3B - More exchange and transport systems
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Why and how is food broken down during digestion?

What enzymes are carbohydrates broken down by?
Amylase + Membrane bound diasaccharides
How does amylase break down carbs?

How do membrane bound disaccharides break down carbs?
Membrane-bound disaccharidases are enzymes, like maltase, sucrase, and lactase, that are embedded in the cell membranes of epithelial cells lining the small intestine (ileum). These enzymes break down disaccharides (double sugars like maltose, sucrose, and lactose) into monosaccharides (simple sugars like glucose, fructose, and galactose) through a process called hydrolysis
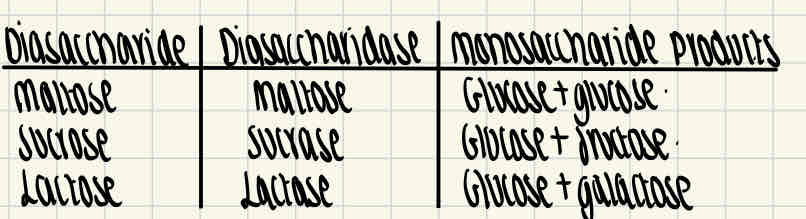
What are the disaccharidase and monosaccharide products of the diasaccharides maltose, sucrose and lactose?
What are lipids broken down by?
Bile salts + Lipase
How do bile salts break down lipids?

How does lipase break down lipids?

What are proteins broken down by?

How do endopeptides break down protein and what are 3 examples of endopeptidases?

How do exopeptidases break down protein and what are dipeptidases?

Where are products of digestion absorbed?
Across the ileum epithelium into the blood stream
How are monosaccharides (e.g: glucose + fructose) absorbed?

How are monoglycerides and fatty acids absorbed?

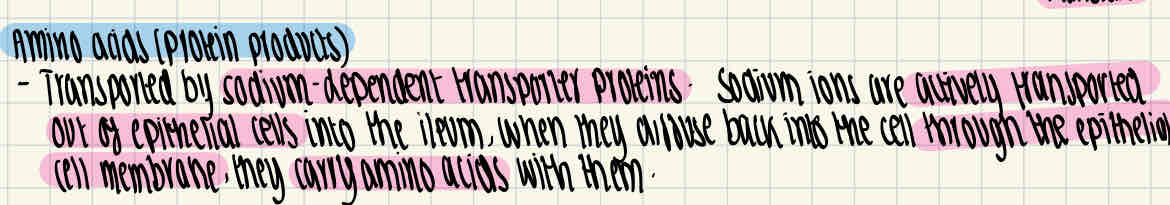
How are amino acids absorbed?
What is haemoglobin and how does it transport oxygen around the body?

What is oxyhaemoglobin and what are the equations to represent this?
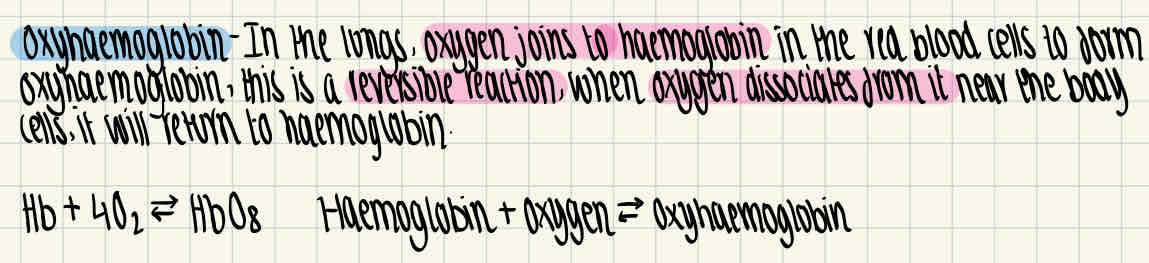
What is partial pressure of oxygen (pO₂) and partial pressure of carbon dioxide (pCO₂)?
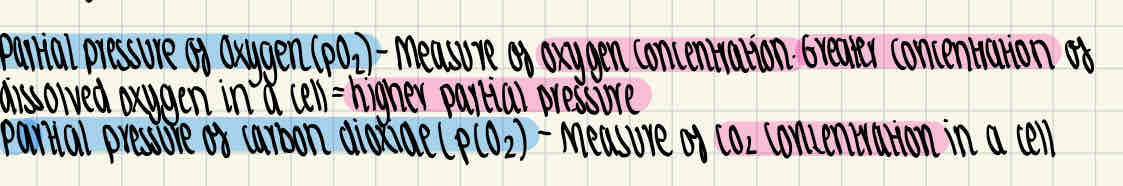
What does haemoglobin’s affinity for oxygen depend on?
Partial pressure of oxygen, for example, oxygen loads onto Hb when there’s a high PO₂ and unloads when there’s low PO₂.
Where does haemoglobin travel around the body to collect/deliver oxygen and how is this affected by pO₂?

Dissociation curve showing pO₂ in relation to Hb saturated with oxygen
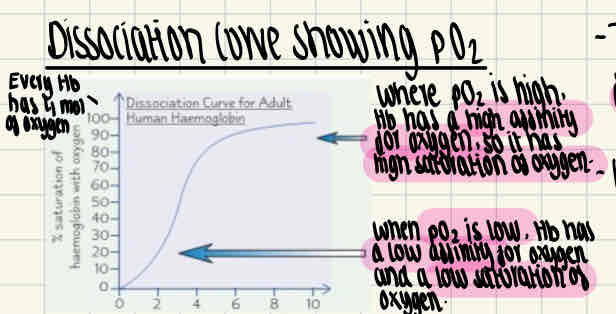
Why is this curve s-shaped?

How does pCO₂ affect oxygen unloading?

What is the bohr effect and how is this shown on a graph?

How does Hb differ in animals living in different environments?

What is the circulatory system generally made up of and how does it work?

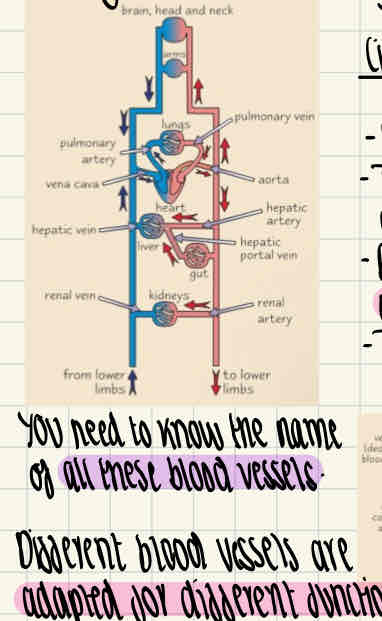
Labelled diagram of the circulatory system
Types of blood vessels - Arteries

Arterioles

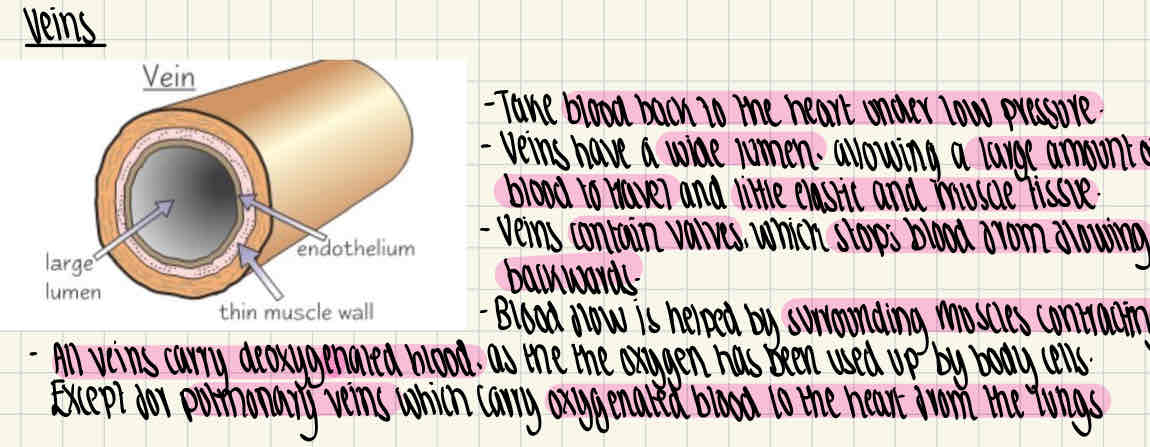
Veins
Capillaries

What is tissue fluid?

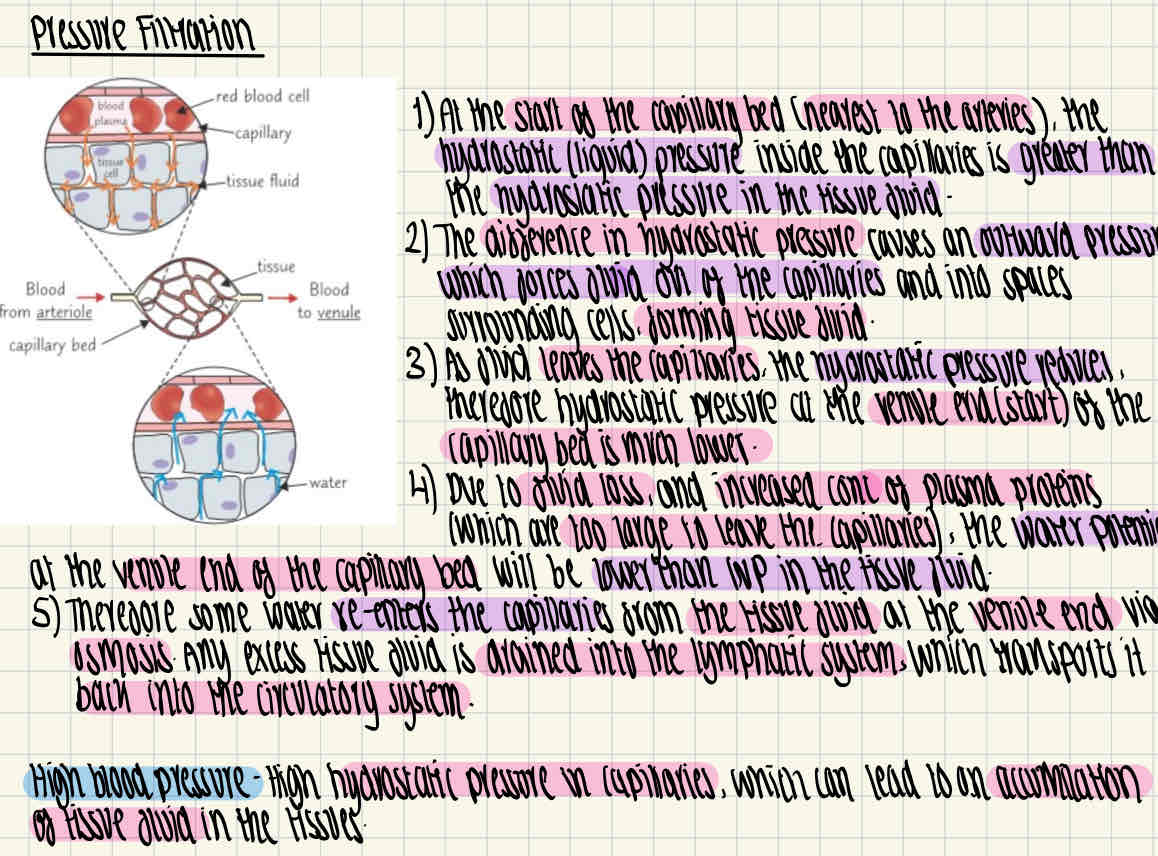
What is pressure filtration and how does it work?
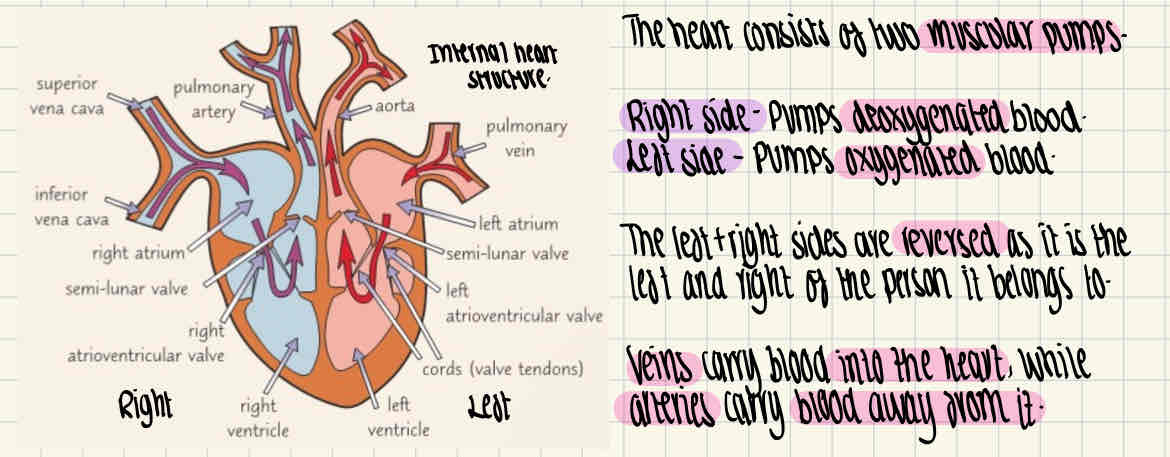
What is the internal structure of the heart and the general functions of L+R side, veins + arteries?
What are the functions of the left and right ventricles of the heart?

What is the function of the atrioventricular valves of the heart?

What is the function of the semi-lunar valves in the heart?

What is the function of the cords (valve tendons) in the heart?

What is the general functions of valves in the heart?

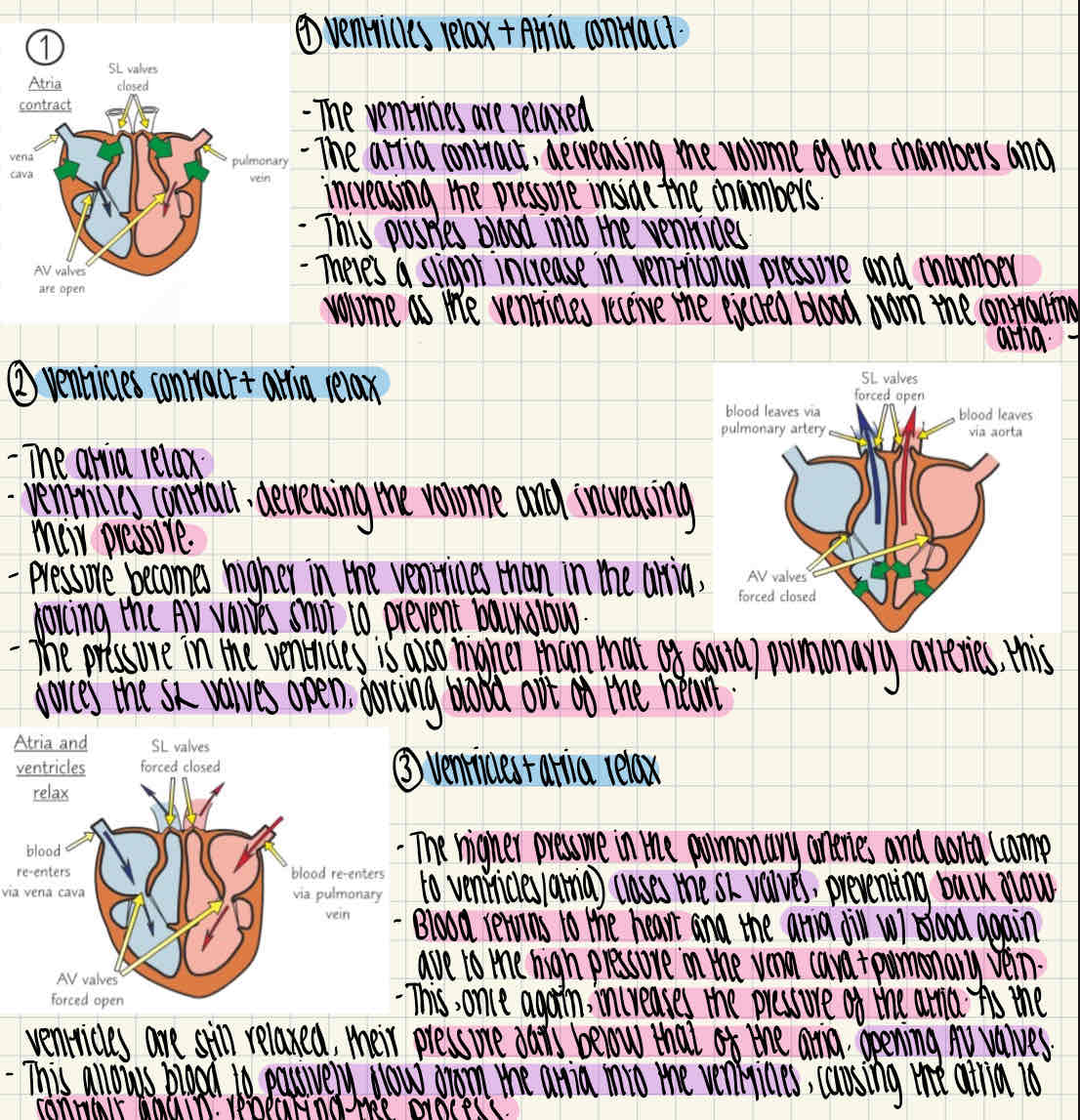
What is the cardiac cycle?

What are the 3 stages of the cardiac cycle and what happens in each stage?
What do most cardiovascular diseases begin with?
Cardio = heart, vascular = blood vessels. They mostly begin with atheroma formation.
How does atheroma formation occur?

What is coronary heart disease?

Atheroma increase risk of aneurysm and thrombosis. What is an aneurysm and how does this affect occur?

What is thrombosis and how does this occur?

What is a myocardial infraction?

How does myocardial infraction occur?

Risk factors for cardiovascular disease - High blood cholesterol and poor diet

High blood pressure

Smoking

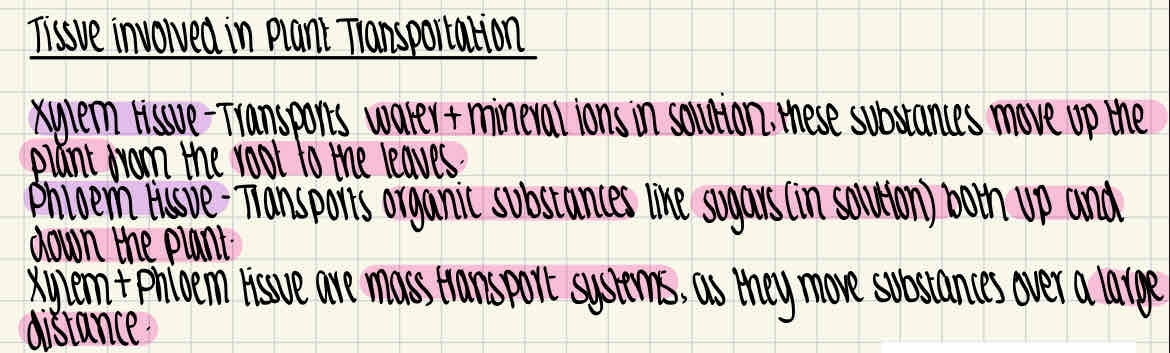
What are the two tissues involved in plant mass transportation?
What is the structure of xylem vessels?

What is the cohesion-tension theory of water transport?

What is transpiration and how does it occur?

What are the 4 factors affecting transpiration rate?
Light intensity, temperature, humidity and wind

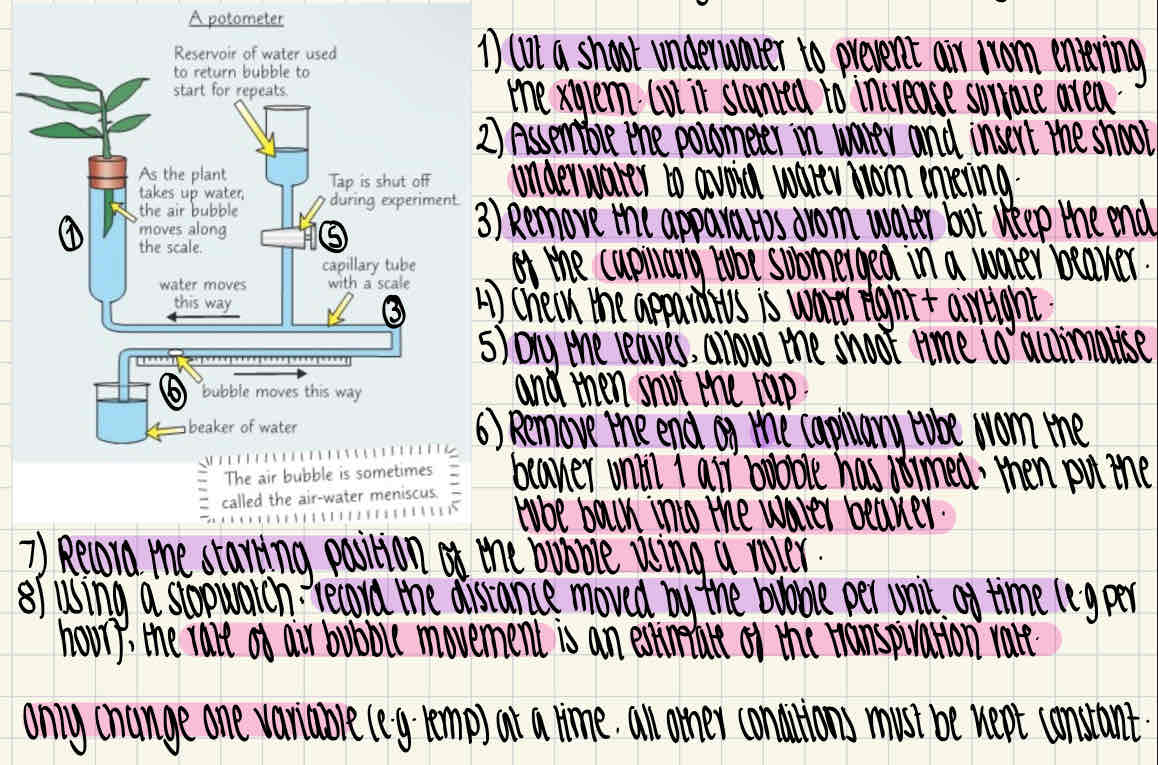
What is a potometer?

How can a potometer be used in a practical to estimate transpiration rate?
How to dissect a plant to prepare a sample of a xylem/phloem for the microscope

What is phloem tissue for?

What is the structure of the phloem and what are the important cell types?
do not have organelles*

What is translocation?

How is translocation maintained by enzymes?

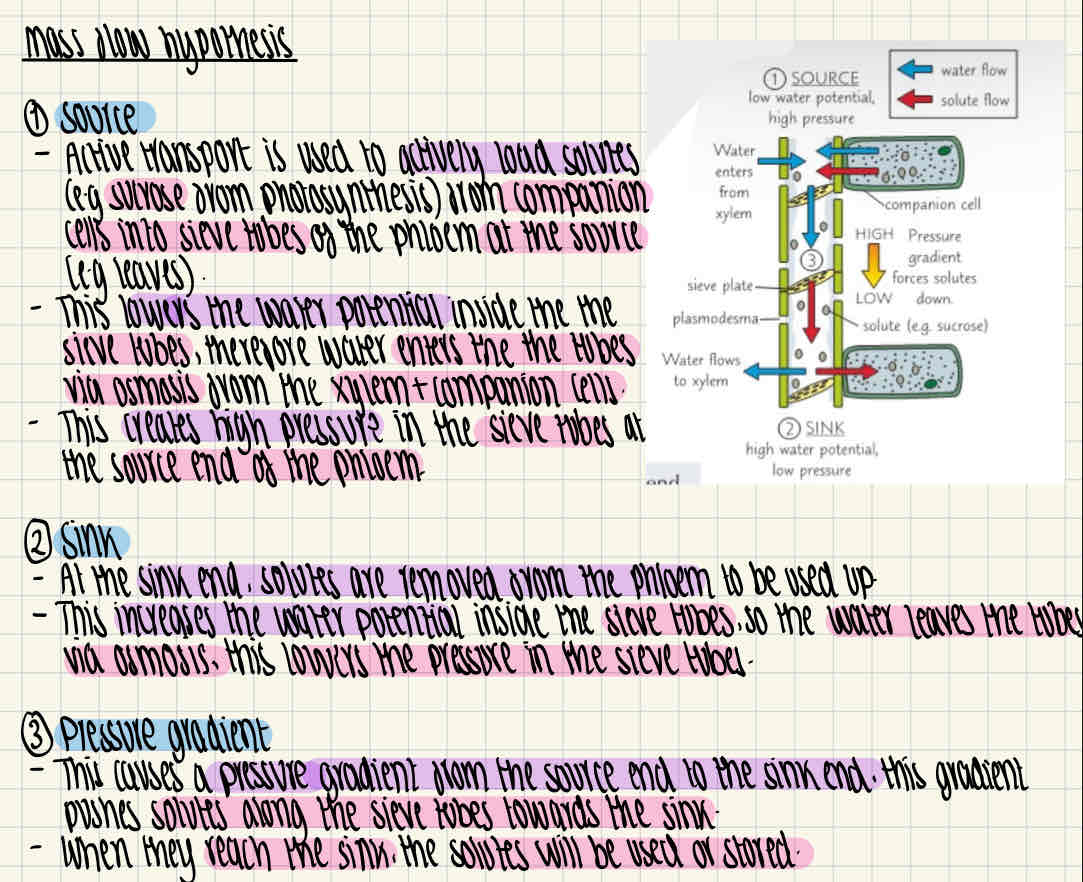
What are the stages of the mass flow hypothesis?
What is supporting evidence for the mass flow hypothesis?

What is contradictory evidence to the mass flow hypothesis?

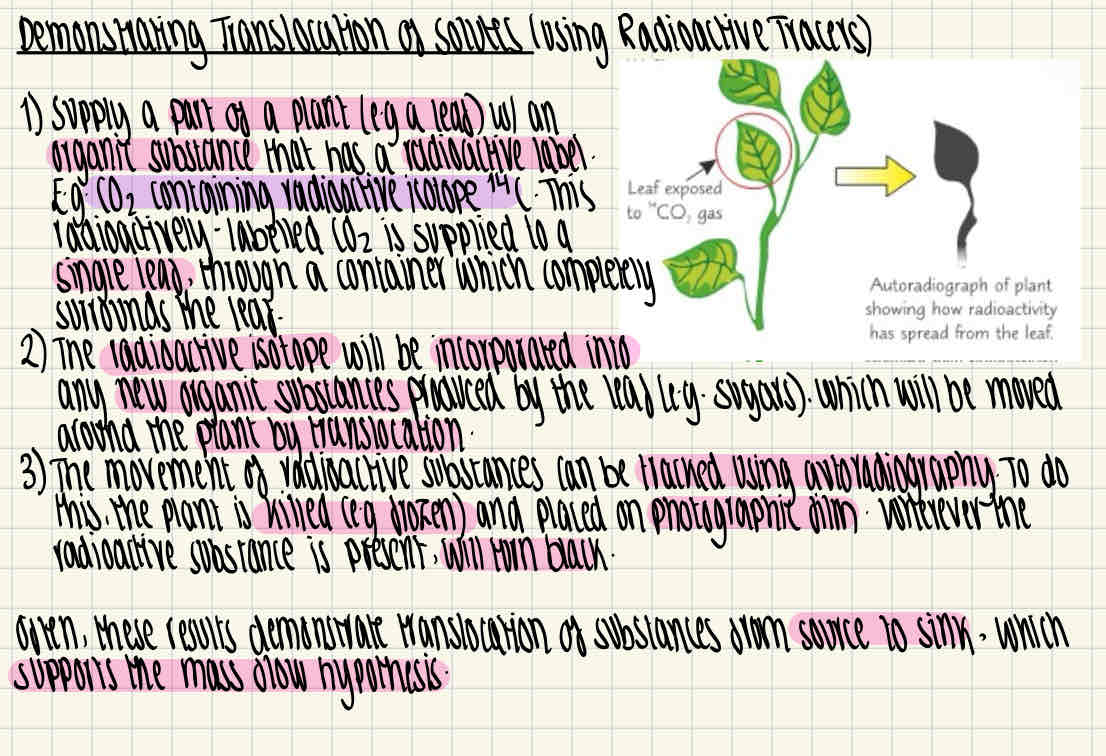
Hw can translocation of solutes be demonstrated using radioactive tracers in a practical?