4.4.3: Controlling MNCs
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
power of MNCs
powerful
contribute significantly to global wealth and job creation
help with inward investment and building foreign currency reserves for developing nations
benefits consumers
effectively use world resources
profits invested in useful R&D
criticised for being too powerful and exploiting stakeholders
operate as monopolists
exploit consumers through high prices
dominate markets
make it difficult for small firms to survive
maximimise profits
use working practices polluting the environment or consuming large quantities of non renewable resources
control flows of profit and revenue through countries with low tax rates and avoid tax payments
difficult for national governments to control MNCs
can easily relocate and take FDI, tax revenue and employment
political influence
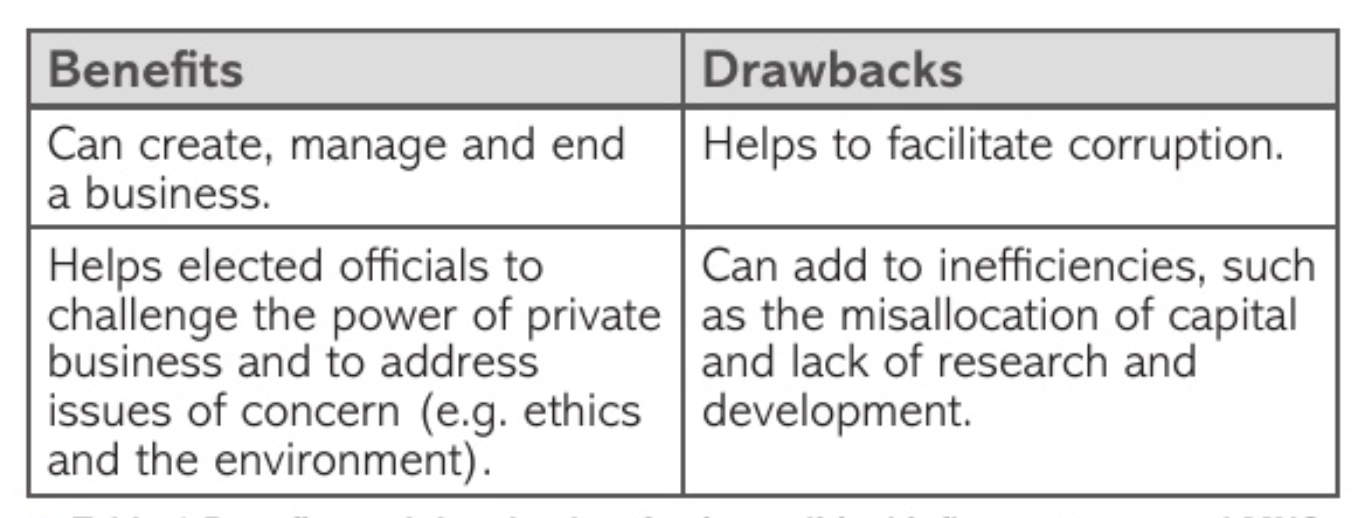
SOEs:
large MNCs owned by the state - state owned enterprises SOEs
effective method of control
political power exercised to create, manage and end a business
extensive political influence over organisations
lead to commercial and ethical issues
drawbacks of state ownership:
corruption - SOEs might be favoured by powerful politicians
state owned operations may take the capital other firms might better employ
politicians or regulators decide where funding should go
inefficient businesses may be given more money than they need and not be subject to competitive forces that reduce price and improve efficiency
shareholders and other investor rights ignored
mot true beneficiaries of the business
actual beneficiaries - politicians
ignores investment expenditure
less competitive pressure from other firms with state ownership
less incentive
non SOEs:
also important for non SOEs
national strategic priorities, boost employment or regulate financial institutions
privately owned businesses controlled using a number of political initatives:
tarrifs
quotas
regulations
local content requirement
direct/indirect ownership restrictions
support domestic industries through subsidies or tax breaks
lobbying by politicians to influence business decisions
politicians retiring to seats on the boards of plcs
legal control
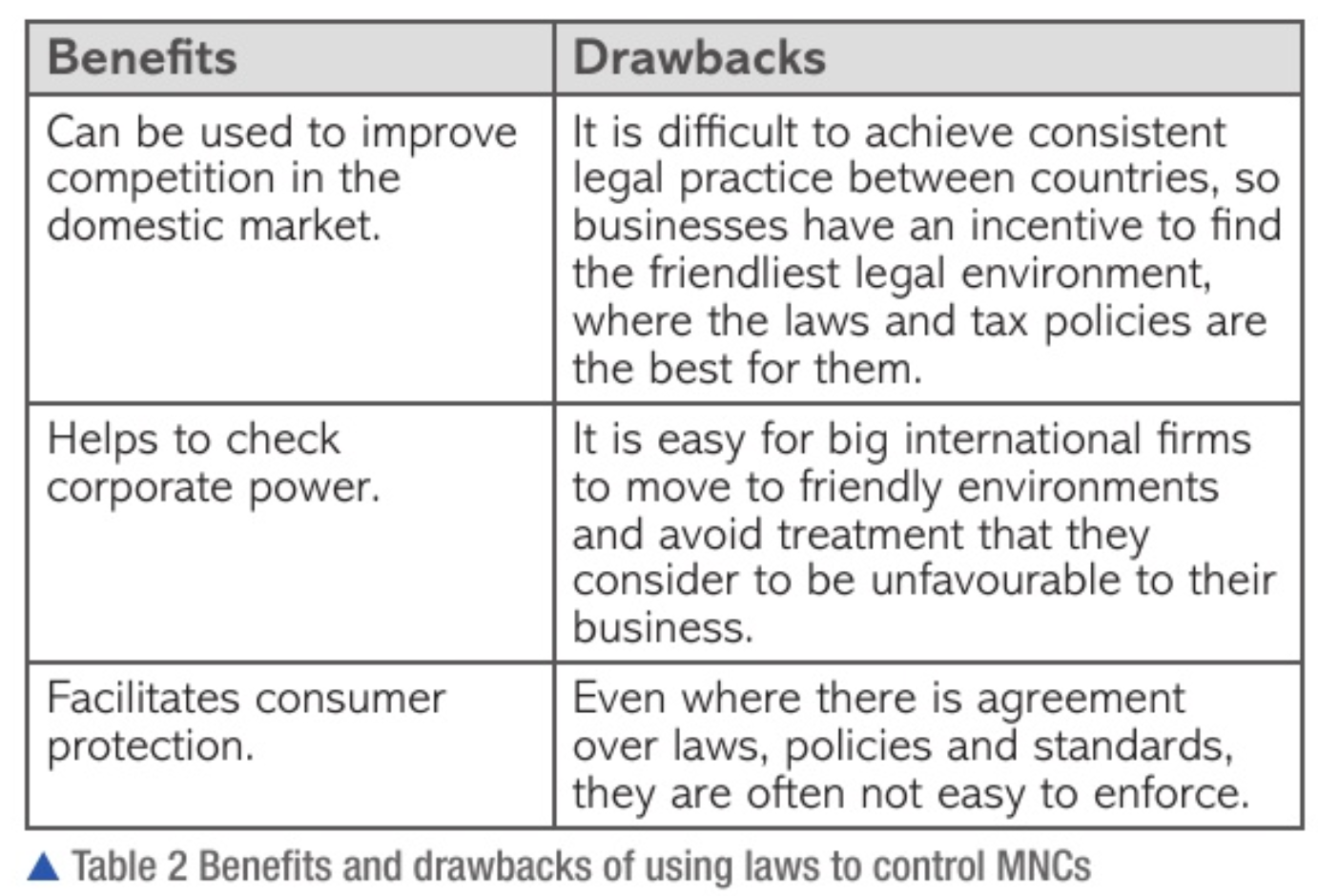
competition policy
exists to promote competition
ensures markets operate as efficiently as possible
specialised agencies set up to protect producers and consumers from unfair or anti-competitive practices
ensures firms don’t abuse market power, fix prices, or use pricing strategies to drive out competition, and don’t work together illegally
taxation policy
used to raise revenue
may help control MNC activities
low corporate tax = attracts huge FDI
may upset politicians in other countries
tax avoidance = big companies use differing systems to avoid tax
legislation
provide legal framework for business operations
system of incentives and penalties to ensure at-risk groups
too much intervention = discourages enterprise, deters foreign investment
prevents growth in income
reduces job creation
decreases tax revenue
reduces consumer choice
too little intervention = may not give attention to stakeholders best interest
legislation to penalise companies damaging environment, exploiting employees, engaging in anti-competitive practices, bullying suppliers and exploiting consumers
consumer pressure
apply pressure by avoiding products
forced to consider a wide range of social, political and historical sensitivities when marketing products in ethnically and culturally diverse regions
use of review systems allows customers to write freely about their experiences
companies want to avoid bad reviews
pressure groups
company behaviour may violate what many people consider acceptable but not break any laws
publicise bad behaviour and threaten to damage the image of form
voluntary organisations
methods to control MNCs:
boycotting - withdrawing from commercial or social relations
media criticism - criticised in the media, protest movements
direct action - demonstrations, protests, strikes or sabotage to achieve a political or social goal
lobbying - taking issues directly to government in an effort to influence change
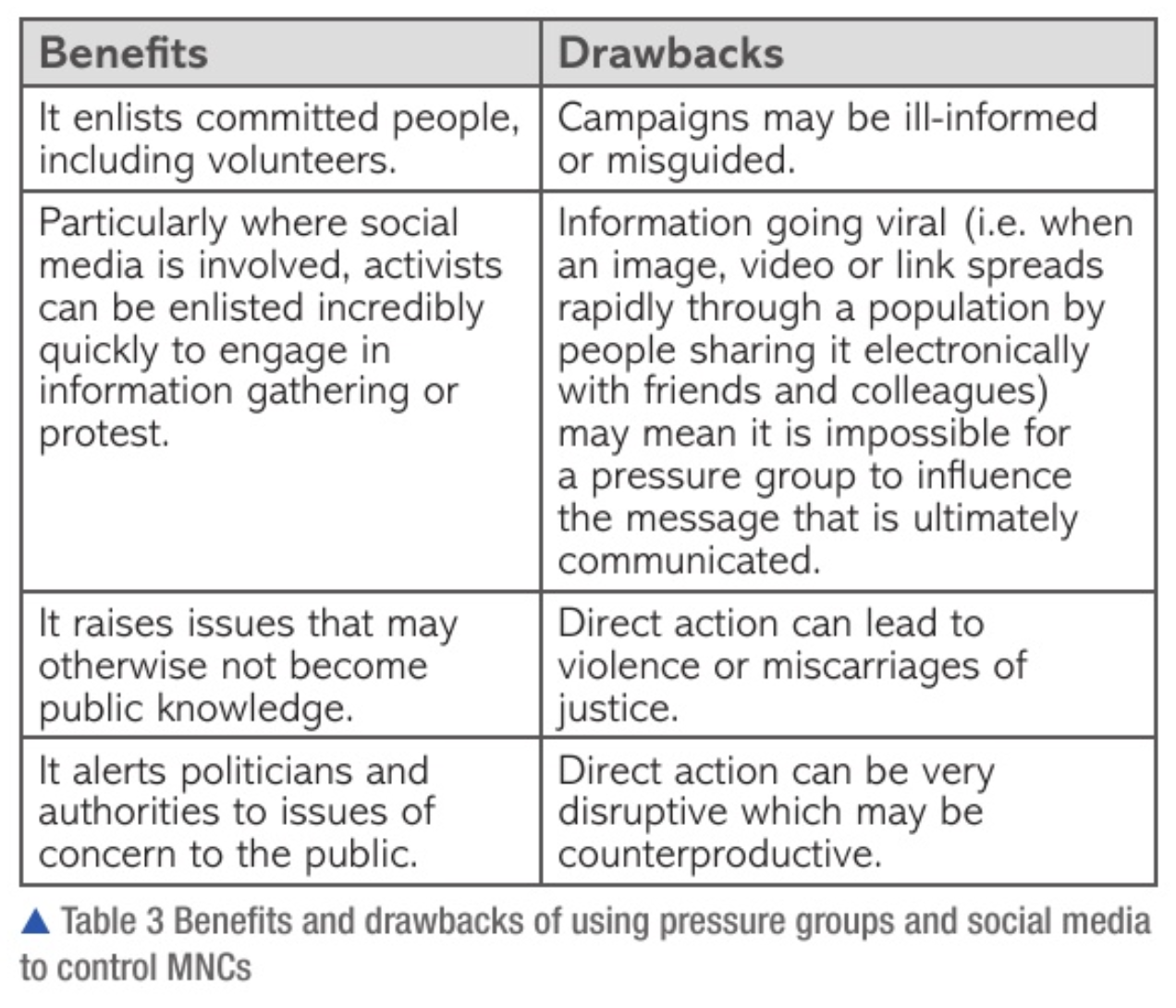
social media
interaction between electronic and mobile devices, applications and people, that allows users to create content
controls MNC behaviour by:
making information collection easier
increasing social awareness
ensuring greater transparency
bringing together people to create social authority to challenge large companies
self-regulation
group of firms in the same industry agree to follow a set of rules and guidelines to ensure proper conduct
guidelines specific to industry
designed to ensure companies maintain common standards
address issues such as health and safety, ethical behaviour, responsibility to employees and consumers and environmental practices
code of practice
these companies also practice self-policing
signed up businesses monitor their own activities
set performance targets
advantages of self-regulation:
avoids rigorous, expensive government regulation and compliance costs
needs of stakeholders better served
improved image and reputation
easier for business to encourage its employees to adopt ethical behaviour and principles
benefits taxpayers
disadvantage: conflict of interest - difficult to comply if financial performance is threatened