Biochem. Exam 2
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
What is the difference between Hemoglobin and Myoglobin?
Hemoglobin: in blood, transports oxygen, 4 subunits (2α, 2β), can carry 4 O₂ molecules, tetrameric
Myoglobin: in muscles, stores oxygen, one chain, binds oxygen tightly (high affinity), monomeric
How were the first proteins 3D structure discovered?
x-ray crystallography
What was the model for the fact that protein sequence could lead to disease?
Sickle Cell Anemia
What are the curves for Myoglobin and Hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin: sigmodial
Myoglobin: hyperbolic
What is a Heme?
a cofactor of a subunit that has a central Fe+2 to bind O2
How many coordination sites does the central Fe2+ heme have?
6 (4 to protoporphyrin, 1 to His and 1 to O2)
What happens in oxygen binding?
oxygen binding pulls iron into the heme plane → tiny movement → whole protein shifts
Why can functional MRI (fMRI) detect brain activity using hemoglobin?
Oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin have different magnetic properties.
Why does hemoglobin exhibit cooperative binding while myoglobin does not?
Hemoglobin has four subunits, and oxygen binding to one subunit induces a conformational change that increases affinity in the others.
What does “Hemoglobin binds oxygen cooperatively” mean?
the binding of one oxygen molecule increases the affinity for the next oxygen molecule.
What is the T state of Hemoglobin?
T (tense state): low O2 affinity, deoxy. form (on graph: bottom of sigmodial curve)
What is the R state of Hemoglobin?
R state (relaxed): high oxygen affinity, oxy form (on graph: top of sigmodial curve)
What is the Bohr Effect?
H⁺ and CO₂ push hemoglobin into T state.
This makes hemoglobin release oxygen in active tissues (like muscle)
[tissues working harder need more O2]
H+ and CO2 are ___ effectors, meaing ….
H+ and CO2 are _allosteric__ effectors, meaing they bind to hemoglobin in hard working cells, changing the shape and signalling for need for more O2)
How can His promote the T state?
At low pH, His is protonated, and forms salt bridge within a b subunit and a confirmation that favors T state
How does CO2 promote the T state?
reacts with the terminal amino groups of proteins near the interface, inducing a change in charge from positive (or nuetral) to negative
Adding H+ will ___ the pH, shifting the sigmodial curve to the ___
Adding H+ will __lower_ the pH, shifting the sigmodial curve to the _right__
What is Sickle Cell Anemia?
mutation of Glu to Val in beta-chain, creating a hydrophobic patch on protein surface → hemoglobin fibers form → red cells become sickle-shaped, causing clots, pain, or organ damage
What are Enzymes?
biological catalysts (mostly proteins, some RNAs)
How are enzymes changed in a rxn?
Enzymes are not consumed or permanently changed in the reaction.
Enzymes ___ rxns but do not change the overall _____
Enzymes _speed up__ rxns but do not change the overall _Delta-G (free energy)__
What is an active site?
Substrate binds at a 3D cleft/pocket called the active site.
Active sites are usually…
nonpolar, excludes water.
Substrate + enzyme → ______→ product + enzyme.
Substrate + enzyme → ES complex → product + enzyme.
What are the two key features of enzymes?
Catalytic Power – speeds reactions up by factors of 10¹⁰ to 10²⁰.
Specificity – recognizes only certain substrates.
The Protease Chymotrypsin cuts where
next to aromatics (Phe, Tyr, Trp)
The Protease Trypsin cuts where
cuts after Lys or Arg.
The Protease Papain cuts where
almost anywhere
Who invented the Lock and Key Model?
Fischer
What is the Lock and Key Model?
substrate fits exactly
Who founded the Induced Fit Model?
Koshland
What is the Induced Fit Model?
enzyme changes shape when substrate binds
How can enzymes achieve catalytic power?
interaction of peptide bond of substrate with the catalytic triad (Ser, His, Asp)
What are Cofactors? Examples?
Some enzymes need helpers:
Coenzymes (organic, from vitamins).
Metals (Zn²⁺, Mg²⁺, etc.).
Negative ΔG →
spontaneous (exergonic)
Positive ΔG →
nonspontaneous (endergonic)
Zero ΔG →
equilibirum
Delta-G is
Free Energy
Enzymes ____ change ΔG.
do not
What does an endergonic and exergonic rxn look like?
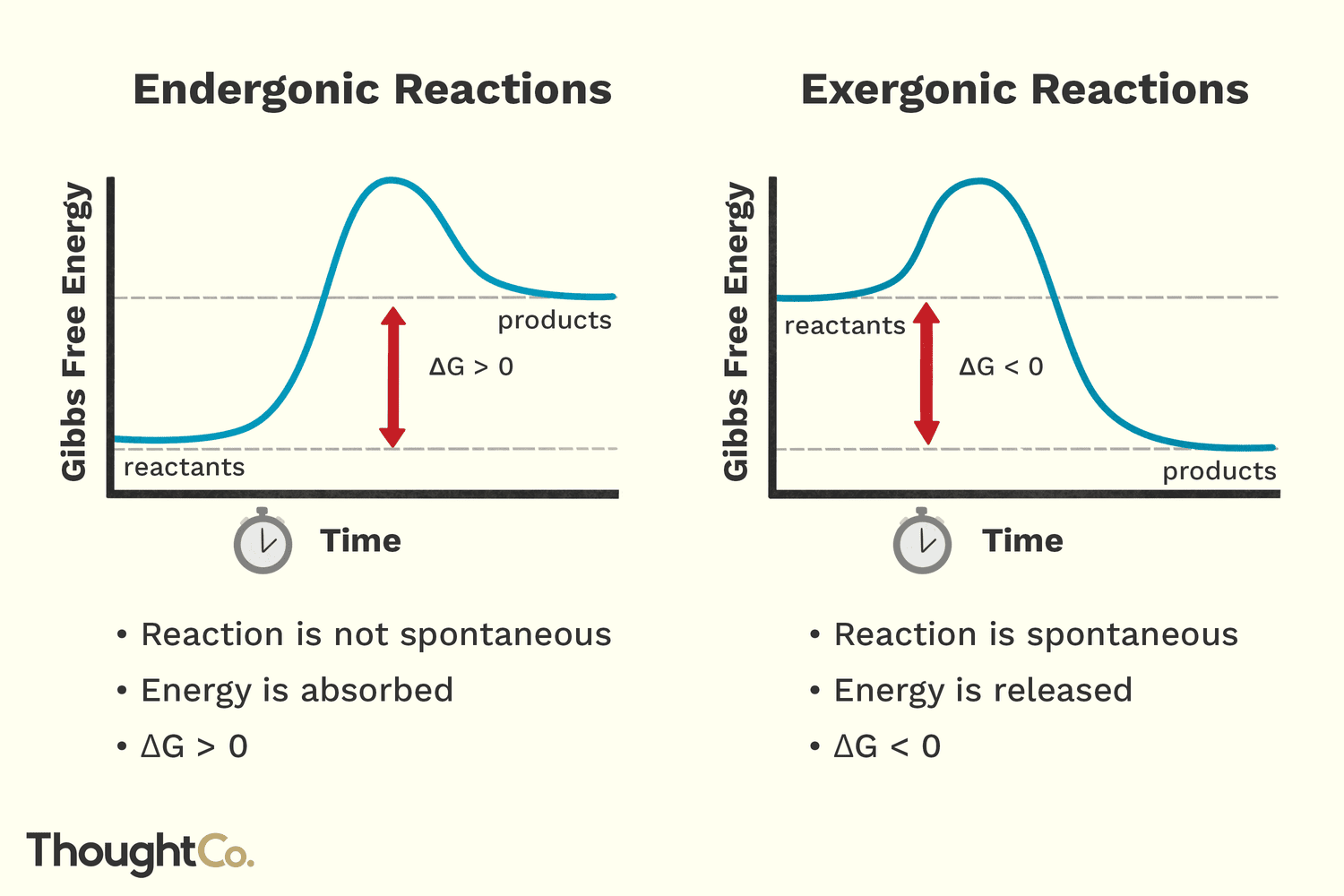
Polymerization of DNA + hydrolysis of PPi is an example of a…
coupled reaction (endergonic rxn + exergonic rxn = negative Delta-G)
What is the activation energy?
energy to go from the substrate to the transition state
Enzymes ___ the activation energy (Delta-G Hash) required for the rxn to begin
lower
Enzymes work to ___the transition state. Stabilization of the transition state __ the activation energy.
Enzymes work to _stablize__the transition state. Stabilization of the transition state _lowers_ the activation energy.
Enzymes bind to substrates with weak ___ interactions
noncovalent
What are the steps to the formation of E-S complex?
Aligning the substrate(s) with the enzyme so the enzymatic rxn can happen
Desolvation - stripping off water molecules from the groups that need to come close together
inducing strain in bonds that need to break
The Free Energy Difference Delta-G =
Delta-G naught+1.37log(products/reactants)
How could you shift a rxn toward the reactants?
increase the concentration of products to give them more energy
What does a Michaelis-Menton Graph look like?
hyperbolic curve
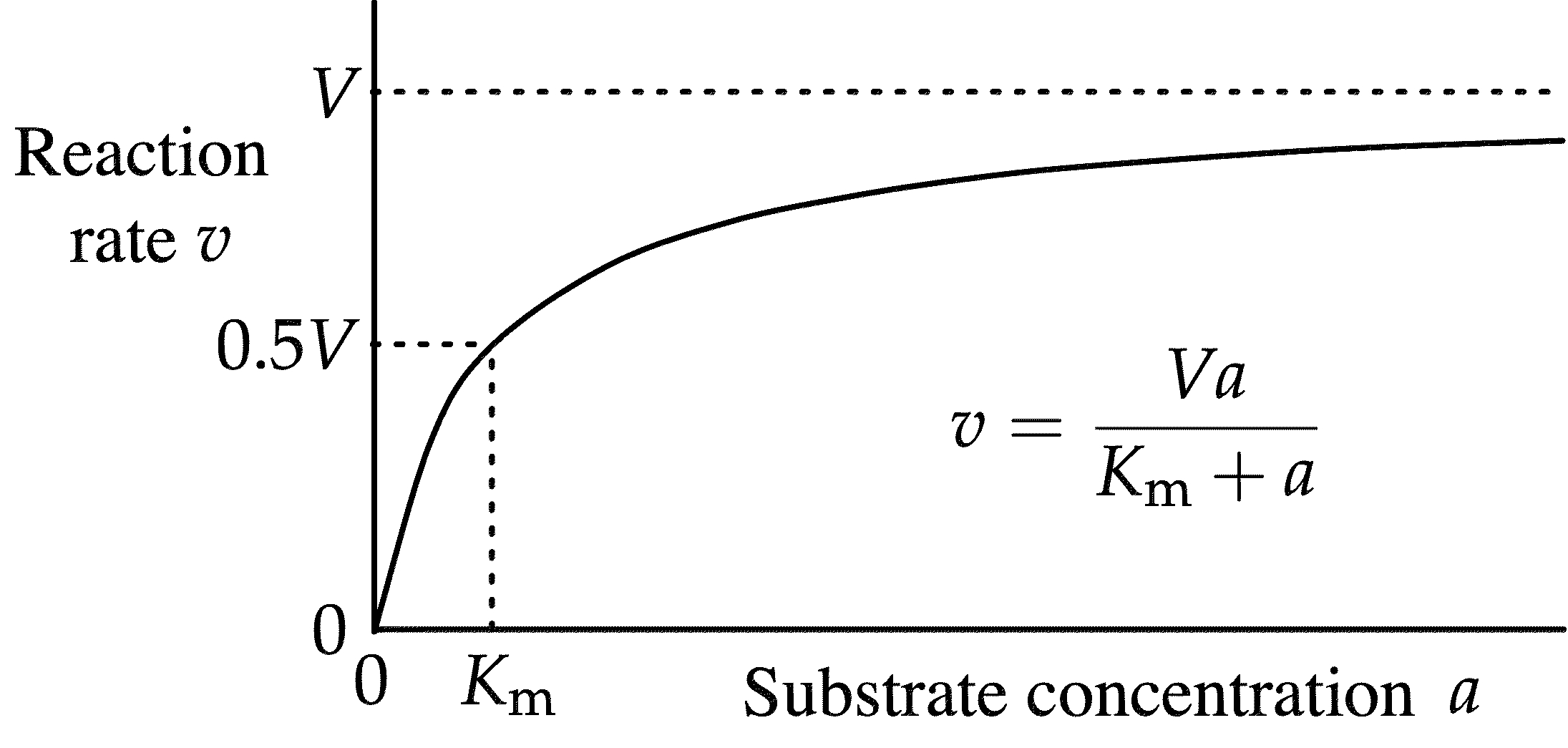
In a Michaelis-Menton graph, what is the Vmax?
Vmax = maximum velocity at full enzyme saturation
In a Michaelis-Menton graph, what is the Km?
substrate concentration at ½ Vmax → tells binding affinity
What does a low Km mean? High Km?
Low Km = strong binding.
High Km = weak binding.
What does a Lineweaver-Burk Plot look like?
a straight line
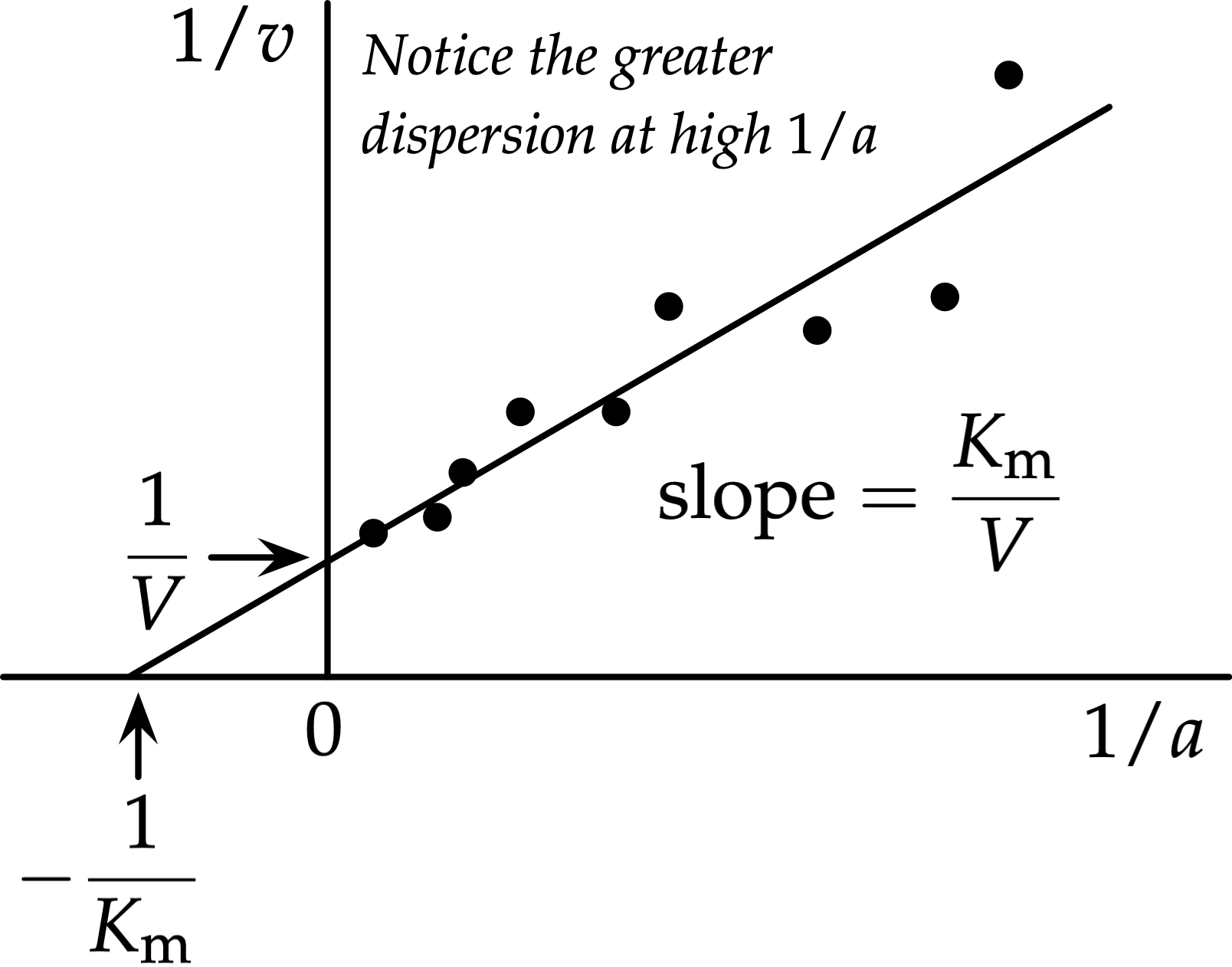
What is the Vmax and Km from a Lineweaver-Burk plot?
Vmax= 1/y-intercept
Km= -1/x-intercept
What is the Turnover Number (Kcat)?
• Number of substrate molecules converted to product per second per enzyme molecule.
• Better measure of enzyme efficiency than just Vmax.
What are allosteric enzymes?
class of enzymes whose catalytic activity is not constant or is regulated
Have multiple subunits, show cooperativity.
What is the curve of allosteric enzymes?
sigmoidal (S-shaped)
Allosteric activators shift the curve ___, while allosteric inhibitors shift the curve ____
Allosteric activators shift the curve _left__, while allosteric inhibitors shift the curve __right__
Amanita mushroom is an example of an ____
inhibitor, inhibiting translocation activity of RNA polymerase 2
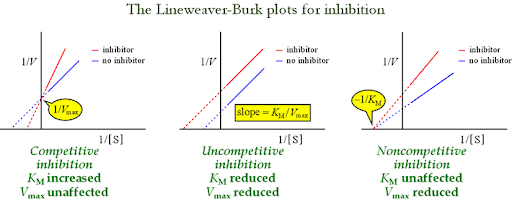
What are the types of Reversible Inhibitors?
Competitive: look like substrate, bind the active site. ↑Km, Vmax same.
Noncompetitive: bind elsewhere, block catalysis. Vmax ↓, Km same.
Uncompetitive: bind only ES complex. Both Vmax ↓ and Km ↓.
What are Irreversible inhibitors? Examples?
covalently bind enzyme (ex: penicillin, suicide inhibitors)
Penicillin works as an ____
Inhibitor, Penicillin irreversibly blocks bacterial cell wall synthesis.
What are the 4 major classes of biomolecules?
proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, carbohydrates
What are the functions of carbohydrates?
1. Energy storage (glycogen, starch).
2. Structural roles (cellulose, chitin, nucleic acids).
3. Cell signaling (glycoproteins, glycolipids).
What are the basic units of monosaccharides?
aldoses (aldehyde group) or ketoses (ketone group).
What is a Ketone?

What is an Aldehyde?
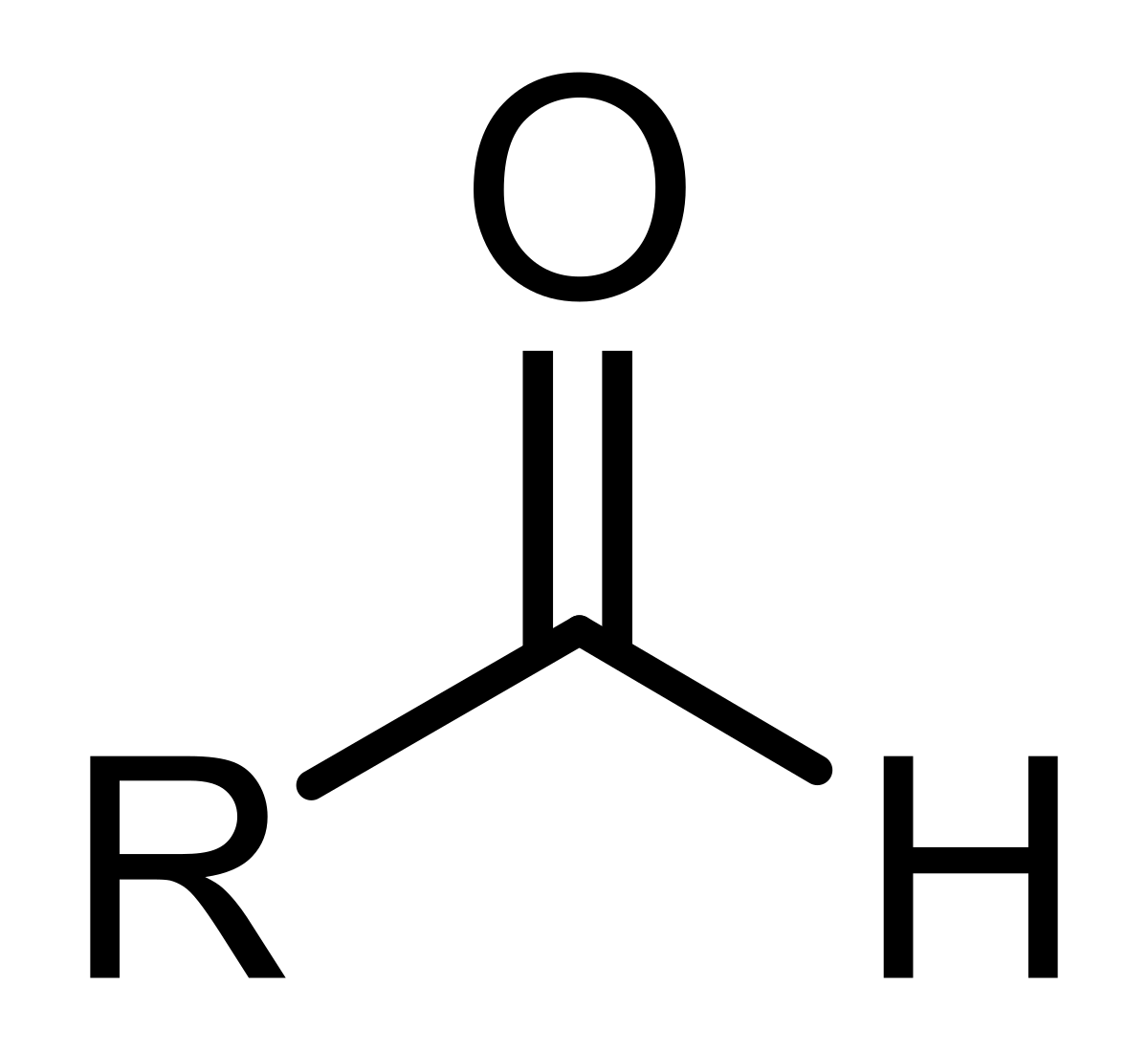
Glucose is a …
monosaccharide
What is the difference between D and L forms?
L: OH on left side of highest chiral carbon
D: OH on right side of highest chiral carbon (most common in nature)
Disacchardies have the ___ bond
O-glycosdic bond
Sucrose is a…
disaccharide
Glycogen, starch, cellulose, and glycosylated proteins are…
polysaccharides
What is Maltose?
Glucose + Glucose
What is Lactose?
Galactose + Glucose
What is Sucrose?
Glucose + Fructose
What structural change occurs when hemoglobin fibers form in sickle cell anemia?
RBCs deform into rigid, sickle shapes
Why is the Bohr Effect beneficial for metabolizing tissues?
It increases oxygen release in tissues where metabolism produces H⁺ and CO₂
At low oxygen concentrations (such as in tissues), hemoglobin is predominantly in the:
T state, to favor oxygen release
Why does the Glu → Val mutation in hemoglobin cause problems?
It introduces a hydrophobic patch that promotes aggregation in the T-state
Enzyme specificity is mainly dictated by:
The 3D structure of both enzyme and substrate
The specificity of chymotrypsin is primarily due to:
The enzyme’s interaction with the amino acid R group of the substrate
Which property of a reaction tells us whether the reaction will occur spontaneously?
The free energy difference (ΔG)
A negative ΔG indicates that a reaction is:
Exergonic, releases energy
What is the primary reason enzymes increase the rate of reactions?
They lower the Gibbs free energy of activation (ΔG‡)
Which of the following correctly represents the basic sequence of an enzymatic reaction?
E + S ⇌ ES → E + P
The Induced Fit model suggests that:
The enzyme changes shape slightly when the substrate binds, reinforcing weak interactions
If an enzyme has a large Km value, what does this imply?
The enzyme requires high substrate concentration to reach Vmax
Why is the Lineweaver–Burk plot especially useful?
It makes enzyme inhibition patterns easier to distinguish
What is Vmax in the Michaelis-Menten graph?
The maximum reaction velocity when the enzyme is fully saturated
Which type of inhibitor allows the enzyme to regain its activity after the inhibitor is removed?
Reversible inhibitor
Allosteric enzymes typically:
Have multiple active sites that can bind substrates, activators, or inhibitors
Noncompetitive inhibitors (NCI) bind to:
A different site on the enzyme, not the substrate site
If an enzyme has a turnover number (Kcat) of 1000 s⁻¹, this means:
Each enzyme molecule converts 1000 substrate molecules per second at saturation
On a Lineweaver–Burk plot, the lines representing uncompetitive inhibition are:
Parallel to the line without inhibitor
What part of the enzyme often reacts with suicide inhibitors?
R groups of amino acids in the enzyme
What are Enantiomers, Distereomers, and Epimers?
-Enantiomers: perfect mirror images
-Diastereomers: isomers with variations in asymmetric carbon(s) but are not mirror images (Allose and Mannose)
-Epimers: distereomers that differ at only one center such as D-Glucose and D-Mannose