Blood/ Circulation
1/173
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
174 Terms
What is the purpose of cirulation? Which ones are slow and fast
Transport nutrients and wastes (energy, electrolytes). Often can be relatively slow.
Transport gasses (Oxygen to muscles, release Carbon Dioxide). Often must be fast.
Transport heat (from core to periphery). Often must be fast.
Control body functions by transporting hormones. Often can be relatively slow.
What can small organism use
use diffusion to exchange nutrients, gasses, and heat with the environment.
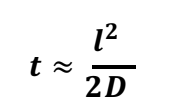
What is L and D
L = diffusion legnth
D= diffusion coefficient
What can larger organism not rely on?
cannot rely on diffusion
What must large organism move?
must move water, nutrients, and dissolved gasses through “circulation:” bulk movement of fluids.
Most animals (like insects, crustaceans, and mollusks)
use what kind of circulatory system
Open circulatory system
what pumps blood? what is blood not confined to
One or many hearts pump blood, but blood is not confined to blood vessels.
Where does blood flow
Blood flows freely around body tissue
What does open circulatory systems in insects transport? What does it not transport?
transport nutrients but NOT gasses
What do insects have for gas exchange
(insects have small tubes called “trachea” for gas exchange)
What do many Open circulatory systems not need
do NOT need fast fluid flow.
What do Animals like earthworms,fish,reptiles and mammals use?
Some animals (like earthworms, fish, reptiles and mammals) use a “closed” circulatory system.
What happens to closed cirulatory systems in order to move fluid
Closed circulatory systems are pressurized to move fluid
How many hearts do earthworms have? what does it help?
(Earthworms have five hearts to help pump blood).
What are the benefits of a closed ciruclatory system
• Fast transport of blood through vessels (arteries and veins).
• Blood can be directed to (or away from) specific tissues.
• Blood volumes for closed circulatory systems ≈ 10% of body weight (compared to 30-60% of body weight for open circulatory systems).
• Specialized carriers can travel in vessels and transport hormones or nutrients to specific sites
• Filtration of blood by kidneys
What do humans only have 1 of
Humans only have one heart
What must blood vessels be
must be small enough for diffusion to be able to exchange nutrients and gasses with tissues.
How to go from one big heart to many small capillaries?
Branching
What do arteries from the heart branch into? What do they convey?
Arteries from the heart branch into smaller “Arterioles”
that convey blood to tissues.
What do arterioles branch into? what does it connect to?
Arterioles branch several times into very small “Capillaries,” that connect the arterioles to “venules.”
Where do Venules Join and form? where/what does it return
Venules join to form “veins” to return blood to heart.
What does shear thinning help to reduce
helps to reduce the resistance in very small
capillaries.
What is there still even with shear thinning?
there is still substantial resistance in capillaries.
What causes blood pressure to drop
Resistance in small vessels and capillaries converts pressure energy to heat causing blood pressure to drop
Where must blood pressure start from? What could happen?
The blood pressure must start high in the larger vessels. Otherwise, there could be “ischemia”
What is Ischemia?
ischemia is low blood flow in capilarries
Where does blood flow down?
Blood flows down a pressure gradient
What happens as blood vessels branch?
As blood vessels branch, the cross-sectional area increases.
How does blood flow in capillaries?
Blood flows more slowly in capillaries.
What does slow blood flow facilitate?
facilitates nutrient and gas exchange with tissues.
What is blood? What is blood composed of?
A “connective tissue” composed of PLASMA & FORMED ELEMENTS
What is plasma? How much does it make up? What does it contain
the liquid component of blood, making up around 55% of its volume, and containing vital proteins
What is Albumins? What is it a major contributor to? What does it transport?
Albumins – 60% of plasma proteins
Major contributor to osmotic pressure of the blood. •
Transport compounds such as bilirubin, ions, fatty acids, and drugs.
What is Globulins? What does it transport?
Globulins – 35% of plasma proteins (Antibodies)
(transport lipids, hormones, vitamins, etc.)
What is another word for Antibodies
immunoglobulins
What is Fibrinogen? What do they form?
Fibrinogen – 4% of plasma proteins
• Join together to form fibrin in order to start clotting
process.
What are formed elements?
Platelets, white blood cells, & Red blood cells
What are platelets
membranes filled with proteins and growth factors
Why are platelets important
Important for blood clotting and repairing tissue damage.
Imagine that a blood vessel branches. Each branch (B) is a “bifurcation” into two equal parts with half the radius of the larger vessel (A). What will happen to the TOTAL resistance
The branches will have much MORE resistance than the main artery
What is cool propety of Blood?
the viscosity of blood (η) decreases with shear rate.
What is the main problem in viscosity and shear? Why is it a problem in smaller pipes?
“resistance”
because resistance increases SO MUCH with smaller pipes.
What needs to be brought in for Nutrient, gas , hormone exchange and waste removal
Blood must be brought into close proximity with tissues for
nutrient/gas/hormone exchange, waste removal,
What needs to happen for flow and capillary filtration
Blood pressure in small vessels must be enough for flow and
capillary filtration.
What do Big vessels at high pressure have? What equation would model this? And what could it lead to in walls?
BIG vessels at high pressures have lots of tension
(Laplace’s equation: T = P * r)
in walls (could lead to aneurisms)
What does blood exhibit? what is the result?
Although blood exhibits “shear thinning,” SMALL capillaries result in HIGH resistance to flow
What requires the heart/ large vessels to operate? At what pressure?
Maintaining blood pressure in small vessels requires the heart and large vessels to operate at relatively HIGH pressure.
What are Leukocytes
(White Blood Cells)
what do leukocytes respond to
Immune response to pathogens.
What are Erythrocytes
Erythrocytes (Red Blood Cells)
What do Erythrocytes transport?
Transport gases within the blood (especially oxygen)
Where are Formed Elements produced? what is the process called?
Formed elements are produced in the bone
marrow in a process called “hematopoesis.”
What can differentiate into all different types of formed elements.
A single “stem” cell, called the “Hematopoetic” stem cell, can differentiate into all different types of formed elements.
What does Heme mean?
“Heme” from “
What does Haima mean
blood
What does Poesis mean
“to make” as in “poetry.”)
What stimulates Hematopoesis
Cytokines, thrombopotein, Colony-stiumulating factors
What does Cyto mean
Cell
What does Kinos mean
movement
Where is Thrombopoietin found? what does it stimulate?
Thrombopoietin (TPO) found From liver. Stimulates production of platelets.
How are Colony-stimulating factors released? what is stimulated?
Released by lymphocytes and other cells during immune response to stimulate production of leukocytes.
What does Erythropoietin stimulate?
Stimulates production of erythrocytes.
What does Erythropoietin produce in response? Whats another name?
Produced by cells in kidney in response of low blood oxygen (hypoxia).
How much is Plasmas Viscosity compared to water
Plasma has a viscosity of ~1.8 times that of water.
How much is Whole bloods viscosity compared to water
Whole blood has a viscosity 3-4 times that of water.
What causes the Viscosity of Blood to increase?
Viscosity of blood increases with hematocrit
How much blood does the heart pump in one day?
In one day the heart pumps about 2,000 gallons of blood.
How far does blood circulate through and where?
Blood circulates through 60,000 miles of arteries, veins, and capillaries.
How many times does the heart beat on average? how many times per day?
The heart beats an average of 70 times in one minute or over 100,000 times a day.
What is heart rate related to
Heart rate is related to body size.
What is a canarys (birds) heart rate
A canary has a heart rate of 1000 beats per minute.
What is a new borns heart rate
The newborn human has a heart rate of 130 BPM
What is an adults heart rate
the adult human has a heart rate of 70 BPM.
What does a human heart consist of
The heart consists of 4 chambers
What are the 4 chambers of the heart? What is the atria superior to?
2 Atria & 2 Ventricles (Atria is superior to ventricles)
What are the 2 seperate chambers the heart pumps blood into? Where does the blood go?
Pulmonary Circuit (deoxygenated blood to lungs)
Systemic Circuit (Oxygenated blood to body)
What does the Atria receive
Blood
What does the Atria not need?
Doesnt need strong muscles
What do ventricles do?
Pump Blood
What are Ventricles described as
Very muscular
What does Auricles act as?
pressure relief and extra blood storage for atria.
What does the right side of the heart receive
Blood from the systemic body circuit and pumps blood to the pulmonary lung circuit
What does the left side of the heart receive
receives blood from the ”pulmonary” lung circuit, and pumps blood to the “systemic” body circuit.
What is heart rate (HR)?
The number of times your heart beats per minute
What is a normal resting heart rate
55-100bpm 75BPM
60 BPM is considered what?
60 bpm: “bradycardia”
What does bradycardia mean
“bradus” meaning “slow”) (slow heart rate)
100 BPM is considered what?
100 bpm: “tachycardia”
What does Tachycardia mean
“tachycardia” (Greek: “Tachy” meaning “swift”) (Fast heart rate)
What is blood pressure
The force of blood pushing against vessel walls when the heart beats
A persons blood pressure is 120/80 What do these numbers mean
120 = Systolic
80 = Diastolic
What does Systolic mean
To contract
What does Diastole mean
Seperation Expansion
During the cardiac cycle what is Late Disatole
Both sets of chambers are relaxed and ventricles fill passively from venous ”diastolic” pressure.
During the cardiac cycle what is Atrial systole
Atrial contraction forces additional blood into ventricles.
During the cardiac cycle what is Ventricular systole A. What is the first sound
Ventricles contract. Pressure closes valves between atria and ventricles. First sound: “Lub”
During the cardiac cycle what is Ventriclar systole B? what does it open? Where does blood flow?
Ventricular pressure exceeds pressure in arteries, opening “semilunar” valves. Blood flows from heart into arteries.
During the cardiac cycle what is Ventriclar diastole. What is the Second sound?
Ventricles relax. Some “backflow” of blood closes semilunar valves. Second sound:“Dub”
In heart valves what are Mechanical Valves made of
made up of cells, collagen, and elastin (proteins)
In Heart valves where is the atrioventricular located
Located between atrium and ventricle