Chapter 12 - Labour Productivity
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
long run economic growth
sustained increase in economy’s productive capacity due to increase in LRAS
importance of long run economic growth
relates to productivity growth which maintains economic growth and economic welfare and prosperity
productivity growth contributes to
higher wages
lower prices
higher profits
increased tax revenue
strong EG
higher wages
as productivity rise, labour cost to produce 1 unit of output fall
profit increase, firm can up wage
lower prices
productivity rise, labour cost fall, business can reduce price
IC improve, equitible income distribution(creates more jobs in diff sectors)
higher profit
productivity rise, unit COP fall
price fall, IC up, X revenue rise
increased tax revenue
biz profit increase, gov receive more tax revenue
gov spend on public service, SOL improve
strong EG
as productivity rise, economic capacity improve, thus GDPfe shift right
more room for economic expansion
driving forces for long run EG
labour productivity
capital deepening
technological progress
labour productivity
measure of g/s produced for every hour worked
as labour productivity improve, efficient workforce lead to economic growth
capital deepening
increase in physical assets
help improve production and efficiency, improve EG
technological progress
technological innovations lead to efficient production, EG improve
labour productivity
output per labour hour worked
output/labour input
China’s C19 policy affected global supply chains, thus although labour hours increase, output still stagnant, hence fall in labour productivity
multifactor productivity
output per unit of combined inputs
GDP/labour hours+capital input
factors affecting labour productivity growth
human capital
capital deepening
technological progress
human capital
increase in education and specialisation in workforce
include labour market turnover, labour market hoarding, demographic development, education and training
labour market turnover
increase in job mobility boosts labour productivity if it results in better job matching and labour reallocation to more productive firms
labour productivity depends on productivity of sectors
BUT short term, productivity may fall as worker have to relearn
labour market hoarding
firms hold onto more workers than needed
labour underutilization, labour productivity fall
demographic development
aging population may lead to fall in labour supply
firms must adopt labour saving techniques
education and training
educated workers more efficient
capital deepening
increase in proportion of capital stock to num of labour hours worked
may increase labour productivity and output
technological progress
level of innovation and advances in tech that allow businesses to produce more output with the same level of input
impact of changes in labour productivity on UE
structural UE
real wage UE
residual UE
structural UE
UE due to skill mismmatch
shifting of resources lead to structural UE
real wage UE
UE due to high wage, thus employers dont want hire
if gov implement labour market reform, lead to enteprise level bargaining, thus decentralize wage and real wage UE fall
residual UE
UE due to being unfit to work
gov implement infrastructure reform, EG: healthcare infrastructure, employees recover and start work faster, residual UE fall
aggregate production function
reflects law of diminshing return: with each increase in input, output increase by smaller amount
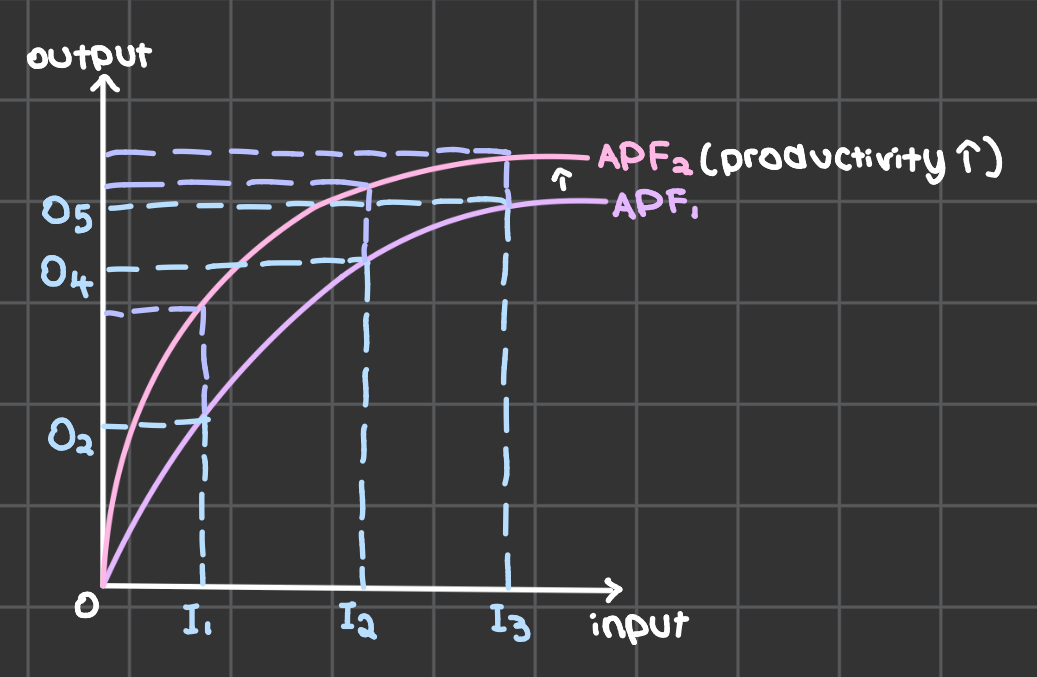
gov objective
improve efficiency of market by improving competition and removing unecassary regulations
gov policies that influence labour productivity
(Please Take Donuts For Lunch To Never Ignore Teacher)
public reform
taxation reform
deregulation
financial reform
labour market reform
tariff reform
national competition policy reform
infrastructure reform
trade reform
public reform
privatisation - sale of publically owned assets to private investor, improve efficiency by forcing firms to be answerable to shareholders
corporatisation - forcing gov business enteprise to face same market as other businesses, must aim to make profit since they dont receive any gov benefits
taxation reform
reduces extent to which tax system distorts allocation of resources
EG: introduction of GST(10% tax on ALL g/s) to replace WST, replace 3 tier wholesale system
RESULT: business cost fall, encourage investment
deregulation
remove bureautic barriers to enter market
make industry more efficient
financial reform
open banking sector to new competition
many banks in industry, more money to borrow/lend
no need raise IR
labour market reform
improve functioning of labour market as a policy solution to reduce structural UE
EG: workplace relations act 1996, paved way for enteprise level bargaining, decentralize wages
RESULT: flexible wages, fairness, cooperation, improved workplace participation, less strikes
tariff reform
reduces effective rate of protection
EG: tariff on passenger motor vehicles reduced to 5% in 2010
RESULT: efficient industry, e.o.s
national competition policy reform
most extensive microeconomic reform package in recent Aus history
EG: establishment of Aus Comp and Consumer Commission - competition watchdog to ensure businesses dont engage in anti-competitive conduct, allow private firm to compete with GBEs
RESULT: price determined by market forces
infrastructure reform
provide building blocks for business to further invest in productivity measures
EG: transport infrastructure - reduce commute and delivery times, more time for worker to do productive taks
trade reform
obtain reductions in internal support and subsidies to foreign competitors to gain access to foreign markets and eliminate export subsidies
EG: WTO create fair trading environment, maximise FTA oppurtunities