light dependent reaction
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
how are thylakoids adapted for the light dependent reaction?
large SA - can contain more chlorophyll and e- carriers
ATP synthase channels - allow the synthesis of ATP
selectively permeable - allows a H+ gradient to be established
what happens when a chlorophyll molecule absorbs light energy?
a pair of e- become excited and are raised to a higher E level
the e- leave the chlorophyll molecule and are passed onto an e- carrier - chlorophyll gets oxidised and the e- carrier gets reduced
the e- are passed along a series of e- carriers in the thylakoid membranes
each e- carrier is at a slightly lower energy E stage so e- lose E as they are passed along
what is the e- transport chain?
series of membrane bound e- carrier proteins
give the key stages of the light dependent reaction:
PSII:
absorption of light energy and photoionisation
photolysis of water
e- transfer along the e- transport chain and chemiosmotic synthesis of ATP
PSI:
e- transfer along the e- transport chain and chemiosmotic synthesis of ATP
overall final step: reduction of NADP → NADPH
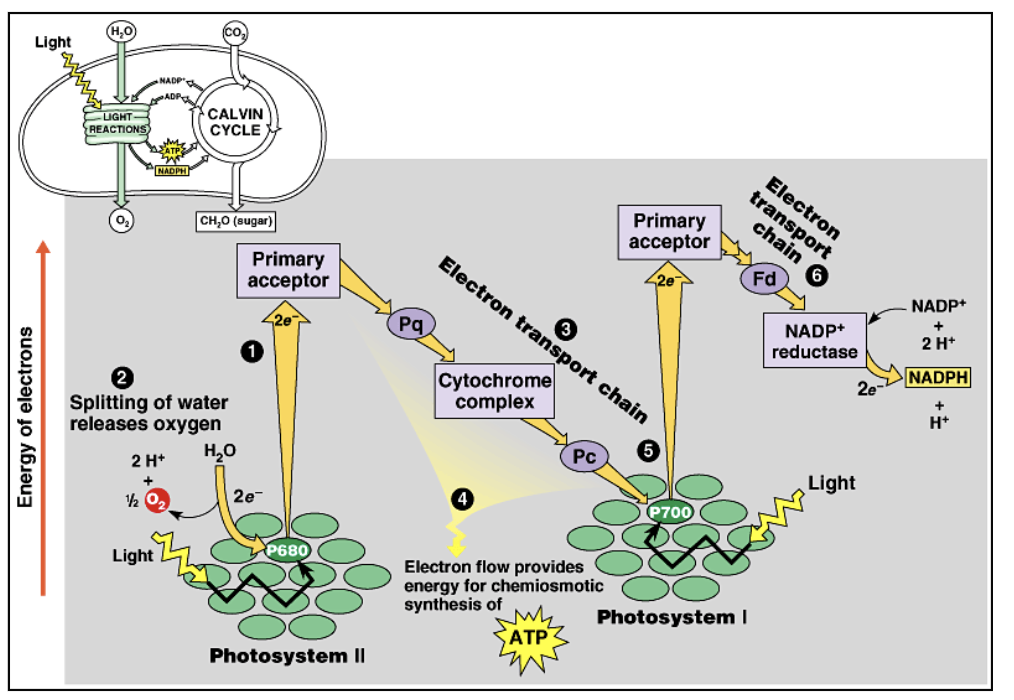
describe the absorption of light energy and photoionisation:
light absorbed by accessory pigments and E transferred to chlorophyll a
photoionisation = primary e- acceptor captures excited e- from chlorophyll a
this initiates the oxidation of chlorophyll
describe the photolysis of water and give the equation:
chlorophyll a is now +vely charged, causing photolysis to occur
photolysis = the splitting of H2O into H+ ions and O2 molecules
H2O → 2H+ + 2e- + ½ O2
chlorophyll a accepts an e- from water to replace the one lost to the primary e- acceptor
describe e- transfer along the e- transport chain:
e- passes from the primary e- acceptor down the e- transport chain, causing it to lose E
the E lost from the e- is used for the chemiosmotic synthesis of ATP
when the e- reaches the bottom of the ETC, it replaces the last e- excited in photosystem I
describe the chemiosmotic synthesis of ATP:
e- from 1o e- acceptor travel down an e- transport chain, losing energy which is used to pump H+ across the thylakoid membrane into the thylakoid space
H+ diffuse into the stroma via ATP synthase
this movement combines ADP + Pi → ATP
describe the reduction of NADP:
e- passes down another ETC
H+ from photolysis and e- are accepted by NADP - final e- acceptor
NADP is reduced to NADPH by NADP reductase - catalysed by dehydrogenase
NADPH carried into LIR
give the eqn for the reduction of NADP to NADPH:
NADP + 2H+ + 2e- → NADPH
what is a coenzyme? give an example:
coenzyme = organic, non protein compound which catalyses a reaction through binding with another enzyme
e.g. NADP