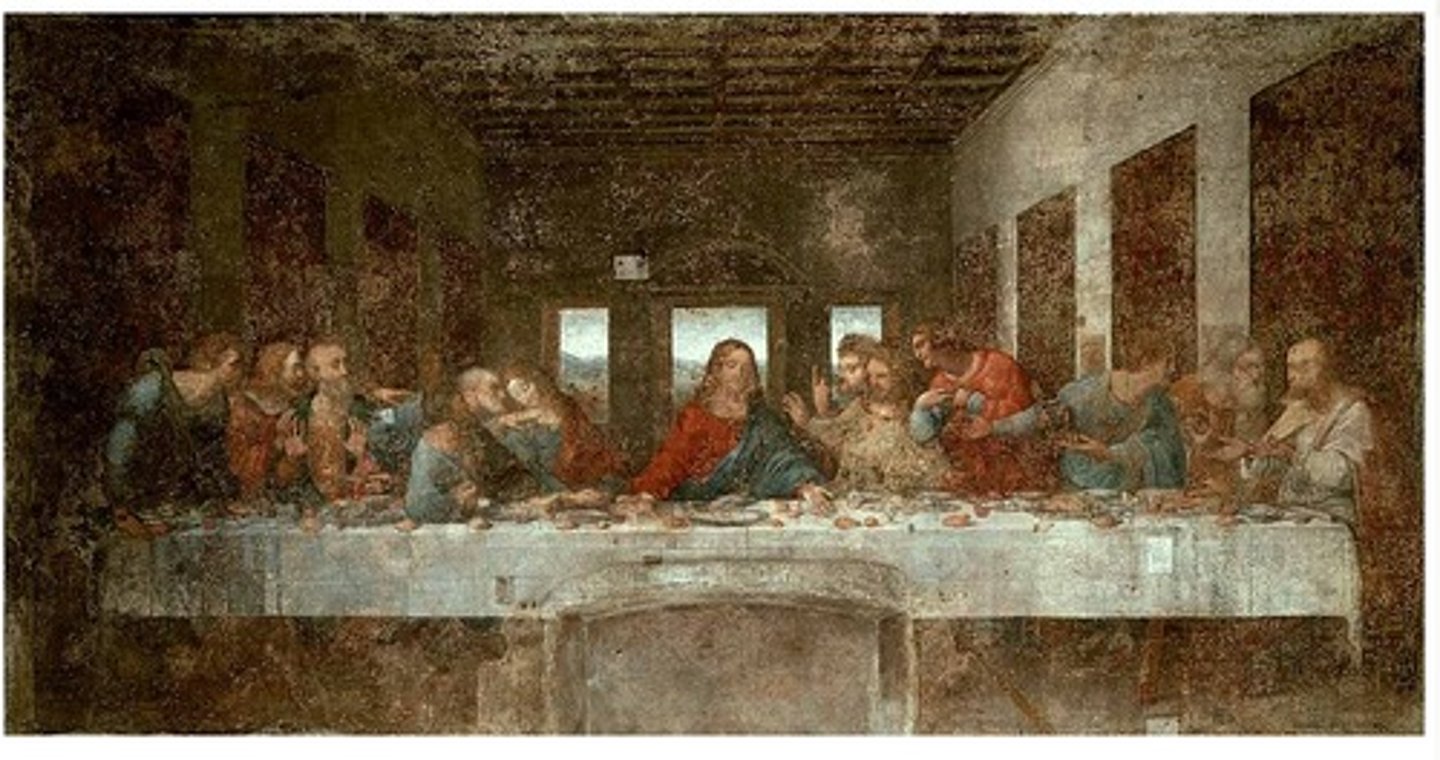
Leonardo di Vinci
The Last Supper

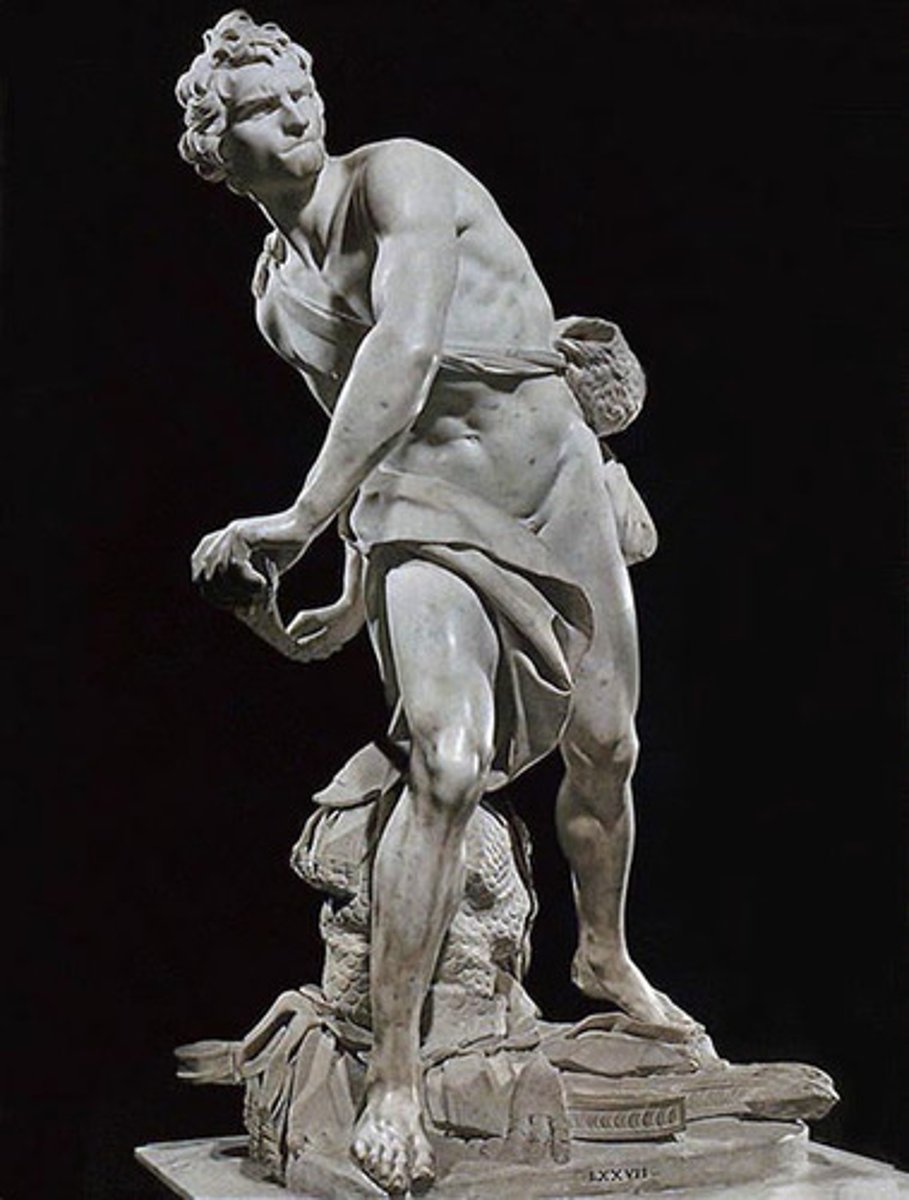
Michelangelo
David

Michelangelo
Sistine Chapel ceiling
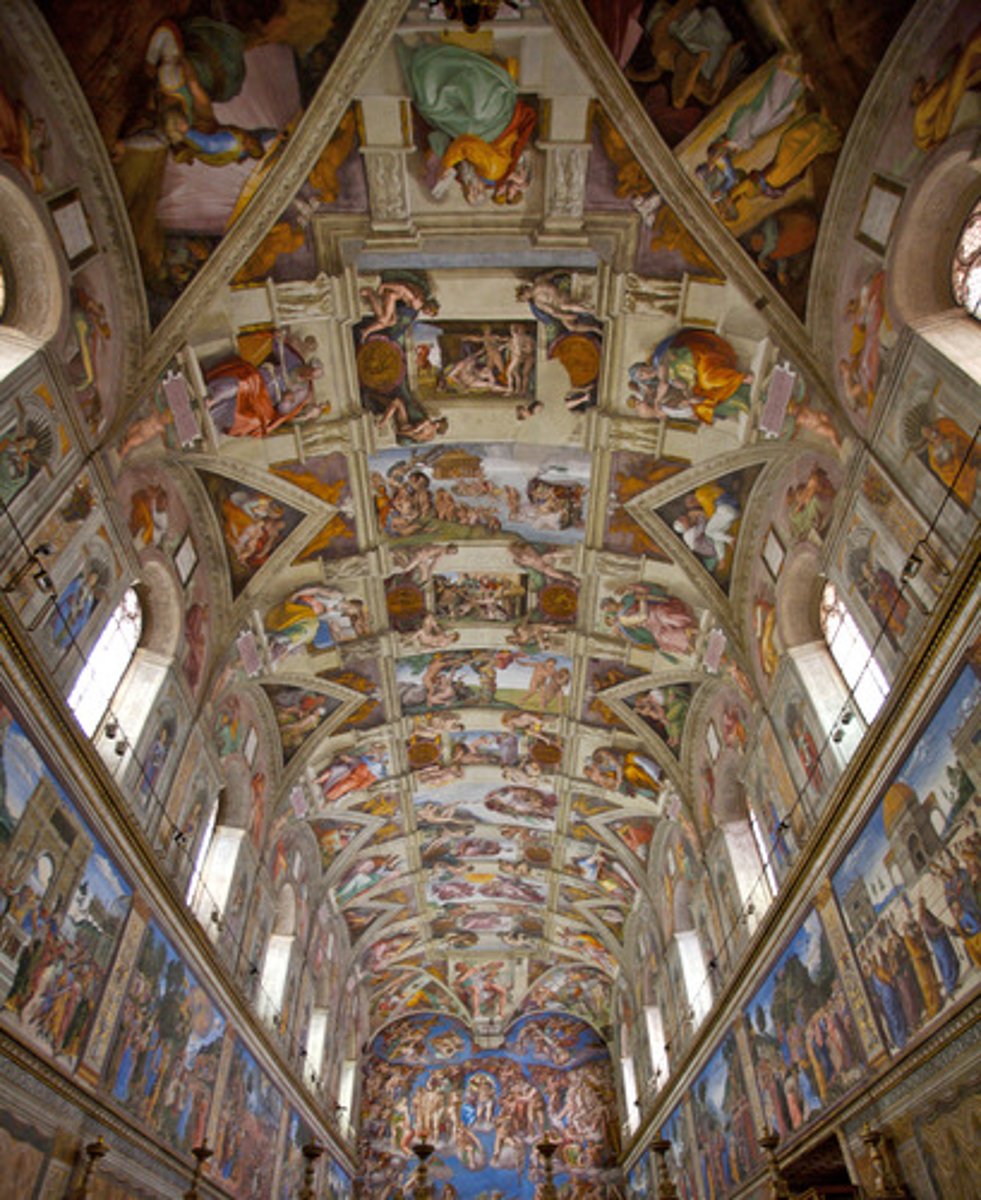

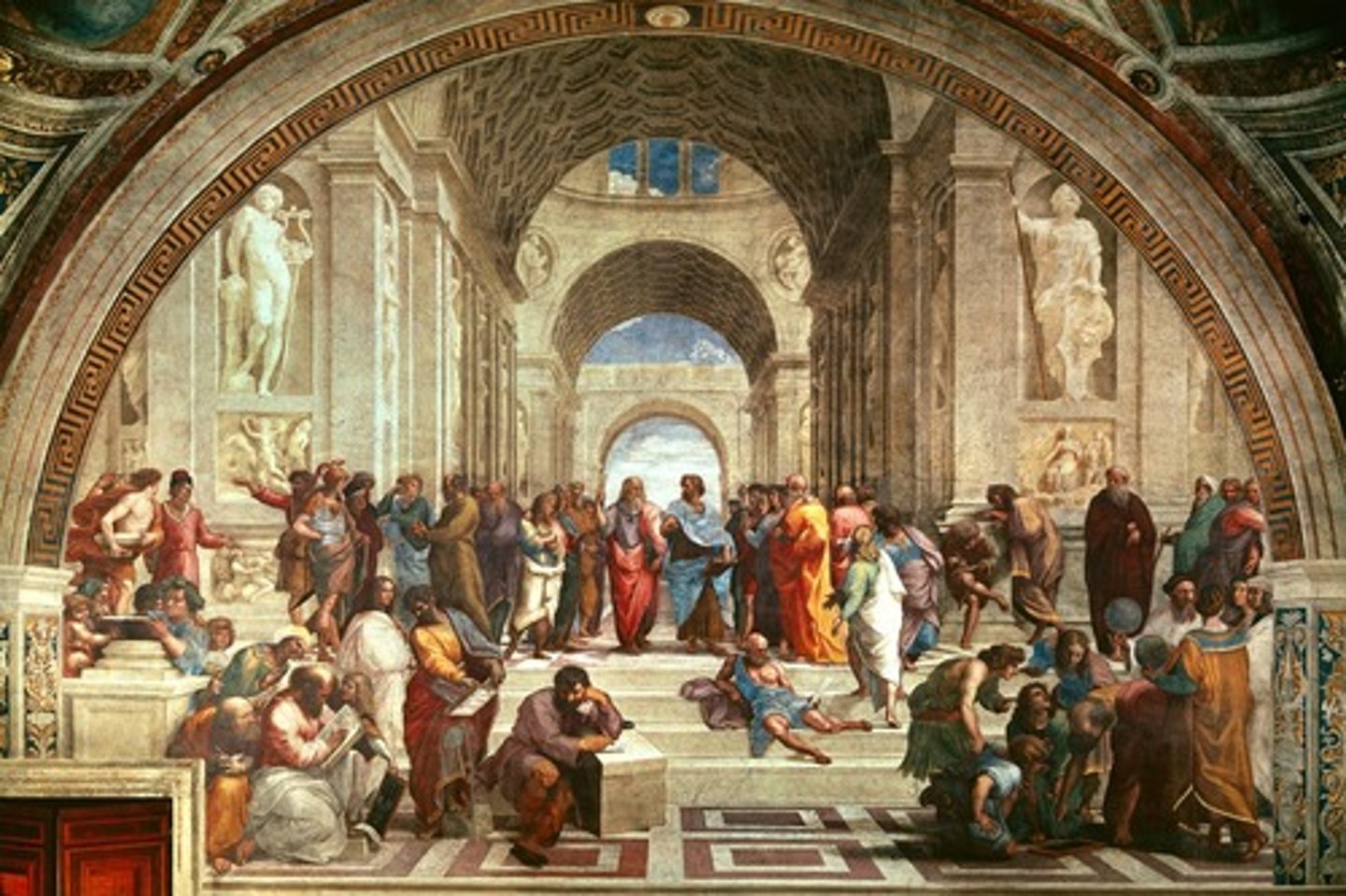
Raphael
School of Athens

Sofonisba Anguissola
Self-portrait at the easel
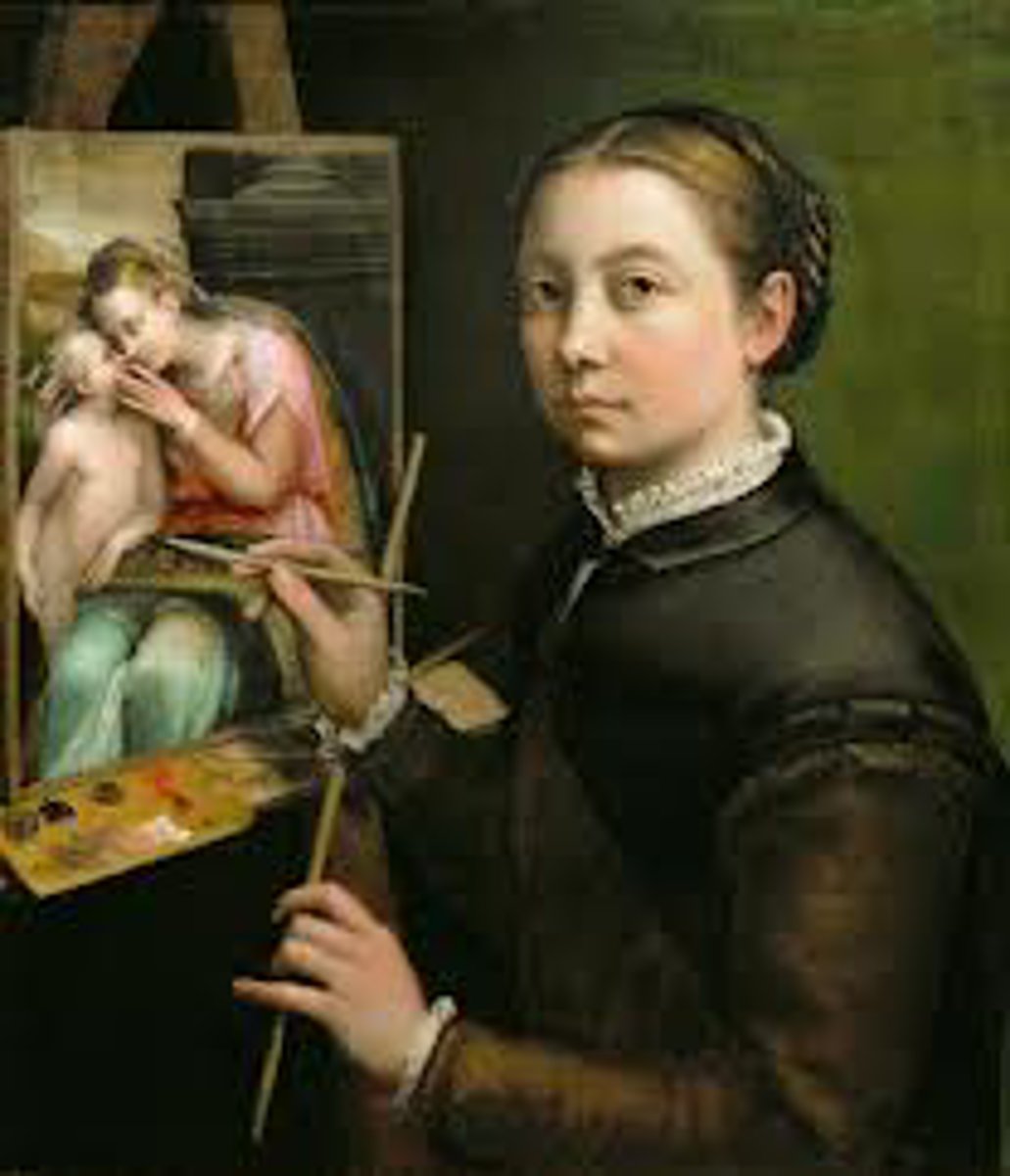
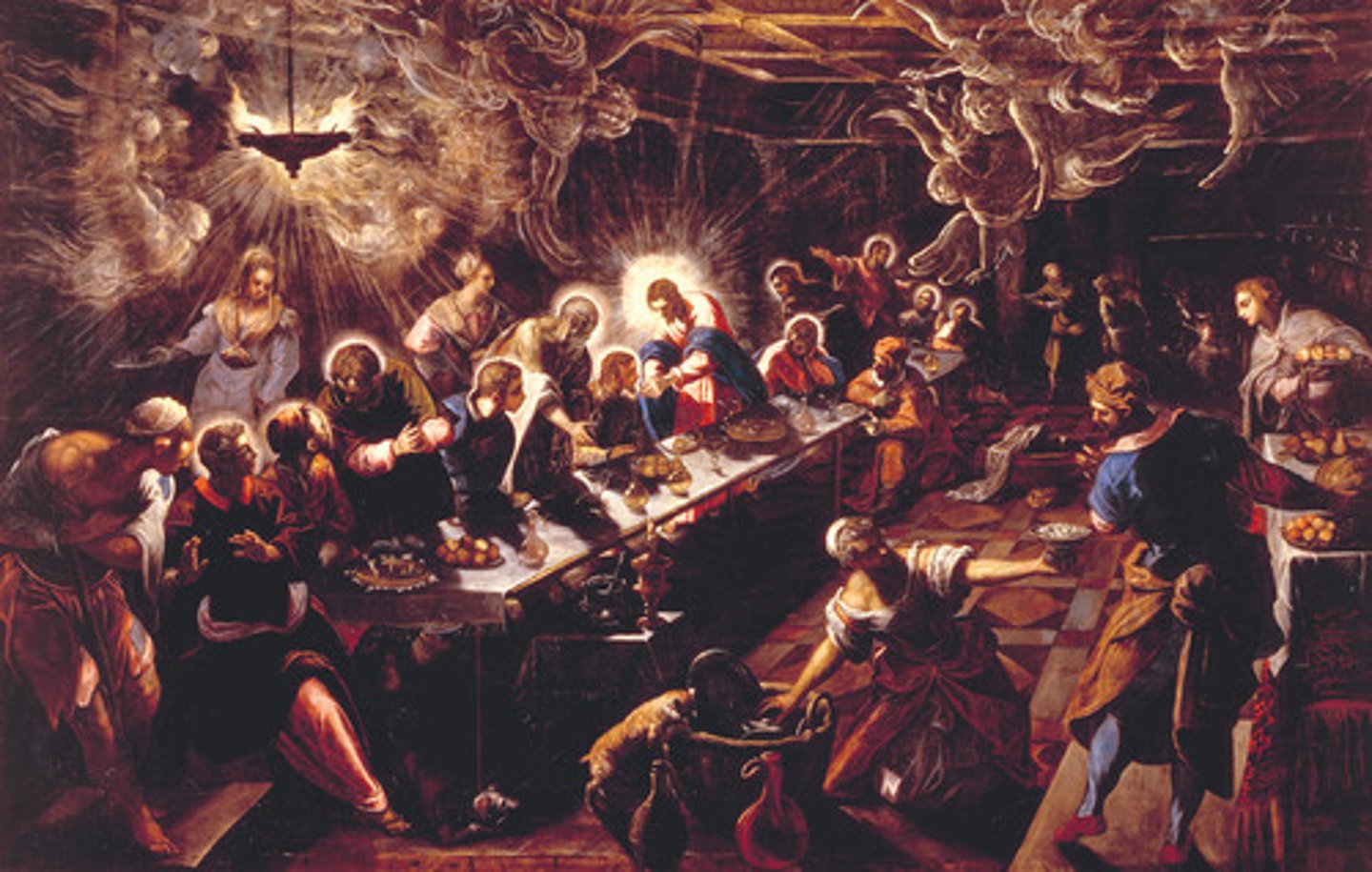
Tintoretto
The Last Supper (not da Vinci's)

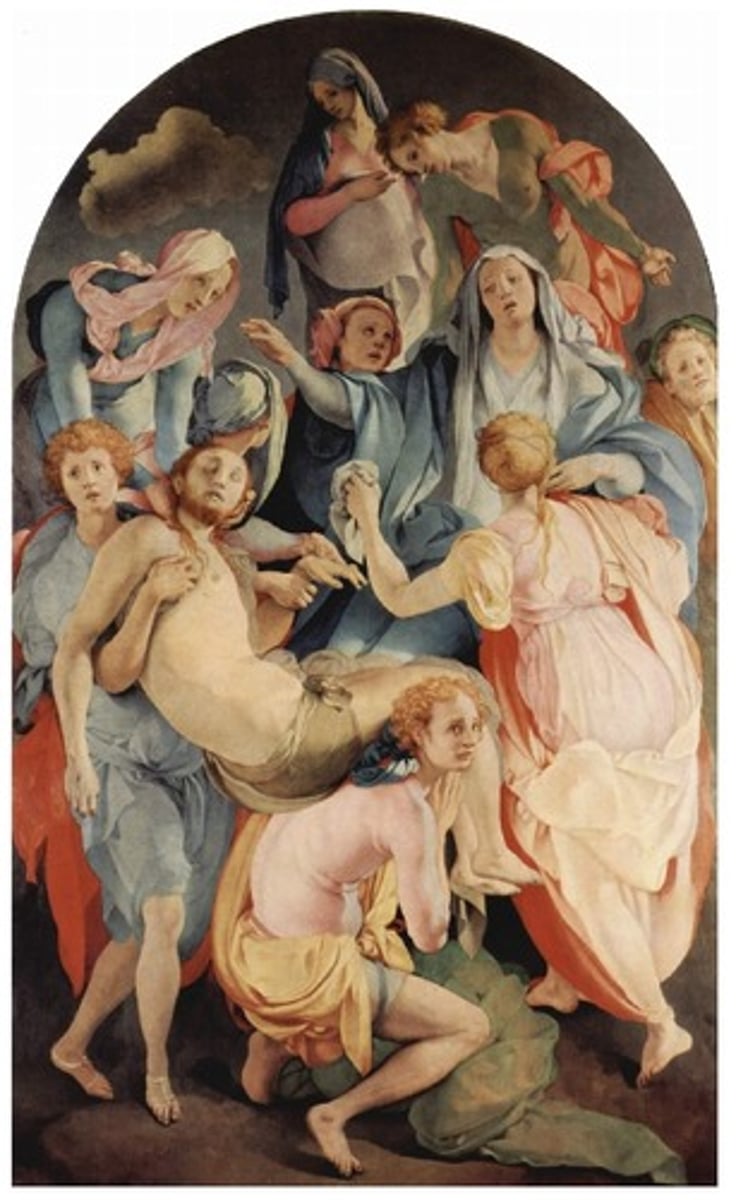
Carravaggio
Entombment of Christ

Rembrandt
Self-Portrait
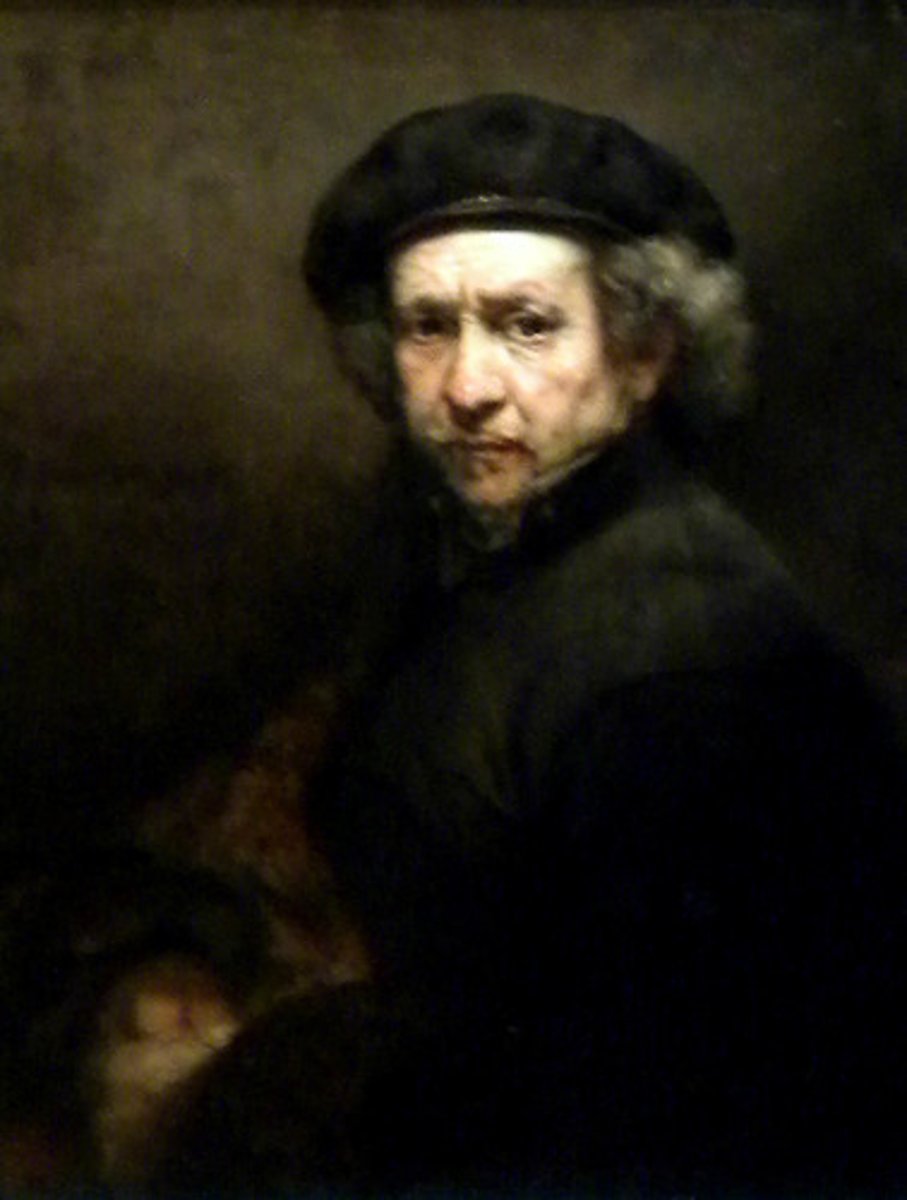

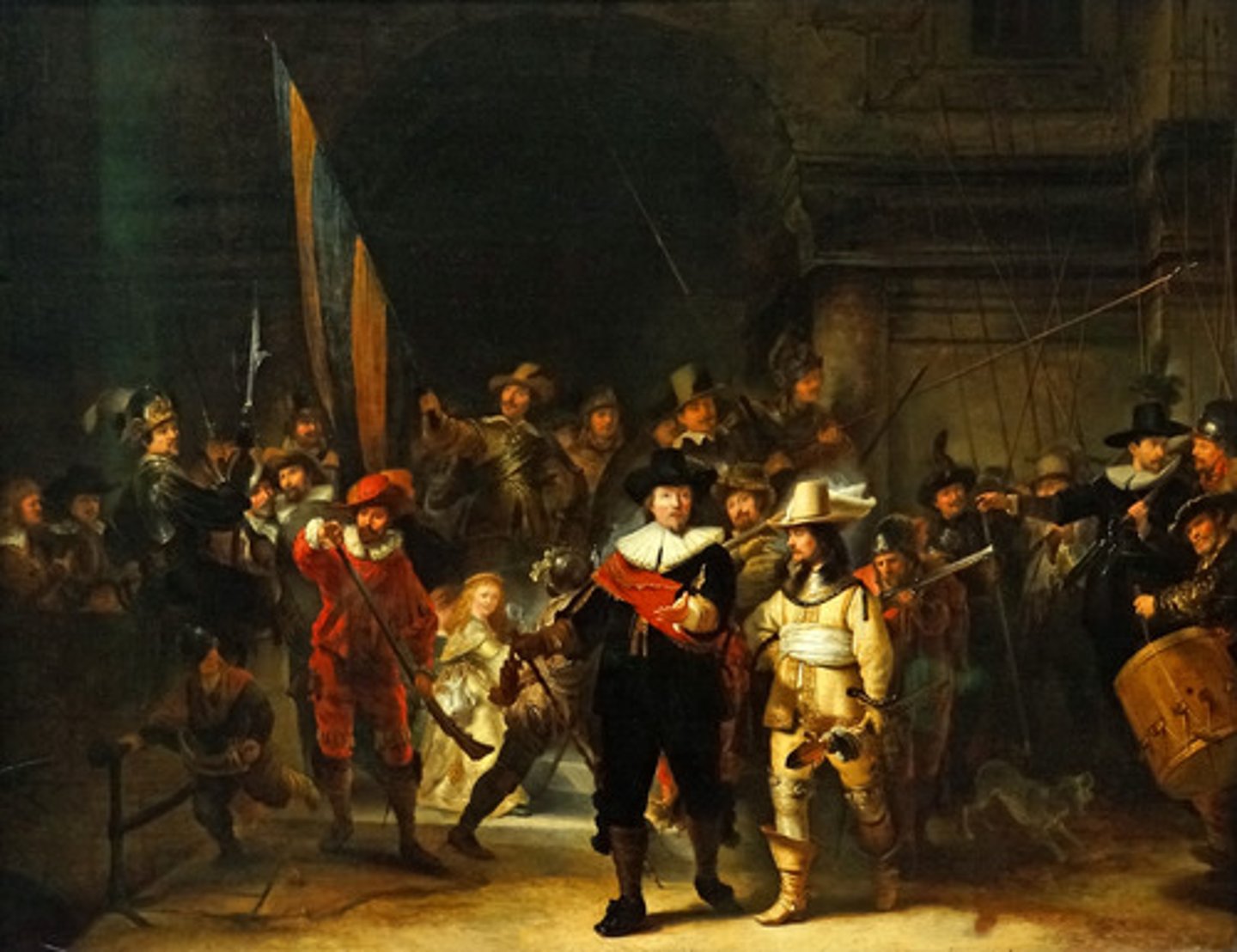
Rembrandt
Sortie of Captain Banning Cocq's Company of the Civic Guard (The Night Watch)

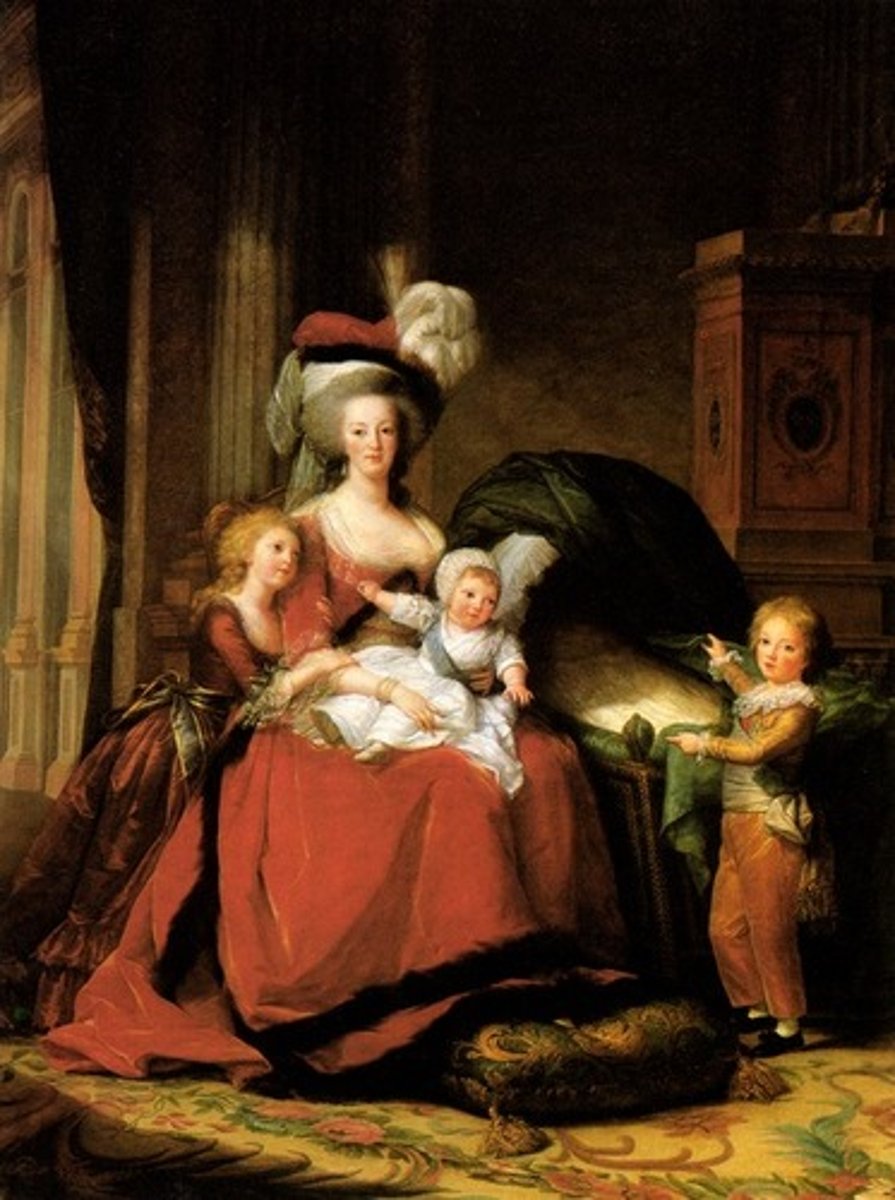
Elisabeth Vigee-Lebrun
Marie Antoinette and Her Children

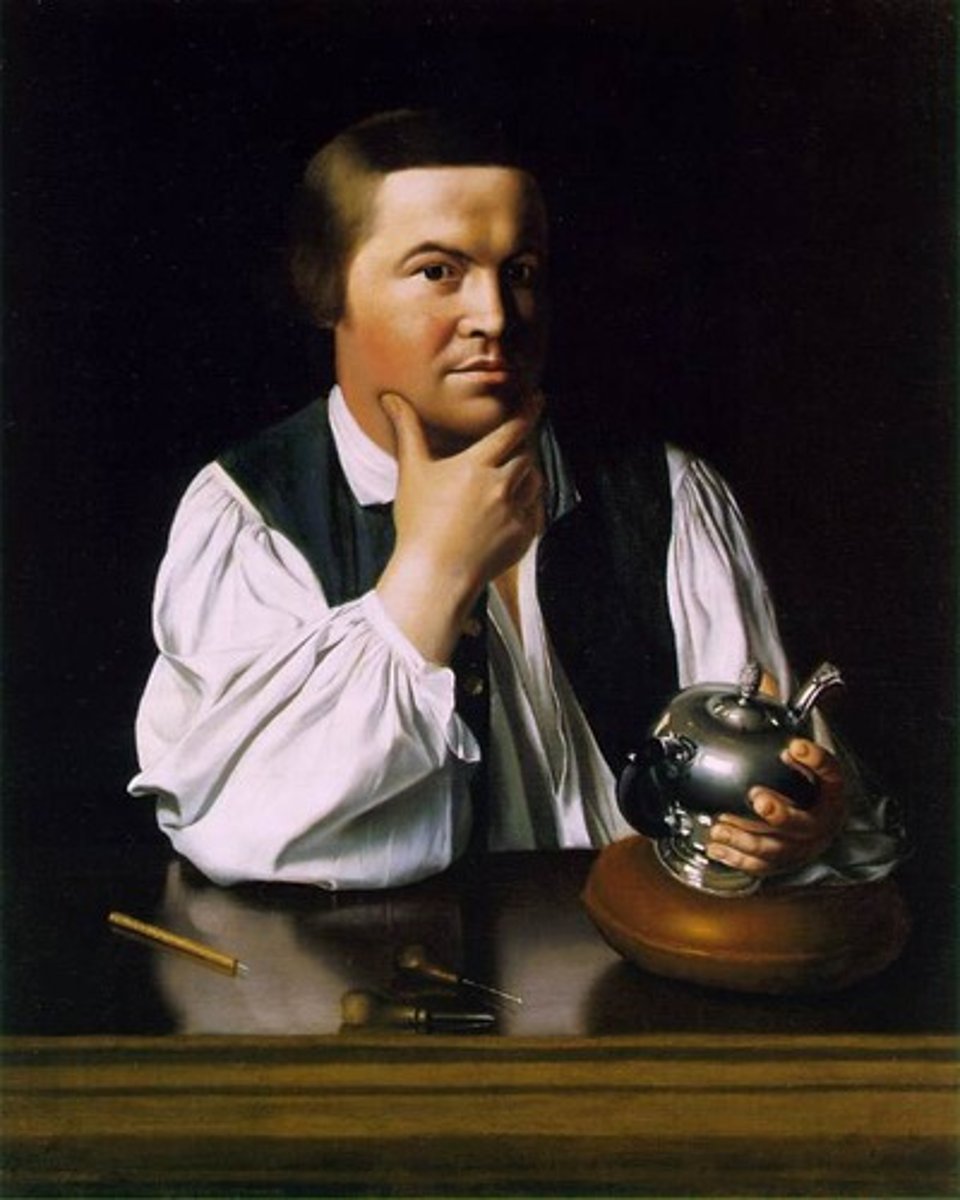
John Singleton Copley
Paul Revere

form
all visual aspects of art
style
appearance of art which includes the particular manner of presentation; types include representational, stylized, abstract, and nonrepresentational
composition
how elements are arranged in a work
content
an idea communicated through the form; comprises of the subject matter; includes the subject and message; some themes include religious, political, daily life, portrait, nature, and fantasy
representational style
naturalistic; when the figures and objects are close to life
stylized style
any time the work seems more or less close to life, but fails to meet all of the representational criteria
abstract style
art where the forms are distorted, but one can still identify the images
nonrepresentational style
art made up of geometric shapes or lines and you cannot identify any forms such as figures or objects in it
religious theme
art that deals with religion or the sacred (gods/divine); made to worship, bring respect, or teach about
political theme
any art that deals with political or social event or issues
daily life theme
everyday life scene
portrait theme
focuses on a person (or people)
nature theme
usually about beauty of nature
fantasy theme
dream-like and deals with made-up figures and out-of-this-world experience
line
a path traced by a moving point; outline, contour, and implied line
outline
a line that shows or creates the outer edges of a shape
contour
describe the shape of the object; include the interior details
implied line
a line not actually drawn but suggested by elements in the work
direction and movement
a lead through an image
shape
a two-dimensional shape and any two-dimensional image
implied shape
what our mind perceives the visual information as a whole, even though the whole does not exist
mass
a three-dimensional form that occupies a volume of a space
actual texture
tactile, a quality we can experience through touch
visual texture
texture that is seen, but cannot be felt
space
interacts with the lines, shapes, colors, and textures of an artwork that give it definition
three-dimensional space
three-dimensional artwork that stands in the actual space which our bodies stand
implied space
suggests depth in two dimensions
linear perspective
forms diminishing in size as they recede from parallel lines receding to a vanishing point on a horizon line
foreshortening
the visual phenomena whereby an elongated object projecting toward or away from a viewer appears shorter than its actual length
atmospheric perspective
when distant objects appear less distinct, paler, and bluer than nearby objects
isometric perspective
use of diagonal lines to convey recession without parallel lines converging
time and motion
signs that remind us of motion or the passage of time
color
hue; element of art that is produced by light
color theory
the study of white light separated into spectral colors by a prism and colors of the visible spectrum
color properties
color, value, and intensity
hue
the dimension of color that is determined by the wavelength of light; what we know as the color names blue, green, and so forth
value
The lightness or darkness of a color
intensity
The brightness or dullness of a color